
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 563-574.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.250306
• 研究报告 • 上一篇
黄福灯1,#, 吴春艳1,#, 郝媛媛1, 韩一飞1, 张小斌1,*( ), 孙会锋2,*(
), 孙会锋2,*( ), 潘刚3
), 潘刚3
收稿日期:2025-02-17
修回日期:2025-04-11
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2025-07-21
通讯作者:
*email: 525588094@qq.com,zhangxb@zaas.ac.cn作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
HUANG Fudeng1,#, WU Chunyan1,#, HAO Yuanyuan1, HAN Yifei1, ZHANG Xiaobin1,*( ), SUN Huifeng2,*(
), SUN Huifeng2,*( ), PAN Gang3
), PAN Gang3
Received:2025-02-17
Revised:2025-04-11
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-07-21
Contact:
*email: 525588094@qq.com,zhangxb@zaas.ac.cnAbout author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】探明叶鞘对氮素响应的重要基因,为水稻氮素高效利用的遗传改良提供科学依据。【方法】将粳稻品种秀水134种植在低氮(LN)、中氮(MN)和高氮(HN)的渗漏池中,选取抽穗后第10天的倒二叶叶鞘进行转录组测序分析,以鉴定叶鞘对氮素响应的重要基因。【结果】转录组数据比较分析显示,三种氮素水平间存在1791个差异表达基因。其中HN与MN、MN与LN、以及HN与LN组间的上调和下调表达基因数分别为312个和155个,263个和160个,1059个和542个。三种施氮水平间的共有上调和下调差异表达基因分别为15个和53个,涉及营养元素吸收和转运、生物与非生物胁迫响应、植物激素响应以及光调控等生理生化过程。基于GO富集分析和KEGG代谢途经分析,最终鉴定出参与氮素利用及光合作用的已知功能基因分别为6个和4个,以及50个功能未知基因,推测这些基因在倒二叶叶鞘的氮素响应中发挥重要作用。【结论】研究结果初步明确了叶鞘对不同氮素水平响应的重要基因,这些基因在氮素利用的信号转导途径中发挥重要作用。
黄福灯, 吴春艳, 郝媛媛, 韩一飞, 张小斌, 孙会锋, 潘刚. 不同氮肥水平下水稻倒二叶叶鞘的转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 563-574.
HUANG Fudeng, WU Chunyan, HAO Yuanyuan, HAN Yifei, ZHANG Xiaobin, SUN Huifeng, PAN Gang. Transcriptome Analysis of Top Second Leaf Sheath of Rice Under Different Nitrogen Fertilizer Levels[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(4): 563-574.
| 基因 ID | 正向引物 Forward primer(5’-3’) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os07g48020 | GCTCCAAGGTGAACTCCTAATT | CACCGTACCTATACTTGTGGTT |
| LOC_Os07g08160 | GCCCTTCGTCAACGTCTAATTA | CCCTAGCTAGCTACCCAGTATA |
| LOC_Os11g25260 | CAGTTACTTGCATTATGGGCTC | ATGTACCATTGAATTCGCGAAG |
| LOC_Os09g12290 | AGTGGAAAGAGCTTCTACGAAA | TCATAATAGTGGCATGCTACGT |
| LOC_Os07g08150 | GTACTTGCGTATGTACTGGGTA | CACTATCAAGCTTGCTACTTGC |
| LOC_Os01g14410 | CTTCAATTCGATCCTCGCTAAG | CGCCATTGCAAATAACTCAAAC |
| LOC_Os10g01080 | AAACACAAACACTGACGCC | GAGAAGCTACCGGACTTGTG |
| LOC_Os02g02120 | GCCATAAAGCGCTCAAAGATTA | CTTCCACTTCTAAGCAACAACC |
| LOC_Os04g27670 | CATTTTGAGTCTGTATGCGTGA | TGCTGCTTTTCTGTTTACTTCC |
表1 qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| 基因 ID | 正向引物 Forward primer(5’-3’) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os07g48020 | GCTCCAAGGTGAACTCCTAATT | CACCGTACCTATACTTGTGGTT |
| LOC_Os07g08160 | GCCCTTCGTCAACGTCTAATTA | CCCTAGCTAGCTACCCAGTATA |
| LOC_Os11g25260 | CAGTTACTTGCATTATGGGCTC | ATGTACCATTGAATTCGCGAAG |
| LOC_Os09g12290 | AGTGGAAAGAGCTTCTACGAAA | TCATAATAGTGGCATGCTACGT |
| LOC_Os07g08150 | GTACTTGCGTATGTACTGGGTA | CACTATCAAGCTTGCTACTTGC |
| LOC_Os01g14410 | CTTCAATTCGATCCTCGCTAAG | CGCCATTGCAAATAACTCAAAC |
| LOC_Os10g01080 | AAACACAAACACTGACGCC | GAGAAGCTACCGGACTTGTG |
| LOC_Os02g02120 | GCCATAAAGCGCTCAAAGATTA | CTTCCACTTCTAAGCAACAACC |
| LOC_Os04g27670 | CATTTTGAGTCTGTATGCGTGA | TGCTGCTTTTCTGTTTACTTCC |
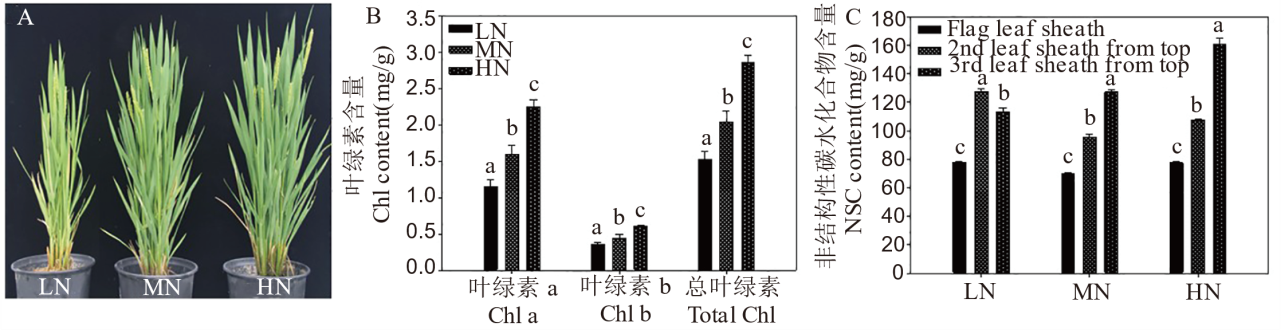
图1 不同氮肥水平下水稻植株表型、叶绿素含量及叶鞘NSC含量 LN、MN和HN分别代表低氮、中氮和高氮。
Fig. 1. Phenotypes of rice plants, NSC contents and chlorophyll contents in leaf sheath under different nitrogen fertilizer levels LN, MN, and HN represent low nitrogen, medium nitrogen, and high nitrogen levels, respectively.
