
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 23-34.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7075
林晗1, 徐江民1, 胡瑚倩1, 郑安1, 徐婉璐1, 漏平1, 王跃星2, 曾大力2,*( ), 饶玉春1,2,*(
), 饶玉春1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-06-20
修回日期:2017-08-21
出版日期:2018-01-10
发布日期:2018-01-10
通讯作者:
曾大力,饶玉春
作者简介:共同第一作者:林晗, 徐江民, 胡瑚倩;
基金资助:
Han LIN1, Jiangmin XU1, Huqian HU1, An ZHENG1, Wanlu XU1, Ping LOU1, Yuexing WANG2, Dali ZENG2,*( ), Yuchun RAO1,2,*(
), Yuchun RAO1,2,*( )
)
Received:2017-06-20
Revised:2017-08-21
Online:2018-01-10
Published:2018-01-10
Contact:
Dali ZENG, Yuchun RAO
About author:These authors contributed equally to this work:LIN Han, XU Jiangmin, HU Huqian;
摘要:
【目的】 本研究旨在筛选与水稻苗期耐不同金属离子连锁的分子遗传标记,为探讨水稻耐不同金属离子胁迫的遗传研究提供参考。【方法】 以典型籼粳交(春江06/台中本地1号)双单倍体(DH)群体为材料,系统考查该群体及其双亲耐4种金属离子(Fe2+、Cd2+、Al3+、Na+)胁迫的情况,利用业已构建并完善的该群体加密的分子连锁图谱,对耐这4种金属离子胁迫的QTL进行检测分析。另外,利用实时定量PCR技术检测处理前后相关基因的表达变化情况。【结果】 发现耐各种金属离子胁迫的QTL共8个,分别位于水稻第1、2、4、6、9、10和11染色体上,其中Fe2+处理后检测到的QTL贡献率最大,达到24.47%(阈值为7.78),位于第1染色体上RM1297–RM1061,同时对该区间与耐胁迫相关基因的表达分析发现这些基因在处理前和处理后表达水平存在不同程度的差异;Cd2+处理后检测到1个QTL,位于第1染色体上;Al3+处理后检测到QTL共5个,分别位于第2、4、6、10、11染色体上;Na+处理后检测到QTL有1个,位于第9染色体上。【结论】 根据不同金属离子胁迫处理后DH群体的表型差异进行QTL分析,发现耐各种金属离子胁迫的QTL共8个,并初步定位于各染色体的遗传标记区间,这为精细定位并克隆相应QTL,进而探明水稻耐金属离子胁迫QTL的分子调控机制奠定了基础。
中图分类号:
林晗, 徐江民, 胡瑚倩, 郑安, 徐婉璐, 漏平, 王跃星, 曾大力, 饶玉春. 水稻耐金属离子胁迫的QTL分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(1): 23-34.
Han LIN, Jiangmin XU, Huqian HU, An ZHENG, Wanlu XU, Ping LOU, Yuexing WANG, Dali ZENG, Yuchun RAO. Identifying of QTLs for Resistance to Metal Irons Stress in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(1): 23-34.
| 分子标记 Marker | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward prime(5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse prime(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| OsActin1 | TGGCATCTCTCAGCACATTCC | TGCACAATGGATGGGTCAGA |
| LOC_Os01g50030 | AGTGAAAACAGCTGGGCATG | GCATTCTTGTGGTGACCGTT |
| LOC_Os01g50060 | TGTGGGGTTAGCTCTTGGAG | TTTCACCGTTCAGCACCTTG |
| LOC_Os01g50110 | TTTGGCGATCAGTTCTGTGC | TGCTCGTCGTTGATCAGAGA |
| LOC_Os01g50360 | GGCTCTGAATGGGTTTTGGG | ATGTAAGGCAGTCAGGACCC |
| LOC_Os01g50720 | GTGAACAATGCGCTCGAGAG | AAATGTGTCATGCCCTGCTC |
| LOC_Os01g50820 | ATGCTCATCTACTTCCCGCA | CACTCCCGGCTGTAGTACTC |
| LOC_Os01g50940 | CCGCCGGAAGATTTCATGAG | GCCTTGACCACCTCCTTCTT |
| LOC_Os01g51260 | GCTCACGGTGTCACTCAATC | AGAAAGATTGGCTGGTGGGA |
| LOC_Os01g51430 | CTGGGCATGAGAAGTTTCGG | CCAAACAAGAGCAGCCACAT |
| LOC_Os01g52110 | CTTGCGAGAAATGGAGGAGC | CTTGCACTTCTGGCACTTGT |
| LOC_Os01g52160 | TCGCTTTCCATCTAGAGCCA | CATACGGCGTGATATCCCCT |
| LOC_Os01g52450 | TGCTGCTGGGATATATGGCA | CTCCATCCACAGCAATCACG |
表1 实时荧光定量PCR的引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences of real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR.
