
中国水稻科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 303-315.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230908
周甜1, 吴少华1, 康建宏1,*( ), 吴宏亮1, 杨生龙2,*(
), 吴宏亮1, 杨生龙2,*( ), 王星强1, 李昱3, 黄玉峰4
), 王星强1, 李昱3, 黄玉峰4
收稿日期:2023-09-18
修回日期:2024-02-01
出版日期:2024-05-10
发布日期:2024-05-13
通讯作者:
*email: kangjianhong@163.com;
shlyangnx@163.com
基金资助:
ZHOU Tian1, WU Shaohua1, KANG Jianhong1,*( ), WU Hongliang1, YANG Shenglong2,*(
), WU Hongliang1, YANG Shenglong2,*( ), WANG Xingqiang1, LI Yu3, HUANG Yufeng4
), WANG Xingqiang1, LI Yu3, HUANG Yufeng4
Received:2023-09-18
Revised:2024-02-01
Online:2024-05-10
Published:2024-05-13
Contact:
*email: kangjianhong@163.com;
shlyangnx@163.com
摘要:
【目的】研究不同种植方式对水稻籽粒淀粉形成及关键酶活性的影响,为宁夏水稻直播栽培技术提供参考。【方法】2020-2021年在宁夏回族自治区原种场,选取富源四号(FY4)、宁粳28号(NJ28)、宁粳43号(NJ43)和宁粳50号(NJ50)为试验材料,设置保墒旱直播(Z1)、旱播后上水(Z2)以及插秧(Z3)三种种植方式,采用裂区设计,研究不同种植方式对水稻产量、淀粉含量及关键酶活性的影响。【结果】不同种植方式下,直播稻具有更高的直链淀粉和总淀粉含量,插秧稻具有更高的支链淀粉含量,总淀粉含量表现为Z2>Z1>Z3,支链淀粉含量表现为Z3>Z2>Z1。2021年Z1种植方式下 NJ28直链淀粉含量最高达到21.90%,Z3种植方式下 NJ28支链淀粉含量最高达到51.64%。籽粒淀粉合成积累主要与淀粉合成关键酶活性有关,与Z3相比,Z1和Z2显著降低了AGP和GBSS活性;插秧显著提高了FY4和NJ43的UGP和SBE活性,直播显著提高了NJ28和NJ50的UGP和SBE活性;不同种植方式下,Z1对SSS活性的提高更显著。在Z3种植方式下,NJ43的AGP活性最大值为28.53 U/(g·min),较Z2和Z1提高了4.1%和8.4%,NJ28的GBSS活性最大值为10.36 U/(g·min),较Z2和Z1处理提高了11.2%和13.5%。在Z1种植方式下,NJ50的SSS活性最大值为20.05 U/(g·min)。与插秧稻相比,直播稻千粒重和结实率显著高于插秧稻,但直播稻穗长和穗粒数显著降低,使得插秧稻产量均显著高于直播稻。2020年Z3种植方式下NJ50 产量高达898 kg/666.7m2,较Z1和Z2高了30.7%和39.4%。【结论】与插秧种植相比直播方式下水稻产量降低,但直播处理显著提高千粒重以及结实率,同时直播方式可以提高水稻籽粒淀粉形成关键酶的活性,增加直链淀粉含量,使得水稻籽粒总淀粉含量增加。
周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315.
ZHOU Tian, WU Shaohua, KANG Jianhong, WU Hongliang, YANG Shenglong, WANG Xingqiang, LI Yu, HUANG Yufeng. Effects of Planting Patterns on Starch Content and Activities of Key Starch Enzymes in Rice Grains[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 303-315.
| 年份 Year | 有机质 Organic matter(g/kg) | 全氮 Total N(g/kg) | 全磷 Total P(g/kg) | 碱解氮 Alkeline N(mg/kg) | 有效磷 Available P(mg/kg) | 速效钾 Available K(mg/kg) | pH值 pH value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 21.8 | 0.73 | 0.87 | 52.82 | 21.62 | 165.28 | 8.42 |
| 2021 | 20.5 | 0.70 | 0.98 | 53.91 | 22.58 | 160.51 | 8.37 |
表1 试验地耕层土壤基本理化性状
Table 1. Basic physical and chemical properties of arable layer soil in the test site
| 年份 Year | 有机质 Organic matter(g/kg) | 全氮 Total N(g/kg) | 全磷 Total P(g/kg) | 碱解氮 Alkeline N(mg/kg) | 有效磷 Available P(mg/kg) | 速效钾 Available K(mg/kg) | pH值 pH value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 21.8 | 0.73 | 0.87 | 52.82 | 21.62 | 165.28 | 8.42 |
| 2021 | 20.5 | 0.70 | 0.98 | 53.91 | 22.58 | 160.51 | 8.37 |
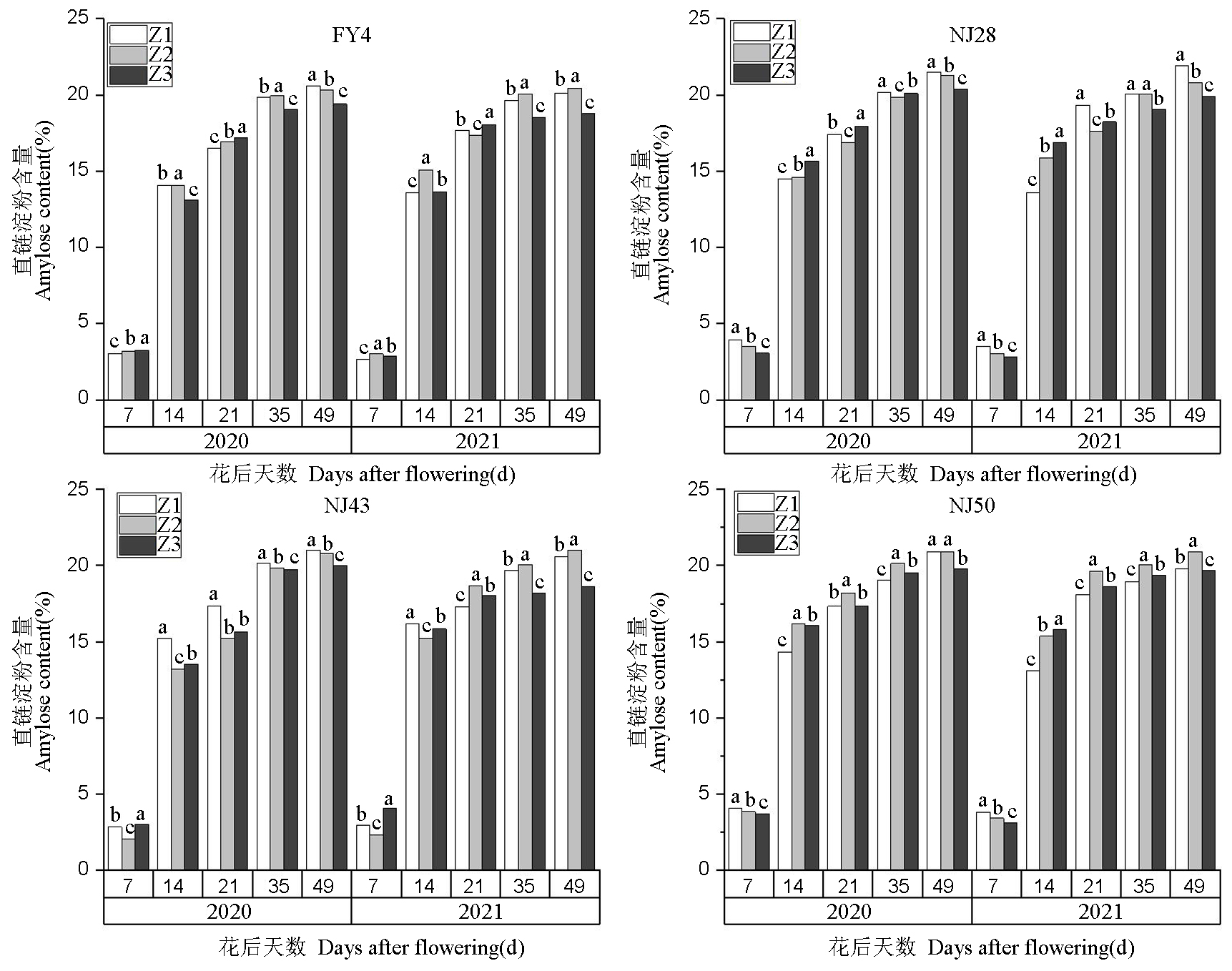
图1 不同种植方式下水稻籽粒直链淀粉含量的变化不同小写字母表示0.05水平上差异显著。FY4:富源四号;NJ28:宁粳28;NJ43:宁粳43;NJ50:宁粳50。Z1:保墒旱直播;Z2:旱播后上水;Z3:插秧。下同。
Fig. 1. Changes of amylose content in rice grains under different planting methods Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level. FY4, Fuyuan 4; NJ28, Ningjing 28; NJ43, Ningjing 43; NJ50, Ningjing 50. Z1, Dry direct seeding; Z2, Watering after sowing; Z3, Transplanting. The same below.
| 淀粉 Starch | 处理 Treatment | a | b | k | R2 | Tmax (d) | Vmax (mg·g−1·d−1) | P (d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直链淀粉 Amylose | FY4 | Z1 | 19.281 | 58.589 | 0.349 | 0.991 | 11.663 | 1.682 | 17.959 |
| Z2 | 19.473 | 60.270 | 0.362 | 0.988 | 11.323 | 1.762 | 17.392 | ||
| Z3 | 18.647 | 62.991 | 0.360 | 0.999 | 11.508 | 1.678 | 17.612 | ||
| NJ28 | Z1 | 20.567 | 35.813 | 0.304 | 0.992 | 11.771 | 1.563 | 18.998 | |
| Z2 | 19.686 | 63.800 | 0.376 | 0.984 | 11.053 | 1.850 | 16.896 | ||
