
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 529-542.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240814
收稿日期:2024-08-30
修回日期:2025-02-13
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2025-07-21
通讯作者:
*email: ljliu@yzu.edu.cn基金资助:
ZHOU Yang, YE Fan, LIU Lijun*( )
)
Received:2024-08-30
Revised:2025-02-13
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-07-21
Contact:
*email: ljliu@yzu.edu.cn摘要:
土壤盐碱化是当前全球粮食安全面临的主要挑战之一,水稻是滨海滩涂和盐碱地改良首选的粮食作物,提高耐盐性对稳定盐碱地水稻生产至关重要。促生微生物是生物改良土壤盐碱化的重要组成部分。耐盐型促生微生物如丛枝菌根真菌、芽孢杆菌和假单胞菌等,可以通过激活土壤酶活性、生成胞外多糖、增强抗氧化酶活性、调节渗透代谢、调节植物激素等方式来缓解盐胁迫对水稻的生长发育造成不利影响。本文总结了上述三种促生微生物提高盐胁迫下水稻抗性的不同途径和相关机理,指出现阶段研究领域存在的欠缺并对今后的研究提出展望,以期为盐碱地改良和水稻高产提供理论和实践依据。
周洋, 叶凡, 刘立军. 典型促生微生物提高盐胁迫水稻抗性的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 529-542.
ZHOU Yang, YE Fan, LIU Lijun. Research Progress of Typical Plant Growth-promoting Microorganism Enhancing Salt Stress Resistance in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(4): 529-542.
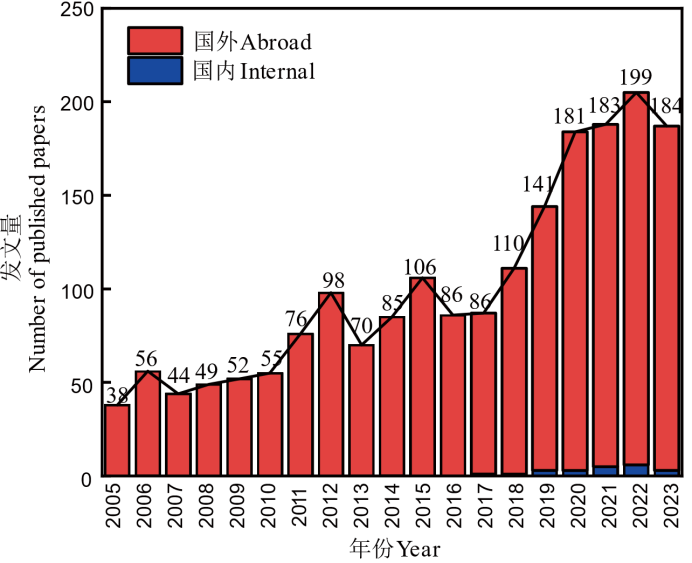
图1 2005—2023年促生微生物缓解盐胁迫水稻的相关论文年发文量分布
Fig. 1. Annual distribution of papers related to alleviating salt stress by growth-promoting microorganisms in rice from 2005 to 2023
| 植物促生微生物 PGPM | 菌剂浓度 Microbial inoculant concentration | 盐胁迫时间 Salt stressstress exposure time | 盐胁迫浓度 Salinity stress level | 改善方式 Microbial mediation mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 枯草芽孢杆菌 Bacillus subtilis, SSA4[ | 50 mL 3×108 CFU/mL | 22 d | 300 mmol/L | 改善A、Ci、Gs、E、呼吸速率,提高APX、MDHAR、DHAR以及GSH活性, 降低H2O2和MDA积累,抑制GR和DHA活性 |
| 暹罗芽孢杆菌 Bacillus siamensis[ | 100 μg/mL 108 CFU/mL | 0‒15 d | 200 mmol/L | 提高根长、茎长、发芽率和根系定殖力,增加脯脯氨酸、脂肪酸、多元醇、IAA、铁载体含量以及生物膜合成 |
| 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, SN13[ | 1×107 CFU/mL | 25 d | 200 mmol/L | 提高ACCD和NADP-苹果酸酶活性,增加肌醇和甘油含量,维持微生物群落多样性, 降低乙烯合成量 |
| 龙舌兰芽孢杆菌 Bacillus tequilensis, UPMRB9[ | 108−109 CFU/mL | 19 d | EC:8 dS/m | 增加N、P、Ca、TSS、IAA含量,调节SOD、POD和CAT活性,调节Na+/K+和相对含水量,减少电解质渗漏 |
| 芽孢杆菌 Bacillus, PVS11[ | 1×107 CFU/mL | 14 d | 300 mmol/L | 提高钾、磷酸盐、铁载体、叶绿素a、叶绿素b、总类胡萝卜素有机碳含量以及脲酶活性 |
表1 不同种芽孢杆菌缓解水稻盐胁迫的生理机制
Table 1. Physiological mechanism of different species of Bacillus alleviating salt stress in rice
| 植物促生微生物 PGPM | 菌剂浓度 Microbial inoculant concentration | 盐胁迫时间 Salt stressstress exposure time | 盐胁迫浓度 Salinity stress level | 改善方式 Microbial mediation mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 枯草芽孢杆菌 Bacillus subtilis, SSA4[ | 50 mL 3×108 CFU/mL | 22 d | 300 mmol/L | 改善A、Ci、Gs、E、呼吸速率,提高APX、MDHAR、DHAR以及GSH活性, 降低H2O2和MDA积累,抑制GR和DHA活性 |
| 暹罗芽孢杆菌 Bacillus siamensis[ | 100 μg/mL 108 CFU/mL | 0‒15 d | 200 mmol/L | 提高根长、茎长、发芽率和根系定殖力,增加脯脯氨酸、脂肪酸、多元醇、IAA、铁载体含量以及生物膜合成 |
| 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, SN13[ | 1×107 CFU/mL | 25 d | 200 mmol/L | 提高ACCD和NADP-苹果酸酶活性,增加肌醇和甘油含量,维持微生物群落多样性, 降低乙烯合成量 |
| 龙舌兰芽孢杆菌 Bacillus tequilensis, UPMRB9[ | 108−109 CFU/mL | 19 d | EC:8 dS/m | 增加N、P、Ca、TSS、IAA含量,调节SOD、POD和CAT活性,调节Na+/K+和相对含水量,减少电解质渗漏 |
| 芽孢杆菌 Bacillus, PVS11[ | 1×107 CFU/mL | 14 d | 300 mmol/L | 提高钾、磷酸盐、铁载体、叶绿素a、叶绿素b、总类胡萝卜素有机碳含量以及脲酶活性 |
| 植物促生微生物 PGPM | 菌剂浓度 Microbial inoculant concentration | 盐胁迫时间 Salt stressstress exposure time(d) | 盐胁迫浓度 Salinity stress level | 改善方式 Microbial mediation mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 斯氏假单胞菌 Pseudomonas stutzeri, A1501[ | 10 mL(8×107 CFU/mL) | 0~7 | 120 mmol/L | 增加株高、根部鲜质量和干质量以及ACCD活性 |
| 铜绿假单胞菌 Pseudomonas aeruginosa[ | 6×108 CFU/mL | 28 | 150 mmol/L | 加速清除ROS,降低脂质过氧化、DNA片段化、膜通透性以及细胞凋亡 |
| 假产碱假单胞菌 Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes[ | 6×108 CFU/mL | 0 | 25 g/L | 增强细胞活力,降低细胞膜指数、细胞半胱天冬酶样蛋白酶活性和细胞程序性死亡 |
| 荧光假单胞菌 Pseudomonas fluorescens, RS1[ | 1 mL (1×107 CFU/mL)) | 10 | 10 mL 0.85% | 增加锌和钾吸收,提高根长、根质量、茎长和茎质量 |
| 恶臭假单胞菌 Pseudomonas putida[ | 1 L(108 CFU/mL) | 0 | EC:7.1 dS/m | 提高茎粗、分蘖数、总叶绿素、生物量、收获指数、每穗实粒数和产量,改善CAT活性, 减少叶片H2O2含量 |
表2 不同种假单胞菌缓解水稻盐胁迫的生理机制
Table 2. Physiological mechanism of different species of Pseudomonas alleviating salt stress in rice
| 植物促生微生物 PGPM | 菌剂浓度 Microbial inoculant concentration | 盐胁迫时间 Salt stressstress exposure time(d) | 盐胁迫浓度 Salinity stress level | 改善方式 Microbial mediation mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 斯氏假单胞菌 Pseudomonas stutzeri, A1501[ | 10 mL(8×107 CFU/mL) | 0~7 | 120 mmol/L | 增加株高、根部鲜质量和干质量以及ACCD活性 |
| 铜绿假单胞菌 Pseudomonas aeruginosa[ | 6×108 CFU/mL | 28 | 150 mmol/L | 加速清除ROS,降低脂质过氧化、DNA片段化、膜通透性以及细胞凋亡 |
| 假产碱假单胞菌 Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes[ | 6×108 CFU/mL | 0 | 25 g/L | 增强细胞活力,降低细胞膜指数、细胞半胱天冬酶样蛋白酶活性和细胞程序性死亡 |
