
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (5): 529-542.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.221111
肖大康1, 胡仁1, 韩天富2, 张卫峰3, 侯俊1,*( ), 任科宇2,*(
), 任科宇2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-23
修回日期:2023-02-27
出版日期:2023-09-10
发布日期:2023-09-13
通讯作者:
*email: 基金资助:
XIAO Dakang1, HU Ren1, HAN Tianfu2, ZHANG Weifeng3, HOU Jun1,*( ), REN Keyu2,*(
), REN Keyu2,*( )
)
Received:2022-11-23
Revised:2023-02-27
Online:2023-09-10
Published:2023-09-13
Contact:
*email: 摘要:
【目的】 合理的氮肥用量和运筹能够有效提高水稻产量和氮肥利用率。明确氮肥用量和运筹对水稻产量及其构成因子的影响可为水稻高产高效生产提供理论指导。【方法】 基于119篇已发表的有关稻田氮肥管理的论文,采用整合分析(Meta-analysis)的方法量化了不同施氮量、基肥+分蘖肥、穗肥、种植区域和土壤性质等条件下氮肥管理对水稻产量及其构成因子的影响,并探究了我国各水稻主产区提高产量构成因子以获得高产的适宜措施。【结果】 与不施氮肥相比,施用氮肥能够显著提高水稻实际产量(+42.2%)和理论产量(+43.1%),有效穗数和每穗粒数分别增加了33.2%和13.5%,而结实率和千粒重分别下降了4.2%和1.6%。在不同施氮量和氮肥运筹下,水稻产量及其构成因子存在显著差异。水稻实际和理论产量在施氮量为150~200 kg/hm2时增幅最大,有效穗数和每穗粒数在施氮量为250~300 kg/hm2时增幅最大。另外,随着施氮量的增加,水稻的结实率和千粒重显著下降。基肥+分蘖肥的氮比例(基肥+分蘖肥占总施氮量的比例)为30%~50%和穗肥氮比例为10%~30%时,水稻增产幅度最大;基肥+分蘖肥氮比例(≤70%)增加,水稻有效穗数的提升幅度呈上升趋势,而每穗粒数和结实率的提升幅度呈下降趋势;穗肥氮比例(穗肥占总施氮量的比例)增加(≤30%),每穗粒数和结实率的提升幅度呈上升趋势。对于不同稻区而言,水稻产量及其构成因子的提升幅度存在显著差异,主要表现为东北单季稻区产量增幅最大,长江流域单双季稻区次之,南方单双季稻区和云贵川湘高原单季稻区最小。所有稻区均通过增加有效穗数和穗粒数以获得高产。水稻实际和理论产量的增幅受SOM(土壤有机质)影响较小,各SOM水平间的增幅差异不超过4.39%和2.26%,而受土壤TN(总氮)、AN(有效氮)、AP(有效磷)、AK(速效钾)的含量变化影响较大,但亚组间没有显著差异。【结论】 我国水稻的推荐施氮量不宜超过250 kg/hm2,推荐基肥+分蘖肥比例不要超过总施氮量的70%,穗肥比例10%~30%时更有利于水稻增产。在保证水稻有效穗数和穗粒数前提下,提高结实率是所有稻区未来增产的关键,需通过化学调控、适宜的栽培密度和优良品种等综合管理措施来实现。
肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542.
XIAO Dakang, HU Ren, HAN Tianfu, ZHANG Weifeng, HOU Jun, REN Keyu. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Consumption and Operation on Rice Yield and Its Components in China:A Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 529-542.
| 解释变量 Explanatory variables | 分组 Group |
|---|---|
| 施氮量 N application level/(kg·hm−2) | ≤50; (50-100]; (100-150]; (150-200]; (200-250]; (250-300]; (300-350];>350 |
| 基肥+分蘖肥比例 N ratio of basal+tillering fertilizer/total N/% | ≤30; (30-50]; (50-70];>70 |
| 穗肥比例 Ratio of topdressing for panicle initiation/% | ≤10; (10-30]; (30-50];>50 |
| 水稻种植区域 Rice planting area | 长江流域单双季稻区、南方单双季稻区、云贵川湘山地高原单季稻区、东北单季稻区 Single and double cropping rice area in the Yangtze River basin; Single and double cropping rice area in South China; Single-season rice region in Yunnan, Guizhou, Sichuan and Hunan provinces; Single-season rice region in Northease China |
| 有机质含量 SOM(soil organic matter)/(g·kg−1) | ≤10; 10-20; >20 |
| 全氮含量 TN(total nitrogen)/(g·kg−1) | ≤1; 1-1.5; >1.5 |
| 碱解氮含量 AN(available nitrogen)/(mg·kg−1) | ≤90; 90-150; >150 |
| 速效磷含量 AP(available phosphorus)/(mg·kg−1) | ≤10; 10-20; >20 |
| 速效钾含量 AK(available potassium)/(mg·kg−1) | ≤80; 80-160; >160 |
表1 氮肥管理对水稻产量及其构成因子效应数据库解释变量的分组
Table 1. Classification and grouping of explanatory variables of nitrogen management on rice yield and component factors.
