
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 379-391.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220712
黄亚茹1, 徐鹏1, 王乐乐1, 贺一哲1, 王辉1, 柯健1, 何海兵1, 武立权1,2, 尤翠翠1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-29
修回日期:2023-01-26
出版日期:2023-07-10
发布日期:2023-07-17
通讯作者:
*email: youcuicui516@126.com
基金资助:
HUANG Yaru1, XU Peng1, WANG Lele1, HE Yizhe1, WANG Hui1, KE Jian1, HE Haibing1, WU Liquan1,2, YOU Cuicui1( )
)
Received:2022-07-29
Revised:2023-01-26
Online:2023-07-10
Published:2023-07-17
Contact:
*email: youcuicui516@126.com
摘要:
【目的】 明确外源海藻糖对大穗型粳稻籽粒灌浆结实的影响。【方法】 以大穗型粳稻品系W1844为试验材料,在孕穗末期叶面喷施浓度分别为0、15、30、50、70、100 mmol/L的海藻糖,分别标记为T0、T15、T30、T50、T70、T100。研究不同浓度海藻糖对大穗型粳稻W1844光合特性、茎鞘物质积累与转运、籽粒灌浆特性和产量的影响。【结果】 1)喷施不同浓度海藻糖均能提高水稻产量,以T50处理的水稻产量最高。与T0相比,T50处理下的产量平均增加7.71%,强势粒的结实率与千粒重分别提高4.36%和5.92%,弱势粒的结实率与千粒重分别提高11.98%和10.01%。由此可见,海藻糖对弱势粒灌浆结实的改善效果更好。2)海藻糖处理改变了籽粒灌浆特性。与T0相比,T50处理下强、弱势粒达到最大灌浆速率的时间分别缩短了3.70 d与3.93 d;灌浆前期强、弱势粒的平均灌浆速率分别提高了16.57%、28.03%;灌浆中期强、弱势粒平均灌浆速率分别提高了20.74%、24.54%。此外,T50处理下,强、弱势粒达到最大灌浆速率时的粒重分别比T0增加了6.74%和7.36%。3)海藻糖处理显著提高水稻剑叶的光合特性。T50处理下水稻叶片的净光合速率、气孔导度和蒸腾速率分别比T0平均提高了31.08%、42.58%和10.42%。4)海藻糖处理促进了抽穗期茎鞘非结构性碳水化合物(NSC)的积累与转运。与T0处理相比,T50处理下抽穗期茎鞘NSC含量平均增加11.63%,茎鞘物质转运量平均提升28.52%,且对籽粒贡献率增加18.18%。这可能是由于茎鞘蔗糖转运基因OsSUT2、OsSUT4和OsSUT5上调表达,促进了茎鞘的物质转运。【结论】 外源海藻糖可有效地改善大穗型粳稻的灌浆结实,这可能是由于海藻糖处理能提高剑叶净光合速率,上调蔗糖转运基因的表达,促进茎鞘NSC的积累与转运,从而加快了强、弱势粒的灌浆,提高了其结实率和粒重。在本研究条件下,50 mmol/L海藻糖处理对大穗型水稻W1844籽粒灌浆结实的改善效果最好。
黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391.
HUANG Yaru, XU Peng, WANG Lele, HE Yizhe, WANG Hui, KE Jian, HE Haibing, WU Liquan, YOU Cuicui. Effects of Exogenous Trehalose on Grain Filling Characteristics and Yield Formation of japonica Rice Cultivar W1844[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 379-391.
| 基因名称 Gene name | 登录号 Accession | 上游引物 Up-primer(5’-3’) | 上游引物 Down-primer (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OsSUT2 | Os12g0641400 | AACCTCAAGTCGGCCTTTCT | CTGTGCTAGGGTGATCTGCT |
| OsSUT3 | Os10g0404500 | ACATCCAGCCTTGGAAGACG | CTTGCAGTCCTCAGTCGTGT |
| OsSUT4 | Os02g0827200 | GACAAGGTCTGGCAACAGGA | CCTCCCCCAAAGAGAGCATC |
| OsSUT5 | Os02g0576600 | CGTTCGCTGTGTTGTCGTTA | GCCAATAAACAAGGCAGCCA |
表1 实时荧光定量PCR引物
Table 1. PCR primers for real-time fluorescence quantitative.
| 基因名称 Gene name | 登录号 Accession | 上游引物 Up-primer(5’-3’) | 上游引物 Down-primer (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OsSUT2 | Os12g0641400 | AACCTCAAGTCGGCCTTTCT | CTGTGCTAGGGTGATCTGCT |
| OsSUT3 | Os10g0404500 | ACATCCAGCCTTGGAAGACG | CTTGCAGTCCTCAGTCGTGT |
| OsSUT4 | Os02g0827200 | GACAAGGTCTGGCAACAGGA | CCTCCCCCAAAGAGAGCATC |
| OsSUT5 | Os02g0576600 | CGTTCGCTGTGTTGTCGTTA | GCCAATAAACAAGGCAGCCA |
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 穗粒数 Grain No. per panicle | 结实率Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·667m−2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 强势粒 SS | 弱势粒 IS | 强势粒 SS | 弱势粒 IS | |||||
| 2021 | T0 | 254.33±3.84 b | 86.94±1.31 b | 74.83±0.74 d | 26.94±0.17 b | 23.30±0.10 d | 682.84±18.27 c | |
| T15 | 267.67±7.51 a | 87.71±0.60 b | 79.44±0.57 c | 27.44±0.13 ab | 23.86±0.16 c | 704.50±9.99 bc | ||
| T30 | 271.00±4.04 a | 90.86±0.45 a | 82.23±0.55 ab | 27.83±0.10 ab | 24.43±0.20 b | 727.87±10.60 ab | ||
| T50 | 267.67±0.88 a | 91.47±0.89 a | 83.60±1.06 a | 28.30±0.52 a | 25.12±0.18 a | 741.23±1.34 a | ||
