
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (6): 597-608.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.221205
胡佳晓1, 刘进1,2, 崔迪2, 勒思1, 周慧颖1, 韩冰2, 孟冰欣1, 余丽琴1, 韩龙植2, 马小定2,*( ), 黎毛毛1,*(
), 黎毛毛1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-13
修回日期:2023-02-14
出版日期:2023-11-10
发布日期:2023-11-14
通讯作者:
*email: maxiaoding@caas.cn;Lmm3056@163.com
作者简介:第一联系人:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
HU Jiaxiao1, LIU Jin1,2, CUI Di2, LE Si1, ZHOU Huiying1, HAN Bing2, MENG Bingxin1, YU Liqin1, HAN Longzhi2, MA Xiaoding2,*( ), LI Maomao1,*(
), LI Maomao1,*( )
)
Received:2022-12-13
Revised:2023-02-14
Online:2023-11-10
Published:2023-11-14
Contact:
*email: maxiaoding@caas.cn;Lmm3056@163.com
About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要:
【目的】 稻穗是水稻产量的主要承载者,发掘穗部性状相关的主效QTL对进一步精细定位、克隆和育种利用具有重要意义。【方法】 以粳稻日本晴为受体、东乡野生稻为供体构建的一套染色体片段置换系(chromosome segment substitution lines, CSSLs)群体为材料,在4个生态环境下进行穗部性状表型鉴定与主效QTL定位分析。【结果】 不同生态环境下CSSL群体穗部性状存在较大幅度变异,东乡野生稻染色体片段的导入显著改变背景亲本的穗部性状,具有明显的增产效应;早季、中季、晚季和海南环境下共检测到64个控制每穗颖花数和籽粒大小的QTL,其中qPL2、qSN1.2、qSN2、qFGN3、qTGW2、qTGW12.1和qSL2在3个环境下稳定表达,21个QTL在2个环境下被重复检测到,其余QTL仅在单一环境下被发现;主效QTL qSN1.1、qSN1.2、qSN2、qSN3和qSN12对每穗颖花数具有明显的影响,多个QTL聚合具有明显调控每穗颖花数的功能;主效QTL qSL2、qSL3.2、qSLW3.1、qSLW3.2、qTGW8.1和qSLW10对籽粒大小具有明显的影响。这些位点分别作用于粒长、粒宽和长宽比,相互作用、共同决定籽粒大小;同时,穗部性状QTL成簇分布于10个染色体区段,其中主效QTL簇qGNS1.1、qGNS1.3、qGNS2.1、qGNS3.1、qGNS9、qGNS10和qGNS12包含多个调控每穗颖花数及籽粒大小性状的QTL,可在不同环境下稳定表达。来自东乡野生稻的等位基因具有明显调控产量表型的功能。【结论】 研究结果不仅为东乡野生稻优异基因发掘奠定基础,也可为水稻穗部性状的分子育种提供新基因源。
胡佳晓, 刘进, 崔迪, 勒思, 周慧颖, 韩冰, 孟冰欣, 余丽琴, 韩龙植, 马小定, 黎毛毛. 利用东乡野生稻染色体片段置换系鉴定穗部性状主效QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 597-608.
HU Jiaxiao, LIU Jin, CUI Di, LE Si, ZHOU Huiying, HAN Bing, MENG Bingxin, YU Liqin, HAN Longzhi, MA Xiaoding, LI Maomao. Mapping Major QTLs for Panicle Traits Using CSSLs of Dongxiang Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 597-608.
| 性状 Trait | 环境 Environment | 日本晴 Nipponbare | 染色体置换系群体 CSSL population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值±标准差 Mean±SD Mean±Sd | 变幅Range Range | 峰度Kurtosis Skewness | 偏度Skewness Kurtosis | ||||
| 穗长 | E1 | 22.37 | 21.80±1.74 | 15.68~27.78 | −0.01 | 1.93 | |
| PL | E2 | 21.40 | 22.32±2.00 | 17.78~28.03 | 0.59 | 0.42 | |
| E3 | 21.55 | 22.29±2.03 | 16.64~26.96 | 0.00 | 0.17 | ||
| E4 | 19.68 | 19.97±1.56 | 15.07~24.94 | 0.36 | 1.10 | ||
| 颖花数 | E1 | 110.08 | 93.64±18.20 | 61.00~160.70 | 0.93 | 1.46 | |
| SN | E2 | 104.00 | 104.73±17.69 | 71.67~151.40 | 0.35 | −0.14 | |
| E3 | 75.71 | 72.90±17.54 | 41.00~158.00 | 1.63 | 1.94 | ||
| E4 | 54.90 | 58.06±14.23 | 34.93~124.47 | 1.97 | 2.44 | ||
| 实粒数 | E1 | 90.42 | 80.39±17.95 | 20.10~121.70 | −0.46 | 1.17 | |
| FGN | E2 | 84.30 | 80.03±16.83 | 22.00~119.40 | −0.58 | 1.18 | |
| E3 | 63.00 | 57.56±16.90 | 5.30~118.33 | 0.50 | 1.74 | ||
| E4 | 33.53 | 41.26±16.88 | 3.13~94.73 | 0.69 | 1.11 | ||
| 结实率 | E1 | 82.00 | 85.63±10.48 | 28.76~96.01 | −3.08 | 1.10 | |
| SF/% | E2 | 80.92 | 77.03±13.22 | 21.77~96.51 | −1.81 | 1.15 | |
| E3 | 83.21 | 78.50±12.12 | 9.23~96.64 | −2.40 | 1.90 | ||
| E4 | 61.81 | 70.10±19.48 | 5.35~96.78 | −0.93 | 0.61 | ||
| 千粒重 | E1 | 25.57 | 23.03±2.88 | 15.42~31.12 | −0.17 | −0.21 | |
| TGW/g | E2 | 25.68 | 24.48±2.04 | 15.86~28.87 | −1.12 | 2.64 | |
| E3 | 26.58 | 25.81±1.77 | 19.71~30.01 | −0.40 | 0.53 | ||
| E4 | 25.89 | 25.54±2.44 | 12.86~33.50 | −1.41 | 2.23 | ||
| 粒长 | E1 | 7.43 | 7.71±0.34 | 6.70~8.70 | 0.44 | 0.95 | |
| SL/mm | E2 | 6.93 | 7.06±0.39 | 6.27~8.82 | 1.76 | 1.22 | |
| E3 | 7.30 | 7.46±0.30 | 6.70~8.25 | 0.30 | −0.02 | ||
| E4 | 7.60 | 7.68±0.34 | 6.70~8.60 | 0.61 | 1.09 | ||
| 粒宽 | E1 | 3.35 | 3.29±0.14 | 2.70~3.55 | −0.98 | 2.01 | |
| SW/mm | E2 | 3.37 | 3.31±0.15 | 2.46~3.58 | −2.49 | 1.34 | |
| E3 | 3.00 | 3.10±0.12 | 2.80~3.50 | 0.34 | 0.38 | ||
| E4 | 3.38 | 3.27±0.12 | 2.87~3.51 | −0.86 | 1.30 | ||
| 长宽比 | E1 | 2.22 | 2.35±0.15 | 2.06~3.00 | 1.10 | 3.20 | |
| SLW | E2 | 2.06 | 2.15±0.22 | 1.87~3.55 | 1.15 | 1.97 | |
| E3 | 2.43 | 2.41±0.13 | 2.12~2.78 | 0.34 | 0.25 | ||
| E4 | 2.25 | 2.35±0.14 | 2.04~2.79 | 0.60 | 1.02 | ||
表1 亲本和CSSL群体穗部性状表型分析
Table 1. Performance of panicle traits from the parent and CSSL populations.