| 性状 Trait | 低氮 LN | 中氮 MN | 高氮 HN |
|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height(cm) | 78.07±0.64 b | 81.67±0.88 a | 83.43±1.03 a |
| 千粒重 1000-grain weight(g) | 13.69±0.08 c | 21.30±0.81 a | 17.90±1.12 b |
| 单株有效穗数 Effective pancle number | 8.33±0.33 a | 8.67±0.33 a | 9.00±0.58 a |
| 穗干质量 Panicle dry weight(g) | 3.62±0.10 a | 1.86±0.42 b | 1.51±0.05 b |
| 每穗总粒数 Grain number per panicle | 99.67±1.45 c | 152.00±1.15 b | 166.67±1.76 a |
| 结实率 Seed-setting rate(%) | 77.27±9.87 b | 92.40±2.00 a | 93.08±1.34 a |
表2 不同施氮水平下的水稻主要农艺性状
Table 2. Main agronomic traits of rice under different nitrogen fertilizer levels
| 性状 Trait | 低氮 LN | 中氮 MN | 高氮 HN |
|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height(cm) | 78.07±0.64 b | 81.67±0.88 a | 83.43±1.03 a |
| 千粒重 1000-grain weight(g) | 13.69±0.08 c | 21.30±0.81 a | 17.90±1.12 b |
| 单株有效穗数 Effective pancle number | 8.33±0.33 a | 8.67±0.33 a | 9.00±0.58 a |
| 穗干质量 Panicle dry weight(g) | 3.62±0.10 a | 1.86±0.42 b | 1.51±0.05 b |
| 每穗总粒数 Grain number per panicle | 99.67±1.45 c | 152.00±1.15 b | 166.67±1.76 a |
| 结实率 Seed-setting rate(%) | 77.27±9.87 b | 92.40±2.00 a | 93.08±1.34 a |
| 基因 ID | 基因注释 Gene annotation | FPKM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LN | MN | HN | ||
| LOC_Os07g08150 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein Early light-induced protein | 300.51 | 95.23 | 11.46 |
| LOC_Os01g14410 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein | 372.04 | 143.45 | 24.47 |
| LOC_Os10g01080 | SOR/SNZ家族蛋白SOR/SNZ family protein | 163.38 | 70.66 | 22.57 |
| LOC_Os07g08160 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein | 268.08 | 103.47 | 14.41 |
| LOC_Os11g01210 | PPR蛋白Pentatricopeptide repeat protein | 23.31 | 14.53 | 5.44 |
| LOC_Os12g01210 | PPR蛋白Pentatricopeptide repeat protein | 18.86 | 11.60 | 4.45 |
| LOC_Os01g45110 | 花青素-3-O-β-葡萄糖苷转移酶Anthocyanin 3-O-beta-glucosyltransferase | 4.93 | 1.72 | 0.75 |
| LOC_Os01g53330 | 花青素-5,3-O-糖苷转移酶Anthocyanidin 5,3-O-glucosyltransferase | 16.97 | 7.89 | 2.66 |
| LOC_Os09g26580 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 21.29 | 15.22 | 6.63 |
| LOC_Os07g06800 | 3-酮-5-α-类固醇-4-脱氢酶3-oxo-5-alpha-steroid 4-dehydrogenase | 17.75 | 5.66 | 2.04 |
| LOC_Os03g17460 | IN2-1蛋白 | 2.37 | 1.20 | 0.42 |
| LOC_Os07g44110 | 细胞色素P450 72A1 Cytochrome P450 72A1 | 1.37 | 0.51 | 0.34 |
| LOC_Os07g04820 | 蛋白激酶Protein kinase | 1.37 | 0.76 | 0.21 |
| LOC_Os08g07730 | 转移酶家族蛋白Transferase family protein | 4.16 | 2.26 | 0.74 |
| LOC_Os08g10010 | 酰基去饱和酶Acyl-desaturase | 0.79 | 0.60 | 0.10 |
表3 不同施氮水平间的共有下调表达基因
Table 3. Differentially expressed genes among the three groups
| 基因 ID | 基因注释 Gene annotation | FPKM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LN | MN | HN | ||
| LOC_Os07g08150 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein Early light-induced protein | 300.51 | 95.23 | 11.46 |
| LOC_Os01g14410 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein | 372.04 | 143.45 | 24.47 |
| LOC_Os10g01080 | SOR/SNZ家族蛋白SOR/SNZ family protein | 163.38 | 70.66 | 22.57 |
| LOC_Os07g08160 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein | 268.08 | 103.47 | 14.41 |
| LOC_Os11g01210 | PPR蛋白Pentatricopeptide repeat protein | 23.31 | 14.53 | 5.44 |
| LOC_Os12g01210 | PPR蛋白Pentatricopeptide repeat protein | 18.86 | 11.60 | 4.45 |
| LOC_Os01g45110 | 花青素-3-O-β-葡萄糖苷转移酶Anthocyanin 3-O-beta-glucosyltransferase | 4.93 | 1.72 | 0.75 |
| LOC_Os01g53330 | 花青素-5,3-O-糖苷转移酶Anthocyanidin 5,3-O-glucosyltransferase | 16.97 | 7.89 | 2.66 |
| LOC_Os09g26580 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 21.29 | 15.22 | 6.63 |
| LOC_Os07g06800 | 3-酮-5-α-类固醇-4-脱氢酶3-oxo-5-alpha-steroid 4-dehydrogenase | 17.75 | 5.66 | 2.04 |
| LOC_Os03g17460 | IN2-1蛋白 | 2.37 | 1.20 | 0.42 |
| LOC_Os07g44110 | 细胞色素P450 72A1 Cytochrome P450 72A1 | 1.37 | 0.51 | 0.34 |
| LOC_Os07g04820 | 蛋白激酶Protein kinase | 1.37 | 0.76 | 0.21 |
| LOC_Os08g07730 | 转移酶家族蛋白Transferase family protein | 4.16 | 2.26 | 0.74 |
| LOC_Os08g10010 | 酰基去饱和酶Acyl-desaturase | 0.79 | 0.60 | 0.10 |
| 基因 ID | 基因注释 Gene annotation | FPKM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LN | MN | HN | ||
| LOC_Os03g58290 | 色氨酸合成酶Indole-3-glycerol phosphate lyase | 0.21 | 2.53 | 13.95 |
| LOC_Os03g58300 | 色氨酸合成酶Indole-3-glycerol phosphate lyase | 0.00 | 0.95 | 2.28 |
| LOC_Os07g48020 | 过氧化物酶前体Peroxidase precursor | 12.80 | 31.09 | 98.47 |
| LOC_Os11g18366 | 环阿屯醇合酶Cycloartenol synthase | 0.91 | 4.17 | 7.69 |