| 解释变量 Explanatory variables | 分组 Group |
|---|---|
| 施氮量 N application level/(kg·hm−2) | ≤50; (50-100]; (100-150]; (150-200]; (200-250]; (250-300]; (300-350];>350 |
| 基肥+分蘖肥比例 N ratio of basal+tillering fertilizer/total N/% | ≤30; (30-50]; (50-70];>70 |
| 穗肥比例 Ratio of topdressing for panicle initiation/% | ≤10; (10-30]; (30-50];>50 |
| 水稻种植区域 Rice planting area | 长江流域单双季稻区、南方单双季稻区、云贵川湘山地高原单季稻区、东北单季稻区 Single and double cropping rice area in the Yangtze River basin; Single and double cropping rice area in South China; Single-season rice region in Yunnan, Guizhou, Sichuan and Hunan provinces; Single-season rice region in Northease China |
| 有机质含量 SOM(soil organic matter)/(g·kg−1) | ≤10; 10-20; >20 |
| 全氮含量 TN(total nitrogen)/(g·kg−1) | ≤1; 1-1.5; >1.5 |
| 碱解氮含量 AN(available nitrogen)/(mg·kg−1) | ≤90; 90-150; >150 |
| 速效磷含量 AP(available phosphorus)/(mg·kg−1) | ≤10; 10-20; >20 |
| 速效钾含量 AK(available potassium)/(mg·kg−1) | ≤80; 80-160; >160 |

图1 施氮对水稻产量和产量构成因子的影响 括号内为样本数;虚线为辅助线。
Fig. 1. Effects of nitrogen application on rice yield and yield components. Number of samples in parentheses; The dotted line is the auxiliary line.

图2 不同施氮量下水稻实际产量(A)、理论产量(B)、有效穗数(C)、每穗粒数(D)、结实率(E)、千粒重(F)的增幅 n为样本数;虚线为辅助线。
Fig. 2. Increase range of actual yield (A), theoretical yield (B), number of effective panicles (C), number of grains per panicle (D), seed setting rate (E) and thousand grain weight (F) of rice under various nitrogen levels. n is the number of samples; The dotted line is the auxiliary line.

图3 不同基肥+分蘖肥比例下水稻实际产量(A)、理论产量(B)、有效穗数(C)、每穗粒数(D)、结实率(E)、千粒重(F)的增幅 n为样本数;虚线为辅助线。
Fig. 3. Increase range of actual yield (A), theoretical yield (B), number of effective panicles (C), number of grains per panicle (D), seed setting rate (E) and 1000-grain weight (F) of rice under different basal+tillering fertilizer ratios. n is the number of samples; The dotted line is the auxiliary line.

图4 不同穗肥比例下水稻实际产量(A)、理论产量(B)、有效穗数(C)、每穗粒数(D)、结实率(E)、千粒重(F)的增幅 n为样本数。
Fig. 4. Increase range of actual yield (A), theoretical yield (B), number of effective panicles (C), number of grains per panicle (D), seed setting rate (E) and 1000 grain weight (F) of rice under different ratios of topdressing for panicle initiation. n is the number of samples.
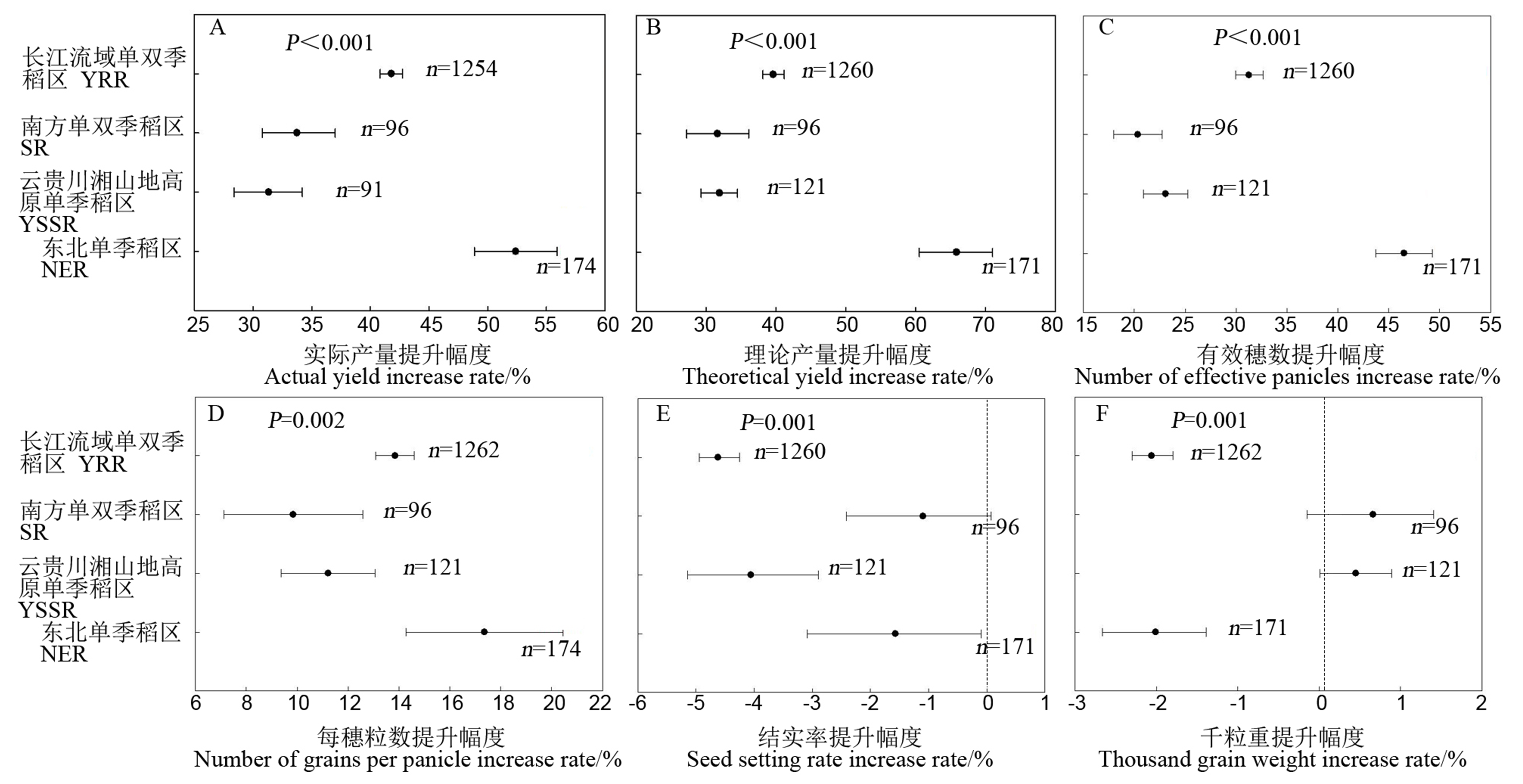
图5 不同稻区水稻实际产量(A)、理论产量(B)、有效穗数(C)、每穗粒数(D)、结实率(E)、千粒重(F)的增幅 YRR-长江流域单双季稻区; SR-南方单双季稻区; YSSR-云贵川湘山地高原单季稻区; NER-东北单季稻区。
Fig. 5. Increase range of actual yield, theoretical yield, effective panicles (A), grains per panicle (B), seed setting rate (C) and 1000 grain weight (D) of rice in different rice areas. YRR, Single and double cropping rice area in the Yangtze River basin; SR, Single and double cropping rice area in South China; YSSR, Yunnan-Guizhou Sichuan-Hunan mountainous plateau single-season rice region; NER, Northeast single-season rice region.
