
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 233-243.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.221006
段敏1, 谢留杰1, 高秀莹2, 唐海娟2, 黄善军1, 潘晓飚1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-24
修回日期:2022-11-07
出版日期:2023-05-10
发布日期:2023-05-16
通讯作者:
*email: xbpan@163.com
基金资助:
DUAN Min1, XIE Liujie1, GAO Xiuying2, TANG Haijuan2, HUANG Shanjun1, PAN Xiaobiao1,*( )
)
Received:2022-10-24
Revised:2022-11-07
Online:2023-05-10
Published:2023-05-16
Contact:
*email: xbpan@163.com
摘要:
【目的】为突破传统杂交转育方法对水稻两系不育系选育的限制,利用CRISPR/Cas9技术对籼型恢复系台恢31的温敏雄性核不育基因TMS5进行编辑,以获得全新水稻温敏雄性不育系。【方法】选择水稻温敏不育基因TMS5第1外显子的2段序列作为靶点,构建双靶点pHUE411-TMS5-gRNA载体,通过农杆菌侵染获得116株T0代转基因植株。【结果】经鉴定获得3种类型纯合突变体tms5-1、tms5-2和tms5-3,每一种突变均导致TMS5氨基酸序列的缺失。分期播种试验结果显示,幼穗分化敏感期温度为27℃时,tms5-1和tms5-3自交结实率分别为0.56%、0.03%,表现为高度不育,而tms5-2则完全不育。与野生型台恢31相比,不育系TB52S(即tms5-2)单株穗数增多,穗长变短,株高及每穗总粒数相较WT均下降25%,花药发白瘦小,无花粉粒充实,柱头、颖壳没有显著差异。TB52S幼穗分化4期时进行温度处理,确认TB52S的育性转换温度为26℃。TB52S分别与籼、粳型恢复系配组,F1的结实率超过90%。【结论】利用CRISPR/Cas9技术对籼型恢复系台恢31的温敏雄性核不育基因TMS5进行编辑,获得能够稳定遗传的水稻广亲和温敏雄性不育系TB52S,为两系不育系选育提供新的技术支撑。
段敏, 谢留杰, 高秀莹, 唐海娟, 黄善军, 潘晓飚. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制广亲和水稻温敏雄性不育系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 233-243.
DUAN Min, XIE Liujie, GAO Xiuying, TANG Haijuan, HUANG Shanjun, PAN Xiaobiao. Creation of Thermo-sensitive Genic Male Sterile Rice Lines with Wide Compatibility Based on CRISPR/Cas9 Technology[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 233-243.
| 引物名称 Primer | 寡核苷酸序列 (5’-3’) Oligonucleotide sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| T5T1-BsF | ATATATGGTCTCTGGCGAACAGCGGCAAGTCATCGC |
| T5T1-BsR | ATTATTGGTCTCTAAACTCACCTTGAGGTCCCTCCTC |
| T5T1-F0 | GAACAGCGGCAAGTCATCGCGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC |
| T5T2-R0 | AACTCACCTTGAGGTCCCTCCTCGCTTCTTGGTGCC |
| T5U3-F | GACAGGCGTCTTCTACTGGTGCTA |
| T5U3-R | TCACAAATTATCAGCACGCTAGTC |
| T5-SF1 | GACAGGCGTCTTCTACTGGTGCTA |
| T5-SF2 HYG-F | GGCCAGCAATTACGAGTCCTTCTA GCGTCTGCTGCTCCATACAA |
| HYG-R | TGACATTGGGGAGTTTAGCG |
| T5-F | CCAACGCATAGCAGTAGTCG |
| T5-R | AATGAAATCTGCCATCGTATC |
表1 本研究涉及的PCR扩增及测序引物
Table 1. Primers used for amplification and sequencing.