| Z3 | 19.351 | 151.392 | 0.474 | 0.995 | 10.590 | 2.293 | 15.226 | ||
| NJ43 | Z1 | 19.508 | 110.349 | 0.431 | 0.986 | 10.913 | 2.102 | 16.011 | |
| Z2 | 19.580 | 93.890 | 0.385 | 0.984 | 11.798 | 1.885 | 17.505 | ||
| Z3 | 18.487 | 58.831 | 0.382 | 0.993 | 10.667 | 1.766 | 16.419 | ||
| NJ50 | Z1 | 19.405 | 33.744 | 0.309 | 0.994 | 11.388 | 1.499 | 18.498 | |
| Z2 | 20.138 | 69.300 | 0.392 | 0.997 | 10.812 | 1.974 | 16.418 | ||
| Z3 | 19.081 | 99.355 | 0.442 | 0.997 | 10.404 | 2.108 | 15.375 | ||
| 支链淀粉 Amylopectin | FY4 | Z1 | 48.446 | 13.557 | 0.149 | 0.983 | 17.496 | 1.805 | 32.242 |
| Z2 | 48.867 | 13.600 | 0.148 | 0.986 | 17.636 | 1.808 | 32.482 | ||
| Z3 | 48.586 | 14.583 | 0.153 | 0.988 | 17.515 | 1.858 | 31.876 | ||
| NJ28 | Z1 | 48.904 | 11.363 | 0.133 | 0.984 | 18.273 | 1.626 | 34.794 | |
| Z2 | 48.251 | 11.170 | 0.136 | 0.981 | 17.744 | 1.641 | 33.900 | ||
| Z3 | 49.631 | 10.515 | 0.126 | 0.978 | 18.673 | 1.563 | 36.111 | ||
| NJ43 | Z1 | 49.095 | 13.104 | 0.149 | 0.988 | 17.268 | 1.829 | 32.014 | |
| Z2 | 48.175 | 13.414 | 0.157 | 0.984 | 16.537 | 1.891 | 30.532 | ||
| Z3 | 48.335 | 13.457 | 0.156 | 0.990 | 16.663 | 1.885 | 30.748 | ||
| NJ50 | Z1 | 47.257 | 13.003 | 0.152 | 0.986 | 16.876 | 1.796 | 31.332 | |
| Z2 | 47.700 | 11.823 | 0.143 | 0.979 | 17.273 | 1.705 | 32.638 | ||
| Z3 | 48.211 | 12.563 | 0.142 | 0.981 | 17.822 | 1.711 | 33.296 | ||
| 总淀粉 Total starch | FY4 | Z1 | 66.844 | 16.092 | 0.184 | 0.985 | 15.100 | 3.075 | 27.041 |
| Z2 | 67.423 | 15.195 | 0.179 | 0.985 | 15.201 | 3.017 | 27.476 | ||
| Z3 | 65.970 | 17.278 | 0.190 | 0.989 | 14.997 | 3.134 | 26.561 | ||
| NJ28 | Z1 | 68.074 | 13.013 | 0.167 | 0.982 | 15.365 | 2.842 | 28.522 | |
| Z2 | 66.912 | 12.886 | 0.171 | 0.978 | 14.948 | 2.860 | 27.797 | ||
| Z3 | 66.476 | 13.017 | 0.175 | 0.976 | 14.664 | 2.908 | 27.220 | ||
| NJ43 | Z1 | 68.097 | 14.407 | 0.180 | 0.986 | 14.821 | 3.064 | 27.027 | |
| Z2 | 67.562 | 16.166 | 0.187 | 0.987 | 14.882 | 3.159 | 26.632 | ||
| Z3 | 66.240 | 14.337 | 0.184 | 0.989 | 14.472 | 3.047 | 26.413 | ||
| NJ50 | Z1 | 65.880 | 14.527 | 0.183 | 0.986 | 14.623 | 3.014 | 26.630 | |
| Z2 | 66.152 | 14.768 | 0.189 | 0.979 | 14.246 | 3.126 | 25.871 | ||
| Z3 | 65.444 | 14.938 | 0.188 | 0.978 | 14.382 | 3.076 | 26.070 | ||
表2 不同种植方式下水稻籽粒淀粉组分积累特征参数
Table 2. Characteristic parameters of starch component accumulation in rice grains under different planting patterns
| 淀粉 Starch | 处理 Treatment | a | b | k | R2 | Tmax (d) | Vmax (mg·g−1·d−1) | P (d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直链淀粉 Amylose | FY4 | Z1 | 19.281 | 58.589 | 0.349 | 0.991 | 11.663 | 1.682 | 17.959 |
| Z2 | 19.473 | 60.270 | 0.362 | 0.988 | 11.323 | 1.762 | 17.392 | ||
| Z3 | 18.647 | 62.991 | 0.360 | 0.999 | 11.508 | 1.678 | 17.612 | ||
| NJ28 | Z1 | 20.567 | 35.813 | 0.304 | 0.992 | 11.771 | 1.563 | 18.998 | |
| Z2 | 19.686 | 63.800 | 0.376 | 0.984 | 11.053 | 1.850 | 16.896 | ||
| Z3 | 19.351 | 151.392 | 0.474 | 0.995 | 10.590 | 2.293 | 15.226 | ||
| NJ43 | Z1 | 19.508 | 110.349 | 0.431 | 0.986 | 10.913 | 2.102 | 16.011 | |
| Z2 | 19.580 | 93.890 | 0.385 | 0.984 | 11.798 | 1.885 | 17.505 | ||
| Z3 | 18.487 | 58.831 | 0.382 | 0.993 | 10.667 | 1.766 | 16.419 | ||
| NJ50 | Z1 | 19.405 | 33.744 | 0.309 | 0.994 | 11.388 | 1.499 | 18.498 | |
| Z2 | 20.138 | 69.300 | 0.392 | 0.997 | 10.812 | 1.974 | 16.418 | ||
| Z3 | 19.081 | 99.355 | 0.442 | 0.997 | 10.404 | 2.108 | 15.375 | ||
| 支链淀粉 Amylopectin | FY4 | Z1 | 48.446 | 13.557 | 0.149 | 0.983 | 17.496 | 1.805 | 32.242 |
| Z2 | 48.867 | 13.600 | 0.148 | 0.986 | 17.636 | 1.808 | 32.482 | ||