| 分子标记 Marker | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward prime(5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse prime(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| OsActin1 | TGGCATCTCTCAGCACATTCC | TGCACAATGGATGGGTCAGA |
| LOC_Os01g50030 | AGTGAAAACAGCTGGGCATG | GCATTCTTGTGGTGACCGTT |
| LOC_Os01g50060 | TGTGGGGTTAGCTCTTGGAG | TTTCACCGTTCAGCACCTTG |
| LOC_Os01g50110 | TTTGGCGATCAGTTCTGTGC | TGCTCGTCGTTGATCAGAGA |
| LOC_Os01g50360 | GGCTCTGAATGGGTTTTGGG | ATGTAAGGCAGTCAGGACCC |
| LOC_Os01g50720 | GTGAACAATGCGCTCGAGAG | AAATGTGTCATGCCCTGCTC |
| LOC_Os01g50820 | ATGCTCATCTACTTCCCGCA | CACTCCCGGCTGTAGTACTC |
| LOC_Os01g50940 | CCGCCGGAAGATTTCATGAG | GCCTTGACCACCTCCTTCTT |
| LOC_Os01g51260 | GCTCACGGTGTCACTCAATC | AGAAAGATTGGCTGGTGGGA |
| LOC_Os01g51430 | CTGGGCATGAGAAGTTTCGG | CCAAACAAGAGCAGCCACAT |
| LOC_Os01g52110 | CTTGCGAGAAATGGAGGAGC | CTTGCACTTCTGGCACTTGT |
| LOC_Os01g52160 | TCGCTTTCCATCTAGAGCCA | CATACGGCGTGATATCCCCT |
| LOC_Os01g52450 | TGCTGCTGGGATATATGGCA | CTCCATCCACAGCAATCACG |
| 性状 Trait | 阈值 Threshold value | 区间 Interval | 染色体 Chr. | 贡献率 Phenotypic variations explained/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 亚铁胁迫2 d后平均最长根长 | 7.78 | RM1297 | –RM1061 | 1 | 24.47 |
| The average longest root length after 2 d of ferrous treatment | |||||
| 亚铁胁迫4 d后平均最长根长 | 7.78 | RM1297 | –RM1061 | 1 | 23.01 |
| The average longest root length after 4 d of ferrous treatment | |||||
| 镉胁迫2 d后平均最长根长 | 7.96 | RM3411 | –RM212 | 1 | 6.40 |
| The average longest root length after 2 d of cadmium treatment | |||||
| 铝胁迫根平均伸长量 | 7.69 | SSIII-1 | –RM3306 | 4 | 11.11 |
| The average root elongation after aluminum treatment | RM1370 | –SBE1 | 6 | 9.29 | |
| 铝胁迫根相对伸长率 | 7.69 | RM324 | –RM341 | 2 | 11.66 |
| Relative root elongation rate after aluminum treatment | RM1083 | –SSII-1 | 10 | 8.68 | |
| RM286 | –RM1812 | 11 | 8.84 | ||
| 钠胁迫叶片枯死率Withered leaf rate after sodium treatment | 7.71 | RM1026 | –RM205 | 9 | 12.21 |
表2 DH群体中水稻萌发期耐金属离子胁迫QTL定位
Table 2 Location of QTLs related to tolerance to metal ions at the rice germination stage in the DH population.
