
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (6): 609-616.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.221109
谢开珍1,2, 张建明2, 程灿2, 周继华2, 牛付安2, 孙滨2, 张安鹏2, 闻伟军3, 代雨婷2, 胡启琰2, 邱越2, 曹黎明2,4,*( ), 储黄伟2,4,*(
), 储黄伟2,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-19
修回日期:2023-02-23
出版日期:2023-11-10
发布日期:2023-11-14
通讯作者:
*email: chuhuangwei@saas.sh.cn;clm079@163.com
基金资助:
XIE Kaizhen1,2, ZHANG Jianming2, CHENG Can2, ZHOU Jihua2, NIU Fuan2, SUN Bin2, ZHANG Anpeng2, WEN Weijun3, DAI Yuting2, HU Qiyan2, QIU Yue2, CAO Liming2,4,*( ), CHU Huangwei2,4,*(
), CHU Huangwei2,4,*( )
)
Received:2022-11-19
Revised:2023-02-23
Online:2023-11-10
Published:2023-11-14
Contact:
*email: chuhuangwei@saas.sh.cn;clm079@163.com
摘要:
【目的】 稻米直链淀粉含量(amylose content, AC)是决定稻米食味品质最为重要的因素之一。筛选具有低直链淀粉含量的水稻种质资源并探究其遗传机制,对于选育具有优质食味品质的水稻新品种具有重要意义。【方法】 测定了22个三系杂交稻的恢复系品种的直链淀粉含量,并利用一个来源于恢复系繁38和申恢26杂交后代的双单倍体(Doubled haploid,DH)群体,分析了控制直链淀粉含量的QTL位点。【结果】 在22个恢复系中发现了2个低直链淀粉含量的品系繁32和繁38,其直链淀粉含量分别为11.39%±0.01%和10.58%±0.13%。与其他携带Wxmp等位基因的低直链淀粉材料不同,繁32和繁38携带Wxb等位基因。利用DH群体进行QTL分析,结果共检测到了5个控制直链淀粉含量的QTL 位点(qAC1.1、qAC1.2、qAC5、qAC6.1和qAC6.2)。其中qAC6.1和qAC6.2两年均能检测到。qAC6.2是一个主效QTL位点,其表型贡献率超过30%。【结论】 这些结果表明,繁38中低直链淀粉含量的表型可能主要由qAC6.2位点控制,可为深入研究水稻直链淀粉合成调节机理,及利用分子标记辅助选择技术选育低直链淀粉含量的水稻新品种奠定了基础。
谢开珍, 张建明, 程灿, 周继华, 牛付安, 孙滨, 张安鹏, 闻伟军, 代雨婷, 胡启琰, 邱越, 曹黎明, 储黄伟. 低直链淀粉含量水稻种质资源的鉴定与QTL定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 609-616.
XIE Kaizhen, ZHANG Jianming, CHENG Can, ZHOU Jihua, NIU Fuan, SUN Bin, ZHANG Anpeng, WEN Weijun, DAI Yuting, HU Qiyan, QIU Yue, CAO Liming, CHU Huangwei. Identification and QTL Mapping of Rice Germplasm Resources with Low Amylose Content[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 609-616.
| 名称 Name | 引物序列 Primer sequence | PCR产物 PCR product/bp |
|---|---|---|
| Wx-1F | CAATGCAACGTACGCCAAGCCGA | 1911 |
| Wx-1R | GTACACGACGACGGAGGGGAACCT | |
| Wx-2F | ACAACCACCATGTCGGCTCTCACCA | 1687 |
| Wx-2R | GGTGAGCACCCTGTCGGCTTCCA | |
| Wx-3F | GAGCTGACAACCCTGCACTACTGTCCA | 2005 |
| Wx-3R | AACCACTGGTTCATTCGTCTCTCATCCA |
表1 Waxy基因测序引物
Table 1. The sequencing primer of Waxy gene.