| 性状 Trait | 环境 Environment | 日本晴 Nipponbare | 染色体置换系群体 CSSL population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值±标准差 Mean±SD Mean±Sd | 变幅Range Range | 峰度Kurtosis Skewness | 偏度Skewness Kurtosis | ||||
| 穗长 | E1 | 22.37 | 21.80±1.74 | 15.68~27.78 | −0.01 | 1.93 | |
| PL | E2 | 21.40 | 22.32±2.00 | 17.78~28.03 | 0.59 | 0.42 | |
| E3 | 21.55 | 22.29±2.03 | 16.64~26.96 | 0.00 | 0.17 | ||
| E4 | 19.68 | 19.97±1.56 | 15.07~24.94 | 0.36 | 1.10 | ||
| 颖花数 | E1 | 110.08 | 93.64±18.20 | 61.00~160.70 | 0.93 | 1.46 | |
| SN | E2 | 104.00 | 104.73±17.69 | 71.67~151.40 | 0.35 | −0.14 | |
| E3 | 75.71 | 72.90±17.54 | 41.00~158.00 | 1.63 | 1.94 | ||
| E4 | 54.90 | 58.06±14.23 | 34.93~124.47 | 1.97 | 2.44 | ||
| 实粒数 | E1 | 90.42 | 80.39±17.95 | 20.10~121.70 | −0.46 | 1.17 | |
| FGN | E2 | 84.30 | 80.03±16.83 | 22.00~119.40 | −0.58 | 1.18 | |
| E3 | 63.00 | 57.56±16.90 | 5.30~118.33 | 0.50 | 1.74 | ||
| E4 | 33.53 | 41.26±16.88 | 3.13~94.73 | 0.69 | 1.11 | ||
| 结实率 | E1 | 82.00 | 85.63±10.48 | 28.76~96.01 | −3.08 | 1.10 | |
| SF/% | E2 | 80.92 | 77.03±13.22 | 21.77~96.51 | −1.81 | 1.15 | |
| E3 | 83.21 | 78.50±12.12 | 9.23~96.64 | −2.40 | 1.90 | ||
| E4 | 61.81 | 70.10±19.48 | 5.35~96.78 | −0.93 | 0.61 | ||
| 千粒重 | E1 | 25.57 | 23.03±2.88 | 15.42~31.12 | −0.17 | −0.21 | |
| TGW/g | E2 | 25.68 | 24.48±2.04 | 15.86~28.87 | −1.12 | 2.64 | |
| E3 | 26.58 | 25.81±1.77 | 19.71~30.01 | −0.40 | 0.53 | ||
| E4 | 25.89 | 25.54±2.44 | 12.86~33.50 | −1.41 | 2.23 | ||
| 粒长 | E1 | 7.43 | 7.71±0.34 | 6.70~8.70 | 0.44 | 0.95 | |
| SL/mm | E2 | 6.93 | 7.06±0.39 | 6.27~8.82 | 1.76 | 1.22 | |
| E3 | 7.30 | 7.46±0.30 | 6.70~8.25 | 0.30 | −0.02 | ||
| E4 | 7.60 | 7.68±0.34 | 6.70~8.60 | 0.61 | 1.09 | ||
| 粒宽 | E1 | 3.35 | 3.29±0.14 | 2.70~3.55 | −0.98 | 2.01 | |
| SW/mm | E2 | 3.37 | 3.31±0.15 | 2.46~3.58 | −2.49 | 1.34 | |
| E3 | 3.00 | 3.10±0.12 | 2.80~3.50 | 0.34 | 0.38 | ||
| E4 | 3.38 | 3.27±0.12 | 2.87~3.51 | −0.86 | 1.30 | ||
| 长宽比 | E1 | 2.22 | 2.35±0.15 | 2.06~3.00 | 1.10 | 3.20 | |
| SLW | E2 | 2.06 | 2.15±0.22 | 1.87~3.55 | 1.15 | 1.97 | |
| E3 | 2.43 | 2.41±0.13 | 2.12~2.78 | 0.34 | 0.25 | ||
| E4 | 2.25 | 2.35±0.14 | 2.04~2.79 | 0.60 | 1.02 | ||
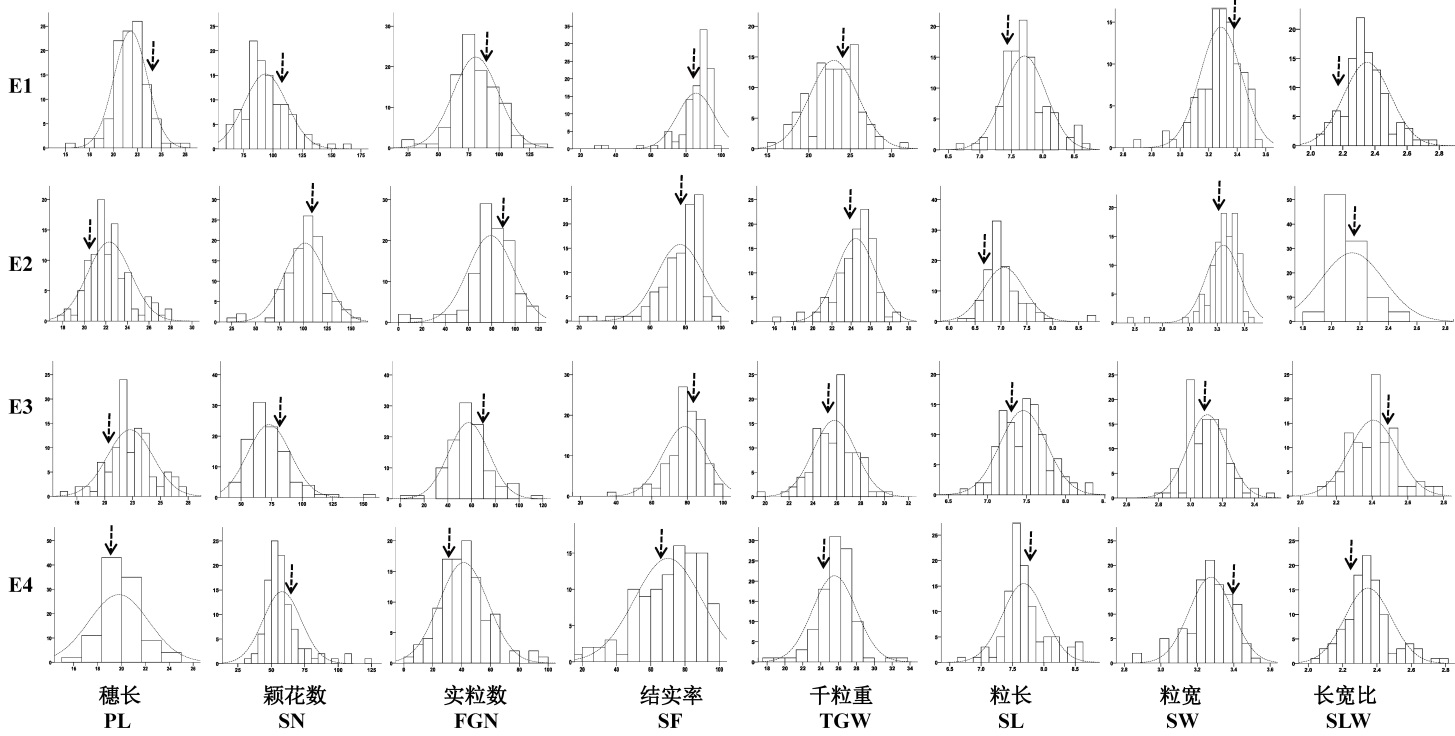
图1 不同环境下水稻CSSL群体穗部性状表型分布 E1、E2、E3和E4分别表示江西早季、中季、晚季和海南;虚线箭头表示日本晴相应性状的表型值。
Fig. 1. Identification of panicle traits at multi-environments in CSSL populations. E1, E2, E3, E4 indicate the early season, middle season, late season in Jiangxi Province and Hainan, respectively; Dashed arrows indicate the phenotypic values of Nipponbare; PL, Panicle length; SN, Spikelet number, FGN, Filled grain number per panicle; SF, Spikelet fertility; TGW, Thousand grain weight; SL, Seed length; SW, Seed width; SLW, Seed length-width ratio, respectively. The same below.