| 性状 Trait | 阈值 Threshold value | 区间 Interval | 染色体 Chr. | 贡献率 Phenotypic variations explained/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 亚铁胁迫2 d后平均最长根长 | 7.78 | RM1297 | –RM1061 | 1 | 24.47 |
| The average longest root length after 2 d of ferrous treatment | |||||
| 亚铁胁迫4 d后平均最长根长 | 7.78 | RM1297 | –RM1061 | 1 | 23.01 |
| The average longest root length after 4 d of ferrous treatment | |||||
| 镉胁迫2 d后平均最长根长 | 7.96 | RM3411 | –RM212 | 1 | 6.40 |
| The average longest root length after 2 d of cadmium treatment | |||||
| 铝胁迫根平均伸长量 | 7.69 | SSIII-1 | –RM3306 | 4 | 11.11 |
| The average root elongation after aluminum treatment | RM1370 | –SBE1 | 6 | 9.29 | |
| 铝胁迫根相对伸长率 | 7.69 | RM324 | –RM341 | 2 | 11.66 |
| Relative root elongation rate after aluminum treatment | RM1083 | –SSII-1 | 10 | 8.68 | |
| RM286 | –RM1812 | 11 | 8.84 | ||
| 钠胁迫叶片枯死率Withered leaf rate after sodium treatment | 7.71 | RM1026 | –RM205 | 9 | 12.21 |
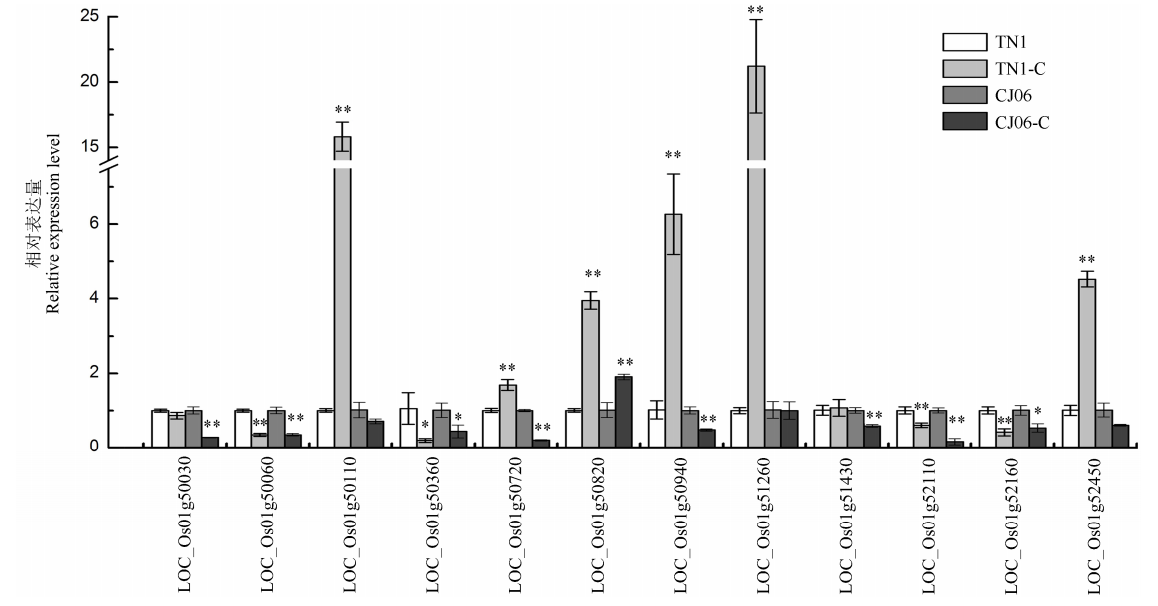
图4 耐铁相关基因的表达情况分析 TN1-C和春江06-C代表1.75×103 mg/L铁离子处理。*,**分别表示铁离子处理与对照间差异达0.05和0.01显著水平。
Fig. 4. Expression analysis of Fe2+ tolerance genes. TN1-C and CJ06-C represent 1.75×103 mg/L iron treatment. *, ** represent significant difference between the treatment and the control at the 0.05 and 0.01 level, respectively.
