
中国水稻科学 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 171-180.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.9051
杜志敏, 刘晓琳, 邵丹蕾, 张楠, 王祎玮, 王镜博, 伍晓康, 胡涛, 夏原野, 徐海*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-04-30
修回日期:2019-06-16
出版日期:2020-03-10
发布日期:2020-03-10
通讯作者:
徐海
基金资助:
Zhimin DU, Xiaolin LIU, Danlei SHAO, Nan ZHANG, Yiwei WANG, Jingbo WANG, Xiaokang WU, Tao HU, Yuanye XIA, Hai XU*( )
)
Received:2019-04-30
Revised:2019-06-16
Online:2020-03-10
Published:2020-03-10
Contact:
Hai XU
摘要:
【目的】研究氮肥减施后中日粳稻品种杂交构建的重组自交系(RIL)群体株型、产量和米质性状的变化规律及其相互关系。【方法】以中国东北地区典型的直立穗型水稻辽粳5号与日本的优质米水稻秋田小町(弯曲穗型)杂交构建的RIL群体为试材,在高氮和低氮两种施肥模式下,调查株型、产量及米质性状,分析三者间的关系,探讨高产、稳产、高食味值类型株系的共同特征。【结果】氮肥减施后RIL群体齐穗期提前,株高降低,剑叶、倒2叶、倒3叶叶片变窄变短,剑叶基角变小,倒3叶基角变大,结实率、千粒重、经济系数增大,单株穗数减少,产量下降,糙米率和精米率提高,食味值提高。在两种施肥模式下,高产高食味值类型株系与低产低食味类型株系的显著区别是植株较高,叶片长,穗子长,一次枝梗结实率高,着粒密度较小;高产稳产类型株系的共同特征是剑叶较窄、剑叶基角较大;高产稳产高食味值类型株系的共同特征是剑叶和倒2叶较窄。【结论】株型特征可以用来间接选择高产、稳产、高食味值的水稻品种。
中图分类号:
杜志敏, 刘晓琳, 邵丹蕾, 张楠, 王祎玮, 王镜博, 伍晓康, 胡涛, 夏原野, 徐海. 减氮后中日粳稻品种杂交后代株型、产量和米质的变化及其相互关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 171-180.
Zhimin DU, Xiaolin LIU, Danlei SHAO, Nan ZHANG, Yiwei WANG, Jingbo WANG, Xiaokang WU, Tao HU, Yuanye XIA, Hai XU. Variation of Plant Type, Yield and Quality of Hybrid Progenies of Chinese and Japanese Japonica Rice Varieties Under Nitrogen Reduction Practice and Their Interrelation[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(2): 171-180.
| 施肥模式 Fertilization practice | 基肥 Basal fertilizer (05-15) | 促蘖肥Topdressing for tillering (05-28) | 保蘖肥Fertilizer for tiller growth (06-20) | 穗肥Panicle fertilizer (07-12) | 粒肥Grain fertilizer (08-05) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尿素Urea | 磷酸二铵DAP | 氯化钾KCl | 尿素Urea | 尿素Urea | 尿素Urea | 氯化钾KCl | 尿素Urea | |||||
| 高肥HFP | 150 | 150 | 112.5 | 150 | 75 | 90 | 75 | 0 | ||||
| 低肥LFP | 0 | 150 | 112.5 | 75 | 0 | 45 | 75 | 18 | ||||
表1 高氮、低氮两种施肥模式
Table 1 Two fertilization practices of high nitrogen and low nitrogen levels. kg/hm2
| 施肥模式 Fertilization practice | 基肥 Basal fertilizer (05-15) | 促蘖肥Topdressing for tillering (05-28) | 保蘖肥Fertilizer for tiller growth (06-20) | 穗肥Panicle fertilizer (07-12) | 粒肥Grain fertilizer (08-05) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尿素Urea | 磷酸二铵DAP | 氯化钾KCl | 尿素Urea | 尿素Urea | 尿素Urea | 氯化钾KCl | 尿素Urea | |||||
| 高肥HFP | 150 | 150 | 112.5 | 150 | 75 | 90 | 75 | 0 | ||||
| 低肥LFP | 0 | 150 | 112.5 | 75 | 0 | 45 | 75 | 18 | ||||
| 性状 Trait | 低肥区 Low fertilizer pattern | 高肥区 High fertilizer pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height /cm | 113.32** | 121.86 |
| 颈穗弯曲度Panicle curvature /° | 45.58 | 44.80 |
| 剑叶基角Flag leaf angle /° | 13.21* | 14.13 |
| 倒2叶基角TLA2/° | 11.90 | 11.74 |
| 倒3叶基角TLA3/° | 17.26** | 15.58 |
| 剑叶长FLL/cm | 29.83 | 29.99 |
| 剑叶宽FLW/cm | 1.30** | 1.36 |
| 倒2叶长TSLL2/cm | 37.31** | 38.30 |
| 倒2叶宽TSLW2/cm | 1.10** | 1.18 |
| 倒3叶长TSLL3/cm | 38.39** | 41.26 |
| 倒3叶宽TSLW3/cm | 1.01** | 1.09 |
| 穗长Panicle length /cm | 20.85 | 20.82 |
| 一次枝梗数NPRB | 11.34** | 11.72 |
| 二次枝梗数NSRB | 26.82 | 26.11 |
| 一次枝梗结实率SSRPRB/% | 96.03** | 94.24 |
| 二次枝梗结实率SSRSRB/% | 86.76** | 76.99 |
| 着粒密度Grain density /(粒·dm-1) | 68.55 | 69.52 |
表2 氮肥减施后中日粳稻品种杂交后代株型性状的变化
Table 2 Variation of plant type traits of the RIL population under high and low fertilization patterns.
