
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 650-664.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.241006
张海鹏, 李莞意, 廖福兴, 马美子, 张洪程, 杨艳菊*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-17
修回日期:2025-03-07
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-09-10
通讯作者:
*email: yangyanju@yzu.edu.cn基金资助:
ZHANG Haipeng, LI Wanyi, LIAO Fuxing, MA Meizi, ZHANG Hongcheng, YANG Yanju*( )
)
Received:2024-10-17
Revised:2025-03-07
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-09-10
摘要:
【目的】钼是硝酸还原酶的活性组分,在硝态氮的还原和氮素代谢过程中具有核心作用。探究纳米钼对水稻根系形态、有机酸分泌及其与硝态氮吸收的关系,有望为新型纳米肥料提高水稻硝态氮吸收利用提供理论依据。【方法】以南粳9108为研究对象,以硝态氮为氮源的水培实验设置不施钼 (0 μg/L)、钼酸钠组(50、100、200、400 μg/L)和纳米钼组(50、100、200、400 μg/L)处理, 分析水稻根系形态、根系分泌有机酸和氮含量等的差异。【结果】外源钼显著增加了水稻根干质量、总根长、根体积、根总表面积、总吸收面积和活跃吸收面积,较不施钼处理显著优化了水稻根系形态。在相同钼添加量条件下,纳米钼处理效果显著高于钼酸钠处理。外源钼处理的根系氧化力和还原力、有机酸分泌量均显著增加,根系生理活动增强;随着钼添加量增加,钼酸钠处理组根系氧化力和还原力呈先增加后下降趋势,除乙酸外,苹果酸、酒石酸、琥珀酸、柠檬酸和草酸含量不同钼浓度处理间无差异;纳米钼处理的根系氧化力、还原力和有机酸量均随施用量的增加而增加。因子分析和冗余分析结果表明,水稻根系形态指标、根系氧化还原力及有机酸分泌量与根系氮含量正相关,外源钼添加通过改善水稻根系形态和生理特征促进水稻根系对硝态氮的吸收。【结论】外源钼通过增加水稻根长、根表面积、有机酸分泌量,增强根系氧化还原能力,改善了根系形态生理活性,进而增加了水稻根系对硝态氮的吸收。相同钼施用量条件下,纳米钼的促进效果优于钼酸钠。生产上可以通过适当添加钼肥特别是纳米钼肥来改善水稻根系形态及生理功能,增强水稻根系对硝态氮的吸收和利用。
张海鹏, 李莞意, 廖福兴, 马美子, 张洪程, 杨艳菊. 纳米钼对水稻根系形态生理和硝态氮吸收的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 650-664.
ZHANG Haipeng, LI Wanyi, LIAO Fuxing, MA Meizi, ZHANG Hongcheng, YANG Yanju. Effects of Nano-molybdenum on Root Morpho-physiological Traits and Nitrate Uptake in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(5): 650-664.
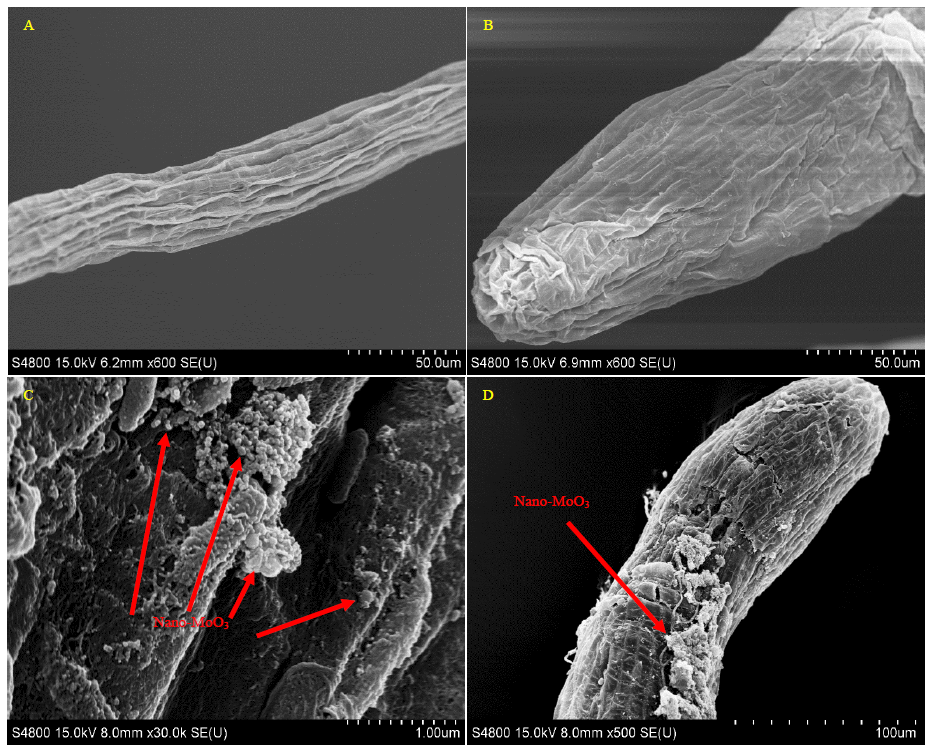
图1 纳米钼在水稻根系表面吸附的扫描电镜图 A、B为对照(CK)处理;C、D为添加200 μg/L纳米钼处理。
Fig. 1. SEM images of the adsorption of nano-MoO3 on the surface of rice roots A and B, No Mo treatment; C and D, 200 μg/L nano-MoO3 treatment.
