
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 703-710.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240906
• 研究报告 • 上一篇
杨行洲1,2, 崔苗苗1,2, 魏利辉2, 顾爱国3, 李东霞1, 乐秀虎1,*( ), 冯辉2,*(
), 冯辉2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-18
修回日期:2024-11-27
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-09-10
通讯作者:
*email: lexiuhu@163.com;email: fenghui@jaas.ac.cn
基金资助:
YANG Xingzhou1,2, CUI Miaomiao1,2, WEI Lihui2, GU Aiguo3, LI Dongxia1, LE Xiuhu1,*( ), FENG Hui2,*(
), FENG Hui2,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-18
Revised:2024-11-27
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-09-10
Contact:
*email: lexiuhu@163.com;email: fenghui@jaas.ac.cn
摘要:
【目的】miR3979-3p参与水稻响应多种生物和非生物胁迫,在拟禾本科根结线虫(Meloidogyne graminicola)侵染的根组织中下调表达,因此探究miR3979-3p对根结线虫与水稻互作中的作用具有重要意义。【方法】利用人工合成的双链miR3979(ds-miR3979)浸泡水稻根组织,采用qPCR测量水稻内源miR3979-3p的表达水平,通过平板接种和组织染色观察二龄幼虫的趋性和侵染能力,结合盆钵接种评价ds-miR3979处理对水稻根结产生和线虫发育的影响。【结果】100~800 nmol/L ds-miR3979处理12~24 h对二龄幼虫的运动活性无显著影响;与ddH2O处理的对照相比,400 nmol/L ds-miR3979浸泡根系12~24 h显著提高了立针期和三叶期水稻根系和叶片miR3979-3p的表达水平;连续显微观察2~8 h,发现二龄幼虫向水稻根尖移动趋性降低,集聚在根尖周围的线虫数量显著减少;同时,平板接种1~3 d侵入根内的线虫数量减少,盆钵接种7~21 d根系上的根结数目、根内雌虫数量和占比显著下降,且雌虫的发育进程延缓。【结论】人工合成的ds-miR3979可被水稻吸收并上调内源miR3979-3p表达,进而影响根结线虫的侵染和雌虫发育。
杨行洲, 崔苗苗, 魏利辉, 顾爱国, 李东霞, 乐秀虎, 冯辉. 外源miR3979处理水稻对拟禾本科根结线虫趋性、侵染和发育的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 703-710.