| 名称 Name | 引物序列 Primer sequence | PCR产物 PCR product/bp |
|---|---|---|
| Wx-1F | CAATGCAACGTACGCCAAGCCGA | 1911 |
| Wx-1R | GTACACGACGACGGAGGGGAACCT | |
| Wx-2F | ACAACCACCATGTCGGCTCTCACCA | 1687 |
| Wx-2R | GGTGAGCACCCTGTCGGCTTCCA | |
| Wx-3F | GAGCTGACAACCCTGCACTACTGTCCA | 2005 |
| Wx-3R | AACCACTGGTTCATTCGTCTCTCATCCA |
| 序号 Number | 名称 Name | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 序号 Number | 名称 Name | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C45 | 15.43±0.30 | 12 | 繁35 Fan 35 | 13.86±0.00 |
| 2 | 繁1 Fan 1 | 14.50±0.04 | 13 | 繁38 Fan 38 | 10.58±0.13 |
| 3 | 繁3 Fan 3 | 18.12±0.34 | 14 | 繁42 Fan 42 | 16.54±0.13 |
| 4 | 繁6 Fan 6 | 17.82±0.21 | 15 | 繁43 Fan 43 | 16.80±0.21 |
| 5 | 繁15 Fan 15 | 17.61±0.34 | 16 | 申CR1 Shen CR1 | 15.69±0.21 |
| 6 | 繁16 Fan 16 | 18.46±0.17 | 17 | 申CR2 Shen CR2 | 9.64±0.04 |
| 7 | 繁17 Fan 17 | 17.95±0.09 | 18 | 申CR3 Shen CR3 | 18.50±0.04 |
| 8 | 繁24 Fan 24 | 15.82±0.17 | 19 | 申CR4 Shen CR4 | 10.20±0.09 |
| 9 | 申恢26 Shenhui 26 | 17.48±0.13 | 20 | 申CR5 Shen CR5 | 14.07±0.13 |
| 10 | 繁29 Fan 29 | 16.50±0.09 | 21 | 申CR6 Shen CR6 | 13.39±0.13 |
| 11 | 繁32 Fan32 | 11.39±0.00 | 22 | 申CR7 Shen CR7 | 14.33±0.13 |
表2 不同水稻恢复系品种直链淀粉含量
Table 2. Amylose content in different restorer rice lines.