| 荧光假单胞菌 Pseudomonas fluorescens, RS1[ | 1 mL (1×107 CFU/mL)) | 10 | 10 mL 0.85% | 增加锌和钾吸收,提高根长、根质量、茎长和茎质量 |
| 恶臭假单胞菌 Pseudomonas putida[ | 1 L(108 CFU/mL) | 0 | EC:7.1 dS/m | 提高茎粗、分蘖数、总叶绿素、生物量、收获指数、每穗实粒数和产量,改善CAT活性, 减少叶片H2O2含量 |
| 供试菌剂 Experimental microbial inoculant | 菌剂用量 Dosage of bacterial inoculant | 盐胁迫时间 Salt stressstress exposure time | 盐胁迫浓度 Salinity stress level | 改善方式 Microbial mediation mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根内根孢囊霉 Rhizophagus intraradices[ | 5 g/盆[0.6%(w/w)菌根化基质] 5 g/pot[0.6%(w/w) mycorrhizal inoculum substrate] | 30 d | 100 mmol/L | 提高N、P、K、微量元素、水分、株高、干物质,增强抗氧化酶和土壤酶活性,降低Na+吸收,减少H2O2和MDA合成 |
| 幼套近明球囊霉 Claroideoglomus etunicatum, EEZ 163[ | 700个孢子/盆 700 spores per pot | 35 d | 150 mmol/L | 改善光合特性(包括净光合速率、气孔导度、蒸腾速率,增强rubisco活性),提高可溶性糖和叶绿素a含量;同时提高ΦPSⅡ,降低ΦNPQ,减轻光诱导损伤 |
| 光壁无梗囊霉 Acaulospora laevis[ | 700个孢子/盆 700 spores per pot | 60 d | 120 mmol/L | 改善地上部K+/Na+,提高叶绿素含量、根生物量、小穗育性以及籽粒产量,降低地上部Na+/根Na+ |
表3 不同种丛枝菌根真菌缓解水稻盐胁迫的生理机制
Table 3. Physiological mechanism of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviating salt stress in rice
| 供试菌剂 Experimental microbial inoculant | 菌剂用量 Dosage of bacterial inoculant | 盐胁迫时间 Salt stressstress exposure time | 盐胁迫浓度 Salinity stress level | 改善方式 Microbial mediation mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根内根孢囊霉 Rhizophagus intraradices[ | 5 g/盆[0.6%(w/w)菌根化基质] 5 g/pot[0.6%(w/w) mycorrhizal inoculum substrate] | 30 d | 100 mmol/L | 提高N、P、K、微量元素、水分、株高、干物质,增强抗氧化酶和土壤酶活性,降低Na+吸收,减少H2O2和MDA合成 |
| 幼套近明球囊霉 Claroideoglomus etunicatum, EEZ 163[ | 700个孢子/盆 700 spores per pot | 35 d | 150 mmol/L | 改善光合特性(包括净光合速率、气孔导度、蒸腾速率,增强rubisco活性),提高可溶性糖和叶绿素a含量;同时提高ΦPSⅡ,降低ΦNPQ,减轻光诱导损伤 |
| 光壁无梗囊霉 Acaulospora laevis[ | 700个孢子/盆 700 spores per pot | 60 d | 120 mmol/L | 改善地上部K+/Na+,提高叶绿素含量、根生物量、小穗育性以及籽粒产量,降低地上部Na+/根Na+ |
| [1] | 王才林, 张亚东, 赵凌, 路凯, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 梁文化, 孙明法, 严国红. 耐盐碱水稻研究现状、问题与建议[J]. 中国稻米, 2019, 25(1): 1-6. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Zhao L, Lu K, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Zhou L H, Zhao C F, Liang W H, Sun M F, Yan G H. Research status, problems and suggestions on salt-alkali tolerant rice[J]. China Rice, 2019, 25(1): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 马晨, 马履一, 刘太祥, 左海军, 张博, 刘寅. 盐碱地改良利用技术研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2010, 23(2): 28-32. |
| Ma C, Ma L Y, Liu T X, Zuo H J, Zhang B, Liu Y. Research progress on saline land improvement technology[J]. World Forestry Research, 2010, 23(2): 28-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 王佳丽, 黄贤金, 钟太洋, 陈志刚. 盐碱地可持续利用研究综述[J]. 地理学报, 2011, 66(5): 673-684. |
| Wang J L, Huang X J, Zhong T Y, Chen Z G. Review on sustainable utilization of salt-affected land[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2011, 66(5): 673-684. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Miller A K, Nielsen B L. Analysis of gene expression changes in plants grown in salty soil in response to inoculation with halophilic bacteria[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(7): 3611. |
| [5] | 袁喜丽, 高慧, 李磊, 周玉兰, 孟海英, 乌日格斯格勒. 微生物菌剂对盐碱地农作物产量与品质的影响研究[J]. 新农民, 2024(1): 87-89. |
| Yuan X L, Gao H, Li L, Zhou Y L, Meng H Y, Wurige Sigele. A study on the effects of microbial agents on crop yield and quality in saline alkali land[J]. New Farmers, 2024(1): 87-89. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 张莹莹, 李新畅, 檀建新, 丁贵江, 张婷, 陈磊, 郑然, 任杰, 石爱丽. 微生物菌肥对水稻产量及土壤成分的影响研究[J]. 绿色科技, 2023(3): 82-85. |
| Zhang Y Y, Li X C, Tan J X, Ding G J, Zhang T, Chen L, Zheng R, Ren J, Shi A L. Effect of microbial fertilizer on rice yield composition and soil composition[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2023(3): 82-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 彭轶楠, 赵廷伟, 梁燕, 王治业, 季彬. 施用复合微生物菌肥对河西走廊盐碱地的改良效果[J]. 中南农业科技, 2024(3): 3-8. |
| Peng Y N, Zhao T W, Liang Y, Wang Z Y, Ji B. Improvement effect of compound microbial fertilizer on saline-alkali land in Hexi Corridor[J]. South-Central Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024(3): 3-8. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 张蛟, 龙锡恩, 崔士友, 韩继军, 陈澎军, 缪源卿. 盐逆境下促生菌对水稻生长、产量及稻米品质的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2024, 52(1): 69-75. |
| Zhang J, Long X E, Cui S Y, Han J J, Chen P J, Miao Y Q. Influences of different growth promoting bacteria on growth, yield and quality of rice under salt stress[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 52(1): 69-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 孟天瑶, 朱旺, 汪璐璐, 张徐彬, 许轲, 戴其根, 周桂生, 韦还和. 水稻产量形成对盐-旱复合胁迫的响应与生理机制[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2024, 45(1): 18-26. |
