
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 643-649.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240501
杨佳欣1, 管玉圣1, 杜润2, 李贤勇1, 蔡座坤2, 王楚桃1, 阳启样2, 何永歆1, 朱子超1,*( ), 张毅2,*(
), 张毅2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-04
修回日期:2024-07-28
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-09-10
通讯作者:
*email: zichaozhu@126.com;基金资助:
YANG Jiaxin1, GUAN Yusheng1, DU Run2, LI Xianyong1, CAI Zuokun2, WANG Chutao1, YANG Qiyang2, HE Yongxin1, ZHU Zichao1,*( ), ZHANG Yi2,*(
), ZHANG Yi2,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-04
Revised:2024-07-28
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-09-10
摘要:
【目的】水稻杂种优势利用技术已发展到第三代,环境非敏感型隐性核雄性不育是第三代杂交稻的必需性状,而香味是许多水稻育种计划的重要目标。另外,水稻芽鞘紫线是极早期表现的一种明显稳定的花青素性状,有利于杂交种纯度的简单、快速和准确鉴定。本研究目的是将II-32B制备成香型、无芽鞘紫线的环境非敏感型隐性核雄性不育材料,为研发方便纯度鉴定的香型第三代杂交稻创造核心种质。【方法】利用CRISPR/Cas9技术,同时对优良水稻亲本II-32B的花粉发育相关基因OsbHLH141、香味基因OsBadh2以及芽鞘紫线基因OsMYB76进行敲除。【结果】获得了三个基因同时发生突变的材料,突变体表现为芽鞘紫线等花青素性状缺失,稻米具有香味且雄性不育。【结论】本研究成功获得了以II-32B为背景的香型、无芽鞘紫线的环境非敏感型隐性核雄性不育种质。
杨佳欣, 管玉圣, 杜润, 李贤勇, 蔡座坤, 王楚桃, 阳启样, 何永歆, 朱子超, 张毅. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制无芽鞘紫线的香型环境非敏感隐性核雄性不育种质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 643-649.
YANG Jiaxin, GUAN Yusheng, DU Run, LI Xianyong, CAI Zuokun, WANG Chutao, YANG Qiyang, HE Yongxin, ZHU Zichao, ZHANG Yi. Creating a Fragrant Environment-insensitive Recessive Genic Male Sterile Germplasm Lacking Coleoptile Purple Lines by CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(5): 643-649.
