
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 801-812.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240612
李荣欣1,2, 王波2, 肖素勤2, 殷富有2, 张建红3, 钟巧芳2, 陈玲2, 李金璐2, 杨和生3, 程在全2,*( ), 刘丽2,*(
), 刘丽2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-19
修回日期:2024-07-12
出版日期:2025-11-10
发布日期:2025-11-19
通讯作者:
* email:czquan-99@163.com;liuliyaas@163.com
基金资助:
LI Rongxin1,2, WANG Bo2, XIAO Suqin2, YIN Fuyou2, ZHANG Jianhong3, ZHONG Qiaofang2, CHEN Ling2, LI Jinlu2, YANG Hesheng3, CHENG Zaiquan2,*( ), LIU Li2,*(
), LIU Li2,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-19
Revised:2024-07-12
Online:2025-11-10
Published:2025-11-19
Contact:
* email:czquan-99@163.com;liuliyaas@163.com
摘要:
【目的】疣粒野生稻是稻属中唯一的旱生且保存较多原始性状的耐荫野生稻。本研究旨在丰富疣粒野生稻的遗传基础,为疣粒野生稻优异基因的载体构建提供信息参考。【方法】采用二代测序技术对云南疣粒野生稻叶绿体基因组进行测序、组装和注释,进而运用RStudio和MEGA分析其密码子偏好性及系统发育。【结果】疣粒野生稻叶绿体基因组全长135,937 bp,总GC含量39.0%,有效密码子(ENC)平均值为48.09,密码子偏好性较弱;ENC-plot、PR2-plot及中性绘图分析显示选择压力对疣粒野生稻叶绿体基因组密码子偏好性有重要决定作用,且密码子偏好性主要调控自我复制与光合系统相关基因;共鉴定出16个优势密码子,其中14个以A/U结尾,2个以G/C结尾;通过系统发育分析明确了疣粒野生稻叶绿体基因组与短药野生稻的亲缘关系较近。【结论】本研究丰富了疣粒野生稻基因组的基本组成和遗传信息,为水稻优异光合基因挖掘及物种进化研究奠定了基础。
李荣欣, 王波, 肖素勤, 殷富有, 张建红, 钟巧芳, 陈玲, 李金璐, 杨和生, 程在全, 刘丽. 野生稻叶绿体基因组组装与密码子偏好性分析及系统发育研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 801-812.
LI Rongxin, WANG Bo, XIAO Suqin, YIN Fuyou, ZHANG Jianhong, ZHONG Qiaofang, CHEN Ling, LI Jinlu, YANG Hesheng, CHENG Zaiquan, LIU Li. Assembly, Codon Usage Bias, and Phylogenetic Analysis of Chloroplast Genome of Oryza meyeriana[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 801-812.
| 种类 Category | 基因分组 Gene group | 基因名 Gene name |
|---|---|---|
| 光合系统 Photosynthesis | 光系统Ⅰ Subunits of photosystem Ⅰ | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ |
| 光系统Ⅱ Subunits of photosystem Ⅱ | psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ | |
| NADH脱氢酶亚基 Subunits of NADH dehydrogenase | ndhA*, ndhB*(2), ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH(2), ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK | |
| 细胞色素b/f复合体亚基 Subunits of cytochrome b/f complex | petA, petB*, petD*, petG, petL, petN | |
| ATP合成酶 Subunits of ATP synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, atpF*, atpH, atpI | |
| Rubisco大亚基 Large subunit of rubisco | rbcL | |
| 自我复制 Self-replication | 核糖体蛋白大亚基 Large ribosomal subunit | rpl14, rpl16*, rpl2*(2), rpl20, rpl22, rpl23(2), rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 |
| 核糖体蛋白小亚基 Small ribosomal subunit | rps11, rps12*(3), rps14, rps15(2), rps16*, rps18, rps19(2), rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7(2), rps8 | |
| RNA聚合酶亚基 Subunits of RNA polymerase | rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1, rpoC2 | |
| 核糖体RNA Ribosomal RNAs | rrn16S(2), rrn23S(2), rrn4.5S(2), rrn5S(2) | |
| 转运RNA Transfer RNAs | trnA-UGC*(2), trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnG-UCC, trnH-GUG(2), trnI-CAU(2), trnI-GAU*(2), trnK-UUU*, trnL-CAA(2), trnL-UAA*, trnL-UAG, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU(2), trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG(2), trnR-UCU, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC(2), trnV-UAC*, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA, trnfM-CAU | |