| T70 | 260.00±3.05 a | 89.62±0.91 ab | 80.64±0.56 bc | 27.92±0.25 ab | 24.25±0.07 bc | 706.43±6.84 bc | ||
| T100 | 266.67±2.67 a | 89.96±1.37 ab | 79.79±0.57 bc | 27.78±0.14 ab | 23.79±0.21 cd | 706.97±7.67 bc | ||
| 2022 | T0 | 258.45±1.24 b | 85.83±0.11 b | 72.13±0.37 b | 25.44±0.13 c | 21.87±0.26 c | 641.49±4.76 b | |
| T30 | 264.57±0.98 a | 88.07±0.27 ab | 79.13±0.74 a | 26.47±0.09 b | 23.41±0.31 b | 676.06±5.25 a | ||
| T50 | 268.19±1.58 a | 88.77±0.23 a | 80.93±0.39 a | 27.13±0.01 a | 24.54±0.16 a | 685.48±1.77 a | ||
表2 外源海藻糖对水稻产量及其构成因素的影响
Table 2. Effect of exogenous trehalose on rice yield and its components.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 穗粒数 Grain No. per panicle | 结实率Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(kg·667m−2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 强势粒 SS | 弱势粒 IS | 强势粒 SS | 弱势粒 IS | |||||
| 2021 | T0 | 254.33±3.84 b | 86.94±1.31 b | 74.83±0.74 d | 26.94±0.17 b | 23.30±0.10 d | 682.84±18.27 c | |
| T15 | 267.67±7.51 a | 87.71±0.60 b | 79.44±0.57 c | 27.44±0.13 ab | 23.86±0.16 c | 704.50±9.99 bc | ||
| T30 | 271.00±4.04 a | 90.86±0.45 a | 82.23±0.55 ab | 27.83±0.10 ab | 24.43±0.20 b | 727.87±10.60 ab | ||
| T50 | 267.67±0.88 a | 91.47±0.89 a | 83.60±1.06 a | 28.30±0.52 a | 25.12±0.18 a | 741.23±1.34 a | ||
| T70 | 260.00±3.05 a | 89.62±0.91 ab | 80.64±0.56 bc | 27.92±0.25 ab | 24.25±0.07 bc | 706.43±6.84 bc | ||
| T100 | 266.67±2.67 a | 89.96±1.37 ab | 79.79±0.57 bc | 27.78±0.14 ab | 23.79±0.21 cd | 706.97±7.67 bc | ||
| 2022 | T0 | 258.45±1.24 b | 85.83±0.11 b | 72.13±0.37 b | 25.44±0.13 c | 21.87±0.26 c | 641.49±4.76 b | |
| T30 | 264.57±0.98 a | 88.07±0.27 ab | 79.13±0.74 a | 26.47±0.09 b | 23.41±0.31 b | 676.06±5.25 a | ||
| T50 | 268.19±1.58 a | 88.77±0.23 a | 80.93±0.39 a | 27.13±0.01 a | 24.54±0.16 a | 685.48±1.77 a | ||
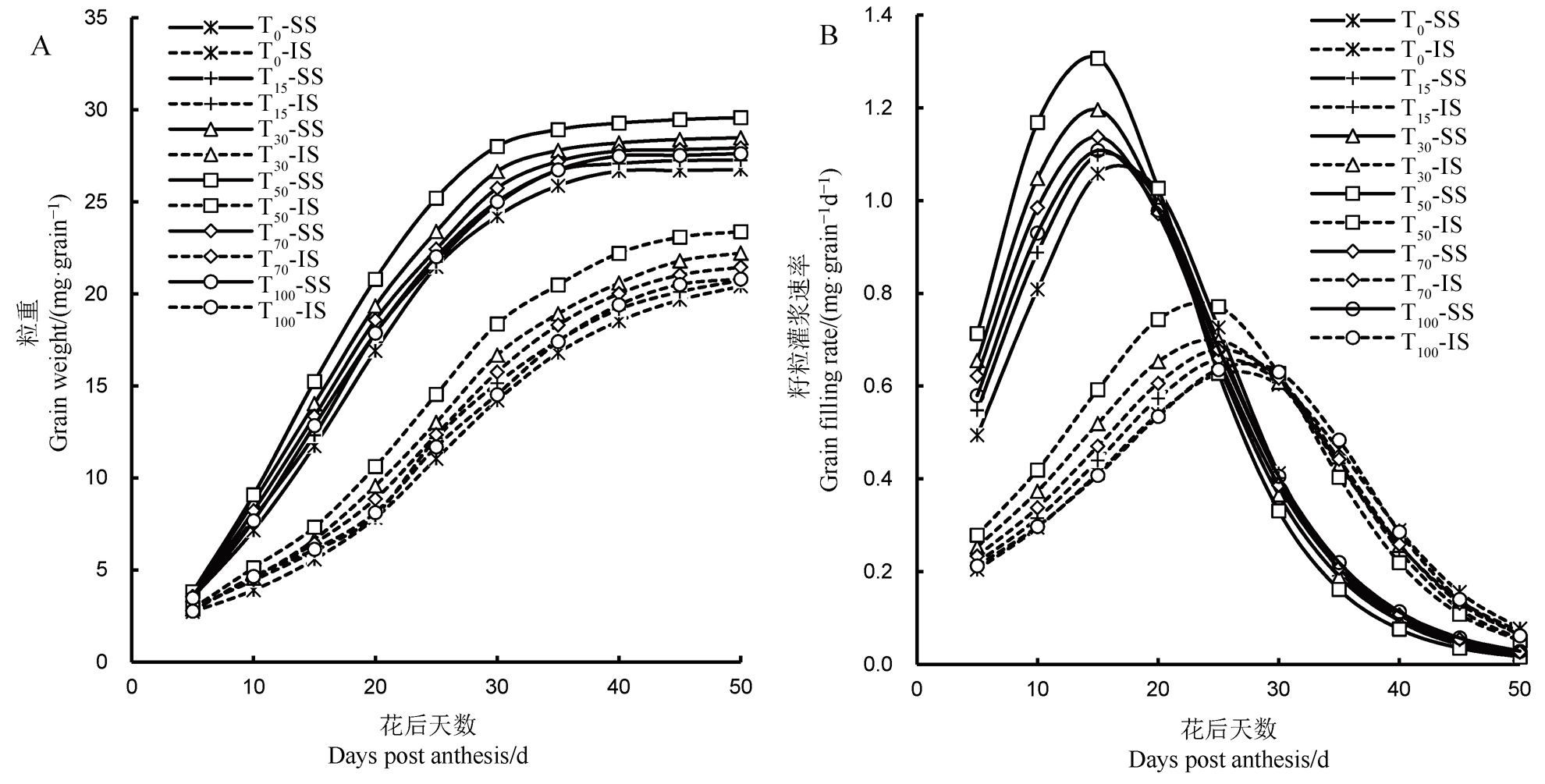
图2 2021年外源海藻糖处理下水稻粒重及灌浆速率的变化 SS-强势粒; IS-弱势粒; T0、T15、T30、T50、T70和T100分别表示海藻糖喷施浓度为0、15、30、50、70和100 mmol/L。
Fig. 2. Changes in rice grain weight and grain filling rate under exogenous trehalose treatments in 2021. SS, Superior spikelets; IS, Inferior spikelets; T0, T15, T30, T50, T70 and T100 represent the spraying concentrations of trehalose are 0, 15, 30, 50, 70, and 100 mmol/L, respectively.
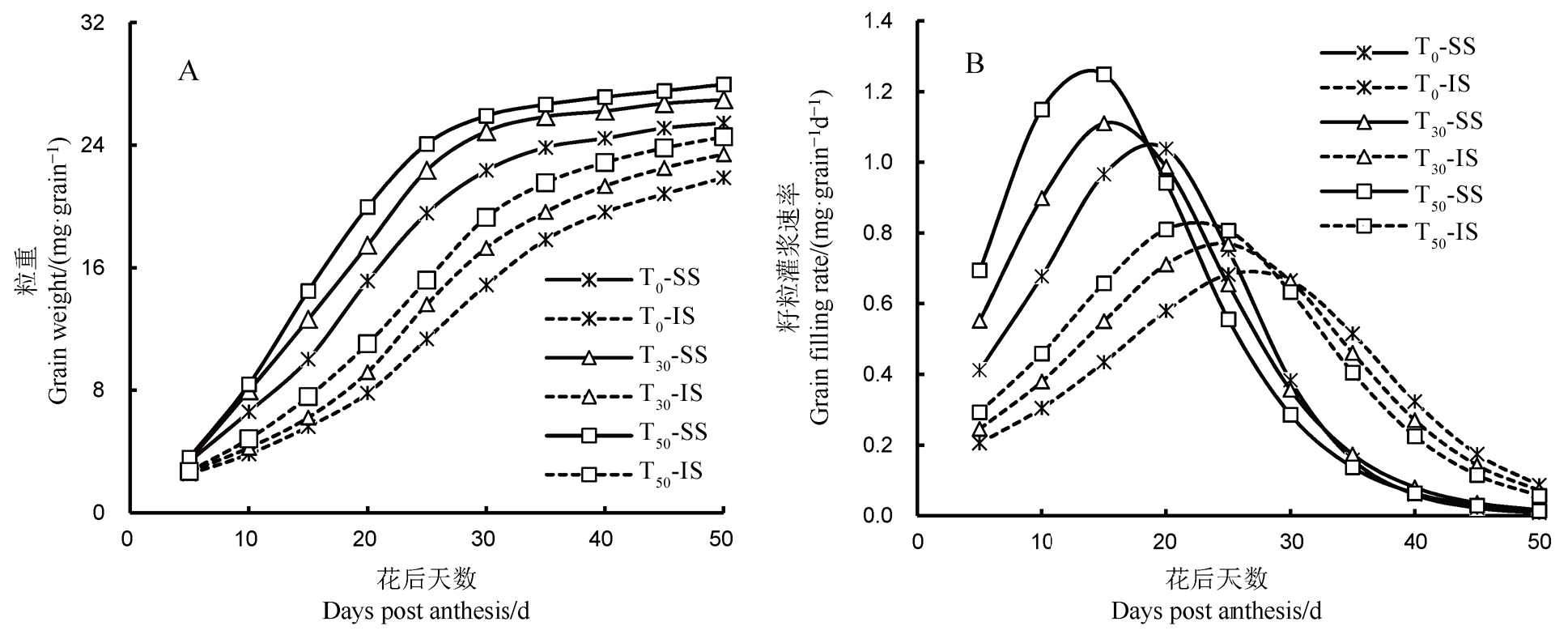
图3 2022年外源海藻糖处理下水稻粒重及灌浆速率的变化 SS-强势粒; IS-弱势粒; T0、T15、T30、T50、T70和T100分别表示海藻糖喷施浓度为0、15、30、50、70和100 mmol/L。
Fig. 3. Changes in rice grain weight and grain filling rate under exogenous trehalose treatments in 2022. SS, Superior spikelets; IS, Inferior spikelets; T0, T15, T30, T50, T70 and T100, represent the spraying concentrations of trehalose are 0, 15, 30, 50, 70, and 100 mmol/L.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 起始生长势 R0 | 最大灌浆速率 GRmax /(mg·grain-1 d-1) | 达到最大灌浆 速率的时间 Tmax/d | 平均灌浆速率 GRmean /(mg·grain-1 d-1) | 最大灌浆速率 时粒重 Wmax/(mg·grain-1) | 活跃灌浆期 D/d | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS | IS | SS | IS | SS | IS | SS | IS | SS | IS | SS | IS | |||||||
| 2021 | T0 | 0.1497 | 0.0792 | 1.0842 | 0.6331 | 16.96 | 26.68 | 0.7208 | 0.4113 | 13.02 | 12.00 | 37.55 | 50.59 | |||||
| T15 | 0.1783 | 0.0772 | 1.1045 | 0.6595 | 15.93 | 25.95 | 0.7391 | 0.4259 | 13.44 | 12.36 | 37.46 | 49.04 | ||||||
