
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 760-770.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240707
陈伟1,3, 叶元妹1, 赵剑华1, 冯志明1,2, 陈宗祥1,2, 胡珂鸣1,2, 左示敏1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-09
修回日期:2024-08-12
出版日期:2025-11-10
发布日期:2025-11-19
通讯作者:
* email:smzuo@yzu.edu.cn
基金资助:
CHEN Wei1,3, YE Yuanmei1, ZHAO Jianhua1, FENG Zhiming1,2, CHEN Zongxiang1,2, HU Keming1,2, ZUO Shimin1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-09
Revised:2024-08-12
Online:2025-11-10
Published:2025-11-19
Contact:
* email:smzuo@yzu.edu.cn
摘要:
【目的】抽穗期是决定水稻品种种植区域和生态适应性的关键农艺性状。本研究通过对优良食味中熟晚粳品种南粳46(简称NJ46)的抽穗期基因进行编辑,以缩短NJ46的生育期,扩大其种植区域。【方法】利用CRISPR/Cas9技术,以DTH8和Ghd2为靶基因,构建pCAMBIA1305-Actin:Cas9-sgRNADTH8与pCAMBIA1305-Actin:Cas9-sgRNAGhd2编辑载体,用农杆菌介导的植物转化方法转化NJ46,筛选不含外源成分的纯合编辑系,并考察其抽穗期、农艺性状及品质相关性状。【结果】对DTH8的编辑获得了3个比NJ46抽穗期提早22~36 d的无外源成分纯合突变系(NJ46-dth8-1~-3),对Ghd2的编辑获得了3个比NJ46抽穗期提早14~15 d的无外源成分纯合突变系(NJ46-ghd2-1~-3)。分别在苏中和苏北测定了各基因纯合突变系的抽穗期、主要农艺性状及品质性状,与相应生态区推广品种南粳9108、南粳518进行比较,发现NJ46-ghd2-1单株产量显著高于南粳9108,但抽穗期和品质与之相当,好于另外2个敲除系;NJ46-dth8-1与南粳518在单株产量、主要品质性状上均无显著差异,好于另外2个敲除系。【结论】定向编辑南粳46中的DTH8和Ghd2基因,获得适宜苏北和苏中生态区种植的优良食味粳稻新种质,有助于扩大优良食味水稻品种的推广种植区域。
陈伟, 叶元妹, 赵剑华, 冯志明, 陈宗祥, 胡珂鸣, 左示敏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术改良南粳46抽穗期[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 760-770.
CHEN Wei, YE Yuanmei, ZHAO Jianhua, FENG Zhiming, CHEN Zongxiang, HU Keming, ZUO Shimin. Modifying Heading Date of Nanjing 46 via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Genome Editing[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 760-770.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') | 用途 Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| DTH8-gF-1 | GGCACGTGAGCCGCATCATGAAGCGG | 构建 DTH8靶点1敲除载体 Construction of DTH8 target 1 knockout vector |
| DTH8-gR-1 | AAACCCGCTTCATGATGCGGCTCACG | |
| DTH8-gF-2 | GGCAAAGATCTCCAAGGAGTCGAAGG | 构建 DTH8靶点2敲除载体 Construction of DTH8 target 2 knockout vector |
| DTH8-gR-2 | AAACCCTTCGACTCCTTGGAGATCTT | |
| Ghd2-gF | GGCAGCGTCGGGCAGCTGCTCTCGAGG | 构建 Ghd2敲除载体 Construction of Ghd2 knockout vector |
| Ghd2-gR | AAACCCTCGAGAGCAGCTGCCCGACGC | |
| Hpt-F | CGGAAGTGCTTGACATTG | 转基因检测 Transgenic detection |
| Hpt-R | GACCTCGTATTGGGAATCC | |
| sgRNA-F | AAGGAATCTTTAAACATACGAACAGATC | 单克隆测序鉴定 Monoclonal sequencing identification Sequencing for Monoclonal |
| Cas9-F | ACTCGAACGCGACCAACTTA | 载体检测 Vector assay |
| Cas9-R | ATCTGCAGAATTGCCCTTCG | |
| DTH8-F | CGAAGGAGCAGGACAGGTTC | DTH8 敲除靶点测序鉴定 Sequencing for DTH8 knockout target |