| 其他基因 Other gene | 成熟酶 Maturase | matK |
| 蛋白酶 Protease | clpP | |
| 外膜蛋白 Envelope membrane protein | cemA | |
| 乙酰辅酶A羧化酶亚基 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase | accD | |
| c型细胞色素合成基因 Synthesis factor of c-cytochrome | ccsA | |
| 翻译起始因子 Initiation factor of translation | infA | |
| 未知功能基因 Unknown function gene | 保守开放阅读框 Conserve open reading frame | ycf3**, ycf4, ycf68(2) |
| *:有一个内含子的基因; **:有两个内含子的基因;括号中数字表示多拷贝基因的拷贝数。 *, Gene with one intron; **, Gene with two introns; Values in the brackets refer to number of copies of multi-copy genes. | ||
表1 疣粒野生稻叶绿体基因组基因注释
Table 1. The gene annotation of chloroplast genome of Oryza meyeriana
| 种类 Category | 基因分组 Gene group | 基因名 Gene name |
|---|---|---|
| 光合系统 Photosynthesis | 光系统Ⅰ Subunits of photosystem Ⅰ | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ |
| 光系统Ⅱ Subunits of photosystem Ⅱ | psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ | |
| NADH脱氢酶亚基 Subunits of NADH dehydrogenase | ndhA*, ndhB*(2), ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH(2), ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK | |
| 细胞色素b/f复合体亚基 Subunits of cytochrome b/f complex | petA, petB*, petD*, petG, petL, petN | |
| ATP合成酶 Subunits of ATP synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, atpF*, atpH, atpI | |
| Rubisco大亚基 Large subunit of rubisco | rbcL | |
| 自我复制 Self-replication | 核糖体蛋白大亚基 Large ribosomal subunit | rpl14, rpl16*, rpl2*(2), rpl20, rpl22, rpl23(2), rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 |
| 核糖体蛋白小亚基 Small ribosomal subunit | rps11, rps12*(3), rps14, rps15(2), rps16*, rps18, rps19(2), rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7(2), rps8 | |
| RNA聚合酶亚基 Subunits of RNA polymerase | rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1, rpoC2 | |
| 核糖体RNA Ribosomal RNAs | rrn16S(2), rrn23S(2), rrn4.5S(2), rrn5S(2) | |
| 转运RNA Transfer RNAs | trnA-UGC*(2), trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnG-UCC, trnH-GUG(2), trnI-CAU(2), trnI-GAU*(2), trnK-UUU*, trnL-CAA(2), trnL-UAA*, trnL-UAG, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU(2), trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG(2), trnR-UCU, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC(2), trnV-UAC*, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA, trnfM-CAU | |
| 其他基因 Other gene | 成熟酶 Maturase | matK |
| 蛋白酶 Protease | clpP | |
| 外膜蛋白 Envelope membrane protein | cemA | |
| 乙酰辅酶A羧化酶亚基 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase | accD | |
| c型细胞色素合成基因 Synthesis factor of c-cytochrome | ccsA | |
| 翻译起始因子 Initiation factor of translation | infA | |
| 未知功能基因 Unknown function gene | 保守开放阅读框 Conserve open reading frame | ycf3**, ycf4, ycf68(2) |
| *:有一个内含子的基因; **:有两个内含子的基因;括号中数字表示多拷贝基因的拷贝数。 *, Gene with one intron; **, Gene with two introns; Values in the brackets refer to number of copies of multi-copy genes. | ||