| T30 | 0.2304 | 0.0890 | 1.1983 | 0.7005 | 14.43 | 24.28 | 0.8063 | 0.4588 | 13.33 | 12.59 | 35.80 | 49.43 | ||||||
| T50 | 0.2442 | 0.0929 | 1.3176 | 0.7818 | 13.94 | 23.34 | 0.8864 | 0.5112 | 13.79 | 13.28 | 33.66 | 46.41 | ||||||
| T70 | 0.2254 | 0.0804 | 1.1377 | 0.6794 | 14.75 | 25.45 | 0.7657 | 0.4411 | 13.06 | 12.64 | 37.05 | 49.58 | ||||||
| T100 | 0.2098 | 0.0698 | 1.1088 | 0.6514 | 15.33 | 27.42 | 0.7454 | 0.4174 | 13.08 | 12.95 | 37.64 | 50.88 | ||||||
| 2022 | T0 | 0.1183 | 0.0842 | 1.0556 | 0.6931 | 18.54 | 26.95 | 0.6901 | 0.4517 | 12.97 | 12.34 | 36.31 | 49.19 | |||||
| T30 | 0.1439 | 0.1001 | 1.1450 | 0.7670 | 16.58 | 24.34 | 0.7580 | 0.5066 | 13.52 | 12.53 | 35.92 | 46.63 | ||||||
| T50 | 0.2335 | 0.1085 | 1.2818 | 0.8326 | 14.17 | 22.43 | 0.8612 | 0.5494 | 13.95 | 12.84 | 33.08 | 44.99 | ||||||
表3 水稻籽粒灌浆过程的Richards方程参数
Table 3. Parameters of Richards equation during rice grain filling period.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 起始生长势 R0 | 最大灌浆速率 GRmax /(mg·grain-1 d-1) | 达到最大灌浆 速率的时间 Tmax/d | 平均灌浆速率 GRmean /(mg·grain-1 d-1) | 最大灌浆速率 时粒重 Wmax/(mg·grain-1) | 活跃灌浆期 D/d | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS | IS | SS | IS | SS | IS | SS | IS | SS | IS | SS | IS | |||||||
| 2021 | T0 | 0.1497 | 0.0792 | 1.0842 | 0.6331 | 16.96 | 26.68 | 0.7208 | 0.4113 | 13.02 | 12.00 | 37.55 | 50.59 | |||||
| T15 | 0.1783 | 0.0772 | 1.1045 | 0.6595 | 15.93 | 25.95 | 0.7391 | 0.4259 | 13.44 | 12.36 | 37.46 | 49.04 | ||||||
| T30 | 0.2304 | 0.0890 | 1.1983 | 0.7005 | 14.43 | 24.28 | 0.8063 | 0.4588 | 13.33 | 12.59 | 35.80 | 49.43 | ||||||
| T50 | 0.2442 | 0.0929 | 1.3176 | 0.7818 | 13.94 | 23.34 | 0.8864 | 0.5112 | 13.79 | 13.28 | 33.66 | 46.41 | ||||||
| T70 | 0.2254 | 0.0804 | 1.1377 | 0.6794 | 14.75 | 25.45 | 0.7657 | 0.4411 | 13.06 | 12.64 | 37.05 | 49.58 | ||||||
| T100 | 0.2098 | 0.0698 | 1.1088 | 0.6514 | 15.33 | 27.42 | 0.7454 | 0.4174 | 13.08 | 12.95 | 37.64 | 50.88 | ||||||
| 2022 | T0 | 0.1183 | 0.0842 | 1.0556 | 0.6931 | 18.54 | 26.95 | 0.6901 | 0.4517 | 12.97 | 12.34 | 36.31 | 49.19 | |||||
| T30 | 0.1439 | 0.1001 | 1.1450 | 0.7670 | 16.58 | 24.34 | 0.7580 | 0.5066 | 13.52 | 12.53 | 35.92 | 46.63 | ||||||
| T50 | 0.2335 | 0.1085 | 1.2818 | 0.8326 | 14.17 | 22.43 | 0.8612 | 0.5494 | 13.95 | 12.84 | 33.08 | 44.99 | ||||||
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 灌浆前期Early stage of grain filling | 灌浆中期Middle stage of grain filling | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天数 Days/d | 平均速率 MGR/(mg·grain−1 d−1) | 贡献率 RGC/% | 天数 Days/d | 平均速率 MGR/(mg·grain−1 d−1) | 贡献率 RGC/% | |||||||
| 2021 | T0-SS | 8.81±0.23 d | 0.69±0.01 e | 22.31±0.58 e | 16.29±1.20 c | 0.95±0.03 c | 57.27±0.13 b | |||||
| T0-IS | 16.77±0.40 b | 0.38±0.00 i | 30.67±0.52 cd | 19.83±1.31 a | 0.56±0.01 f | 53.28±0.66 c | ||||||
| T15-SS | 7.57±0.24 e | 0.71±0.02 d | 19.43±0.17 f | 16.72±1.13 c | 0.97±0.01 c | 58.38±0.36 ab | ||||||
| T15-IS | 16.60±0.43 b | 0.41±0.00 h | 32.64±0.58 b | 18.71±1.26 ab | 0.58±0.00 ef | 52.24±0.06 de | ||||||
| T30-SS | 6.25±0.58 ef | 0.77±0.01 b | 16.75±0.28 g | 16.36±1.62 c | 1.05±0.03 b | 59.30±0.17 a | ||||||
| T30-IS | 14.23±0.57 c | 0.44±0.00 g | 27.89±0.35 d | 20.10±1.45 a | 0.62±0.00 e | 54.72±0.35 c | ||||||
| T50-SS | 6.26±0.12 f | 0.80±0.02 a | 16.78±0.18 g | 15.37±1.42 c | 1.15±0.00 a | 59.27±0.09 a | ||||||