| 性状 Trait | 低肥区 Low fertilizer pattern | 高肥区 High fertilizer pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height /cm | 113.32** | 121.86 |
| 颈穗弯曲度Panicle curvature /° | 45.58 | 44.80 |
| 剑叶基角Flag leaf angle /° | 13.21* | 14.13 |
| 倒2叶基角TLA2/° | 11.90 | 11.74 |
| 倒3叶基角TLA3/° | 17.26** | 15.58 |
| 剑叶长FLL/cm | 29.83 | 29.99 |
| 剑叶宽FLW/cm | 1.30** | 1.36 |
| 倒2叶长TSLL2/cm | 37.31** | 38.30 |
| 倒2叶宽TSLW2/cm | 1.10** | 1.18 |
| 倒3叶长TSLL3/cm | 38.39** | 41.26 |
| 倒3叶宽TSLW3/cm | 1.01** | 1.09 |
| 穗长Panicle length /cm | 20.85 | 20.82 |
| 一次枝梗数NPRB | 11.34** | 11.72 |
| 二次枝梗数NSRB | 26.82 | 26.11 |
| 一次枝梗结实率SSRPRB/% | 96.03** | 94.24 |
| 二次枝梗结实率SSRSRB/% | 86.76** | 76.99 |
| 着粒密度Grain density /(粒·dm-1) | 68.55 | 69.52 |
| 性状 Trait | 低肥区 Low fertilizer pattern | 高肥区 High fertilizer pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 单株穗数Panicle number per plant | 10.36** | 13.50 |
| 每穗粒数Grain number per panicle | 139.90 | 142.22 |
| 结实率Seed setting rate /% | 90.92** | 85.03 |
| 千粒重Thousand grain weight /g | 25.24** | 24.19 |
| 经济系数Economic index | 0.58** | 0.54 |
| 产量Yield /(kg·hm-2) | 7725.45** | 9054.30 |
表3 氮肥减施后中日粳稻品种杂交RIL群体产量性状的变化
Table 3 Variation of yeild traits of the RIL population under high and low fertilization patterns.
| 性状 Trait | 低肥区 Low fertilizer pattern | 高肥区 High fertilizer pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 单株穗数Panicle number per plant | 10.36** | 13.50 |
| 每穗粒数Grain number per panicle | 139.90 | 142.22 |
| 结实率Seed setting rate /% | 90.92** | 85.03 |
| 千粒重Thousand grain weight /g | 25.24** | 24.19 |
| 经济系数Economic index | 0.58** | 0.54 |
| 产量Yield /(kg·hm-2) | 7725.45** | 9054.30 |
| 性状 Trait | 低肥区 Low fertilizer pattern | 高肥区 High fertilizer pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 糙米率Brown rice rate | 79.12 ** | 78.20 |
| 精米率Milled rice rate | 70.02* | 69.22 |
| 整精米率Head rice rate | 64.72 | 63.78 |
| 垩白粒率Chalky rice rate | 25.76 | 27.34 |
| 垩白度Chalk degree | 8.90 | 10.34 |
| 白度值White value | 17.68 | 18.66 |
| 直链淀粉含量Amylose content | 19.88 | 19.95 |
| 蛋白质含量Protein content | 7.35 ** | 7.72 |
| 食味值Taste value | 71.82 ** | 64.76 |
表4 氮肥减施后中日水稻品种杂交RIL群体的米质性状的变化
Table 4 Variation of quality traits of the RIL population under high and low fertilization patterns.
| 性状 Trait | 低肥区 Low fertilizer pattern | 高肥区 High fertilizer pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 糙米率Brown rice rate | 79.12 ** | 78.20 |
| 精米率Milled rice rate | 70.02* | 69.22 |
| 整精米率Head rice rate | 64.72 | 63.78 |
| 垩白粒率Chalky rice rate | 25.76 | 27.34 |
| 垩白度Chalk degree | 8.90 | 10.34 |
| 白度值White value | 17.68 | 18.66 |
| 直链淀粉含量Amylose content | 19.88 | 19.95 |
| 蛋白质含量Protein content | 7.35 ** | 7.72 |
| 食味值Taste value | 71.82 ** | 64.76 |
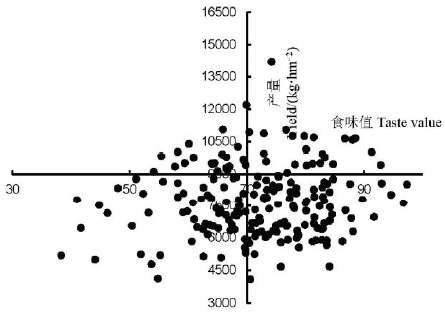
图2 低肥区辽粳5/秋田小町RIL群体产量和食味值分布
Fig. 2. Distribution of grain yield and taste value of the RIL population derived from Liaojing 5/Akita Komachi in low fertilizer level plot.