YANG Xingzhou, CUI Miaomiao, WEI Lihui, GU Aiguo, LI Dongxia, LE Xiuhu, FENG Hui. Effects of Exogenous miR3979 on Chemotaxis, Infection and Development of Root Knot Nematode Meloidogyne graminicola in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(5): 703-710.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5’-3’) Sequence(5’-3’) | 目的 Aim |
|---|---|---|
| miR3979-3p.RT | GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGCTTCTCTCC | RT-PCR |
| miR390-5p.RT | GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGGCGCT | |
| miR3979-3p.F | TCCCGCCTTCGGGGGAGGAG | qPCR |
| miR390-5p.F | TGACCAAAGCTCAGGAGGGAT | |
| Universal R | GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT |
表1 本研究所用引物
Table 1. Primers used in this study
| 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5’-3’) Sequence(5’-3’) | 目的 Aim |
|---|---|---|
| miR3979-3p.RT | GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGCTTCTCTCC | RT-PCR |
| miR390-5p.RT | GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGGCGCT | |
| miR3979-3p.F | TCCCGCCTTCGGGGGAGGAG | qPCR |
| miR390-5p.F | TGACCAAAGCTCAGGAGGGAT | |
| Universal R | GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT |
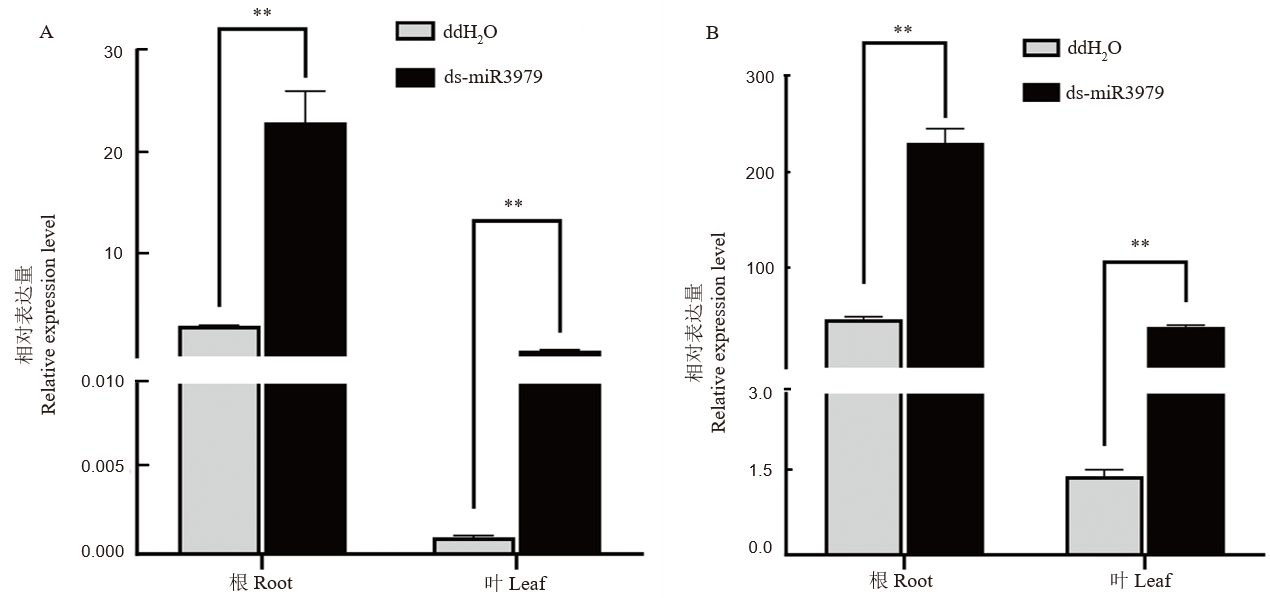
图2 ds-miR3979处理后水稻内源miR3979-3p水平 A~B, 400 nmol/L ds-miR3979浸泡水稻根系12 h(A)或24 h(B)后, minR3979-3P相对表达量,以ddH2O处理作为对照。每个处理3个重复;**, P<0.01。
Fig. 2. Relative expression of miR3979-3p in rice plants treated with ds-miR3979 solution A-B, Relative expression of miR3979-3p in roots and shoots of rice treated with 400 nmol/L ds-miR3979 solution for 12 h (A) or 24 h (B). Each treatment repeated three times. **, P < 0.01.