| 项目 Item | 有效穗数Number of effective panicles | 每穗粒数Number of grains per panicle | 结实率Seed setting rate | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | |||||||||
| SOM (g·kg−1) | ≤10 | 35.43 | 31.78, | 39.11 | 111 | 18.72 | 14.58, | 23.01 | 111 | −6.19 | −7.55, | −4.86 | 111 | ||||
| 10-20 | 26.19 | 22.09, | 29.65 | 226 | 20.83 | 17.93, | 24.00 | 211 | −3.11 | −6.00, | −0.88 | 208 | |||||
| >20 | 35.05 | 33.78, | 36.33 | 986 | 11.76 | 10.68, | 12.77 | 986 | −4.07 | −5.13, | −3.38 | 986 | |||||
| TN (g·kg−1) | ≤1 | 41.72 | 36.45, | 47.18 | 106 | 14.64 | 11.58, | 17.74 | 88 | −3.05 | −4.70, | −1.46 | 88 | ||||
| 1-1.5 | 31.59 | 29.18, | 33.75 | 435 | 8.59 | 7.50, | 9.74 | 434 | −5.20 | −6.58, | −4.27 | 435 | |||||
| >1.5 | 33.96 | 32.46, | 35.46 | 594 | 14.04 | 12.52, | 15.43 | 584 | −4.16 | −5.87, | −3.13 | 594 | |||||
| AN (mg·kg−1) | ≤90 | 38.00 | 36.10, | 39.99 | 309 | 9.97 | 8.56, | 11.34 | 309 | −3.90 | −4.66, | −3.19 | 309 | ||||
| 90-150 | 32.46 | 30.50, | 34.25 | 485 | 19.34 | 17.59, | 21.17 | 488 | −4.35 | −4.97, | −3.69 | 485 | |||||
| >150 | 33.22 | 31.05, | 35.35 | 235 | 6.62 | 3.94, | 8.74 | 235 | −6.42 | −10.27, | −3.99 | 235 | |||||
| AP (mg·kg−1) | ≤10 | 29.03 | 23.08, | 33.60 | 148 | 10.62 | 6.52, | 14.00 | 148 | −8.95 | −15.60, | −4.24 | 148 | ||||
| 10-20 | 35.09 | 33.08, | 37.05 | 388 | 14.20 | 12.61, | 15.84 | 388 | −3.56 | −4.15, | −2.98 | 388 | |||||
| >20 | 33.58 | 32.27, | 34.96 | 922 | 15.02 | 13.91, | 16.21 | 907 | −4.07 | −4.52, | −3.59 | 904 | |||||
| AK (mg·kg−1) | ≤80 | 35.84 | 33.90, | 37.82 | 357 | 11.39 | 10.31, | 12.55 | 357 | −3.20 | −3.74, | −2.65 | 357 | ||||
| 80-160 | 33.58 | 32.05, | 35.08 | 920 | 16.77 | 15.49, | 18.13 | 905 | −4.69 | −5.95, | −3.76 | 902 | |||||
| >160 | 29.12 | 26.63, | 31.59 | 194 | 7.51 | 5.18, | 9.77 | 194 | −5.51 | −6.76, | −4.30 | 194 | |||||
| 项目 Item | 千粒重Thousand grain weight | 实际产量Actual yield | 理论产量Theoretical yield | ||||||||||||||
| 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | |||||||||
| SOM (g·kg−1) | ≤10 | −3.94 | −9.95, | 0.75 | 111 | 43.40 | 38.39, | 48.60 | 111 | 44.89 | 33.55, | 55.35 | 111 | ||||
| 10-20 | −1.53 | −3.20, | −0.19 | 229 | 39.49 | 33.26, | 44.56 | 223 | 45.15 | 33.38, | 55.01 | 208 | |||||
| >20 | −1.30 | −2.11, | −0.42 | 986 | 43.88 | 41.99, | 45.83 | 956 | 42.89 | 40.45, | 45.31 | 986 | |||||
| TN (g·kg−1) | ≤1 | −5.12 | −11.28, | −0.35 | 106 | 55.02 | 48.78, | 61.91 | 106 | 51.33 | 37.20, | 64.54 | 88 | ||||