| 位点 Locus | 标记 Marker | LOD值 LOD value | 贡献率PVE /% | 加性效应Additive effect | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | ||||
| 穗长 Panicle length | |||||||||||||||
| qPL1 | DX-C1-9 | 2.63 | 9.64 | 0.66 | |||||||||||
| qPL2 | DX-C2-13 | 3.39 | 3.26 | 3.20 | 13.35 | 12.88 | 11.91 | 0.91 | 1.06 | 0.65 | |||||
| qPL5.1 | DX-C5-8 | 2.48 | 9.56 | 2.16 | |||||||||||
| qPL5.2 | 05-041 | 4.16 | 14.34 | −0.98 | |||||||||||
| qPL7 | DX-C7-2 | 3.75 | 14.19 | 1.13 | |||||||||||
| qPL8 | DX-C8-3 | 2.93 | 10.04 | −3.09 | |||||||||||
| qPL10 | DX-S10-1 | 2.78 | 10.43 | 0.93 | |||||||||||
| qPL12 | DX-C12-12 | 2.83 | 10.39 | −0.74 | |||||||||||
| 颖花数 Spikelet number | |||||||||||||||
| qSN1.1 | DX-C1-3 | 2.49 | 2.52 | 11.38 | 9.05 | 7.57 | 6.71 | ||||||||
| qSN1.2 | DX-C1-16 | 3.28 | 3.13 | 6.14 | 13.38 | 10.93 | 17.85 | −24.24 | −21.27 | −21.72 | |||||
| qSN2 | DX-C2-2 | 7.38 | 4.72 | 10.69 | 23.38 | 18.37 | 29.90 | 34.07 | 25.93 | 29.37 | |||||
| qSN3 | indel-c3-12 | 2.62 | 7.44 | −7.31 | |||||||||||
| qSN12 | DX-S12-3 | 2.97 | 5.06 | 9.14 | 12.98 | −15.88 | −19.53 | ||||||||
| 实粒数 Filled grain number | |||||||||||||||
| qFGN1.1 | DX-C1-2 | 2.10 | 3.50 | 6.96 | 11.08 | 6.01 | 8.37 | ||||||||
| qFGN1.2 | DX-C1-16 | 5.58 | 5.83 | 18.19 | |||||||||||
| qFGN2.1 | DX-C2-2 | 2.58 | 7.45 | 18.61 | |||||||||||
| qFGN2.2 | DX-S2-14 | 5.76 | 6.05 | 22.59 | |||||||||||
| qFGN3 | DX-C3-8 | 5.03 | 5.42 | 2.39 | 16.14 | 19.12 | 6.68 | −10.69 | −12.18 | −7.94 | |||||
| qFGN4 | DX-C4-12 | 2.76 | 5.57 | 9.78 | 5.83 | 20.99 | 7.33 | ||||||||
| qFGN5 | DX-C5-4 | 3.02 | 10.74 | 30.95 | |||||||||||
| qFGN6 | 06-037 | 3.03 | 2.99 | 8.19 | |||||||||||
| qFGN11 | DX-C11-8 | 14.00 | 17.84 | −54.59 | |||||||||||
| qFGN12 | DX-C12-2 | 10.89 | 12.89 | 23.54 | |||||||||||
| 结实率 Seed fertility | |||||||||||||||
| qSF1 | DX-C1-7 | 4.28 | 14.28 | −5.61 | |||||||||||
| qSF2.1 | DX-C2-1 | 2.53 | 4.42 | −10.92 | |||||||||||
| qSF2.2 | indel-c2-3 | 3.38 | 6.02 | −7.51 | |||||||||||
| qSF3.1 | indel-c3-2 | 5.64 | 19.40 | −20.64 | |||||||||||
| qSF3.2 | DX-S3-12-2 | 6.60 | 19.59 | 5.88 | |||||||||||
| qSF4 | DX-C4-12 | 3.48 | 14.17 | 8.82 | |||||||||||
| qSF5 | DX-C5-4 | 7.93 | 24.08 | 24.02 | |||||||||||
| qSF6 | 06-013 | 4.11 | 13.66 | −7.90 | |||||||||||
| qSF9.1 | DX-C9-4 | 11.83 | 25.63 | −18.78 | |||||||||||
| qSF9.2 | DX-C9-10 | 6.42 | 3.86 | 12.20 | 12.01 | −18.07 | −17.42 | ||||||||
| qSF12 | DX-C12-10 | 3.72 | 6.67 | −5.57 | |||||||||||
表2 染色体置换系定位水稻穗部性状QTL
Table 2. Putative QTL of the panicle traits in CSSL populations.
| 位点 Locus | 标记 Marker | LOD值 LOD value | 贡献率PVE /% | 加性效应Additive effect | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | ||||
| 穗长 Panicle length | |||||||||||||||
| qPL1 | DX-C1-9 | 2.63 | 9.64 | 0.66 | |||||||||||
| qPL2 | DX-C2-13 | 3.39 | 3.26 | 3.20 | 13.35 | 12.88 | 11.91 | 0.91 | 1.06 | 0.65 | |||||
| qPL5.1 | DX-C5-8 | 2.48 | 9.56 | 2.16 | |||||||||||
| qPL5.2 | 05-041 | 4.16 | 14.34 | −0.98 | |||||||||||
| qPL7 | DX-C7-2 | 3.75 | 14.19 | 1.13 | |||||||||||
| qPL8 | DX-C8-3 | 2.93 | 10.04 | −3.09 | |||||||||||
| qPL10 | DX-S10-1 | 2.78 | 10.43 | 0.93 | |||||||||||
| qPL12 | DX-C12-12 | 2.83 | 10.39 | −0.74 | |||||||||||
| 颖花数 Spikelet number | |||||||||||||||
| qSN1.1 | DX-C1-3 | 2.49 | 2.52 | 11.38 | 9.05 | 7.57 | 6.71 | ||||||||
| qSN1.2 | DX-C1-16 | 3.28 | 3.13 | 6.14 | 13.38 | 10.93 | 17.85 | −24.24 | −21.27 | −21.72 | |||||
| qSN2 | DX-C2-2 | 7.38 | 4.72 | 10.69 | 23.38 | 18.37 | 29.90 | 34.07 | 25.93 | 29.37 | |||||
| qSN3 | indel-c3-12 | 2.62 | 7.44 | −7.31 | |||||||||||
| qSN12 | DX-S12-3 | 2.97 | 5.06 | 9.14 | 12.98 | −15.88 | −19.53 | ||||||||
| 实粒数 Filled grain number | |||||||||||||||
| qFGN1.1 | DX-C1-2 | 2.10 | 3.50 | 6.96 | 11.08 | 6.01 | 8.37 | ||||||||
| qFGN1.2 | DX-C1-16 | 5.58 | 5.83 | 18.19 | |||||||||||
| qFGN2.1 | DX-C2-2 | 2.58 | 7.45 | 18.61 | |||||||||||