| 靶点名称 Target name | 引物序列(5΄-3΄) Sequence(5΄-3΄) |
|---|---|
| OsbHLH141 target 1 | CTGGTGGAACAGAAGAGGCA TGG |
| OsbHLH141 target 2 | TGGGAAACAACCCATAATTT TGG |
| OsBadh2 target 1 | TTTACTGGGAGTTATGAAAC TGG |
| OsMYB76 target 1 | AGCACGCTCAGCCGCAAGAT CGG |
表1 本研究所用到的靶点序列
Table 1. Target sequences used in this study
| 靶点名称 Target name | 引物序列(5΄-3΄) Sequence(5΄-3΄) |
|---|---|
| OsbHLH141 target 1 | CTGGTGGAACAGAAGAGGCA TGG |
| OsbHLH141 target 2 | TGGGAAACAACCCATAATTT TGG |
| OsBadh2 target 1 | TTTACTGGGAGTTATGAAAC TGG |
| OsMYB76 target 1 | AGCACGCTCAGCCGCAAGAT CGG |
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物序列(5΄-3΄) Forward primer sequence(5΄-3΄) | 反向引物序列(5΄-3΄) Reverse primer sequence(5΄-3΄) | 目的 Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cas393F/R | TCGAGAACGGTCGTAAGAGGA | TGTAACGCTTCCTGTCGATGGT | 转基因检测Transgenic detection |
| 141F10/R10 | CTCCAGTTAGGGTACCATGGTACT | CGGAATTCCTCACTGGCCTCATCGATGA | 测序Sequencing |
| APCSF1/R1 | CGGAATTCCAGGACTTGTTTGGAGCTTGC | GGGGTACCTGCTCGTCTGGGACCAGTAT | 测序Sequencing |
| OsC1F4/R3 | CAGTCTCACACCGCACAG | ACGGAAACCCGCAACTGC | 测序Sequencing |
| 141F8/R8 | CCATGGTACTCAATCTCATC | GTCCTGAACTTCACATTTAG | 分子标记检测Molecular marker detection |
| 141F9/R9 | GGTGATGCCATTGAGTATAT | GAGCTGATTGTCTTGATCAT | 分子标记检测Molecular marker detection |
| APMF3/R3 | CATGTATACCCCATCAATGG | GCTCAAAGTGTCTTGATCAC | 分子标记检测Molecular marker detection |
| CMDF1/R1 | CGAACAGACAATGAAATCAAG | CACGACGGAGCTGGACGAC | 分子标记检测Molecular marker detection |
表2 本研究所用到的引物序列