| Meng T L, Zhu W, W L L, Zhang X B, Xu K, Dai Q G, Zhou G S, Wei H H. Response of rice yield formation to combined salinity-drought stress and its physiological mechanism[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition, 2024, 45(1): 18-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 张婉霞. 几株芽孢杆菌防治党参根腐病效果评价及作用机理研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2023. |
| Zhang W X. Effect evaluation and mechanism study of several Bacillus strains on root rot of Codonopsis pilosula[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiatong University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 孙一航, 刘学生, 林宇龙. 盐胁迫对植物根际环境影响的研究[J]. 草学, 2023(2): 1-4. |
| Sun Y H, Liu X S, Lin Y L. Effects of salt stress on plant rhizosphere environment[J]. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2023(2): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 陈瑞蕊, 张建伟, 董洋, 林先贵, 冯有智. 盐度对滨海土壤细菌多样性和群落构建过程的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(5): 1816-1824. |
| Chen R R, Zhang J W, Dong Y, Lin X G, Feng Y Z. Effects of salinity on soil bacterial diversity and assembly processes in coastal soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(5): 1816-1824. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 弋良朋, 张辉. 滨海4种盐生植物根际土壤酶活性特征与主要养分的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(2): 270-275. |
| Yi L P, Zhang W. Characteristics of soil enzymatic activitys and relationship with the main nutrient in the rhizosphere of four littoral halophytes[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(2): 270-275. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Kumar A, Singh S, Mukherjee A, Rastogi R P, Verma J P. Salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting Bacillus pumilus strain JPVS11 to enhance plant growth attributes of rice and improve soil health under salinity stress[J]. Microbiological Research, 2021, 242: 126616. |
| [15] | 韦江璐, 覃英, 谢显秋, 陈教云, 董登峰, 邢永秀, 李杨瑞. 促生菌对土壤养分、酶活性及细菌群落功能多样性的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 2020, 51(10): 2348-2357. |
| Wei J L, Tan Y, Xie X Q, Chen J Y, Dong D F, Xing Y X, Li Y R. Effects of growth-promoting bacteria on soil nutrient, enzyme activity and bacterial community function diversity[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2020, 51(10): 2348-2357. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 孙宇瑞. 土壤含水率和盐分对土壤电导率的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2000(4): 39-41. |
| Sun Y R. Experimental survey for the effects of soil water content and soil salinity on soil electrical conductivity[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2000(4): 39-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Sultana S, Alam S, Karim M M. Screening of siderophore-producing salt-tolerant rhizobacteria suitable for supporting plant growth in saline soils with iron limitation[J]. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, 2021, 4: 100150. |
| [18] | 邹禹. LRR型受体蛋白激酶OsRPK1通过生长素信号转导和极性运输调控高盐胁迫下水稻的根系结构[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2013. |
| Zou Y. OsRPKl, A leucine rich repeat receptor protein kinase in iuce,modulates root syetem architectire under high salt stress by regulating auxin signal transduction and polar transport[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 李静, 崔继哲, 弭晓菊. 生长素与植物逆境胁迫关系的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2012(6): 13-17. |
| Li J, Cui J Z, Mi X J. Progress of studies on relationship between auxin and plant response to abiotic stress[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2012(6): 13-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Etesami H, Maheshwari D K. Use of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) with multiple plant growth promoting traits in stress agriculture: Action mechanisms and future prospects[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 156: 225-246. |
| [21] | Vimal S R, Singh J S, Prasad S M. Prospective of indole-3-acteic acid (IAA) and endophytic microbe Bacillus subtilis strain SSA4 in paddy seedlings development and ascorbate-glutathione (AsA-GSH) cycle regulation to mitigate NaCl toxicity[J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2023, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/S12033-027-00743-W. |
| [22] | Jha B, Gontia I, Hartmann A. The roots of the halophyte Salicornia brachiata are a source of new halotolerant diazotrophic bacteria with plant growth-promoting potential[J]. Plant and Soil, 2012, 356(1): 265-277. |