| 引物名称 Primer | 寡核苷酸序列 (5’-3’) Oligonucleotide sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| T5T1-BsF | ATATATGGTCTCTGGCGAACAGCGGCAAGTCATCGC |
| T5T1-BsR | ATTATTGGTCTCTAAACTCACCTTGAGGTCCCTCCTC |
| T5T1-F0 | GAACAGCGGCAAGTCATCGCGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC |
| T5T2-R0 | AACTCACCTTGAGGTCCCTCCTCGCTTCTTGGTGCC |
| T5U3-F | GACAGGCGTCTTCTACTGGTGCTA |
| T5U3-R | TCACAAATTATCAGCACGCTAGTC |
| T5-SF1 | GACAGGCGTCTTCTACTGGTGCTA |
| T5-SF2 HYG-F | GGCCAGCAATTACGAGTCCTTCTA GCGTCTGCTGCTCCATACAA |
| HYG-R | TGACATTGGGGAGTTTAGCG |
| T5-F | CCAACGCATAGCAGTAGTCG |
| T5-R | AATGAAATCTGCCATCGTATC |
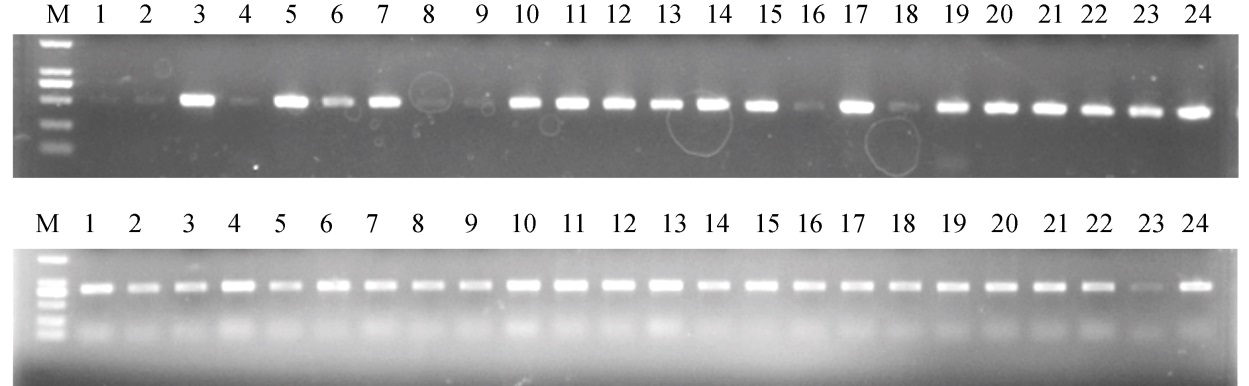
图2 T0代转基因植株(部分)阳性检测结果 M―标记;1~24―T0单株。A―潮霉素标记, 条带大小506 bp;B―载体+基因片段, 条带大小831 bp。扩增出相应片段表示植株为阳性。
Fig. 2. Positive identification of T0 transgenic plants (partial). M, Marker; 1-24, T0 plants. A, Hygromycin gene, 506 bp in length; B, The band with 831 bp length was amplified by primer T5U3-F/R. The 863 bp fragment means a positive test result.