| T50-IS | 13.98±0.46 c | 0.48±0.01 f | 28.46±0.40 d | 18.73±1.07 ab | 0.69±0.01 d | 54.43±0.06 c | ||||||
| T70-SS | 6.28±0.17 f | 0.75±0.02 bc | 16.62±0.18 g | 16.95±1.10 bc | 0.99±0.00 c | 59.35±1.01 a | ||||||
| T70-IS | 15.75±0.28 b | 0.43±0.01 g | 30.85±0.69 c | 19.39±1.53 a | 0.60±0.00 ef | 53.21±0.70 cd | ||||||
| T100-SS | 6.77±0.19 ef | 0.71±0.03 d | 17.24±0.35 g | 17.13±1.29 bc | 0.97±0.01 c | 59.13±0.51 a | ||||||
| T100-IS | 18.05±0.38 a | 0.41±0.00 h | 35.06±0.64 a | 18.73±1.56 ab | 0.58±0.00 ef | 50.89±0.65 e | ||||||
| 2022 | T0-SS | 6.51±0.02 d | 0.64±0.01 b | 18.23±0.32 c | 17.20±0.10 c | 0.93±0.02 c | 58.82±0.68 a | |||||
| T0-IS | 14.84±0.05 e | 0.37±0.00 d | 26.24±0.13 b | 21.14±0.62 a | 0.58±0.01 e | 55.50±0.23 b | ||||||
| T30-SS | 6.11±0.0.02 f | 0.73±0.01 a | 16.82±0.23 d | 16.77±0.14 cd | 1.01±0.02 b | 59.28±0.26 a | ||||||
| T30-IS | 13.73±0.02 a | 0.42±0.03 c | 26.53± 0.06 a | 21.37±0.17 a | 0.68±0.02 d | 55.11±0.08 a | ||||||
| T50-SS | 5.93±0.03 b | 0.75±0.01 a | 16.58± 0.21 d | 15.89±0.17 d | 1.12±0.03 a | 59.34±0.64 a | ||||||
| T50-IS | 12.98±0.02 c | 0.48±0.01 c | 26.23± 0.13 b | 19.87± 0.25 b | 0.73±0.02 d | 55.51±0.36 b | ||||||
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 灌浆后期Late stage of grain filling | ||||||||||
| 天数 Days/d | 平均速率 MGR/(mg·grain−1 d−1) | 贡献率 RGC/% | ||||||||||
| 2021 | T0-SS | 19.64±1.12 de | 0.27±0.00 c | 19.42±0.23 c | ||||||||
| T0-IS | 19.16±1.34 de | 0.16±0.00 g | 15.05±0.12 e | |||||||||
| T15-SS | 21.80±1.51 bc | 0.27±0.00 c | 21.18±0.29 b | |||||||||
| T15-IS | 17.17±2.17 fg | 0.17±0.00 f | 14.12±0.19 f | |||||||||
| T30-SS | 22.99±1.66 ab | 0.29±0.00 b | 22.95±0.29 a | |||||||||
| T30-IS | 20.90±1.92 cd | 0.18±0.00 e | 16.39±0.21 d | |||||||||
| T50-SS | 21.59±2.57 bc | 0.32±0.00 a | 22.95±0.18 a | |||||||||
| T50-IS | 19.19±1.85 de | 0.20±0.00 d | 16.11±0.10 d | |||||||||
| T70-SS | 23.91±2.41 a | 0.27±0.00 c | 23.03±0.16 a | |||||||||
| T70-IS | 18.66±1.83 ef | 0.18±0.00 e | 14.94±0.07 e | |||||||||
| T100-SS | 23.74±2.04 a | 0.27±0.00 c | 22.63±0.69 a | |||||||||
| T100-IS | 16.14±1.18 g | 0.17±0.00 f | 13.06±0.17 g | |||||||||
| 2022 | T0-SS | 23.19±0.17 a | 0.27±0.01 b | 21.95±0.13 b | ||||||||
| T0-IS | 22.95±0.19 ab | 0.17±0.00 d | 17.26±0.21 c | |||||||||
| T30-SS | 23.52±0.31 a | 0.29±0.01 a | 22.90±0.16 a | |||||||||
| T30-IS | 23.47±0.17 a | 0.19±0.01 e | 17.98±0.12 d | |||||||||
| T50-SS | 22.43±0.20 a | 0.31±0.01 a | 23.08±0.17 a | |||||||||
| T50-IS | 21.58±0.26 c | 0.21±0.01 c | 17.25±0.08 c | |||||||||
表4 外源海藻糖处理下水稻籽粒灌浆前期、中期和后期特征参数
Table 4. Parameters of pre-, mid- and post-grain filling of rice under exogenous trehalose treatments.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 灌浆前期Early stage of grain filling | 灌浆中期Middle stage of grain filling | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天数 Days/d | 平均速率 MGR/(mg·grain−1 d−1) | 贡献率 RGC/% | 天数 Days/d | 平均速率 MGR/(mg·grain−1 d−1) | 贡献率 RGC/% | |||||||
| 2021 | T0-SS | 8.81±0.23 d | 0.69±0.01 e | 22.31±0.58 e | 16.29±1.20 c | 0.95±0.03 c | 57.27±0.13 b | |||||
| T0-IS | 16.77±0.40 b | 0.38±0.00 i | 30.67±0.52 cd | 19.83±1.31 a | 0.56±0.01 f | 53.28±0.66 c | ||||||
| T15-SS | 7.57±0.24 e | 0.71±0.02 d | 19.43±0.17 f | 16.72±1.13 c | 0.97±0.01 c | 58.38±0.36 ab | ||||||