| LOC_Os02g02120 | 类受体蛋白激酶OsWAK receptor-like protein kinase | 3.88 | 13.72 | 24.3 |
| LOC_Os02g17400 | 富含亮氨酸的重复蛋白Leucine rich repeat protein | 0.64 | 1.55 | 4.18 |
| LOC_Os09g12290 | 双功能天冬氨酸激酶Bifunctional aspartokinase/homoserine dehydrogenase | 2.72 | 3.89 | 13.90 |
| LOC_Os11g25260 | 核苷酸三磷酸酶Nucleoside-triphosphatase | 2.65 | 5.47 | 15.06 |
| LOC_Os06g35940 | 类植物开花控制同源基因FT-like12 homologous to Flowering Locus T gene | 0.08 | 1.01 | 3.71 |
| LOC_Os04g27670 | 萜烯合酶家族Terpene synthase family | 15.00 | 36.16 | 136.51 |
| LOC_Os05g47540 | 含保守肽的uORF Conserved peptide uORF-containing transcript | 0.00 | 1.26 | 2.60 |
| LOC_Os05g48200 | 谷氨酸合成酶Glutamate synthase | 5.05 | 21.13 | 54.38 |
| LOC_Os07g35340 | DUF26激酶DUF26 kinases | 0.27 | 1.16 | 2.72 |
| LOC_Os07g45550 | 表达蛋白Expessed protein | 0.50 | 1.64 | 3.32 |
| LOC_Os01g03310 | 胰酶抑制剂前体Bran trypsin inhibitor precursor | 0.78 | 3.10 | 10.34 |
| LOC_Os05g28740 | 含广泛逆境蛋白结构域的蛋白Universal stress protein domain containing protein | 35.66 | 72.48 | 195.92 |
| LOC_Os11g40970 | 类受体蛋白激酶前体Receptor-like protein kinase precursor | 1.73 | 4.37 | 11.32 |
| LOC_Os07g46280 | β-甘露糖苷酶Beta-mannosidase | 0.75 | 4.60 | 11.13 |
| LOC_Os12g43380 | 塔乌马提Thaumatin | 0.86 | 3.06 | 9.25 |
| LOC_Os08g30510 | 表达蛋白Expessed protein | 8.73 | 17.48 | 76.58 |
| LOC_Os11g25330 | 核苷酸三磷酸酶Nucleoside-triphosphatase | 1.39 | 2.71 | 7.83 |
| LOC_Os08g39840 | 脂氧酶Lipoxygenase | 1.27 | 4.13 | 7.16 |
| LOC_Os01g49320 | 糖基水解酶Glycosyl hydrolase | 0.19 | 0.75 | 2.63 |
| LOC_Os04g49210 | 2-氧草酰乙酸-3-双加氧酶2-oxoglutarate 3-dioxygenase | 0.12 | 1.37 | 4.13 |
| LOC_Os01g32364 | β-甘露糖苷酶Beta-mannosidase | 0.80 | 1.71 | 3.81 |
| LOC_Os11g24140 | 类质体蓝素结构域蛋白Plastocyanin-like domain containing protein | 5.27 | 10.93 | 66.45 |
| LOC_Os01g66860 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶Serine/threonine protein kinase | 0.97 | 5.02 | 16.31 |
| LOC_Os10g02880 | O-甲基转移酶O-methyltransferase | 0.18 | 1.44 | 2.72 |
| LOC_Os01g58910 | 生长素诱导蛋白Auxin-induced protein | 0.73 | 2.02 | 4.53 |
| LOC_Os05g47790 | 表达蛋白Expessed protein | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.73 |
| LOC_Os04g52780 | 富亮氨酸重复受体蛋白激酶前体Leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase precursor | 0.07 | 0.39 | 1.19 |
| LOC_Os03g17200 | 植物特异结构域 TIGR01589家族蛋白Plant-specific domain TIGR01589 family protein | 3.52 | 8.74 | 44.84 |
| LOC_Os12g24020 | 含类硫化酶结构域的蛋白Rhodanese-like domain containing protein | 0.37 | 0.73 | 3.84 |
| LOC_Os09g08130 | 吲哚-3-甘油磷酸合酶Indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase | 0.46 | 1.02 | 1.98 |
| LOC_Os05g46350 | 含IQ钙调素基序结构域的蛋白IQ calmodulin-binding motif domain containing protein | 0.34 | 1.55 | 3.96 |
| LOC_Os04g57350 | 含EH结构域蛋白EH domain-containing protein | 0.26 | 0.92 | 2.02 |
| LOC_Os06g22290 | 含豆科凝集素β结构域的蛋白Legume lectins beta domain containing protein | 0.11 | 0.36 | 0.84 |
表4 不同施氮水平间的共有上调差异表达基因
Table 4. Differentially expressed genes among the three groups
| 基因 ID | 基因注释 Gene annotation | FPKM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LN | MN | HN | ||
| LOC_Os03g58290 | 色氨酸合成酶Indole-3-glycerol phosphate lyase | 0.21 | 2.53 | 13.95 |
| LOC_Os03g58300 | 色氨酸合成酶Indole-3-glycerol phosphate lyase | 0.00 | 0.95 | 2.28 |
| LOC_Os07g48020 | 过氧化物酶前体Peroxidase precursor | 12.80 | 31.09 | 98.47 |
| LOC_Os11g18366 | 环阿屯醇合酶Cycloartenol synthase | 0.91 | 4.17 | 7.69 |
| LOC_Os02g02120 | 类受体蛋白激酶OsWAK receptor-like protein kinase | 3.88 | 13.72 | 24.3 |
| LOC_Os02g17400 | 富含亮氨酸的重复蛋白Leucine rich repeat protein | 0.64 | 1.55 | 4.18 |
| LOC_Os09g12290 | 双功能天冬氨酸激酶Bifunctional aspartokinase/homoserine dehydrogenase | 2.72 | 3.89 | 13.90 |
| LOC_Os11g25260 | 核苷酸三磷酸酶Nucleoside-triphosphatase | 2.65 | 5.47 | 15.06 |
| LOC_Os06g35940 | 类植物开花控制同源基因FT-like12 homologous to Flowering Locus T gene | 0.08 | 1.01 | 3.71 |
| LOC_Os04g27670 | 萜烯合酶家族Terpene synthase family | 15.00 | 36.16 | 136.51 |
| LOC_Os05g47540 | 含保守肽的uORF Conserved peptide uORF-containing transcript | 0.00 | 1.26 | 2.60 |
| LOC_Os05g48200 | 谷氨酸合成酶Glutamate synthase | 5.05 | 21.13 | 54.38 |
| LOC_Os07g35340 | DUF26激酶DUF26 kinases | 0.27 | 1.16 | 2.72 |
| LOC_Os07g45550 | 表达蛋白Expessed protein | 0.50 | 1.64 | 3.32 |
| LOC_Os01g03310 | 胰酶抑制剂前体Bran trypsin inhibitor precursor | 0.78 | 3.10 | 10.34 |
| LOC_Os05g28740 | 含广泛逆境蛋白结构域的蛋白Universal stress protein domain containing protein | 35.66 | 72.48 | 195.92 |
| LOC_Os11g40970 | 类受体蛋白激酶前体Receptor-like protein kinase precursor | 1.73 | 4.37 | 11.32 |
| LOC_Os07g46280 | β-甘露糖苷酶Beta-mannosidase | 0.75 | 4.60 | 11.13 |