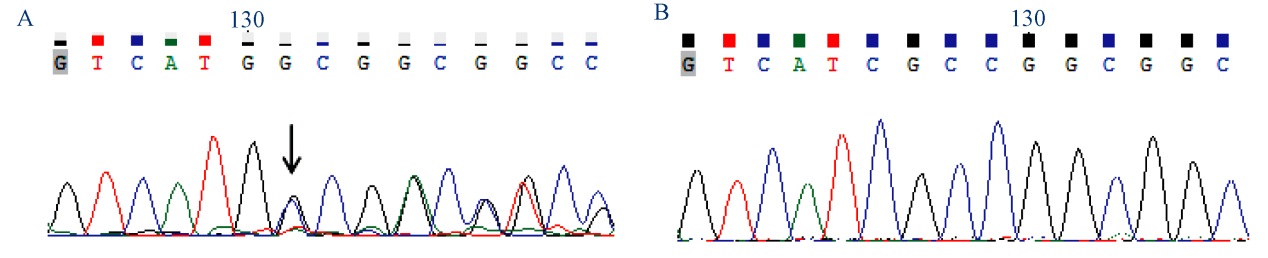
图3 T0代转基因植株及野生型(台恢31) TMS5第一靶点测序结果 A, T0代杂合植株第一靶点测序结果, 箭头表示双峰开始位置;B, 野生型(台恢31)第一靶点测序结果。
Fig. 3. Sequencing of the first target site of TMS5 in T0 transgenic plants and WT (Taihui 31). A, Sequencing of T0 transgenic plants at the first target site. The arrow indicates the starting point of double peaks; B, Sequencing results of WT.
| 播种期 Sowing date | 突变体类型 Mutant type | 播始历期 Days from sowing to heading/d | 幼穗分化敏感期 Young panicle differentiation period | 敏感期温度均值 Mean temperature of period/℃ | 自交结实率 Self-fertilization rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05-14(I) | tms5-1 | 90 | 07-23 -7月29日 | 27.0 | 0.56±1.26 |
| tms5-2 | 91 | 07-24 -7月30日 | 27.4 | 0 | |
| tms5-3 | 90 | 07-23 -7月29日 | 27.0 | 0.03±0.13 | |
| 05-24(II) | tms5-1 | 87 | 07-30 -8月5日 | 28.1 | 0 |
| tms5-2 | 87 | 07-30 -8月5日 | 28.1 | 0 | |
| tms5-3 | 86 | 07-29 -8月4日 | 28.3 | 0 | |
| 06-04(III) | tms5-1 | 79 | 08-02 -8月8日 | 27.8 | 0 |
| tms5-2 | 80 | 08-03 -8月9日 | 27.8 | 0 | |
| tms5-3 | 80 | 08-03 -8月9日 | 27.8 | 0 | |
| 06-14(IV) | tms5-1 | 76 | 08-09 -8月15日 | 27.3 | 0 |
| tms5-2 | 77 | 08-10 -8月16日 | 27.0 | 0 | |
| tms5-3 | 76 | 08-09 -8月15日 | 27.3 | 0 |
表2 tms5突变体分期播种的不育性鉴定
Table 2. Sterility identification of tms5 mutants seeded at different dates.
| 播种期 Sowing date | 突变体类型 Mutant type | 播始历期 Days from sowing to heading/d | 幼穗分化敏感期 Young panicle differentiation period | 敏感期温度均值 Mean temperature of period/℃ | 自交结实率 Self-fertilization rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05-14(I) | tms5-1 | 90 | 07-23 -7月29日 | 27.0 | 0.56±1.26 |
| tms5-2 | 91 | 07-24 -7月30日 | 27.4 | 0 | |
| tms5-3 | 90 | 07-23 -7月29日 | 27.0 | 0.03±0.13 | |
| 05-24(II) | tms5-1 | 87 | 07-30 -8月5日 | 28.1 | 0 |
| tms5-2 | 87 | 07-30 -8月5日 | 28.1 | 0 | |
| tms5-3 | 86 | 07-29 -8月4日 | 28.3 | 0 | |
| 06-04(III) | tms5-1 | 79 | 08-02 -8月8日 | 27.8 | 0 |
| tms5-2 | 80 | 08-03 -8月9日 | 27.8 | 0 | |
| tms5-3 | 80 | 08-03 -8月9日 | 27.8 | 0 | |
| 06-14(IV) | tms5-1 | 76 | 08-09 -8月15日 | 27.3 | 0 |
| tms5-2 | 77 | 08-10 -8月16日 | 27.0 | 0 | |
| tms5-3 | 76 | 08-09 -8月15日 | 27.3 | 0 |
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height/cm | 单株穗数 Panicles per plant | 每穗总粒数 Grains per panicle | 穗长 Panicle length/cm | 柱头外露率 Chapiter exposure percentage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TB52S | 86.1±3.0 | 13.5±2.0 | 243.2±63.4 | 23.0±1.9 | 53.3±3.7 |
| 台恢31 Taihui 31(WT) | 113.3±3.1 | 8.3±0.6 | 316.3±71.7 | 26.8±2.0 | - |
表3 水稻温敏核不育系TB52S农艺性状
Table 3. Agronomic traits of thermo-sensitive genic male sterile mutant TB52S.