| [23] | 师晨娟, 刘勇, 荆涛. 植物激素抗逆性研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2006(5): 21-26. |
| Shi C J, Liu Y, Jing T. Review on stress-resistance of phytohormone[J]. World Forestry Research, 2006(5): 21-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 李金涛, 杨玉娜, 柴梦梦, 胡启琰, 杨文倩, 袁景佳, 李杨意, 董钰, 刘彬文, 樊海燕. 乙烯调控水稻根系生长素合成及运输研究[J]. 信阳师范学院学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 33(3): 377-384. |
| Li J T, Yang Y N, Cai M M, Hu Q Y, Yang W Q, Yuan J J, Li Y Y, Dong Y, Liu B W, Fan H Y. Research of Ethylene modulated auxin biosynthesis and transport in rice root[J]. Journal of Xinyang Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 33(3): 377-384. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 胡玉婕, 朱秀玲, 丁延芹, 杜秉海, 汪城墙. 芽孢杆菌的耐盐促生机制研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(9): 64-74. |
| Hu Y J, Zhu X L, Ding Y Q, Du B H, Wang C Q. Research progress on salt tolerance and growth-promoting mechanism of bacillus[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2020, 36(9): 64-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Misra S, Chauhan P S. ACC deaminase-producing rhizosphere competent Bacillus spp. mitigate salt stress and promote Zea mays growth by modulating ethylene metabolism[J]. 3 Biotech, 2020, 10(3): 119. |
| [27] | 常汇琳, 聂守军, 刘晴, 刘宇强, 马成, 王婧泽, 宗天鹏, 孙中华. 盐胁迫对水稻生长发育的影响及外源物质对其调节作用的研究进展[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2022(8): 68-73. |
| Chang H L, Nie S J, Liu Q, Liu Y Q, Ma C, Wang J Z, Zong T P, Sun Z H. Research progress on effects of salt stress on growth and development in rice and regulation mechanism of exogenous substances[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022(8): 68-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Shahzad R, Khan A L, Bilal S, Waqas M, Kang S M, Lee I J. Inoculation of abscisic acid-producing endophytic bacteria enhances salinity stress tolerance in Oryza sativa[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2017, 136: 68-77. |
| [29] | Tiwari S, Prasad V, Chauhan P S, Lata C. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens confers tolerance to various abiotic stresses and modulates plant response to phytohormones through osmoprotection and gene expression regulation in rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1510. |
| [30] | Prittesh P, Avnika P, Kinjal P, Jinal H N, Sakthivel K, Amaresan N. Amelioration effect of salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria on growth and physiological properties of rice (Oryza sativa) under salt-stressed conditions[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2020, 202(9): 2419-2428. |
| [31] | 张丽丽, 倪善君, 张战, 赵一洲, 李鑫, 毛艇, 刘研, 刘福才. 外源赤霉素对盐胁迫下水稻种子萌发及幼苗生长的缓释效应[J]. 中国稻米, 2018, 24(2): 42-46. |
| Zhang L L, Ni S J, Zhang Z, Zhao Y Z, Li X, Mao T, Liu Y, Liu Fu C. Su stained release effects of exogenous GA3 on germination and growth of rice seedling under salt stress[J]. China Rice, 2018, 24(2): 42-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Gutiérrez-Mañero F J, Ramos-Solano A B, Probanza A A, Mehouachi A J, Tadeo B F R, Talon B M. The plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria Bacillus Pumilus and Bacillus licheniformis produce high amounts of physiologically active gibberellins[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2001, 111(2): 206-211. |
| [33] | Khan M A, Asaf S, Khan A L, Adhikari A, Jan R, Ali S, Imran M, Kim K, Lee I. Plant growth-promoting endophytic bacteria augment growth and salinity tolerance in rice plants[J]. Plant Biology, 2020, 22(5): 850-862. |
| [34] | Joo G J, Kim Y M, Kim J T, Rhee I K, Kim J H, Lee I J. Gibberellins-producing rhizobacteria increase endogenous gibberellins content and promote growth of red peppers[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2005, 43(6): 510-515. |
| [35] | 常硕其, 粟琳, 欧阳翔. 水稻产量提高与光合作用之间相互关系[J]. 生命科学, 2024, 36(10) 1305-1310. |
| Chang S Q, Su L, Ouyang X. The relationship between rice yield growth and photosynthesis[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2024, 36(10): 1305-1310. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Zhao Y, Deng Y, Wang Y H, Lou Y R, He L F, Liu T, Yan Z M, Zhuang J, Xiong A S. Changes in carotenoid concentration and expression of carotenoid biosynthesis genes in daucus carota taproots in response to increased salinity[J]. Horticulturae, 2022, 8(7): 650. |
| [37] | Dutta B, Datta A, Dey A, Ghosh A K, Bandopadhyay R. Establishment of seed biopriming in salt stress mitigation of rice plants by mangrove derived Bacillus sp[J]. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 2023, 48: 102626. |