| Z3 | 48.586 | 14.583 | 0.153 | 0.988 | 17.515 | 1.858 | 31.876 | ||
| NJ28 | Z1 | 48.904 | 11.363 | 0.133 | 0.984 | 18.273 | 1.626 | 34.794 | |
| Z2 | 48.251 | 11.170 | 0.136 | 0.981 | 17.744 | 1.641 | 33.900 | ||
| Z3 | 49.631 | 10.515 | 0.126 | 0.978 | 18.673 | 1.563 | 36.111 | ||
| NJ43 | Z1 | 49.095 | 13.104 | 0.149 | 0.988 | 17.268 | 1.829 | 32.014 | |
| Z2 | 48.175 | 13.414 | 0.157 | 0.984 | 16.537 | 1.891 | 30.532 | ||
| Z3 | 48.335 | 13.457 | 0.156 | 0.990 | 16.663 | 1.885 | 30.748 | ||
| NJ50 | Z1 | 47.257 | 13.003 | 0.152 | 0.986 | 16.876 | 1.796 | 31.332 | |
| Z2 | 47.700 | 11.823 | 0.143 | 0.979 | 17.273 | 1.705 | 32.638 | ||
| Z3 | 48.211 | 12.563 | 0.142 | 0.981 | 17.822 | 1.711 | 33.296 | ||
| 总淀粉 Total starch | FY4 | Z1 | 66.844 | 16.092 | 0.184 | 0.985 | 15.100 | 3.075 | 27.041 |
| Z2 | 67.423 | 15.195 | 0.179 | 0.985 | 15.201 | 3.017 | 27.476 | ||
| Z3 | 65.970 | 17.278 | 0.190 | 0.989 | 14.997 | 3.134 | 26.561 | ||
| NJ28 | Z1 | 68.074 | 13.013 | 0.167 | 0.982 | 15.365 | 2.842 | 28.522 | |
| Z2 | 66.912 | 12.886 | 0.171 | 0.978 | 14.948 | 2.860 | 27.797 | ||
| Z3 | 66.476 | 13.017 | 0.175 | 0.976 | 14.664 | 2.908 | 27.220 | ||
| NJ43 | Z1 | 68.097 | 14.407 | 0.180 | 0.986 | 14.821 | 3.064 | 27.027 | |
| Z2 | 67.562 | 16.166 | 0.187 | 0.987 | 14.882 | 3.159 | 26.632 | ||
| Z3 | 66.240 | 14.337 | 0.184 | 0.989 | 14.472 | 3.047 | 26.413 | ||
| NJ50 | Z1 | 65.880 | 14.527 | 0.183 | 0.986 | 14.623 | 3.014 | 26.630 | |
| Z2 | 66.152 | 14.768 | 0.189 | 0.979 | 14.246 | 3.126 | 25.871 | ||
| Z3 | 65.444 | 14.938 | 0.188 | 0.978 | 14.382 | 3.076 | 26.070 | ||
| 变量 Variable | 作用因子 Effect of factors | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 直接通径系数 Direct path coefficients | 间接通径系数 Indirect path coefficients | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合计 Total | AGP | UGP | SSS | GBSS | SBE | ||||
| 直连淀粉 Amylose | AGP | 0.703 | 0.337 | 0.366 | −0.015 | 0.054 | 0.239 | 0.088 | |
| UDPG | 0.118 | 0.191 | −0.073 | −0.008 | 0.040 | −0.037 | −0.068 | ||
| SSS | 0.283 | 0.225 | 0.058 | 0.036 | 0.047 | 0.062 | −0.086 | ||
| GBSS | 0.939 | 0.489 | 0.450 | 0.347 | −0.094 | 0.134 | 0.064 | ||
| SBE | 0.355 | 0.545 | −0.190 | 0.142 | −0.193 | −0.209 | 0.071 | ||
| 支链淀粉 | AGP | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | |
| Amylopectin | UDPG | 0.132 | 0.214 | −0.082 | −0.009 | 0.045 | −0.041 | −0.076 | |
| SSS | 0.081 | 0.064 | 0.017 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.018 | −0.025 | ||
| GBSS | 0.248 | 0.129 | 0.119 | 0.091 | −0.025 | 0.035 | 0.017 | ||
| SBE | 0.458 | 0.702 | −0.244 | 0.183 | −0.249 | −0.270 | 0.091 | ||
| 总淀粉 Total starch | AGP | 0.498 | 0.239 | 0.259 | −0.011 | 0.038 | 0.169 | 0.062 | |
| UDPG | 0.096 | 0.156 | −0.060 | −0.007 | 0.032 | −0.030 | −0.055 | ||
| SSS | 0.082 | 0.065 | 0.017 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 0.018 | −0.025 | ||
| GBSS | 0.302 | 0.157 | 0.145 | 0.111 | −0.030 | 0.043 | 0.020 | ||
| SBE | 0.367 | 0.563 | −0.196 | 0.146 | −0.199 | −0.216 | 0.073 | ||
表3 2020年和2021年水稻花后21 d淀粉含量和淀粉合成关键酶的通径分析
Table 3. Path analysis of starch content and key enzymes of starch synthesis 21 days after flowering in 2020 and 2021
| 变量 Variable | 作用因子 Effect of factors | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 直接通径系数 Direct path coefficients | 间接通径系数 Indirect path coefficients | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合计 Total | AGP | UGP | SSS | GBSS | SBE | ||||
| 直连淀粉 Amylose | AGP | 0.703 | 0.337 | 0.366 | −0.015 | 0.054 | 0.239 | 0.088 | |
| UDPG | 0.118 | 0.191 | −0.073 | −0.008 | 0.040 | −0.037 | −0.068 | ||