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因 Gene | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|
| 甲基转移酶 Methyltransferase | ||
| 29610 | LOC_Os01g50480 | SAM依赖性羧基甲基转移酶 SAM dependent carboxyl methyltransferase |
| 29597 | LOC_Os01g50610 | SAM依赖性羧基甲基转移酶 SAM dependent carboxyl methyltransferase |
| 50898 | LOC_Os01g50030 | 磷酸乙醇胺N-甲基转移酶 Phosphoethanolamine N-methyltransferase |
| 结构域蛋白 Domain containing protein | ||
| 50218 | LOC_Os01g50940 | 螺旋-环-螺旋DNA结合结构域蛋白 Helix-loop-helix DNA-binding domain containing protein |
| 50214 | LOC_Os01g51140 | 螺旋-环-螺旋DNA结合结构域蛋白 Helix-loop-helix DNA-binding domain containing protein |
| 29628 | LOC_Os01g50360 | NAC结构域蛋白 NAC domain containing protein |
| 50236 | LOC_Os01g50900 | Cupin结构域蛋白 Cupin domain containing protein |
| 50239 | LOC_Os01g51010 | 未知功能结构域292蛋白 DUF292 domain containing protein |
| 49652 | LOC_Os01g51990 | AN1锌指结构域蛋白 AN1-like zinc finger domain containing protein |
| 16764 | LOC_Os01g52410 | MYB类DNA结合结构域蛋白 MYB-like DNA-binding domain containing protein |
| 49619 | LOC_Os01g52160 | 重金属相关蛋白结构域 Heavy metal-associated domain containing protein |
| 转录因子 Transcription factor | ||
| 29592 | LOC_Os01g50720 | MYB转录因子家族 MYB family transcription factor |
| 50207 | LOC_Os01g51260 | MYB转录因子家族 MYB family transcription factor |
| 49627 | LOC_Os01g52090 | 转录因子样蛋白 Transcription factor like protein |
| 1822 | LOC_Os01g51610 | 转录因子 Transcription factor |
| 1976 | LOC_Os01g50110 | MYB转录因子 MYB transcription factor |
| 1805 | LOC_Os01g51690 | WRKY转录因子 WRKY transcription factor |
| 转运蛋白 Transporter | ||
| 49616 | LOC_Os01g52130 | 硫酸盐转运蛋白 Sulfate transporter |
| 29598 | LOC_Os01g50616 | 磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白 Phosphatidylinositol transfer |
| 29637 | LOC_Os01g50060 | ACC脱氨酶 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase |
| 29639 | LOC_Os01g50080 | MDR类ABC运输蛋白 MDR-like ABC transporter |
| 29641 | LOC_Os01g50100 | ABC运输蛋白,ATP结合蛋白 ABC transporter, ATP-binding protein |
| 2459 | LOC_Os01g50820 | 高亲和性硝酸盐转运蛋白 High affinity nitrate transporters |
| 蛋白家族 Family protein | ||
| 29590 | LOC_Os01g50700 | 脱水蛋白家族 Dehydrin family protein |
| 28943 | LOC_Os01g51400 | 富亮氨酸重复蛋白家族 Leucine rich repeat family protein |
| 锌指蛋白 Zinc finger protein | ||
| 28911 | LOC_Os01g51710 | 锌指结构域蛋白 Zinc knuckle domain containing protein |
| 29595 | LOC_Os01g50750 | C3HC4型锌指结构域蛋白质 Zinc finger, C3HC4 type domain containing protein |
| 49623 | LOC_Os01g52030 | 锌指蛋白A20和AN1域包含胁迫相关蛋白Zinc finger A20 and AN1 domain-containing stress-associated protein |
| 49639 | LOC_Os01g52110 | 环锌指蛋白 Ring zinc finger protein |
| 酶 Enzyme | ||
| 16778 | LOC_Os01g52450 | 己糖激酶 Hexokinase |
| 49650 | LOC_Os01g51860 | 紫黄质脱环氧化酶 Violaxanthin de-epoxidase |
| 通道蛋白 Channel protein | ||
| 49625 | LOC_Os01g52070 | 钾通道AKT1 potassium channel AKT1 |
表3 水稻第1染色体中预测的耐铁相关基因
Table 3 The predicted genes involved in resistance to Fe toxicity on rice chromosome 1.