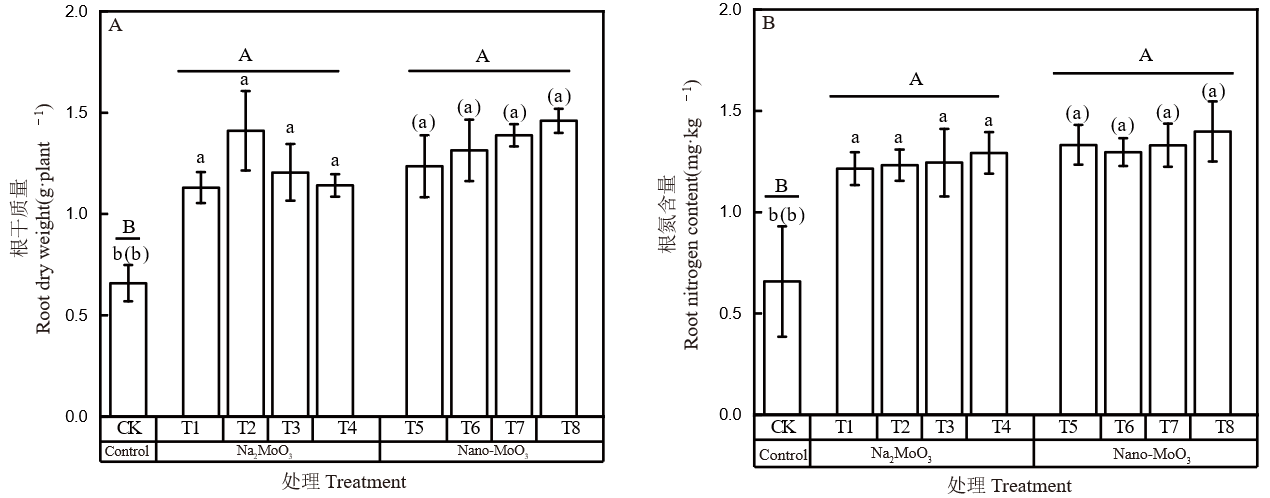
图2 不同外源钼处理对水稻根系干质量和氮含量的影响 不同小写字母表示离子钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);括号内不同小写字母表示纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);不同大写字母表示对照、钼酸钠和纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。CK: 不施钼; T1~T4: 50 μg/L, 100 μg/L, 200 μg/L, 400 μg/L 钼酸钠; T5~T8: 50 μg/L, 100 μg/L, 200 μg/L, 400 μg/L 纳米钼(Nano-MoO3)。下同。
Fig. 2. Effect of different exogenous molybdenum treatments on dry weight and nitrogen content in rice roots Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among Na2MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different lowercase letters in brackets indicate significant differences among Nano-MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05. CK, Zero Mo application ; T1-T4, 50 μg/L, 100 μg/L, 200 μg/L and 400 μg/L sodium molybdate; T5-T8, 50 μg/L, 100 μg/L, 200 μg/L and 400 μg/L Nano-MoO3. The same below.
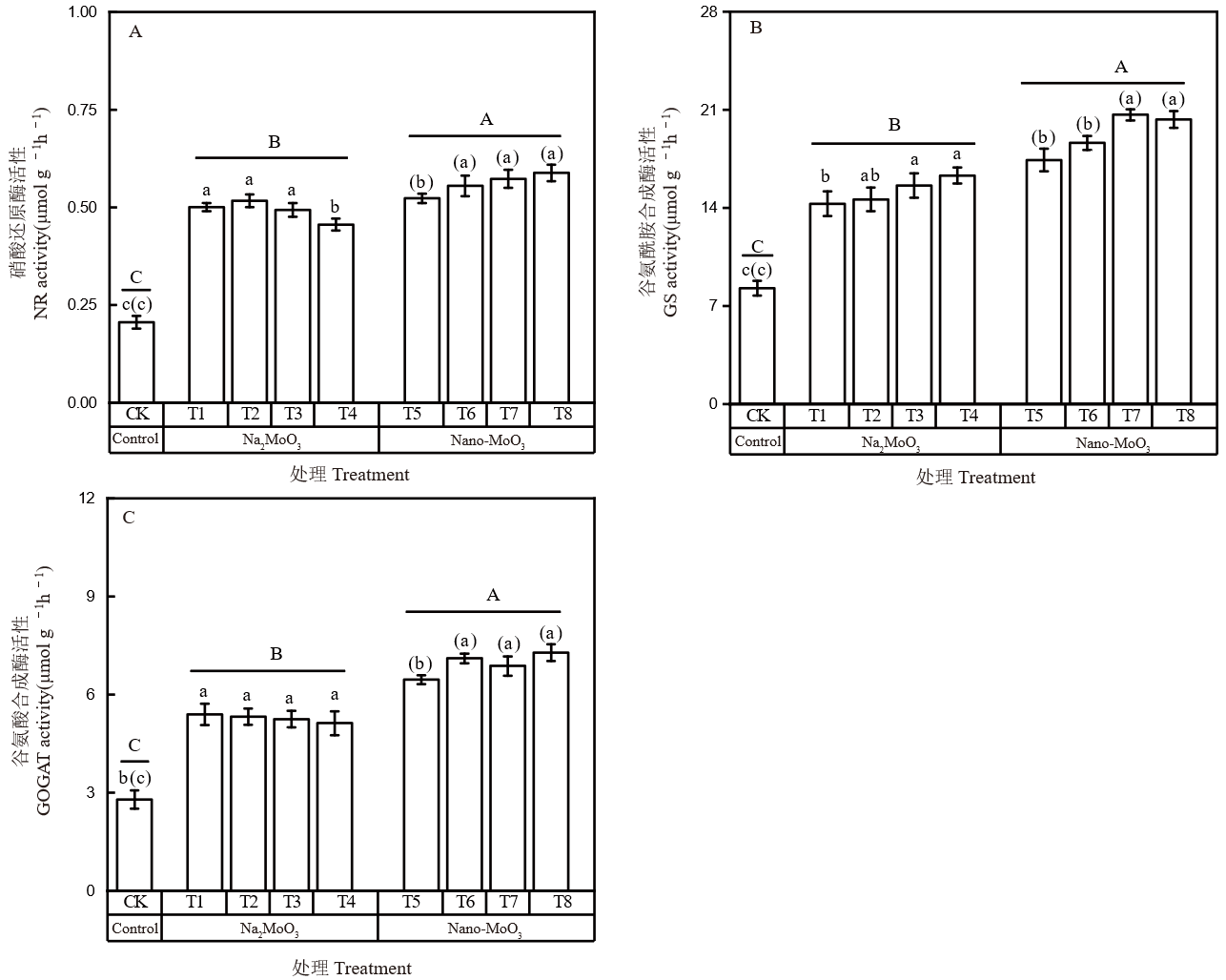
图3 不同外源钼处理对水稻根系氮代谢酶活性的影响 不同小写字母表示离子钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);括号内不同小写字母表示纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);不同大写字母表示对照、钼酸钠和纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 3. Effects of different exogenous molybdenum treatments on nitrogen metabolic enzyme activities in rice roots Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among Na2MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different lowercase letters in brackets indicate significant differences among Nano-MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05.