| DTH8-R | TTGATGGTCTTCCGCTTCTCG | |
| Ghd2-F | TGACGCCTTCCTGTGCCAGGGGTG | Ghd2 敲除靶点测序鉴定 Sequencing for Ghd2 knockout target |
| Ghd2-R | GTCCGACGACTCCACCGCCATCTC |
表1 本研究所用的引物
Table 1. Primers used in this research
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') | 用途 Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| DTH8-gF-1 | GGCACGTGAGCCGCATCATGAAGCGG | 构建 DTH8靶点1敲除载体 Construction of DTH8 target 1 knockout vector |
| DTH8-gR-1 | AAACCCGCTTCATGATGCGGCTCACG | |
| DTH8-gF-2 | GGCAAAGATCTCCAAGGAGTCGAAGG | 构建 DTH8靶点2敲除载体 Construction of DTH8 target 2 knockout vector |
| DTH8-gR-2 | AAACCCTTCGACTCCTTGGAGATCTT | |
| Ghd2-gF | GGCAGCGTCGGGCAGCTGCTCTCGAGG | 构建 Ghd2敲除载体 Construction of Ghd2 knockout vector |
| Ghd2-gR | AAACCCTCGAGAGCAGCTGCCCGACGC | |
| Hpt-F | CGGAAGTGCTTGACATTG | 转基因检测 Transgenic detection |
| Hpt-R | GACCTCGTATTGGGAATCC | |
| sgRNA-F | AAGGAATCTTTAAACATACGAACAGATC | 单克隆测序鉴定 Monoclonal sequencing identification Sequencing for Monoclonal |
| Cas9-F | ACTCGAACGCGACCAACTTA | 载体检测 Vector assay |
| Cas9-R | ATCTGCAGAATTGCCCTTCG | |
| DTH8-F | CGAAGGAGCAGGACAGGTTC | DTH8 敲除靶点测序鉴定 Sequencing for DTH8 knockout target |
| DTH8-R | TTGATGGTCTTCCGCTTCTCG | |
| Ghd2-F | TGACGCCTTCCTGTGCCAGGGGTG | Ghd2 敲除靶点测序鉴定 Sequencing for Ghd2 knockout target |
| Ghd2-R | GTCCGACGACTCCACCGCCATCTC |
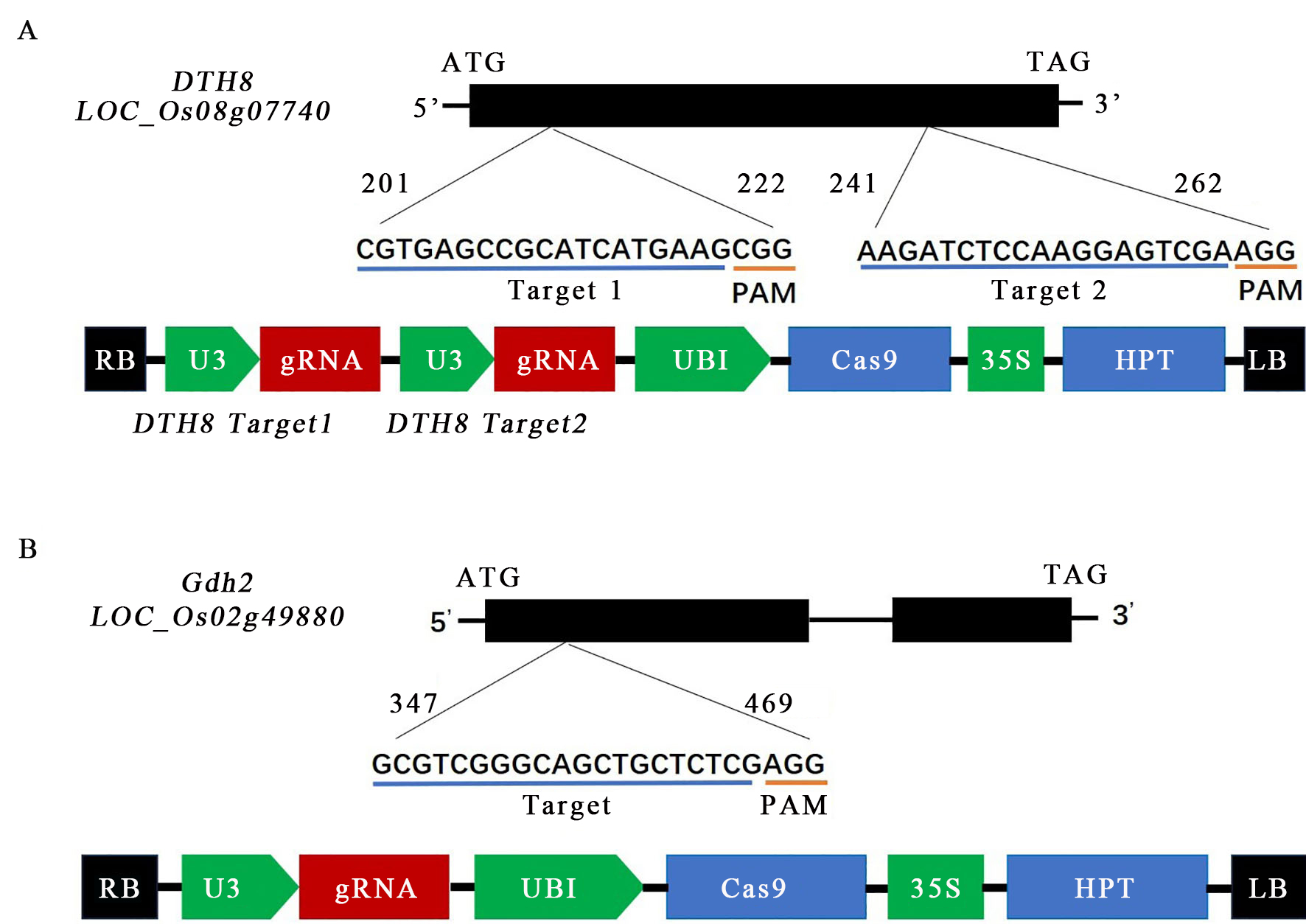
图1 DTH8(A)和Ghd2(B)基因敲除靶点位置及载体pCAMBIA1305-Actin:Cas9-sgRNA组成
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of DTH8 and Ghd2 gene editing targets and structure of pCAMBIA1305-Actin:Cas9-sgRNA
| 靶点 Target | 潜在脱靶序列 Off-target sequence | 脱靶指数 Off-score | 潜在基因 Gene | 区域 Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTH8-Target1 | ACATCAGCCGCATCATGAAGAAG | 0.153 | LOC_Os01g61810 | CDS |
| ACATCAGCCGCATCATGAAGAAG | 0.153 | LOC_Os05g38820 | CDS | |
| ACATGAGCAGCATCAAGAAGGAG | 0.152 | LOC_Os02g16909 | Utr | |
| TCGTGAGTCGCTTCATGGAGCGG | 0.117 | LOC_Os08g36774 | Intron | |
| DTH8-Target2 | CAAGAGCTCCAGGGAGACGGAGG | 0.168 | LOC_Os08g13020 | Intron |
| CAAAATCCCCAAGGAGTAGACAG | 0.126 | LOC_Os07g46910 | CDS | |
| CAAGATCTCCAAAGTATTGATGG | 0.119 | Null | Intergenic | |
| GGAGCTCTCCAATGAGTCGATGG | 0.110 | LOC_Os01g32660 | Intron | |
| Ghd2-Target | CCTAGCCGAGCATCAAAACCGGG | 0.270 | Null | Intergenic |
| GCGTCGTGCAGCTGGTCTCGCGG | 0.197 | LOC_Os01g03420 | CDS | |
| GCGTCAGGGAGCTGCTATCGAGG | 0.157 | LOC_Os04g43350 | CDS | |
| GCCTCCGGCTGCTGATCTCGTGG | 0.143 | LOC_Os05g45430 | CDS |