Table 2. Primer sequences used in this study
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物序列(5΄-3΄) Forward primer sequence(5΄-3΄) | 反向引物序列(5΄-3΄) Reverse primer sequence(5΄-3΄) | 目的 Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cas393F/R | TCGAGAACGGTCGTAAGAGGA | TGTAACGCTTCCTGTCGATGGT | 转基因检测Transgenic detection |
| 141F10/R10 | CTCCAGTTAGGGTACCATGGTACT | CGGAATTCCTCACTGGCCTCATCGATGA | 测序Sequencing |
| APCSF1/R1 | CGGAATTCCAGGACTTGTTTGGAGCTTGC | GGGGTACCTGCTCGTCTGGGACCAGTAT | 测序Sequencing |
| OsC1F4/R3 | CAGTCTCACACCGCACAG | ACGGAAACCCGCAACTGC | 测序Sequencing |
| 141F8/R8 | CCATGGTACTCAATCTCATC | GTCCTGAACTTCACATTTAG | 分子标记检测Molecular marker detection |
| 141F9/R9 | GGTGATGCCATTGAGTATAT | GAGCTGATTGTCTTGATCAT | 分子标记检测Molecular marker detection |
| APMF3/R3 | CATGTATACCCCATCAATGG | GCTCAAAGTGTCTTGATCAC | 分子标记检测Molecular marker detection |
| CMDF1/R1 | CGAACAGACAATGAAATCAAG | CACGACGGAGCTGGACGAC | 分子标记检测Molecular marker detection |
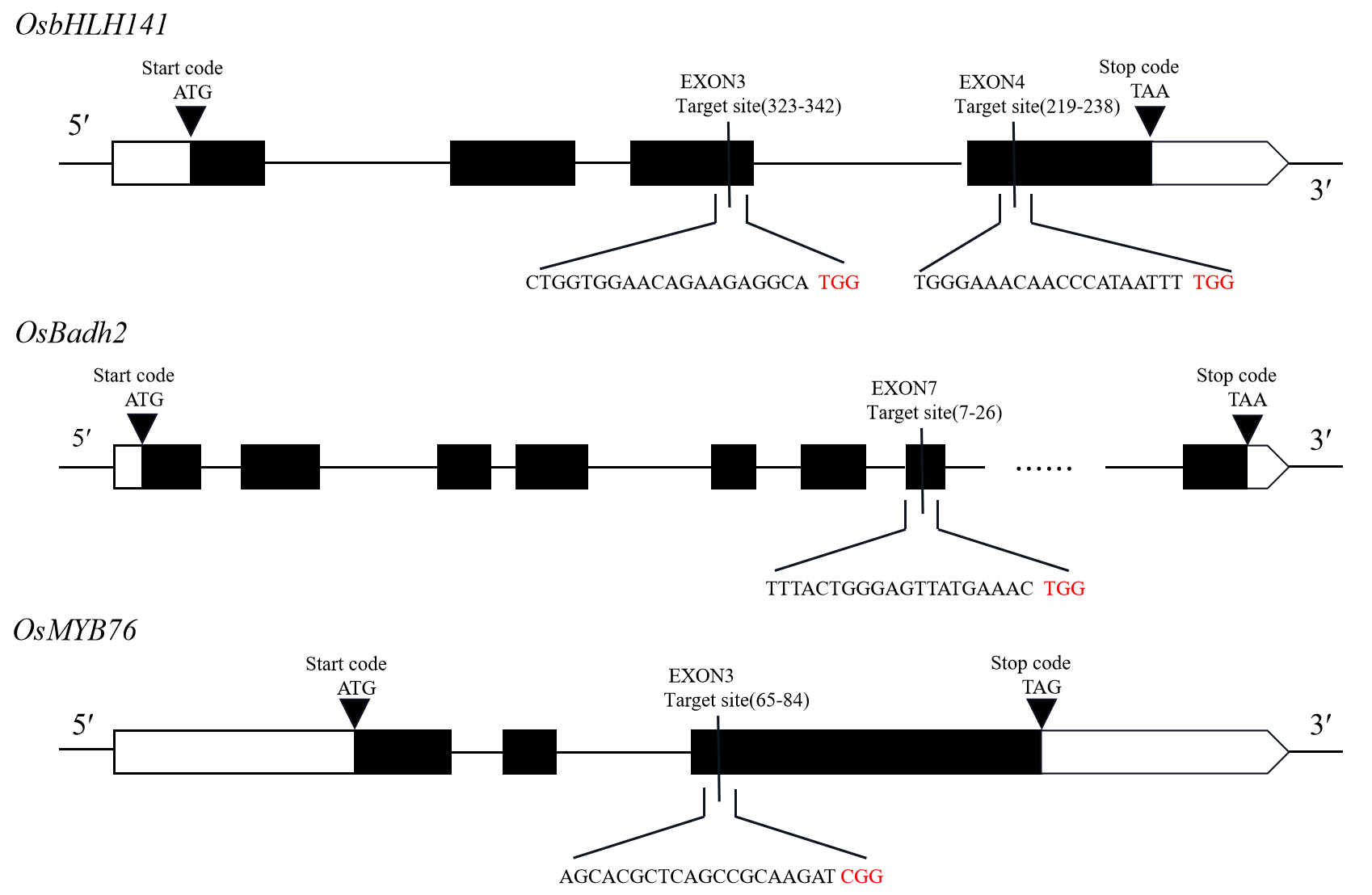
图1 OsbHLH141、OsBadh2及OsMYB76基因结构和靶点位置 黑色序列为靶点序列,红色字母表示PAM序列。白色区域表示非翻译区,黑色区域表示外显子。
Fig.1. Schematic diagram of targeted sites of OsbHLH141, OsBadh2 and OsMYB76 The black sequences are target sequences and the red underlined sequences are PAM sequences. The white regions are UTRs, and the black regions are exons.

图2 T0代植株突变检测 T0代测序结果,下划线部分为靶点,红色字体部分为PAM序列。
Fig. 2. Mutation detection of T0 generation plants Sequencing results of mutation of T0 generation, the underlined sequences are targets, and the red font parts are PAM sequences.