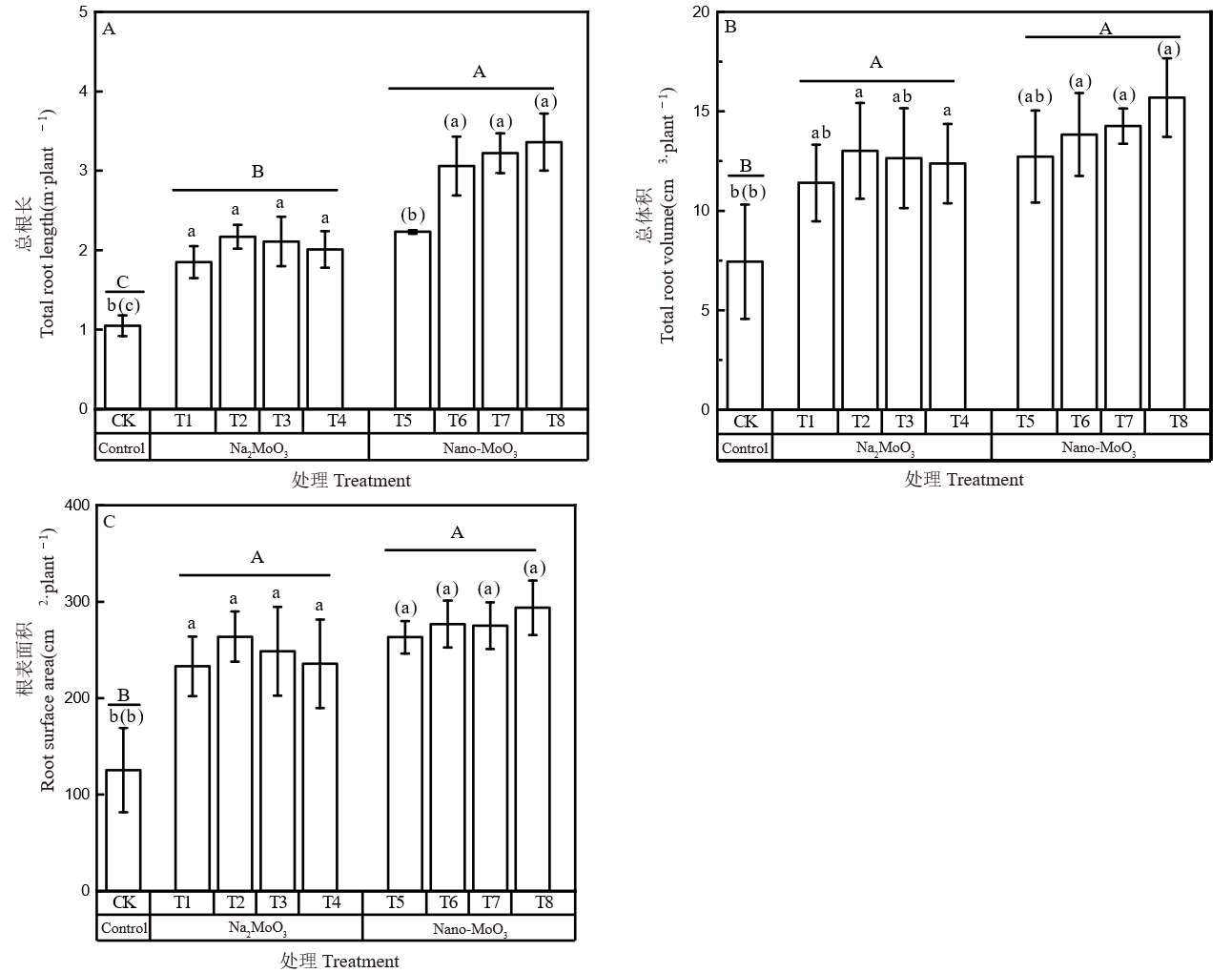
图4 不同外源钼处理对水稻根系形态特征的影响 不同小写字母表示离子钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);括号内不同小写字母表示纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);不同大写字母表示对照、钼酸钠和纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 4. Effects of different exogenous molybdenum treatments on morphological characteristics of rice roots Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among Na2MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different lowercase letters in brackets indicate significant differences among Nano-MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05.
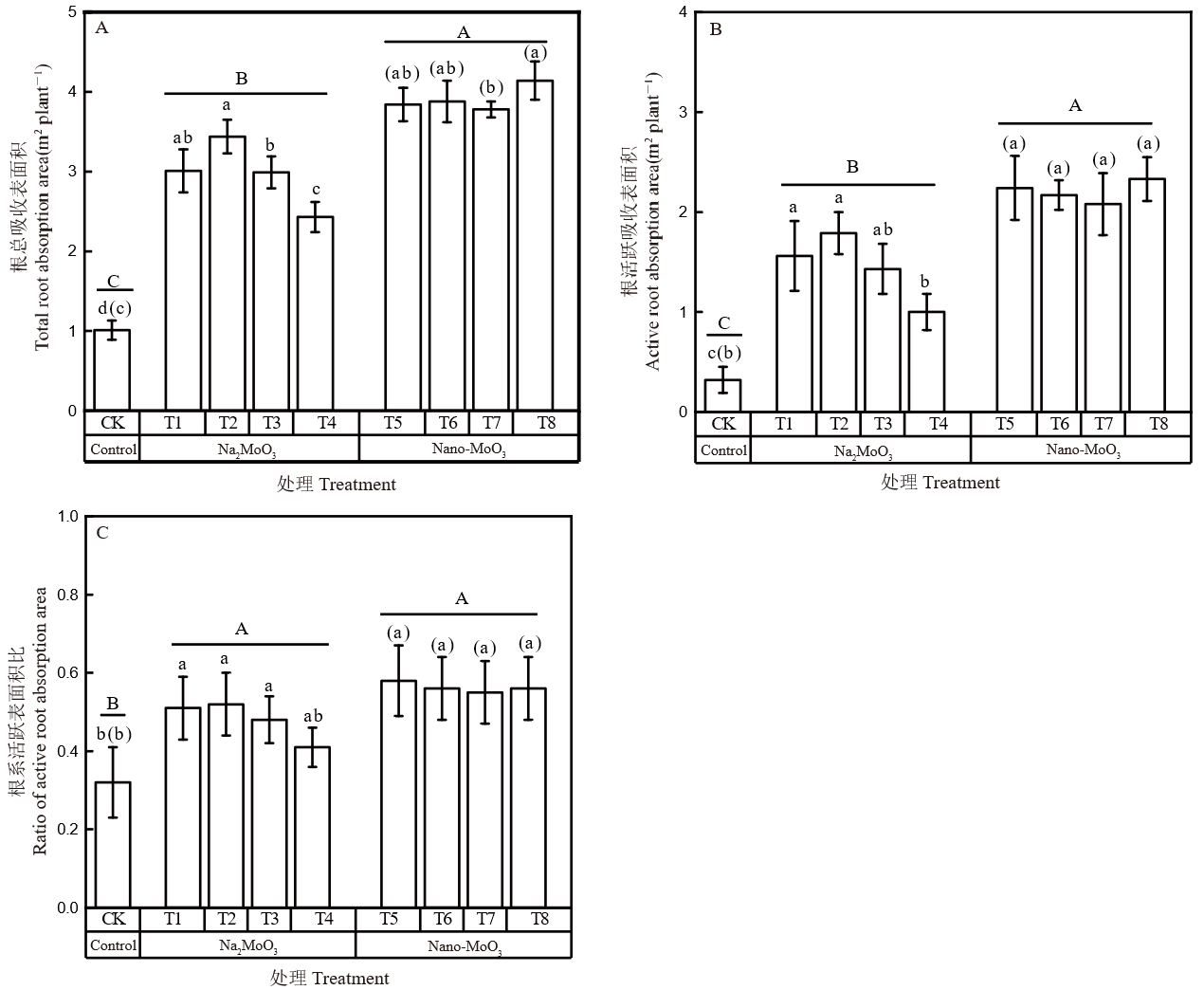
图5 不同外源钼处理对水稻根表面特性的影响 不同小写字母表示离子钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);括号内不同小写字母表示纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);不同大写字母表示对照、钼酸钠和纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 5. Effects of different exogenous molybdenum treatments on rice root surface characteristics Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among Na2MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different lowercase letters in brackets indicate significant differences among Nano-MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05.