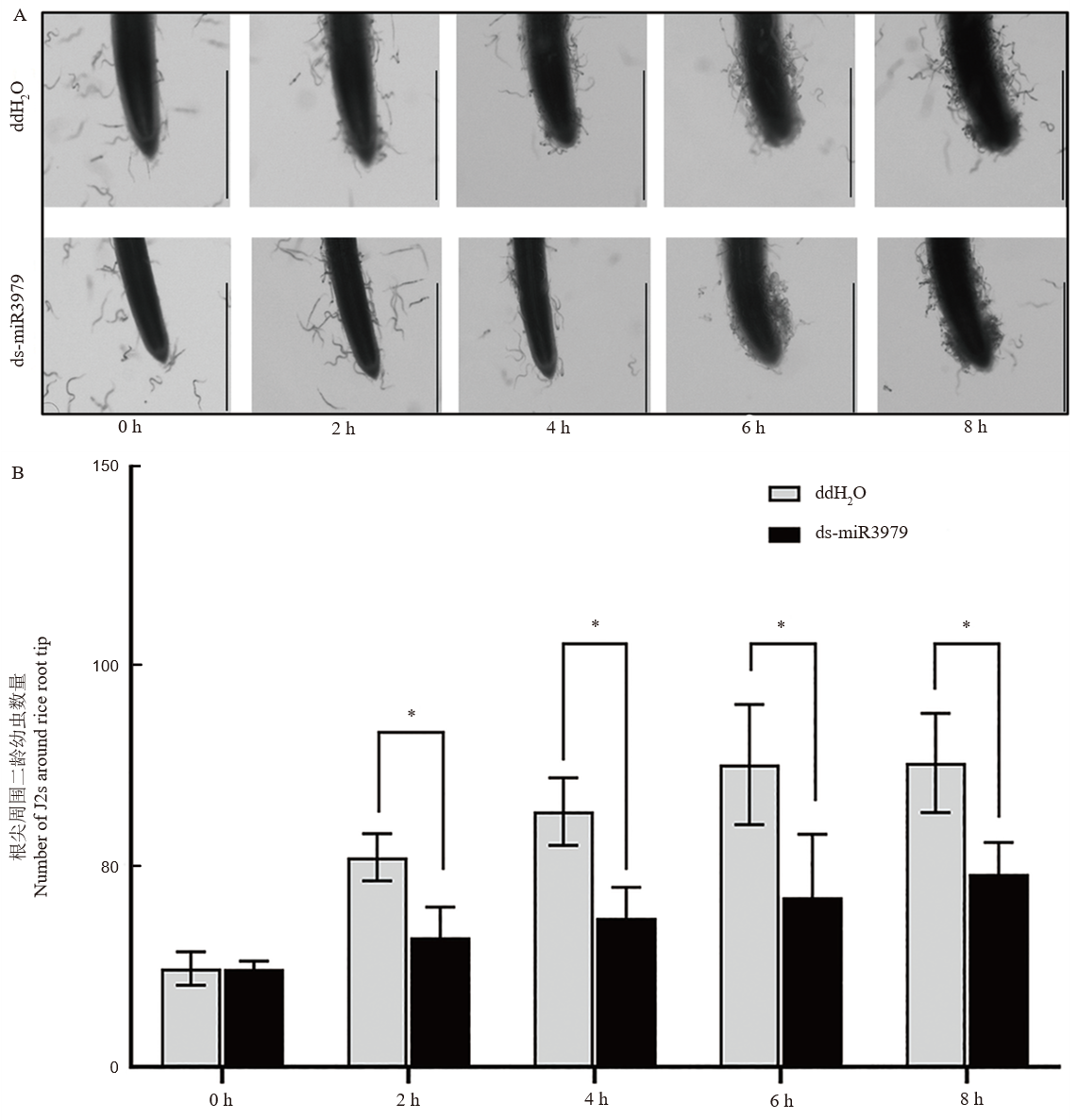
图3 ds-miR3979处理的水稻对二龄幼虫的趋性影响 A, 线虫向水稻根尖迁移观察;B, 聚集在水稻根尖周围的线虫数量。截取用400 nmol/L ds-miR3979浸泡水稻根系12 h的2 cm长根段用于实验,以ddH2O处理作为对照,每个处理5个重复。图中标尺=1 mm;*, P<0.05。
Fig. 3. Chems tabis of J2 towards rice roots treated with ds-miR3979 solution A. Chemotaxis of J2s towards rice root tips. B. Number of J2s around rice root tips. Rice roots were soaked into 400 nmol/L ds-miR3979 solution or ddH2O for 12 h and then cut into 2 cm length for the assay. Each treatment repeated three times. Scale bar = 1 mm; *, P < 0.05.