| T15-IS | 16.60±0.43 b | 0.41±0.00 h | 32.64±0.58 b | 18.71±1.26 ab | 0.58±0.00 ef | 52.24±0.06 de | ||||||
| T30-SS | 6.25±0.58 ef | 0.77±0.01 b | 16.75±0.28 g | 16.36±1.62 c | 1.05±0.03 b | 59.30±0.17 a | ||||||
| T30-IS | 14.23±0.57 c | 0.44±0.00 g | 27.89±0.35 d | 20.10±1.45 a | 0.62±0.00 e | 54.72±0.35 c | ||||||
| T50-SS | 6.26±0.12 f | 0.80±0.02 a | 16.78±0.18 g | 15.37±1.42 c | 1.15±0.00 a | 59.27±0.09 a | ||||||
| T50-IS | 13.98±0.46 c | 0.48±0.01 f | 28.46±0.40 d | 18.73±1.07 ab | 0.69±0.01 d | 54.43±0.06 c | ||||||
| T70-SS | 6.28±0.17 f | 0.75±0.02 bc | 16.62±0.18 g | 16.95±1.10 bc | 0.99±0.00 c | 59.35±1.01 a | ||||||
| T70-IS | 15.75±0.28 b | 0.43±0.01 g | 30.85±0.69 c | 19.39±1.53 a | 0.60±0.00 ef | 53.21±0.70 cd | ||||||
| T100-SS | 6.77±0.19 ef | 0.71±0.03 d | 17.24±0.35 g | 17.13±1.29 bc | 0.97±0.01 c | 59.13±0.51 a | ||||||
| T100-IS | 18.05±0.38 a | 0.41±0.00 h | 35.06±0.64 a | 18.73±1.56 ab | 0.58±0.00 ef | 50.89±0.65 e | ||||||
| 2022 | T0-SS | 6.51±0.02 d | 0.64±0.01 b | 18.23±0.32 c | 17.20±0.10 c | 0.93±0.02 c | 58.82±0.68 a | |||||
| T0-IS | 14.84±0.05 e | 0.37±0.00 d | 26.24±0.13 b | 21.14±0.62 a | 0.58±0.01 e | 55.50±0.23 b | ||||||
| T30-SS | 6.11±0.0.02 f | 0.73±0.01 a | 16.82±0.23 d | 16.77±0.14 cd | 1.01±0.02 b | 59.28±0.26 a | ||||||
| T30-IS | 13.73±0.02 a | 0.42±0.03 c | 26.53± 0.06 a | 21.37±0.17 a | 0.68±0.02 d | 55.11±0.08 a | ||||||
| T50-SS | 5.93±0.03 b | 0.75±0.01 a | 16.58± 0.21 d | 15.89±0.17 d | 1.12±0.03 a | 59.34±0.64 a | ||||||
| T50-IS | 12.98±0.02 c | 0.48±0.01 c | 26.23± 0.13 b | 19.87± 0.25 b | 0.73±0.02 d | 55.51±0.36 b | ||||||
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 灌浆后期Late stage of grain filling | ||||||||||
| 天数 Days/d | 平均速率 MGR/(mg·grain−1 d−1) | 贡献率 RGC/% | ||||||||||
| 2021 | T0-SS | 19.64±1.12 de | 0.27±0.00 c | 19.42±0.23 c | ||||||||
| T0-IS | 19.16±1.34 de | 0.16±0.00 g | 15.05±0.12 e | |||||||||
| T15-SS | 21.80±1.51 bc | 0.27±0.00 c | 21.18±0.29 b | |||||||||
| T15-IS | 17.17±2.17 fg | 0.17±0.00 f | 14.12±0.19 f | |||||||||
| T30-SS | 22.99±1.66 ab | 0.29±0.00 b | 22.95±0.29 a | |||||||||
| T30-IS | 20.90±1.92 cd | 0.18±0.00 e | 16.39±0.21 d | |||||||||
| T50-SS | 21.59±2.57 bc | 0.32±0.00 a | 22.95±0.18 a | |||||||||
| T50-IS | 19.19±1.85 de | 0.20±0.00 d | 16.11±0.10 d | |||||||||
| T70-SS | 23.91±2.41 a | 0.27±0.00 c | 23.03±0.16 a | |||||||||
| T70-IS | 18.66±1.83 ef | 0.18±0.00 e | 14.94±0.07 e | |||||||||
| T100-SS | 23.74±2.04 a | 0.27±0.00 c | 22.63±0.69 a | |||||||||
| T100-IS | 16.14±1.18 g | 0.17±0.00 f | 13.06±0.17 g | |||||||||
| 2022 | T0-SS | 23.19±0.17 a | 0.27±0.01 b | 21.95±0.13 b | ||||||||
| T0-IS | 22.95±0.19 ab | 0.17±0.00 d | 17.26±0.21 c | |||||||||
| T30-SS | 23.52±0.31 a | 0.29±0.01 a | 22.90±0.16 a | |||||||||
| T30-IS | 23.47±0.17 a | 0.19±0.01 e | 17.98±0.12 d | |||||||||
| T50-SS | 22.43±0.20 a | 0.31±0.01 a | 23.08±0.17 a | |||||||||
| T50-IS | 21.58±0.26 c | 0.21±0.01 c | 17.25±0.08 c | |||||||||
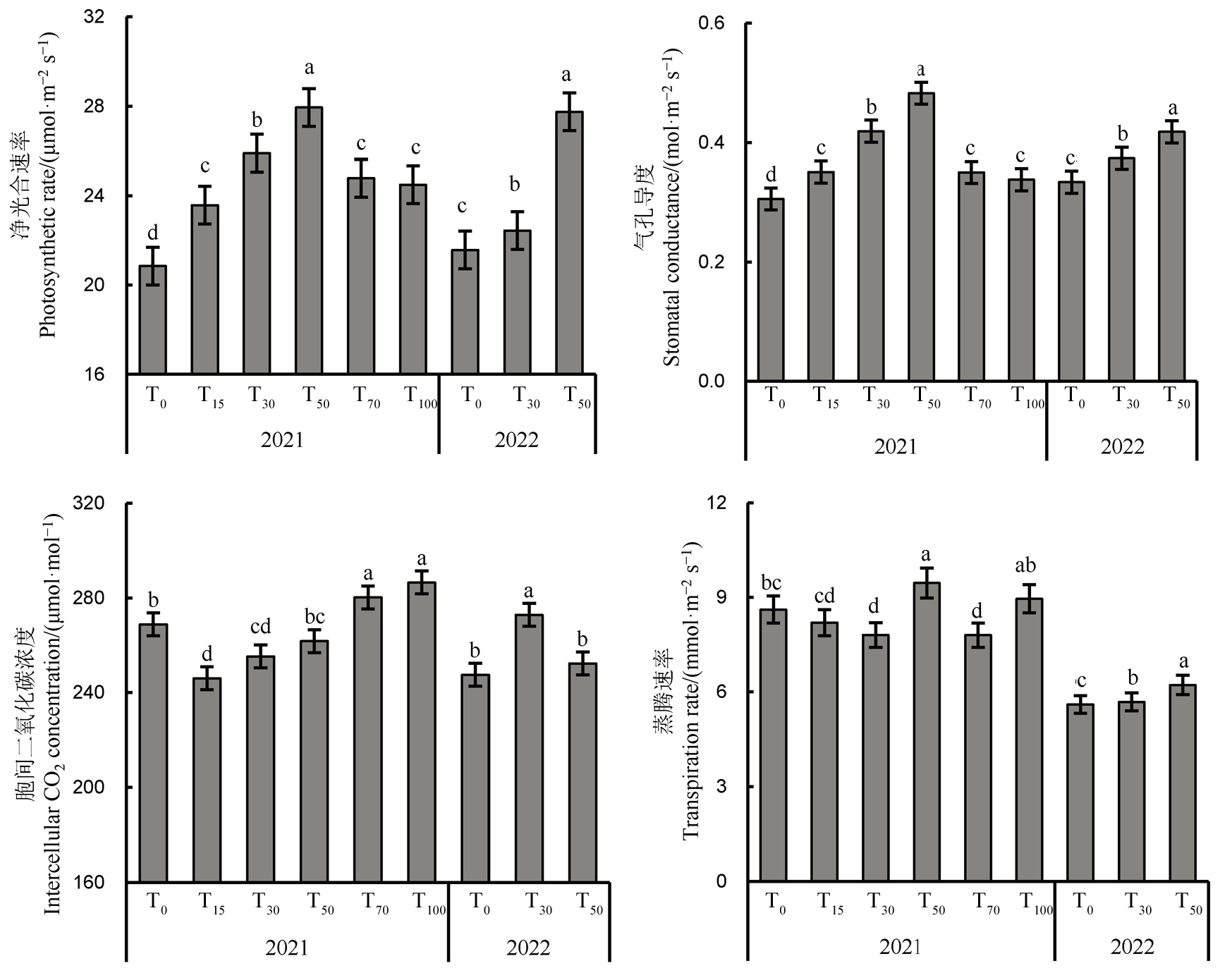