| 序号 Number | 名称 Name | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 序号 Number | 名称 Name | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C45 | 15.43±0.30 | 12 | 繁35 Fan 35 | 13.86±0.00 |
| 2 | 繁1 Fan 1 | 14.50±0.04 | 13 | 繁38 Fan 38 | 10.58±0.13 |
| 3 | 繁3 Fan 3 | 18.12±0.34 | 14 | 繁42 Fan 42 | 16.54±0.13 |
| 4 | 繁6 Fan 6 | 17.82±0.21 | 15 | 繁43 Fan 43 | 16.80±0.21 |
| 5 | 繁15 Fan 15 | 17.61±0.34 | 16 | 申CR1 Shen CR1 | 15.69±0.21 |
| 6 | 繁16 Fan 16 | 18.46±0.17 | 17 | 申CR2 Shen CR2 | 9.64±0.04 |
| 7 | 繁17 Fan 17 | 17.95±0.09 | 18 | 申CR3 Shen CR3 | 18.50±0.04 |
| 8 | 繁24 Fan 24 | 15.82±0.17 | 19 | 申CR4 Shen CR4 | 10.20±0.09 |
| 9 | 申恢26 Shenhui 26 | 17.48±0.13 | 20 | 申CR5 Shen CR5 | 14.07±0.13 |
| 10 | 繁29 Fan 29 | 16.50±0.09 | 21 | 申CR6 Shen CR6 | 13.39±0.13 |
| 11 | 繁32 Fan32 | 11.39±0.00 | 22 | 申CR7 Shen CR7 | 14.33±0.13 |
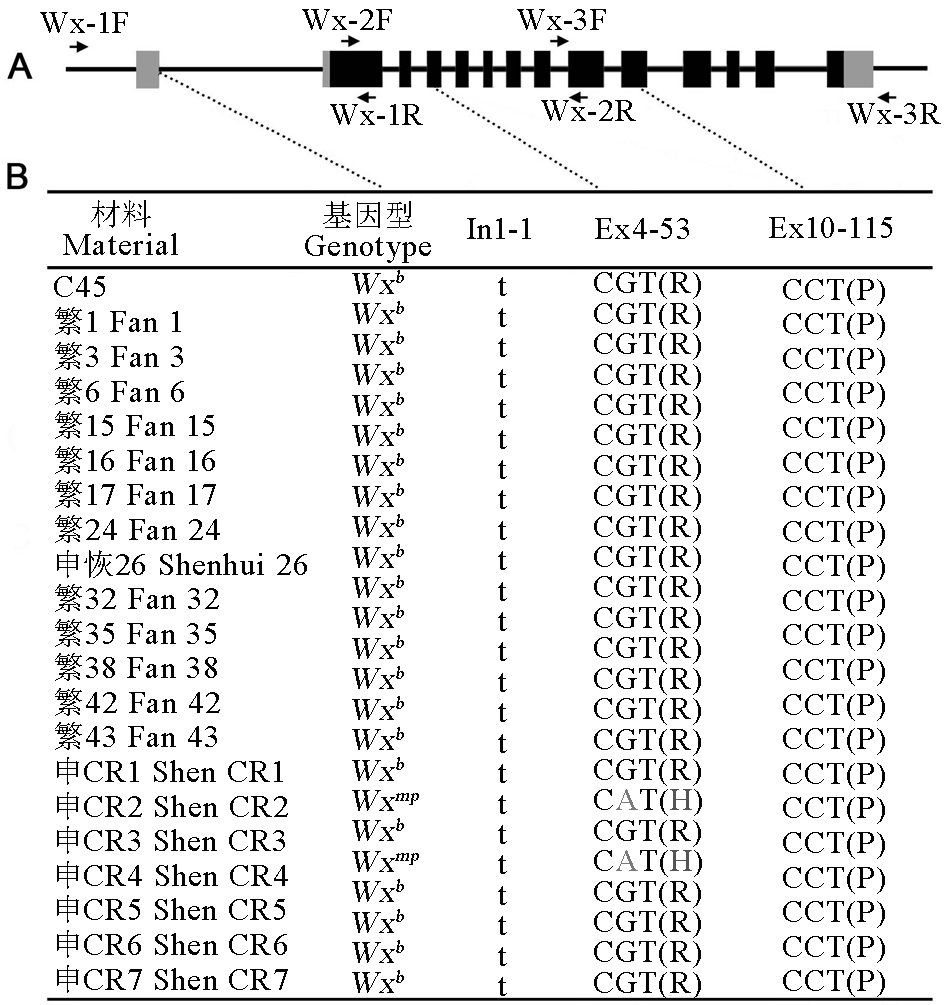
图2 不同直链淀粉含量水稻Wx基因型鉴定 A―Wx基因结构和PCR扩增引物,其中黑色方框表示编码区,灰色方框表示非翻译区;B―22个品种的Wx基因型。
Fig. 2. Genotyping of Wx genes in rice with different amylose contents. A, Gene structure and PCR primers for Wx gene, black and grey boxes indicate coding region and untranslated region, respectively. B, Genotype of Wx gene in 22 cultivars.