| SSS | 0.283 | 0.225 | 0.058 | 0.036 | 0.047 | 0.062 | −0.086 | ||
| GBSS | 0.939 | 0.489 | 0.450 | 0.347 | −0.094 | 0.134 | 0.064 | ||
| SBE | 0.355 | 0.545 | −0.190 | 0.142 | −0.193 | −0.209 | 0.071 | ||
| 支链淀粉 | AGP | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | |
| Amylopectin | UDPG | 0.132 | 0.214 | −0.082 | −0.009 | 0.045 | −0.041 | −0.076 | |
| SSS | 0.081 | 0.064 | 0.017 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.018 | −0.025 | ||
| GBSS | 0.248 | 0.129 | 0.119 | 0.091 | −0.025 | 0.035 | 0.017 | ||
| SBE | 0.458 | 0.702 | −0.244 | 0.183 | −0.249 | −0.270 | 0.091 | ||
| 总淀粉 Total starch | AGP | 0.498 | 0.239 | 0.259 | −0.011 | 0.038 | 0.169 | 0.062 | |
| UDPG | 0.096 | 0.156 | −0.060 | −0.007 | 0.032 | −0.030 | −0.055 | ||
| SSS | 0.082 | 0.065 | 0.017 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 0.018 | −0.025 | ||
| GBSS | 0.302 | 0.157 | 0.145 | 0.111 | −0.030 | 0.043 | 0.020 | ||
| SBE | 0.367 | 0.563 | −0.196 | 0.146 | −0.199 | −0.216 | 0.073 | ||
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 穗长 Panicle length (cm) | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 结实率 Seed setting rate (%) | 产量 Yield (kg/666.7m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | FY4 | Z1 | 16.51±0.59 b | 96.50±23.50 b | 26.29±1.19 a | 93.65±6.56 a | 655.40±154.50 c |
| Z2 | 14.50±0.80 c | 83.67±33.76 c | 25.36±5.16 b | 90.44±2.55 b | 661.40±72.60 b | ||
| Z3 | 19.67±3.07 a | 159.00±44.40 a | 24.23±1.34 c | 72.19±12.28 c | 808.80±60.40 a | ||
| NJ28 | Z1 | 18.40±2.00 a | 99.14±14.86 c | 28.06±7.25 a | 88.90±0.28 b | 699.30±107.40 b | |
| Z2 | 17.67±0.27 b | 115.50±20.10 b | 26.30±0.81 b | 91.77±2.31 a | 565.40±318.90 c | ||
| Z3 | 17.13±0.13 b | 122.38±8.62 a | 25.70±0.50 c | 86.31±2.69 c | 890.10±132.60 a | ||
| NJ43 | Z1 | 15.00±0.30 c | 94.00±12.60 c | 25.38±0.47 a | 87.59±2.14 b | 546.40±20.00 b | |
| Z2 | 15.62±3.58 b | 106.00±28.40 b | 26.37±3.46 a | 89.81±0.53 a | 515.60±266.10 c | ||
| Z3 | 17.00±0.25 a | 145.80±5.27 a | 26.20±2.11 a | 80.66±6.43 c | 738.80±97.50 a | ||
| NJ50 | Z1 | 15.71±3.49 c | 97.86±13.74 c | 29.56±0.75 a | 93.43±1.88 a | 622.20±225.20 b | |
| Z2 | 16.67±4.33 b | 107.00±85.80 b | 26.50±3.39 b | 89.88±6.62 c | 544.00±212.90 c | ||
| Z3 | 19.75±0.25 a | 155.50±16.90 a | 26.30±2.09 b | 92.60±2.30 b | 898.00±138.20 a | ||
| 2021 | FY4 | Z1 | 17.10±0.60 b | 95.00±11.20 c | 25.51±1.89 b | 94.48±0.40 a | 664.45±93.35 c |
| Z2 | 17.89±0.41 ab | 115.67±23.47 b | 27.03±0.12 a | 95.91±8.40 a | 687.12±33.93 b | ||
| Z3 | 19.69±2.39 a | 107.89±22.09 a | 24.76±0.45 c | 86.74±6.53 b | 821.10±73.10 a | ||
| NJ28 | Z1 | 19.77±0.27 a | 113.23±23.37 b | 28.52±0.99 a | 92.17±4.03 a | 740.42±11.62 b | |
| Z2 | 15.24±4.43 c | 119.40±22.93 a | 28.68±0.14 a | 93.92±6.76 a | 752.63±133.19 a | ||
| Z3 | 17.47±2.03 b | 103.94±27.46 c | 27.60±0.60 a | 92.64±3.68 a | 636.07±161.31 c | ||
| NJ43 | Z1 | 16.43±1.87 b | 104.39±25.41 c | 28.08±1.23 a | 85.94±3.15 b | 635.63±111.84 b | |
| Z2 | 15.56±2.34 b | 110.39±23.21 a | 26.41±0.58 b | 94.62±0.20 a | 705.33±77.33 a | ||
| Z3 | 19.60±0.20 a | 109.43±7.57 b | 26.60±0.31 b | 82.87±11.06 c | 620.88±46.42 c | ||
| NJ50 | Z1 | 17.84±1.56 b | 98.35±24.65 c | 29.87±1.94 a | 94.66±4.91 b | 701.67±115.88 c | |
| Z2 | 17.70±2.30 b | 102.91±39.29 b | 28.66±0.46 c | 96.90±5.76 a | 728.63±94.04 b | ||
| Z3 | 19.40±1.80 a | 110.04±55.76 a | 29.27±0.36 b | 91.67±0.31 c | 738.93±26.27 a | ||
| 品种 Variety(V) | NS | NS | ** | NS | NS | ||
| 种植方式Growing method(G) | ** | NS | NS | ** | NS | ||