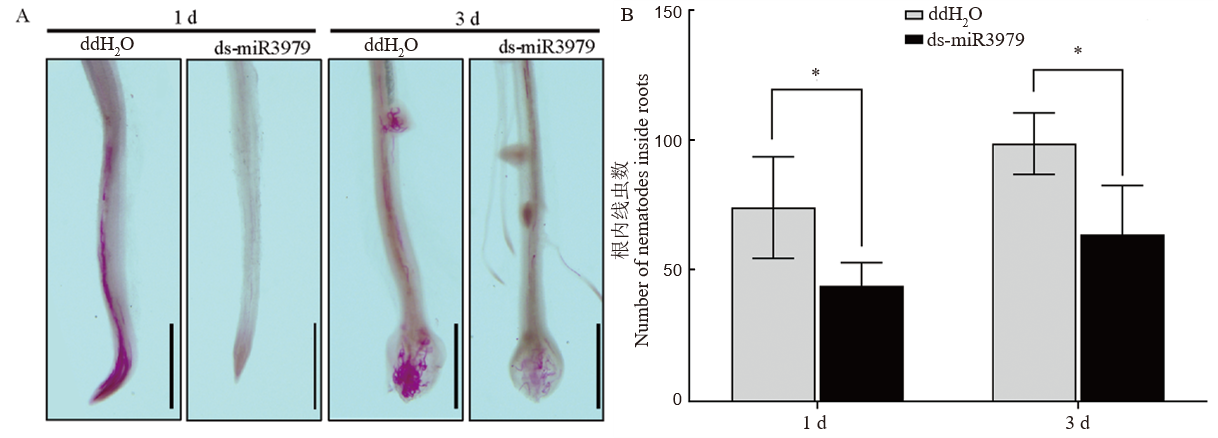
图4 ds-miR3979处理水稻对二龄幼虫早期侵入的影响 A, 接种后1 d和3 d侵入根部线虫染色观察;B, 接种后1 d和3 d侵入根部的线虫数量调查。400 nmol/L ds-miR3979浸泡水稻根系12 h后接种线虫,同时以ddH2O处理作为对照。每个处理6个重复。图中标尺=1 mm;*, P<0.05。
Fig. 4. Early infection of J2 in rice roots treated with ds-miR3979 solution A, J2s inside the roots stained with acid fuchsin at 1 and 3 days after inoculation (dpi); B, Number of J2s in roots at 1 and 3 days after inoculation. Rice root were soaked into 400 nmol/L ds-miR3979 solution or ddH2O for 12 h. Each treatment repeated six times. Scale = 1 mm. *, P < 0.05.
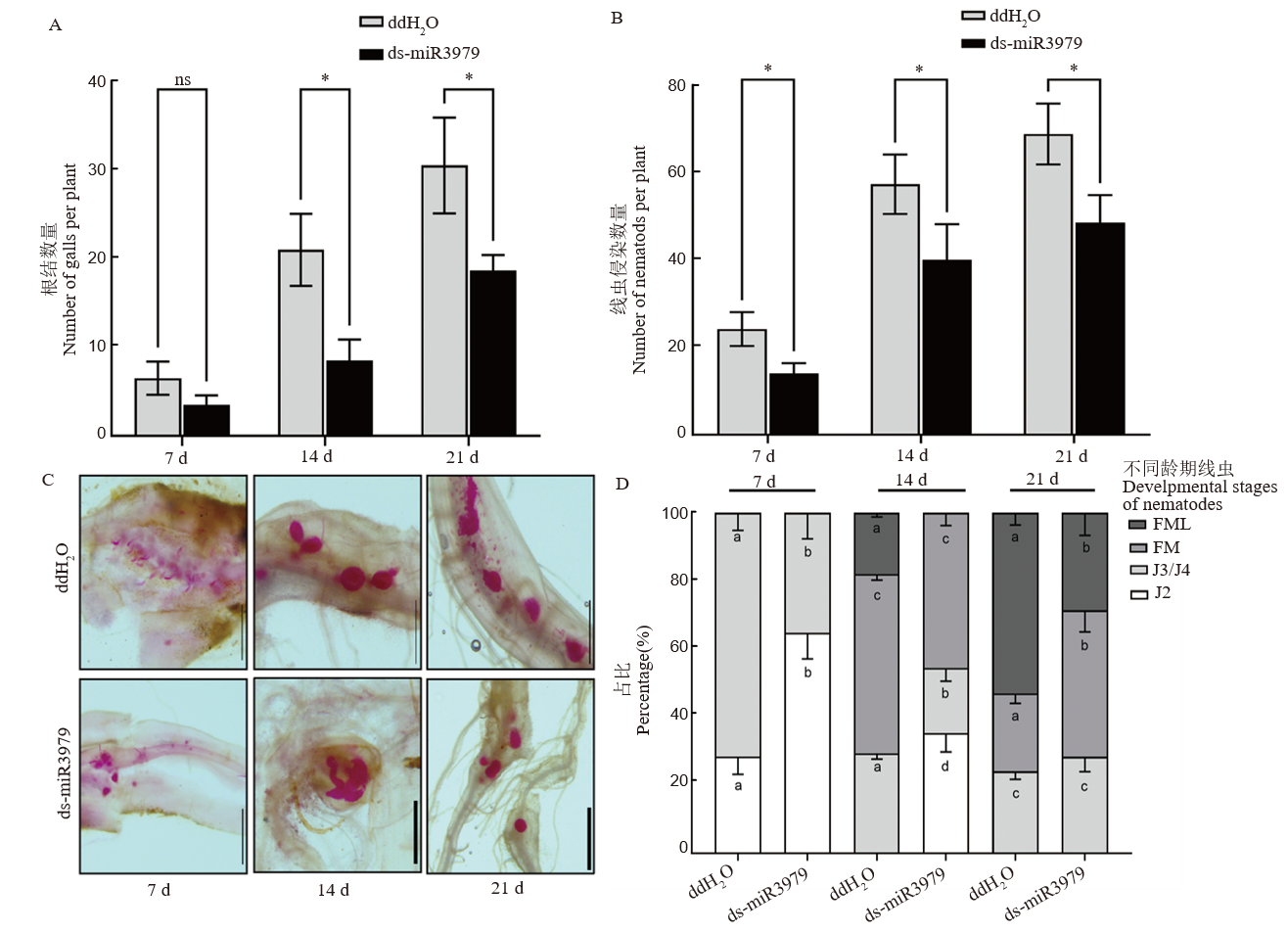
图5 ds-miR3979处理水稻对拟禾本科根结线虫发育影响 A~B: 线虫接种不同时间诱导的根结数量(A)和根系线虫侵染数量(B); C: 根内线虫染色观察; D: 根内不同发育阶段线虫百分占比。J2和J3/4: 二龄和三/四龄幼虫; FM: 正在发育的雌虫; FML: 正在产卵的雌虫。400 nmol/L ds-miR3979浸泡水稻根系24 h后接种线虫,同时以ddH2O处理作为对照,每个处理6个重复。图中标尺=1 mm;不同小写字母表示同一接种时间同一龄期线虫百分占比的差异显著性(P<0.05);ns表示无显著差异;*, P<0.05。
Fig. 5. Development of M. graminicola in rice treated with ds-miR3979 solution A and B, Number of galls (A) and nematodes (B) in roots at 7, 14, and 21 day after inoculation (dpi); C, Nematodes in the roots stained with acid fuchsin; D, percentage of different stages of nematodes in the roots. J2, Second stage juvenile; J3/4, Third/fourth stage juvenile; FM, Developing female, FML, Egg-caying female. Rice roots were soaked into 400 nmol/L ds-miR3979 solution or ddH2O for 24 h. Each treatment repeated six times. Scale = 1 mm. Different letters in a column (D) indicate significant difference for identical developmental stages between control and treatment at the same time point at P<0.05; ns, No significant difference; *, P<0.05.