表2 敲除靶点的潜在脱靶位点分析
Table 2. Potential off-target analysis
| 靶点 Target | 潜在脱靶序列 Off-target sequence | 脱靶指数 Off-score | 潜在基因 Gene | 区域 Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTH8-Target1 | ACATCAGCCGCATCATGAAGAAG | 0.153 | LOC_Os01g61810 | CDS |
| ACATCAGCCGCATCATGAAGAAG | 0.153 | LOC_Os05g38820 | CDS | |
| ACATGAGCAGCATCAAGAAGGAG | 0.152 | LOC_Os02g16909 | Utr | |
| TCGTGAGTCGCTTCATGGAGCGG | 0.117 | LOC_Os08g36774 | Intron | |
| DTH8-Target2 | CAAGAGCTCCAGGGAGACGGAGG | 0.168 | LOC_Os08g13020 | Intron |
| CAAAATCCCCAAGGAGTAGACAG | 0.126 | LOC_Os07g46910 | CDS | |
| CAAGATCTCCAAAGTATTGATGG | 0.119 | Null | Intergenic | |
| GGAGCTCTCCAATGAGTCGATGG | 0.110 | LOC_Os01g32660 | Intron | |
| Ghd2-Target | CCTAGCCGAGCATCAAAACCGGG | 0.270 | Null | Intergenic |
| GCGTCGTGCAGCTGGTCTCGCGG | 0.197 | LOC_Os01g03420 | CDS | |
| GCGTCAGGGAGCTGCTATCGAGG | 0.157 | LOC_Os04g43350 | CDS | |
| GCCTCCGGCTGCTGATCTCGTGG | 0.143 | LOC_Os05g45430 | CDS |

图2 PCR筛选T0代阳性单株 M: DNA标记;1: 阴性对照;2: 阳性对照;3~24: T0代突变单株。
Fig. 2. Screening of positive mutant plants by PCR in T0 M, DNA marker; 1, Negative control; 2, Positive control; 3−24, T0 mutation plants.
| 靶位点 Target | 阳性株数Positive plants | 突变率 Mutation ratio(%) | 突变基因型比率 Mutant genotype ratio(%) | 突变类型比率 Ratio of mutation types(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纯合突变率Homozygous | 杂合突变率Heterozygous | 双等位突变率 Bi-allele | 碱基插入 Insert | 碱基缺失Deletion | ||||
| DTH8 Target 1 | 36 | 36.1 | 30.8 | 15.4 | 53.8 | 0.0 | 100.0 | |
| DTH8 Target 2 | 36 | 44.4 | 31.3 | 18.8 | 50.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | |
| Ghd2 Target | 25 | 84.0 | 28.6 | 23.8 | 47.6 | 9.5 | 90.5 | |
表3 T0突变体突变基因型和突变类型频率
Table 3. Ratios of mutant genotype and mutation types in T0 transgenic plants
| 靶位点 Target | 阳性株数Positive plants | 突变率 Mutation ratio(%) | 突变基因型比率 Mutant genotype ratio(%) | 突变类型比率 Ratio of mutation types(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纯合突变率Homozygous | 杂合突变率Heterozygous | 双等位突变率 Bi-allele | 碱基插入 Insert | 碱基缺失Deletion | ||||
| DTH8 Target 1 | 36 | 36.1 | 30.8 | 15.4 | 53.8 | 0.0 | 100.0 | |
| DTH8 Target 2 | 36 | 44.4 | 31.3 | 18.8 | 50.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | |
| Ghd2 Target | 25 | 84.0 | 28.6 | 23.8 | 47.6 | 9.5 | 90.5 | |

图3 PCR筛选无外源转基因成分的突变植株 M: DNA 标记;WT: 阳性对照;1~3: DTH8突变株;4~6: Ghd2突变株。
Fig. 3. PCR screening of mutant plants without exogenous components M, DNA marker; WT, Positive control; 1−3, DTH8 mutation plants; 4−6, Ghd2 mutation plants.