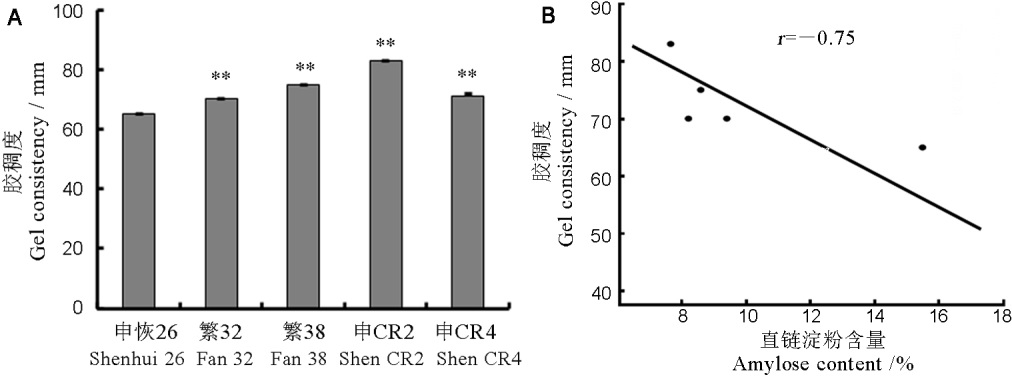
图4 胶稠度及其与直链淀粉含量的相关性 A―低直链淀粉品种繁32、繁38、申CR2和申CR4的胶稠度与申恢26相比显著增加(**P<0.01);B―胶稠度与直链淀粉含量显著负相关(r=−0.75)。
Fig. 4. Determination of gel consistency and its relationship with amylose content. A, The gel consistency(GC) of low amylose varieties Fan 32, Fan 38, Shen CR2 and Shen CR4 was significantly increased compared to Shenhui 26(**P < 0.01). B, The GC exhibited a significant negative correlation with the amylose content(r=−0.75).
| 年份 Year | 位点 Locus | 染色体 Chromosome | 遗传区间 Genetic range | 物理区间 Physical range/bp | LOD值 LOD value | 贡献率 PVE/% | 加性效应 Additive effect/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | qAC1.1 | 1 | ch1-336—ch1-344 | 27 294 708—27 633 625 | 4.03 | 10.76 | ―0.64 |
| qAC6.1 | 6 | ch6-42—ch6-44 | 4 722 458—5 120 945 | 5.00 | 13.81 | 0.73 | |
| qAC6.2 | 6 | ch6-143—ch6-200 | 7 984 061—9 393 696 | 11.04 | 33.80 | 1.14 | |
| 2021 | qAC1.2 | 1 | ch1-357—ch1-359 | 27 973 902—28 090 735 | 4.75 | 9.24 | ―0.64 |
| qAC5 | 5 | ch5-56—ch5-59 | 7 001 034—7 208 572 | 4.35 | 8.41 | 0.61 | |
| qAC6.1 | 6 | ch6-42—ch6-44 | 4 722 458—5 120 945 | 6.10 | 12.44 | 0.75 | |
| qAC6.2 | 6 | ch6-143—ch6-200 | 7 984 061—9 393 696 | 13.87 | 32.14 | 1.20 |
表3 控制稻米直链淀粉含量基因的QTL定位
Table 3. Preliminary mapping of QTL for genes controlling amylose content in rice.