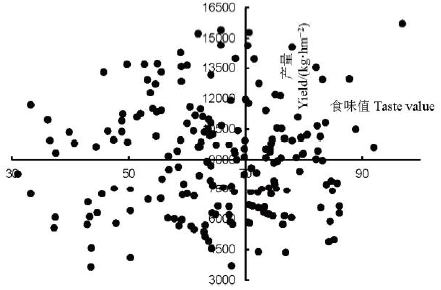
图3 高肥区辽粳5/秋田小町RIL群体产量和食味值分布
Fig. 3. Distribution of grain yield and taste value of the RIL population derived from Liaojing 5/Akita Komachi in high fertilizer level plot.
| 类别 Type | 低产低食味值类型 LYLTV | 低产高食味值类型 LYHTV | 高产低食味值类型 HYLTV | 高产高食味值类型 HYHTV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height /cm | 105.89 c | 117.47 a | 111.27 b | 118.58 a |
| 颈穗弯曲度Panicle curvature /° | 39.38 b | 48.77 a | 46.63 ab | 48.40 a |
| 剑叶基角Flag leaf angle/° | 11.56 b | 14.17 a | 13.17 ab | 13.86 a |
| 倒2叶基角TLA2/° | 11.17 a | 12.36 a | 11.83 a | 12.09 a |
| 倒3叶基角TLA3/° | 16.38 a | 17.94 a | 17.74 a | 16.43 a |
| 剑叶长FLL/cm | 26.57 b | 31.44 a | 29.77 a | 32.16 a |
| 剑叶宽FLW/cm | 1.33 a | 1.28 a | 1.31 a | 1.30 a |
| 倒2叶长TSLL2/cm | 33.98 c | 39.02 ab | 37.05 b | 39.67 a |
| 倒2叶宽TSLW2/cm | 1.14 a | 1.07 b | 1.12 ab | 1.10 ab |
| 倒3叶长TSLL3/cm | 35.59 b | 39.84 a | 38.27 b | 40.19 a |
| 倒3叶宽TSLW3/cm | 1.04 a | 1.00 a | 1.02 a | 0.99 a |
| 穗长Panicle length/cm | 19.22 b | 21.70 a | 21.10 a | 21.57 a |
| 一次枝梗数NPRB | 11.11 ab | 11.31 ab | 11.75 a | 11.71 a |
| 二次枝梗数NSRB | 26.84 a | 26.20 a | 28.43 a | 27.77 a |
| 一次枝梗结实率SSRPRB/% | 95.77 b | 96.16 ab | 95.43 b | 96.81 a |
| 二次枝梗结实率SSRSRB/% | 86.21 a | 87.06 a | 86.22 a | 87.59 a |
| 着粒密度Grain density/(粒·dm-1) | 74.30 a | 63.95 c | 73.34 ab | 67.07 bc |
表5 低肥区不同产量与食味类型株系在株型性状上的差异
Table 5 Differences in plant type traits between plant lines with different yield and taste types at low fertilizer level.
| 类别 Type | 低产低食味值类型 LYLTV | 低产高食味值类型 LYHTV | 高产低食味值类型 HYLTV | 高产高食味值类型 HYHTV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height /cm | 105.89 c | 117.47 a | 111.27 b | 118.58 a |
| 颈穗弯曲度Panicle curvature /° | 39.38 b | 48.77 a | 46.63 ab | 48.40 a |
| 剑叶基角Flag leaf angle/° | 11.56 b | 14.17 a | 13.17 ab | 13.86 a |
| 倒2叶基角TLA2/° | 11.17 a | 12.36 a | 11.83 a | 12.09 a |
| 倒3叶基角TLA3/° | 16.38 a | 17.94 a | 17.74 a | 16.43 a |
| 剑叶长FLL/cm | 26.57 b | 31.44 a | 29.77 a | 32.16 a |
| 剑叶宽FLW/cm | 1.33 a | 1.28 a | 1.31 a | 1.30 a |
| 倒2叶长TSLL2/cm | 33.98 c | 39.02 ab | 37.05 b | 39.67 a |
| 倒2叶宽TSLW2/cm | 1.14 a | 1.07 b | 1.12 ab | 1.10 ab |
| 倒3叶长TSLL3/cm | 35.59 b | 39.84 a | 38.27 b | 40.19 a |
| 倒3叶宽TSLW3/cm | 1.04 a | 1.00 a | 1.02 a | 0.99 a |
| 穗长Panicle length/cm | 19.22 b | 21.70 a | 21.10 a | 21.57 a |
| 一次枝梗数NPRB | 11.11 ab | 11.31 ab | 11.75 a | 11.71 a |
| 二次枝梗数NSRB | 26.84 a | 26.20 a | 28.43 a | 27.77 a |
| 一次枝梗结实率SSRPRB/% | 95.77 b | 96.16 ab | 95.43 b | 96.81 a |
| 二次枝梗结实率SSRSRB/% | 86.21 a | 87.06 a | 86.22 a | 87.59 a |
| 着粒密度Grain density/(粒·dm-1) | 74.30 a | 63.95 c | 73.34 ab | 67.07 bc |
| 类别 Type | 低产低食味值类型 LYLTV | 低产高食味值类型 LYHTV | 高产低食味值类型 HYLTV | 高产高食味值类型 HYHTV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height /cm | 115.29 b | 121.63 a | 124.40 a | 127.44 a |
| 颈穗弯曲度Panicle curvature/° | 43.46 ab | 46.68 ab | 41.82 b | 49.86 a |
| 剑叶基角Flag leaf angle/° | 13.77 ab | 12.95 b | 14.32 ab | 15.54 a |
| 倒2叶基角TLA2/° | 11.29 a | 10.94 b | 12.44 a | 12.03 a |
| 倒3叶基角TLA3/° | 14.49 b | 15.49 a | 16.13 a | 16.33 a |
| 剑叶长FLL/cm | 27.50 b | 31.90 a | 29.39 b | 32.72 a |
| 剑叶宽FLW/cm | 1.38 a | 1.32 b | 1.39 a | 1.31 b |
| 倒2叶长TSLL2/cm | 35.76 b | 40.21 a | 37.75 a | 41.03 a |
| 倒2叶宽TSLW2/cm | 1.21 a | 1.13 b | 1.20 a | 1.12 b |
| 倒3叶长TSLL3/cm | 38.83 b | 41.61 a | 41.84 a | 43.52 a |
| 倒3叶宽TSLW3/cm | 1.12 a | 1.06 ab | 1.11 a | 1.03 b |
| 穗长Panicle length /cm | 19.58 c | 21.52 ab | 20.77 b | 22.02 a |
| 一次枝梗数NPRB | 11.30 c | 11.56 bc | 12.11 a | 11.83 ab |
| 二次枝梗数NSRB | 25.22 b | 25.74 b | 27.63 a | 25.25 b |
| 一次枝梗结实率SSRPRB/% | 92.77 b | 94.61 a | 94.54 a | 95.52 a |
| 二次枝梗结实率SSRSRB/% | 72.68 c | 78.00 ab | 76.82 bc | 82.59 a |
| 着粒密Grain density/(粒·dm-1) | 71.68 a | 65.08 b | 73.76 a | 63.72 b |
表6 高肥区不同产量与食味类型株系在株型性状上的差异
Table 6 Differences in plant type traits between plant lines with different yield and taste types at high fertilizer level.