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因 Gene | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|
| 甲基转移酶 Methyltransferase | ||
| 29610 | LOC_Os01g50480 | SAM依赖性羧基甲基转移酶 SAM dependent carboxyl methyltransferase |
| 29597 | LOC_Os01g50610 | SAM依赖性羧基甲基转移酶 SAM dependent carboxyl methyltransferase |
| 50898 | LOC_Os01g50030 | 磷酸乙醇胺N-甲基转移酶 Phosphoethanolamine N-methyltransferase |
| 结构域蛋白 Domain containing protein | ||
| 50218 | LOC_Os01g50940 | 螺旋-环-螺旋DNA结合结构域蛋白 Helix-loop-helix DNA-binding domain containing protein |
| 50214 | LOC_Os01g51140 | 螺旋-环-螺旋DNA结合结构域蛋白 Helix-loop-helix DNA-binding domain containing protein |
| 29628 | LOC_Os01g50360 | NAC结构域蛋白 NAC domain containing protein |
| 50236 | LOC_Os01g50900 | Cupin结构域蛋白 Cupin domain containing protein |
| 50239 | LOC_Os01g51010 | 未知功能结构域292蛋白 DUF292 domain containing protein |
| 49652 | LOC_Os01g51990 | AN1锌指结构域蛋白 AN1-like zinc finger domain containing protein |
| 16764 | LOC_Os01g52410 | MYB类DNA结合结构域蛋白 MYB-like DNA-binding domain containing protein |
| 49619 | LOC_Os01g52160 | 重金属相关蛋白结构域 Heavy metal-associated domain containing protein |
| 转录因子 Transcription factor | ||
| 29592 | LOC_Os01g50720 | MYB转录因子家族 MYB family transcription factor |
| 50207 | LOC_Os01g51260 | MYB转录因子家族 MYB family transcription factor |
| 49627 | LOC_Os01g52090 | 转录因子样蛋白 Transcription factor like protein |
| 1822 | LOC_Os01g51610 | 转录因子 Transcription factor |
| 1976 | LOC_Os01g50110 | MYB转录因子 MYB transcription factor |
| 1805 | LOC_Os01g51690 | WRKY转录因子 WRKY transcription factor |
| 转运蛋白 Transporter | ||
| 49616 | LOC_Os01g52130 | 硫酸盐转运蛋白 Sulfate transporter |
| 29598 | LOC_Os01g50616 | 磷脂酰肌醇转移蛋白 Phosphatidylinositol transfer |
| 29637 | LOC_Os01g50060 | ACC脱氨酶 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase |
| 29639 | LOC_Os01g50080 | MDR类ABC运输蛋白 MDR-like ABC transporter |
| 29641 | LOC_Os01g50100 | ABC运输蛋白,ATP结合蛋白 ABC transporter, ATP-binding protein |
| 2459 | LOC_Os01g50820 | 高亲和性硝酸盐转运蛋白 High affinity nitrate transporters |
| 蛋白家族 Family protein | ||
| 29590 | LOC_Os01g50700 | 脱水蛋白家族 Dehydrin family protein |
| 28943 | LOC_Os01g51400 | 富亮氨酸重复蛋白家族 Leucine rich repeat family protein |
| 锌指蛋白 Zinc finger protein | ||
| 28911 | LOC_Os01g51710 | 锌指结构域蛋白 Zinc knuckle domain containing protein |
| 29595 | LOC_Os01g50750 | C3HC4型锌指结构域蛋白质 Zinc finger, C3HC4 type domain containing protein |
| 49623 | LOC_Os01g52030 | 锌指蛋白A20和AN1域包含胁迫相关蛋白Zinc finger A20 and AN1 domain-containing stress-associated protein |
| 49639 | LOC_Os01g52110 | 环锌指蛋白 Ring zinc finger protein |
| 酶 Enzyme | ||
| 16778 | LOC_Os01g52450 | 己糖激酶 Hexokinase |
| 49650 | LOC_Os01g51860 | 紫黄质脱环氧化酶 Violaxanthin de-epoxidase |
| 通道蛋白 Channel protein | ||
| 49625 | LOC_Os01g52070 | 钾通道AKT1 potassium channel AKT1 |
| [1] | Zhang H,Zhang J,Yan J,Gou F,Mao Y,Tang G,Botella J R,Zhu J K.Short tandem target mimic rice lines uncover functions of miRNAs in regulating important agronomic traits.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2017,114(20):5277-5282. |
| [2] | Zeng D,Tian Z,Rao Y,Dong G,Yang Y,Huang L,Leng Y,Xu J,Sun C,Zhang G,Hu J,Zhu L,Gao Z,Hu X,Guo L,Xiong G,Wang Y,Li J,Qian Q.Rational design of high-yield and superior-quality rice. Nat Plants,2017,3: 17031. |