| [1] | Bologna N G, Voinnet O. The diversity, biogenesis, and activities of endogenous silencing small RNAs in Arabidopsis[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2014, 65: 473-503. |
| [2] | Borges F, Martienssen R A. The expanding world of small RNAs in plants[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2015, 16(12): 727-741. |
| [3] | Molnar A, Melnyk C, Baulcombe D C. Silencing signals in plants: A long journey for small RNAs[J]. Genome Biology, 2011, 12(1): 215. |
| [4] | Li S, Wang X, Xu W, Liu T, Cai C, Chen L, Clark C B, Ma J. Unidirectional movement of small RNAs from shoots to roots in interspecific heterografts[J]. Nature Plants, 2021, 7(1): 50-59. |
| [5] | Betti F, Ladera-Carmona M J, Weits D A, Ferri G, Iacopino S, Novi G, Svezia B, Kunkowska A B, Santaniello A, Piaggesi A, Loreti E, Perata P. Exogenous miRNAs induce post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants[J]. Nature Plants, 2021, 7(10): 1379-1388. |
| [6] | Li T, Li H, Zhang Y X, Liu J Y. Identification and analysis of seven H₂O₂-responsive miRNAs and 32 new miRNAs in the seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica)[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 39(7): 2821-2833. |
| [7] | Nguyen D Q, Nguyen N L, Nguyen V T, Tran T H G, Nguyen T H, Nguyen T K L, Nguyen H H. Comparative analysis of microRNA expression profiles in shoot and root tissues of contrasting rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.) with different salt stress tolerance[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(5): e0286140. |
| [8] | Bakhshi B, Mohseni Fard E, Nikpay N, Ali Ebrahimi M, Bihamta M R, Mardi M, Salekdeh G H. microRNA signatures of drought signaling in rice root[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(6): e0156814. |
| [9] | Liu Q, Zhang H. Molecular identification and analysis of arsenite stress-responsive miRNAs in rice[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2012, 60(26): 6524-6536. |
| [10] | Sato Y, Nosaka-Takahashi M, Suzuki T, Shimizu-Sato S. Small RNAs in Rice: Molecular Species and Their Functions[M]. Rice Genomics, Genetics and Breeding, Singapore: Springer Nature, 2018: 21-36. |
| [11] | Xu D, Mou G, Wang K, Zhou G. MicroRNAs responding to southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus infection and their target genes associated with symptom development in rice[J]. Virus Research, 2014, 190: 60-68. |
| [12] | Wu Y, Lü W, Hu L, Rao W, Zeng Y, Zhu L, He Y, He G. Identification and analysis of brown planthopper-responsive microRNAs in resistant and susceptible rice plants[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 8712. |
| [13] | Javed M, Reddy B, Sheoran N, Ganesan P, Kumar A. Unraveling the transcriptional network regulated by miRNAs in blast-resistant and blast-susceptible rice genotypes during Magnaporthe oryzae interaction[J]. Gene, 2023, 886: 147718. |
| [14] | Jeong D H, Park S, Zhai J, Gurazada S G R, De Paoli E, Meyers B C, Green P J. Massive analysis of rice small RNAs: Mechanistic implications of regulated microRNAs and variants for differential target RNA cleavage[J]. The Plant Cell, 2011, 23(12): 4185-4207. |