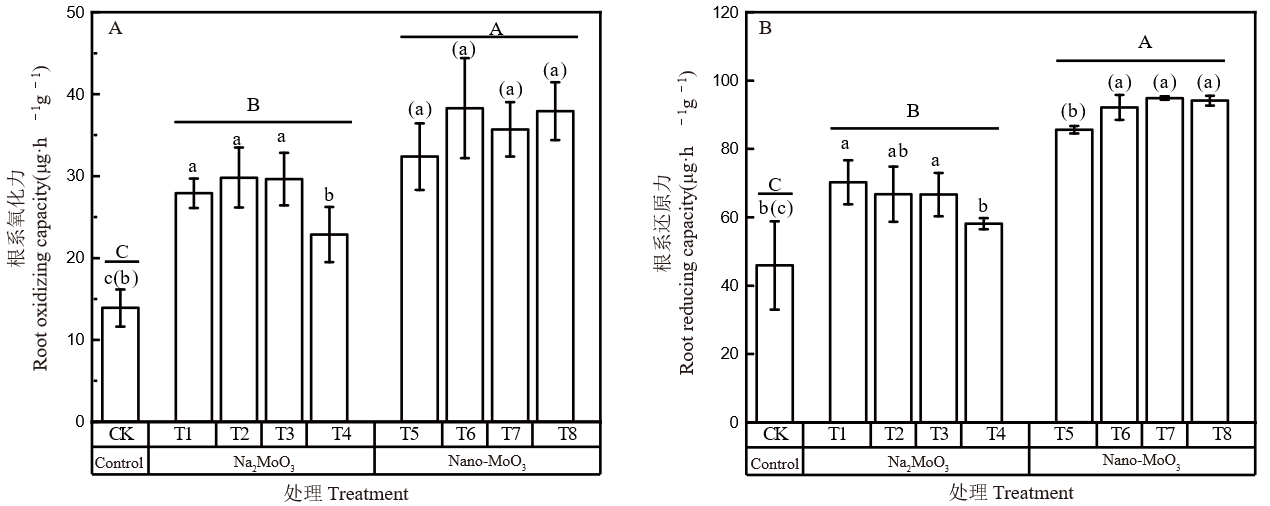
图6 不同外源钼处理对水稻根系氧化还原力的影响 不同小写字母表示离子钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);括号内不同小写字母表示纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);不同大写字母表示对照、钼酸钠和纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 6. Effects of different exogenous molybdenum treatments on redox potential of rice roots Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among Na2MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different lowercase letters in brackets indicate significant differences among Nano-MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences molybdenum varities at P < 0.05.
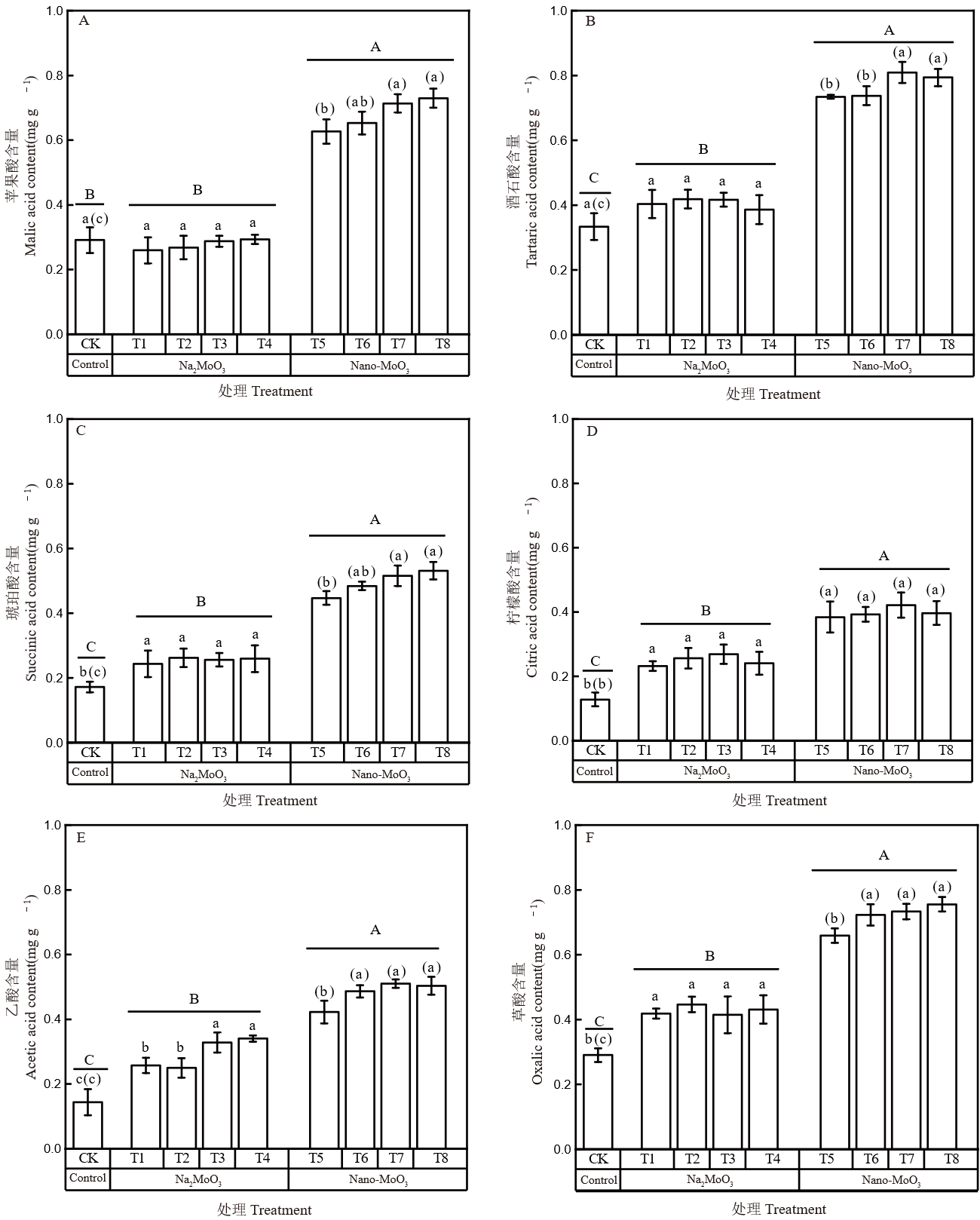
图7 不同外源钼处理对水稻根系有机酸分泌的影响 不同小写字母表示离子钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);括号内不同小写字母表示纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05);不同大写字母表示对照、钼酸钠和纳米钼处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 7. Effects of different exogenous molybdenum treatments on organic acid secretion by rice roots Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among Na2MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different lowercase letters in brackets indicate significant differences among Nano-MoO3 treatments at P < 0.05. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05.