| 1-1.5 | −0.58 | −2.98, | 2.45 | 435 | 35.66 | 33.43, | 38.15 | 417 | 33.51 | 28.21, | 37.77 | 423 | |||||
| >1.5 | −1.93 | −2.78, | −0.91 | 594 | 41.03 | 38.22, | 43.52 | 576 | 43.96 | 40.33, | 47.14 | 594 | |||||
| AN (mg·kg−1) | ≤90 | −2.50 | −4.34, | −0.93 | 309 | 47.92 | 44.54, | 51.69 | 309 | 42.19 | 38.56, | 45.56 | 309 | ||||
| 90-150 | −0.79 | −2.00, | 1.34 | 488 | 41.72 | 38.21, | 44.67 | 458 | 49.17 | 45.73, | 52.79 | 473 | |||||
| >150 | 0.53 | −0.78, | 2.83 | 235 | 39.67 | 37.08, | 42.40 | 229 | 33.62 | 26.30, | 40.02 | 235 | |||||
| AP (mg·kg−1) | ≤10 | −1.18 | −5.20, | 3.28 | 148 | 31.00 | 21.99, | 38.24 | 148 | 28.42 | 13.03, | 42.28 | 148 | ||||
| 10-20 | −3.12 | −4.86, | −1.74 | 388 | 42.49 | 40.27, | 44.82 | 379 | 44.14 | 40.17, | 47.73 | 388 | |||||
| >20 | −1.25 | −2.22, | 0.02 | 925 | 44.83 | 42.56, | 47.08 | 898 | 45.62 | 42.92, | 48.48 | 904 | |||||
| AK (mg·kg−1) | ≤80 | −1.51 | −3.85, | 0.70 | 357 | 44.86 | 40.72, | 49.32 | 336 | 44.27 | 40.02, | 48.16 | 357 | ||||
| 80-160 | −1.68 | −2.79, | −0.29 | 923 | 42.72 | 40.62, | 44.67 | 908 | 46.24 | 42.36, | 50.10 | 902 | |||||
| >160 | −1.66 | −2.34, | −0.97 | 194 | 35.77 | 29.12, | 40.97 | 194 | 28.99 | 25.29, | 32.66 | 194 | |||||
表4 不同土壤全氮和速效氮含量下水稻产量及构成因子的增幅
Table 4. Increase range of rice yield and its components under various soil total nitrogen and available nitrogen contents.
| 项目 Item | 有效穗数Number of effective panicles | 每穗粒数Number of grains per panicle | 结实率Seed setting rate | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | |||||||||
| SOM (g·kg−1) | ≤10 | 35.43 | 31.78, | 39.11 | 111 | 18.72 | 14.58, | 23.01 | 111 | −6.19 | −7.55, | −4.86 | 111 | ||||
| 10-20 | 26.19 | 22.09, | 29.65 | 226 | 20.83 | 17.93, | 24.00 | 211 | −3.11 | −6.00, | −0.88 | 208 | |||||
| >20 | 35.05 | 33.78, | 36.33 | 986 | 11.76 | 10.68, | 12.77 | 986 | −4.07 | −5.13, | −3.38 | 986 | |||||
| TN (g·kg−1) | ≤1 | 41.72 | 36.45, | 47.18 | 106 | 14.64 | 11.58, | 17.74 | 88 | −3.05 | −4.70, | −1.46 | 88 | ||||
| 1-1.5 | 31.59 | 29.18, | 33.75 | 435 | 8.59 | 7.50, | 9.74 | 434 | −5.20 | −6.58, | −4.27 | 435 | |||||
| >1.5 | 33.96 | 32.46, | 35.46 | 594 | 14.04 | 12.52, | 15.43 | 584 | −4.16 | −5.87, | −3.13 | 594 | |||||
| AN (mg·kg−1) | ≤90 | 38.00 | 36.10, | 39.99 | 309 | 9.97 | 8.56, | 11.34 | 309 | −3.90 | −4.66, | −3.19 | 309 | ||||
| 90-150 | 32.46 | 30.50, | 34.25 | 485 | 19.34 | 17.59, | 21.17 | 488 | −4.35 | −4.97, | −3.69 | 485 | |||||
| >150 | 33.22 | 31.05, | 35.35 | 235 | 6.62 | 3.94, | 8.74 | 235 | −6.42 | −10.27, | −3.99 | 235 | |||||
| AP (mg·kg−1) | ≤10 | 29.03 | 23.08, | 33.60 | 148 | 10.62 | 6.52, | 14.00 | 148 | −8.95 | −15.60, | −4.24 | 148 | ||||