图4 2021和2022年外源海藻糖对水稻剑叶光合特性的影响 SS-强势粒; IS-弱势粒; T0、T15、T30、T50、T70和T100分别表示海藻糖喷施浓度为0、15、30、50、70和100 mmol/L; 竖线代表均值±标准误,不同字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 4. Effects of exogenous trehalose on photosynthetic characteristics of rice flag leaf in 2021 and 2022. SS, Superior spikelets; IS, Inferior spikelets; T0, T15, T30, T50, T70 and T100 represent the spraying concentrations of trehalose are 0, 15, 30, 50, 70, and 100 mmol/L. The vertical bars indicate mean ± standard error (SE); Different letters indicate significant difference (P<0.05) among different treatments.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 抽穗期NSC总量TMNSC at heading /(g·m−2) | 成熟期NSC总量TMNSC at maturity/(g·m−2) | NSC转运量 TNSC/(g·m−2) | NSC转运率 TRNSC/% | 对籽粒的贡献率 CNSC/% | 糖花比 Sugar-spikelet ratio /(mg·spikelet-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | T0 | 210.54±1.11 d | 111.22±0.45 d | 99.33±0.29 f | 47.18±0.50 d | 13.42±0.41 d | 3.81±0.05 c |
| T15 | 221.54±4.13 c | 112.89±0.04 c | 108.65±0.63 d | 49.04±0.30 c | 14.11±0.39 c | 3.91±0.19 bc | |
| T30 | 232.82±0.49 a | 109.61±0.24 e | 123.22±0.64 b | 52.92±0.42 b | 15.03±0.57 b | 3.96±0.10 ab | |
| T50 | 236.18±0.32 a | 107.42±0.10 f | 128.76±0.48 a | 54.52±0.55 a | 15.51±0.44 a | 4.05±0.02 a | |
| T70 | 227.06±0.22 b | 114.33±0.32 b | 112.46±0.73 c | 49.53±0.35 c | 14.06±0.33 c | 3.85±0.04 bc | |
| T100 | 220.03±0.61 c | 115.39±0.25 a | 104.64±0.70 e | 47.56±0.49 d | 13.59±0.49 d | 3.82±0.06 c | |
| 2022 | T0 | 238.91±10.71 c | 123.41±2.40 c | 115.50±13.08 b | 48.31±1.28 b | 12.01±0.39 b | 4.39±0.20 b |
| T30 | 259.60±9.14 b | 123.00±1.42 b | 136.61±10.13 a | 52.60±1.33 a | 13.48±0.25 a | 4.66±0.19 a | |
| T50 | 265.39±4.91 a | 118.22±1.11 a | 147.17±5.72 a | 55.46±0.41 a | 14.31±0.56 a | 4.70±0.39 a |
表5 外源海藻糖对水稻茎鞘NSC的积累与转运的影响
Table 5. Effect of exogenous trehalose on the accumulation and transport of NSC in rice stems and sheaths.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 抽穗期NSC总量TMNSC at heading /(g·m−2) | 成熟期NSC总量TMNSC at maturity/(g·m−2) | NSC转运量 TNSC/(g·m−2) | NSC转运率 TRNSC/% | 对籽粒的贡献率 CNSC/% | 糖花比 Sugar-spikelet ratio /(mg·spikelet-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | T0 | 210.54±1.11 d | 111.22±0.45 d | 99.33±0.29 f | 47.18±0.50 d | 13.42±0.41 d | 3.81±0.05 c |
| T15 | 221.54±4.13 c | 112.89±0.04 c | 108.65±0.63 d | 49.04±0.30 c | 14.11±0.39 c | 3.91±0.19 bc | |
| T30 | 232.82±0.49 a | 109.61±0.24 e | 123.22±0.64 b | 52.92±0.42 b | 15.03±0.57 b | 3.96±0.10 ab | |
| T50 | 236.18±0.32 a | 107.42±0.10 f | 128.76±0.48 a | 54.52±0.55 a | 15.51±0.44 a | 4.05±0.02 a | |
| T70 | 227.06±0.22 b | 114.33±0.32 b | 112.46±0.73 c | 49.53±0.35 c | 14.06±0.33 c | 3.85±0.04 bc | |
| T100 | 220.03±0.61 c | 115.39±0.25 a | 104.64±0.70 e | 47.56±0.49 d | 13.59±0.49 d | 3.82±0.06 c | |
| 2022 | T0 | 238.91±10.71 c | 123.41±2.40 c | 115.50±13.08 b | 48.31±1.28 b | 12.01±0.39 b | 4.39±0.20 b |
| T30 | 259.60±9.14 b | 123.00±1.42 b | 136.61±10.13 a | 52.60±1.33 a | 13.48±0.25 a | 4.66±0.19 a | |
| T50 | 265.39±4.91 a | 118.22±1.11 a | 147.17±5.72 a | 55.46±0.41 a | 14.31±0.56 a | 4.70±0.39 a |
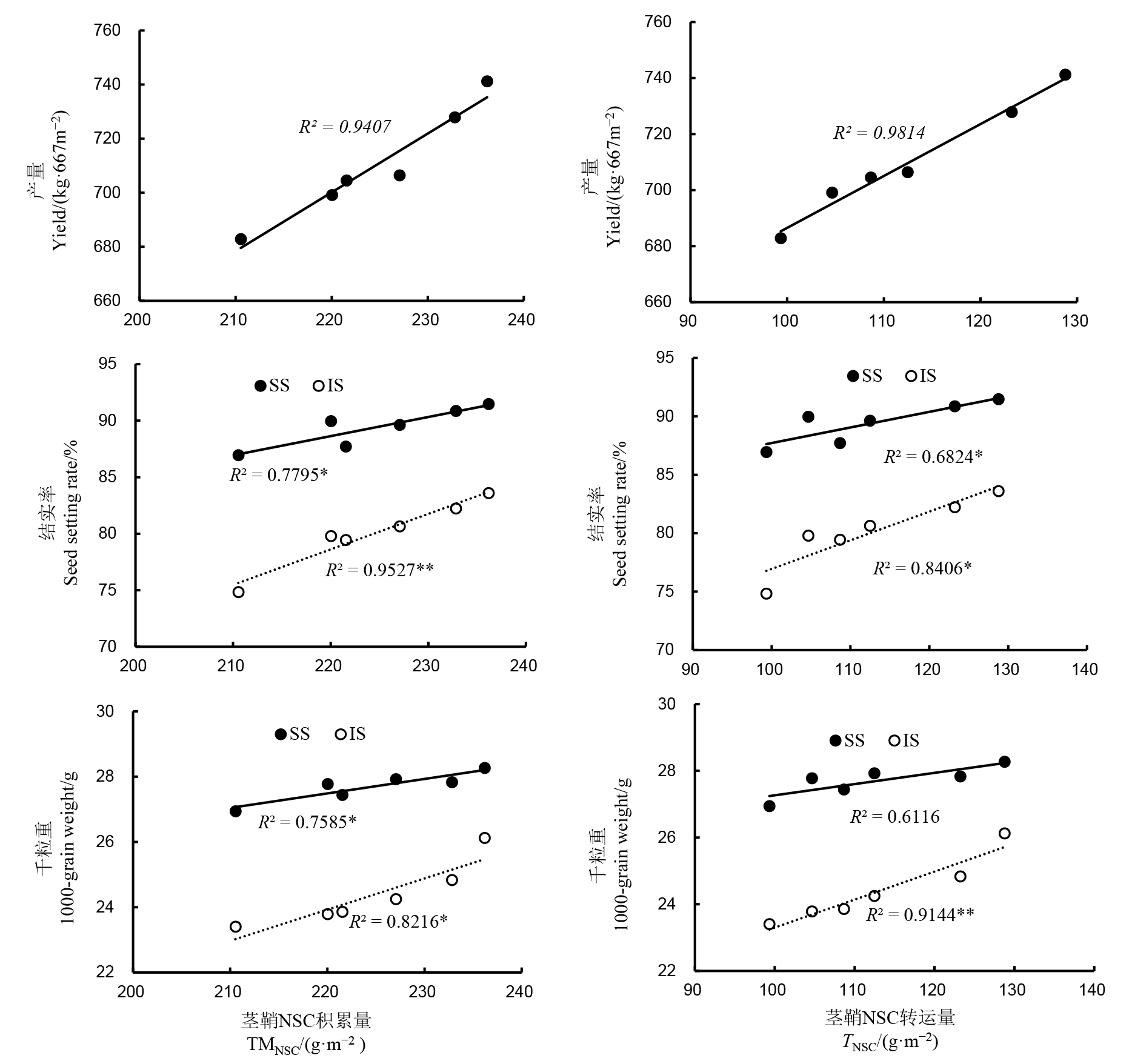
图5 外源海藻糖处理下水稻茎鞘NSC转运量与产量及结实性的关系
Fig. 5. Relationship of NSC transport in rice stems and sheaths with yield and grain-setting under exogenous trehalose treatments. TMNSC, Total biomass of NSC in stems and sheaths; TNSC, Translocation of NSC from stems and sheaths to grains during grain filling stage; R20.05=0.6581; R20.01=0.8413; *, ** Significant correlation at P = 0.05 and P = 0.01 levels, respectively.