| 基因 Gene | GC1(%) | GC2(%) | GC3(%) | GC_all(%) | 有效密 码子数 ENC | 基因 Gene | GC1(%) | GC2(%) | GC3(%) | GC_all(%) | 有效密码子数ENC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rps12 | 53.78 | 48.74 | 27.73 | 43.42 | 46.66 | petA | 53.89 | 35.20 | 33.64 | 40.91 | 48.83 |
| psbA | 49.44 | 43.22 | 35.03 | 42.56 | 39.47 | rps18 | 34.76 | 39.02 | 26.83 | 33.54 | 42.30 |
| matK | 41.07 | 31.68 | 30.76 | 34.50 | 47.22 | rpl20 | 41.67 | 39.17 | 30.00 | 36.94 | 55.84 |
| psbD | 53.11 | 43.50 | 36.72 | 44.44 | 46.90 | clpP | 53.00 | 38.25 | 39.17 | 43.47 | 52.57 |
| psbC | 53.59 | 44.94 | 33.12 | 43.88 | 44.81 | psbB | 54.22 | 46.17 | 32.02 | 44.14 | 47.85 |
| rpoB | 49.91 | 38.20 | 31.60 | 39.90 | 49.02 | petB | 48.61 | 41.20 | 29.17 | 39.66 | 42.27 |
| rpoC1 | 49.34 | 38.21 | 30.01 | 39.19 | 50.15 | petD | 51.55 | 39.13 | 30.43 | 40.37 | 48.26 |
| rpoC2 | 48.37 | 36.36 | 31.12 | 38.62 | 50.40 | rpoA | 46.15 | 36.69 | 29.59 | 37.48 | 50.54 |
| rps2 | 40.93 | 40.93 | 33.33 | 38.40 | 50.78 | rps11 | 50.00 | 57.64 | 22.22 | 43.29 | 41.59 |
| atpI | 47.58 | 36.29 | 32.26 | 38.71 | 50.79 | infA | 45.37 | 37.04 | 42.59 | 41.67 | 61.00 |
| atpF | 47.83 | 33.70 | 32.07 | 37.86 | 48.81 | rps8 | 41.61 | 41.61 | 27.74 | 36.98 | 41.83 |
| atpA | 55.91 | 39.96 | 31.10 | 42.32 | 46.79 | rpl14 | 54.84 | 37.10 | 26.61 | 39.52 | 53.66 |
| rps14 | 41.35 | 45.19 | 32.69 | 39.74 | 40.55 | rpl16 | 51.09 | 54.01 | 26.28 | 43.80 | 37.23 |
| psaB | 48.57 | 43.13 | 33.74 | 41.81 | 49.64 | rps3 | 43.75 | 30.00 | 25.42 | 33.06 | 46.49 |
| psaA | 52.06 | 43.54 | 36.09 | 43.90 | 49.60 | rpl22 | 40.00 | 36.67 | 34.67 | 37.11 | 46.54 |
| ycf3 | 47.95 | 37.43 | 33.33 | 39.57 | 58.34 | ndhB | 42.27 | 38.94 | 33.07 | 38.10 | 46.72 |
| rps4 | 48.51 | 37.13 | 25.74 | 37.13 | 49.23 | rps7 | 50.32 | 45.22 | 23.57 | 39.70 | 47.03 |
| ndhJ | 48.75 | 36.88 | 31.87 | 39.17 | 48.30 | ndhH | 50.76 | 34.52 | 27.92 | 37.73 | 47.00 |
| ndhK | 42.11 | 43.72 | 30.36 | 38.73 | 47.60 | ndhF | 37.69 | 38.78 | 25.31 | 33.92 | 44.56 |
| ndhC | 52.07 | 34.71 | 32.23 | 39.67 | 59.96 | ccsA | 33.85 | 40.99 | 26.40 | 33.75 | 43.62 |
| atpE | 52.90 | 39.13 | 36.23 | 42.75 | 57.29 | ndhD | 40.52 | 36.73 | 31.74 | 36.33 | 45.12 |
| atpB | 54.71 | 41.48 | 30.46 | 42.22 | 47.32 | ndhE | 40.20 | 32.35 | 25.49 | 32.68 | 50.51 |
| rbcL | 57.53 | 43.93 | 31.59 | 44.35 | 47.59 | ndhG | 46.89 | 34.46 | 25.42 | 35.59 | 41.40 |
| ycf4 | 49.46 | 40.32 | 34.95 | 41.58 | 46.13 | ndhI | 38.12 | 38.67 | 28.73 | 35.17 | 50.78 |
| cemA | 42.42 | 27.71 | 32.03 | 34.05 | 51.88 | ndhA | 42.70 | 36.64 | 25.07 | 34.80 | 44.99 |
| GC1, GC2, GC3和GC_all分别代表第1位、第2位、第3位碱基和所有碱基GC含量。下同。 GC1, GC2, GC3, and GC_all represent the GC content of the first, second, and third codon positions as well as the overall GC content of all bases, respectively. The same below. | |||||||||||
表2 疣粒野生稻叶绿体基因组基因的有效密码子数
Table 2. Effective number of codon of chloroplast genome of Oryza meyeriana