| 年份 Year | 位点 Locus | 染色体 Chromosome | 遗传区间 Genetic range | 物理区间 Physical range/bp | LOD值 LOD value | 贡献率 PVE/% | 加性效应 Additive effect/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | qAC1.1 | 1 | ch1-336—ch1-344 | 27 294 708—27 633 625 | 4.03 | 10.76 | ―0.64 |
| qAC6.1 | 6 | ch6-42—ch6-44 | 4 722 458—5 120 945 | 5.00 | 13.81 | 0.73 | |
| qAC6.2 | 6 | ch6-143—ch6-200 | 7 984 061—9 393 696 | 11.04 | 33.80 | 1.14 | |
| 2021 | qAC1.2 | 1 | ch1-357—ch1-359 | 27 973 902—28 090 735 | 4.75 | 9.24 | ―0.64 |
| qAC5 | 5 | ch5-56—ch5-59 | 7 001 034—7 208 572 | 4.35 | 8.41 | 0.61 | |
| qAC6.1 | 6 | ch6-42—ch6-44 | 4 722 458—5 120 945 | 6.10 | 12.44 | 0.75 | |
| qAC6.2 | 6 | ch6-143—ch6-200 | 7 984 061—9 393 696 | 13.87 | 32.14 | 1.20 |
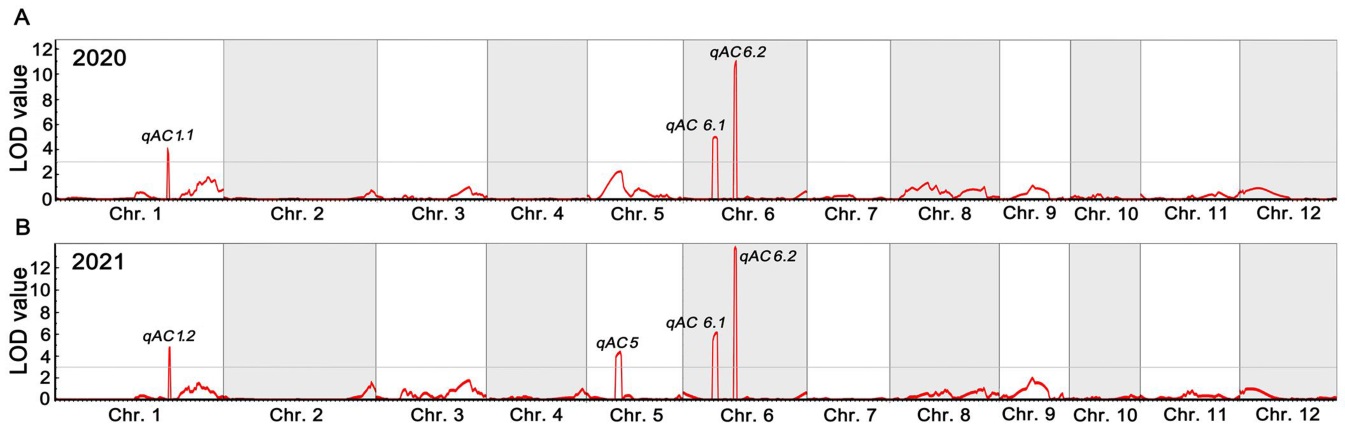
图6 2020年(A)和2021年(B)来源于申恢26/繁38的DH群体直链淀粉含量的QTL定位
Fig. 6. QTL mapping for amylose content of DH population derived from Shenhui 26/Fan 38 in 2020(A) and 2021(B).
| [1] | 吴云飞, 张勇, 王磊磊, 余徐润, 熊飞. 水稻籽粒淀粉品质的影响因素及其机制研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(6): 1-8. |
| Wu Y F, Zhang Y, Wang L L, Yu X R, Xiong F. Starch quality of rice grain: Research progress on influencing factors and mechanism[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 37(6): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 夏朵, 周浩, 何予卿. 稻米品质的遗传研究及分子育种进展[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2022, 41(1): 48-61. |
| Xia D, Zhou H, He Y Q. Progress on genetic study and molecular breeding of rice quality[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022, 41(1): 48-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Asaoka M, Okuno K, Fuwa H. Effect of environmental temperature at the milky stage on amylose content and fine structure of amylopectin of waxy and nonwaxy endosperm starches of rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 1985, 49(2): 373-379. |
| [4] | Tian Z X, Qian Q, Liu Q Q, Yan M X, Liu X F, Yan C J, Liu G F, Gao Z Y, Tang S Z, Zeng D L, Wang Y H, Yu J M, Gu M H, Li J Y. Allelic diversities in rice starch biosynthesis lead to a diverse array of rice eating and cooking qualities[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2009, 106(51): 21760-21765. |
| [5] | Qiao W H, Chen Y T, Wang R S, Wei X, Cao L R, Zhang W X, Yang Q W. Nucleotide diversity in waxy gene and validation of single nucleotide polymorphism in relation to amylose content in chinese microcore rice germplasm[J]. Crop Science, 2012, 52(4): 1689-1697. |
| [6] | Wang Z Y, Wu Z L, Xing Y Y, Zheng F G, Guo X L, Zhang W G, Hong M M. Nucleotide sequence of rice waxy gene[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1990, 18(19): 5898. |
| [7] | Zhang C, Zhu J, Chen S, Fan X, Li Q, Lu Y, Wang M, Yu H, Yi C, Tang S, Gu M, Liu Q. Wxlv, the ancestral allele of rice waxy gene[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(8): 1157-1166. |