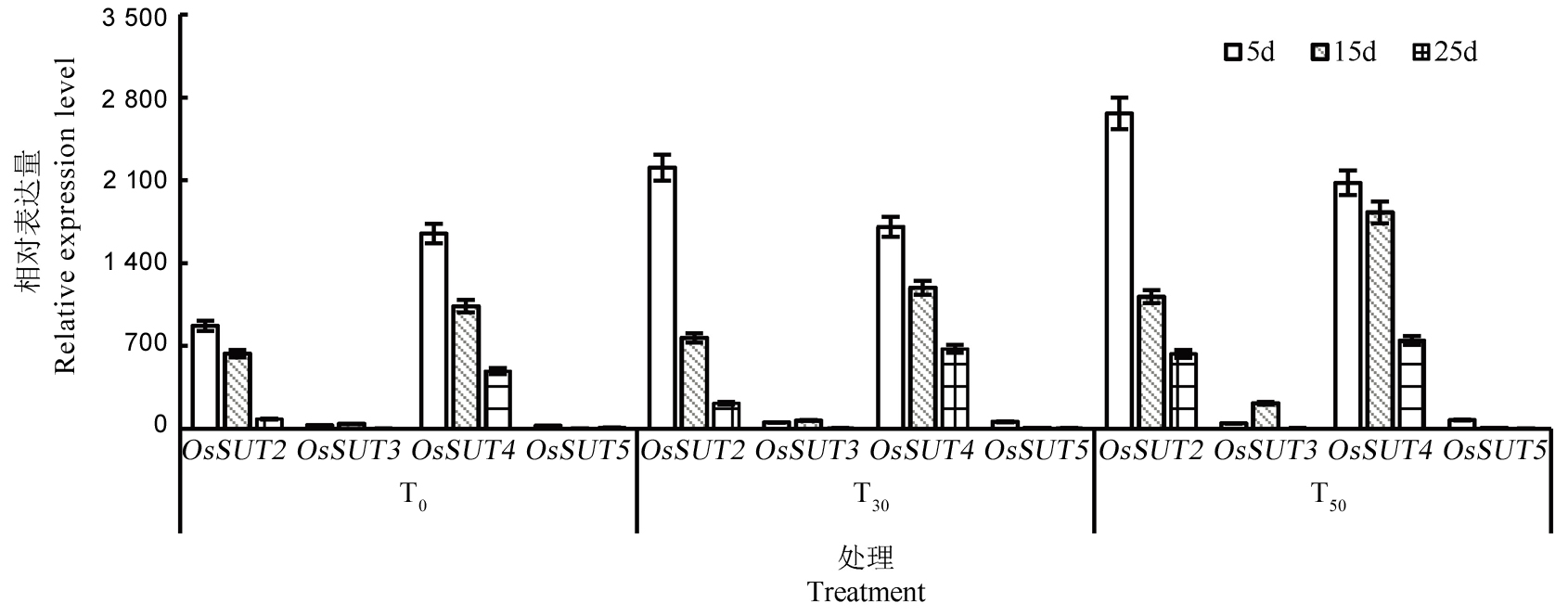
图6 外源海藻糖处理下水稻茎鞘OsSUT基因的表达水平 T0、T30、T50分别表示海藻糖喷施浓度为0、30、50 mmol/L。5d, 15d, 25d分别表示花后5d, 15d和25d。
Fig. 6. Relative mRNA level of OsSUT gene in rice stems and sheaths under exogenous trehalose treatments. T0, T30, T50, Trehalose concentrations of 0, 30, 50 mmol/L. 5d, 15d, 25d represent 5, 15, 25 days post anthesis, respectively.
| [1] | Khush G S. What it will take to feed 5.0 billion rice consumers in 2030[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2005, 59(1): 1-6. |
| [2] | 谢光辉, 杨建昌, 王志琴, 朱庆森. 水稻籽粒灌浆特性及其与籽粒生理活性的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2001, 27(5): 557-565. |
| Xie G H, Yang J C, Wang Z Q, Zhu Q S. Grain filling characteristics of rice and their relationships to physiological activities of grains[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2001, 27(5): 557-565. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 黄农荣, 钟旭华, 王丰, 郑海波. 超级杂交稻结实期根系活力与籽粒灌浆特性研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2006, 39(9): 1772-1779. |
| Huang N R, Zhong X H, Wang F, Zheng H B. Root vigor and grain-filling characteristics in super hybrid rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2006, 39(9): 1772-1779. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Tsutomu I, Toshiaki M, Ryu O, Tohru Y. Morphological development of rice caryopses located at the different positions in a panicle from early to middle stage of grain filling[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2003, 30(11): 1139-1149. |
| [5] | Mohapatra P K, Patel R, Sahu S K. Time of flowering affects grain quality and spikelet partitioning within the rice panicle[J]. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology, 1993, 20(2): 231-241. |
| [6] | Naik P K, Mohapatra P K. Ethylene inhibitors promote male gametophyte survival in rice[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 1999, 28(1): 29-39. |
| [7] | You C C, Zhu H L, Xu B B, Huang W X, Wang S H, Ding Y F, Liu Z H, Li G H, Chen L, Ding C Q, Tang S. Effect of removing superior spikelets on grain filling of inferior spikelets in rice[J]. Frontiers Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1161. |
| [8] | 李哲, 姜沣益, 代梦雪, 李宇星, 张文静, 马尚宇, 黄正来, 樊永惠. 外源海藻糖对高温胁迫小麦干物质积累和籽粒灌浆的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2022, 42(5): 614-622. |
| Li Z, Jiang F Y, Dai M X, Li Y X, Zhang W J, Ma S Y, Huang Z L, Fan Y H. Effect of exogenous trehalose on dry matter accumulation and grain filling of wheat under heat stress[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2022, 42(5): 614-622. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Liang Z M, Luo J, Wei B, Liao Y C, Liu Y. Trehalose can alleviate decreases in grain number per spike caused by low-temperature stress at the booting stage by promoting floret fertility in wheat[J]. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2021, 207(4): 717-732. |
| [10] | Luo Y, Xie Y, He D, Wang W, Yuan S. Exogenous trehalose protects photosystem II by promoting cyclic electron flow under heat and drought stresses in winter wheat[J]. Plant Biology, 2021, 23(5): 770-776. |
| [11] | Luo Y, Gao Y M, Wang W, Zou C J. Application of trehalose ameliorates heat stress and promotes recovery of winter wheat seedlings[J]. Biologia Plantarum, 2014, 58(2): 395-398. |
| [12] | 李金花, 张春艳, 刘浩, 李永春. 海藻糖的特性及其在植物抗逆性中的应用[J]. 江西农业学报, 2011, 23(6): 25-27. |
| Li J H, Zhang C Y, Liu H, Li Y C. Characteristics of trehalose and its application in improving stress tolerance of plants[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2011, 23(6): 25-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Wingler A, Fritzius T, Wiemken A, Boller T, Aeschbacher R A. Trehalose induces the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase gene, ApL3, and starch synthesis in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2000, 124(1): 105-114. |
| [14] | Kolbe A, Tiessen A, Schluepmann H, Paul M, Ulrich S, Geigenberger P. Trehalose 6-phosphate regulates starch synthesis via posttranslational redox activation of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2005, 102(31): 11118-11123. |
| [15] | Iturriaga G, Suárez R, Nova-Franco B. Trehalose metabolism: From osmoprotection to signaling[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2009, 10(9): 3793-3810. |
| [16] | Yadav U P, Ivakov A, Feil R, Duan G Y, Walther D, Giavalisco P, Piques M, Carillo P, Hubberten H, Stitt M, Lunn J E. The sucrose-trehalose 6-phosphate (Tre6P) nexus: Specificity and mechanisms of sucrose signalling by Tre6P[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(4): 1051-1068. |
| [17] | Richards F J. A flexible growth function for empirical use[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1959, 10(2): 290-301. |
| [18] | Zhang C X, Fu G F, Yang X Q, Yang Y J, Zhao X, Chen T T, Zhang X F, Jin Q Y, Tao L X. Heat stress effects are stronger on spikelets than on flag leaves in rice due to differences in dissipation capacity[J]. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2016, 202(5): 394-408. |
| [19] | Yoshida S. Physiological aspects of grain yield[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 1972, 23(1): 437-464. |
| [20] | Yang J C, Zhang J H. Grain filling of cereals under soil drying[J]. The New Phytologist, 2006, 169(2): 223-236. |
| [21] | Aoki N, Hirose T, Scofield G N, Whitfeld P R, Furbank R T. The sucrose transporter gene family in rice[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2003, 44(3): 223-232. |
| [22] | Mohapatra P, Patel R, Sahu S. Time of flowering affects grain quality and spikelet partitioning within the rice panicle[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 1993, 20(2): 231-241. |
| [23] | Ishimaru T, Matsuda T, Ohsugi R, Yamagishi T. Morphological development of rice caryopses located at the different positions in a panicle from early to middle stage of grain filling[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2003, 30(11): 1139-1149. |
| [24] | Ao H J, Wang S H, Zou Y B. Study on yield stability and dry matter characteristics of super hybrid rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(7): 1927-1936. |
| [25] | Yang J C, Zhang J H. Grain-filling problem in ‘super’ rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010, 61(1): 1-5. |
| [26] | Khater M A, Dawood M G, Sadak M S, Shalaby M A, El-Awadi M E, El-Din K G. Enhancement the performance of cowpea plants grown under drought conditions via trehalose application[J]. Middle East Journal of Agriculture Research, 2018, 7(3): 782-800. |
| [27] | Luo Y, Xie Y, Li W, Wei M, Dai T, Li Z, Wang B. Physiological and transcriptomic analyses reveal exogenous trehalose is involved in the responses of wheat roots to high temperature stress[J]. Plants, 2021, 10(12): 2644. |
| [28] | Luo Y, Wang Y, Xie Y, Gao Y, Li W, Lang S. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses of the effects of exogenous trehalose on heat tolerance in wheat[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(9): 5194. |