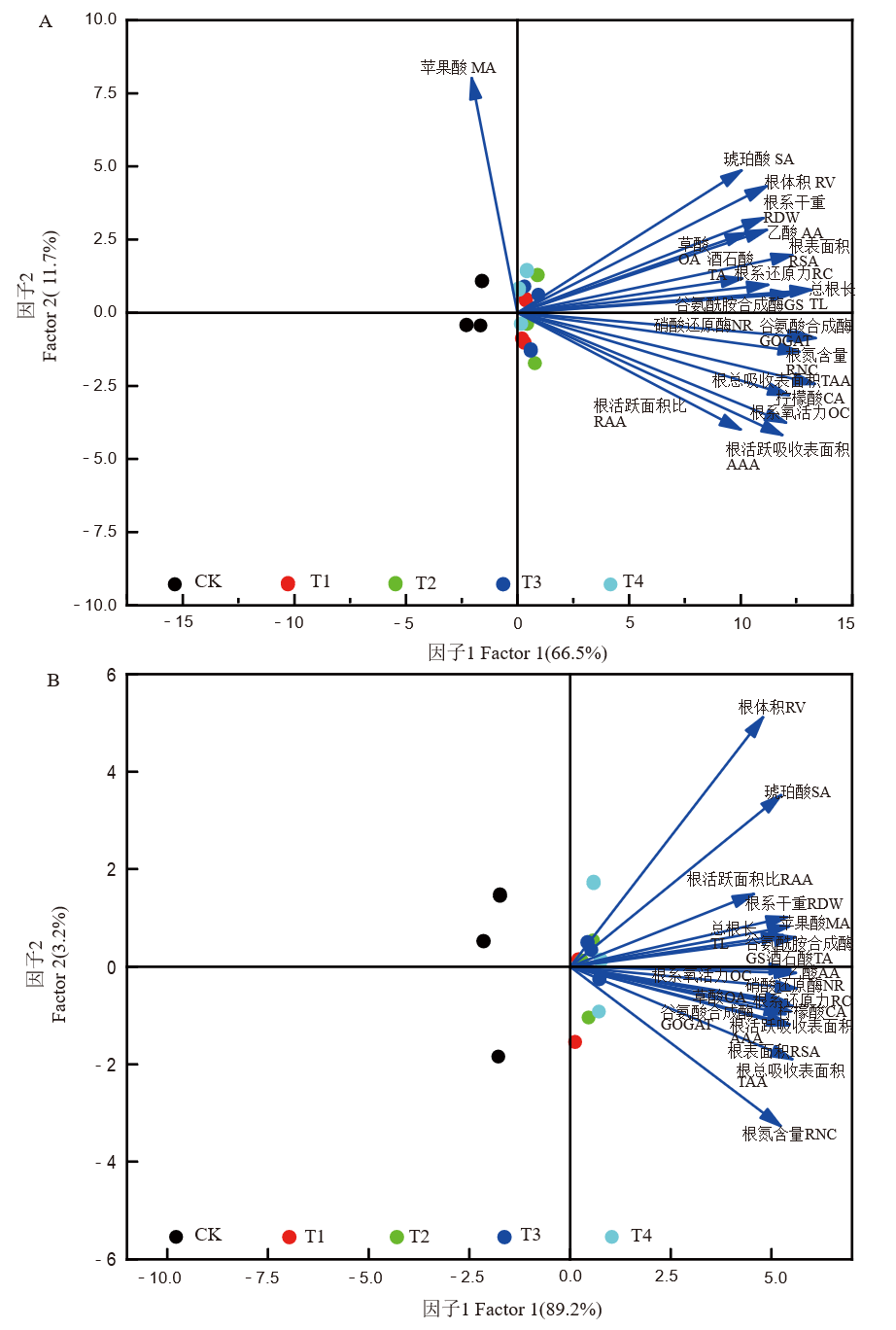
图8 钼酸钠(A)和纳米钼(B)处理的水稻植株氮含量与根系生理生化因子分析
Fig. 8. Factor analysis of nitrogen content in rice plants and physiological and biochemical indicators of roots under Na2MoO3 treatments(A) and Nano-MoO3 treatments(B) MA, Malic acid; SA, Succinic acid; OA, Oxalic acid; TA, Tartaric acid; CA, Citric acid; AA, Acetic acid; RV, Root volume; RDW, Root dry weight; RSA, Root surface area; TL, Total root length; TAA, Total absorption area; AAA, Active absorption area; RAA, Active area ratio of root; RC, Reduction capacity; OC, Oxidation capacity; GS, Glutamine synthetase; NR, Nitrate reductase; GOGAT, Glutamate synthetase; RNC, Root nitrogen content.