| 10-20 | 35.09 | 33.08, | 37.05 | 388 | 14.20 | 12.61, | 15.84 | 388 | −3.56 | −4.15, | −2.98 | 388 | |||||
| >20 | 33.58 | 32.27, | 34.96 | 922 | 15.02 | 13.91, | 16.21 | 907 | −4.07 | −4.52, | −3.59 | 904 | |||||
| AK (mg·kg−1) | ≤80 | 35.84 | 33.90, | 37.82 | 357 | 11.39 | 10.31, | 12.55 | 357 | −3.20 | −3.74, | −2.65 | 357 | ||||
| 80-160 | 33.58 | 32.05, | 35.08 | 920 | 16.77 | 15.49, | 18.13 | 905 | −4.69 | −5.95, | −3.76 | 902 | |||||
| >160 | 29.12 | 26.63, | 31.59 | 194 | 7.51 | 5.18, | 9.77 | 194 | −5.51 | −6.76, | −4.30 | 194 | |||||
| 项目 Item | 千粒重Thousand grain weight | 实际产量Actual yield | 理论产量Theoretical yield | ||||||||||||||
| 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | 增幅Increase/% | Bootstrap CI/% | n | |||||||||
| SOM (g·kg−1) | ≤10 | −3.94 | −9.95, | 0.75 | 111 | 43.40 | 38.39, | 48.60 | 111 | 44.89 | 33.55, | 55.35 | 111 | ||||
| 10-20 | −1.53 | −3.20, | −0.19 | 229 | 39.49 | 33.26, | 44.56 | 223 | 45.15 | 33.38, | 55.01 | 208 | |||||
| >20 | −1.30 | −2.11, | −0.42 | 986 | 43.88 | 41.99, | 45.83 | 956 | 42.89 | 40.45, | 45.31 | 986 | |||||
| TN (g·kg−1) | ≤1 | −5.12 | −11.28, | −0.35 | 106 | 55.02 | 48.78, | 61.91 | 106 | 51.33 | 37.20, | 64.54 | 88 | ||||
| 1-1.5 | −0.58 | −2.98, | 2.45 | 435 | 35.66 | 33.43, | 38.15 | 417 | 33.51 | 28.21, | 37.77 | 423 | |||||
| >1.5 | −1.93 | −2.78, | −0.91 | 594 | 41.03 | 38.22, | 43.52 | 576 | 43.96 | 40.33, | 47.14 | 594 | |||||
| AN (mg·kg−1) | ≤90 | −2.50 | −4.34, | −0.93 | 309 | 47.92 | 44.54, | 51.69 | 309 | 42.19 | 38.56, | 45.56 | 309 | ||||
| 90-150 | −0.79 | −2.00, | 1.34 | 488 | 41.72 | 38.21, | 44.67 | 458 | 49.17 | 45.73, | 52.79 | 473 | |||||
| >150 | 0.53 | −0.78, | 2.83 | 235 | 39.67 | 37.08, | 42.40 | 229 | 33.62 | 26.30, | 40.02 | 235 | |||||
| AP (mg·kg−1) | ≤10 | −1.18 | −5.20, | 3.28 | 148 | 31.00 | 21.99, | 38.24 | 148 | 28.42 | 13.03, | 42.28 | 148 | ||||
| 10-20 | −3.12 | −4.86, | −1.74 | 388 | 42.49 | 40.27, | 44.82 | 379 | 44.14 | 40.17, | 47.73 | 388 | |||||
| >20 | −1.25 | −2.22, | 0.02 | 925 | 44.83 | 42.56, | 47.08 | 898 | 45.62 | 42.92, | 48.48 | 904 | |||||
| AK (mg·kg−1) | ≤80 | −1.51 | −3.85, | 0.70 | 357 | 44.86 | 40.72, | 49.32 | 336 | 44.27 | 40.02, | 48.16 | 357 | ||||
| 80-160 | −1.68 | −2.79, | −0.29 | 923 | 42.72 | 40.62, | 44.67 | 908 | 46.24 | 42.36, | 50.10 | 902 | |||||
| >160 | −1.66 | −2.34, | −0.97 | 194 | 35.77 | 29.12, | 40.97 | 194 | 28.99 | 25.29, | 32.66 | 194 | |||||

图7 氮水平对水稻实际产量(A)、理论产量(B)和构成因子(C)的影响
Fig. 7. Effect of nitrogen level on actual yield (A), theoretical yield (B) and yield component factors (C) of rice.