| 品种×种植方式V×G | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
表4 不同种植方式对水稻产量及其构成因素的影响
Table 4. Effects of different planting methods on grain yield and its component factors
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 穗长 Panicle length (cm) | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 结实率 Seed setting rate (%) | 产量 Yield (kg/666.7m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | FY4 | Z1 | 16.51±0.59 b | 96.50±23.50 b | 26.29±1.19 a | 93.65±6.56 a | 655.40±154.50 c |
| Z2 | 14.50±0.80 c | 83.67±33.76 c | 25.36±5.16 b | 90.44±2.55 b | 661.40±72.60 b | ||
| Z3 | 19.67±3.07 a | 159.00±44.40 a | 24.23±1.34 c | 72.19±12.28 c | 808.80±60.40 a | ||
| NJ28 | Z1 | 18.40±2.00 a | 99.14±14.86 c | 28.06±7.25 a | 88.90±0.28 b | 699.30±107.40 b | |
| Z2 | 17.67±0.27 b | 115.50±20.10 b | 26.30±0.81 b | 91.77±2.31 a | 565.40±318.90 c | ||
| Z3 | 17.13±0.13 b | 122.38±8.62 a | 25.70±0.50 c | 86.31±2.69 c | 890.10±132.60 a | ||
| NJ43 | Z1 | 15.00±0.30 c | 94.00±12.60 c | 25.38±0.47 a | 87.59±2.14 b | 546.40±20.00 b | |
| Z2 | 15.62±3.58 b | 106.00±28.40 b | 26.37±3.46 a | 89.81±0.53 a | 515.60±266.10 c | ||
| Z3 | 17.00±0.25 a | 145.80±5.27 a | 26.20±2.11 a | 80.66±6.43 c | 738.80±97.50 a | ||
| NJ50 | Z1 | 15.71±3.49 c | 97.86±13.74 c | 29.56±0.75 a | 93.43±1.88 a | 622.20±225.20 b | |
| Z2 | 16.67±4.33 b | 107.00±85.80 b | 26.50±3.39 b | 89.88±6.62 c | 544.00±212.90 c | ||
| Z3 | 19.75±0.25 a | 155.50±16.90 a | 26.30±2.09 b | 92.60±2.30 b | 898.00±138.20 a | ||
| 2021 | FY4 | Z1 | 17.10±0.60 b | 95.00±11.20 c | 25.51±1.89 b | 94.48±0.40 a | 664.45±93.35 c |
| Z2 | 17.89±0.41 ab | 115.67±23.47 b | 27.03±0.12 a | 95.91±8.40 a | 687.12±33.93 b | ||
| Z3 | 19.69±2.39 a | 107.89±22.09 a | 24.76±0.45 c | 86.74±6.53 b | 821.10±73.10 a | ||
| NJ28 | Z1 | 19.77±0.27 a | 113.23±23.37 b | 28.52±0.99 a | 92.17±4.03 a | 740.42±11.62 b | |
| Z2 | 15.24±4.43 c | 119.40±22.93 a | 28.68±0.14 a | 93.92±6.76 a | 752.63±133.19 a | ||
| Z3 | 17.47±2.03 b | 103.94±27.46 c | 27.60±0.60 a | 92.64±3.68 a | 636.07±161.31 c | ||
| NJ43 | Z1 | 16.43±1.87 b | 104.39±25.41 c | 28.08±1.23 a | 85.94±3.15 b | 635.63±111.84 b | |
| Z2 | 15.56±2.34 b | 110.39±23.21 a | 26.41±0.58 b | 94.62±0.20 a | 705.33±77.33 a | ||
| Z3 | 19.60±0.20 a | 109.43±7.57 b | 26.60±0.31 b | 82.87±11.06 c | 620.88±46.42 c | ||
| NJ50 | Z1 | 17.84±1.56 b | 98.35±24.65 c | 29.87±1.94 a | 94.66±4.91 b | 701.67±115.88 c | |
| Z2 | 17.70±2.30 b | 102.91±39.29 b | 28.66±0.46 c | 96.90±5.76 a | 728.63±94.04 b | ||
| Z3 | 19.40±1.80 a | 110.04±55.76 a | 29.27±0.36 b | 91.67±0.31 c | 738.93±26.27 a | ||
| 品种 Variety(V) | NS | NS | ** | NS | NS | ||
| 种植方式Growing method(G) | ** | NS | NS | ** | NS | ||
| 品种×种植方式V×G | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| [1] | 朱德峰, 张玉屏, 陈惠哲, 王亚梁. 中国水稻栽培技术发展与展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2021, 27(4): 45-49. |
| Zhu D F, Zhang Y P, Chen H Z, Wang Y L. Development and prospect of rice cultivation techniques in China[J]. China Rice, 2021, 27(4): 45-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 吴汉, 吴含, 钱娜, 柯健, 郭爽爽. 江淮地区不同灌溉与种植方式对水稻产量及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2022, 41(6): 39-46. |
| Wu H, Wu H, Qian N, Ke J, Guo S S. Effects of different irrigation and plantingpatterns on rice yield and water use efficiency in Jianghuai region[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2022, 41(6): 39-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Liu H, Hussain S, Zheng M, Peng S, Huang J, Cui K, Nie L. Dry direct-seeded rice as an alternative to transplanted-flooded rice in Central China[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2015, 35(1): 285-294. |