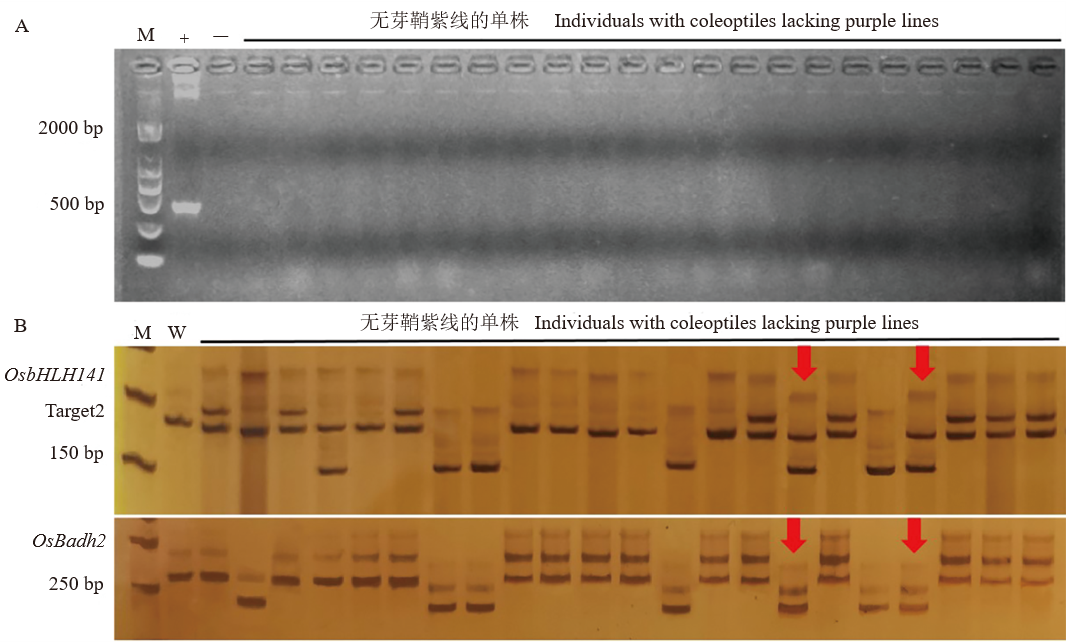
图3 F2代单株检测 A:F2代植株转基因成分检测,M为2000 bp 标记,“+”为阳性对照,“−”为阴性对照;B:F2代无花青素色植株分子标记检测,M为50 bp 标记,W代表野生型对照,红色箭头为OsbHLH141大片段缺失杂合突变和OsBadh2大片段双等位突变。
Fig. 3. Detection of F2 single plants A, Transgenic component detection of F2. M, 2000 bp marker; "+" is the positive control, and "−" is the negative control; B, Molecular marker assistant selection of F2 without anthocyanine pigment. M is 50 bp marker, W is the wild-type control, and the red arrows are the large fragment heterozygous mutations of OsbHLH141 and the large fragment heterozygous biallelic mutations of OsBadh2.
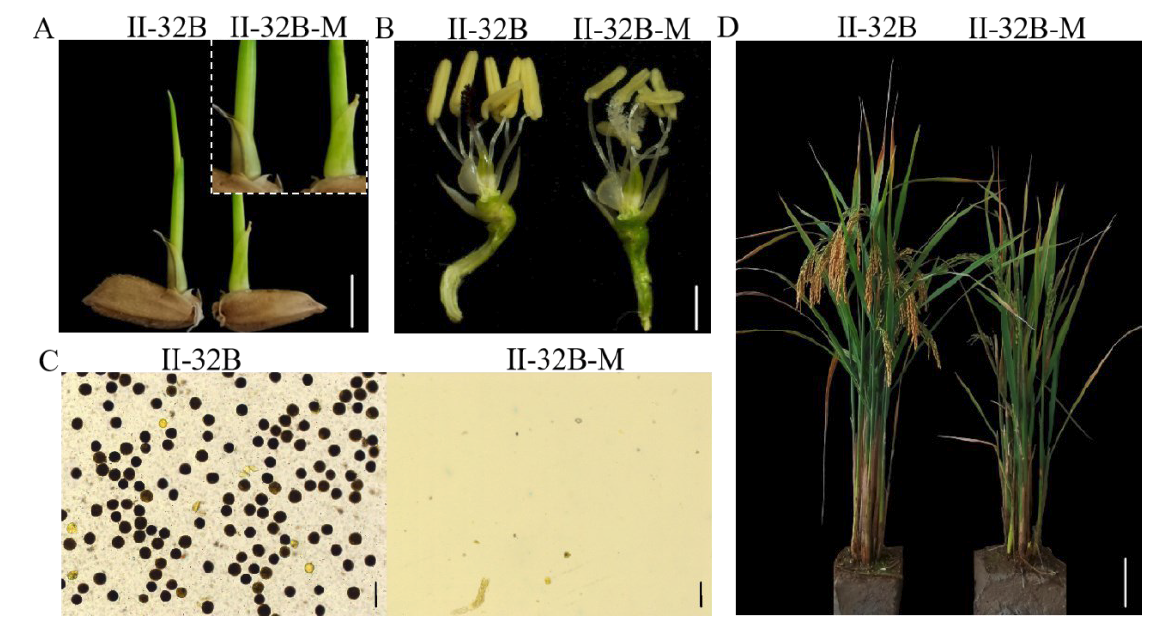

图4 F2代植株三基因突变单株芽鞘紫线和育性观察 A:野生型和突变体的芽鞘对比,标尺=2 mm;B:野生型和突变体的去壳颖花对比,标尺= 50 μm;C:野生型与突变体的花粉碘染对比,标尺= 100 μm;D:野生型和突变体植株对比,标尺= 10 cm。
Fig. 4. Observation of coleoptile purple line and fertility of a single plant with three mutated genes in F2 A, Comparison of coleoptile between wild-type and mutant, Bar=2 mm; B, Comparison of spikelets with glume removed between wild-type and mutant, Bar = 50 μm; C, Comparison of pollen iodine staining between wild-type and mutant, Bar = 100 μm; D, Comparison between wild-type and mutant plants, Bar= 10 cm.
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number | 穗长 Panicle length (cm) | 每穗粒数 No. of grains per panicle | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 结实率 Seed setting rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型 WT | 98.04±2.25 | 14.80±1.48 | 23.22±0.55 | 201.20±16.44 | 22.89±0.26 | 94.49±1.28 |
| 突变体Mutant | 90.77±1.48*** | 12.33±1.03* | 22.20±0.66* | 191.83±12.45 | / | / |
表3 农艺性状的比较
Table 3. Comparison of agronomic traits between wild type and mutant
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number | 穗长 Panicle length (cm) | 每穗粒数 No. of grains per panicle | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 结实率 Seed setting rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型 WT | 98.04±2.25 | 14.80±1.48 | 23.22±0.55 | 201.20±16.44 | 22.89±0.26 | 94.49±1.28 |
| 突变体Mutant | 90.77±1.48*** | 12.33±1.03* | 22.20±0.66* | 191.83±12.45 | / | / |
| [1] | 郭韬, 余泓, 邱杰, 李家洋, 韩斌, 林鸿宣. 中国水稻遗传学研究进展与分子设计育种[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2019, 49(10): 1185-1212. |
| Guo T, Yu H, Qiu J, Li J Y, Han B, Lin H X. Advances in rice genetics and breeding by molecular design in China[J]. Scientia Sinica: Vitae, 2019, 49(10): 1185-1212. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 邓兴旺, 王海洋, 唐晓艳, 周君莉, 陈浩东, 何光明, 陈良碧, 许智宏. 杂交水稻育种将迎来新时代[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2013, 43(10): 864-868. |