| [8] | Teng B, Zeng R, Wang Y, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Zhu H, Ding X, Li W, Zhang G. Detection of allelic variation at the Wx locus with single-segment substitution lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2012, 30(1): 583-595. |
| [9] | Zhang C, Yang Y, Chen S, Liu X, Zhu J, Zhou L, Lu Y, Li Q, Fan X, Tang S, Gu M, Liu Q. A rare Waxy allele coordinately improves rice eating and cooking quality and grain transparency[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(5): 889-901. |
| [10] | Zhou H, Xia D, Zhao D, Li Y, Li P, Wu B, Gao G, Zhang Q, Wang G, Xiao J, Li X, Yu S, Lian X, He Y. The origin of Wxla provides new insights into the improvement of grain quality in rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(5): 878-880. |
| [11] | Liu X, Ding Q, Wang W, Pan Y, Tan C, Qiu Y, Chen Y, Li H, Li Y, Ye N, Xu N, Wu X, Ye R, Liu J, Ma C. Targeted deletion of the first intron of the wxb allele via CRISPR/CAS9 significantly increases grain amylose content in rice[J]. Rice (New York, NY), 2022, 15(1): 1. |
| [12] | Cai X L, Wang Z Y, Xing Y Y, Zhang J L, Hong M M. Aberrant splicing of intron 1 leads to the heterogeneous 5' UTR and decreased expression of waxy gene in rice cultivars of intermediate amylose content[J]. The Plant Journal, 1998, 14(4): 459-465. |
| [13] | Sato H, Suzuki Y, Sakai M, Imbe T. Molecular characterization of wx-mq, a novel mutant gene for low-amylose content in endosperm of rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Breeding Science, 2002, 52: 131-135. |
| [14] | 陈智慧, 王芳权, 许扬, 王军, 李文奇, 范方军, 仲维功, 杨杰. 软米基因Wx-mp在部分粳稻品种资源中的分布[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2019, 20(4): 975-981. |
| Chen Z H, Wang F Q, Xu Y, Wang J, Li W Q, Fan F J, Zhong W G, Yang J. The distribution of low amylose content allele Wx-mp in japonica rice[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2019, 20(4): 975-981. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Zhu Y, Cai X L, Wang Z Y, Hong M M. An interaction between a MYC protein and an EREBP protein is involved in transcriptional regulation of the rice Wx gene[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003, 278(48): 47803-47811. |
| [16] | Wang J C, Xu H, Zhu Y, Liu Q Q, Cai X L. OsbZIP58, a basic leucine zipper transcription factor, regulates starch biosynthesis in rice endosperm[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(11): 3453-3466. |
| [17] | Bello B K, Hou Y, Zhao J, Jiao G, Wu Y, Li Z, Wang Y, Tong X, Wang W, Yuan W, Wei X, Zhang J. NF-YB1-YC12-bHLH144 complex directly activates Wx to regulate grain quality in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(7): 1222-1235. |
| [18] | Zeng D, Yan M, Wang Y, Liu X, Qian Q, Li J. Du1, encoding a novel Prp1 protein, regulates starch biosynthesis through affecting the splicing of Wxb pre-mRNAs in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 65(4): 501-509. |
| [19] | Igarashi H, Ito H, Shimada T, Kang D J, Hamada S. A novel rice dull gene, LowAC1, encodes an RNA recognition motif protein affecting Waxyb pre-mRNA splicing[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 162: 100-109. |