| qFGN2.2 | DX-S2-14 | 5.76 | 6.05 | 22.59 | |||||||||||
| qFGN3 | DX-C3-8 | 5.03 | 5.42 | 2.39 | 16.14 | 19.12 | 6.68 | −10.69 | −12.18 | −7.94 | |||||
| qFGN4 | DX-C4-12 | 2.76 | 5.57 | 9.78 | 5.83 | 20.99 | 7.33 | ||||||||
| qFGN5 | DX-C5-4 | 3.02 | 10.74 | 30.95 | |||||||||||
| qFGN6 | 06-037 | 3.03 | 2.99 | 8.19 | |||||||||||
| qFGN11 | DX-C11-8 | 14.00 | 17.84 | −54.59 | |||||||||||
| qFGN12 | DX-C12-2 | 10.89 | 12.89 | 23.54 | |||||||||||
| 结实率 Seed fertility | |||||||||||||||
| qSF1 | DX-C1-7 | 4.28 | 14.28 | −5.61 | |||||||||||
| qSF2.1 | DX-C2-1 | 2.53 | 4.42 | −10.92 | |||||||||||
| qSF2.2 | indel-c2-3 | 3.38 | 6.02 | −7.51 | |||||||||||
| qSF3.1 | indel-c3-2 | 5.64 | 19.40 | −20.64 | |||||||||||
| qSF3.2 | DX-S3-12-2 | 6.60 | 19.59 | 5.88 | |||||||||||
| qSF4 | DX-C4-12 | 3.48 | 14.17 | 8.82 | |||||||||||
| qSF5 | DX-C5-4 | 7.93 | 24.08 | 24.02 | |||||||||||
| qSF6 | 06-013 | 4.11 | 13.66 | −7.90 | |||||||||||
| qSF9.1 | DX-C9-4 | 11.83 | 25.63 | −18.78 | |||||||||||
| qSF9.2 | DX-C9-10 | 6.42 | 3.86 | 12.20 | 12.01 | −18.07 | −17.42 | ||||||||
| qSF12 | DX-C12-10 | 3.72 | 6.67 | −5.57 | |||||||||||
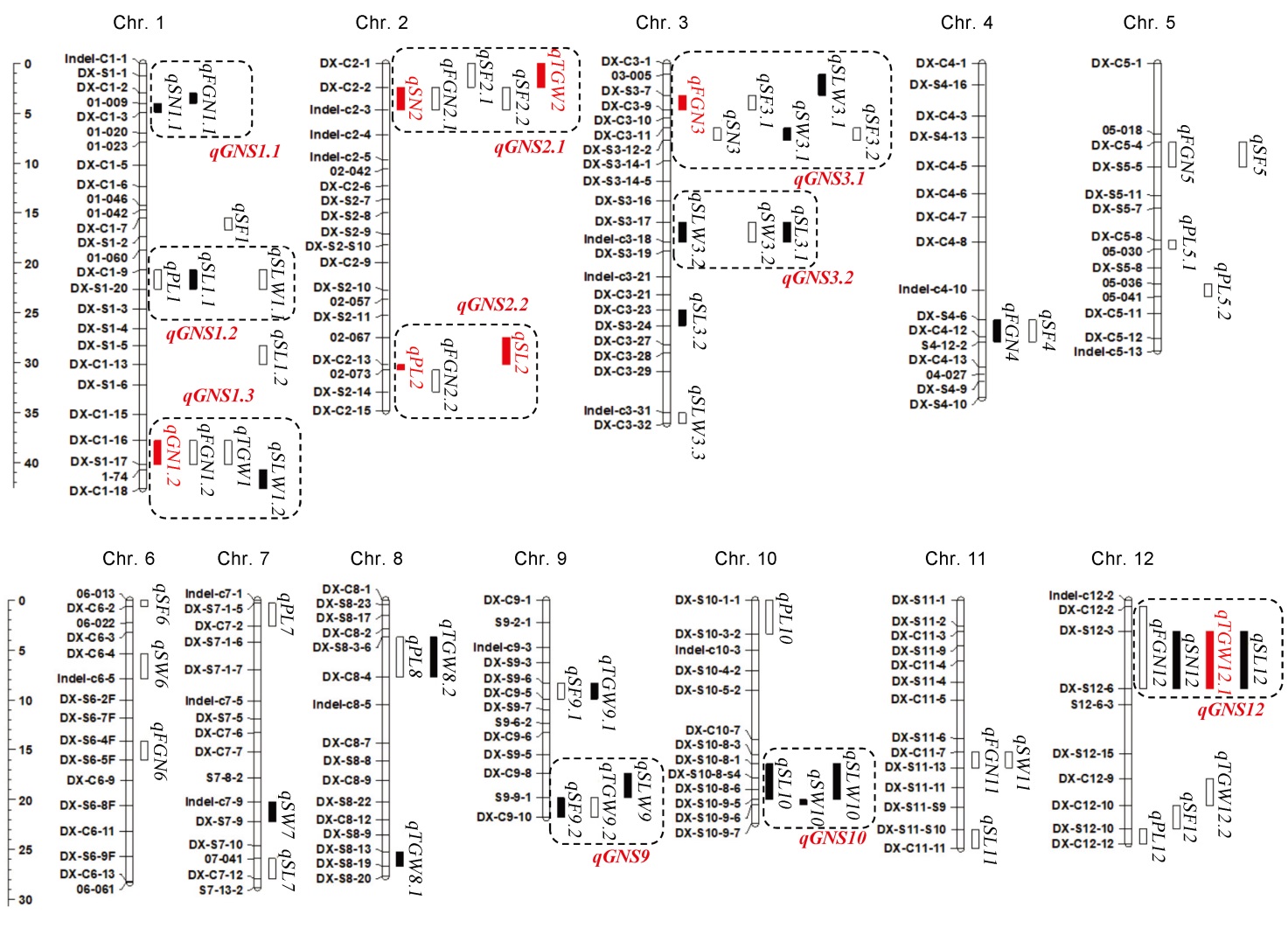
图2 水稻穗部性状QTL在染色体上的分布 白色、黑色和红色方框分别代表在单一、两个和三个以上环境中检测到的穗部性状相关的QTL。
Fig. 2. Location of QTL detected for panicle traits in genetic map. The white, black, and red boxes represent QTLs related to panicle traits detected in a single, two, and three or more environments, respectively.
| 性状 Trait | 位点 Locus | 标记 Marker | LOD值 LOD value | 贡献率PVE/% | 加性效应Additive effect | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | |||||
| 千粒重 | qTGW1 | DX-C1-16 | 2.50 | 10.37 | −2.78 | |||||||||||
| TGW | qTGW2 | 02-008 | 4.09 | 3.20 | 2.44 | 10.62 | 9.04 | 10.01 | −2.54 | −1.97 | −2.83 | |||||
| qTGW8.1 | DX-S8-14 | 2.93 | 3.05 | 7.50 | 8.65 | −1.25 | −1.13 | |||||||||
| qTGW8.2 | DX-C8-3 | 4.00 | 2.03 | 11.52 | 7.55 | −3.13 | −3.47 | |||||||||
| qTGW9.1 | DX-C9-4 | 2.90 | 2.30 | 8.15 | 8.49 | 1.34 | 1.54 | |||||||||
| qTGW9.2 | DX-C9-10 | 3.27 | 8.50 | −2.26 | ||||||||||||
| qTGW12.1 | S12-6-3 | 5.13 | 4.50 | 2.45 | 13.63 | 15.54 | 9.32 | −2.36 | −3.20 | −1.50 | ||||||
| qTGW12.2 | DX-C12-9 | 3.50 | 6.80 | −1.37 | ||||||||||||
| 粒长 | qSL1.1 | DX-S1-20 | 7.56 | 3.04 | 21.24 | 10.95 | −0.27 | −0.20 | ||||||||
| SL | qSL1.2 | DX-S1-5 | 3.32 | 13.59 | −0.19 | |||||||||||
| qSL2 | 02-067 | 3.11 | 2.73 | 2.64 | 7.45 | 11.29 | 7.84 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.14 | ||||||
| qSL3.1 | DX-S3-17 | 3.80 | 6.13 | 10.39 | 15.60 | 0.28 | 0.37 | |||||||||
| qSL3.2 | DX-C3-23 | 8.06 | 6.26 | 24.28 | 16.00 | 0.26 | 0.25 | |||||||||
| qSL7 | 07-041 | 2.56 | 10.62 | 0.09 | ||||||||||||
| qSL10 | DX-C10-8 | 3.44 | 2.87 | 8.24 | 8.44 | 0.19 | 0.16 | |||||||||
| qSL11 | DX-S11-10 | 3.96 | 10.84 | −0.20 | ||||||||||||
| qSL12 | S12-6-3 | 2.80 | 3.30 | 7.06 | 6.50 | 0.30 | 0.28 | |||||||||
| 粒宽 | qSW3.1 | DX-S3-14-1 | 3.31 | 2.49 | 13.22 | 9.73 | 0.10 | |||||||||
| SW | qSW3.2 | DX-S3-17 | 2.51 | 7.84 | −0.11 | |||||||||||
| qSW6 | DX-C6-4 | 2.69 | 8.82 | |||||||||||||
| qSW7 | indel-c7-9 | 2.33 | 2.74 | 8.93 | 8.02 | −0.08 | −0.07 | |||||||||
| qSW10 | DX-C10-10 | 2.70 | 2.74 | 9.84 | 11.31 | −0.09 | −0.07 | |||||||||
| qSW11 | DX-S11-13 | 2.78 | 11.47 | 0.09 | ||||||||||||
| 长宽比 | qSLW1.1 | DX-S1-20 | 4.51 | 15.66 | −0.09 | |||||||||||
| SLW | qSLW1.2 | DX-C1-18 | 2.71 | 2.62 | 11.20 | 9.20 | 0.16 | 0.14 | ||||||||
| qSLW3.1 | DX-C3-1 | 4.52 | 2.78 | 16.73 | 8.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | |||||||||
| qSLW3.2 | DX-S3-17 | 3.68 | 4.81 | 12.54 | 14.70 | −0.09 | 0.20 | |||||||||
| qSLW3.3 | DX-C3-32 | 3.07 | 10.88 | 0.10 | ||||||||||||
| qSLW9 | DX-C9-8 | 3.69 | 2.16 | 13.98 | 6.98 | −0.20 | 0.07 | |||||||||
| qSLW10 | DX-C10-8 | 3.84 | 2.39 | 11.48 | 8.36 | 0.12 | 0.06 | |||||||||
表3 水稻籽粒大小相关性状QTL分析
Table 3. QTL mapping for seed size related traits in rice.