| Deng X W, Wang H Y, Tang X Y, Zhou J L, Chen H D, He G M, Chen L B, Xu Z H. Hybrid rice breeding welcomes a new era of molecular crop design[J]. Scientia Sinica: Vitae, 2013, 43(10): 864-868. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Song S, Wang T, Li Y, Hu J, Kan R, Qiu M, Deng Y, Liu P, Zhang L, Dong H, Li C, Yu D, Li X, Yuan D, Yuan L, Li L. A novel strategy for creating a new system of third-generation hybrid rice technology using a cytoplasmic sterility gene and a genic male-sterile gene[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19(2): 251-260. |
| [4] | 李翔, 杜双林, 朱文平, 张毅. 水稻隐性雄性不育突变体osnp3的败育特征及基因定位[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(11): 106-112. |
| Li X, Du S L, Zhu W P, Zhang Y. Sterile characterization and gene mapping of a recessive male sterile mutant osnp3 in rice[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(11): 106-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Yajima I, Yanai T, Nakamura M, Sakakibara H, Hayashi K. Volatile flavor components of cooked Kaorimai (scented rice, O. sativa japonica)[J]. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 1979, 43(12): 2425-2429. |
| [6] | Buttery R G, Ling L C, Juliano B O, Turnbaugh J G. Cooked rice aroma and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 1983, 31(4): 823-826. |
| [7] | Bradbury L M T, Fitzgerald T L, Henry R J, Jin Q, Waters D L E. The gene for fragrance in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2005, 3(3): 363-370. |
| [8] | Tian Y, Zhou Y, Gao G, Zhang Q, Li Y, Lou G, He Y. Creation of two-line fragrant glutinous hybrid rice by editing the Wx and OsBADH2 genes via the CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(1): 849. |
| [9] | 李景芳, 温舒越, 赵利君, 陈庭木, 周振玲. 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术创制耐盐香稻[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37 (5): 478-485. |
| Li J F, Wen S Y, Zhao L J, Chen T M, Zhou Z L. Development of aromatic salt-tolerant rice based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 478-485. | |
| [10] | 胡景涛, 黄文章, 严明建. 几种杂交水稻种子纯度鉴定的方法及其应用前景[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(4): 1493-1495+1536. |
| Hu J T, Huang W Z, Yan M J. Methods for identifying the purity of hybrid rice seeds and their application prospects[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 37(4): 1493-1495, 1536. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 张毅, 李云峰, 刘晓锋, 林茂祥, 沈福成, 何光华, 杨正林, 杨光伟. 水稻芽鞘紫线遗传分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2004(11): 1693-1698. |