| 类别 Type | 低产低食味值类型 LYLTV | 低产高食味值类型 LYHTV | 高产低食味值类型 HYLTV | 高产高食味值类型 HYHTV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height /cm | 115.29 b | 121.63 a | 124.40 a | 127.44 a |
| 颈穗弯曲度Panicle curvature/° | 43.46 ab | 46.68 ab | 41.82 b | 49.86 a |
| 剑叶基角Flag leaf angle/° | 13.77 ab | 12.95 b | 14.32 ab | 15.54 a |
| 倒2叶基角TLA2/° | 11.29 a | 10.94 b | 12.44 a | 12.03 a |
| 倒3叶基角TLA3/° | 14.49 b | 15.49 a | 16.13 a | 16.33 a |
| 剑叶长FLL/cm | 27.50 b | 31.90 a | 29.39 b | 32.72 a |
| 剑叶宽FLW/cm | 1.38 a | 1.32 b | 1.39 a | 1.31 b |
| 倒2叶长TSLL2/cm | 35.76 b | 40.21 a | 37.75 a | 41.03 a |
| 倒2叶宽TSLW2/cm | 1.21 a | 1.13 b | 1.20 a | 1.12 b |
| 倒3叶长TSLL3/cm | 38.83 b | 41.61 a | 41.84 a | 43.52 a |
| 倒3叶宽TSLW3/cm | 1.12 a | 1.06 ab | 1.11 a | 1.03 b |
| 穗长Panicle length /cm | 19.58 c | 21.52 ab | 20.77 b | 22.02 a |
| 一次枝梗数NPRB | 11.30 c | 11.56 bc | 12.11 a | 11.83 ab |
| 二次枝梗数NSRB | 25.22 b | 25.74 b | 27.63 a | 25.25 b |
| 一次枝梗结实率SSRPRB/% | 92.77 b | 94.61 a | 94.54 a | 95.52 a |
| 二次枝梗结实率SSRSRB/% | 72.68 c | 78.00 ab | 76.82 bc | 82.59 a |
| 着粒密Grain density/(粒·dm-1) | 71.68 a | 65.08 b | 73.76 a | 63.72 b |

图4 氮肥减施后辽粳5/秋田小町RIL群体产量变动百分比的次数分布
Fig. 4. Percentage change in yield of the RIL population derived from the cross between Liaojing 5 and Akita Komachi after reducing fertilizer.
| 类型 Trait | 高产稳产 HYSY | 高产不稳产 HYIY | 低产稳产 LYSY | 低产不稳产 LYIY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗长Panicle length/cm | 21.51 a | 21.21 a | 20.86 a | 20.18 a |
| 一次枝梗数NPB | 12.16 a | 11.99 ab | 11.40 b | 11.41 b |
| 二次枝梗数NSB | 26.04 a | 26.81 a | 24.99 a | 25.59 a |
| 一次枝梗结实率FRPB/% | 94.56 a | 94.95 a | 93.35 a | 93.58 a |
| 二次枝梗结实率FRSB/% | 74.30 a | 79.48 a | 74.47 a | 74.98 a |
| 着粒密度Grain density/(粒∙dm-1) | 68.47 a | 70.16 a | 66.58 a | 69.90 a |
| 株高Plant height /cm | 121.32 ab | 125.99 a | 118.86 ab | 117.50 b |
| 颈穗弯曲度Panicle curvature/° | 41.92 a | 45.14 a | 46.82 a | 44.01 a |
| 剑叶基角Flag leaf angle/° | 17.86 a | 14.45 b | 11.96 b | 13.98 b |
| 倒2叶基角TLA2/° | 13.42 a | 12.17 a | 10.09 b | 11.54 ab |
| 倒3叶基角TLA3/° | 18.09 a | 16.00 ab | 14.55 b | 15.03 b |
| 剑叶长FLL/cm | 30.62 a | 30.64 a | 29.31 a | 29.28 a |
| 剑叶宽FLW/cm | 1.21 b | 1.38 a | 1.32 a | 1.36 a |
| 倒2叶长TSLL2/cm | 38.40 a | 39.04 a | 38.01 a | 37.40 a |
| 倒2叶宽TSLW2/cm | 1.10 b | 1.18 ab | 1.16 ab | 1.19 a |
| 倒3叶长TSLL3/cm | 40.30 a | 42.70 a | 40.27 a | 39.84 a |
| 倒3叶宽TSLW3/cm | 1.01 a | 1.09 a | 1.06 a | 1.10 a |
表7 产量及其稳定性类型株系的株型特征
Table 7 Plant type traits of high-yield and stable-yield lines.
