
中国水稻科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 246-255.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230907
缪军1,2, 冉金晖1, 徐梦彬1,3, 卜柳冰1, 王平1, 梁国华1,2,*( ), 周勇1,2,*(
), 周勇1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-14
修回日期:2023-12-08
出版日期:2024-05-10
发布日期:2024-05-13
通讯作者:
*email: ricegb@yzu.edu.cn;
zhouyong@yzu.edu.cn
基金资助:
MIAO Jun1,2, RAN Jinhui1, XU Mengbin1,3, BO Liubing1, WANG Ping1, LIANG Guohua1,2,*( ), ZHOU Yong1,2,*(
), ZHOU Yong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-14
Revised:2023-12-08
Online:2024-05-10
Published:2024-05-13
Contact:
*email: ricegb@yzu.edu.cn;
zhouyong@yzu.edu.cn
摘要:
【目的】探究水稻异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基RGG2在提高水稻抗旱性中的作用。【方法】利用酵母双杂交和荧光素酶互补实验,鉴定RGG2与RGB1的相互作用。施加外源ABA,检测RGG2的表达水平和RGG2过量表达系的种子萌发率,用于阐明RGG2是否参与ABA响应。通过比较野生型和RGG2过量表达系的离体叶片失水率和干旱处理后的植株存活率,解析RGG2在干旱胁迫响应中的作用。【结果】RGG2与RGB1之间存在相互作用。RGG2的表达水平可以被ABA、PEG-6000和干旱处理显著诱导。ABA处理条件下,日本晴和武运粳7号背景下RGG2过量表达系种子萌发率和根长均明显下降,且显著低于野生型,表明RGG2正调控ABA响应。过量表达系离体叶片的失水率低于野生型,但干旱条件下的植株存活率高于野生型。干旱处理条件下,多个ABA和干旱胁迫响应相关基因的表达被诱导,并且在过量表达系中的表达水平明显高于野生型。【结论】RGG2正调控ABA和干旱胁迫响应,过量表达RGG2可以提高水稻抗旱性。
缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255.
MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255.
| 引物名称 | 前引物 | 后引物 |
|---|---|---|
| Primer name | Forward (5’-3’) | Reverse (5’-3’) |
| RGG2-BD | AAAGAATTCATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAACGGGGAGG | AAAGGATCCCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGATGCC |
| RGG2-AD | gccatggaggccagtgaattcATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAAC | cagctcgagctcgatggatccCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGA |
| RGB1-AD | AAACCCGGGTATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAGCTCA | AAAGGATCCTCAAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCGCTGAA |
| RGB1-BD | atggccatggaggccgaattcATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAG | ccgctgcaggtcgacggatccTCAAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCG |
| RGG2-cLUC | tacgcgtcccggggcggtaccATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAAC | acgaaagctctgcaggtcgacCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGA |
| RGB1-nLUC | acgggggacgagctcggtaccATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAG | cgcgtacgagatctggtcgacAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCGCT |
| OsActin-qPCR | GATGACCCAGATCATGTTTG | GGGCGATGTAGGAAAGC |
| RGG2-qPCR | GCAGGATGAACTGAACGAGC | GGATGCCCACCATTTGTTA |
| OsLEA3-qPCR | GCCGTGAATGATTTCCCTTTG | CACACCCGTCAGAAATCCTCC |
| OsRAB16A-qPCR | CATGGACAAGATCAAGGAGAAGC | CTTATTATTCAGGAAGGTGACGTGG |
| OsNCED4-qPCR | GATTGCACGGCACCTTCATT | CTCTGTAATTTGATTTTTCACTGGCTAAT |