| [3] | 张赓.还原性铁、锰对水稻生长影响及其在冷浸田中毒害的消减措施研究.武汉: 华中农业大学,2013. |
| Zhang G.Effects of Fe2+ and Mn2+ on rice growth and the abatement measures in logging water soil. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University,2013. () | |
| [4] | 陈慧茹.土壤重金属暴露对水稻和玉米体内重金属分布的影响.合肥: 安徽大学,2015. |
| Chen H R.The Influence on distribution of heavy meatals in rice and maize with exposure of soil heavy meatals. Hefei: Anhui University,2015. () | |
| [5] | 王恒.吉林省土壤—水稻系统环境质量分析评估及重金属复合污染研究.北京:中国科学院研究生院,2014. |
| Wang H.Soil quality and heavy metals contamination in soil-rice system in Jilin Province. Beijing: Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2014. () | |
| [6] | 吴迪,杨秀珍,李存雄,周超,秦樊鑫.贵州典型铅锌矿区水稻土壤和水稻中重金属含量及健康风险评价.农业环境科学学报,2013,32(10):1992-1998. |
| Wu D,Yang X Z,Li C X,Zhou C,Qin F X.Concentrations and health risk assessments of heavy metals in soil and rice in Zinc-lead mining area in Guizhou Province, China.J Agro-Environ Sci,2013,32(10):1992-1998. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 袁玲花,徐加宽,严士敏,韩妍,赵江宁,王余龙,董桂春,杨连新.土壤铜胁迫对不同籼型水稻品种产量和品质的影响.农业环境科学学报,2008,27(2):435-441. |
| Yuan L H,Xu J K,Yan S M,Han Y,Zhao J N,Wang Y L,Dong G C,Yang L X.Effects of soil Cu stress on grain yield and quality of Indica rice cultivars.J Agro-Environ Sci,2008,27(2):435-441. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 曹方彬.水稻重金属积累的品种与环境效应及调控技术研究.杭州: 浙江大学,2014. |
| Cao F B.Cultivar and environmental effects and regulation of heavy metal accumulation in rice. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University,2014. () | |
| [9] | 卢志红,朱美英,石庆华,潘晓华,徐丰华,邱俊.硫硅配施对铜胁迫下水稻幼苗生长及其吸收累积铜的影响.江西农业大学学报,2013,35(6):1134-1139. |
| Lu Z H,Zhu M Y,Shi Q H,Pan X H,Xu F H,Qiu J.Effect of sulfur and silicon fertilizer on growth and absorption of copper in rice seedling under copper stress.Acta Agric Univ Jiangxi,2013,35(6):1134-1139. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 饶玉春,郑婷婷,马伯军,钱前,曾大力.微量元素铁、锰、铜对水稻生长的影响及缺素防治.中国稻米,2012,18(4):31-35. |
| Rao Y C,Zheng T T,Ma B J,Qian Q,Zeng D L.Effects of trace elements iron, manganese and copper on rice growth and prevention and control of nutrient deficiency.China Rice,2012,18(4):31-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Wu L B,Mohamad Y S,Gregorio G,Mathias M,Becker M.Genetic and physiological analysis of tolerance to acute iron toxicity in rice.Rice,2014,7: 8. |
| [12] | 骆旭添.水稻苗期耐镉胁迫的QTL定位及其与环境互作效应分析.福州: 福建农林大学,2007. |
| Luo X T.QTL mapping for seeding Cd tolerance in rice(Oryza sativa L.) and analysis of QTL×environment interaction. Fuzhou: Fujian Agricultural and forestry University,2005. () | |
| [13] | Ueno D,Koyama E,Kono I,Jian M.Identification of a novel major quantitative trait locus controlling distribution of Cd between roots and shoots in rice. Plant Cell Physiol,2009,50(12):2223-2233. |
| [14] | Ueno D,Yamaji N,Kono I,Huang C F,Ando T,Yano M,Ma J F.Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2010,107(38):16500-16505. |
| [15] | 井文,章文华.水稻耐盐基因定位与克隆及品种耐盐性分子标记辅助选择改良研究进展.中国水稻科学,2017,31(2):111-123. |