| [29] | Zhao D Q, Li T T, Hao Z J, Cheng M L, Tao J. Exogenous trehalose confers high temperature stress tolerance to herbaceous peony by enhancing antioxidant systems, activating photosynthesis, and protecting cell structure[J]. Cell Stress and Chaperones, 2019, 24(1): 247-257. |
| [30] | Chen L, Deng Y, Zhu H L, Hu Y X, Jiang Z G, Tang S, Wang S H, Ding Y F. The initiation of inferior grain filling is affected by sugar translocation efficiency in large panicle rice[J]. Rice, 2019, 12(1): 1-13. |
| [31] | Islam M N, Masud A A C, Alam M M, Islam M N, Rahman M L, Hasanuzzaman M. Osmolyte-induced water deficit stress mitigation during panicle initiation stage in transplanted rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Science Today, 2022, 9(1): 9-20. |
| [32] | 李敏, 罗德强, 江学海, 蒋明金, 李树杏, 姬广梅, 李立江, 周维佳. 高产氮高效型灿稻品种的籽粒灌浆特性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2020, 22(9): 22-30. |
| Li M, Luo D Q, Jiang X H, Jiang M J, Li S X, Ji G M, Li L J, Zhou W J. Grain filling characteristics of the ricecultivar with high yield and high nitrogen use efficieney[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Techrology, 2020, 22(9): 22-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 唐益平, 李向峰, 王辉, 胡王琴, 任楚婷, 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 尤翠翠, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权. 茎鞘非结构性碳水化合物对大穗型粳稻强、弱势粒灌浆与品质的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2021, 36(5): 107-117. |
| Tang Y P, Li X F, Wang H, Hu W Q, Ren C T, Huang Y R, Xu P, You C C, Ke J, He H B, Wu L Q. Effect of non-structural carbohydrate in stem and sheath on grain filling and quality of superior and inferior spikelets in large-panicle japonica rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2021, 36(5): 107-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 顾俊荣, 韩立宇, 董明辉, 陈培峰, 乔中英. 不同穗型粳稻干物质运转与颖花形成及籽粒灌浆结实的差异研究[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2017, 38(4): 68-73+88. |
| Gu J R, Han L Y, Dong M H, Chen P F, Qiao Z Y. Studies on the difference of dry matter accumulation and transportation, spikelets formation and the grain filling of Japonica rice varieties with different panicle types[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition, 2017, 38(4): 68-73+88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 朱庆森, 曹显祖, 骆亦其. 水稻籽粒灌浆的生长分析[J]. 作物学报, 1988, 14(3): 182-193. |
| Zhu Q S, Cao X Z, Luo Y Q. Growth analysis on process of grain filling in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1988, 14(3): 182-193. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Teng Z, Yu H, Wang G, Meng S, Liu B, Yi Y, Chen Y, Zheng Q, Liu L, Yang J, Duan M, Zhang J, Ye N. Synergistic interaction between ABA and IAA due to moderate soil drying promotes grain filling of inferior spikelets in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2022, 109(6): 1457-1472. |
| [37] | Okamura M, Arai-Sanoh Y, Yoshida H, Mukouyama T, Adachia S, Yabe S, Nakagawa H, Tsutsumi K, Taniguchi Y, Kobayashia N, Kondo M. Characterization of high-yielding rice cultivars with different grain-filling properties to clarify limiting factors for improving grain yield[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018, 219: 139-147. |
| [38] | Cock J H, Yoshida S. Accumulation of 14C-labelled carbohydrate before flowering and its subsequent redistribution and respiration in the rice plant[J]. Japanese Journal of Crop Science, 1972, 41(2): 226-234. |
| [39] | Tsukaguchi T, Horie T, Ohnishi M. Filling percentage of rice spikelets as affected by availability of non-structural carbohydrates at the initial phase of grain filling[J]. Japanese Journal of Crop Science, 1996, 65(3): 445-452. |
| [40] | Liang J S, Cao X Z, Zhang H Y, Song P, Zhu Q S. The changes and affecting factors of stem-sheath reserve contents of rice during grain filling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science. 1994, 8(3): 151-156. |
| [41] | Xie G H, Yang J C, Wang Z Q. Grain filling characteristics of rice and their relationships to physiological activities of grains[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica. 2001, 27(5): 557-565. |
| [42] | Murty P S S, Murty K S. Spikelet sterility in relation to nitrogen and carbohydrate contents in rice[J]. Indian J Plant Physiology, 1982, 25: 40-48. |
| [43] | Venkateswarlu B, Visperas R M. Source-sink relationships in crop plants: A review[J]. IRRI Research Paper Series, 1987, 125:1-19. |
| [44] | Garg A K, Kim J K, Owens T G, Ranwala A P, Choi Y D, Kochian L V, Wu R J. Trehalose accumulation in rice plants confers high tolerance levels to different abiotic stresses[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2002, 99(25): 15898-15903. |
| [45] | Shahbaz M, Abid A, Masood A, Waraich E A. Foliar-applied trehalose modulates growth, mineral nutrition, photosynthetic ability, and oxidative defense system of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under saline stress[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2017, 40(4): 584-599. |
| [46] | Fu J, Huang Z, Wang Z, Yang J, Zhang J. Pre-anthesis non-structural carbohydrate reserve in the stem enhances the sink strength of inferior spikelets during grain filling of rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2011, 123(2): 170-182. |
| [47] | Liang X G, Gao Z, Shen S, Panl M J, Zhang L, Zhao X, Lin S, Wu G, Chen X M, Zhou S L. Differential ear growth of two maize varieties to shading in the field environment: effects on whole plant carbon allocation and sugar starvation response[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2020, 251: 153194. |
| [48] | Eom J S, Cho J I, Reinders A, Lee S W, Yoo Y, Tuan P Q, Choi S B, Bang G, Park Y I, Cho M H, Bhoo S H, An G, Hahn T R, Ward J M, Jeon J S. Impaired function of the tonoplast-localized sucrose transporter in rice, OsSUT2, limits the transport of vacuolar reserve sucrose and affects plant growth[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 157(1): 109-119. |
| [49] | Aoki N, Hirose T, Scofield G N, Whitfeld P R, Furbank R T. The sucrose transporter gene family in rice[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2003, 44(3): 223-232. |
| [1] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [2] | 贾琰, 杨亮, 邹德堂, 瞿炤珺, 王敬国, 刘化龙, 王晋, 赵宏伟. 孕穗期冷水胁迫下施用外源物质对寒地粳稻氮光合效率及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 443-456. |
| [3] | 潘俊峰, 王博, 崔克辉, 黄见良, 聂立孝. 氮肥对水稻节间和叶鞘非结构性碳水化合物积累转运特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(3): 273-282. |
| [4] | 裴鹏刚, 张均华, 朱练峰, 胡志华, 金千瑜. 秸秆还田耦合施氮水平对水稻光合特性、氮素吸收及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(3): 282-290. |
| [5] | 张卫星#,孙成效#,闵捷,段彬伍,朱智伟*. 水稻生育中后期使用外源植酸对产量和米质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(6): 603-609. |
| [6] | 朱齐超,危常州* ,李美宁,朱金龙,吴诚,王佳. 氮肥运筹对膜下滴灌水稻生长和产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(4): 440-446. |
| [7] | 饶立华,薛建明,蒋德安,洪键,陈玉银. 钾营养对杂交稻光合作用动态及产量形成的效应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1990, 4(3): 106-112 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||