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height/cm | 单株穗数 Panicles per plant | 每穗总粒数 Grains per panicle | 穗长 Panicle length/cm | 柱头外露率 Chapiter exposure percentage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TB52S | 86.1±3.0 | 13.5±2.0 | 243.2±63.4 | 23.0±1.9 | 53.3±3.7 |
| 台恢31 Taihui 31(WT) | 113.3±3.1 | 8.3±0.6 | 316.3±71.7 | 26.8±2.0 | - |
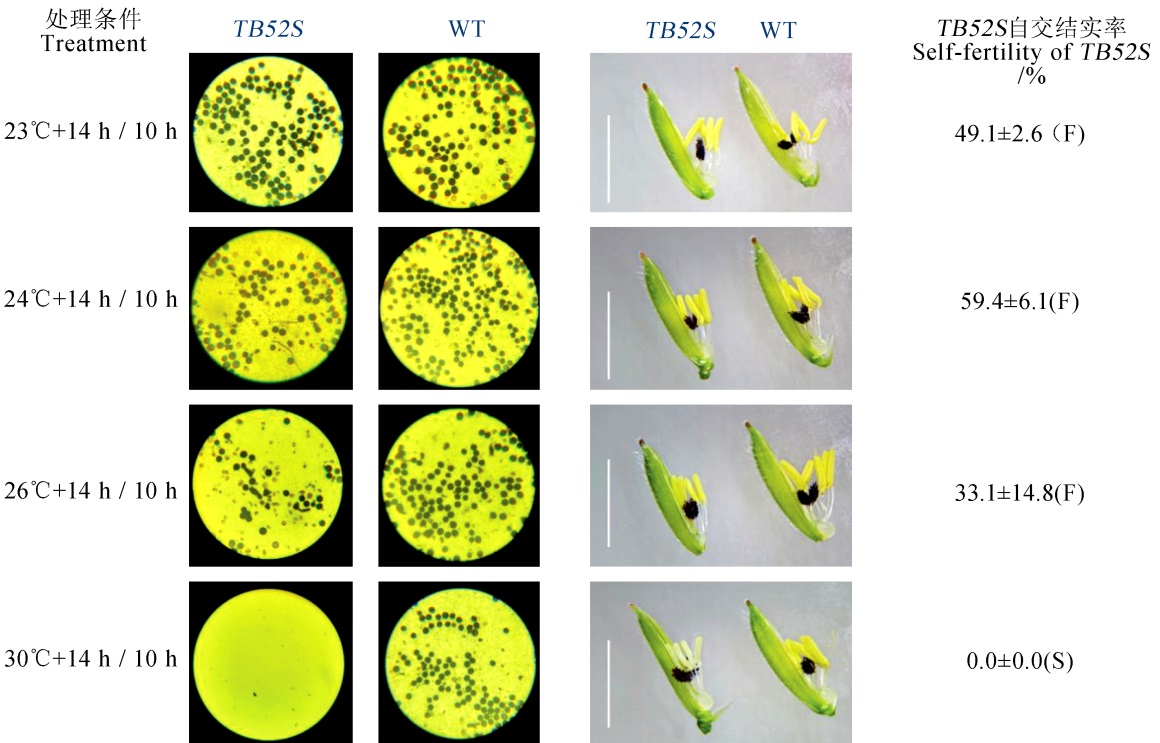
图8 突变体TB52S在不同温度处理下的花粉育性、花药形态及自交结实率(比例尺为5 mm,F表示可育,S表示不育)
Fig. 8. Pollen fertility and self-fertilization rate of TB52S mutant under different temperature treatments during the young panicle differentiation. (Bar=5 mm; F, Fertile; S, Sterile)
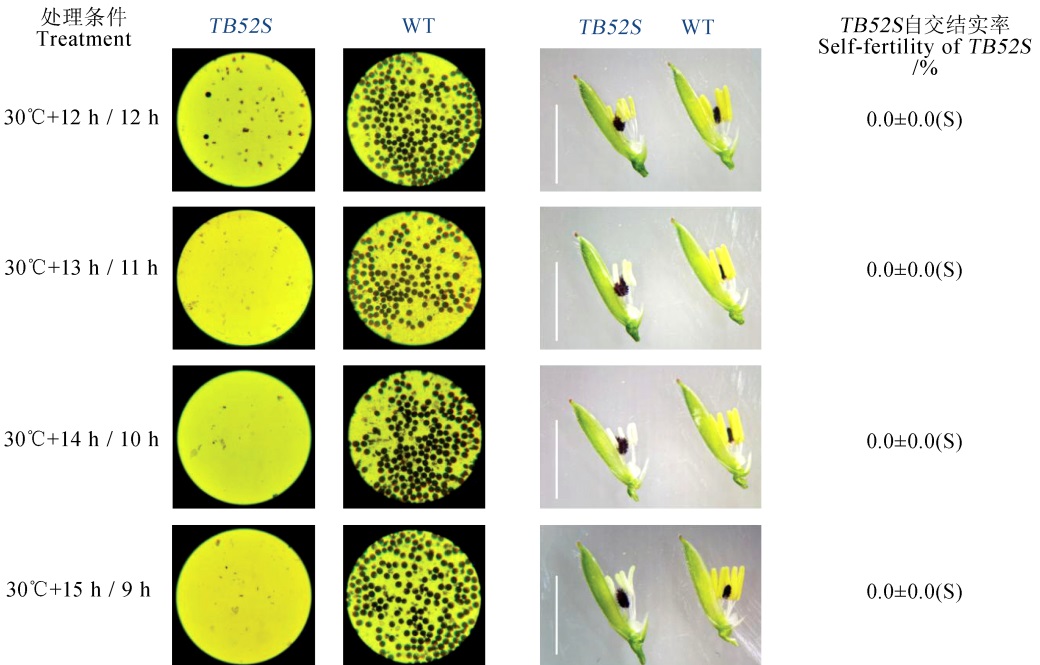
图9 突变体TB52S在不同光照长度处理下的花粉育性、花药形态及自交结实率(比例尺为5 mm,S表示不育)
Fig. 9. Pollen fertility and self-fertilization rate of TB52S mutant under different photoperiod period treatments during the young panicle differentiation. (Bar=5 mm; S showed sterile)
| 组合 Combination | 株高 Plant height/cm | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number | 穗长 Panicle length /cm | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 单株产量 Yield per plant/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TB52S/台恢1050 TB52S/Taihui 1050 | 122.3 | 10.3 | 24.7 | 209.4 | 93.3 | 28.8 | 60.2 |
| TB52S/台恢468 TB52S/Taihui 468 | 129.3 | 13.7 | 24.8 | 246.0 | 90.9 | 26.8 | 79.2 |
| TB52S/台恢1628 TB52S/Taihui 1628 | 139.3 | 11.0 | 27.3 | 288.9 | 88.9 | 26.4 | 75.1 |
| TB52S/TP39 | 126.3 | 8.3 | 21.5 | 258.2 | 96.1 | 24.6 | 49.9 |
| TB52S/HR11 | 125.7 | 7.0 | 25.0 | 316.7 | 90.8 | 25.2 | 50.8 |
| TB52S/HR4 | 123.7 | 8.3 | 24.8 | 307.0 | 94.6 | 25.4 | 55.6 |
表4 水稻温敏核不育系突变体TB52S与不同恢复系配组F1农艺性状
Table 4. Agronomic traits of F1 hybrids derived from the cross between TB52S and restorer lines.