| 类型 Trait | 高产稳产 HYSY | 高产不稳产 HYIY | 低产稳产 LYSY | 低产不稳产 LYIY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗长Panicle length/cm | 21.51 a | 21.21 a | 20.86 a | 20.18 a |
| 一次枝梗数NPB | 12.16 a | 11.99 ab | 11.40 b | 11.41 b |
| 二次枝梗数NSB | 26.04 a | 26.81 a | 24.99 a | 25.59 a |
| 一次枝梗结实率FRPB/% | 94.56 a | 94.95 a | 93.35 a | 93.58 a |
| 二次枝梗结实率FRSB/% | 74.30 a | 79.48 a | 74.47 a | 74.98 a |
| 着粒密度Grain density/(粒∙dm-1) | 68.47 a | 70.16 a | 66.58 a | 69.90 a |
| 株高Plant height /cm | 121.32 ab | 125.99 a | 118.86 ab | 117.50 b |
| 颈穗弯曲度Panicle curvature/° | 41.92 a | 45.14 a | 46.82 a | 44.01 a |
| 剑叶基角Flag leaf angle/° | 17.86 a | 14.45 b | 11.96 b | 13.98 b |
| 倒2叶基角TLA2/° | 13.42 a | 12.17 a | 10.09 b | 11.54 ab |
| 倒3叶基角TLA3/° | 18.09 a | 16.00 ab | 14.55 b | 15.03 b |
| 剑叶长FLL/cm | 30.62 a | 30.64 a | 29.31 a | 29.28 a |
| 剑叶宽FLW/cm | 1.21 b | 1.38 a | 1.32 a | 1.36 a |
| 倒2叶长TSLL2/cm | 38.40 a | 39.04 a | 38.01 a | 37.40 a |
| 倒2叶宽TSLW2/cm | 1.10 b | 1.18 ab | 1.16 ab | 1.19 a |
| 倒3叶长TSLL3/cm | 40.30 a | 42.70 a | 40.27 a | 39.84 a |
| 倒3叶宽TSLW3/cm | 1.01 a | 1.09 a | 1.06 a | 1.10 a |
| 类型 Type | 高产稳产 高食味值HSYHTV | 高产稳产 低食味值HSYLTV | 高产不稳产 高食味值HUYHTV | 高产不稳产 低食味值HUYLTV | 低产稳产 高食味值LSYHTV | 低产稳产 低食味值LSYLTV | 低产不稳产 高食味值LUYHTV | 低产不稳产低食味值LUYLTV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗长Panicle length/cm | 22.22 a | 21.20 abc | 21.99 ab | 20.70 abc | 21.83 ab | 19.30 c | 21.30 abc | 19.63 bc |
| 一次枝梗数NPRB | 11.73 ab | 12.34 a | 11.85 ab | 12.08 ab | 11.56 ab | 11.14 b | 11.56 ab | 11.34 ab |
| 二次枝梗数NSRB | 22.93 b | 27.37 ab | 25.32 ab | 27.79 a | 25.50 ab | 24.18 ab | 25.91 ab | 25.44 ab |
| 一次枝梗结实率SSRPRB/% | 95.80 a | 94.03 a | 95.46 a | 94.61 a | 93.19 a | 93.62 a | 95.60 a | 92.59 a |
| 二次枝梗结实率SSRSRB/% | 77.41 a | 72.97 a | 82.44 a | 77.56 a | 74.92 a | 73.74 a | 80.14 a | 72.46 a |
| 着粒密度Grain density/(粒·dm-1) | 58.45 b | 72.77 a | 64.03 ab | 74.14 a | 64.20 ab | 70.39 ab | 65.70 ab | 71.96 a |
| 株高Plant height /cm | 129.53 a | 117.80 ab | 127.47 ab | 125.03 ab | 120.76 ab | 115.82 b | 122.23 ab | 115.18 b |
| 颈穗弯曲度Panicle curvature/° | 54.63 a | 36.47 b | 49.49 ab | 42.32 ab | 47.25 ab | 46.12 ab | 46.28 ab | 42.90 ab |
| 剑叶基角Flag leaf angle/° | 19.70 a | 17.07 ab | 15.48 b | 13.78 bc | 11.04 c | 13.42 bc | 14.27 bc | 13.84 bc |
| 倒2叶基角TSLA/° | 13.10 a | 13.56 a | 11.94 ab | 12.32 ab | 9.42 b | 11.17 ab | 12.00 ab | 11.31 ab |
| 倒3叶基角TTLA/° | 16.90 ab | 18.60 a | 16.16 ab | 15.91 ab | 15.29 ab | 13.38 b | 15.63 ab | 14.73 ab |
| 剑叶长FLL/cm | 35.12 a | 28.68 bc | 32.60 ab | 29.37 bc | 31.38 abc | 25.99 c | 32.25 ab | 27.82 bc |
| 剑叶宽FLW/cm | 1.10 c | 1.25 b | 1.32 ab | 1.41 a | 1.32 ab | 1.32 ab | 1.32 ab | 1.39 ab |
| 倒2叶长TSLL2/cm | 43.65 a | 36.16 ab | 40.80 bc | 37.90 bc | 39.95 abc | 34.92 c | 40.39 abc | 35.93 bc |
| 倒2叶宽TSLW2/cm | 0.99 b | 1.15 a | 1.13 a | 1.21 a | 1.14 a | 1.19 a | 1.13 a | 1.22 a |
| 倒3叶长TSLL3/cm | 44.99 a | 38.30 b | 43.40 ab | 42.24 ab | 41.22 ab | 38.75 b | 41.88 ab | 38.84 b |
| 倒3叶宽TSLW3/cm | 0.93 b | 1.05 ab | 1.04 ab | 1.12 a | 1.05 ab | 1.09 a | 1.07 ab | 1.12 a |
表8 不同产量、食味值及产量稳定性类型株系的株型性状差异
Table 8 Characters of plant type of lines with high and stable yield and high taste value.