| 基因 Gene | GC1(%) | GC2(%) | GC3(%) | GC_all(%) | 有效密 码子数 ENC | 基因 Gene | GC1(%) | GC2(%) | GC3(%) | GC_all(%) | 有效密码子数ENC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rps12 | 53.78 | 48.74 | 27.73 | 43.42 | 46.66 | petA | 53.89 | 35.20 | 33.64 | 40.91 | 48.83 |
| psbA | 49.44 | 43.22 | 35.03 | 42.56 | 39.47 | rps18 | 34.76 | 39.02 | 26.83 | 33.54 | 42.30 |
| matK | 41.07 | 31.68 | 30.76 | 34.50 | 47.22 | rpl20 | 41.67 | 39.17 | 30.00 | 36.94 | 55.84 |
| psbD | 53.11 | 43.50 | 36.72 | 44.44 | 46.90 | clpP | 53.00 | 38.25 | 39.17 | 43.47 | 52.57 |
| psbC | 53.59 | 44.94 | 33.12 | 43.88 | 44.81 | psbB | 54.22 | 46.17 | 32.02 | 44.14 | 47.85 |
| rpoB | 49.91 | 38.20 | 31.60 | 39.90 | 49.02 | petB | 48.61 | 41.20 | 29.17 | 39.66 | 42.27 |
| rpoC1 | 49.34 | 38.21 | 30.01 | 39.19 | 50.15 | petD | 51.55 | 39.13 | 30.43 | 40.37 | 48.26 |
| rpoC2 | 48.37 | 36.36 | 31.12 | 38.62 | 50.40 | rpoA | 46.15 | 36.69 | 29.59 | 37.48 | 50.54 |
| rps2 | 40.93 | 40.93 | 33.33 | 38.40 | 50.78 | rps11 | 50.00 | 57.64 | 22.22 | 43.29 | 41.59 |
| atpI | 47.58 | 36.29 | 32.26 | 38.71 | 50.79 | infA | 45.37 | 37.04 | 42.59 | 41.67 | 61.00 |
| atpF | 47.83 | 33.70 | 32.07 | 37.86 | 48.81 | rps8 | 41.61 | 41.61 | 27.74 | 36.98 | 41.83 |
| atpA | 55.91 | 39.96 | 31.10 | 42.32 | 46.79 | rpl14 | 54.84 | 37.10 | 26.61 | 39.52 | 53.66 |
| rps14 | 41.35 | 45.19 | 32.69 | 39.74 | 40.55 | rpl16 | 51.09 | 54.01 | 26.28 | 43.80 | 37.23 |
| psaB | 48.57 | 43.13 | 33.74 | 41.81 | 49.64 | rps3 | 43.75 | 30.00 | 25.42 | 33.06 | 46.49 |
| psaA | 52.06 | 43.54 | 36.09 | 43.90 | 49.60 | rpl22 | 40.00 | 36.67 | 34.67 | 37.11 | 46.54 |
| ycf3 | 47.95 | 37.43 | 33.33 | 39.57 | 58.34 | ndhB | 42.27 | 38.94 | 33.07 | 38.10 | 46.72 |
| rps4 | 48.51 | 37.13 | 25.74 | 37.13 | 49.23 | rps7 | 50.32 | 45.22 | 23.57 | 39.70 | 47.03 |
| ndhJ | 48.75 | 36.88 | 31.87 | 39.17 | 48.30 | ndhH | 50.76 | 34.52 | 27.92 | 37.73 | 47.00 |
| ndhK | 42.11 | 43.72 | 30.36 | 38.73 | 47.60 | ndhF | 37.69 | 38.78 | 25.31 | 33.92 | 44.56 |
| ndhC | 52.07 | 34.71 | 32.23 | 39.67 | 59.96 | ccsA | 33.85 | 40.99 | 26.40 | 33.75 | 43.62 |
| atpE | 52.90 | 39.13 | 36.23 | 42.75 | 57.29 | ndhD | 40.52 | 36.73 | 31.74 | 36.33 | 45.12 |
| atpB | 54.71 | 41.48 | 30.46 | 42.22 | 47.32 | ndhE | 40.20 | 32.35 | 25.49 | 32.68 | 50.51 |
| rbcL | 57.53 | 43.93 | 31.59 | 44.35 | 47.59 | ndhG | 46.89 | 34.46 | 25.42 | 35.59 | 41.40 |
| ycf4 | 49.46 | 40.32 | 34.95 | 41.58 | 46.13 | ndhI | 38.12 | 38.67 | 28.73 | 35.17 | 50.78 |
| cemA | 42.42 | 27.71 | 32.03 | 34.05 | 51.88 | ndhA | 42.70 | 36.64 | 25.07 | 34.80 | 44.99 |
| GC1, GC2, GC3和GC_all分别代表第1位、第2位、第3位碱基和所有碱基GC含量。下同。 GC1, GC2, GC3, and GC_all represent the GC content of the first, second, and third codon positions as well as the overall GC content of all bases, respectively. The same below. | |||||||||||
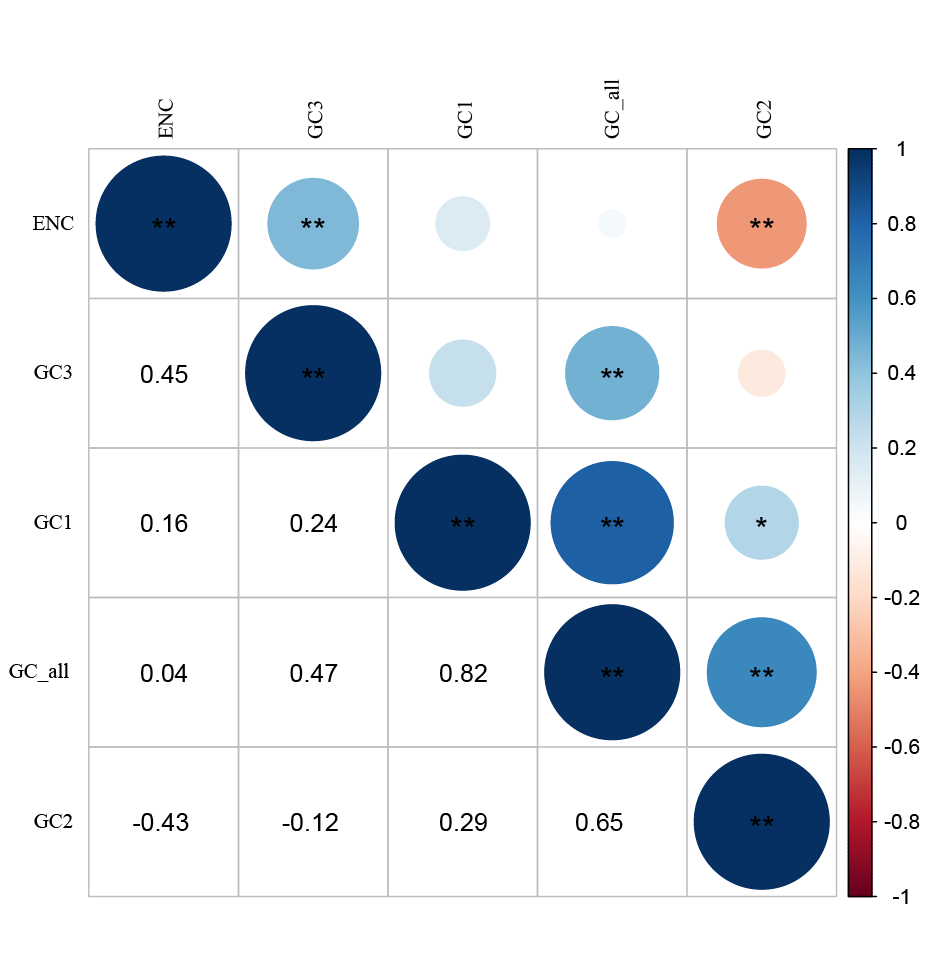
图2 疣粒野生稻叶绿体基因组密码子参数的皮尔逊相关性分析 *代表显著水平(P<0.05);**代表极显著水平(P<0.01)。
Fig. 2. Pearson correlation analysis of codon parameters in chloroplast genomes of Oryza meyeriana *indicate significant correlation at 0.05 level; **indicate significant correlation at 0.01 level.