| [4] | 张洪程, 胡雅杰, 杨建昌, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 高辉, 郭保卫, 邢志鹏, 胡群. 中国特色水稻栽培学发展与展望[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(7): 1301-1321. |
| Zhang H C, Hu Y J, Yang J C, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Gao H, Guo B W, Xing Z P, Hu Q. Development and prospect of rice cultivation with Chinese characteristics[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(7): 1301-1321. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 轧宗杰, 卢树昌, 侯琨. 水稻旱直播栽培发展现状、问题及应用前景[J]. 作物杂志, 2020(2): 9-15. |
| Gan Z J, Lu S C, Hou K. Development status, problems and application prospect of dry direct seeding cultivation of rice[J]. Crops, 2020, 36(2): 9-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 唐荣莉, 唐兴隆, 张巫军, 段秀建, 李经勇, 姚雄. 丘陵山区单季中稻不同种植方式的经济与生态可持续性评估[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2023, 31(1): 90-101. |
| Tang R L, Tang X L, Zhang W J, Duan X J, Li J Y, Yao X. Evaluation of economic and ecological sustainability of different planting patterns of single cropping medium rice in hilly and mountainous areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2023, 31(1): 90-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 匡炜, 魏征, 戴力, 赵杨, 梁玉刚, 罗先富, 张玉烛, 方宝华. 不同种植方式对双季稻生育期及产量的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2022, 37(6): 142-149. |
| Kuang W, Wei Z, Dai L, Zhao Y, Liang Y G, Luo X F, Zhang Y C, Fang B H. Effects of different planting patterns on growth period and yield of double cropping rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2022, 37(6): 142-149. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 张晓丽, 陶伟, 高国庆, 陈雷, 郭辉, 张华, 唐茂艳, 梁天锋. 直播栽培对双季早稻生育期、抗倒伏能力及产量效益的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2023, 56(2): 249-263. |
| Zhang X L, Tao W, Gao G Q, Chen L, Guo Hi, Zhang H, Tang M Y, Liang T F. Effects of direct seeding cultivation on growth period, lodging resistance and yield benefit of double cropping early rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2023, 56(2): 249-263. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 孙永健, 郑洪帧, 徐徽, 杨志远, 贾现文, 程洪彪, 马均. 机械旱直播方式促进水稻生长发育提高产量[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(20): 10-18. |
| Sun Y J, Zheng H F, Xu H, Jerry Y, Jia X W, Cheng H B, Ma J. Mechanical dry direct seeding promotes the growth and development of rice and increases its yield.[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(20): 10-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Verma D K, Srivastav P P. Isolation, modification, and characterization of rice starch with emphasis on functional properties and industrial application: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2022, 62(24): 6577-6604. |
| [11] | Gilbert R G, Witt T, Hasjim J. What is being learned about starch properties from multiple-level characterization[J]. Cereal Chemistry, 2013, 90(4): 312-325. |
| [12] | 彭立功, 龚静, 兰艳, 王锦, 隋晓东, 丁春邦, 李天. 水分胁迫对宜香优2115籽粒淀粉合成及产量的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2021, 36(5): 77-86. |
| Peng L G, Gong J, Lan Y, Wang J, Sui X D, Ding C B, Li T. Effects of water stress on starch synthesis and yield of Yixiangyou 2115[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2021, 36(5): 77-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 赵宏伟, 吕艳超, 许晶, 夏楠, 贾琰, 邹德堂. 施氮量对盐胁迫下寒地粳稻籽粒淀粉积累及相关酶活性的影响. 东北农业大学学报, 2015, 46(8): 1-8. |