| 组合 Combination | 株高 Plant height/cm | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number | 穗长 Panicle length /cm | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 单株产量 Yield per plant/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TB52S/台恢1050 TB52S/Taihui 1050 | 122.3 | 10.3 | 24.7 | 209.4 | 93.3 | 28.8 | 60.2 |
| TB52S/台恢468 TB52S/Taihui 468 | 129.3 | 13.7 | 24.8 | 246.0 | 90.9 | 26.8 | 79.2 |
| TB52S/台恢1628 TB52S/Taihui 1628 | 139.3 | 11.0 | 27.3 | 288.9 | 88.9 | 26.4 | 75.1 |
| TB52S/TP39 | 126.3 | 8.3 | 21.5 | 258.2 | 96.1 | 24.6 | 49.9 |
| TB52S/HR11 | 125.7 | 7.0 | 25.0 | 316.7 | 90.8 | 25.2 | 50.8 |
| TB52S/HR4 | 123.7 | 8.3 | 24.8 | 307.0 | 94.6 | 25.4 | 55.6 |
| [1] | 牟同敏. 中国两系法杂交水稻研究进展和展望[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(35): 3761-3769. |
| Mou T M. The research progress and prospects of two-line hybrid rice in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(35): 3761-3769. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 王宝和, 徐建军, 吴银慧, 朱金燕, 李生强, 周勇, 程小涛, 梁国华. 水稻光温敏雄性核不育系广占63S不育基因PTGMS2-1的遗传分析与分子定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(4): 429-432. |
| Wang B H, Xu J J, Wu Y H, Zhu J Y, Li S Q, Zhou Y, Cheng X T, Liang G H. Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of a photoperiod-thermo-sensitive genic male sterile gene (PTGMS2-1) in rice line Guangzhan 63S[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2010, 24(4): 429-432. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Liu N, Shan Y, Wang F P, Xu C G, Peng K M, Li X H, Zhang Q F. Identification of an 85-kb DNA fragment containing pms1, a locus for photoperiod-sensitive genic male sterility in rice[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2001, 266: 271-275. |
| [4] | Zhang Q F, Shen B Z, Dai X K, Mei M H, Saghai M M A, Li Z B. Using bulked extremes and recessive class to map genes for photoperiod sensitive genic male sterility in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1994, 91: 8675-8679. |
| [5] | Lu Q, Li X, Guo D, Xu C G, Zhang Q F. Localization of pms3, a gene for photoperiod-sensitive genic male sterility, to a 28.4-kb DNA fragment[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2005, 273: 507-511. |
| [6] | Zhou H, Liu Q J, Li J, Jiang D G, Zhou L Y, Wu P, Lu S, Li F, Zhu L Y, Liu Z L, Chen L T, Liu Y G, Zhuang C X. Photoperiod- and thermo-sensitive genic male sterility in rice are caused by a point mutation in a novel noncoding RNA that produces a small RNA[J]. Cell Research, 2012, 22: 649-660. |
| [7] | Xu J J, Wang B H, Wu Y H, Du P N, Wang J, Wang M, Yi C D, Gu M H, Liang G H. Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of ptgms2-1, the photoperiod- thermo-sensitive genic male sterile gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2011, 122: 365-372. |
| [8] | Wang B, Xu W W, Wang J Z, Wu W, Zheng H G, Yang Z Y, Ray J D, Nguyen H T. Tagging and mapping the thermo-sensitive genic male-sterile gene in rice(Oryza sativa L.) with molecular markers[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1995, 91: 1111-1114. |
| [9] | Lopez M T, Toojinda T, van Avichit A, Tragoonrung S. Microsatellite markers flanking the tms2 gene facilitated tropical TGMS rice line development[J]. Crop Science, 2003, 43: 2267-2271. |
| [10] | Subudhi P K, Borkakati R, Virmani S S. Molecular mapping of a thermo-sensitive genetic male-sterility gene in rice using bulked segregant analysis[J]. Genome, 1997, 40: 188-194. |