| 类型 Type | 高产稳产 高食味值HSYHTV | 高产稳产 低食味值HSYLTV | 高产不稳产 高食味值HUYHTV | 高产不稳产 低食味值HUYLTV | 低产稳产 高食味值LSYHTV | 低产稳产 低食味值LSYLTV | 低产不稳产 高食味值LUYHTV | 低产不稳产低食味值LUYLTV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗长Panicle length/cm | 22.22 a | 21.20 abc | 21.99 ab | 20.70 abc | 21.83 ab | 19.30 c | 21.30 abc | 19.63 bc |
| 一次枝梗数NPRB | 11.73 ab | 12.34 a | 11.85 ab | 12.08 ab | 11.56 ab | 11.14 b | 11.56 ab | 11.34 ab |
| 二次枝梗数NSRB | 22.93 b | 27.37 ab | 25.32 ab | 27.79 a | 25.50 ab | 24.18 ab | 25.91 ab | 25.44 ab |
| 一次枝梗结实率SSRPRB/% | 95.80 a | 94.03 a | 95.46 a | 94.61 a | 93.19 a | 93.62 a | 95.60 a | 92.59 a |
| 二次枝梗结实率SSRSRB/% | 77.41 a | 72.97 a | 82.44 a | 77.56 a | 74.92 a | 73.74 a | 80.14 a | 72.46 a |
| 着粒密度Grain density/(粒·dm-1) | 58.45 b | 72.77 a | 64.03 ab | 74.14 a | 64.20 ab | 70.39 ab | 65.70 ab | 71.96 a |
| 株高Plant height /cm | 129.53 a | 117.80 ab | 127.47 ab | 125.03 ab | 120.76 ab | 115.82 b | 122.23 ab | 115.18 b |
| 颈穗弯曲度Panicle curvature/° | 54.63 a | 36.47 b | 49.49 ab | 42.32 ab | 47.25 ab | 46.12 ab | 46.28 ab | 42.90 ab |
| 剑叶基角Flag leaf angle/° | 19.70 a | 17.07 ab | 15.48 b | 13.78 bc | 11.04 c | 13.42 bc | 14.27 bc | 13.84 bc |
| 倒2叶基角TSLA/° | 13.10 a | 13.56 a | 11.94 ab | 12.32 ab | 9.42 b | 11.17 ab | 12.00 ab | 11.31 ab |
| 倒3叶基角TTLA/° | 16.90 ab | 18.60 a | 16.16 ab | 15.91 ab | 15.29 ab | 13.38 b | 15.63 ab | 14.73 ab |
| 剑叶长FLL/cm | 35.12 a | 28.68 bc | 32.60 ab | 29.37 bc | 31.38 abc | 25.99 c | 32.25 ab | 27.82 bc |
| 剑叶宽FLW/cm | 1.10 c | 1.25 b | 1.32 ab | 1.41 a | 1.32 ab | 1.32 ab | 1.32 ab | 1.39 ab |
| 倒2叶长TSLL2/cm | 43.65 a | 36.16 ab | 40.80 bc | 37.90 bc | 39.95 abc | 34.92 c | 40.39 abc | 35.93 bc |
| 倒2叶宽TSLW2/cm | 0.99 b | 1.15 a | 1.13 a | 1.21 a | 1.14 a | 1.19 a | 1.13 a | 1.22 a |
| 倒3叶长TSLL3/cm | 44.99 a | 38.30 b | 43.40 ab | 42.24 ab | 41.22 ab | 38.75 b | 41.88 ab | 38.84 b |
| 倒3叶宽TSLW3/cm | 0.93 b | 1.05 ab | 1.04 ab | 1.12 a | 1.05 ab | 1.09 a | 1.07 ab | 1.12 a |
| [1] | 张维理, 徐爱国, 冀宏杰, Kolbe H.中国农业面源污染形势估计及控制对策: Ⅲ.中国农业面源污染控制中存在问题分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2004, 37(7): 1026-1033. |
| Zhang W L, Xu A G, Ji H J, Kolbe H.Estimation of agricultural non-point source pollution in China and the alleviating strategies: Ⅲ. A review of policies and practices for agricultural non-point source pollution control in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2004, 37(7):1026-1033. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 张洪程, 马群, 杨雄, 李敏, 葛梦婕, 李国业, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 高辉, 刘艳阳. 水稻品种氮肥群体最高生产力及其增长规律[J]. 作物学报, 2012, 38(1): 86-98. |
| Zhang H C, Ma Q Y, Xiong, L M, Ge M J, Li G Y, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Gao H, and Liu Y Y. The highest population productivity of nitrogen fertilization and its variation rules in rice cultivars[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(1): 86-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 霍中洋, 顾海永, 马群, 杨雄, 李敏, 李国业, 戴其根, 许轲, 魏海燕, 高辉, 芦燕, 张洪程. 不同氮肥群体最高生产力水稻品种的氮素吸收利用差异[J]. 作物学报, 2012, 38(11): 2061-2068. |
| Huo Z Y, Gu H Y, Ma Q, Yang X, Li M, Li G Y, Dai Q G, Xu K,Wei H Y, Gao H, Lu Y,Zhang H C.Differences of nitrogen absorption and utilization in rice varieties with different productivity levels[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(11): 2061-2068. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 张庆, 殷春渊, 张洪程, 魏海燕, 马群, 杭杰, 李敏, 李国业. 水稻氮高产高效与低产低效两类品种株型特征差异研究[J]. 作物学报, 2010, 36(6): 1011-1021. |
| Zhang Q, Yin C Y, Zhang H C, Wei H Y, Ma Q, Hang J, Li M,Li G Y.Differences of plant-type characteristics between rice cultivars with high and low levels in yield and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2010, 36(6): 1011-1021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 王伟妮, 鲁剑巍, 何予卿等. 氮、磷、钾肥对水稻产量、品质及养分吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(6): 645-653. |
| Wang W N, Luj W, He Y Q, Li X K, Li H.Effects of N, P, K fertilizer application on grain yield, quality, nutrient uptake and utilization of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(6): 645-653. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 孙永健, 孙园园, 严奉君, 杨志远, 徐徽, 李玥, 王海月, 马均. 氮肥后移对不同氮效率水稻花后碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(3): 407-419. |
| Sun Y J, Sun Y Y, Yan F J, Yang Z Y, Xu H, Li Y, Wang H Y,Ma J.Effects of postponing nitrogen topdressing on post-anthesis carbon and nitrogen metabolism in rice cultivars with different nitrogen use efficiencies[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 407-419. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 袁隆平. 选育超高产杂交水稻的进一步设想[J]. 杂交水稻, 2012, 27(6): 1-2. |