| [38] | Cazzonelli C I. Carotenoids in nature: Insights from plants and beyond[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2011, 38(11): 833-847. |
| [39] | Shultana R, Kee Zuan A T, Yusop M R, Saud H M. Characterization of salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and the effect on growth and yield of saline-affected rice[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(9): e0238537. |
| [40] | Gunasekaran Y, Thiyageshwari S, Ariyan M, Roy Choudhury A, Park J H, Selvi D, Chithra L, Anandham R. Alleviation of sodic stress in rice by exploring the exopolysaccharide-producing sodic-tolerant bacteria[J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(9): 1451. |
| [41] | Bisht N, Singh T, Ansari M M, Joshi H, Mishra S K, Chauhan P S. Plant growth-promoting Bacillus amyloliquefaciens orchestrate homeostasis under nutrient deficiency exacerbated drought and salinity stress in Oryza sativa L. seedlings[J]. Planta, 2024, 261(1): 8. |
| [42] | Oubaha B, Rathore R S, Bagri J, Singhal N K, Mazumdar K, Rishi V, Pareek A, Singla-Pareek S L. Bacillus siamensis strain BW enhances rice growth and salinity tolerance through redox equilibrium and hormone modulation[J]. Current Plant Biology, 2024, 37: 100321. |
| [43] | Shultana R, Kee Zuan A T, Yusop M R, Saud H M, El-Shehawi A M. Bacillus tequilensis strain ‘UPMRB9’ improves biochemical attributes and nutrient accumulation in different rice varieties under salinity stress[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(12): e0260869. |
| [44] | 付冰清. 铅胁迫下接种假单胞菌对苦楝根际土壤微生物群落结构的影响[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2022. |
| Fu B Q. Effects of inoculation with Pseudomonas sp. on microbial community structure in rhizosphere soil of Melia azedarach under lead stress[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | Zeng Q, Man X, Huang Z, Zhuang L, Yang H, Sha Y. Effects of rice blast biocontrol strain Pseudomonas alcaliphila Ej2 on the endophytic microbiome and proteome of rice under salt stress[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14: 1129614. |
| [46] | de Souza Silva C M M, de Castro V L S S, de Oliveira P R, de Holanda Nunes Maia A. Influence of Pseudomonas putida AF7 inoculation on soil enzymes[J]. Ecotoxicology, 2009, 18(8): 1182-1187. |
| [47] | Nakbanpote W, Panitlurtumpai N, Sangdee A, Sakulpone N, Sirisom P, Pimthong A. Salt-tolerant and plant growth-promoting bacteria isolated from Zn/Cd contaminated soil: Identification and effect on rice under saline conditions[J]. Journal of Plant Interactions, 2014, 9(1): 379-387. |
| [48] | Mirza M S, Mehnaz S, Normand P, Prigent-Combaret C, Moënne-Loccoz Y, Bally R, Malik K A. Molecular characterization and PCR detection of a nitrogen-fixing Pseudomonas strain promoting rice growth[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2006, 43(2): 163-170. |
| [49] | Alharbi K, Osman H S, Rashwan E, Hafez E M, Omara A E. Stimulating the growth, anabolism, antioxidants, and yield of rice plants grown under salt stress by combined application of bacterial inoculants and nano-silicon[J]. Plants, 2022, 11(24): 3431. |
| [50] | 徐晨, 刘晓龙, 李前, 王洪君, 王楠, 凌凤楼, 武志海, 张治安. 氮水平对不同时期盐胁迫下水稻生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2018, 37(6): 48-53. |
| Xu C, Liu X L, Li Q, Wang H J, Wang N, Ling F L. Wu Z H, Zhang Z A. Growth and physiological characteristics of rice as affected by NaCl under different nitrogen applications[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2018, 37(6): 48-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [51] | Setiawati M R, Sugiyono L, Kamaluddin N N, Simarmata T. The use of endophytic growth-promoting bacteria to alleviate salinity impact and enhance the chlorophyll, N uptake, and growth of rice seedling[J]. Open Agriculture, 2021, 6(1): 798-806. |
| [52] | Jha Y, Subramanian R B. Paddy plants inoculated with PGPR show better growth physiology and nutrient content under saline conditions[J]. Chilean Journal of Agricultural Research, 2013, 73(3): 213-219. |
| [53] | 沙月霞, 宋双, 黄泽阳. 假单胞菌浸种对盐胁迫下水稻种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2022, 63(2): 4-10. |