| 性状 Trait | 位点 Locus | 标记 Marker | LOD值 LOD value | 贡献率PVE/% | 加性效应Additive effect | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | |||||
| 千粒重 | qTGW1 | DX-C1-16 | 2.50 | 10.37 | −2.78 | |||||||||||
| TGW | qTGW2 | 02-008 | 4.09 | 3.20 | 2.44 | 10.62 | 9.04 | 10.01 | −2.54 | −1.97 | −2.83 | |||||
| qTGW8.1 | DX-S8-14 | 2.93 | 3.05 | 7.50 | 8.65 | −1.25 | −1.13 | |||||||||
| qTGW8.2 | DX-C8-3 | 4.00 | 2.03 | 11.52 | 7.55 | −3.13 | −3.47 | |||||||||
| qTGW9.1 | DX-C9-4 | 2.90 | 2.30 | 8.15 | 8.49 | 1.34 | 1.54 | |||||||||
| qTGW9.2 | DX-C9-10 | 3.27 | 8.50 | −2.26 | ||||||||||||
| qTGW12.1 | S12-6-3 | 5.13 | 4.50 | 2.45 | 13.63 | 15.54 | 9.32 | −2.36 | −3.20 | −1.50 | ||||||
| qTGW12.2 | DX-C12-9 | 3.50 | 6.80 | −1.37 | ||||||||||||
| 粒长 | qSL1.1 | DX-S1-20 | 7.56 | 3.04 | 21.24 | 10.95 | −0.27 | −0.20 | ||||||||
| SL | qSL1.2 | DX-S1-5 | 3.32 | 13.59 | −0.19 | |||||||||||
| qSL2 | 02-067 | 3.11 | 2.73 | 2.64 | 7.45 | 11.29 | 7.84 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.14 | ||||||
| qSL3.1 | DX-S3-17 | 3.80 | 6.13 | 10.39 | 15.60 | 0.28 | 0.37 | |||||||||
| qSL3.2 | DX-C3-23 | 8.06 | 6.26 | 24.28 | 16.00 | 0.26 | 0.25 | |||||||||
| qSL7 | 07-041 | 2.56 | 10.62 | 0.09 | ||||||||||||
| qSL10 | DX-C10-8 | 3.44 | 2.87 | 8.24 | 8.44 | 0.19 | 0.16 | |||||||||
| qSL11 | DX-S11-10 | 3.96 | 10.84 | −0.20 | ||||||||||||
| qSL12 | S12-6-3 | 2.80 | 3.30 | 7.06 | 6.50 | 0.30 | 0.28 | |||||||||
| 粒宽 | qSW3.1 | DX-S3-14-1 | 3.31 | 2.49 | 13.22 | 9.73 | 0.10 | |||||||||
| SW | qSW3.2 | DX-S3-17 | 2.51 | 7.84 | −0.11 | |||||||||||
| qSW6 | DX-C6-4 | 2.69 | 8.82 | |||||||||||||
| qSW7 | indel-c7-9 | 2.33 | 2.74 | 8.93 | 8.02 | −0.08 | −0.07 | |||||||||
| qSW10 | DX-C10-10 | 2.70 | 2.74 | 9.84 | 11.31 | −0.09 | −0.07 | |||||||||
| qSW11 | DX-S11-13 | 2.78 | 11.47 | 0.09 | ||||||||||||
| 长宽比 | qSLW1.1 | DX-S1-20 | 4.51 | 15.66 | −0.09 | |||||||||||
| SLW | qSLW1.2 | DX-C1-18 | 2.71 | 2.62 | 11.20 | 9.20 | 0.16 | 0.14 | ||||||||
| qSLW3.1 | DX-C3-1 | 4.52 | 2.78 | 16.73 | 8.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | |||||||||
| qSLW3.2 | DX-S3-17 | 3.68 | 4.81 | 12.54 | 14.70 | −0.09 | 0.20 | |||||||||
| qSLW3.3 | DX-C3-32 | 3.07 | 10.88 | 0.10 | ||||||||||||
| qSLW9 | DX-C9-8 | 3.69 | 2.16 | 13.98 | 6.98 | −0.20 | 0.07 | |||||||||
| qSLW10 | DX-C10-8 | 3.84 | 2.39 | 11.48 | 8.36 | 0.12 | 0.06 | |||||||||
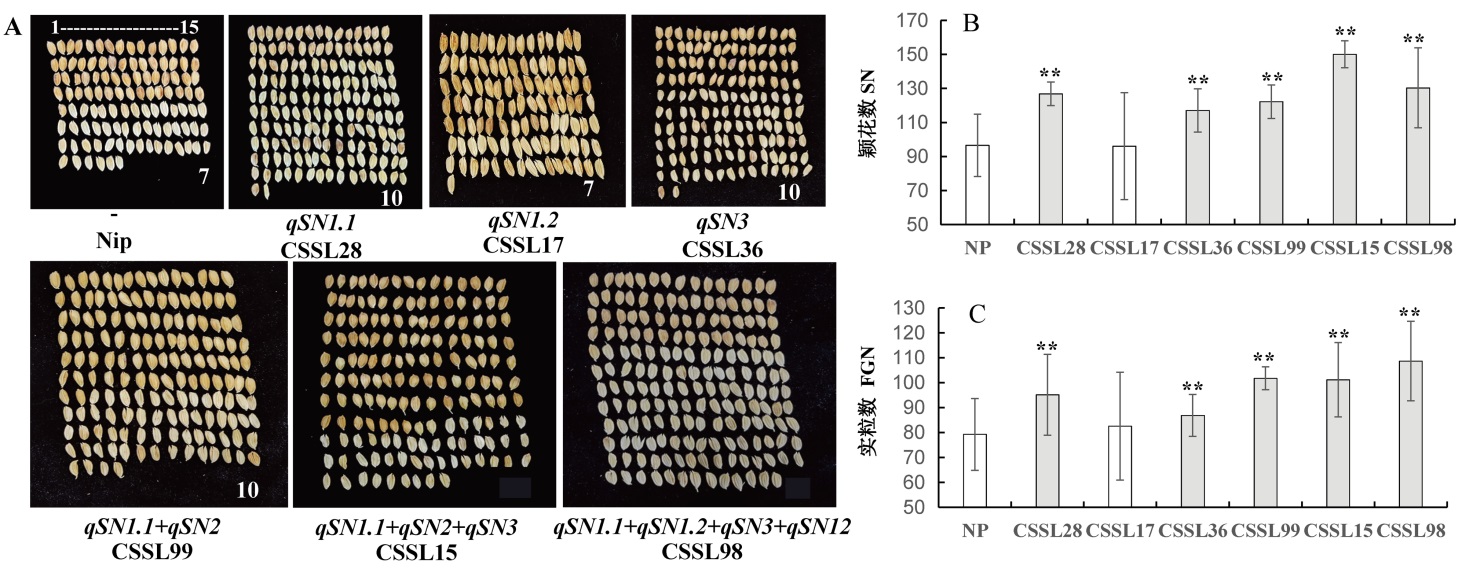
图3 利用CSSL群体验证分析水稻穗粒数主效QTL A图为含有主效QTL的株系每穗颖花数表型;B和C为含有主效QTL的株系每穗颖花数和实粒数,灰色柱和**表示与对照(CK)存在显著差异,白色柱表示与对照无显著差异,对照品种为日本晴。
Fig. 3. Verification and pyramiding of major QTLs of grain number by CSSL populations. A, Phenotype of grain number for these lines containing the major QTLs; B and C, Spikelet and actual grain numbers in lines containing major QTL. The gray bar and ** indicates a significant difference compared to the control NP, and the white column indicates no significant difference with the control, respectively.
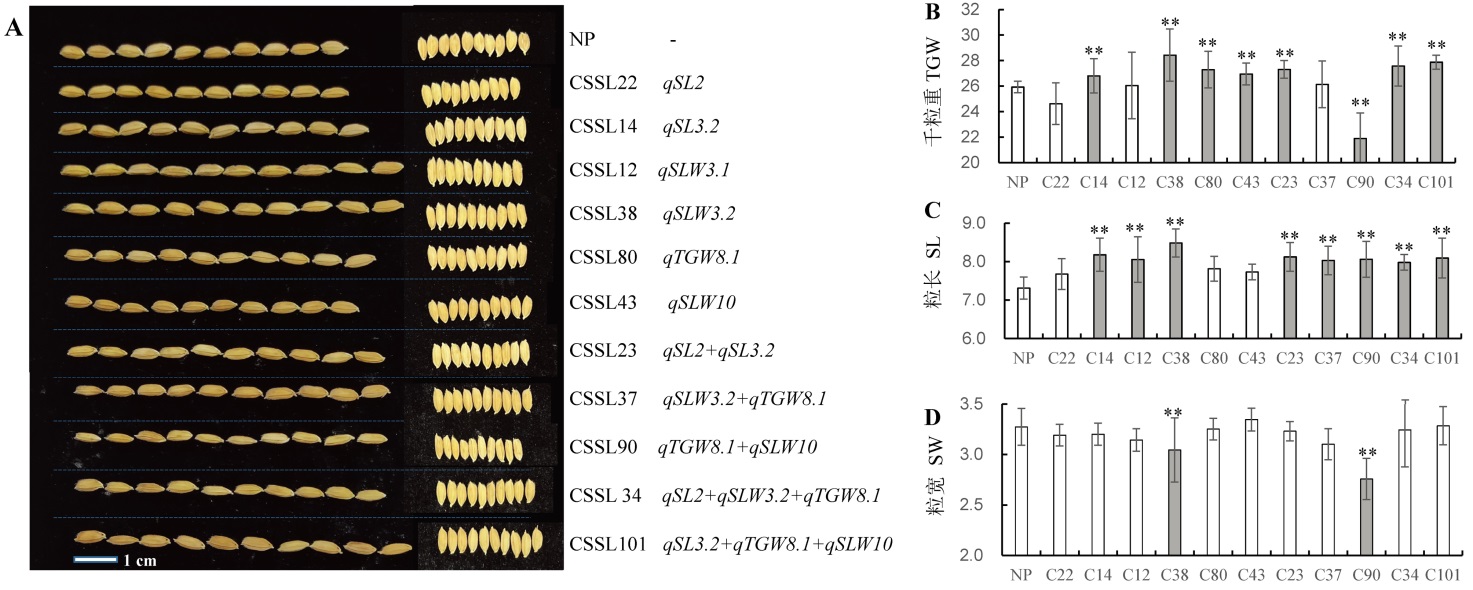
图4 水稻籽粒大小主效QTL验证分析 A图为主效QTL粒长、粒宽;B、C和D分别为CSSL群体家系千粒重、粒长和粒宽,A图中CSSLn在图B~D中缩写为Cn,灰色柱和**表示与日本晴(NP)存在显著差异,白色柱表示与CK无显著差异.