| Yuan L P.Conceiving of breeding further super-high- yield hybrid rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2012, 27(6): 1-2. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 陈温福, 徐正进, 张龙步, 张文忠, 马殿荣. 北方粳型稻超高产育种理论与实践[J]. 中国农业科学, 2007(5): 869-874. |
| Chen W F, Xu Z J, Zhang L B, Zhang W Z, Ma D R.Theories and practices of breeding japonica rice for super high yield[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica. 2007(5): 869-874. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 程式华, 翟虎渠. 水稻亚种间超高产杂交组合若干株型因子的比较[J]. 作物学报, 2000, 26(6): 713-718. |
| Cheng S H, Zhai H Q.Comparison of some plant type components in super high-yielding hybrids of inter- subspecies rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2000, 26(6): 713-718. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 周开达, 马玉清, 刘太清, 沈茂松. 杂交水稻亚种间重穗型组合选育-杂交水稻超高产育种的理论与实践[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 1995,13(4): 403-407. |
| Zhou K D, Ma Y Q, Liu T Q, Shen M S.The breeding of subspecific heavy ear hybrid rice-exploration about super-high yield breeding of hybrid rice[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 1995, 13(4):403-407. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 苏柏元, 朱德峰. 超级稻甬优12 机插单产1000 kg/667m2的产量结构与配套栽培技术[J]. 中国稻米, 2013, 19(4): 97-100. |
| Su B Y, Zhu D F.The yield components and cultivation technology of Yongyou 12 yielding over 1000 kg per 667 m2 through mechanical transplanting[J]. China Rice, 2013, 19(4): 97-100. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 颜振德. 杂交水稻高产群体的干物质生产与分配的研究[J]. 作物学报, 1981, 7(1): 11-18. |
| Yan Z D.Studies on the production and distribution of dry matter in high-yielding populations of hybrid rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1981, 7(1): 11-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 蒋彭炎, 冯来定, 姚长溪. 从水稻稀少平栽培法的高产效应看栽培技术与株型的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1987, 1(2): 111-117. |
| Jiang P Y, Feng L D, Yao C X.The effect of cultivation techniques on plant type in view of the high yield result induced by TFS cultivation method in paddy rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 1987, 1(2): 111-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 凌启鸿, 苏祖芳, 张海泉. 水稻成穗率与群体质量的关系及其影响因素的研究[J]. 作物学报, 1995, 21(4): 463-469. |
| Ling Q H, Su Z F, Zhang H Q.Relationship between earbearing tiller percentage and population quality and its influential factors in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1995, 21(4): 463-469. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 凌启鸿, 张洪程, 蔡建中, 苏祖芳, 凌励. 水稻高产群体质量及其优化控制探讨[J]. 中国农业科学, 1993, 26(6): 1-11. |
| Ling Q H, Zhang H C, Cai J Z, Su Z F, Ling L.Investigation on the population quality of high yield and its optimizing control programme in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1993, 26(6): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 朱德峰, 张玉屏, 陈惠哲, 向镜, 张义凯. 中国水稻高产栽培技术创新与实践[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(17): 3404-3414. |
| Zhu D F, Zhang Y P, Chen H Z, Xiang J, Zhang Y K.Innovation and practice of high-yield rice cultivation technology in china[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(17): 3404-3414. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Peng S B, Tang Q Y, Zou Y B.Current status and challenges of rice production in China.Plant Production Science, 2009, 12(1): 3-8. |
| [18] | 楠谷彰人, 崔晶. 日本水稻生产的发展和新课题[J]. 天津农学院学报, 2012, 19(2): 40-44. |
| Akihito Kwutani, Cui J.Development and new researches on rice production in Japan[J]. Journal of Tianjin Agricultural University, 2012, 19(2): 40-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 徐正进, 陈温福, 张龙步, 杨守仁等. 水稻不同穗型群体冠层光分布的比较研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 1990, 23(4): 10-16. |
| Xu Z J, Chen W F, Zhang L B, Yang S R.Comparative study on light distribution in rice canopies with different panicle types[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1990, 23(4): 10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 李廷亮, 谢英荷, 洪坚平, 冯倩, 孙丞鸿, 王志伟. 施氮量对晋南旱地冬小麦光合特性、产量及氮素利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(4): 704-711. |