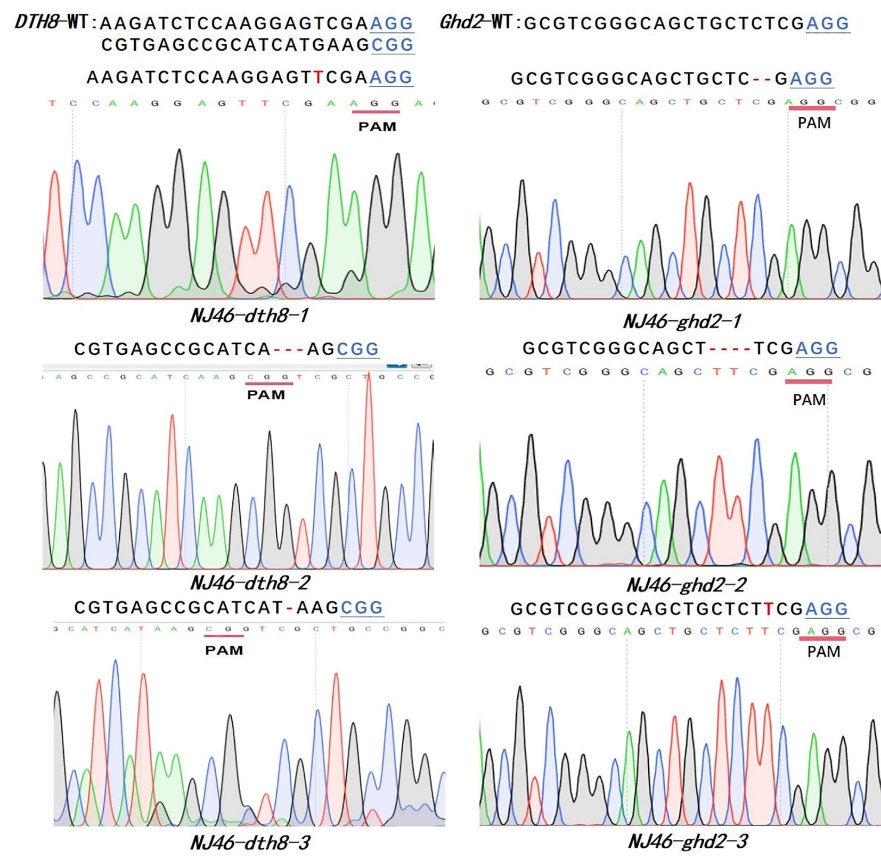
图4 T1代的6种纯合突变类型 红色碱基为插入,红色虚线为碱基缺失,标注下划线的蓝色碱基为PAM。
Fig. 4. Six mutation types of homozygotes in T1 Inserted bases are marked in red, deletions are indicated by red dashed lines, and the underlined blue bases represent PAM sequences.
| T1代基因型 Genotype of T1 generation | T2代分离群体抽穗期 Heading date of T2 segregating population plants(d) | 1:3分离比的渐进显著性 Progressive significance of the separation ratio of 1:3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早 Earlier | 无变化 No change | 晚 Later | ||
| Aa1 | 44 | 142 | 0 | 0.672 |
| Aa2 | 62 | 171 | 0 | 0.570 |
| Aa3 | 56 | 162 | 0 | 0.815 |
| Bb1 | 53 | 170 | 0 | 0.671 |
| Bb2 | 47 | 152 | 0 | 0.653 |
| Bb3 | 62 | 200 | 0 | 0.618 |
表4 NJ46突变体表型分离比χ2测验
Table 4. χ2 test of NJ46 mutants phenotype in T2 segregation population
| T1代基因型 Genotype of T1 generation | T2代分离群体抽穗期 Heading date of T2 segregating population plants(d) | 1:3分离比的渐进显著性 Progressive significance of the separation ratio of 1:3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早 Earlier | 无变化 No change | 晚 Later | ||
| Aa1 | 44 | 142 | 0 | 0.672 |
| Aa2 | 62 | 171 | 0 | 0.570 |
| Aa3 | 56 | 162 | 0 | 0.815 |
| Bb1 | 53 | 170 | 0 | 0.671 |
| Bb2 | 47 | 152 | 0 | 0.653 |
| Bb3 | 62 | 200 | 0 | 0.618 |

图6 DTH8与Ghd2基因突变体的抽穗期表型(比例尺=30 cm) A: DTH8与Ghd2基因突变体(分别命名为NJ46-dth8和NJ46-ghd2)在扬州沿江区域的抽穗期表型; B: NJ46-dth8和NJ46-ghd2突变体在扬州沿江区域的抽穗期天数; C: NJ46-dth8和NJ46-ghd2突变体在高邮抽穗期表型; D: NJ46-dth8和NJ46-ghd2突变体在高邮抽穗期天数; E: NJ46-dth8和NJ46-ghd2突变体在宿迁抽穗期表型; F: NJ46-dth8和NJ46-ghd2突变体在宿迁抽穗期天数。数据用平均数±标准差表示。不同字母代表不同株系间差异显著,LSD多重比较(P<0.05)。
Fig. 6. Phenotypes of DTH8 and Ghd2 mutants in heading stage (Bar=30 cm) A, Phenotypes of DTH8 and Ghd2 mutants (NJ46-dth8 and NJ46-ghd2, respectively) at heading stage in Yangzhou along the Yangtze River; B, Days to heading of NJ46-dth8 and NJ46-ghd2 mutants in Yangzhou along the Yangtze River; C, Phenotypes of NJ46-dth8 and NJ46-ghd2 mutants at heading stage in Gaoyou; D, Days to heading of NJ46-dth8 and NJ46-ghd2 in Gaoyou; E, Phenotypes of NJ46-dth8 and NJ46-ghd2 mutants at heading stage in Suqian; F, Days to heading of NJ46-dth8 and NJ46-ghd2 mutants in Suqian. Values are shown as mean ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference among different lines at P < 0.05 according to LSD multiple range test.