| Zhang Y, Li Y F, Liu X F, Lin M X, Shen F C, He G H, Yang Z L, Yang G W. Analysis on the inheritance of coleoptile purple line in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2004(11): 1693-1698. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Du S, Wang Z, Chen Y, Tan Y, Li X, Zhu W, He G, Lei K, Guo L, Zhang Y. Coleoptile purple line regulated by A-P gene system is a valuable marker trait for seed purity identification in hybrid rice[J]. Rice Science, 2022, 29(5): 451-461. |
| [13] | 张毅. 水稻两个芽鞘紫线相关基因的图位克隆与应用研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2009. |
| Zhang Y. Mapping cloning and application of genes related to purple line in two bud sheaths of rice[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 任光俊, 颜龙安, 谢华安. 三系杂交水稻育种研究的回顾与展望[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(35): 3748-3760. |
| Ren G J, Yan L A, Xie H A. Retrospective and perspective on indica three-line hybrid rice breeding research in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(35): 3748-3760. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Xie K, Minkenberg B, Yang Y. Boosting CRISPR/Cas9 multiplex editing capability with the endogenous tRNA-processing system[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(11): 3570-3575. |
| [16] | 李新奇, 黄群策. 第3代杂交水稻育种技术策略探讨[J]. 杂交水稻, 2020, 35(1): 1-5. |
| Li X Q, Huang Q C. Discussion on the breeding technical strategy of the third-generation hybrid rice breeding[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2020, 35(1): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 李雅礼, 唐华园, 黄群策, 李新奇. 第三代杂交水稻研究与实践[J]. 分子植物育种, 2024, 22(15): 5124-5131. |
| Li Y L, Tang H Y, Huang Q C, Li X Q. Research and application of the third-generation hybrid rice[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2024, 22(15): 5124-5131. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Chang Z, Chen Z, Wang N, Xie G, Lu J, Yan W, Zhou J, Tang X, Deng X W. Construction of a male sterility system for hybrid rice breeding and seed production using a nuclear male sterility gene[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(49): 14145-14150. |
| [19] | 宋丰顺, 倪大虎, 倪金龙, 李莉, 杨剑波. 杂交水稻种子纯度检测方法综述[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(6): 6-11. |
| Song F S, Ni D H, Ni J L, Li L, Yang J B. A review of methods for detecting the purity of hybrid rice seeds[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(6): 6-11. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 张倩倩, 殷春渊, 刘贺梅, 胡秀明, 孟利红. 48份水稻骨干材料香味及Badh2变异类型的鉴定[J]. 种子, 2024, 43(1): 107-113. |