| OsLIP9-qPCR | TGGAATTTGGAAGTGTTTGGC | CCCACACGAAACACAAACTTC |
| OsNAC6-qPCR | CGAGAAGACCAACTGGAT | CAACCTGAGGCTGTTCTT |
| OsABIL3-qPCR | GAGCGGGCAAGGATT | CCGTGGAACGACCATAAC |
表1 用于本研究的引物
Table 1. Primers used in this study
| 引物名称 | 前引物 | 后引物 |
|---|---|---|
| Primer name | Forward (5’-3’) | Reverse (5’-3’) |
| RGG2-BD | AAAGAATTCATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAACGGGGAGG | AAAGGATCCCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGATGCC |
| RGG2-AD | gccatggaggccagtgaattcATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAAC | cagctcgagctcgatggatccCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGA |
| RGB1-AD | AAACCCGGGTATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAGCTCA | AAAGGATCCTCAAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCGCTGAA |
| RGB1-BD | atggccatggaggccgaattcATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAG | ccgctgcaggtcgacggatccTCAAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCG |
| RGG2-cLUC | tacgcgtcccggggcggtaccATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAAC | acgaaagctctgcaggtcgacCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGA |
| RGB1-nLUC | acgggggacgagctcggtaccATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAG | cgcgtacgagatctggtcgacAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCGCT |
| OsActin-qPCR | GATGACCCAGATCATGTTTG | GGGCGATGTAGGAAAGC |
| RGG2-qPCR | GCAGGATGAACTGAACGAGC | GGATGCCCACCATTTGTTA |
| OsLEA3-qPCR | GCCGTGAATGATTTCCCTTTG | CACACCCGTCAGAAATCCTCC |
| OsRAB16A-qPCR | CATGGACAAGATCAAGGAGAAGC | CTTATTATTCAGGAAGGTGACGTGG |
| OsNCED4-qPCR | GATTGCACGGCACCTTCATT | CTCTGTAATTTGATTTTTCACTGGCTAAT |
| OsLIP9-qPCR | TGGAATTTGGAAGTGTTTGGC | CCCACACGAAACACAAACTTC |
| OsNAC6-qPCR | CGAGAAGACCAACTGGAT | CAACCTGAGGCTGTTCTT |
| OsABIL3-qPCR | GAGCGGGCAAGGATT | CCGTGGAACGACCATAAC |
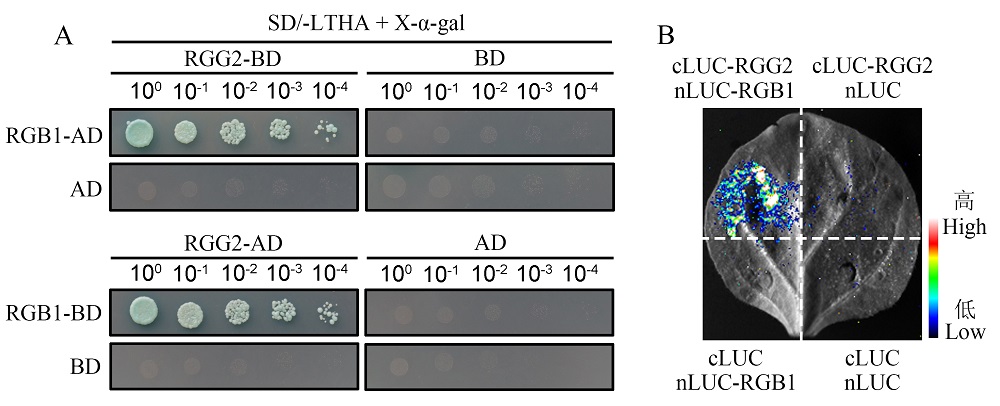
图1 RGG2与RGB1的蛋白互作分析 A: RGG2与RGB1的酵母双杂交互作分析。将RGG2分别克隆到pGBKT7(BD)和pGADT7(AD)载体中,并将RGB1分别克隆到AD和BD载体中,然后进行互作分析。酵母在缺乏Trp,Leu,His和Ade的培养基上生长以确定两种蛋白之间的相互作用;B: RGG2与RGB1的split-LUC互作分析。RGG2与荧光素酶的C端(cLUC)相连,RGB1与荧光素酶的N端(nLUC)相连。侵染烟草叶表皮细胞2 d后检测荧光素酶活性。
Fig. 1. Interaction analysis between RGG2 and RGB1 proteins A, Yeast two-hybrid analysis of RGG2 and RGB1. RGG2 was cloned into pGBKT7 (BD) or pGADT7 (AD) vectors, respectively. RGB1 was cloned into AD and BD vectors, respectively. Yeast was grown on the medium lacking Trp, Leu, His, and Ade to analyze protein interactions; B, Split-LUC analysis of RGG2 and RGB1. RGG2 was linked to the C-terminal fragment of luciferase (cLUC) and RGB1 was linked to the N-terminal fragment of luciferase (nLUC), respectively. Luciferase activity was detected after infestation of N. benthamiana leaves for 2 days.