| 组段区间 Class range | 频数 Frequency number | 频率 Frequency(%) |
|---|---|---|
| [−0.20,−0.05) | 4 | 8 |
| [−0.05,0.05) | 9 | 18 |
| [0.05,0.15) | 25 | 50 |
| [0.15,0.25) | 10 | 20 |
| [0.25,0.35) | 2 | 4 |
表3 ENC比值频率分布
Table 3. Frequency distribution of ENC ratio
| 组段区间 Class range | 频数 Frequency number | 频率 Frequency(%) |
|---|---|---|
| [−0.20,−0.05) | 4 | 8 |
| [−0.05,0.05) | 9 | 18 |
| [0.05,0.15) | 25 | 50 |
| [0.15,0.25) | 10 | 20 |
| [0.25,0.35) | 2 | 4 |
| 氨基酸 AA | 密码子 Codon | RSCU高表达 RSCU high expression | RSCU低表达 RSCU low expression | RSCU差值 △RSCU | RSCU值 RSCU value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phe | UUU | 1.06 | 1.27 | −0.21 | 1.30 |
| UUC* | 0.94 | 0.73 | 0.21 | 0.70 | |
| Leu | UUA*** | 2.08 | 1.35 | 0.73 | 2.00 |
| UUG* | 1.44 | 1.16 | 0.28 | 1.13 | |
| CUU | 1.36 | 1.45 | −0.09 | 1.29 | |
| CUC | 0.00 | 0.48 | −0.48 | 0.42 | |
| CUA | 0.80 | 0.87 | −0.07 | 0.82 | |
| CUG | 0.32 | 0.68 | −0.36 | 0.35 | |
| Ile | AUU** | 1.66 | 1.31 | 0.35 | 1.51 |
| AUC | 0.53 | 0.58 | −0.05 | 0.59 | |
| AUA | 0.81 | 1.11 | −0.30 | 0.91 | |
| Met | AUG | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Val | GUU | 2.05 | 2.00 | 0.05 | 1.54 |
| GUC | 0.10 | 0.44 | −0.34 | 0.46 | |
| GUA*** | 1.74 | 1.11 | 0.63 | 1.47 | |
| GUG | 0.10 | 0.44 | −0.34 | 0.53 | |
| Ser | UCU*** | 1.85 | 1.08 | 0.77 | 1.60 |
| UCC*** | 1.32 | 0.77 | 0.55 | 1.20 | |
| UCA | 0.44 | 1.38 | −0.94 | 1.03 | |
| UCG | 0.18 | 0.62 | −0.44 | 0.53 | |
| Pro | CCU*** | 2.00 | 0.70 | 1.30 | 1.51 |
| CCC | 0.90 | 1.39 | −0.49 | 0.95 | |
| CCA | 0.70 | 0.87 | −0.17 | 1.08 | |
| CCG | 0.40 | 1.04 | −0.64 | 0.46 | |
| Thr | ACU*** | 1.92 | 0.89 | 1.03 | 1.68 |
| ACC | 0.92 | 1.04 | −0.12 | 0.76 | |
| ACA | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.03 | 1.09 | |
| ACG | 0.25 | 1.19 | −0.94 | 0.47 | |
| Ala | GCU*** | 2.17 | 1.66 | 0.51 | 1.77 |
| GCC | 0.54 | 0.68 | −0.14 | 0.56 | |
| GCA | 1.02 | 1.13 | −0.11 | 1.19 | |
| GCG | 0.27 | 0.53 | −0.26 | 0.48 | |
| Tyr | UAU | 1.40 | 1.63 | −0.23 | 1.56 |
| UAC* | 0.60 | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.44 | |
| Ter | UAA*** | 2.40 | 1.80 | 0.60 | 1.44 |
| UAG | 0.00 | 0.60 | −0.60 | 0.84 | |
| His | CAU | 1.16 | 1.20 | −0.04 | 1.45 |
| CAC | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.04 | 0.55 | |
| Gln | CAA* | 1.45 | 1.29 | 0.16 | 1.52 |
| CAG | 0.55 | 0.71 | −0.16 | 0.48 | |
| Asn | AAU | 0.89 | 1.46 | −0.57 | 1.47 |
| AAC*** | 1.11 | 0.54 | 0.57 | 0.53 | |
| Lys | AAA** | 1.35 | 1.03 | 0.32 | 1.46 |
| AAG | 0.65 | 0.97 | −0.32 | 0.54 | |
| Asp | GAU | 1.38 | 1.71 | −0.33 | 1.54 |
| GAC** | 0.63 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.46 | |
| Glu | GAA | 1.37 | 1.64 | −0.27 | 1.48 |
| GAG* | 0.63 | 0.36 | 0.27 | 0.52 | |
| Cys | UGU | 1.71 | 2.00 | −0.29 | 1.47 |
| UGC* | 0.29 | 0.00 | 0.29 | 0.53 | |
| Ter | UGA | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.00 | 0.72 |
| Trp | UGG | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Arg | CGU*** | 1.58 | 0.87 | 0.71 | 1.39 |
| CGC | 0.33 | 0.55 | −0.22 | 0.54 | |
| CGA | 1.52 | 1.64 | −0.12 | 1.32 | |
| CGG | 0.40 | 0.87 | −0.47 | 0.49 | |
| Ser | AGU* | 1.76 | 1.54 | 0.22 | 1.27 |
| AGC | 0.44 | 0.62 | −0.18 | 0.38 | |
| Arg | AGA** | 1.98 | 1.53 | 0.45 | 1.68 |
| AGG | 0.20 | 0.55 | −0.35 | 0.59 | |
| Gly | GGU*** | 1.82 | 1.09 | 0.73 | 1.27 |
| GGC | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.43 | |
| GGA | 1.39 | 1.58 | −0.19 | 1.53 | |
| GGG | 0.24 | 0.85 | −0.61 | 0.77 |
表4 叶绿体基因组各氨基酸的RSCU分析
Table 4. RSCU analysis of amino acids in chloroplast genome
| 氨基酸 AA | 密码子 Codon | RSCU高表达 RSCU high expression | RSCU低表达 RSCU low expression | RSCU差值 △RSCU | RSCU值 RSCU value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phe | UUU | 1.06 | 1.27 | −0.21 | 1.30 |
| UUC* | 0.94 | 0.73 | 0.21 | 0.70 | |
| Leu | UUA*** | 2.08 | 1.35 | 0.73 | 2.00 |
| UUG* | 1.44 | 1.16 | 0.28 | 1.13 | |
| CUU | 1.36 | 1.45 | −0.09 | 1.29 | |
| CUC | 0.00 | 0.48 | −0.48 | 0.42 | |
| CUA | 0.80 | 0.87 | −0.07 | 0.82 | |
| CUG | 0.32 | 0.68 | −0.36 | 0.35 | |
| Ile | AUU** | 1.66 | 1.31 | 0.35 | 1.51 |
| AUC | 0.53 | 0.58 | −0.05 | 0.59 | |
| AUA | 0.81 | 1.11 | −0.30 | 0.91 | |
| Met | AUG | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Val | GUU | 2.05 | 2.00 | 0.05 | 1.54 |