| [1] | FAOSTAT, 2018. Food and agriculture organization of the united nations Statistics Division. |
| [2] | 李辛一. 长期化肥投入对我国粮食产量影响的实证[J]. 中国国际财经, 2016(21): 61-67. |
| Li X Y. Empirical study on the impact of long-term fertilizer input on China's grain output[J]. China International Finance, 2016 (21): 61-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Grassini P, Eskridge K M, Cassman K G. Distinguishing between yield advances and yield plateaus in historical crop production trends[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 1-11. |
| [4] | Sun Y J, Ma J, Sun, Y Y, Xu H, Yang Z Y, Liu S J, Jia X W, Zheng H Z. The effects of different water and nitrogen managements on yield and nitrogen use efficiency in hybrid rice of China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2012, 127: 85-98. |
| [5] | Yi J, Gao J P, Zhang W Z, Zhao Y Z, Zhao C, Zhao Y, Li Z A, Xin W. Delayed timing of tillering fertilizer improved grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in japonica rice[J]. Crop Science, 2020, 60(2): 1021-1033. |
| [6] | 吕小红, 付立东, 宋玉婷, 陈温福. 施氮量对不同株型水稻产量及穗部性状的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2016, 32(3): 542-547. |
| Lv X H, Fu L D, Song Y T, Chen W F. Effects of nitrogen application on yield and panicle traits of rice with different plant types[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Journal, 2016, 32 (3): 542-547. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 王琳, 谢树果, 竭润生, 杜晓秋, 何平, 彭伟. 不同施氮量对川东北地区水稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 耕作与栽培, 2014(6): 12-16. |
| Wang L, Xie S G, Jie R S, Du X Q, He P, Peng W. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency in Northeast Sichuan[J]. Tillage and Cultivation, 2014(6): 12-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 石丽红, 纪雄辉, 朱校奇, 李洪顺, 彭华, 刘昭兵. 提高超级杂交稻库容量的施氮数量和时期运筹[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(6): 1274-1281. |
| Shi L H, Ji X H, Zhu X Q, Li H S, Peng H, Liu Z B. Research on the amount and period of nitrogen application to improve the storage capacity of super hybrid rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43 (6): 1274-1281. | |
| [9] | 陈桂芬, 黄雁飞, 刘斌, 刘淑仪, 黄玉溢, 林昔香, 唐其展. 广西稻区不同水稻品种对氮肥施用量的响应差异[J]. 南方农业学报, 2021, 52(1): 137-144. |
| Chen G F, Huang Y F, Liu B, Liu S Y, Huang Y Y, Lin X X, Tang Q Z. Response differences of different rice varieties to nitrogen fertilizer application in Guangxi rice region[J]. Southern Agricultural Journal, 2021, 52(1): 137-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 孙志广, 王宝祥, 杨波, 徐波, 邢运高, 刘艳, Kazeem B B, 徐大勇. 施氮量对不同水稻品种氮肥利用率和农艺性状的影响[J]. 江西农业学报, 2019, 31(12): 23-28. |
| Sun Z G, Wang B X, Yang B, Xu B, Xing Y G, Liu Y, Bello B K, Xu D Y. Effects of nitrogen application rate on nitrogen use efficiency and agronomic traits of different rice varieties[J]. Jiangxi Agricultural Journal, 2019, 31 (12): 23-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 章星传, 黄文轩, 朱宽宇, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 施氮量对不同水稻品种氮肥利用率与农艺性状的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2018(4): 69-78. |
| Zhang X C, Huang W X, Zhu K Y, Wang Z Q, Effects of nitrogen application rate on nitrogen use efficiency and agronomic traits of different rice varieties[J]. Crop Journal, 2018(4): 69-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 覃夏, 王绍华, 薛利红. 江西鹰潭地区早稻氮素营养光谱诊断模型的构建与应用[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(4): 691-698. |
| Qin X, Wang S H, Xue L H. Construction and application of nitrogen nutrition spectral diagnostic model for early rice in Yingtan area of Jiangxi Province[J]. Chinese Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 44 (4): 691-698. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 薛利红, 覃夏, 李刚华, 杨林章. 基蘖肥氮不同比例对直播早稻群体动态、氮素吸收利用及产量形成的影响[J]. 土壤, 2010, 42(5): 815-821. |
| Xue L H, Qin X, Li G H, Yang L Z. Effects of different ratios of basal tiller fertilizer and nitrogen on population dynamics, nitrogen absorption and utilization and yield formation of direct seeding early rice[J]. Soil, 2010, 42 (5): 815-821. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 王艳, 易军, 高继平, 张丽娜, 杨继芬, 赵艳泽, 辛威, 甄晓溪, 张文忠. 不同叶龄蘖、穗氮肥组合对粳稻产量及氮素利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(1): 102-116. |
| Wang Y, Yi J, Gao J P, Zhang L N, Yang J F, Zhao Y Z, Xin W, Zhen X X, Zhang W Z. Effects of different combinations of nitrogen fertilizer on yield and nitrogen utilization of japonica rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 102-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 武良. 基于总量控制的中国农业氮肥需求及温室气体减排潜力研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2014. |
| Wu L. Research on China's agricultural nitrogen fertilizer demand and greenhouse gas emission reduction potential based on total amount control[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 全国土壤普查办公室. 中国土壤[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1998: 356. |
| National Soil Census Office. China Soil[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1998: 356. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 蔡岸冬, 张文菊, 杨品品, 韩天富, 徐明岗. 基于Meta-Analysis研究施肥对中国农田土壤有机碳及其组分的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(15): 2995-3004. |
| Cai A D, Zhang W J, Yang P P, Han T F, Xu M G. Effects of fertilization on farmland soil organic carbon and its components in China based on Meta-Analysis[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(15): 2995-3004. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Zhang X Y, Fang Q C, Zhang T, Ma W Q, Gerard L,. Velthof, Hou Y, Oenema O, Zhang F S. Benefits and trade-offs of replacing synthetic fertilizers by animal manures in crop production in China: A meta-analysis[J]. Global Change Biology, 2019, 00: 1-13. |