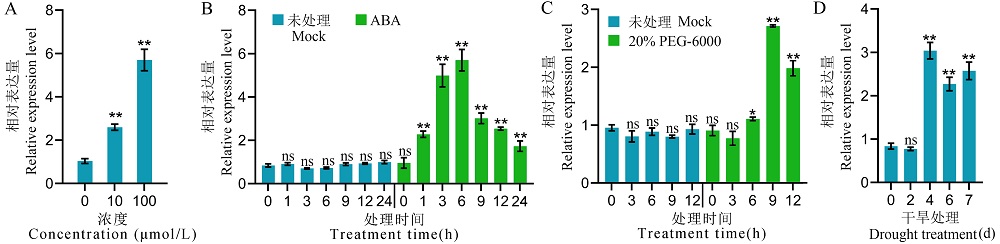
图2 ABA、PEG-6000和干旱处理诱导RGG2的表达 A: 不同ABA浓度处理后RGG2的表达变化。生长2周的日本晴幼苗分别用10 μmol/L和100 μmol/L ABA处理,并在处理6 h取样进行表达分析;B: 100 μmol/L ABA处理不同时间后RGG2的表达变化;C: 20% PEG-6000处理不同时间后RGG2的表达变化;D: 干旱处理不同时间后RGG2的表达变化。试验设置3个重复。数据显示为平均值±标准差。t测验:ns代表无显著差异,*代表P≤0.05;**代表P≤0.01。
Fig. 2. ABA, PEG-6000 and drought treatment induce the expression of RGG2 A, The expression levels of RGG2 after the treatment with ABA at various concentrations. 2-week-old Nipponbare seedlings were treated with 10 and 100 μmol/L ABA, then the samples were collected at 6 h after treatment for expression analysis; B, The expression levels of RGG2 at different times after treatment with and without 100 μmol/L ABA. C, The expression levels of RGG2 at different times after treatment with and without 20% PEG-6000. D, The expression levels of RGG2 at different times after drought treatment. Values represent the mean ± SD (n=3). t-test: ns, Not significant; *, P ≤ 0.05;**, P ≤ 0.01.

图3 日本晴背景下过量表达RGG2增强水稻对ABA的敏感性 A: 不同浓度外源ABA处理下,日本晴和RGG2过量表达系的种子萌发比较。标尺 = 1 cm;B~F: 0 μmol/L(B)、1 μmol/L(C)、2 μmol/L(D)、5 μmol/L(E)、10 μmol/L(F)ABA处理下,日本晴和RGG2过表达系的种子萌发率;G: 不同浓度外源ABA处理84小时的日本晴和RGG2过量表达系的种子萌发率;H: 不同浓度外源ABA处理下,日本晴和RGG2过量表达系的根长比较。试验设置4个重复。数据显示为平均值±标准差。t测验:ns代表无显著差异,*代表P≤0.05,**代表P≤0.01。NIP,日本晴。NIP-OE1和NIP-OE2为日本晴背景下RGG2基因的过量表达系。
Fig. 3. Overexpression of RGG2 in the Nipponbare background increases rice sensitivity to ABA A, Seed germination of NIP and RGG2 overexpression lines exposed to different concentrations of ABA. Scale bars = 1 cm. B-F, Seed germination rates of NIP and RGG2 overexpression lines under 0 μmol/L (B), 1 μmol/L (C), 2 μmol/L (D), 5 μmol/L (E), 10 μmol/L (F) ABA treatment. G, Seed germination rates of NIP and RGG2 overexpression lines with various ABA concentrations treatment for 84 h. H, Root length of NIP and RGG2 overexpression lines under different concentrations of ABA. Values are mean ± SD (n = 4). t-test: ns, not significant; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01. NIP, Nipponbare. NIP-OE1 and NIP-OE2 represent the overexpression lines of RGG2 in the background of Nipponbare.