| GUC | 0.10 | 0.44 | −0.34 | 0.46 | |
| GUA*** | 1.74 | 1.11 | 0.63 | 1.47 | |
| GUG | 0.10 | 0.44 | −0.34 | 0.53 | |
| Ser | UCU*** | 1.85 | 1.08 | 0.77 | 1.60 |
| UCC*** | 1.32 | 0.77 | 0.55 | 1.20 | |
| UCA | 0.44 | 1.38 | −0.94 | 1.03 | |
| UCG | 0.18 | 0.62 | −0.44 | 0.53 | |
| Pro | CCU*** | 2.00 | 0.70 | 1.30 | 1.51 |
| CCC | 0.90 | 1.39 | −0.49 | 0.95 | |
| CCA | 0.70 | 0.87 | −0.17 | 1.08 | |
| CCG | 0.40 | 1.04 | −0.64 | 0.46 | |
| Thr | ACU*** | 1.92 | 0.89 | 1.03 | 1.68 |
| ACC | 0.92 | 1.04 | −0.12 | 0.76 | |
| ACA | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.03 | 1.09 | |
| ACG | 0.25 | 1.19 | −0.94 | 0.47 | |
| Ala | GCU*** | 2.17 | 1.66 | 0.51 | 1.77 |
| GCC | 0.54 | 0.68 | −0.14 | 0.56 | |
| GCA | 1.02 | 1.13 | −0.11 | 1.19 | |
| GCG | 0.27 | 0.53 | −0.26 | 0.48 | |
| Tyr | UAU | 1.40 | 1.63 | −0.23 | 1.56 |
| UAC* | 0.60 | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.44 | |
| Ter | UAA*** | 2.40 | 1.80 | 0.60 | 1.44 |
| UAG | 0.00 | 0.60 | −0.60 | 0.84 | |
| His | CAU | 1.16 | 1.20 | −0.04 | 1.45 |
| CAC | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.04 | 0.55 | |
| Gln | CAA* | 1.45 | 1.29 | 0.16 | 1.52 |
| CAG | 0.55 | 0.71 | −0.16 | 0.48 | |
| Asn | AAU | 0.89 | 1.46 | −0.57 | 1.47 |
| AAC*** | 1.11 | 0.54 | 0.57 | 0.53 | |
| Lys | AAA** | 1.35 | 1.03 | 0.32 | 1.46 |
| AAG | 0.65 | 0.97 | −0.32 | 0.54 | |
| Asp | GAU | 1.38 | 1.71 | −0.33 | 1.54 |
| GAC** | 0.63 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.46 | |
| Glu | GAA | 1.37 | 1.64 | −0.27 | 1.48 |
| GAG* | 0.63 | 0.36 | 0.27 | 0.52 | |
| Cys | UGU | 1.71 | 2.00 | −0.29 | 1.47 |
| UGC* | 0.29 | 0.00 | 0.29 | 0.53 | |
| Ter | UGA | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.00 | 0.72 |
| Trp | UGG | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Arg | CGU*** | 1.58 | 0.87 | 0.71 | 1.39 |
| CGC | 0.33 | 0.55 | −0.22 | 0.54 | |
| CGA | 1.52 | 1.64 | −0.12 | 1.32 | |
| CGG | 0.40 | 0.87 | −0.47 | 0.49 | |
| Ser | AGU* | 1.76 | 1.54 | 0.22 | 1.27 |
| AGC | 0.44 | 0.62 | −0.18 | 0.38 | |
| Arg | AGA** | 1.98 | 1.53 | 0.45 | 1.68 |
| AGG | 0.20 | 0.55 | −0.35 | 0.59 | |
| Gly | GGU*** | 1.82 | 1.09 | 0.73 | 1.27 |
| GGC | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.43 | |
| GGA | 1.39 | 1.58 | −0.19 | 1.53 | |
| GGG | 0.24 | 0.85 | −0.61 | 0.77 |
| 登录号 GenBank code | 物种 Species | 登录号 GenBank code | 物种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| MZ323108.1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | NC027676.1 | Oryza punctata |
| NC034764.1 | Oryza ridleyi | NC030298.1 | Oryza minuta |
| NC034763.1 | Oryza longiglumis | KM088024.1 | Oryza longistaminata |
| KF359917.1 | Oryza brachyantha | KM103377.1 | Oryza glaberrima |
| NC053277.1 | Oryza schlechteri | NC027460.1 | Oryza barthii |
| NC024608.1 | Oryza australiensis | NC008155.1 | Oryza sativa indica Group |
| NC027463.1 | Oryza officinalis | NC005973.1 | Oryza nivara |
| NC034759.1 | Oryza eichingeri | KF562709.1 | Oryza rufipogon (Dongxiang) |
| NC034761.1 | Oryza grandiglumis | MW001303.1 | Oryza sativa temperate japonica |
| NC034760.1 | Oryza alta | KT289404.1 | Oryza sativa tropical japonica |
| NC036934.1 | Oryza coarctata | LC739565.1 | Oryza sativa japonica Group |
表5 构建进化树的物种信息
Table 5. Species information for constructing phylogenetic tree
| 登录号 GenBank code | 物种 Species | 登录号 GenBank code | 物种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| MZ323108.1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | NC027676.1 | Oryza punctata |
| NC034764.1 | Oryza ridleyi | NC030298.1 | Oryza minuta |
| NC034763.1 | Oryza longiglumis | KM088024.1 | Oryza longistaminata |
| KF359917.1 | Oryza brachyantha | KM103377.1 | Oryza glaberrima |
| NC053277.1 | Oryza schlechteri | NC027460.1 | Oryza barthii |
| NC024608.1 | Oryza australiensis | NC008155.1 | Oryza sativa indica Group |
| NC027463.1 | Oryza officinalis | NC005973.1 | Oryza nivara |
| NC034759.1 | Oryza eichingeri | KF562709.1 | Oryza rufipogon (Dongxiang) |
| NC034761.1 | Oryza grandiglumis | MW001303.1 | Oryza sativa temperate japonica |
| NC034760.1 | Oryza alta | KT289404.1 | Oryza sativa tropical japonica |
| NC036934.1 | Oryza coarctata | LC739565.1 | Oryza sativa japonica Group |