| Li T L, Xie Y H, Hong J P, Feng Q, Sun C H,Wang Z W.Effects of nitrogen application rate on photosynthetic characteristics, yield, and nitrogen utilization in rainfed winter Wheat in Southern Shanxi[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(4): 704-711. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 武文明, 陈洪俭, 李金才, 魏凤珍, 王世济, 周向红. 氮肥运筹对孕穗期受渍冬小麦旗叶叶绿素荧光与籽粒灌浆特性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2012, 38(6): 1088-1096. |
| Wu W M, Chen H J, Li J C, Wei F Z, Wang S J,Zhou X H.Effects of nitrogen fertilization on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of flag leaf and grain filling in winter wheat suffered waterlogging at booting stage[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica , 2012, 38(6): 1088-1096. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Fan T L, Xu M G, Zhou G Y, Ding L P.Trends in grain yields and soil organic carbon in a long-term fertilization experiment in the China Loess Plateau.American- Eurasian Journal of Agricultural Environmental Science, 2007, 2: 600-610. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Singh U,. Ladha J.K,. Castillo E. G,. Punzalan G,. Tirol- Padre A,. Duqueza M. Genotypic variation in nitrogen use efficiency in medium and long-duration rice.Field Crops Research, 1998, 58: 35-53. |
| [24] | 江立庚, 曹卫星. 水稻高效利用氮素的生理机制及有效途径[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2002, 16(3) : 261-264. |
| Jiang L G, Cao W X.Physiological mechanism and approaches for efficient nitrogen utilization in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2002, 16(3): 261-264. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 剧成欣, 陶进, 钱希旸, 顾骏飞, 赵步洪, 杨凯鹏, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 不同年代中籼水稻品种的产量与氮肥利用效率[J]. 作物学报, 2015, 41(3): 422-431. |
| Ju C X, Tao J, Qian X Y, Gu J F, Zhao B H, Yang K P, Wang Z Q, And Yang J C. Grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of mid-season indica rice cultivars applied at different decades[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2015, 41(3): 422-431. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 张忠臣, 刘海英, 高红秀, 王露露, 徐振华, 曲莹, 孙静, 金正勋. 施肥量和穴内插秧密度对寒地粳稻产量和品质性状的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2012, 3(22): 99-104 |
| Zhang Z C, Liu H Y, Gao H X, Wang L L, Xu Z H, Qu Y, Sun J, Jin Z X.Effects of seedlings number per hill and fertilizer application on grain yield and quality of japonica rice in cold region[J]. Crops, 2012, 3(22): 99-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 徐海, 宫彦龙, 夏原野, 闫志强, 王华杰, 唐亮, 徐正进. 中日水稻品种杂交后代株型性状的变化及其相互关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(4): 363-372 |
| Xu H, Gong Y L, Xia Y Y, Yan Z Q, Wang H J, Tang L, Xu Z J.Variations in plant type traits and their relationship of progeny derived from the cross between Chinese rice variety and Japanese rice variety[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2015, 29(4): 363-372. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 徐海, 宫彦龙, 夏原野, 杜志敏, 闫志强, 王华杰, 陈温福, 徐正进. 中日水稻品种杂交后代的株型性状与产量和品质的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(3): 283-290. |
| Xu H, Gong Y L, Xia Y Y, Du Z M,Yan Z Q, Wang H J, Chen W F, Xu Z J.Relation of plant type traits with yield and quality in the RIL population derived from cross between Chinese rice variety and Japanese rice variety[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(3): 283-290. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [4] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [5] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [6] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [7] | 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 王岩, 王旺, 王开, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 许轲, 张洪程. 穗分化末期-灌浆初期干旱胁迫对优质食味粳稻根系形态和叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [8] | 雍明玲, 叶苗, 张雨, 陶钰, 倪川, 康钰莹, 张祖建. 不同食味水稻品种稻米淀粉结构与理化特性及其对氮素响应的差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 57-71. |
| [9] | 谢开珍, 张建明, 程灿, 周继华, 牛付安, 孙滨, 张安鹏, 闻伟军, 代雨婷, 胡启琰, 邱越, 曹黎明, 储黄伟. 低直链淀粉含量水稻种质资源的鉴定与QTL定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 609-616. |
| [10] | 朱旺, 张翔, 耿孝宇, 张哲, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根, 许轲, 朱广龙, 周桂生, 孟天瑶. 盐-旱复合胁迫下水稻根系的形态和生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [11] | 邹宇傲, 吴启侠, 周乾顺, 朱建强, 晏军. 孕穗期杂交中稻对淹涝胁迫的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| [12] | 兰金松, 庄慧. 水稻株型的分子机理研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | 袁沛, 周旋, 杨威, 尹凌洁, 靳拓, 彭建伟, 荣湘民, 田昌. 化肥减氮配施对洞庭湖区双季稻产量和田面水氮磷流失风险的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 518-528. |
| [14] | 肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [15] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||