| Jing W,Zhang W.Research progress on gene mapping and cloning for salt tolerance and variety improvement for salt tolerance by molecular marker-assisted selection in rice.Chin J Rice Sci,2017,31(2):111-123. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Ren Z,Gao J,Li L,Cai X,Huang W,Chao D,Zhu M,Wang Z,Luan S,Lin H.A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter.Nat Genet,2005,37(10):1141-1146. |
| [17] | Thomson M J,de Ocampo M,Egdane J,Rahman M A,Sajise A G,Adorada D L,Tumimbang-Raiz E,Blumwald E,Seraj Z I,Singh R K,Gregorio G B,Ismail A M. Characterizing the Saltol quantitative trait locus for salinity tolerance in rice.Rice,2010,3(2):148-160. |
| [18] | Huang C F,Yamaji N,Mitani N,Yano A M,Nagamura B Y.A bacterial-type ABC transporter is involved in aluminum tolerance in rice.Plant Cell,2009,21(2):655-667. |
| [19] | Yamaji N,Huang C F,Nagao S,Yano S,Sato Y,Nagamura Y.A zinc finger transcription factor ART1 regulates multiple genes implicated in aluminum tolerance in rice.Plant Cell,2009,21(10):3339-3349. |
| [20] | Yokosho K,Yamaji N,Fujii-Kashino M,Ma J F.Retrotransposon-mediated aluminum tolerance through enhanced expression of the citrate transporterOsFRDL4. Plant Physiol,2016,172(4):2327-2336. |
| [21] | Li J Y,Liu J,Dong D,Jia X, McCouch S R, Kochian L V. Natural variation underlies alterations in Nramp aluminum transporter (NRAT1) expression and function that play a key role in rice aluminum tolerance.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2014,111(17):6503-6508. |
| [22] | Huang C F,Yamaji N,Chen Z C,Ma J F.A tonoplast-localized half-size ABC transporter is required for internal detoxification of aluminum in rice.Plant J,2012,69(5):857-867. |
| [23] | 饶玉春,杨窑龙,李晓静,马伯军,曾大力.水稻萌发期耐Cu2+胁迫的QTL定位.浙江师范大学学报: 自然科学版,2013,36(2):198-204. |
| Rao Y C,Yang Y L,Li X J,Ma B J,Zeng D L.QTL analysis on copper-resistant at germination stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Zhejiang Normal University: Nat Sci,2013,36(2):198-204. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Zeng F,Wu X,Qiu B,Wu F,Jiang L,Zhang G.Physiological and proteomic alterations in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings under hexavalent chromium stress. Planta,2014,240(2):291-308. |
| [25] | Li C H,Wang G,Zhao J L,Zhang L Q,Ai L F,Han Y F,Sun D Y,Zhang S W,Sun Y.The receptor-like kinaseSIT1 mediates salt sensitivity by activating MAPK3/6 and regulating ethylene homeostasis in rice. Plant Cell,2014,26(6):2538-2553. |
| [26] | Livak K J,Schmittgen T D.Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method.Methods,2001,25: 402-408. |
| [27] | Holmgren G G S,Meyer M W,Cahney R L,Daniels R B. Cadmium, lead, zinc, copper and nickel in agricultural soils of the United States of America.J Environ Qual,1993,22: 335-348. |
| [28] | Xu J K,Yang L X,Wang Z Q,Wang Y L.Toxicity of copper rice growth and accumulation of copper in rice grain in copper contaminated soil.Chemosphere,2006,62(4):602-607. |
| [29] | Dufey I,Hiel M P,Hakizimana P,Draye X,Lutts S,Koné B,Dramé K N,Konaté K A,Sie M,Bertin P.Multienvironment quantitative trait loci mapping and consistency across environments of resistance mechanisms to ferrous iron toxicity in rice.Crop Sci,2012,52(2):539-550. |
| [30] | 叶红霞,李梅,庄杰云,沈圣泉.水稻幼苗对多浓度Fe2+胁迫的QTL联合检测.分子植物育种,2007,5(1):105-109. |