| LOC_Os12g43380 | 塔乌马提Thaumatin | 0.86 | 3.06 | 9.25 |
| LOC_Os08g30510 | 表达蛋白Expessed protein | 8.73 | 17.48 | 76.58 |
| LOC_Os11g25330 | 核苷酸三磷酸酶Nucleoside-triphosphatase | 1.39 | 2.71 | 7.83 |
| LOC_Os08g39840 | 脂氧酶Lipoxygenase | 1.27 | 4.13 | 7.16 |
| LOC_Os01g49320 | 糖基水解酶Glycosyl hydrolase | 0.19 | 0.75 | 2.63 |
| LOC_Os04g49210 | 2-氧草酰乙酸-3-双加氧酶2-oxoglutarate 3-dioxygenase | 0.12 | 1.37 | 4.13 |
| LOC_Os01g32364 | β-甘露糖苷酶Beta-mannosidase | 0.80 | 1.71 | 3.81 |
| LOC_Os11g24140 | 类质体蓝素结构域蛋白Plastocyanin-like domain containing protein | 5.27 | 10.93 | 66.45 |
| LOC_Os01g66860 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶Serine/threonine protein kinase | 0.97 | 5.02 | 16.31 |
| LOC_Os10g02880 | O-甲基转移酶O-methyltransferase | 0.18 | 1.44 | 2.72 |
| LOC_Os01g58910 | 生长素诱导蛋白Auxin-induced protein | 0.73 | 2.02 | 4.53 |
| LOC_Os05g47790 | 表达蛋白Expessed protein | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.73 |
| LOC_Os04g52780 | 富亮氨酸重复受体蛋白激酶前体Leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase precursor | 0.07 | 0.39 | 1.19 |
| LOC_Os03g17200 | 植物特异结构域 TIGR01589家族蛋白Plant-specific domain TIGR01589 family protein | 3.52 | 8.74 | 44.84 |
| LOC_Os12g24020 | 含类硫化酶结构域的蛋白Rhodanese-like domain containing protein | 0.37 | 0.73 | 3.84 |
| LOC_Os09g08130 | 吲哚-3-甘油磷酸合酶Indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase | 0.46 | 1.02 | 1.98 |
| LOC_Os05g46350 | 含IQ钙调素基序结构域的蛋白IQ calmodulin-binding motif domain containing protein | 0.34 | 1.55 | 3.96 |
| LOC_Os04g57350 | 含EH结构域蛋白EH domain-containing protein | 0.26 | 0.92 | 2.02 |
| LOC_Os06g22290 | 含豆科凝集素β结构域的蛋白Legume lectins beta domain containing protein | 0.11 | 0.36 | 0.84 |
| 基因 ID | 基因名称 Gene annotation | 平均FPKM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低氮 LN | 中氮 MN | 高氮 HN | ||
| N循环相关基因Genes related to the nitrogen cycle | ||||
| LOC_Os05g48200 | OsNADH-GOGAT2 | 7.11 | 18.76 | 49.13 |
| LOC_Os04g43070 | OsAMT1;1 | 287.99 | 193.10 | 107.06 |
| LOC_Os01g36720 | OsNRT2.4 | 28.62 | 24.52 | 12.76 |
| LOC_Os08g36480 | OsNIA1 | 44.65 | 33.48 | 21.89 |
| LOC_Os08g36500 | OsNIA2 | 28.34 | 10.90 | 9.95 |
| LOC_Os04g37500 | OsGAD2 | 1.80 | 2.30 | 5.46 |
| 光合作用相关基因Genes related to photosynthesis | ||||
| LOC_Os01g64960 | psbS1 | 602.97 | 386.64 | 217.50 |
| LOC_Os04g59440 | psbS2 | 1,045.47 | 720.18 | 251.92 |
| LOC_Os04g58200 | OsPORA | 6.22 | 9.59 | 25.38 |
| LOC_Os01g14410 | OsELIP | 577.93 | 164.30 | 24.47 |
表5 与氮素利用及光合作用相关的已知功能基因
Table 5. Known functional genes related to nitrogen utilization and photosynthesis
| 基因 ID | 基因名称 Gene annotation | 平均FPKM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低氮 LN | 中氮 MN | 高氮 HN | ||
| N循环相关基因Genes related to the nitrogen cycle | ||||
| LOC_Os05g48200 | OsNADH-GOGAT2 | 7.11 | 18.76 | 49.13 |
| LOC_Os04g43070 | OsAMT1;1 | 287.99 | 193.10 | 107.06 |
| LOC_Os01g36720 | OsNRT2.4 | 28.62 | 24.52 | 12.76 |
| LOC_Os08g36480 | OsNIA1 | 44.65 | 33.48 | 21.89 |
| LOC_Os08g36500 | OsNIA2 | 28.34 | 10.90 | 9.95 |
| LOC_Os04g37500 | OsGAD2 | 1.80 | 2.30 | 5.46 |
| 光合作用相关基因Genes related to photosynthesis | ||||
| LOC_Os01g64960 | psbS1 | 602.97 | 386.64 | 217.50 |
| LOC_Os04g59440 | psbS2 | 1,045.47 | 720.18 | 251.92 |
| LOC_Os04g58200 | OsPORA | 6.22 | 9.59 | 25.38 |
| LOC_Os01g14410 | OsELIP | 577.93 | 164.30 | 24.47 |
| 基因 ID | 基因注释 Gene annotation | FPKM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低氮 LN | 中氮 MN | 高氮 HN | ||
| 持续上调Continuous upregulation | ||||
| LOC_Os07g48020 | 过氧化物酶前体Peroxidase precursor | 14.29 | 31.09 | 122.73 |
| LOC_Os03g58290 | 吲哚-3-甘油磷酸裂解酶Indole-3-glycerol phosphate lyase | 0.21 | 3.61 | 13.95 |
| LOC_Os03g58300 | 吲哚-3-甘油磷酸裂解酶Indole-3-glycerol phosphate lyase | 0.00 | 0.79 | 2.29 |
| LOC_Os02g17400 | 富亮氨酸重复蛋白Leucine rich repeat protein | 0.57 | 1.55 | 4.18 |
| LOC_Os11g18366 | 环艺术醇合成酶Cycloartenol synthase | 1.75 | 4.12 | 9.84 |
| LOC_Os02g02120 | 类受体蛋白激酶OsWAK receptor-like protein kinase | 4.88 | 12.95 | 26.35 |
| LOC_Os11g25260 | 核苷三磷酸酶Nucleoside-triphosphatase | 2.29 | 5.12 | 15.06 |
| LOC_Os09g12290 | 双功能天冬氨酸激酶Bifunctional aspartokinase | 2.29 | 4.69 | 16.69 |
| LOC_Os07g45550 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 0.59 | 1.65 | 3.91 |
| LOC_Os04g27670 | 萜烯合酶Terpene synthase family | 15.00 | 31.68 | 114.17 |
| LOC_Os06g35940 | 类植物开花控制同源基因FT-like12 homologous to Flowering Locus T gene | 0.08 | 1.01 | 3.16 |
| LOC_Os07g35340 | 激酶DUF26 kinases DUF26 | 0.36 | 1.20 | 3.35 |