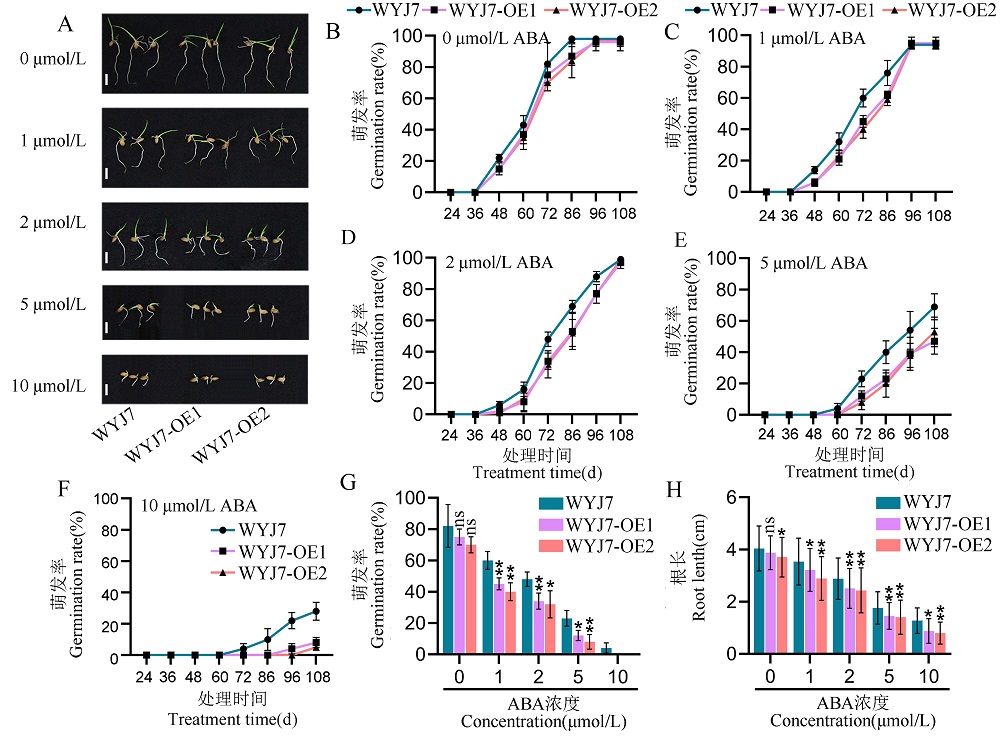
图4 武运粳7号背景下过量表达RGG2增强水稻对ABA的敏感性 A: 不同浓度外源ABA处理下,武运粳7号和RGG2过量表达系的种子萌发比较。标尺 = 1 cm;B~F: 0 μmol/L(B)、1 μmol/L(C)、2 μmol/L(D)、5 μmol/L(E)、10 μmol/L(F)ABA处理下,武运粳7号和RGG2过量表达系的种子萌发率;G: 不同浓度外源ABA处理84 h的武运粳7号和RGG2过量表达系的种子萌发率;H: 不同浓度外源ABA处理下,武运粳7号和RGG2过量表达系的根长比较。试验设置4个重复。数据显示为平均值 ± 标准差。t 测验:ns 代表无显著差异,* 代表P ≤ 0.05,** 代表P ≤ 0.01。WYJ7,武运粳7号。WYJ7-OE1和WYJ7-OE2为武运粳7号背景下RGG2基因的过量表达系。
Fig. 4. Overexpression of RGG2 in the Wuyunjing 7 background increases rice sensitivity to ABA A, Seed germination of WYJ7 and RGG2 overexpression lines (WYJ7-OE1, WYJ7-OE2) at different concentrations of ABA. Scale bars = 1 cm. B-F, Seed germination rates of WYJ7 and RGG2 overexpression lines under 0 μmol/L (B), 1 μmol/L (C), 2 μmol/L (D), 5 μmol/L (E), 10 μmol/L (F) ABA treatment. G, Seed germination rates of WYJ7 and RGG2 overexpression lines under various ABA concentrations treatment for 84h. H, Root length of WYJ7 and RGG2 overexpression lines at different concentrations of ABA. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 4). t-test: ns, not significant; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01. WYJ7, Wuyunjing 7. WYJ7-OE1 and WYJ7-OE2 represent the overexpression lines of RGG2 in the background of Wuyunjing 7.