| 地点 Site | 株系 Line | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 穗长 Panicle length (cm) | 单株有效穗 Effective panicle per plant | 每穗实粒数 Number of grains per panicle | 千粒重 1000-grain weigh(g) | 单株产量 Yield per plant(g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高邮Gaoyou | NJ9108 | 96.31±0.74 b | 16.82±0.41 a | 15.52±0.87 a | 142.10±5.81 a | 27.50±0.01 a | 60.63±2.18 a |
| NJ46-ghd2-1 | 90.23±2.23 a | 16.54±0.62 a | 16.25±1.01 b | 148.33±3.21 b | 28.51±0.05 b | 68.51±3.32 b | |
| NJ46-ghd2-2 | 91.64±1.14 a | 16.13±0.45 a | 16.72±1.51 b | 146.22±7.08 ab | 28.32±0.03 b | 69.10±4.23 b | |
| NJ46-ghd2-3 | 91.12±1.43 a | 16.64±0.32 a | 15.61±1.11 ab | 152.24±3.21 b | 28.13±0.02 ab | 66.74±3.61 b | |
| 宿迁 Suqian | NJ518 | 100.20±1.14 b | 17.80±0.36 b | 15.00±1.51 b | 155.31±5.81 b | 27.80±0.03 a | 64.82±4.21 b |
| NJ46-dth8-1 | 98.55±2.32 b | 18.31±0.28 b | 14.23±0.87 a | 156.24±5.77 b | 28.31±0.02 a | 62.82±3.32 b | |
| NJ46-dth8-2 | 98.12±0.74 b | 18.62±0.28 b | 14.94±0.87 b | 151.35±5.77 b | 28.12±0.03 a | 63.34±2.18 b | |
| NJ46-dth8-3 | 89.30±0.74 a | 15.53±0.30 a | 14.41±0.87 a | 122.11±5.77 a | 30.52±0.01 b | 53.61±2.18 a |
表5 早抽穗突变系与NJ9108和NJ518的农艺性状比较
Table 5. Comparison of agronomic traits of mutants with NJ9108 and NJ518
| 地点 Site | 株系 Line | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 穗长 Panicle length (cm) | 单株有效穗 Effective panicle per plant | 每穗实粒数 Number of grains per panicle | 千粒重 1000-grain weigh(g) | 单株产量 Yield per plant(g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高邮Gaoyou | NJ9108 | 96.31±0.74 b | 16.82±0.41 a | 15.52±0.87 a | 142.10±5.81 a | 27.50±0.01 a | 60.63±2.18 a |
| NJ46-ghd2-1 | 90.23±2.23 a | 16.54±0.62 a | 16.25±1.01 b | 148.33±3.21 b | 28.51±0.05 b | 68.51±3.32 b | |
| NJ46-ghd2-2 | 91.64±1.14 a | 16.13±0.45 a | 16.72±1.51 b | 146.22±7.08 ab | 28.32±0.03 b | 69.10±4.23 b | |
| NJ46-ghd2-3 | 91.12±1.43 a | 16.64±0.32 a | 15.61±1.11 ab | 152.24±3.21 b | 28.13±0.02 ab | 66.74±3.61 b | |
| 宿迁 Suqian | NJ518 | 100.20±1.14 b | 17.80±0.36 b | 15.00±1.51 b | 155.31±5.81 b | 27.80±0.03 a | 64.82±4.21 b |
| NJ46-dth8-1 | 98.55±2.32 b | 18.31±0.28 b | 14.23±0.87 a | 156.24±5.77 b | 28.31±0.02 a | 62.82±3.32 b | |
| NJ46-dth8-2 | 98.12±0.74 b | 18.62±0.28 b | 14.94±0.87 b | 151.35±5.77 b | 28.12±0.03 a | 63.34±2.18 b | |
| NJ46-dth8-3 | 89.30±0.74 a | 15.53±0.30 a | 14.41±0.87 a | 122.11±5.77 a | 30.52±0.01 b | 53.61±2.18 a |
| 地点 Site | 株系 Line | 整精米率 Rate of milled rice(%) | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain percentage(%) | 垩白度 Chalkiness(%) | 食味值 Edibility value | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高邮 Gaoyou | NJ9108 | 70.56±0.26 b | 32.91±0.18 c | 7.07±0.03 b | 71.00±1.52 b | 11.45±0.02 b |
| NJ46-ghd2-1 | 72.21±0.29 b | 12.87±0.20 a | 2.60±0.02 a | 68.70±1.46 ab | 10.14±0.03 a | |
| NJ46-ghd2-2 | 64.52±0.33 a | 17.26±0.14 a | 6.95±0.02 b | 68.30±1.38 a | 10.49±0.03 a | |
| NJ46-ghd2-3 | 71.93±0.26 b | 23.82±0.15 ab | 5.40±0.01 ab | 72.00±1.21 c | 10.32±0.04 a | |
| 宿迁 Suqian | NJ518 | 72.22±0.26 a | 22.26±0.15 a | 5.58±0.02 a | 76.70±1.44 b | 10.00±0.02 a |
| NJ46-dth8-1 | 73.04±0.26 b | 26.14±0.14 a | 6.45±0.01 a | 74.30±1.26 b | 10.31±0.02 a | |
| NJ46-dth8-2 | 72.06±0.26 a | 35.72±0.13 b | 9.00±0.02 b | 53.70±2.20 a | 9.81±0.04 a | |
| NJ46-dth8-3 | 72.32±0.26 a | 28.26±0.23 a | 6.60±0.02 a | 60.30±1.65 a | 10.72±0.03 a |
表6 早抽穗突变系与对照品种NJ9108或NJ518的主要品质性状比较
Table 6. Quality comparison of mutants with NJ9108 and NJ518
| 地点 Site | 株系 Line | 整精米率 Rate of milled rice(%) | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain percentage(%) | 垩白度 Chalkiness(%) | 食味值 Edibility value | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高邮 Gaoyou | NJ9108 | 70.56±0.26 b | 32.91±0.18 c | 7.07±0.03 b | 71.00±1.52 b | 11.45±0.02 b |
| NJ46-ghd2-1 | 72.21±0.29 b | 12.87±0.20 a | 2.60±0.02 a | 68.70±1.46 ab | 10.14±0.03 a | |
| NJ46-ghd2-2 | 64.52±0.33 a | 17.26±0.14 a | 6.95±0.02 b | 68.30±1.38 a | 10.49±0.03 a | |
| NJ46-ghd2-3 | 71.93±0.26 b | 23.82±0.15 ab | 5.40±0.01 ab | 72.00±1.21 c | 10.32±0.04 a | |
| 宿迁 Suqian | NJ518 | 72.22±0.26 a | 22.26±0.15 a | 5.58±0.02 a | 76.70±1.44 b | 10.00±0.02 a |