| [19] | Lam S K, Chen D, Norton R, Armstrong R, Mosier A R. Nitrogen dynamics in grain crop and legume pasture systems under elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration: A meta‐analysis[J]. Global Change Biology, 2012, 18: 2853-2859. |
| [20] | 韩天富, 马常宝, 黄晶, 柳开楼, 薛彦东, 李冬初, 刘立生, 张璐, 刘淑军, 张会民. 基于Meta分析中国水稻产量对施肥的响应特征[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(11): 1918-1929. |
| Han T F, Ma C B, Huang J, Liu K L, Xue Y D, Li D C, Liu L S, Zhang L, Liu S J, Zhang H M. Meta-analysis of the response characteristics of rice yield in China to fertilization[J]. Scientia Agrialltura Sinica, 2019, 52(11): 1918-1929. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Liu C, Lu M, Cui J, Li B, Fang C M. Effects of straw carbon input on carbon dynamics in agricultural soils: A meta-analysis[J]. Global Change Biology, 2014, 20(5): 1366-1381. |
| [22] | 任科宇, 陆东明, 邹洪琴, 王慧颖, 许发辉, 卢昌艾, 段英华. 有机替代对长江流域水稻产量和籽粒含氮量的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2022, 39(4): 716-725. |
| Ren K Y, Lu D M, Zou H Q, Wang H Y, Xu F H, Lu C A, Duan Y H. Effects of organic substitution on rice yield and grain nitrogen content in the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2022, 39(4): 716-725. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Hedges L V, Gurevitch J, Curtis P S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology[J]. Ecology, 1999, 80 (4): 1150-1156. |
| [24] | Wang W N, Lu J W, Ren T, Li X K, Su W, Lu M X. Evaluating regional mean optimal nitrogen rates in combination with indigenous nitrogen supply for rice production[J]. Field Crop Research. 2013, 137, 37-48. |
| [25] | 胡群, 曹利强, 夏敏, 张洪程, 陈厚存, 郭保卫, 魏海燕. 不同施氮量对钵苗机插水稻产量形成及氮素利用率的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(8): 34-37. |
| Hu Q, Cao L Q, Xia M, Zhang H C, Chen H C, Guo B W, Wei H Y. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on Yield Formation and nitrogen use efficiency of pot seedling machine transplanted rice[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science, 2016, 44 (8): 34-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 李木英, 石庆华, 方慧铃, 潘晓华, 谭雪明, 曾勇军. 淦鑫688氮素营养特性及其与群体发育和产量形成的关系[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2009, 31(2): 183-193. |
| Li M Y, Shi Q H, Fang H L, Pan X H, Tan X M, Zeng Y J. Relationship between characteristics of N nutrition, population development and yield formation of Ganxin 688[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2009, 31(2): 183-193. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 张四海, 吴文革, 李泽福, 王元垒, 黄义德, 赵决建, 方文杰. 氮肥运筹对双季晚稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2008(3): 28-31. |
| Zhang S H, Wu W G, Li Z F, Wang Y L, Huang Y D, Zhao J J, Fang W J. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer management on the yield and quality of double cropping late rice[J]. China Soil and Fertilizer, 2008(3): 28-31. | |
| [28] | 王秀斌, 徐新朋, 孙静文, 梁国庆, 刘光荣, 周卫. 氮肥运筹对机插双季稻产量、氮肥利用率及经济效益的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(5): 1167-1176. |
| Wang X B, Xu X P, Sun J W, Liang G Q, Liu G R, Zhou W. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer operation research on yield, nitrogen fertilizer utilization and economic benefits of machine transplanted double cropping rice[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2016, 22(5): 1167-1176 | |
| [29] | 杨晓龙, 方建军, 汪本福, 王红波, 程建平, 周厚财, 周黎, 徐得泽. 不同施氮量对桃优香占产量及农艺性状的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2021, 60(15): 34-37. |
| Yang X L, Fang J J, Wang B F, Wang H B, Cheng J P, Zhou H C, Zhou L, Xu D Z. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on Yield and agronomic characters of peach Youxiang[J]. Hubei Agricultural Science, 2021, 60 (15): 34-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Zakari S A, Asad M A U, Han Z Y, Guan X Y, Zaidi S H R, Gang P, Cheng F M. Senescence-related translocation of nonstructural carbohydrate in rice leaf sheaths under different nitrogen supply[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2020 112(3): 1601-1616. |
| [31] | Yang D Q, Cai T, Luo Y L, Wang Z L. Optimizing plant density and nitrogen application to manipulate tiller growth and increase grain yield and nitrogen-use efficiency in winter wheat[J]. Peer J, 2019, 7, e6484. |
| [32] | 王博博. 不同施氮量对豫南稻区超级杂交稻产量、品质及群体质量的影响研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2016. |
| Wang B B. Study on the effect of different nitrogen application rates on the yield, quality and population quality of super hybrid rice in the southern Henan rice region[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | Zhou W, Lv T F, Yang Z P, Wang T, Fu Y, Chen Y, Hu B H, Ren W J. Morphophysiological mechanism of rice yield increase in response to optimized nitrogen management[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 17226. |
| [34] | Deng F, Wang L, Ren W J, Mei X F, Li S X. Optimized nitrogen managements and poly aspartic acid urea improved dry matter production and yield of indica hybrid rice[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 2015, 145: 1-9. |
| [35] | Kamiji Y H, Yoshida J A, Palta T, Sakuratani T, Shiraiwa T N. Applications that increase plant N during panicle development are highly effective in increasing spikelet number in rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2011 122: 242-247. |