| Sha Y S, Song S, Huang Z Y. Effect of pseudomonas alcaliphila soaking on seed germination and seeding growth of rice under salt stress[J]. Journal of Ningxia Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 2022, 63(2): 4-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [54] | Khumairah F H, Setiawati M R, Fitriatin B N, Simarmata T, Alfaraj S, Ansari M J, El Enshasy H A, Sayyed R Z, Najafi S. Halotolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria isolated from saline soil improve nitrogen fixation and alleviate salt stress in rice plants[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 905210. |
| [55] | Simarmata T, Setiawati M R, Fitriatin B N, Herdiyantoro D, Khumairah F H. Enhancing the ability of rice to adapt and grow under saline stress using selected halotolerant rhizobacterial nitrogen fixer[J]. Open Agriculture, 2023, 8(1): 20220195. |
| [56] | Niknejhad Y, Daneshian J, Rad A S, Pirdashti H, Arzanesh M H. Effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on leaf area duration dynamics of rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants under nitrogen and water limited conditions[J]. Research on Crops, 2013, 14(2): 345-349. |
| [57] | Pahari A, Pradhan A, Nayak S K, Mishra B B. Bacterial siderophore as a plant growth promoter[M]// Microbial Biotechnology. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2017: 163-180. |
| [58] | Arora N K, Mishra J, Singh P, Fatima T. Salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting Pseudomonas atacamensis KSS-6 in combination with organic manure enhances rice yield, improves nutrient content and soil properties under salinity stress[J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2024, 64(6): 2300767. |
| [59] | Gupta A, Tiwari R K, Shukla R, Singh A N, Sahu P K. Salinity alleviator bacteria in rice (Oryza sativa L.), their colonization efficacy, and synergism with melatonin[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 1060287. |
| [60] | Lucas J A, García-Cristobal J, Bonilla A, Ramos B, Gutierrez-Mañero J. Beneficial rhizobacteria from rice rhizosphere confers high protection against biotic and abiotic stress inducing systemic resistance in rice seedlings[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 82: 44-53. |
| [61] | 刘鹏. 耐盐细菌对盐渍化土壤和水稻生长的影响[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2021. |
| Liu P. Effects of salt-tolerant bacteria on saline soil and rice growth[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [62] | Lucas J A, Garcia-Villaraco Velasco A, Ramos B, Gutierrez-Mañero F J. Changes of enzyme activities related to oxidative stress in rice plants inoculated with random mutants of a Pseudomonas fluorescens strain able to improve plant fitness upon biotic and abiotic conditions[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2017, 44(11): 1063-1074. |
| [63] | Jha Y, Subramanian R B. PGPR regulate caspase-like activity, programmed cell death, and antioxidant enzyme activity in paddy under salinity[J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2014, 20(2): 201-207. |
| [64] | Jha Y, Subramanian R B. Reduced cell death and improved cell membrane integrity in rice under salinity by root associated bacteria[J]. Theoretical and Experimental Plant Physiology, 2015, 27(3): 227-235. |
| [65] | 金杰人, 鲁凯珩, 肖明. 荧光假单胞菌的应用与展望[J]. 上海师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 48(5): 526-535. |
| Jin J R, Lu K H, Xiao M. Application and prospect of Pseudomonas fluorescens[J]. Journal of Shanghai Normal University: Natural Sciences, 2019, 48(5): 526-535. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [66] | Etesami H, Mirseyed H H, Ali A H. Bacterial biosynthesis of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-caboxylate (ACC) deaminase, a useful trait to elongation and endophytic colonization of the roots of rice under constant flooded conditions[J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2014, 20(4): 425-434. |
| [67] | Qian L, Song F, Xia J, Wang R. A glucuronic acid-producing endophyte Pseudomonas sp. MCS15 reduces cadmium uptake in rice by inhibition of ethylene biosynthesis[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 876545. |
| [68] | Paul D, Dineshkumar N, Nair S. Proteomics of a plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium, Pseudomonas fluorescens MSP-393, subjected to salt shock[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 22(4): 369-374. |
| [69] | Han Y, Wang R, Yang Z, Zhan Y, Ma Y, Ping S, Zhang L, Lin M, Yan Y. 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase from Pseudomonas stutzeri A1501 facilitates the growth of rice in the presence of salt or heavy metals[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 25(7): 1119-1128. |