| [11] | Yang Q K, Liang C Y, Li J, Jin D M, Ahuang W, Deng Q Y, Wang B. Characterization and identification of the candidate gene of rice thermo-sensitive genic male sterile gene tms5 by mapping[J]. Planta, 2007, 225: 321-330. |
| [12] | 杜茜, 费云燕, 王芳权, 许扬, 王军, 李文奇, 赵凌, 陈智慧, 梁国华, 周勇, 杨杰. 敲除TMS5基因获得温敏不育粳稻新材料[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 429-435. |
| Du Q, Fei Y Y, Wang F Q, Xu Y, Wang J, Li W Q, Zhao L, Chen Z H, Liang G H, Zhou Y, Yang J. Thermo- sensitive male sterile line created by editing TMS5 gene in japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(5): 429-435. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 景润春, 卢洪. CRISPR/Cas9基因组定向编辑技术的发展与在作物遗传育种中的应用[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(7): 1219-1229. |
| Jing R C, Lu H. The development of CRISPR/Cas9 system and its application in crop genome editing[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(7): 1219-1229. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Symington L S, Gautier J. Double-strand break end resection and repair pathway choice[J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 2011, 45: 247-271. |
| [15] | Zhou H, He M, Li J, Chen L, Huang Z F, Zheng S Y, Zhu L Y, Ni E D, Jiang D G, Zhao B R, Zhuang C X. Development of commercial thermo-sensitive genic male sterile rice accelerates hybrid rice breeding using the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated TMS5 editing system[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 37395. |
| [16] | 黄忠明, 周延彪, 唐晓丹, 赵新辉, 周在为, 符星学, 王凯, 史江伟, 李艳锋, 符辰建, 杨远柱. 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术的水稻温敏不育基因tms5突变体的构建[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44 (6): 844-851. |
| Huang Z M, Zhou Y B, Tang X D, Zhao X H, Zhou Z W, Fu X X, Wang K, Shi J W, Li Y F, Fu C J, Yang Y Z. Construction of tms5 mutants in rice based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(6): 844-851. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 陈日荣, 周延彪, 王黛君, 赵新辉, 唐晓丹, 许世冲, 唐倩莹, 符星学, 王凯, 刘选明, 杨远柱. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑水稻温敏不育基因TMS5[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(8): 1157-1165. |
| Chen R R, Zhou Y B, Wang D J, Zhao X H, Tang X D, Xu S C, Tang Q Y, Fu X X, Wang K, Liu X M, Yang Y Z. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing of the thermo- sensitive genic male-sterile gene TMS5 in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(8): 1157-1165. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Barman H N, Sheng Z, Fiaz S, Zhong M, Wu Y W, Cai Y C, Wang W, Jiao G A, Tang S Q, Wei X J, Hu P S. Generation of a new thermo-sensitive genic male sterile rice line by targeted mutagenesis of TMS5 gene through CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19 (1): 109. |
| [19] | Chen Y Y, Wang Z P, Ni H W, Xu Y, Chen Q J, Jiang L J. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated base-editing system efficiently generates gain-of function mutations in Arabidopsis[J]. Science China: Life Science, 2017, 60(5): 520-523. doi: 10.1007/sll427-017-9021-5. |
| [20] | 唐海娟. 根癌农杆菌介导的水稻转基因体系研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2009: 27-32. |
| Tang H J. Study on Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated rice transgenic system[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2009: 27-32. | |
| [21] | Xing H L, Dong L, Wang Z P, Zhang H Y, Han C Y, Liu B, Wang X C, Chen Q J. A CRISPR/Cas9 toolkit for multiplex genome editing in plants[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2014, 14: 327. |