| LOC_Os05g47540 | 含保守肽的uORF Conserved peptide uORF-containing transcript | 0.46 | 1.65 | 3.91 |
| LOC_Os12g43380 | 塔乌马丁Thaumatin | 0.87 | 3.06 | 22.50 |
| LOC_Os01g03310 | 胰酶抑制剂前体Bran trypsin inhibitor precursor | 0.62 | 3.10 | 10.35 |
| LOC_Os11g40970 | 类受体蛋白及激酶前体Receptor-like protein kinase precursor | 1.73 | 4.83 | 11.32 |
| LOC_Os05g28740 | 含通用应激蛋白结构域的蛋白Universal stress protein domain containing protein | 29.68 | 82.90 | 170.62 |
| LOC_Os07g46280 | β-甘露糖苷酶Beta-mannosidase | 1.71 | 4.04 | 11.95 |
| LOC_Os04g49210 | 2-氧酰戊二酸 3-双氧酶2-oxoglutarate 3-dioxygenase | 0.12 | 1.37 | 4.13 |
| LOC_Os01g66860 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶Serine/threonine protein kinase | 1.41 | 5.03 | 13.82 |
| LOC_Os01g49320 | 糖苷水解酶Glycosyl hydrolase | 0.15 | 0.62 | 2.16 |
| LOC_Os01g58910 | 生长素诱导蛋白Auxin-induced protein | 0.73 | 2.02 | 4.53 |
| LOC_Os05g47790 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.73 |
| LOC_Os10g02880 | O-甲基转移酶O-methyltransferase | 0.33 | 1.43 | 3.60 |
| LOC_Os08g39840 | 脂氧化酶Lipoxygenase | 1.74 | 4.13 | 9.37 |
| LOC_Os04g52780 | 富亮氨酸重复受体蛋白激酶Leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase precursor | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.96 |
| LOC_Os05g46350 | 含IQ钙调蛋白结合基序结构域的蛋白IQ calmodulin-binding motif domain containing protein | 0.34 | 1.55 | 3.96 |
| 持续下调Continuous downregulation | ||||
| LOC_Os07g08150 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein | 444.56 | 112.08 | 15.23 |
| LOC_Os01g14410 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein | 577.93 | 164.30 | 24.47 |
| LOC_Os10g01080 | SOR/SNZ 家族蛋白SOR/SNZ family protein | 163.38 | 70.66 | 22.57 |
| LOC_Os01g45110 | 花青素3-O-β-葡萄糖基转移酶Anthocyanidin 3-O-β-glucosyltransferase | 6.53 | 1.73 | 0.68 |
| LOC_Os07g08160 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein | 462.33 | 103.48 | 14.41 |
| LOC_Os11g01210 | PPR蛋白Pentatricopeptide repeat protein | 29.98 | 14.53 | 5.44 |
| LOC_Os12g01210 | PPR蛋白Pentatricopeptide repeat protein | 23.39 | 11.61 | 4.45 |
| LOC_Os01g53330 | 花青素5,3-O-葡萄糖基转移酶Anthocyanidin 5,3-O-glucosyltransferase | 16.97 | 7.33 | 3.32 |
| LOC_Os09g26580 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 33.93 | 15.22 | 7.08 |
| LOC_Os07g06800 | 3-氧-5-α-类固醇 4-脱氢酶3-oxo-5-alpha-steroid 4-dehydrogenase | 17.75 | 5.66 | 2.70 |
| LOC_Os08g07730 | 转移酶家族蛋白Transferase family protein | 4.16 | 2.06 | 0.90 |
| LOC_Os07g44110 | 细胞色素P450 72A1Cytochrome P450 72A1 | 1.37 | 0.62 | 0.29 |
| LOC_Os03g17460 | IN2-1蛋白IN2-1 protein | 5.25 | 1.04 | 0.42 |
| 先上调后下调Initial upregulation followed by downregulation | ||||
| LOC_Os12g16280 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 0.35 | 7.75 | 0.76 |
| LOC_Os04g44230 | 细胞分裂素脱氢酶前体Cytokinin dehydrogenase precursor | 1.86 | 5.01 | 2.08 |
| LOC_Os11g08569 | 环烯醇合成酶Cycloartenol synthase | 0.12 | 1.56 | 0.27 |
| LOC_Os11g02305 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 0.62 | 5.26 | 0.64 |
| LOC_Os06g07040 | 生长素响应家族基因Auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family member | 0.00 | 1.05 | 0.04 |
| LOC_Os03g57640 | 赤霉素受体Gibberellin receptor | 1.26 | 3.73 | 1.77 |
| LOC_Os07g30980 | uvrD/REP解旋酶家族蛋白uvrD/REP helicase family protein | 0.01 | 0.76 | 0.03 |
| LOC_Os09g32290 | 含依赖FAD氧化还原酶结构域的蛋白FAD dependent oxidoreductase protein | 0.30 | 0.80 | 0.33 |
| 先下调后上调Initial downregulation followed by upregulation | ||||
| LOC_Os10g17454 | 含RNA识别基序的蛋白RNA recognition motif containing protein | 37.00 | 9.80 | 26.18 |
| LOC_Os03g22210 | 蛋白前体Protein precursor | 4.61 | 0.03 | 0.75 |
表6 水稻叶鞘中N响应的差异表达基因
Table 6. Differentially expressed genes responsive to nitrogen in rice leaf sheaths
| 基因 ID | 基因注释 Gene annotation | FPKM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低氮 LN | 中氮 MN | 高氮 HN | ||
| 持续上调Continuous upregulation | ||||
| LOC_Os07g48020 | 过氧化物酶前体Peroxidase precursor | 14.29 | 31.09 | 122.73 |
| LOC_Os03g58290 | 吲哚-3-甘油磷酸裂解酶Indole-3-glycerol phosphate lyase | 0.21 | 3.61 | 13.95 |
| LOC_Os03g58300 | 吲哚-3-甘油磷酸裂解酶Indole-3-glycerol phosphate lyase | 0.00 | 0.79 | 2.29 |
| LOC_Os02g17400 | 富亮氨酸重复蛋白Leucine rich repeat protein | 0.57 | 1.55 | 4.18 |
| LOC_Os11g18366 | 环艺术醇合成酶Cycloartenol synthase | 1.75 | 4.12 | 9.84 |
| LOC_Os02g02120 | 类受体蛋白激酶OsWAK receptor-like protein kinase | 4.88 | 12.95 | 26.35 |
| LOC_Os11g25260 | 核苷三磷酸酶Nucleoside-triphosphatase | 2.29 | 5.12 | 15.06 |
| LOC_Os09g12290 | 双功能天冬氨酸激酶Bifunctional aspartokinase | 2.29 | 4.69 | 16.69 |
| LOC_Os07g45550 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 0.59 | 1.65 | 3.91 |