| [70] | Abbas S R, Shahid I, Javed M, Malik K A, Mehnaz S. Contribution of mineral mobilizing fluorescent pseudomonads in growth promotion of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in nutrient deficient soil[J]. South African Journal of Botany, 2024, 166: 88-96. |
| [71] | Norouzinia F, Ansari M H, Aminpanah H, Firouzi S. Alleviation of soil salinity on physiological and agronomic traits of rice cultivars using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and pseudomonas strains under field conditions[J]. Revista de Agricultura Neotropical, 2020, 7(1): 25-42. |
| [72] | 潘龙. 丛植菌根真菌与解磷细菌互作促进土壤有机磷矿化的研究[D]. 新乡: 河南科技学院, 2020. |
| Pan L. Study on the interaction between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria to promote soil organophosphorus mineralization[D]. Xinxiang: Henan Institute of Science and Technology, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [73] | 肖玖军, 邢丹, 毛明明, 王岩. AM真菌对桑树根围土壤团聚体的影响机制[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(3): 773-782. |
| Xiao J J, Xing D, Mao M M, Wang Y. Mechanism of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal affecting soil aggregates in rhizosphere of mulberry(morus alba)[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(3): 773-782. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [74] | 秦泽峰, 谢沐希, 张运龙, 李侠, 李海港, 张俊伶. 丛枝菌根真菌介导的土壤有机碳稳定机制研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(4): 756-766. |
| Qin Z F, Xie M X, Zhang Y L, Li X, Li H G, Zhang J L. Research progress in soil organic carbon stabilization mediated by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(4): 756-766. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [75] | 张思华. 丛枝菌根真菌对水稻耐盐性的调控效应及机理[D]. 牡丹江: 牡丹江师范学院, 2023. |
| Zhang S H. Regulation effect and mechanism of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on salt tolerance of rice[D]. Mudanjiang: Mudanjiang Normal University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [76] | Evelin H, Kapoor R, Giri B. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in alleviation of salt stress: A review[J]. Annals of Botany, 2009, 104(7): 1263-1280. |
| [77] | 卢垟杰. AM 真菌在盐碱地改良方面的应用展望[J]. 土壤科学, 2020, 4(8): 185-189. |
| Lu Y J. Prospect of application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the improvement of saline land[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 4(8): 185-189. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [78] | Narwal E, Annapurna K, Choudhary J, Dhakar R, Singh Y V. Bioprospecting aerobic rice (Oryza sativa) and mycorrhizal interaction for nutrient uptake and plant growth[J]. The Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 91(8): 1236-1241. |
| [79] | 黄洁. 盐胁迫对水稻氮代谢的影响及一氧化氮的调控作用[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020. |
| Huang J. Effects of salt stress on nitrogen metabolism in rice and regulation of nitric oxide[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [80] | Zhang Z, Liao H, Lucas W J. Molecular mechanisms underlying phosphate sensing, signaling, and adaptation in plants[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2014, 56(3): 192-220. |
| [81] | 屈明华, 俞元春, 李生, 张金池. 丛枝菌根真菌对矿质养分活化作用研究进展[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(2): 394-405. |
| Qu M H. Yu Y C, Li S, Zhang J C. Advances in research on activation of mineral nutrients by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2019, 36(2): 394-405. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [82] | 薛英龙, 李春越, 王苁蓉, 王益, 刘津, 常顺, 苗雨, 党廷辉. 丛枝菌根真菌促进植物摄取土壤磷的作用机制[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(6):10-20. |
| Xue Y L, Li C Y, Wang C R, Wang Y, Liu J, Chang S, Miao Y, Dang T W. Mechanisms of Phosphorus uptake from soils by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(6): 10-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [83] | 田全祥. 钾离子通道OsAKT2在水稻适应盐胁迫过程中的生理功能研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2021. |
| Tian Q X. Physiological function of potassium channel OsAKT2 in rice adaptation to salt stress[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [84] | Chandrasekaran M. A meta-analytical approach on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation efficiency on plant growth and nutrient uptake[J]. Agriculture, 2020, 10(9): 370. |
| [85] | Han X, Zhou Y, Li Y, Ren W, Liu K, Zhang W, Zhang H, Tang M. LbKAT3 may assist in mycorrhizal potassium uptake, and overexpression of LbKAT3 may promote potassium, phosphorus, and water transport from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to the host plant[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1161220. |