| Zhao H W, Lu Y C, Xu J, Xia N, Jia J, Zou D T. Effects of nitrogen application rate on grain starch accumulation and related enzyme activities of japonica rice under salt stress[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2015, 46(8): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 程方民, 蒋德安, 吴平, 石春海. 早籼稻籽粒灌浆过程中淀粉合成酶的变化及温度效应特征[J]. 作物学报, 2001(2): 201-206. |
| Cheng F M, Jiang D, Wu P, Shi C H. Changes of starch synthase and characteristics of temperature effect during grain filling in early indica rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2001(2): 201-206. | |
| [15] | Doehlert D C, Kuo T M, Felker F C. Enzymes of sucrose and hexose metabolism in developing kernels of two inbreds of maize[J]. Plant Physiology (Bethesda), 1988, 86(4): 1013-1019. |
| [16] | Nakamura Y N I O, Yuki K, Park S Y, Ohya T. Carbohydrate metabolism in the developing endosperm of rice grains[J]. Plant Cell Physiology, 1989, 30(6): 833-839. |
| [17] | 李太贵, 沈波, 陈能, 罗玉坤. Q酶在水稻籽粒垩白形成中作用的研究[J]. 作物学报, 1997(3): 338-344. |
| Li T G, Shen B, Chen N, Luo Y K. Study on the role of Q enzyme in the formation of rice grain chalkiness[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1997, 23(3): 338-344. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 雷振山, 李猛, 卫云飞, 季新, 刘娟, 王付娟, 刘秋员. 不同种植方式对豫南地区优质食味粳稻产量及品质的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2023, 52(2): 12-20. |
| Lei Z S, Li M, Wei Y F, Ji X, Liu J, Wang F J, Liu Q J. Effects of different planting patterns on yield and quality of high-quality taste japonica rice in southern Henan[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 52(2): 12-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 胡雅杰, 薛建涛, 吴培, 李娈, 丛舒敏, 余恩唯, 倪嘉颢, 张洪程. 施氮量和直播密度对稻米食味品质和淀粉结构的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2022, 37(2): 7-13. |
| Hu Y J, Xue J T, Wu P, Li L, Cong S M, Yu E W, Ni J H, Zhang H C. Effects of nitrogen application rate and direct seeding density on eating quality and starch structure of rice[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2022, 37(2): 7-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Wang W, Peng S, Liu H, Tao Y, Huang J, Cui K, Nie L. The possibility of replacing puddled transplanted flooded rice with dry seeded rice in central China: A review[J]. Field Crop Research, 2017, 214: 310-320. |
| [21] | 刘东华. 干旱胁迫对稻谷品质性状及W_X基因表达的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2014. |
| Liu D H. Effects of drought stress on grain quality traits and Wendy X gene expression in rice[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 陈婷婷, 许更文, 钱希旸, 王志琴, 张耗, 杨建昌. 花后轻干-湿交替灌溉提高水稻籽粒淀粉合成相关基因的表达[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(7): 1288-1299. |
| Chen T T, Xu G W, Qian X Y, Wang Z Q, Zhang H, Yang J C. Light dry-wet alternate irrigation after anthesis increased the expression of genes related to starch synthesis in rice grains[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(7): 1288-1299. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 王维, 蔡一霞, 蔡昆争, 张建华, 杨建昌, 朱庆森. 水分胁迫对贪青水稻籽粒充实及其淀粉合成关键酶活性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2006(7): 972-979. |
| Wang W, Cai Y X, Cai K Z, Zhang J H, Yang J C, Zhu Q S. Effects of Water stress on Grain filling and activities of key enzymes in starch synthesis of greedy green rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2006(7): 972-979. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 韩燕, 徐亚楠, 宋吉青, 柳斌辉, 韩伟, 斋藤信, 白文波. 轻度干热风条件下喷施复合寡糖提高冬小麦叶片生理活性和籽粒淀粉合成关键酶活性[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(12): 2324-2333. |