| NJ46-dth8-1 | 73.04±0.26 b | 26.14±0.14 a | 6.45±0.01 a | 74.30±1.26 b | 10.31±0.02 a | |
| NJ46-dth8-2 | 72.06±0.26 a | 35.72±0.13 b | 9.00±0.02 b | 53.70±2.20 a | 9.81±0.04 a | |
| NJ46-dth8-3 | 72.32±0.26 a | 28.26±0.23 a | 6.60±0.02 a | 60.30±1.65 a | 10.72±0.03 a |
| [1] | 姚伟, 佟越强, 刘棋, 臧华栋, 杨亚东, 戚志强, 曾昭海. 全球水稻生产时空变化特征及贸易趋势分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 2022, 53(6): 1776-1784. |
| Yao W, Tong Y Q, Liu Q, Zang H D, Yang Y D, Qi Z Q, Zeng Z H. Spatiotemporal change characteristics and trade trend of global rice production[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2022, 53(6): 1776-1784. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 彭永彬, 杜晨阳, 郑崇珂, 周晋军, 孙伟, 和亚男, 谢先芝. 水稻抽穗期调控基因Hd6的PARMS标记开发与利用[J]. 山东农业科学, 2022, 54(8): 1-6. |
| Peng Y B, Du C Y, Zheng C K, Zhou J J, Sun W, He Y N, Xie X Z. Development and application of PARMS markers specific for rice heading date regulation gene Hd6[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 54(8): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Zhou S R, Zhu S S, Cui S, Hou H G, Wu H Q, Hao B Y, Cai L, Xu Z, Liu L L, Jiang L, Wang H Y, Wan J M. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of heading date in rice[J]. The New Phytologist, 2021, 230(3): 943-956. |
| [4] | Chen R Z, Deng Y W, Ding Y L, Guo J X, Qiu J, Wang B, Wang C S, Xie Y Y, Zhang Z H, Chen J X, Chen L T, Chu C C, He G C, He Z H, Huang X H, Xing Y Z, Yang S H, Xie D X, Liu Y G, Li J Y. Rice functional genomics: Decades’ efforts and roads ahead[J]. Science China: Life Sciences, 2022, 65(1): 33-92. |
| [5] | 李斌. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制抽穗期改良的水稻新种质[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2022. |
| Li B. Development of new rice germplasms with improved heading date via CRISPR/Cas9 technology[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 蒋丹, 洪广成, 陈倩, 刘石锋, 秦小健. 水稻抽穗期分子调控研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(21): 7071-7077. |
| Jiang D, Hong G C, Chen Q, Liu S F, Qin X J. Research progress in molecular regulation of heading date in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(21): 7071-7077. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 王婧莹, 赵广欣, 邱冠凯, 方军. 水稻抽穗期途径基因的磷酸化、泛素化研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 215-226. |
| Wang J Y, Zhao G X, Qiu G K, Fang J. Advances in research on the modification of the heading date genes in rice by phosphorylation and ubiquitination pathways[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 215-226. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Dai X D, Ding Y N, Tan L B, Fu Y C, Liu F X, Zhu Z F, Sun X Y, Sun X Y, Gu P, Cai H W, Sun C Q. LHD1, an allele of DTH8/Ghd8, controls late heading date in common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon)[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2012, 54(10): 790-799. |
| [9] | Yan W H, Wang P, Chen H X, Zhou H J, Li Q P, Wang C R, Ding Z H, Zhang Y S, Yu S B, Xing Y Z, Zhang Q F. A major QTL, Ghd8, plays pleiotropic roles in regulating grain productivity, plant height, and heading date in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2011, 4(2): 319-330. |
| [10] | Wei X J, Xu J F, Guo H N, Jiang L, Chen S H, Yu C Y, Zhou Z L, Hu P S, Zhai H Q, Wan J M. DTH8 suppresses flowering in rice, influencing plant height and yield potential simultaneously[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 153(4): 1747-1758. |
| [11] | Fan X W, Wang P F, Qi F X, Hu Y, Li S L, Zhang J, Liang L W, Zhang Z Y, Liu J H, Xiong L Z, Xing Y Z. The CCT transcriptional activator Ghd2 constantly delays the heading date by upregulating CO3 in rice[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2023, 50(10): 755-764. |
| [12] | 王静毅, 甘珊珊, 贾彩红, 刘菊华. CRISPR/Cas9技术在热带作物育种中的应用研究进展[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2024, 25(3): 312-322. |
| Wang J Y, Gan S S, Jia C H, Liu J H. Application of CRISPR/Cas9 technology in tropical crops breeding[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2024, 25(3): 3312-322. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 顾爽, 郑文静, 马殿荣. CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑系统在水稻育种应用的研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(10): 3314-3322. |