| [15] | Mantelin S, Bellafiore S, Kyndt T. Meloidogyne graminicola: A major threat to rice agriculture[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2016, 18: 3-15. |
| [16] | Kyndt T, Fernandez D, Gheysen G. Plant-parasitic nematode infections in rice: Molecular and cellular insights[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2014, 52: 135-153. |
| [17] | 刘国坤, 肖顺, 张绍升, 张敦富, 王玉. 拟禾本科根结线虫对水稻根系的侵染特性及其生活史[J]. 热带作物学报, 2011, 32(4): 743-748. |
| Liu G K, Xiao S, Zhang S S, Zhang D F, Wang Y. Infection characteristics and life cycle of Meloidogyne graminicola on rice roots[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2011, 32(4): 743-748. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Niu Y, Xiao L, de Almeida-Engler J, Gheysen G, Peng D, Xiao X, Huang W, Wang G, Xiao Y. Morphological characterization reveals new insights into giant cell development of Meloidogyne graminicola on rice[J]. Planta, 2022, 255(3): 70. |
| [19] | Verstraeten B, Atighi M R, Ruiz-Ferrer V, Escobar C, de Meyer T, Kyndt T. Non-coding RNAs in the interaction between rice and Meloidogyne graminicola[J]. BMC Genomics, 2021, 22(1): 560. |
| [20] | Hui F, Zhou C R, Zhu F, Le X H, Jing D D, Daly P, Zhou D M, Wei L H. Resistance analysis of the rice variety Huaidao 5 against root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2023, 22(10): 3081-3089. |
| [21] | 冯辉, 聂国嫒, 陈曦, 张金凤, 周冬梅, 魏利辉. 拟禾谷根结线虫江苏分离群体形态学和分子鉴定[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2017, 33(4): 794-801. |
| Feng H, Nie G A, Chen X, Zhang J F, Zhou D M, Wei L H. Morphological and molecular identification of Meloidogyne graminicola isolates from Jiangsu Province[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 33(4): 794-801. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Wang C, Lower S, Williamson V M. Application of Pluronic gel to the study of root-knot nematode behaviour[J]. Nematology, 2009, 11(3): 453-464. |
| [23] | Cuperus J T, Fahlgren N, Carrington J C. Evolution and functional diversification of MIRNA genes[J]. The Plant Cell, 2011, 23(2): 431-442. |
| [24] | Schmittgen T D, Livak K J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method[J]. Nat Protocols, 2008, 3(6): 1101-1108. |
| [25] | Koeppe S, Kawchuk L, Kalischuk M. RNA Interference past and future applications in plants[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(11): 9755. |
| [26] | Bilir Ö, Göl D, Hong Y, McDowell J M, Tör M. Small RNA-based plant protection against diseases[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 951097. |
| [27] | Dalakouras A, Wassenegger M, Dadami E, Ganopoulos I, Pappas M L, Papadopoulou K. Genetically modified organism-free RNA interference: Exogenous application of RNA molecules in plants[J]. Plant Physiology, 2020, 182(1): 38-50. |
| [28] | Niu D, Hamby R, Sanchez J N, Cai Q, Yan Q, Jin H. RNAs: A new frontier in crop protection[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2021, 70: 204-212. |
| [29] | 王帅, 魏钰洋, 张羲, 谢佳, 胡展, 孙然锋. 根结线虫趋化性研究进展[J]. 农药学学报, 2022, 24(5): 982-996. DOI: 10.16801/j.issn.1008-7303.2022.0090. |