| LOC_Os04g27670 | 萜烯合酶Terpene synthase family | 15.00 | 31.68 | 114.17 |
| LOC_Os06g35940 | 类植物开花控制同源基因FT-like12 homologous to Flowering Locus T gene | 0.08 | 1.01 | 3.16 |
| LOC_Os07g35340 | 激酶DUF26 kinases DUF26 | 0.36 | 1.20 | 3.35 |
| LOC_Os05g47540 | 含保守肽的uORF Conserved peptide uORF-containing transcript | 0.46 | 1.65 | 3.91 |
| LOC_Os12g43380 | 塔乌马丁Thaumatin | 0.87 | 3.06 | 22.50 |
| LOC_Os01g03310 | 胰酶抑制剂前体Bran trypsin inhibitor precursor | 0.62 | 3.10 | 10.35 |
| LOC_Os11g40970 | 类受体蛋白及激酶前体Receptor-like protein kinase precursor | 1.73 | 4.83 | 11.32 |
| LOC_Os05g28740 | 含通用应激蛋白结构域的蛋白Universal stress protein domain containing protein | 29.68 | 82.90 | 170.62 |
| LOC_Os07g46280 | β-甘露糖苷酶Beta-mannosidase | 1.71 | 4.04 | 11.95 |
| LOC_Os04g49210 | 2-氧酰戊二酸 3-双氧酶2-oxoglutarate 3-dioxygenase | 0.12 | 1.37 | 4.13 |
| LOC_Os01g66860 | 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶Serine/threonine protein kinase | 1.41 | 5.03 | 13.82 |
| LOC_Os01g49320 | 糖苷水解酶Glycosyl hydrolase | 0.15 | 0.62 | 2.16 |
| LOC_Os01g58910 | 生长素诱导蛋白Auxin-induced protein | 0.73 | 2.02 | 4.53 |
| LOC_Os05g47790 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.73 |
| LOC_Os10g02880 | O-甲基转移酶O-methyltransferase | 0.33 | 1.43 | 3.60 |
| LOC_Os08g39840 | 脂氧化酶Lipoxygenase | 1.74 | 4.13 | 9.37 |
| LOC_Os04g52780 | 富亮氨酸重复受体蛋白激酶Leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase precursor | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.96 |
| LOC_Os05g46350 | 含IQ钙调蛋白结合基序结构域的蛋白IQ calmodulin-binding motif domain containing protein | 0.34 | 1.55 | 3.96 |
| 持续下调Continuous downregulation | ||||
| LOC_Os07g08150 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein | 444.56 | 112.08 | 15.23 |
| LOC_Os01g14410 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein | 577.93 | 164.30 | 24.47 |
| LOC_Os10g01080 | SOR/SNZ 家族蛋白SOR/SNZ family protein | 163.38 | 70.66 | 22.57 |
| LOC_Os01g45110 | 花青素3-O-β-葡萄糖基转移酶Anthocyanidin 3-O-β-glucosyltransferase | 6.53 | 1.73 | 0.68 |
| LOC_Os07g08160 | 早期光诱导蛋白Early light-induced protein | 462.33 | 103.48 | 14.41 |
| LOC_Os11g01210 | PPR蛋白Pentatricopeptide repeat protein | 29.98 | 14.53 | 5.44 |
| LOC_Os12g01210 | PPR蛋白Pentatricopeptide repeat protein | 23.39 | 11.61 | 4.45 |
| LOC_Os01g53330 | 花青素5,3-O-葡萄糖基转移酶Anthocyanidin 5,3-O-glucosyltransferase | 16.97 | 7.33 | 3.32 |
| LOC_Os09g26580 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 33.93 | 15.22 | 7.08 |
| LOC_Os07g06800 | 3-氧-5-α-类固醇 4-脱氢酶3-oxo-5-alpha-steroid 4-dehydrogenase | 17.75 | 5.66 | 2.70 |
| LOC_Os08g07730 | 转移酶家族蛋白Transferase family protein | 4.16 | 2.06 | 0.90 |
| LOC_Os07g44110 | 细胞色素P450 72A1Cytochrome P450 72A1 | 1.37 | 0.62 | 0.29 |
| LOC_Os03g17460 | IN2-1蛋白IN2-1 protein | 5.25 | 1.04 | 0.42 |
| 先上调后下调Initial upregulation followed by downregulation | ||||
| LOC_Os12g16280 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 0.35 | 7.75 | 0.76 |
| LOC_Os04g44230 | 细胞分裂素脱氢酶前体Cytokinin dehydrogenase precursor | 1.86 | 5.01 | 2.08 |
| LOC_Os11g08569 | 环烯醇合成酶Cycloartenol synthase | 0.12 | 1.56 | 0.27 |
| LOC_Os11g02305 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein | 0.62 | 5.26 | 0.64 |
| LOC_Os06g07040 | 生长素响应家族基因Auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family member | 0.00 | 1.05 | 0.04 |
| LOC_Os03g57640 | 赤霉素受体Gibberellin receptor | 1.26 | 3.73 | 1.77 |
| LOC_Os07g30980 | uvrD/REP解旋酶家族蛋白uvrD/REP helicase family protein | 0.01 | 0.76 | 0.03 |
| LOC_Os09g32290 | 含依赖FAD氧化还原酶结构域的蛋白FAD dependent oxidoreductase protein | 0.30 | 0.80 | 0.33 |
| 先下调后上调Initial downregulation followed by upregulation | ||||
| LOC_Os10g17454 | 含RNA识别基序的蛋白RNA recognition motif containing protein | 37.00 | 9.80 | 26.18 |
| LOC_Os03g22210 | 蛋白前体Protein precursor | 4.61 | 0.03 | 0.75 |
| [1] | Näsholm T, Kielland K, Ganeteg U. Uptake of organic nitrogen by plants[J]. New Phytologist, 2009, 182: 31-48. |
| [2] | 俞书傲, 樊爽爽. 我国农业区主要粮食作物化肥施用情况分析-化肥施用核算与相对适宜度评价[J]. 经济研究导刊, 2023, 23: 27-30. |
| Yu S A, Fan S S. Analysis of fertilizer application of main food crops in agricultural regions of China: Accounting for fertilizer use and evaluation of relative suitability[J]. Economic Research Guide, 2023, 23: 27-30. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 马波. 不同施氮水平对寒地粳稻群体质量及氮肥利用的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(33): 26-31. |