Fig. 4. Verification and pyramiding of major QTLs of seed size in rice. A represent grain length and grain width of CSSL lines carrying dominant QTL; B, C and D refer to thousand-grain weight, grain length and grain width of CSSL populations. In figure B-D, the CSSLn was abbreviated as Cn, gray bars and ** indicates significant difference with Nipponbare(NP), and then white column indicates no significant difference with Nipponbare(NP), respectively.
| 染色体 Chr. | 主效QTL簇 Major QTL cluster | 区域 Interval | 多效性性状 Pleiotropic trait | 多效性QTL位点 Pleiotropic QTL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | qGNS1.1 | DX-C1-2-DX-C1-3 | SN, FGN | qSN1.1, qFGN1.1 |
| qGNS1.2 | DX-C1-9-DX-S1-20 | PL, SL, SLW | qPL1, qSL1.1, qSLW1.1 | |
| qGNS1.3 | DX-C1-16-DX-C1-18 | SN, FGN, TGW, SLW | qSN1.2, qFGN1.2, qTGW1, qSLW1.2 | |
| 2 | qGNS2.1* | DX-C2-1-indel-C2-3 | SN, FGN, SF, TGW | qSN2, qFGN2.1, qSF2.1, qSF2.2, qTGW2 |
| qGNS2.2 | 20-67-DX-S2-14 | PL, FGN, SL | qPL2, qFGN2.2, qSL2 | |
| 3 | qGNS3.1* | DX-C3-1-DX-C3-11 | SF, SN, FGN, SLW, SL | qSF3.1, qSN3, qFGN3, qSLW3.1, qSW3.1 |
| qGNS3.2 | DX-S3-17-Indel-C3-18 | SLW, SW, SL | qSLW3.2, qSW3, qSL3.2 | |
| 9 | qGNS9 | DX-C9-8-DX-C9-10 | TGW, SF, SLW | qTGW9.1, qSF9.2, qSLW9 |
| 10 | qGNS10 | DX-S10-8-1-DX-S10-9-5 | SL, SW, SLW | qSL10, qSW10, qSLW10 |
| 12 | qGNS12* | DX-C12-2-DX-S12-6 | SN, FGN, TGW, SL | qSN12, qTGW12.1, qSL12, qFGN12 |
表4 水稻穗部性状多效性区域分析
Table 4. Panicle and seed traits QTL hotspot and pleiotropic region in rice.
| 染色体 Chr. | 主效QTL簇 Major QTL cluster | 区域 Interval | 多效性性状 Pleiotropic trait | 多效性QTL位点 Pleiotropic QTL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | qGNS1.1 | DX-C1-2-DX-C1-3 | SN, FGN | qSN1.1, qFGN1.1 |
| qGNS1.2 | DX-C1-9-DX-S1-20 | PL, SL, SLW | qPL1, qSL1.1, qSLW1.1 | |
| qGNS1.3 | DX-C1-16-DX-C1-18 | SN, FGN, TGW, SLW | qSN1.2, qFGN1.2, qTGW1, qSLW1.2 | |
| 2 | qGNS2.1* | DX-C2-1-indel-C2-3 | SN, FGN, SF, TGW | qSN2, qFGN2.1, qSF2.1, qSF2.2, qTGW2 |
| qGNS2.2 | 20-67-DX-S2-14 | PL, FGN, SL | qPL2, qFGN2.2, qSL2 | |
| 3 | qGNS3.1* | DX-C3-1-DX-C3-11 | SF, SN, FGN, SLW, SL | qSF3.1, qSN3, qFGN3, qSLW3.1, qSW3.1 |
| qGNS3.2 | DX-S3-17-Indel-C3-18 | SLW, SW, SL | qSLW3.2, qSW3, qSL3.2 | |
| 9 | qGNS9 | DX-C9-8-DX-C9-10 | TGW, SF, SLW | qTGW9.1, qSF9.2, qSLW9 |
| 10 | qGNS10 | DX-S10-8-1-DX-S10-9-5 | SL, SW, SLW | qSL10, qSW10, qSLW10 |
| 12 | qGNS12* | DX-C12-2-DX-S12-6 | SN, FGN, TGW, SL | qSN12, qTGW12.1, qSL12, qFGN12 |
| [1] | 樊叶杨, 王凯, 庄杰云, 程式华. 水稻产量性状QTL 的克隆研究及育种应用进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2010, 16(6): 1-5. |
| Fan Y Y, Wang K, Zhuang J Y, Cheng S H. Progress on cloning and utilization of QTL for yield traits in rice[J]. China Rice, 2010, 16(6): 1-5. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 沈希宏, 曹立勇, 陈深广, 占小登, 吴伟明, 程式华. 超级杂交稻协优9308重组自交系群体的穗部性状QTL分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(4): 354-362. |
| Shen X H, Cao L Y, Chen S G, Zhan X D, Wu W M, Cheng S H. Dissection of QTLs for panicle traits in recombinant inbred lines derived from super hybrid rice, Xieyou 9308[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(4): 354-362. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 张应洲, 罗荣剑, 圣忠华, 焦桂爱, 唐绍清, 胡培松, 魏祥进. 日本晴/中嘉早17重组自交系产量性状QTL定位[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(19): 3640-3651. |
| Zhang Y Z, Luo R J, Sheng Z H, Jiao G A, Tang S Q, Hu P S, Wei X J. QTL mapping of yield associated traits of Nipponbare×Zhongjiazao 17 RIL population[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(19): 3640-3651. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 姜树坤, 王嘉宇, 姜辉, 洛育, 孙世臣, 张喜娟, 白良明, 陈温福, 张凤鸣, 徐正进. 粳稻穗部结构性状的QTL分析[J]. 植物生理学报, 2013, 49(12): 1347-1354. |
| Jiang S K, Wang J Y, Jiang H, Luo Y, Sun S C, Zhang X J, Bai L M, Chen W F, Zhang F M, Xu Z J. Dissection of QTLs for panicle structure Traits in rice (Oryza sativa L. spp. japonica)[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2013, 49(12): 1347-1354. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 占小登, 于萍, 林泽川, 陈代波, 沈希宏, 张迎信, 付君林, 程式华, 曹立勇. 利用大粒籼/小粒粳重组自交系定位水稻生育期及产量相关性状QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(6): 570-580. |
| Zhan X D, Yu P, Lin Z C, Chen D B, Shen X H, Zhang Y X, Fu J L, Cheng S H, Cao L Y. QTL mapping of heading date and yield related traits in rice using a recombination inbred lines (RILs) population derived from BG1/XLJ[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(6): 570-580. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 程式华, 曹立勇, 庄杰云, 吴伟明. 关于超级稻品种培育的资源和基因利用问题[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(3): 223-228. |
| Cheng S H, Cao L Y, Zhuang J Y, Wu W M. Discussion on germplasm and gene utilization in breeding of super rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(3): 223-228. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 黄勇, 胡勇, 傅向东, 邢永忠. 水稻产量性状的功能基因及其应用[J]. 生命科学, 2016, 28(10): 1147-1155. |
| Huang Y, Hu Y, Fu X D, Xing Y Z. Functional genes for grain yield related traits and their application in rice breeding[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2016, 28(10): 1147-1155. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 姚晓云, 李清, 刘进, 姜树坤, 杨生龙, 王嘉宇, 徐正进. 不同环境下水稻株高和穗长的QTL分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(3): 407-414. |
| Yao X Y, Li Q, Liu J, Jiang S K, Yang S L, Wang J Y, Xu Z J. Dissection of QTLs for plant height and panicle length traits in rice under different environment[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(3): 407-414. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 吴比, 韩忠民, 李志新, 邢永忠. 普通野生稻中增产相关QTL的发掘[J]. 遗传, 2012, 34(2): 215-222. |
| Wu B, Han Z M, Li Z X, Xing Y Z. Discovery of QTLs increasing yield related traits in common wild rice[J]. Hereditas, 2012, 34(2): 215-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 周勇, 陶亚军, 姚锐, 李畅, 谭文琛, 裔传灯, 龚志云, 梁国华. 利用染色体片段代换系定位水稻叶片形态性状QTL[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(11): 1650-1657. |
| Zhou Y, Tao Y J, Yao R, Li C, Tan W C, Yi C D, Gong Z Y, Liang G H. QTL mapping for leaf morphological traits of rice using chromosome segment substitution lines[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43(11): 1650-1657. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 许睿, 张莉珍, 谢先芝, 王艳艳, 黄婧芬, 郑晓明, 张丽芳, 程云连, 郑崇珂, 乔卫华, 杨庆文. 基于染色体置换系的普通野生稻耐盐性QTL定位[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2020, 21(2): 442-451. |