| Gu S Z, Zhen W J, M, Ma D R. Research progress ofof CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing system in rice breeding[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(10): 33314-3322. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Gupta D, Bhattacharjee O, Mandal D, Sen M K, Dey D, Dasgupta A, Kazi T A, Gupta R, Sinharoy S, Acharya K, Chattopadhyay D, Ravichandiran V, Roy S, Ghosh D. CRISPR-Cas9 system: A new-fangled dawn in gene editing[J]. Life Sciences, 2019, 232: 116636. |
| [15] | 林萌萌, 李春娟, 闫彩霞, 孙全喜, 赵小波, 王娟, 苑翠玲, 单世华. CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑技术在作物中的应用[J]. 核农学报, 2021, 35(6): 1329-1339. |
| Lin M M, Li C J, Yan C X, Sun Q X, Zhao X B, Wang J, Yuan C L, Shan S H. Application of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology in crops[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 35(6): 1329-1339. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 牛淑琳, 鞠培娜, 周冠华, 戴南平, 周晋军, 谢先芝, 郑崇珂. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑OsRR22基因创制耐盐水稻种质资源[J]. 山东农业科学, 2023, 55(2): 30-35. |
| Niu S L, Ju P N, Z, Zhou G H, D, Dai N P, Z, Zhou J J, Xie X Z, Zheng C K. Creation of salt-tolerant rice germplasm by editingediting OsRR22 gene via CRISPR/Cas9 technique [e[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 55(2): 30-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 李刚, 高清松, 李伟, 张雯霞, 王健, 程保山, 王迪, 高浩, 徐卫军, 陈红旗, 纪剑辉. 定向敲除SD1基因提高水稻的抗倒性和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 359-367. |
| Li G, Gao Q S, Li W, Zhang W W, Wang J, Cheng B S, Wang D, Gao H, Xu W J, Chen H Q, Ji J H. Directed knockout of SD1 gene improves lodging resistance and blast resistance of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 359-367. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Zhang C J, Yun P, Xia J F, Zhou K N, Wang L L, Zhang J W, Zhao B, Yin D K, Fu Z, Wang Y L, Ma T C, Li Z F, Wu D X. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing of Wx and BADH2 genes created glutinous and aromatic two-line hybrid rice[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2023, 43(4): 24. |
| [19] | Hori K, Ogiso-Tanaka E, Matsubara K, Yamanouchi U, Ebana K, Yano M. Hd16, a gene for casein kinase I, is involved in the control of rice flowering time by modulating the day-length response[J]. The Plant Journal, 2013, 76(1): 36-46. |
| [20] | Matsubara K, Ogiso-Tanaka E, Hori K, Ebana K, Ando T, Yano M. Natural variation in Hd17, a homolog of Arabidopsis ELF3 that is involved in rice photoperiodic flowering[J]. Plant &Cell Physiology, 2012, 53(4): 709-716. |
| [21] | Xue W Y, Xing Y Z, Weng X Y, Zhao Y, Tang W J, Wang L, Zhou H J, Yu S B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F. Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2008, 40(6): 761-767. |
| [22] | Imran M, Shafiq S, T, Tang X R. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated editing ofof BADH2 gene triggeredtriggered fragrance revolution in rice[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2023, 175(1): e13871. |
| [23] | Fiaz S, Ahmad S, Ali Noor M, Wang X K, Younas A, Riaz A, Riaz A, Ali F. Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 system for rice grain quality improvement: Perspectives and opportunities[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(4): 888. |
| [24] | Chen H M, Ye R, Liang Y, Zhang S C, Liu X L, Sun C J, Li F B, Yi J C. Generation of low-cadmium rice germplasms via knockout of OsLCD using CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Journal of Environment Science (China), 2023, 126: 138-152. |
| [25] | Sheng X B, Ai Z Y, Tan Y N, Hu Y Y, Guo X Y, Liu X L, Sun Z Z, Yu D, Chen J, Tang N, Duan M J, Yuan D Y.. Novel salinity-tolerant third-generation hybrid rice developed via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(9): 8025. |
| [26] | Zhang Y, Lin X F, Li L, Piao R H, Wu S Q, Song A Q, Gao M M, Jin Y M. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of Bsr-d1 enhances the blast resistance of rice in Northeast China[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2024, 43(4): 100. |