| [22] | Petolino J F. Genome editing in plants via designed zinc finger nucleases[J]. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology-Plant, 2015, 51(1): 1-8. |
| [23] | Bogdanove A J, Voytas D F. TAL effectors: Customizable proteins for DNA targeting[J]. Science, 2011, 333(6051): 1843-1846. |
| [24] | Ma X L, Zhang Q Y, Zhu Q L, Liu W, Chen Y, Qiu R, Wang B, Yang Z F, Li H Y, Lin Y R, Xie Y Y, Shen R X, Chen S F, Wang Z, Chen Y L, Guo J X, Chen L T, Zhao X C, Liu Y G. A robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(8): 1274-1284. |
| [25] | Xu R F, Li H, Qin R Y, Li J, Qiu C H, Yang Y C, Ma H, Li L, Wei P C, Yang J B. Generation of inheritable and “transgeneclean” targeted genome-modified rice in later generations using the CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015: 11491. |
| [26] | 王加峰, 郑才敏, 刘维, 罗文龙, 王慧, 陈志强, 郭涛. 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术的水稻千粒重基因tgw6突变体的创建[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(8): 1160-1167. |
| Wang J F, Zheng C M, Liu W, Luo W L, Wang H, Chen Z Q, Guo T. Construction of tgw6 mutants in rice based on CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(8): 1160-1167. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 王芳权, 范方军, 李文奇, 朱金燕, 王军, 仲维功, 杨杰. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术敲除水稻Pi21基因的效率分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(5): 469-478. |
| Wang F Q, Fan F J, Li W Q, Zhu J Y, Wang J, Zhong W G, Yang J. Knock-out efficiency analysis of Pi21 gene using CRISPR/Cas9 in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(5): 469-478. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 周海, 周明, 杨远柱, 曹晓风, 庄楚雄. RNase ZS1加工UbL40mRNA控制水稻温敏雄性核不育[J]. 遗传, 2014, 36: 1274. |
| Zhou H, Zhou M, Yang Y Z, Cao X F, Zhuang C X. RNase ZS1 processes UbL40mRNA to control thermo-sensitive genic male sterility in rice[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2014, 36: 1274. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | Liu W, Xie X, Ma X, Li J, Chen J, Liu Y G. DSDecode: A web-based tool for decoding of sequencing chromatograms for genotyping of targeted mutations[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8: 1431-1433. |
| [30] | 程式华, 孙宗修, 斯华敏, 卓丽圣. 水稻两用核不育系育性转换光温反应型的分类研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 1996, 29(4): 11-16. |
| Cheng S H, Sun Z X, Si H M, Zhuo L S. Classification of fertility response to photoperiod and temperature in dual-purpose genic male sterile lines (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1996, 29(4): 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 卢兴桂. 中国光、温敏雄性不育水稻育性生态[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 135-136. |
| Lu X G. Fertility Ecology of Photoperiod- and Thermo-sensitive Genic Male Sterile Rice in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003: 135-136. (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | 朱旭东, 王建林, 熊振民, 严学强. 水稻亚种间杂种优势利用中广亲和性的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1994, 8 (4): 211-216. |
| Zhu X D, Wang J L, Xiong Z M, Yan X Q. Studies on the wide compatibility for utilization of heterosis between indica and japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 1994, 8(4): 211-216. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 万建民. 水稻籼粳交杂种优势利用研究[J]. 杂交水稻, 2010(S1): 15-18. |
| Wan J M. Utilization of strong heterosis between indica and japonica varieties in rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2010, 2010(S1): 15-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||