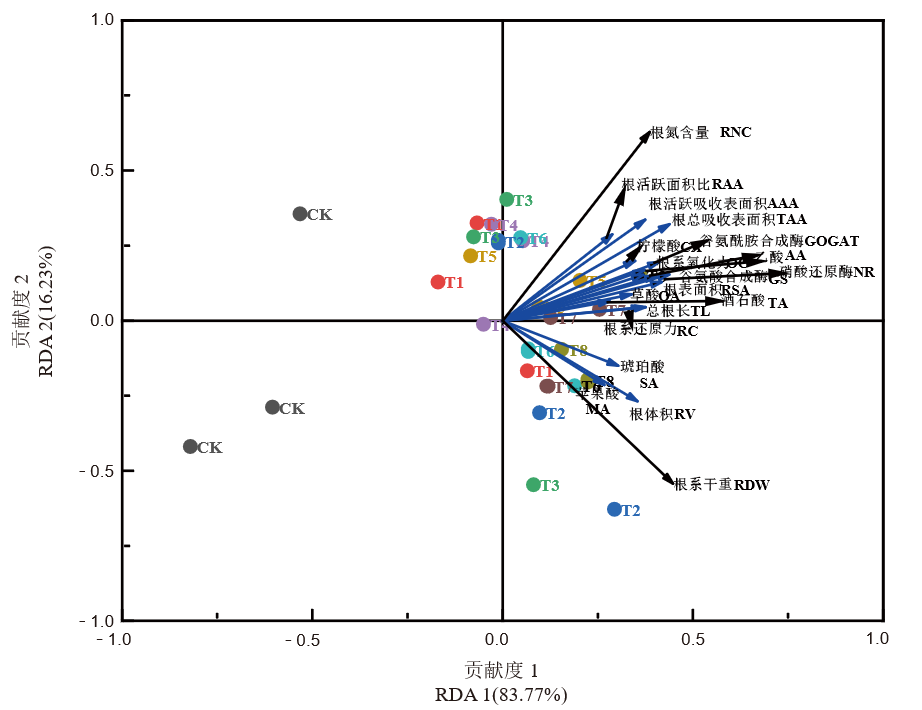
图9 不同外源钼处理下水稻植株氮含量与根系生理生化指标冗余分析
Fig. 9. Redundancy analysis of nitrogen content in rice plants and physiological and biochemical indicators of roots in different exogenous molybdenum treatments MA, Malic acid; SA, Succinic acid; OA, Oxalic acid; TA, Tartaric acid; CA, Citric acid; AA, Acetic acid; RV, Root volume; RDW, Root dry weight; RSA, Root surface area; TL, Total root length; TAA, Total absorption area; AAA, Active absorption area; RAA, Active area ratio of root; RC, Reduction capacity; OC, Oxidation capacity; GS, Glutamine synthetase; NR, Nitrate reductase; GOGAT, Glutamate synthetase; RNC, Root nitrogen content.
| [1] | Yang S, Zhu Y, Zhang R, Liu G D, Wei H Y, Zhang H C, Zhang H P. Mid-stage nitrogen application timing regulates yield formation, quality traits and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline biosynthesis of fragrant rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2022, 287: 108667. |
| [2] | 肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| Xiao D K, Hu R, Han T F, Zhang W F, Hou J, Ren K Y. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer consumption and operation on rice yield and its components in China: A meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Yang Y J, Meng T Z, Qian X Q, Zhang J B, Cai Z C. Evidence for nitrification ability controlling nitrogen use efficiency and N losses via denitrification in paddy soils[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2017, 53(3): 349-356. |
| [4] | Zhang H P, Liao F X, Li W Y, Li Y L, Yang S, Zhang H C, Yang Y J, Shan Y H. Rhizosphere soil nitrification ability controls nitrogen-use efficiency in rice growth period[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2023, 12(2): e429. |
| [5] | 刘时光, 王晓玲, 王元涛, 王晓敏, 宋以萍, 蒋莹莹, 祝贵兵. 稻田土壤氧化亚氮产生潜势、反硝化功能基因丰度和群落结构的垂向分布[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(3): 1040-1050. |
| Liu S G, Wang X L, Wang Y T, Wang X M, Song Y P, Jiang Y Y, Zhu G B. The potential of nitrous oxide, denitrification function gene abundance, and vertical distribution of community structure in paddy soil[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(3): 1040-1050. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Ju X T, Xing G X, Chen X P, Zhang S L, Zhang L J, Liu X J, Cui Z L, Yin B, Christie P, Zhu Z L, Zhang F S. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(9): 3041-3046. |
| [7] | 张文学, 王少先, 夏文建, 孙刚, 刘增兵, 李祖章, 刘光荣. 脲酶抑制剂与硝化抑制剂对稻田土壤硝化、反硝化功能菌的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(6): 897-909. |
| Zhang W X, Wang S X, Xia W J, Sun G, Liu Z B, Li Z Z, Liu G R. Effects of urease inhibitor and nitrification inhibitor on functional nitrifier and denitrifier in paddy soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(6): 897-909. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Zhao X, Zhou Y, Wang S A, Xing G X, Shi W M, Xu R K, Zhu Z L. Nitrogen balance in a highly fertilized rice-wheat double-cropping system in Southern China[J]. Soil Science Society of the America Journal, 2012, 76(3): 1068-1078. |
| [9] | 唐海明, 石丽红, 文丽, 程凯凯, 李超, 龙泽东, 肖志武, 李微艳, 郭勇. 长期施肥对双季稻田根际土壤氮素的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| Tang H M, Shi L H, Wen L, Cheng K K, Li C, Long Z D, Xiao Z W, Li W Y, Guo Y. Effects of different long-term fertilizer managements on rhizosphere soil nitrogen in the double-cropping rice field[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Glass A D M, Britto D T, Kaiser B N, Kinghorn J R, Kronzucker H J, Kumar A, Okamoto M, Rawat S, Siddiqi M Y, Unkles S E, Vidmar J J. The regulation of nitrate and ammonium transport systems in plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2002, 53(370): 855-864. |
| [11] | 李志康, 严冬, 薛张逸, 李思嘉, 刘立军, 张耗, 王志琴, 杨建昌, 顾骏飞. 细胞分裂素对植物生长发育的调控机理研究进展及其在水稻生产中的应用探讨[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 311-324. |
| Li Z K, Yan D, Xue Z Y, Gu Y B, Li S J, Liu L J, Zhang H, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Gu J F. Regulations of plant growth and development by cytokinins and their application in rice production[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(4): 311-324. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Hang J N, Wu B W, Qiu D Y, Yang G, Fang Z M, Zhang M Y. OsNPF3.1, a nitrate, abscisic acid and gibberellin transporter gene, is essential for rice tillering and nitrogen utilization efficiency[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2024, 23(4): 1087-1104. |
| [13] | Zhang H P, Wang R, Chen Z Q, Pu J L, Wang J J, Zhang H C, Yang Y J. Nanoscale molybdenum oxide improves plant growth and increases nitrate utilisation in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2022, 11: e383. |
| [14] | 张艳红, 陈志青, 杨硕, 卢豪, 崔培媛, 杨艳菊, 张洪程, 张海鹏. 增施纳米三氧化钼对水稻产量、品质和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2022, 43(5): 27-36. |
| Zhang Y H, Chen Z Q, Yang S, Lu H, Cui P Y, Yang Y J, Zhang H C, Zhang H P. Effects of nano-sized molybdenum trioxide application on rice yield, grain quality and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University (Agricultural and Life Science Edition), 2022, 43(5): 27-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Li Y D, Jin Q, Yang D S, Cui J H. Molybdenum sulfide induce growth enhancement effect of rice (Oryza sativa L.) through regulating the synthesis of chlorophyll and the expression of aquaporin gene[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66(16): 4013-4021. |
| [16] | 门中华, 李生秀. 钼对冬小麦硝态氮代谢的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2005, 11(2): 205-210. |