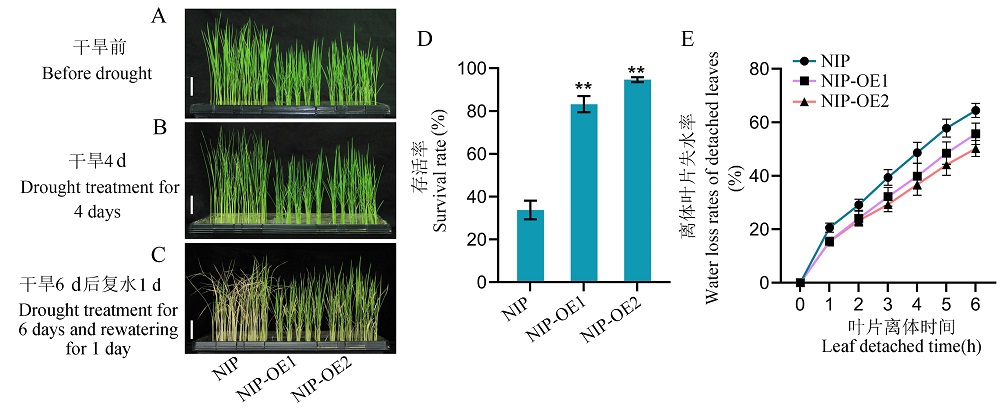
图5 过量表达RGG2可增强水稻抗旱性 A: 正常条件下生长3周的日本晴和RGG2过量表达植株。标尺 = 5 cm;B: 干旱处理4 d的日本晴和RGG2过量表达植株。标尺 = 5 cm;C: 干旱处理6 d后复水1 d的日本晴和RGG2过量表达植株。标尺 = 5 cm;D: 干旱处理复水后日本晴和RGG2过量表达植株存活率。试验设置3个重复;E: 日本晴和RGG2过量表达植株离体叶片失水率。试验设置10个重复。数据显示为平均值 ± 标准差。t 测验:** 代表P ≤ 0.01。NIP,日本晴。NIP-OE1和NIP-OE2为日本晴背景下RGG2基因的过量表达系。
Fig. 5. Overexpression of RGG2 increases the tolerance to drought in rice A, The 3-week-old plants of NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2 grown under normal conditions. Scale bar = 5 cm. B, The plants of NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2 after drought treatment for 4 days. Scale bar = 5 cm. C, The plants of NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2 after drought treatment for 6 days and rewatering for 1 day. Scale bar = 5 cm. D, Survival rates of NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2 after drought treatment and rewatering. Values represent mean ± SD (n = 3). E, Water loss rates of detached leaves of NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2. Values represent mean ± SD (n = 10). t-test: **, P ≤ 0.01. NIP, Nipponbare. NIP-OE1 and NIP-OE2 represent the overexpression lines of RGG2 in the background of Nipponbare.

图6 RGG2促进ABA和干旱胁迫相关基因表达分别干旱0、4和6 d的日本晴和RGG2过量表达系,用于检测OsLEA3、OsRAB16A、OsNCED4、OsLIP9、OsNAC6和OsABIL3的表达水平。试验设置3个重复。数据显示为平均值 ± 标准差。t 测验:ns 代表无显著差异, ** 代表P ≤ 0.01。NIP,日本晴。NIP-OE1和NIP-OE2为日本晴背景下RGG2基因的过量表达系。
Fig. 6. RGG2 promotes the expression of ABA- and drought stress-related genes The expression levels of OsLEA3, OsRAB16A, OsNCED4, OsLIP9, OsNAC6, and OsABIL3 were detected in NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2 under drought treatment for 0, 4, and 6 days, respectively. Values represent mean ± SD (n = 3). t-test: ns, not significant; **, P ≤ 0.01. NIP, Nipponbare. NIP-OE1 and NIP-OE2 represent the overexpression lines of RGG2 in the background of Nipponbare.