| Zhang Q Q, Yin C Y, Liu H M, Hu X M, Meng L H. Identification of fragrance and Badh2 variation types in 48 Oryza sativa L. backbone materials[J]. Seed, 2024, 43(1): 107-113. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 韶也, 胡远艺, 彭彦, 毛毕刚, 刘慧敏, 唐婵娟, 雷斌, 唐丽, 余丽霞, 李文建, 罗武中, 罗治斌, 袁远涛, 李曜魁, 张丹, 周利斌, 柏连阳, 唐文帮, 赵炳然. 基于M1TDS靶向筛选技术的重离子束诱变定向改良杂交水稻卓两优1126性状的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 624-634. |
| [2] | 张来桐, 杨乐, 刘洪, 赵学明, 程涛, 徐振江. 水稻香味物质的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 171-186. |
| [3] | 何勇, 刘耀威, 熊翔, 祝丹晨, 王爱群, 马拉娜, 王廷宝, 张健, 李建雄, 田志宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑OsOFP30基因创制水稻粒型突变体[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [4] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [5] | 李景芳, 温舒越, 赵利君, 陈庭木, 周振玲, 孙志广, 刘艳, 陈海元, 张云辉, 迟铭, 邢运高, 徐波, 徐大勇, 王宝祥. 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术创制耐盐香稻[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 478-485. |
| [6] | 李刚, 高清松, 李伟, 张雯霞, 王健, 程保山, 王迪, 高浩, 徐卫军, 陈红旗, 纪剑辉. 定向敲除SD1基因提高水稻的抗倒性和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 359-367. |
| [7] | 段敏, 谢留杰, 高秀莹, 唐海娟, 黄善军, 潘晓飚. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制广亲和水稻温敏雄性不育系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 233-243. |
| [8] | 王石光, 陆展华, 刘维, 卢东柏, 王晓飞, 方志强, 巫浩翔, 何秀英. 应用CRISPR/Cas9技术与分子标记辅助选择创制广东丝苗米新种质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 29-36. |
| [9] | 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 赵凌, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 张亚东, 王才林. 利用分子标记辅助选择培育优良食味、低谷蛋白香粳稻新品系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 55-65. |
| [10] | 张元野, 尹丽颖, 李荣田, 何明良, 刘欣欣, 潘婷婷, 田晓杰, 卜庆云, 李秀峰. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制Rc基因恢复红稻[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 572-578. |
| [11] | 尹丽颖, 张元野, 李荣田, 何明良, 王芳权, 许扬, 刘欣欣, 潘婷婷, 田晓杰, 卜庆云, 李秀峰. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制高效抗除草剂水稻[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 459-466. |
| [12] | 周永林, 申小磊, 周立帅, 林巧霞, 王朝露, 陈静, 冯慧捷, 张振文, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsLOX10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 348-356. |
| [13] | 李兆伟, 孙聪颖, 零东兰, 曾慧玲, 张晓妹, 范凯, 林文雄. 利用CRISPR/Cas9创建osarf7突变体及其农艺性状调查[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 237-247. |
| [14] | 梁敏敏, 张华丽, 陈俊宇, 戴冬青, 杜成兴, 王惠梅, 马良勇. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制抗稻瘟病香型早籼温敏核不育系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 248-258. |
| [15] | 魏晓东, 张亚东, 赵凌, 路凯, 宋雪梅, 王才林. 稻米香味物质2-乙酰-1-吡咯啉的形成及其影响因素[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 131-138. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||