| Men Z H, Li S X. Effects of molybdenum on nitrate metabolism of winter wheat[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2005, 11(2): 205-210. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 陈志青, 冯源, 王锐, 崔培媛, 卢豪, 魏海燕, 张海鹏, 张洪程. 外源钼对水稻产量形成及氮素利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(9): 2325-2338. |
| Chen Z Q, Feng Y, Wang R, Cui P Y, Lu H, Wei H Y, Zhang H P, Zhang H C. Effects of exogenous molybdenum on yield formation and nitrogen utilization in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(9): 2325-2338. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 冀建华, 吕真真, 刘淑珍, 侯红乾, 刘益仁, 刘秀梅, 李絮花, 蓝贤瑾. 长期施用化肥对南方稻田土壤酸化和盐基离子损失的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2024, 57(13): 2599-2611. |
| Ji J H, Lü Z Z, Liu S Z, Hou H Q, Liu Y R, Liu X M, Li X H, Lan X J. Long-term application of chemical fertilizers induces soil acidification and soil exchangeable base cation loss on paddy in Southern China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2024, 57(13): 2599-2611. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Taran N Y, Gonchar O M, Lopatko K G, Batsmanova L M, Patyka M V, Volkogon M V. The effect of colloidal solution of molybdenum nanoparticles on the microbial composition in rhizosphere of Cicer arietinum L[J]. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2014, 9(1): 289. |
| [20] | Cao X S, Chen X F, Liu Y L, Wang C X, Yue L, Elmer W H, White J C, Wang Z Y, Xing B S. Lanthanum silicate nanomaterials enhance sheath blight resistance in rice: Mechanisms of action and soil health evaluation[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(16): 15821-15835. |
| [21] | Oliveira H C, Seabra A B, Kondak S, Adedokun O P, Kolbert Z. Multilevel approach to plant-nanomaterial relationships: From cells to living ecosystems[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2023, 74(12): 3406-3424. |
| [22] | Ping Y C, Cao D Y, Hu J Y, Lin J Y, Dang C, Xue D W. The application, safety, and challenge of nanomaterials on plant growth and stress tolerance[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2024, 222: 119691. |
| [23] | Dev A, Srivastava A K, Karmakar S. Nanomaterial toxicity for plants[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2018, 16(1): 85-100. |
| [24] | Khot L R, Sankaran S, Maja J M, Ehsani R, Schuster E W. Applications of nanomaterials in agricultural production and crop protection: A review[J]. Crop Protection, 2012, 35: 64-70. |
| [25] | Miralles P, Church T L, Harris A T. Toxicity, uptake, and translocation of engineered nanomaterials in vascular plants[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(17): 9224-9239. |
| [26] | Stolte Bezerra Lisboa Oliveira L, Ristroph K D. Critical review: Uptake and translocation of organic nanodelivery vehicles in plants[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2024, 58(13): 5646-5669. |
| [27] | Juárez-Maldonado A, Tortella G, Rubilar O, Fincheira P, Benavides-Mendoza A. Biostimulation and toxicity: The magnitude of the impact of nanomaterials in microorganisms and plants[J]. Journal of Advanced Research, 2021, 31: 113-126. |
| [28] | Chen S, Kang Z, Peralta-Videa J R, Zhao L J. Environmental implication of MoS2 nanosheets: Effects on maize plant growth and soil microorganisms[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 860: 160362. |
| [29] | 李玉祥, 解双喜, 刘扬, 丁艳峰, 王绍华, 刘正辉, 唐设, 丁承强, 陈琳, 李刚华. 营养液浓度对水稻机插水培毯状苗秧苗素质及产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(24): 201-209. |
| Li Y X, Xie S X, Liu Y, Ding Y F, Wang S H, Liu Z H, Tang S, Ding C Q, Chen L, Li G H. Effects of nutrient solution concentrations on quality and yield of hydroponically grown long-mat rice seedlings under mechanical transplanting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(24): 201-209. | |
| [30] | Liu X, Wang J, Yu Y, Kong L, Liu Y M, Liu Z Q, Li H Y, Wei P W, Liu M L, Zhou H, Bu Q Y, Fang J. Identification and characterization of the rice pre-harvest sprouting mutants involved in molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis[J]. New Phytologist, 2019, 222(1): 275-285. |
| [31] | 李娜, 杨志远, 代邹, 孙永健, 徐徽, 何艳, 蒋明金, 严田蓉, 郭长春, 马均. 水氮管理对不同氮效率水稻根系性状、氮素吸收利用及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(5): 500-512. |
| Li N, Yang Z Y, Dai Z, Sun Y J, Xu H, He Y, Jiang M J, Yan T R, Guo C C, Ma J. Effects of water-nitrogen management on root traits, nitrogen accumulation and utilization and grain yield in rice with different nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(5): 500-512. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 唐清芸, 杨晶晶, 赵蕾, 宋志文, 王国栋, 李玉祥. 施氮量对滴灌水稻根系形态构型和分形特征的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2024, 50(6): 1540-1553. |
| Tang Q Y, Yang J J, Zhao L, Song Z W, Wang G D, Li Y X. Effect of nitrogen application on morphological conformation and fractal characteristics of drip irrigated rice roots[J]. Acta Agronomica Snica, 2024, 50(6): 1540-1553. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | Chen Y, Ding Z X, Yu T Q, Cao L, Duan Y M, Zu Y Q, Li Z R. Accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in three wild rice species and adaptation of root morphology and anatomical structure to native soil heavy metals in Yunnan[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2024, 167: 112601. |
| [34] | Liu K, Li T T, Chen Y, Huang J, Qiu Y Y, Li S Y, Wang H, Zhu A, Zhuo X X, Yu F, Gu J F, Liu L J, Yang J C. Effects of root morphology and physiology on the formation and regulation of large panicles in rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2020, 258: 107946. |