| [1] | Trusov Y, Rookes J E, Chakravorty D, Armour D, Schenk P M, Botella J R. Heterotrimeric G proteins facilitate Arabidopsis resistance to necrotrophic pathogens and are involved in jasmonate signaling[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 140(1): 210-220. |
| [2] | Urano D, Chen J G, Botella J R, Jones A M. Heterotrimeric G protein signalling in the plant kingdom[J]. Open Biology, 2013, 3(3): 120186. |
| [3] | Trusov Y, Rookes J E, Tilbrook K, Chakravorty D, Mason M G, Anderson D, Chen J G, Jones A M, Botella J R. Heterotrimeric G protein gamma subunits provide functional selectivity in Gβγ dimer signaling in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(4): 1235-1250. |
| [4] | Liu J M, Ding P T, Sun T J, Nitta Y, Dong O, Huang X C, Yang W, Li X, Botella J R, Zhang Y L. Heterotrimeric G proteins serve as a converging point in plant defense signaling activated by multiple receptor-like kinases[J]. Plant Physiology, 2013, 161(4): 2146-2158. |
| [5] | Anderson D J, Botella J R. Expression analysis and subcellular localization of the Arabidopsis thaliana G-protein beta-subunit AGB1[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2007, 26(9): 1469-1480. |
| [6] | Brenya E, Trusov Y, Dietzgen R G, Botella J R. Heterotrimeric G-proteins facilitate resistance to plant pathogenic viruses in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2016, 11(8): e1212798. |
| [7] | Trusov Y, Sewelam N, Rookes J E, Kunkel M, Nowak E, Schenk P M, Botella J R. Heterotrimeric G proteins- mediated resistance to necrotrophic pathogens includes mechanisms independent of salicylic acid-, jasmonic acid/ethylene- and abscisic acid-mediated defense signaling[J]. Plant Journal, 2009, 58(1): 69-81. |
| [8] | Subramaniam G, Trusov Y, Lopez-Encina C, Hayashi S, Batley J, Botella J R. Type B heterotrimeric G protein γ-subunit regulates auxin and ABA signaling in tomato[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170(2): 1117-1134. |
| [9] | Jiang K, Frick-Cheng A, Trusov Y, Delgado-Cerezo M, Rosenthal D M, Lorek J, Panstruga R, Booker F L, Botella J R, Molina A, Ort D R, Jones A M. Dissecting arabidopsis Gβ signal transduction on the protein surface[J]. Plant Physiology, 2012, 159(3): 975-983. |
| [10] | Klopffleisch K, Phan N, Augustin K, Bayne R S, Booker K S, Botella J R, Carpita N C, Carr T, Chen J G, Cooke T R, Frick-Cheng A, Friedman E J, Fulk B, Hahn M G, Jiang K, Jorda L, Kruppe L, Liu C, Lorek J, McCann M C, Molina A, Moriyama E N, Mukhtar M S, Mudgil Y, Pattathil S, Schwarz J, Seta S, Tan M, Temp U, Trusov Y, Urano D, Welter B, Yang J, Panstruga R, Uhrig J F, Jones A M. Arabidopsis G-protein interactome reveals connections to cell wall carbohydrates and morphogenesis[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2011, 7: 532. |
| [11] | Miao J, Yang Z F, Zhang D P, Wang Y Z, Xu M B, Zhou L H, Wang J, Wu S J, Yao Y J, Du X, Gu F F, Gong Z Y, Gu M H, Liang G H, Zhou Y. Mutation of RGG2, which encodes a type B heterotrimeric G protein γ subunit, increases grain size and yield production in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(3): 650-664. |
| [12] | Gao Y, Gu H W, Leburu M, Li X H, Wang Y, Sheng J Y, Fang H M, Gu M H, Liang G H. The heterotrimeric G protein β subunit RGB1 is required for seedling formation in rice[J]. Rice, 2019, 12(1): 53. |
| [13] | Utsunomiya Y, Samejima C, Takayanagi Y, Izawa Y, Yoshida T, Sawada Y, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Iwasaki Y. Suppression of the rice heterotrimeric G protein β-subunit gene, RGB1, causes dwarfism and browning of internodes and lamina joint regions[J]. Plant Journal, 2011, 67(5): 907-916. |
| [14] | Tao Y J, Miao J, Wang J, Li W Q, Xu Y, Wang F Q, Jiang Y J, Chen Z H, Fan F J, Xu M B, Zhou Y, Liang G H, Yang J. RGG1, involved in the cytokinin regulatory pathway, controls grain size in rice[J]. Rice, 2020, 13(1): 76. |