| [27] | 张浩, 柳絮, 宣宁, 张华, 高瑞钰, 赵倩倩, 姚方印. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑DTH8基因改良水稻99-25的抽穗期[J]. 华北农学报, 2020, 35(6): 58-66. |
| Zhang H L, Liu X, Xuan N Z, Zhang H, Gao R Y Z, Zhao Q Q, Y, Yao F Y. Editing DTH8 gene using CRISPR/Cas9 technology to improveimprove heading date of rice 99-25[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2020, 35(6): 58-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Zhou S R, Cai L, Wu H Q, Wang B X, Gu B, Cui S, Huang X L, Xu Z, Hao B Y, Hou H G, Hu Y, Li C, Tian Y L, Liu X, Chen L M, Liu S J, Jiang L, Wan J M. Fine-tuning rice heading date through multiplex editing of the regulatory regions of key genes by CRISPR-Cas9[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2024, 22(3): 751-758. |
| [29] | Sun K L, Huang M H, Zong W B, Xiao D D, Lei C, Luo Y Q, Song Y G, Li S T, Hao Y, Luo W N, Xu B Q, Guo X T, Wei G L, Chen L T, Liu Y G, Guo J X. Hd1, Ghd7, and DTH8 synergistically determine the rice heading date and yield-related agronomic traits[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2022, 49(5): 437-447. |
| [30] | Fujino K. Days to heading, controlled by the heading date genes, Hd1 and DTH8, limits rice yield-related traits in Hokkaido, Japan[J]. Breeding Science, 2020, 70(3): 277-282. |
| [31] | Liu J H, Shen J Q, Xu Y, Li X H, Xiao J H, Xiong L Z. Ghd2, a CONSTANS-like gene, confers drought sensitivity through regulation of senescence in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(19): 5785-5798. |
| [32] | 康雪蒙, 薄晋芳, 马梦影, 巩文靓, 姜恭好, 段海燕. 淀粉合成基因与水稻胶稠度、糊化温度和直链淀粉含量相关性分析[J]. 东北农业科学, 2023, 48(1): 4-29. |
| Kang X M, Bo J F, Ma M Y, Gong W J, Jiang G H, Duan H Y. Correlation analysis of starch synthesis genes with rice gel consistency, gelatinization temperature, and amylose content[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 48(1): 4-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 王娟, 吴丽娟, 洪海波, 姚志文, 王磊, 鄂志国. 水稻泛素结合酶E2的生物学功能研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 744-750. |
| [2] | 陶士博, 许娜, 徐正进, 刘畅, 徐铨. 水稻发芽期耐冷基因Cold6的克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 751-759. |
| [3] | 侯桂花, 周立国, 雷建国, 陈虹, 聂元元. 水稻OsRDR5基因功能及作用机制初步解析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 779-788. |
| [4] | 陆帅, 陶涛, 刘冉, 周文玉, 曹蕾, 杨青青, 张明秋, 任鑫哲, 杨芝笛, 徐福祥, 环海东, 龚远航, 张皓程, 金素奎, 蔡秀玲, 高继平, 冷语佳. 水稻长护颖小粒突变体lsg8的表型鉴定与基因克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 813-824. |
| [5] | 邓欢, 刘亚培, 王春连, 郭威, 陈析丰, 纪志远. 水稻抗白叶枯病新基因Xa49(t)的定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 825-831. |
| [6] | 郝雯倩, 蔡兴菁, 杨海东, 吴宇阳, 滕轩, 薛超, 龚志云. 不同类型组蛋白修饰在水稻响应非生物胁迫中的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 575-585. |
| [7] | 王镜博, 苏畅, 冯晶, 姜思旭, 徐海, 崔志波, 赵明辉. 水稻OsAlR1基因耐铝性功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 615-623. |
| [8] | 韶也, 胡远艺, 彭彦, 毛毕刚, 刘慧敏, 唐婵娟, 雷斌, 唐丽, 余丽霞, 李文建, 罗武中, 罗治斌, 袁远涛, 李曜魁, 张丹, 周利斌, 柏连阳, 唐文帮, 赵炳然. 基于M1TDS靶向筛选技术的重离子束诱变定向改良杂交水稻卓两优1126性状的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 624-634. |
| [9] | 徐群, 王珊, 袁筱萍, 金石桥, 晋芳, 郝万军, 吴小碧, 冯跃, 余汉勇, 孙燕飞, 杨窑龙, 魏兴华. 用于水稻品种真实性验证的SNP位点评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 635-642. |
| [10] | 杨佳欣, 管玉圣, 杜润, 李贤勇, 蔡座坤, 王楚桃, 阳启样, 何永歆, 朱子超, 张毅. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制无芽鞘紫线的香型环境非敏感隐性核雄性不育种质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 643-649. |
| [11] | 张海鹏, 李莞意, 廖福兴, 马美子, 张洪程, 杨艳菊. 纳米钼对水稻根系形态生理和硝态氮吸收的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 650-664. |
| [12] | 刘钰婷, 周星, 何辰延, 李秋萍, 艾小凤, 袁玉洁, 刘睿, 杨景文, 刘婷婷, 王丽, 程红, 黄蓉, 李奥运, 胡文, 胡忠, 任万军, 邓飞. 不同光照条件下减穴稳苗配置对水稻茎鞘干物质积累转运特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 665-678. |
| [13] | 杨行洲, 崔苗苗, 魏利辉, 顾爱国, 李东霞, 乐秀虎, 冯辉. 外源miR3979处理水稻对拟禾本科根结线虫趋性、侵染和发育的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 703-710. |
| [14] | 朱鹏, 凌溪铁, 王金彦, 张保龙, 杨郁文, 许轲, 裘实. 机直播条件下不同控草方式对抗除草剂水稻产量和品质差异性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 501-515. |
| [15] | 董立强, 张义凯, 杨铁鑫, 冯莹莹, 马亮, 梁潇, 张玉屏, 李跃东. 北方粳稻密苗机插育秧对秧苗素质及取秧特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 516-528. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||