| [1] | Kirchhoff H. Chloroplast ultrastructure in plants[J]. New Phytologist, 2019, 223(2): 565-574. |
| [2] | Bandaranayake P C G, Naranpanawa N, Chandrasekara CHWMRB, Samarakoon H, Lokuge S, Jayasundara S, Bandaranayake A U, Pushpakumara DKNG, Wijesundara D S A. Chloroplast genome, nuclear ITS regions, mitogenome regions, and skmer analysis resolved the genetic relationship among Cinnamomum species in Sri Lanka[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(9): e0291763. |
| [3] | Zhang E, Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhang X, Wei Y, Zhang L. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Cynanchum acutum subsp. sibiricum (Apocynaceae)[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B: Resources, 2023, 8(9): 993-997. |
| [4] | Testone G, Lamprillo M, Gonnella M, Arnesi G, Sobolev A P, Aiese C R, Giannino D. The chloroplast genome of endive (Cichorium endivia L.): Cultivar structural variants and transcriptome responses to stress due to rain extreme events[J]. Genes (Basel), 2023, 14(9): 1829-1844. |
| [5] | Kousar M, Park J. Comparative analysis of the chloroplast genome of Sicyos angulatus with other seven species of Cucurbitaceae family[J]. Genes (Basel), 2023, 14(9): 1776-1788. |
| [6] | Xu C, Cai X N, Chen Q Z, Zhou H X, Cai Y, Ben A L. Factors affecting synonymous codon usage bias in chloroplast genome of Oncidium Gower Ramsey[J]. Evolutionary Bioinformatics, 2011, 7(7): 271-278. |
| [7] | Doherty A, Mcinerney J O. Translational selection frequently overcomes genetic drift in shaping synonymous codon usage patterns in vertebrates[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2013, 30(10): 2263-2267. |
| [8] | Fages-Lartaud M, Hundvin K, Hohmann-Marriott M F. Mechanisms governing codon usage bias and the implications for protein expression in the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii[J]. The Plant Journal, 2022, 112(4): 919-945. |
| [9] | 高立志, 张寿洲, 周毅, 葛颂, 洪德元. 中国野生稻的现状调查[J]. 生物多样性, 1996, 4(3): 160-166. |
| Gao L Z, Zhang S Z, Zhou Y, Ge S, Hong D Y. A survey of the current status of wild rice in China[J]. Chinese Biodiversity, 1996, 4(3): 160-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 刘学思, 殷富有, 张敦宇, 熊子璇, 刘鑫, 李玉琢, 李俊, 杨顺发, 杨和生, 白成星, 彭钰婷, 刘丽, 钟巧芳, 程在全, 肖素勤. 云南省4个州(市)疣粒野生稻的调查、收集与保护[J]. 杂交水稻, 2023, 38(5): 20-25. |
| Liu X S, Yin F Y, Zhang D Y, Xiong Z X, Liu X, Li X Z, Li J, Yang S F, Yang H S, Bai C X, Peng Y T, Liu L, Zhong Q F, Cheng Z Q, Xiao S Q. Investigation, collection and protection of Oryza meyeriana in four prefectures (cities) of Yunnan Province[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2023, 38(5): 20-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 肖素勤, 殷富有, 张绍松, 余腾琼, 陈玲, 柯学, 付坚, 张敦宇, 钟巧芳, 李定琴, 陈越, 孙治旭, 岳英, 郭顺云, 王玲仙, 黄兴奇, 杨雅云, 王波, 曾民, 李娥贤, 程在全. 云南野生稻资源及其保护[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2017, 18(3): 494-502. |
| Xiao S Q, Yin F Y, Zhang S Y, Yu T Q, Chen L, Ke X, Fu J, Zhang D Y, Zhong Q F, Li D Q, Chen Y, Sun Z X, Yue Y, Guo S Y, Wang L X, Huang X Q, Yang Y Y, Wang B, Zeng M, Li E X, Cheng Z Q. Genetic resources and conservation of Yunnan wild rice species[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2017, 18(3): 494-502. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Masoomi-Aladizgeh F, Masoomi-Aladizgeh F, Jabbari L, Khayam Nekouei R, Aalami A, Atwell B J, Haynes P A. A universal protocol for high-quality DNA and RNA isolation from diverse plant species[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(12): e0295852. |
| [13] | Zhang P, Xu W, Lu X, Wang L. Analysis of codon usage bias of chloroplast genomes in Gynostemma species[J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2021, 27(12): 2727-2737. |
| [14] | Wu K Q, Qian J, Song J Y, Gao H H, Zhu Y J, Xu J, Pang X H, Yao H, Sun C, Li X E, Li C Y, Liu J Y, Xu H B, Chen S L. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e57607. |
| [15] | Yuan S, Nie C, Jia S, Liu T, Zhao J, Peng J, Kong W, Liu W, Gou W, Lei X, Xiong Y, Xiong Y, Yu Q, Ling Y, Ma X. Complete chloroplast genomes of three wild perennial Hordeum species from Central Asia: Genome structure, mutation hotspot, phylogenetic relationships, and comparative analysis[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1170004-1170020. |