| Ma B. Effects of different nitrogen application level on group quality and nitrogen utilization ratio of Japonica rice in the cold region[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(33): 26-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 郭兆武, 萧浪涛, 罗孝和, 李合松, 吴成春, 康朵兰. 超级杂交稻“两优培九”剑叶叶鞘的光合功能[J]. 作物学报, 2007, 33(9): 1508-1515. |
| Guo Z W, Xiao L T, Luo X H, Li H S, Wu C C, Kang D L. Photosynthetic function of the flag leaf sheath for super hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2007, 33(9): 1508-1515. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 潘俊峰, 王博, 崔克辉, 黄见良, 聂立孝. 氮肥对水稻节间和叶鞘非结构性碳水化合物积累转运特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(3): 273-282. |
| Pan J F, Wang B, Cui K H, Huang J L, Nie L X. Effects of nitrogen application on accumulation and translocation of nonstructural carbohydrates in internodes and sheaths of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(3): 273-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Wu H, Zeng C, Zhang Z, Wu D, Dai W, Liu H, Dai H. Characteristics of grain filling and starch accumulation of brewing functional indica rice in southern Sichuan eco-region[J]. Open Access Library Journal, 2022, 9: e8707. |
| [7] | 金泽艳. OsBG2调控水稻籽粒大小及种子休眠的机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2024. |
| Jin Z Y. Mechanism of OsBG2 regulates grain size and seed dormancy in rice[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2024. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 陈亮, 丁枫, 蔡丽萍, 周彬, 石妍, 占怡玉, 范智权, 王淑琼, 饶梦. 不同硅浓度对粳稻形态和光合生理机制的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(31): 15100-15102, 15110. |
| Chen L, Ding F, Cai L P, Zhou B, Shi Y, Zhan Y Y, Fan Z Q, Wang S Q, Rao M. Effects of silicon in different concentrations on morphology and photosynthetic physiological mechanism of japonica rice[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 2012, 40(31): 15100-15102, 15110. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 黄建华, 袁道强, 陈世锋. 生物化学实验[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009. |
| Huang J H, Yuan D Q, Chen S F. Biochemistry Experiment[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 周驰燕, 李国辉, 许轲, 张晨晖, 杨子君, 张芬芳, 霍中洋, 戴其根, 张洪程. 不同类型水稻品种茎叶维管束与同化物运转特征[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(8): 2053-2065. |
| Zhou C Y, Li G H, Xu K, Zhang C H, Yang Z J, Zhang F F, Huo Z Y, Dai Q G, Zhang H C. Characteristics of vascular bundle of peduncle and flag leaf and assimilates translocation in leaves and stems of different types of rice varieties[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(8): 2053-2065. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 左慧, 尹淑霞, 李亚明, 王铁梅, 朱正辛, 陈亚东, 郭倩倩. 黑麦草氮素吸收利用的调控机制研究进展[J]. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(4): 96-106. |
| Zuo H, Yin S X, Li Y M, Wang T M, Zhu Z X, Chen Y D, Guo Q Q. Research progress on physiological and molecular mechanism of nitrogen absorption and utilization of ryegrass[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(4): 96-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 刘天奇, 高红秀, 谢威, 张雪晴, 陈娜娜, 梅雪锋, 邢佳妮, 徐振华, 张忠臣. 水稻分蘖期氮素应答的转录组动态分析[J]. 华北农学报, 2021, 36(1): 44-53. |
| Liu T Q, Gao H X, Xie W, Zhang X Q, Chen N N, Mei X F, Xing J N, Xu Z H, Zhang Z C. Dynamic transcriptome analysis of rice response to nitrogen treatment at tillering stage[J]. Acta Agricultural Boreali-Sinica, 2021, 36(1): 44-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Xu G, Fan X, Miller A J. Plant nitrogen assimilation and use efficiency[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2012, 63: 153-182. |
| [14] | Kant S. Understanding nitrate uptake, signaling and remobilisation for improving plant nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 2018, 74: 89-96. |
| [15] | Liu X, Hu B, Chu C. Nitrogen assimilation in plants: Current status and future prospects[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2022, 49(5): 394-404. |
| [16] | Tamura W, Kojima S, Toyokawa A, Watanabe H, Tabuchi-Kobayashi M, Hayakawa T, Yamaya T. Disruption of a novel NADH-glutamate synthase2 gene caused marked reduction in spikelet number of rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2011, 2: 57. |
| [17] | Yamaya T, Kusano M. Evidence supporting distinct functions of three cytosolic glutamine synthetases and two NADH-glutamate synthases in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(19): 5519-5525. |
| [18] | Hao D L, Zhou J Y, Yang S Y, Qi W, Yang K J, Su Y H. Function and regulation of ammonium transporters in plants[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(10): 3557. |