| [86] | da Silva H F O, Tavares O C H, de Souza da Silva L, Zonta E, da Silva E M R, Saggin O J Jr, Nobre C P, Berbara R L L, García A C. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and humic substances increased the salinity tolerance of rice plants[J]. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 2022, 44: 102472. |
| [87] | 潘晶, 黄翠华, 罗君, 彭飞, 薛娴. 盐胁迫对植物的影响及AMF提高植物耐盐性的机制[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(4): 361-372. |
| Pan J, Huang C H, Luo J, Peng F, Xue X. Effects of salt stress on plant and the mechanism of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhancing salt tolerance of plants[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2018, 33(4): 361-372. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [88] | Tisarum R, Theerawitaya C, Samphumphuang T, Polispitak K, Thongpoem P, Singh H P, Cha-Um S. Alleviation of salt stress in upland rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica cv. leum Pua) using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 348. |
| [89] | Yooyongwech S, Tisarum R, Samphumphuang T, Phisalaphong M, Cha-Um S. Integrated strength of osmotic potential and phosphorus to achieve grain yield of rice under water deficit by arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 5999. |
| [90] | Xu C, Li Q, Liu X, Wang H, Ling F. Effects of nitrogen supply level on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of rice under salt stress[J]. Emirates Journal of Food and Agriculture, 2019: 741. |
| [91] | Zhang B, Shi F, Zheng X, Pan H Y, Wen Y Q, Song F Q. Effects of AMF compound inoculants on growth, ion homeostasis, and salt tolerance-related gene expression in Oryza sativa L. under salt treatments[J]. Rice, 2023, 16(1). |
| [92] | Porcel R, Redondo-Gómez S, Mateos-Naranjo E, Aroca R, Garcia R, Ruiz-Lozano J M. Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis ameliorates the optimum quantum yield of photosystem II and reduces non-photochemical quenching in rice plants subjected to salt stress[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2015, 185: 75-83. |
| [93] | Parvin S, Van Geel M, Yeasmin T, Verbruggen E, Honnay O. Effects of single and multiple species inocula of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the salinity tolerance of a Bangladeshi rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivar[J]. Mycorrhiza, 2020, 30(4): 431-444. |
| [1] | 朱鹏, 凌溪铁, 王金彦, 张保龙, 杨郁文, 许轲, 裘实. 机直播条件下不同控草方式对抗除草剂水稻产量和品质差异性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 501-515. |
| [2] | 董立强, 张义凯, 杨铁鑫, 冯莹莹, 马亮, 梁潇, 张玉屏, 李跃东. 北方粳稻密苗机插育秧对秧苗素质及取秧特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 516-528. |
| [3] | 朱建平, 李霞, 李文奇, 许扬, 王芳权, 陶亚军, 蒋彦婕, 陈智慧, 范方军, 杨杰. 水稻粉质胚乳突变体we1的表型分析与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 543-551. |
| [4] | 黄福灯, 吴春艳, 郝媛媛, 韩一飞, 张小斌, 孙会锋, 潘刚. 不同氮肥水平下水稻倒二叶叶鞘的转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 563-574. |
| [5] | 卢椰子, 邱结华, 蒋楠, 寇艳君, 时焕斌. 稻瘟病菌效应子研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 287-294. |
| [6] | 王超瑞, 周宇琨, 温雅, 张瑛, 法晓彤, 肖治林, 张耗. 秸秆还田方式对稻田土壤特性和温室气体排放的影响及其水肥互作调控[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 295-305. |
| [7] | 王雅宣, 王新峰, 杨后红, 刘芳, 肖晶, 蔡玉彪, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊. 稻飞虱适应水稻抗性机制的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 306-321. |
| [8] | 黄涛, 魏兆根, 陈玘, 程泽, 刘欣, 王广达, 胡珂鸣, 谢文亚, 陈宗祥, 冯志明, 左示敏. 水稻类病斑突变体lm52的基因克隆及其广谱抗病性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 322-330. |
| [9] | 马顺婷, 胡运高, 高方远, 刘利平, 牟昌铃, 吕建群, 苏相文, 刘松, 梁毓玉, 任光俊, 郭鸿鸣. 水稻真核翻译起始因子OseIF6.2调控粒型的功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 331-342. |
| [10] | 张彬涛, 刘聪聪, 郭明亮, 杨绍华, 吴世强, 郭龙彪, 朱义旺. 水稻OsDR8基因的稻瘟病抗性评价及优异单倍型鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 343-351. |
| [11] | 韦新宇, 曾跃辉, 肖长春, 黄建鸿, 阮宏椿, 杨旺兴, 邹文广, 许旭明. 水稻康丰B抗稻瘟病基因Pi-kf2(t)的克隆与功能验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 352-364. |
| [12] | 李文奇, 许扬, 王芳权, 朱建平, 陶亚军, 李霞, 范方军, 蒋彦婕, 陈智慧, 杨杰. 广谱抗稻瘟病基因PigmR的KASP标记开发及应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 365-372. |
| [13] | 韦还和, 汪璐璐, 马唯一, 张翔, 左博源, 耿孝宇, 朱旺, 朱济邹, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 戴其根. 盐−旱复合胁迫下粳稻品种南粳9108籽粒灌浆特性及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 373-386. |
| [14] | 沈智达, 余秋华, 张斌, 曹玉东, 王少华, 王红飞, 伍永清, 戴志刚, 李小坤. 磷肥施用量对湖北省直播水稻产量、磷素积累及利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 399-411. |
| [15] | 何勇, 张诗骞, 王志成, 詹逍康, 丁一可, 刘晓瑞, 马素素, 田志宏. 印度梨形孢与复合肥组合施用对水稻机插秧秧苗素质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 412-422. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||