| [35] | Rajendran S, Park H, Kim J, Park S J, Shin D, Lee J H, Song Y H, Paek N C, Kim C M. Methane emission from rice fields: Necessity for molecular approach for mitigation[J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31(2): 159-178. |
| [36] | Ma J, Bei Q C, Wang X J, Lan P, Liu G, Lin X W, Liu Q, Lin Z B, Liu B J, Zhang Y H, Jin H Y, Hu T L, Zhu J G, Xie Z B. Impacts of Mo application on biological nitrogen fixation and diazotrophic communities in a flooded rice-soil system[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 649: 686-694. |
| [37] | Imran M, Hussain S, Rana M S, Saleem M H, Rasul F, Ali K H, Potcho M P, Pan S G, Duan M Y, Tang X R. Molybdenum improves 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, grain quality traits and yield attributes in fragrant rice through efficient nitrogen assimilation under cadmium toxicity[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 211: 111911. |
| [38] | Imran M, Sun X C, Hussain S, Rana M S, Saleem M H, Riaz M, Tang X R, Khan I, Hu C X. Molybdenum supply increases root system growth of winter wheat by enhancing nitric oxide accumulation and expression of NRT genes[J]. Plant and Soil, 2021, 459(1): 235-248. |
| [39] | Li M S, Zhang P, Guo Z L, Zhao W C, Li Y B, Yi T J, Cao W D, Gao L, Tian C F, Chen Q, Ren F Z, Rui Y K, White J C, Lynch I. Dynamic transformation of nano-MoS2 in a soil-plant system empowers its multifunctionality on soybean growth[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2024, 58(2): 1211-1222. |
| [40] | Yang J H, Song Z Y, Ma J, Han H Y. Toxicity of molybdenum-based nanomaterials on the soybean-rhizobia symbiotic system: Implication for nutrition[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2020, 3(6): 5773-5782. |
| [41] | Chai Y N, Schachtman D P. Root exudates impact plant performance under abiotic stress[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2022, 27(1): 80-91. |
| [42] | Tao K, Jensen I T, Zhang S, Villa-Rodríguez E, Blahovska Z, Salomonsen C L, Martyn A, Björgvinsdóttir Þ N, Kelly S, Janss L, Glasius M, Waagepetersen R, Radutoiu S. Nitrogen and Nod factor signaling determine Lotus japonicus root exudate composition and bacterial assembly[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 3436. |
| [43] | 李宝珍, 辛伟杰, 徐国华. 氮饥饿水稻利用不同形态氮素的差异及其生理机制[J]. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(2): 273-279. |
| Li B Z, Xin W J, Xu G H. Physiological mechanisms in uptake and use of different forms of nitrogen by nitrogen starved rice crop[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(2): 273-279. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | Guo N, Zhang S N, Gu M J, Xu G H. Function, transport, and regulation of amino acids: What is missing in rice?[J] The Crop Journal, 2021, 9(3): 530-542. |
| [45] | 顾嘉怡, 吕欣平, 周宇琨, 孟庆好, 王琛, 张瑛, 张耗. 水稻根系分泌物对氮素吸收利用的影响研究进展[J]. 杂交水稻, 2024, 39(4): 9-15. |
| Gu J Y, Lü X P, Zhou Y K, Meng Q H, Wang C, Zhang Y, Zhang H. Research progress on the effects of root exudates on nitrogen uptake and utilization in rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2024, 39(4): 9-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | Zhang H, Zhang J H, Yang J C. Improving nitrogen use efficiency of rice crop through an optimized root system and agronomic practices[J]. Crop and Environment, 2023, 2(4): 192-201. |
| [1] | 郝雯倩, 蔡兴菁, 杨海东, 吴宇阳, 滕轩, 薛超, 龚志云. 不同类型组蛋白修饰在水稻响应非生物胁迫中的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 575-685. |
| [2] | 王镜博, 苏畅, 冯晶, 姜思旭, 徐海, 崔志波, 赵明辉. 水稻OsAlR1基因耐铝性功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 615-623. |
| [3] | 韶也, 胡远艺, 彭彦, 毛毕刚, 刘慧敏, 唐婵娟, 雷斌, 唐丽, 余丽霞, 李文建, 罗武中, 罗治斌, 袁远涛, 李曜魁, 张丹, 周利斌, 柏连阳, 唐文帮, 赵炳然. 基于M1TDS靶向筛选技术的重离子束诱变定向改良杂交水稻卓两优1126性状的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 624-634. |
| [4] | 徐群, 王珊, 袁筱萍, 金石桥, 晋芳, 郝万军, 吴小碧, 冯跃, 余汉勇, 孙燕飞, 杨窑龙, 魏兴华. 用于水稻品种真实性验证的SNP位点评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 635-642. |
| [5] | 刘钰婷, 周星, 何辰延, 李秋萍, 艾小凤, 袁玉洁, 刘睿, 杨景文, 刘婷婷, 王丽, 程红, 黄蓉, 李奥运, 胡文, 胡忠, 任万军, 邓飞. 不同光照条件下减穴稳苗配置对水稻茎鞘干物质积累转运 特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 665-678. |
| [6] | 杨行洲, 崔苗苗, 魏利辉, 顾爱国, 李东霞, 乐秀虎, 冯辉. 外源miR3979处理水稻对拟禾本科根结线虫趋性、侵染和发育的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 703-710. |
| [7] | 朱鹏, 凌溪铁, 王金彦, 张保龙, 杨郁文, 许轲, 裘实. 机直播条件下不同控草方式对抗除草剂水稻产量和品质差异性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 501-515. |
| [8] | 董立强, 张义凯, 杨铁鑫, 冯莹莹, 马亮, 梁潇, 张玉屏, 李跃东. 北方粳稻密苗机插育秧对秧苗素质及取秧特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 516-528. |
| [9] | 周洋, 叶凡, 刘立军. 典型促生微生物提高盐胁迫水稻抗性的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 529-542. |
| [10] | 朱建平, 李霞, 李文奇, 许扬, 王芳权, 陶亚军, 蒋彦婕, 陈智慧, 范方军, 杨杰. 水稻粉质胚乳突变体we1的表型分析与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 543-551. |
| [11] | 黄福灯, 吴春艳, 郝媛媛, 韩一飞, 张小斌, 孙会锋, 潘刚. 不同氮肥水平下水稻倒二叶叶鞘的转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 563-574. |
| [12] | 卢椰子, 邱结华, 蒋楠, 寇艳君, 时焕斌. 稻瘟病菌效应子研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 287-294. |
| [13] | 王超瑞, 周宇琨, 温雅, 张瑛, 法晓彤, 肖治林, 张耗. 秸秆还田方式对稻田土壤特性和温室气体排放的影响及其水肥互作调控[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 295-305. |
| [14] | 王雅宣, 王新峰, 杨后红, 刘芳, 肖晶, 蔡玉彪, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊. 稻飞虱适应水稻抗性机制的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 306-321. |
| [15] | 黄涛, 魏兆根, 陈玘, 程泽, 刘欣, 王广达, 胡珂鸣, 谢文亚, 陈宗祥, 冯志明, 左示敏. 水稻类病斑突变体lm52的基因克隆及其广谱抗病性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 322-330. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||