| [36] | Shiratsuchi H Y, Ohdaira J, Takanashi[J] . Relationship between dry weight at heading and the number of spikelets on individual rice tillers[J]. Plant Production Science, 2007, 10: 430-441. |
| [37] | 朱莉, 李贵勇, 周伟, 朱世林, 李珍珍, 夏海晓, 陶有凤, 任万军, 胡剑锋. 不同生态条件下氮高效水稻品种干物质积累和产量特性[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(6): 1015-1028. |
| Zhu L, Li G Y, Zhou W, Zhu S L, Li Z Z, Xia H X, Tao Y F, Ren W J, Hu J F. Dry matter accumulation and yield characteristics of nitrogen efficient rice varieties under different ecological conditions[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(6): 1015-1028. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 徐富贤, 熊洪, 张林, 郭晓艺, 朱永川, 刘茂, 周兴兵. 西南稻区杂交中稻产量的地域差异及其高效施氮量研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(2): 273-282. |
| Xu F X, Xiong H, Zhang L, Guo X Y, Zhu Y C, Liu M, Zhou X B. Study on regional differences in hybrid rice yield and its high-efficiency nitrogen application in southwest rice region[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2012, 18(2): 273-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 蒋聪, 段玉云, 杨旭昆, 吴志刚, 邹茜. 云南省高原粳稻主要农艺性状与产量的多重分析[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(21): 74-83. |
| Jiang C, Duan Y Y, Yang X K, Wu Z G, Zou Q. Multiple analysis of main agronomic characters and yield of plateau Japonica rice in Yunnan Province[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2020, 48(21): 74-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 付景, 王越涛, 尹海庆, 王生轩, 王付华, 陈献功, 王亚, 杨文博, 白涛. 施氮量对沿黄粳稻根系形态、生理特性及产量的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2017, 46(7): 18-25. |
| Fu J, Wang Y T, Yin H Q, Wang S X, Wang F H, Chen X G, Wang Y, Yang W B, Bai T. Effects of Nitrogen Application on root morphology, physiological characteristics and yield of japonica rice along the Yellow River[J]. Henan Agricultural Science, 2017, 46 (7): 18-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 李晓峰, 程金秋, 梁健, 陈梦云, 任红茹, 张洪程, 霍中洋, 戴其根, 许轲, 魏海燕, 郭保卫. 秸秆全量还田与氮肥运筹对机插粳稻产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(6): 912-924. |
| Li X F, Cheng J Q, Liang J, Chen M Y, Ren H R, Zhang H C, Huo Z Y, Dai Q G, Xu K, Wei H Y, Guo B B. Effects of full straw returning and nitrogen fertilizer management on yield and nitrogen absorption and utilization of machine- transplanted japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Crops, 2017, 43(6): 912-924. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 赵建红, 李玥, 孙永健, 李应洪, 孙加威, 代邹, 谢华英, 徐徽, 马均. 灌溉方式和氮肥运筹对免耕厢沟栽培杂交稻氮素利用及产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(3): 609-617. |
| Zhao J H, Li Y, Sun Y J, Li Y H, Sun J W, Dai Z, Xie H Y, Xu H, Ma J. Effects of irrigation methods and nitrogen fertilizer management on nitrogen utilization and yield of hybrid rice cultivated in no-till Xianggou[J]. Journal of Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2016, 22(3): 609-617. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 曹小闯, 刘晓霞, 马超, 田仓, 朱练峰, 吴龙龙, 张均华, 金千瑜, 朱春权, 孔亚丽, 虞轶俊. 干湿交替灌溉改善稻田根际氧环境进而促进氮素转化和水稻氮素吸收[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(1): 1-14. |
| Cao X C, Liu X X, Ma C, Tian C, Zhu L F, Wu L L, Zhang J H, Jin Q Y, Zhu C Q, Kong Y L, Yu Y J. Alternate wet and dry irrigation improves the rhizosphere oxygen environment of rice fields, thereby promoting nitrogen transformation and rice nitrogen absorption[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(1): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 何军, 何天楷, 张宇航, 钟盛建, 高明利, 赵树君, 陈扬, 朱子荣, 陈莹. 不同水肥处理水稻氮磷吸收利用及产量试验研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2020, 39(6): 67-72. |
| He J, He T K, Zhang Y H, Zhong S J, Gao M L, Zhao S J, Chen Y, Zhu Z R, Chen Y,. Experimental study on nitrogen and phosphorus absorption and utilization and yield of rice under different water and fertilizer treatments[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2020, 39(6): 67-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | 陈海飞, 冯洋, 蔡红梅, 徐芳森, 周卫, 刘芳, 庞再明, 李登荣. 氮肥与移栽密度互作对低产田水稻群体结构及产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(6): 1319-1328. |
| Chen H F, Feng Y, Cai H M, Xu F S, Zhou W, Liu F, Pang Z M, Li D R. Effects of interaction between nitrogen fertilizer and transplanting density on population structure and yield of rice in low yield fields[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2014, 20 (6): 1319-1328. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | 袁帅, 苏雨婷, 王晓玉, 陈平平, 易镇邪. 氮肥运筹与化学调控对湘南超级杂交早稻茎蘖利用特征和产量的影响[J]. 杂交水稻, 2021, 36(5): 79-88. |
| Yuan S, Su Y T, Wang X Y, Chen P P, Yi Z X. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer management and chemical regulation on stem and tiller utilization characteristics and yield of super hybrid early hybrid rice in southern Hunan[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2021, 36(5): 79-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [6] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [7] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [8] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [9] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [10] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [11] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [12] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [13] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [14] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [15] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||