| Ye H X,Li M,Zhuang J Y,Shen S Q.Analysis of gene effects of tolerance to high Fe2+ stress at seedling stage in rice.Mol Plant Breed,2007,5(1):105-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 陈志德.水稻不同品种耐镉性鉴定及耐镉胁迫相关性状的QTL定位.南京: 南京农业大学,2010. |
| Chen Z D.Mapping of cadmium tolerance and resistance to cadmium stress related traits in different rice varieties. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University,2010. () | |
| [32] | 孙勇,臧金萍,王韵,朱苓华.利用回交导入系群体发掘水稻种质资源中的有利耐盐QTL.作物学报,2007,33(10):1611-1617. |
| Sun Y,Zang J P,Wang Y,Zhu L H.Mining favorable salt-tolerant QTL from rice germplasm using a backcrossig introgression line population.Acta Agrono Sin,2007,33(10):1611-1617. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 汪斌,兰涛,吴为人.盐胁迫下水稻苗期Na+含量的QTL定位.中国水稻科学,2007,21(6):585-590. |
| Wang B,Lan T,Wu W R.Mapping of QTLs for content in rice seedlings under salt stress.Chin J Rice Sci,2007,21(6):585-590. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 褚绍尉,王林,刘桂富,刘向东,卢永根,傅雪琳.广东高州普通野生稻耐铝性及其QTL定位.华北农学报,2013,28(3):12-18. |
| Chu S W,Wang L,Liu G F,Liu X D,Lu Y G,Fu X L.Aluminum tolerance identification and QTL mapping inOryza rufipogon indigenous to Gaozhou. Acta Agric Boreali-Sin,2013,28(3):12-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 沈圣泉,庄杰云,舒小丽,包劲松,夏英武.水稻幼苗耐Al3+胁迫的QTL定位分析.作物学报,2006,32(4):479-483. |
| Shen S Q,Zhuang J Y,Shu X L,Bao J S,Xia Y W.Analysis of QTLs mapping of tolerance to high Al3+ stress at seedling stage in rice.Acta Agron Sin,2006,32(4):479-483. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Ma J F,Shen R,Zhao Z,Wissuwa M,Takeuchi Y,Ebitani T,Yano M.Response of rice to Al stress and identification of quantitative trait loci for Al tolerance.Plant Cell Physiol,2002,43(6):652-659. |
| [37] | Suzuki A,Suzuki T,Tanabe F,Toki S,Washida H,Wu C Y,Takaiwa F.Cloning and expression of five myb- related genes from rice seed.Gene,1997,198(1-2):393-398. |
| [38] | Ogawa S,Miyamoto K,Nemoto K,Sawasaki T,Yamane H,Nojiri H,Okada K.OsMYC2, an essential factor for JA-inductive sakuranetin production in rice, interacts with MYC2-like proteins that enhance its transactivation ability. Sci Rep,2017,7: 40175. |
| [39] | Dubos C,Stracke R,Grotewold E,Weisshaar B,Martin C,Lepiniec L.MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis.Trends Plant Sci,2010,15(10):573-581. |
| [40] | Wang R,Jing W,Xiao L,Jin Y,Shen L,Zhang W.The rice high-affinity potassium transporter1;1 is involved in salt tolerance and regulated by an MYB-type transcription factor.Plant Physiol,2015,168(3):1076-1090. |
| [41] | Nozoye T,Inoue H,Takahashi M,Ishimaru Y,Nakanishi H,Mori S,Nishizawa N K.The expression of iron homeostasis- related genes during rice germination.Plant Mol Biol,2007,64(1-2):35-47. |
| [42] | Wu L B,Ueda Y,Lai S K,Frei M.Shoot tolerance mechanisms to iron toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Environ,2017,40(4):570-584. |
| [43] | Quinet M,Vromman D,Clippe A,Bertin P,Lequeux H,Dufey I,Lutts S,Lefèvre I.Combined transcriptomic and physiological approaches reveal strong differences between short- and long-term response of rice (Oryza sativa) to iron toxicity. Plant Cell Environ,2012,35(10):1837-1859 |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||