| Wang S, Wei Y Y, Zhang X, Xie J, Hu Z, Sun R F. Research progress on chemotaxis of root-knot nematodes[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2022, 24(5): 982-996. DOI: 10.16801/j.issn.1008-7303.2022.0090. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Ghorbanzadeh Z, Hamid R, Jacob F, Mirzaei M, Zeinalabedini M, Abdirad S, Atwell B J, Haynes P A, Ghafari M R, Salekdeh G H. MicroRNA profiling of root meristematic zone in contrasting genotypes reveals novel insight into rice response to water deficiency[J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2022, 42(6): 3814-3834. |
| [31] | 张静文. 普通野生稻(Oryza rufipogon Griff.)干旱胁迫相关的 microRNAs 的鉴定与功能分析[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017. |
| Zhang J W. Identification and functional analysis of drought stress-related microRNAs in Oryza rufipogon Griff.[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | Chowdhury A T, Hasan M N, Bhuiyan F H, Islam M Q, Nayon M R W, Rahaman M M, Hoque H, Jewel N A, Ashrafuzzaman M, Prodhan S H. Identification, characterization of Apyrase (APY) gene family in rice (Oryza sativa) and analysis of the expression pattern under various stress conditions[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(5): e0273592. |
| [1] | 王娟, 吴丽娟, 洪海波, 姚志文, 王磊, 鄂志国. 水稻泛素结合酶E2的生物学功能研究进展 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 744-750. |
| [2] | 陶士博, 许娜, 徐正进, 刘畅, 徐铨. 水稻发芽期耐冷基因Cold6的克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 751-759. |
| [3] | 陈伟, 叶元妹, 赵剑华, 冯志明, 陈宗祥, 胡珂鸣, 左示敏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术改良南粳46抽穗期 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 760-770. |
| [4] | 侯桂花, 周立国, 雷建国, 陈虹, 聂元元. 水稻OsRDR5基因功能及作用机制初步解析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 779-788. |
| [5] | 李荣欣, 王波, 肖素勤, 殷富有, 张建红, 钟巧芳, 陈玲, 李金璐, 杨和生, 程在全, 刘丽. 野生稻叶绿体基因组组装与密码子偏好性分析及系统发育研究 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 801-812. |
| [6] | 陆帅, 陶涛, 刘冉, 周文玉, 曹蕾, 杨青青, 张明秋, 任鑫哲, 杨芝笛, 徐福祥, 环海东, 龚远航, 张皓程, 金素奎, 蔡秀玲, 高继平, 冷语佳. 水稻长护颖小粒突变体lsg8的表型鉴定与基因克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 813-824. |
| [7] | 邓欢, 刘亚培, 王春连, 郭威, 陈析丰, 纪志远. 水稻抗白叶枯病新基因Xa49(t)的定位分析 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 825-831. |
| [8] | 郝雯倩, 蔡兴菁, 杨海东, 吴宇阳, 滕轩, 薛超, 龚志云. 不同类型组蛋白修饰在水稻响应非生物胁迫中的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 575-585. |
| [9] | 王镜博, 苏畅, 冯晶, 姜思旭, 徐海, 崔志波, 赵明辉. 水稻OsAlR1基因耐铝性功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 615-623. |
| [10] | 韶也, 胡远艺, 彭彦, 毛毕刚, 刘慧敏, 唐婵娟, 雷斌, 唐丽, 余丽霞, 李文建, 罗武中, 罗治斌, 袁远涛, 李曜魁, 张丹, 周利斌, 柏连阳, 唐文帮, 赵炳然. 基于M1TDS靶向筛选技术的重离子束诱变定向改良杂交水稻卓两优1126性状的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 624-634. |
| [11] | 徐群, 王珊, 袁筱萍, 金石桥, 晋芳, 郝万军, 吴小碧, 冯跃, 余汉勇, 孙燕飞, 杨窑龙, 魏兴华. 用于水稻品种真实性验证的SNP位点评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 635-642. |
| [12] | 张海鹏, 李莞意, 廖福兴, 马美子, 张洪程, 杨艳菊. 纳米钼对水稻根系形态生理和硝态氮吸收的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 650-664. |
| [13] | 刘钰婷, 周星, 何辰延, 李秋萍, 艾小凤, 袁玉洁, 刘睿, 杨景文, 刘婷婷, 王丽, 程红, 黄蓉, 李奥运, 胡文, 胡忠, 任万军, 邓飞. 不同光照条件下减穴稳苗配置对水稻茎鞘干物质积累转运特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 665-678. |
| [14] | 朱鹏, 凌溪铁, 王金彦, 张保龙, 杨郁文, 许轲, 裘实. 机直播条件下不同控草方式对抗除草剂水稻产量和品质差异性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 501-515. |
| [15] | 董立强, 张义凯, 杨铁鑫, 冯莹莹, 马亮, 梁潇, 张玉屏, 李跃东. 北方粳稻密苗机插育秧对秧苗素质及取秧特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 516-528. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||