| Han Y, Xu Y N, Song J Q, Liu B H, Han W, Saito S, Bai W B. Spraying compound oligosaccharides under mild dry and hot air conditions increased the physiological activities of winter wheat leaves and the activities of key enzymes in grain starch synthesis. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(12): 2324-2333. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 王春雨, 余华清, 何艳, 郭长春, 张绍文, 杨志远, 马均. 播栽方式与施氮量对杂交籼稻氮肥利用特征及产量的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(12): 1792-1801. |
| Wang C Y, Yu H Q, He Y, Guo C C, Zhang S W, Yang Z Y, Ma J. Effects of sowing methods and nitrogen application rates on nitrogen utilization characteristics and yield of Indica Hybrid Rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(12): 1792-1801. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 唐志强, 张丽颖, 何娜, 马作斌, 赵明珠, 王昌华, 郑文静, 银永安, 王辉. 机械旱直播对水稻生育进程、光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2021(5): 87-94. |
| Tang Z Q, Zhang L Y, He N, Ma Z B, Zhao M Z, Wang C H, Zheng W J, Yin Y A, Wang H. Effects of mechanical dry direct seeding on growth process, photosynthetic characteristics and yield of rice[J]. Crops, 2021, (5): 87-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 徐令旗, 郭晓红, 张佳柠, 赵洋, 李晓蕾, 刘绍峰, 崔致远, 安懿亮, 吕艳东. 不同有机肥对旱直播水稻品质的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2022, 37(1): 137-146. |
| Xu L Q, Guo X H, Zhang J N, Zhao Y, Li X L, Liu S F, Cui Z Y, An Y L, Lü Y D. Effects of different organic fertilizers on the quality of dry direct seeding rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2022, 37 (1): 137-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 徐令旗, 郭晓红, 兰宇辰, 崔致远, 张佳柠, 吕艳东. 不同有机肥对旱直播水稻干物质积累和产量的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2021, 36(2): 188-195 |
| Xu L Q, Guo X H, Lan Y C, Cui Z Y, Zhang J N, Lu Y D. Effects of different organic fertilizers on dry matter accumulation and yield of dry direct seeding rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2021, 36(2): 188-195. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 汪邑晨, 朱本顺, 周磊, 朱骏, 杨仲南. 光/温敏核不育系的不育机理及两系杂交稻的发展与展望 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 463-474. |
| [2] | 许用强, 徐军, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 王丹英, 曾宇翔, 符冠富. 水稻花粉管生长及其对非生物逆境胁迫的响应机理研究进展 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 495-506. |
| [3] | 何勇, 刘耀威, 熊翔, 祝丹晨, 王爱群, 马拉娜, 王廷宝, 张健, 李建雄, 田志宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑OsOFP30基因创制水稻粒型突变体 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [4] | 吕阳, 刘聪聪, 杨龙波, 曹兴岚, 王月影, 童毅, Mohamed Hazman, 钱前, 商连光, 郭龙彪. 全基因组关联分析(GWAS)鉴定水稻氮素利用效率候选基因 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 516-524. |
| [5] | 杨好, 黄衍焱, 王剑, 易春霖, 石军, 谭楮湉, 任文芮, 王文明. 水稻中八个稻瘟病抗性基因特异分子标记的开发及应用 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 525-534. |
| [6] | 蒋鹏, 张林, 周兴兵, 郭晓艺, 朱永川, 刘茂, 郭长春, 熊洪, 徐富贤. 冬水田轻简化栽培杂交稻蓄留再生稻产量形成特点 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [7] | 杨铭榆, 陈志诚, 潘美清, 张汴泓, 潘睿欣, 尤林东, 陈晓艳, 唐莉娜, 黄锦文. 烟-稻轮作下减氮配施生物炭对水稻茎鞘同化物转运和产量 形成的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 555-566. |
| [8] | 熊家欢, 张义凯, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 姚坚, 张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [9] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [10] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [11] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [12] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [13] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [14] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [15] | 吴玥, 梁铖玮, 赵辰妃, 孙健, 马殿荣. 直播稻田杂草稻灾害发生及生态型的演变特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||