| [15] | Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Mao H L, Lu T T, Han B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F. GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 112(6): 1164-1171. |
| [16] | Huang X Z, Qian Q, Liu Z B, Sun H Y, He S Y, Luo D, Xia G M, Chu C C, Li J Y, Fu X D. Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2009, 41(4): 494-497. |
| [17] | Zhou Y, Zhu J Y, Li Z Y, Yi C D, Liu J, Zhang H G, Tang S Z, Gu M H, Liang G H. Deletion in a quantitative trait gene qPE9-1 associated with panicle erectness improves plant architecture during rice domestication[J]. Genetics, 2009, 183(1): 315-324. |
| [18] | Urano D, Jones A M. Heterotrimeric G protein-coupled signaling in plants[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2014, 65: 365-384. |
| [19] | Pandey S. Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling in plants: conserved and novel mechanisms[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2019, 70: 213-238. |
| [20] | Wang Y J, Wang Y L, Deng D X. Multifaceted plant G protein: Interaction network, agronomic potential, and beyond[J]. Planta, 2019, 249(5): 1259-1266. |
| [21] | Mao H L, Sun S Y, Yao J L, Wang C R, Yu S B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F. Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(45): 19579-19584. |
| [22] | Sun S Y, Wang L, Mao H L, Shao L, Li X H, Xiao J H, Ouyang Y D, Zhang Q F. A G-protein pathway determines grain size in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 851. |
| [23] | Kunihiro S, Saito T, Matsuda T, Inoue M, Kuramata M, Taguchi-Shiobara F, Youssefian S, Berberich T, Kusano T. Rice DEP1, encoding a highly cysteine-rich G protein γ subunit, confers cadmium tolerance on yeast cells and plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(14): 4517-4527. |
| [24] | Zhang D P, Zhou Y, Yin J F, Yan X J, Lin S, Xu W F, Baluška F, Wang Y P, Xia Y J, Liang G H, Liang J S. Rice G-protein subunits qPE9-1 and RGB1 play distinct roles in abscisic acid responses and drought adaptation[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(20): 6371-6384. |
| [25] | Liu Q, Han R X, Wu K, Zhang J Q, Ye Y F, Wang S S, Chen J F, Pan Y J, Li Q, Xu X P, Zhou J W, Tao D Y, Wu Y J, Fu X D. G-protein βγ subunits determine grain size through interaction with MADS-domain transcription factors in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 852. |
| [26] | Wang Y Y, Lv Y, Yu H P, Hu P, Wen Y, Wang J G, Tan Y Q, Wu H, Zhu L X, Wu K X, Chai B Z, Liu J L, Zeng D L, Zhang G H, Zhu L, Gao Z Y, Dong G J, Ren D Y, Shen L, Zhang Q, Li Q, Guo L B, Xiong G S, Qian Q, Hu J. GR5 acts in the G-protein pathway to regulate grain size in rice[J]. Plant Communications, 2023: 100673. |
| [27] | Swain D M, Sahoo R K, Srivastava V K, Tripathy B C, Tuteja R, Tuteja N. Function of heterotrimeric G-protein γ subunit RGG1 in providing salinity stress tolerance in rice by elevating detoxification of ROS[J]. Planta, 2017, 245(2): 367-383. |
| [28] | Yadav D K, Islam S M, Tuteja N. Rice heterotrimeric G-protein gamma subunits (RGG1 and RGG2) are differentially regulated under abiotic stress[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2012, 7(7): 733-740. |
| [29] | Kan Y, Mu X R, Zhang H, Gao J, Shan J X, Ye W W, Lin H X. TT2 controls rice thermotolerance through SCT1-dependent alteration of wax biosynthesis[J]. Nature Plants, 2022, 8(1): 53-67. |
| [30] | Zhang H L, Yu F F, Xie P, Sun S Y, Qiao X H, Tang S Y, Chen C X, Yang S, Mei C, Yang D K, Wu Y R, Xia R, Li X, Lu J, Liu Y X, Xie X W, Ma D M, Xu X, Liang Z W, Feng Z H, Huang X H, Yu H, Liu G F, Wang Y C, Li J Y, Zhang Q F, Chen C, Ouyang Y D, Xie Q. A Gγ protein regulates alkaline sensitivity in crops[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6638): eade8416. |