| Xu R, Zhang L Z, Xie X Z, Wang Y Y, Huang J F, Zheng X M, Zhang L F, Cheng Y L, Zheng C K, Qiao W H, Yang Q W. QTL mapping revealed salt tolerance traits from Oryza rufipogon using chromosome segment substitution lines[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resource, 2020, 21(2): 442-451. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 钟代彬, 罗利军, 应存山. 野生稻有利基因转移研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2000, 14(2): 103-106. |
| Zhong D B, Luo L J, Ying C S. Advances on transferring elite gene from wild rice species into cultivated rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2000, 14(2): 103-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 杨庆文, 张万霞, 贺丹霞, 陈大洲, 戴陆元, 陈成斌, 黄坤德. 中国野生稻原生境保护方法研究[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2003, 4(1): 63-67. |
| Yang Q W, Zhang W X, He D X, Chen D Z, Dai L Y, Chen C B, Huang K D. Studies on in-situ conservation methods of wild rice in China[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2003, 4(1): 63-67 (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Fan J J, Hua H, Luo Z W, Zhang Q, Chen M J, Gong J Y, Wei X, Huang Z H, Huang X H, Wang Q. Whole-genome sequencing of 117 chromosome segment substitution lines for genetic analyses of complex traits in rice[J]. Rice, 2022, 15: 5 |
| [15] | 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 赵凌, 张亚东, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 于新, 王才林. 利用染色体片段置换系群体检测水稻叶片形态QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27: 26-34. |
| Zhou L H, Zhao C F, Zhao L, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Yu X, Wang C L. QTL detection for leaf morphology of rice using chromosome segment substitution lines[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27: 26-34 (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 丁膺宾, 张莉珍, 许睿, 王艳艳, 郑晓明, 张丽芳, 程云连, 吴凡, 杨庆文, 乔卫华, 兰进好. 基于染色体片段置换系的野生稻粒长QTL qGL12的精细定位[J]. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(18): 3435-3444. |
| Ding Y B, Zhang L Z, Xu R, Wang Y Y, Zheng X M, Zhang L F, Cheng Y L, Wu F, Yang Q W, Qiao W H, Lan J H. Fine mapping of grain length associated QTL, qGL12in wild rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a chromosome segment substitution line[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(18): 3435-3444. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Ma X D, Han B, Tang J H, Zhang J N, Cui D, Geng L Y, Zhou H Y, Li M M, Han L Z. Construction of chromosome segment substitution lines of Dongxiang common wild rice (Oryza rufifipogon Griff) in the background of the japonica rice cultivar Nipponbare (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Physiology Biochemistry, 2019, 144: 274-282. |
| [18] | Wang J K, Li H H, Zhang L Y.QTL ICI Mapping V4.0[2014]. http://www.isbreeding.net. |
| [19] | McCouch S R. Gene nomenclature system for rice[J]. Rice, 2008, 1: 72-84. |
| [20] | 赵芳明, 张桂权, 曾瑞珍, 杨正林, 凌英华, 桑贤春, 何光华. 利用单片段代换系研究水稻产量相关性状QTL加性及上位性效应[J]. 作物报, 2012, 38(11): 2007-2014. |
| Zhao F M, Zhang G Q, Zeng R Z, Yang Z L, Ling Y H, Sang X C, He G H. Epistatic and additive effects of QTLs for yield-related traits using single segment substitution lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(11): 2007-2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 佘东, 刘强明, 李大露, 梁银凤, 刘二宝, 党小景, 洪德林. 利用II-32B/A7444组合CSSL群体定位水稻7个穗部性状QTL[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(5): 658-668. |
| She D, Liu Q M, Li D L, Liang Y F, Liu E B, Dang X J, Hong D L. Mapping QTLs for seven panicle traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using chromosome segment substitution lines derived from II-32B/A7444[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43(5): 658-668. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Guo L B, Ye G Y. Use of major quantitative trait loci to improve grain yield of rice[J]. Rice Science, 2014, 21(2): 65-82. |
| [23] | 吴亚辉, 陶星星, 肖武名, 郭涛, 刘永柱, 王慧, 陈志强. 水稻穗部性状的QTL分析[J]. 作物学报, 2014, 40(2): 214-221. |
| Wu Y H, Tao X X, Xiao W M, Guo T, Liu Y Z, Wang H, Chen Z Q. Dissection of QTLs for panicle traits in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(2): 214-221. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 任春元, 范淑秀, 刘进, 朱琳, 杨绮文, 刘丹, 马殿荣, 王嘉宇. 不同年份水稻抽穗期和穗部性状QTL分析[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2017, 48(1): 78-83. |
| Ren C Y, Fan S X, Liu J, Zhu L, Yang Q W, Liu D, Ma D R, Wang J Y. QTL analysis for heading stage and panicle traits at different years in rice[J]. Journal Shenyang Agricultural University, 2017, 48(1): 78-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 赵建国, 蒋开锋, 杨莉, 杨乾华, 万先齐, 曹应江, 游书梅, 罗婧, 张涛, 郑家奎. 水稻产量相关性状QTL定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(4): 344-352. |
| Zhao J G, Jiang K F, Yang L, Yang Q H, Wan X Q, Cao Y J, You S M, Luo J, Zhang T, Zheng J K. QTL mapping for yield related components in a RIL population of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(4): 344-352. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 胡大维, 圣忠华, 陈炜, 李潜龙, 魏祥进, 邵高能, 焦桂爱, 王建龙, 胡培松, 谢黎虹, 唐绍清. 超级稻品种中嘉早17高产相关性状的QTL定位[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(10): 1434-1447. |
| Hu D W, Sheng Z H, Chen W, Li Q L, Wei X J, Shao G N, Jiao G A, Wang J L, Hu P S, Xie L H, Tang S Q. Identification of QTLs associated with high yield of super rice variety Zhongjiazao 17[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43(10): 1434-1447. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 刘进, 黎毛毛, 姚晓云, 王棋, 李慧, 王嘉宇. 水稻穗部性状QTL分析[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2018, 40(3): 435-443. |
| Liu J, Li M M, Yao X Y, Wang Q, Li H, Wang J Y. Mapping of QTLs of panicle and seed traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2018, 40(3): 435-443. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 韩保林, 顾朝剑, 张洪凯, 廖泳祥, 彭永彬, 张红宇, 徐培洲, 吴先军. 水稻穗部性状的QTL定位及上位性分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2017, 15(6): 2218- 2227. |
| Han B L, Gu C J, Zhang H K, Liao Y X, Peng Y B, Zhang H Y, Xu P Z, Wu X J. QTL mapping and epistasis analysis for panicle traits in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2017, 15 (6): 2218- 2227. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Liu J, Yu L Q, Ma X D, Zhou H Y, Cui D, Hu J X, Le S, Han B, Chen W, Han L Z, Li M M. Identification of the major QTL cluster qGNPS4.1 for grain number and panicle structure in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Breeding, 2022, 141: 223-235. |
| [30] | Kiyoaki K, Yuji H. Development and characterization of chromosome segment substitution lines derived from backcross between japonica donor rice cultivar Yukihikari and japonica recipient cultivar Kirara 397[J]. Breeding Science, 2021, 71: 283-290. |