| [16] | Li H, Wu M, Lai Q, Zhou W, Song C. Complete chloroplast of four Sanicula taxa (Apiaceae) endemic to China: lights into genome structure, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationships[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2023, 23(1): 444-460. |
| [17] | Ogihara Y, Isono K, Kojima T, Endo A, Hanaoka M, Shiina T, Terachi T, Utsugi S, Murata M, Mori N, Takumi S, Ikeo K, Gojobori T, Murai R, Murai K, Matsuoka Y, Ohnishi Y, Tajiri H, Tsunewaki K. Structural features of a wheat plastome as revealed by complete sequencing of chloroplast DNA[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2002, 266(5): 740-746. |
| [18] | Maier R M, Neckermann K, Igloi G L, Ssel H K. Complete sequence of the maize chloroplast genome: Gene content, hotspots of divergence and fine tuning of genetic information by transcript editing[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1995, 251(5): 614-628. |
| [19] | Saski C, Lee S B, Fjellheim S, Guda C, Jansen R K, Luo H, Tomkins J, Rognli O A, Daniell H, Clarke J L. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Hordeum vulgare, Sorghum bicolor and Agrostis stolonifera, and comparative analyses with other grass genomes[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2007, 115(4): 571-590. |
| [20] | Middleton C P, Senerchia N, Stein N, Akhunov E D, Keller B, Wicker T, Kilian B. Sequencing of chloroplast genomes from wheat, barley, rye and their relatives provides a detailed insight into the evolution of the Triticeae tribe[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(3): e85761. |
| [21] | Song Y, Chen Y, Lv J, Xu J, Zhu S, Li M, Chen N. Development of chloroplast genomic resources for Oryza species discrimination[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1854-1863. |
| [22] | Wambugu P W, Brozynska M, Furtado A, Waters D L, Henry R J. Relationships of wild and domesticated rices (Oryza AA genome species) based upon whole chloroplast genome sequences[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 13957-13965. |
| [23] | Hao J, Liang Y, Ping J, Li J, Shi W, Su Y, Wang T. Chloroplast gene expression level is negatively correlated with evolutionary rates and selective pressure while positively with codon usage bias in Ophioglossum vulgatum L[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2022, 22(1): 580-592. |
| [24] | Chi X, Zhang F, Dong Q, Chen S. Insights into comparative genomics, codon usage bias, and phylogenetic relationship of species from Biebersteiniaceae and Nitrariaceae based on complete chloroplast genomes[J]. Plants (Basel), 2020, 9(11): 1065-1079. |
| [25] | Li C, Zhou L, Nie J, Wu S, Li W, Liu Y, Liu Y. Codon usage bias and genetic diversity in chloroplast genomes of Elaeagnus species (Myrtiflorae: Elaeagnaceae)[J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2023, 29(2): 239-251. |
| [26] | Shen L, Chen S, Liang M, Qu S, Feng S, Wang D, Wang G. Comparative analysis of codon usage bias in chloroplast genomes of ten medicinal species of Rutaceae[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2024, 24(1): 424-437. |
| [27] | Kaiser E, Correa Galvis V, Armbruster U. Efficient photosynthesis in dynamic light environments: A chloroplast's perspective[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 2019, 476(19): 2725-2741. |
| [28] | Cejudo F J, Gonzalez M C, Perez-Ruiz J M. Redox regulation of chloroplast metabolism[J]. Plant Physiology, 2021, 186(1): 9-21. |
| [29] | Vaughan D A. The Wild Relative of Rice: A Genetic Resources Handbook[M]. 1994. |
| [30] | Asaf S, Waqas M, Khan A L, Khan M A, Kang S M, Imran Q M, Shahzad R, Bilal S, Yun B W, Lee I J. The complete chloroplast genome of wild rice (Oryza minuta) and its comparison to related species[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 304-318. |
| [31] | Gao L L, Hong Z H, Wang Y, Wu G Z. Chloroplast proteostasis: A story of birth, life, and death[J]. Plant Communications, 2023, 4(1): 100424-100448. |
| [1] | 陈涛,张震,柴荣耀,王教瑜,毛雪琴,邱海萍,杜新法,姜华,王立安. 浙江省水稻纹枯病菌的遗传分化与致病力研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(1): 67-72 . |
| [2] | 王玲,黄世文 ,王全永,鄂志国,王磊,张建萍,朱德峰,傅强. 稗草病原真菌AAE的分子鉴定及其粗蛋白诱导水稻的稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(3): 327-330 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||