| [31] | Golldack D, Lüking I, Yang O. Plant tolerance to drought and salinity: Stress regulating transcription factors and their functional significance in the cellular transcriptional network[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2011, 30(8): 1383-1391. |
| [32] | Ferrero-Serrano Á, Assmann S M. The α-subunit of the rice heterotrimeric G protein, RGA1, regulates drought tolerance during the vegetative phase in the dwarf rice mutant d1[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(11): 3433-3443. |
| [33] | Jangam A P, Pathak R R, Raghuram N. Microarray analysis of rice d1 (RGA1) mutant reveals the potential role of G-protein alpha subunit in regulating multiple abiotic stresses such as drought, salinity, heat, and cold[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 11. |
| [34] | Swain D M, Sahoo R K, Chandan R K, Ghosh S, Kumar R, Jha G, Tuteja N. Concurrent overexpression of rice G-protein β and γ subunits provide enhanced tolerance to sheath blight disease and abiotic stress in rice[J]. Planta, 2019, 250(5): 1505-1520. |
| [35] | Suharsono U, Fujisawa Y, Kawasaki T, Iwasaki Y, Satoh H, Shimamoto K. The heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunit acts upstream of the small GTPase Rac in disease resistance of rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(20): 13307-13312. |
| [36] | Komatsu S, Yang G, Hayashi N, Kaku H, Umemura K, Iwasaki Y. Alterations by a defect in a rice G protein α subunit in probenazole and pathogen-induced responses[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 2004, 27(7): 947-957. |
| [37] | Yang W S, Wu K, Wang B, Liu H H, Guo S Y, Guo X Y, Luo W, Sun S Y, Ouyang Y D, Fu X D, Chong K, Zhang Q F, Xu Y Y. The RING E3 ligase CLG1 targets GS3 for degradation via the endosome pathway to determine grain size in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(10): 1699-1713. |
| [38] | Xu D B, Chen M, Ma Y N, Xu Z S, Li L C, Chen Y F, Ma Y Z. A G-protein β subunit, AGB1, negatively regulates the ABA response and drought tolerance by down-regulating AtMPK6-related pathway in Arabidopsis[J]. PloS One, 2015, 10(1): e0116385. |
| [1] | 汪邑晨, 朱本顺, 周磊, 朱骏, 杨仲南. 光/温敏核不育系的不育机理及两系杂交稻的发展与展望 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 463-474. |
| [2] | 许用强, 徐军, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 王丹英, 曾宇翔, 符冠富. 水稻花粉管生长及其对非生物逆境胁迫的响应机理研究进展 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 495-506. |
| [3] | 何勇, 刘耀威, 熊翔, 祝丹晨, 王爱群, 马拉娜, 王廷宝, 张健, 李建雄, 田志宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑OsOFP30基因创制水稻粒型突变体 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [4] | 吕阳, 刘聪聪, 杨龙波, 曹兴岚, 王月影, 童毅, Mohamed Hazman, 钱前, 商连光, 郭龙彪. 全基因组关联分析(GWAS)鉴定水稻氮素利用效率候选基因 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 516-524. |
| [5] | 杨好, 黄衍焱, 王剑, 易春霖, 石军, 谭楮湉, 任文芮, 王文明. 水稻中八个稻瘟病抗性基因特异分子标记的开发及应用 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 525-534. |
| [6] | 杨铭榆, 陈志诚, 潘美清, 张汴泓, 潘睿欣, 尤林东, 陈晓艳, 唐莉娜, 黄锦文. 烟-稻轮作下减氮配施生物炭对水稻茎鞘同化物转运和产量 形成的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 555-566. |
| [7] | 熊家欢, 张义凯, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 姚坚, 张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [8] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [9] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [10] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [11] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [12] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [13] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [14] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [15] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||