| [20] | Isshiki M, Matsuda Y, Takasaki A, Wong H L, Satoh H, Shimamoto K. Du3, a mRNA cap-binding protein gene, regulates amylose content in japonica rice seeds[J]. Plant Biotechnology, 2008, 25: 483-487. |
| [21] | Cai Y, Zhang W, Fu Y, Shan Z, Xu J, Wang P, Kong F, Jin J, Yan H, Ge X, Wang Y, You X, Chen J, Li X, Chen W, Chen X, Ma J, Tang X, Zhang J, Bao Y, Jiang L, Wang H, Wan J. Du13 encodes a C2H2 zinc-finger protein that regulates Wxb pre-mRNA splicing and microRNA biogenesis in rice endosperm[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20(7): 1387-1401. |
| [22] | 黄祎雯, 孙滨, 程灿, 牛付安, 周继华, 张安鹏, 涂荣剑, 李瑶, 姚瑶, 代雨婷, 谢开珍, 陈小荣, 曹黎明, 储黄伟. 对水稻种子耐储性QTL的研究[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(9): 2255-2264. |
| Huang Y Wen, Sun B, Cheng C, Niu F A, Zhou J H, Zhang A P, Tu R J, Li Y, Yao Y, Dai Y T, Xie K Z, Chen X R, Cao L M, Chu H W. QTL mapping of seed storage tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(9): 2255-2264. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Su Y, Rao Y, Hu S, Yang Y, Gao Z, Zhang G, Liu J, Hu J, Yan M, Dong G, Zhu L, Guo L, Qian Q, Zeng D. Map-based cloning proves qGC-6, a major QTL for gel consistency of japonica/indica cross, responds by Waxy in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2011, 123(5): 859-867. |
| [24] | 储黄伟, 程灿, 牛付安, 周继华, 涂荣剑, 罗忠永, 王新其, 曹黎明. 8个稻瘟病抗性基因在三系杂交粳稻亲本中的分布[J]. 上海农业学报, 2018, 34(1): 8-13. |
| Chu H W, Cheng C, Niu F A, Zhou J H, Tu R J, Luo Z Y, Wang X Q, Cao L M. Distribution of 8 rice blast-resistant genes in parents of three-line hybrid rice[J]. Acta Agricultural Shanghai, 2018, 34(1): 8-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Meng L, Li H, Zhang L, Wang J. QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations[J]. The Crop Journal, 2015, 3(3): 269-283. |
| [26] | Wang H, Zhu S, Dang X, Liu E, Hu X, Eltahawy M S, Zaid I U, Hong D. Favorable alleles mining for gelatinization temperature, gel consistency and amylose content in Oryza sativa by association mapping[J]. BMC Genetics, 2019, 20(1): 34. |
| [27] | Zhang A, Gao Y, Li Y, Ruan B, Yang S, Liu C, Zhang B, Jiang H, Fang G, Ding S, Jahan N, Xie L, Dong G, Xu Z, Gao Z, Guo L, Qian Q. Genetic analysis for cooking and eating quality of super rice and fine mapping of a novel locus qGC10 for gel consistency[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 342. |
| [28] | Huang L, Gu Z, Chen Z, Yu J, Chu R, Tan H, Zhao D, Fan X, Zhang C, Li Q, Liu Q. Improving rice eating and cooking quality by coordinated expression of the major starch synthesis-related genes, SSⅡ and Wx, in endosperm[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2021, 106(4-5): 419-432. |
| [29] | Gao Z, Zeng D, Cui X, Zhou Y, Yan M, Huang D, Li J, Qian Q. Map-based cloning of the ALK gene, which controls the gelatinization temperature of rice[J]. Science in China Series C: Life Sciences, 2003, 46(6): 661-668. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||