| [31] | Zhu J Y, Zhou Y, Liu Y H, Wang Z D, Tang Z X, Yi C D, Tang S Z, Gu M H, Liang G H. Fine mapping of a major QTL controlling panicle number in rice[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2011, 27(2): 171-180. |
| [32] | Yang W F, Liang J Y, Hao Q W, Luan X, Tan Q Y, Lin S W, Zhu H T, Liu G F, Liu Z P, Wang S K, Zhang G Q. Fine mapping of two grain chalkiness QTLs sensitive to high temperature in rice[J]. Rice, 2021, 14: 33. |
| [33] | 孙妍, 苏龙, 乔卫华, 郑晓明, 齐兰, 丁膺宾, 许睿, 张丽芳, 程云连, 兰进好, 杨庆文. 基于染色体片段置换系的野生稻粒宽QTL-qGW8.1的精细定位[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2018, 19(1): 135-142. |
| Sun Y, Su L, Qiao W H, Zheng X M, Qi L, Ding Y B, Xu R, Zhang L F, Cheng Y L, Lan J H, Yang Q W. Fine mapping of a wild rice grain width QTL-qGW8.1 using a chromosome segment substitution line[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2018, 19(1): 135-142. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 黄涛, 王燕宁, 钟奇, 程琴, 杨朦朦, 王鹏, 吴光亮, 黄诗颖, 李才敬, 余剑峰, 贺浩华, 边建民. 利用染色体片段置换系群体定位和分析水稻粒重和粒型QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 159-170. |
| Huang T, Wang Y N, Zhong Q, Cheng Q, Yang M M, Wang P, Wu G L, Huang S Y, Li C J, Yu J F, He H H, Bian J M. Mapping and analysis of QTLs for rice grain weight and grain shape using chromosome segment substitution line population[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 159-170. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 向思茜, 李儒香, 徐光益, 邓岢莉, 余金琎, 李苗苗, 杨正林, 凌英华, 桑贤春, 何光华, 赵芳明. 基于水稻长大粒染色体片段代换系Z66的粒型QTL的鉴定及其聚合分析[J]. 作物学报, 2023, 49(3): 731-743. |
| Xiang S Q, Li R X, Xu G Y, Deng K L, Yu J J, Li M M, Yang Z L, Ling Y H, Sang X C, He G H, Zhao F M. Identification and pyramid analysis of QTLs for grain size based on rice long large-grain chromosome segment substitution line Z66[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 731-743. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 杨梯丰, 董景芳, 赵均良, 周炼, 杨武, 马雅美, 王健, 陈洛, 陈建松, 吴伟, 李雯慧, 刘斌, 张少红. 基于单片段代换系的水稻芽期耐冷QTL定位和聚合[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2022, 22(6): 1726-1736. |
| Yang T F, Dong J F, Zhao J L, Zhou L, Yang W, Ma Y M, Wang J, Chen L, Chen J S, Wu W, Li W H, Liu B, Zhang S H. Identification and pyramiding of QTLs for cold tolerance at the bud bursting stage by use of single segment substitution lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2022, 22(6): 1726-1736. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 王小雷, 李炜星, 曾博虹, 孙晓棠, 欧阳林娟, 陈小荣, 贺浩华, 朱昌兰. 基于染色体片段置换系对水稻粒形及千粒重QTL检测与稳定性分析[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(10): 1517-1525. |
| Wang X L, Li W X, Zeng B H, Sun X T, Ou-Yang L J, Chen X R, He H H, Zhu C L. QTL detection and stability analysis of rice grain shape and thousand-grain weight based on chromosome segment substitution lines[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(10): 1517-1525. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | Yuan H, Gao P, Hu X L, Yuan M, Xu Z Y, Jin M Y, Song W C, Zhan S J, Zhu X B, Tu B, Li T, Wang Y P, Ma B T, Qin P, Chen W L, Li S G. Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of qGSN5, a novel quantitative trait locus coordinating grain size and grain number in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2022, 135: 51-64. |
| [39] | Cao L Y, Wu J L, Fan Y Y, Cheng S H, Zhuang J Y. QTL analysis for heading date and yield traits using recombinant inbred lines of indica rice grown in different cropping seasons[J]. Plant Breeding, 2010, 129(6): 676-682. |
| [40] | Yao X Y, Wang J Y, Liu J, Wang W, Yang S L, Zhang Y, Xu Z J. Comparison and analysis of QTLs for grain and hull thickness related traits in two recombinant inbred line populations (RILs) in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2016, 15(11): 2437-2450. |
| [41] | 罗兰, 雷丽霞, 刘进, 张瑞华, 金桂秀, 崔迪, 黎毛毛, 马小定, 赵正武, 韩龙植. 利用东乡普通野生稻染色体片段置换系定位产量相关性状QTL[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(7): 1391-1401. |
| Luo L, Lei L X, Liu J, Zhang R H, Jin G X, Cui D, Li M M, Ma X D, Zhao Z W, Han L Z. Mapping QTLs for yield-related traits using chromosome segment substitution lines of Dongxiang common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) and Nipponbare (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2021, 47(7): 1391-1401. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 姚晓云, 陈春莲, 熊运华, 黄永萍, 彭志勤, 刘进, 尹建华. 水稻加工和外观品质性状QTL鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 507-517. |
| [2] | 黄涛, 王燕宁, 钟奇, 程琴, 杨朦朦, 王鹏, 吴光亮, 黄诗颖, 李才敬, 余剑峰, 贺浩华, 边建民. 利用染色体片段置换系群体定位和分析水稻粒重和粒型QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 159-170. |
| [3] | 吴婷, 李霞, 黄得润, 黄凤林, 肖宇龙, 胡标林. 应用东乡野生稻回交重组自交系分析水稻耐低氮产量相关性状QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 499-511. |
| [4] | 刘进, 姚晓云, 刘丹, 余丽琴, 李慧, 王棋, 王嘉宇, 黎毛毛. 不同生态环境下水稻穗部性状QTL鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 124-134. |
| [5] | 林晗, 徐江民, 胡瑚倩, 郑安, 徐婉璐, 漏平, 王跃星, 曾大力, 饶玉春. 水稻耐金属离子胁迫的QTL分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(1): 23-34. |
| [6] | 胡标林, 黄得润, 肖叶青, 何强生, 万勇, 樊叶杨. 应用东乡野生稻回交重组自交系群体分析糙米矿质含量QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(1): 43-50. |
| [7] | 张杰, 郑蕾娜, 蔡跃, 尤小满, 孔飞, 汪国湘, 燕海刚, 金洁, 王亮, 张文伟, 江玲. 稻米淀粉RVA谱特征值与直链淀粉、蛋白含量的相关性及QTL定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(1): 31-39. |
| [8] | 胡雅杰, 钱海军, 曹伟伟, 邢志鹏, 张洪程, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 郭保卫. 机插方式和密度对不同穗型水稻品种产量及其构成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(5): 493-506. |
| [9] | 左示敏1,2,康厚祥2,李前前1 ,陈宗祥1 ,张亚芳1,刘文德2,王国梁2,陈红旗3, * ,潘学彪1,* . 引进水稻种质穗部性状相关基因全基因组关联分析及利用探讨[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(6): 649-658. |
| [10] | 王兰,黄李超,代丽萍,杨窑龙,徐杰,冷语佳,张光恒,胡江,朱丽,高振宇,董国军,郭龙彪,钱前,曾大力*. 利用日本晴/9311重组自交系群体定位水稻成熟期叶形相关性状QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(6): 589-597. |
| [11] | 占小登,于萍,林泽川,陈代波,沈希宏,张迎信,付君林,程式华* ,曹立勇*. 利用大粒籼/小粒粳重组自交系定位水稻生育期及产量相关性状QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(6): 570-580. |
| [12] | 王智权1,2 ,江玲1,尹长斌3,王晓玲2,雷建国2,肖宇龙2 ,刘喜1 ,刘世家1 ,陈亮明1 ,余传元2 ,万建民1,3,*. 水稻产量相关农艺性状杂种优势位点的定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(6): 569-576. |
| [13] | 周丽慧,赵春芳,赵凌,张亚东,朱镇,陈涛,赵庆勇,姚姝,于新,王才林*. 利用染色体片段置换系群体检测水稻叶片形态QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(1): 26-34. |
| [14] | 林静 ,朱镇 ,方先文 ,王艳平 ,张所兵 ,王才林*. 利用染色体片段置换系定位水稻赖氨酸含量的QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(6): 737-740. |
| [15] | 林静,朱文银,张亚东,朱镇,赵凌,陈涛,赵庆勇,周丽慧,方先文,王艳平,王才林. 利用染色体片段置换系定位水稻芽期耐冷性QTL |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||