| [19] | Wu X, Xie X, Yang S, Yin Q, Cao H, Dong X, Hui J, Liu Z, Jia Z, Mao C, Yuan L. OsAMT1;1 and OsAMT1;2 coordinate root morphological and physiological responses to ammonium for efficient nitrogen foraging in rice[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2022, 63(9): 1309-1320. |
| [20] | Lee S, Marmagne A, Park J, Fabien C, Yim Y, Kim S J, Kim T H, Lim P O, Masclaux-Daubresse C, Nam H G. Concurrent activation of OsAMT1;2 and OsGOGAT1 in rice leads to enhanced nitrogen use efficiency under nitrogen limitation[J]. The Plant Journal, 2020, 103(1): 7-20. |
| [21] | Li C, Tang Z, Wei J, Qu H, Xie Y, Xu G. The OsAMT1.1 gene functions in ammonium uptake and ammonium-potassium homeostasis over low and high ammonium concentration ranges[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2016, 43(11): 639-649. |
| [22] | 杨东, 游晴如, 谢鸿光, 涂诗航, 董瑞霞, 张水金. 氮肥水平对超级稻Ⅱ优航1号生长中后期生理生化特性的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2008, 30(1): 7-10, 30. |
| Yang D, You Q R, Xie H G, Tu S H, Dong R X, Zhang S J. Effect of N-fertilizer levels on physio biochemistry in the middle and late growth stage of super hybrid rice Ⅱ Youhang1[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2008, 30(1): 7-10, 30 (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Oner F. Effects of nitrogen doses on stomatal characteristics, chlorophyll content, and agronomic traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)[J]. PeerJ, 2024, 12: e18792. |
| [24] | Sakuraba Y, Rahman M L, Cho S H, Kim Y S, Koh H J, Yoo S C, Paek N C. The rice faded green leaf locus encodes protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase B and is essential for chlorophyll synthesis under high light conditions[J]. The Plant Journal, 2013, 74(1): 122-133. |
| [25] | Zulfugarov I S, Tovuu A, Lee C H. Acceleration of cyclic electron flow in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.) deficient in the PsbS protein of Photosystem II[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 84: 233-239. |
| [26] | Cronshagen U, Herzfeld F. Distribution of the early light-inducible protein in the thylakoids of developing pea chloroplasts[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1990, 193(2): 361-366. |
| [27] | Yamagata H, Bowler C. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding early light-inducible protein from soybean (Glycine max L.)[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 1997, 61(12): 2143-2144. |
| [28] | Montané M H, Kloppstech K. The family of light-harvesting-related proteins (LHCs, ELIPs, HLIPs): Was the harvesting of light their primary function?[J]. Gene, 2000, 258(1/2): 1-8. |
| [29] | Hutin C, Nussaume L, Moise N, Moya I, Kloppstech K, Havaux M. Early light-induced proteins protect Arabidopsis from photooxidative stress[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(8): 4921-4926. |
| [30] | Tzvetkova-Chevolleau T, Franck F, Alawady A E, Dall’Osto L, Carrière F, Bassi R, Grimm B, Nussaume L, Havaux M. The light stress-induced protein ELIP2 is a regulator of chlorophyll synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. The Plant Journal, 2007, 50(5): 795-809. |
| [31] | Hayami N, Sakai Y, Kimura M, Saito T, Tokizawa M, Iuchi S, Kurihara Y, Matsui M, Nomoto M, Tada Y, Yamamoto Y Y. The responses of Arabidopsis early light-induced Protein2 to ultraviolet B, high light, and cold stress are regulated by a transcriptional regulatory unit composed of two elements[J]. Plant Physiology, 2015, 169(1): 840-855. |
| [1] | 朱鹏, 凌溪铁, 王金彦, 张保龙, 杨郁文, 许轲, 裘实. 机直播条件下不同控草方式对抗除草剂水稻产量和品质差异性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 501-515. |
| [2] | 董立强, 张义凯, 杨铁鑫, 冯莹莹, 马亮, 梁潇, 张玉屏, 李跃东. 北方粳稻密苗机插育秧对秧苗素质及取秧特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 516-528. |
| [3] | 周洋, 叶凡, 刘立军. 典型促生微生物提高盐胁迫水稻抗性的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 529-542. |
| [4] | 朱建平, 李霞, 李文奇, 许扬, 王芳权, 陶亚军, 蒋彦婕, 陈智慧, 范方军, 杨杰. 水稻粉质胚乳突变体we1的表型分析与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 543-551. |
| [5] | 卢椰子, 邱结华, 蒋楠, 寇艳君, 时焕斌. 稻瘟病菌效应子研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 287-294. |
| [6] | 王超瑞, 周宇琨, 温雅, 张瑛, 法晓彤, 肖治林, 张耗. 秸秆还田方式对稻田土壤特性和温室气体排放的影响及其水肥互作调控[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 295-305. |
| [7] | 王雅宣, 王新峰, 杨后红, 刘芳, 肖晶, 蔡玉彪, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊. 稻飞虱适应水稻抗性机制的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 306-321. |
| [8] | 黄涛, 魏兆根, 陈玘, 程泽, 刘欣, 王广达, 胡珂鸣, 谢文亚, 陈宗祥, 冯志明, 左示敏. 水稻类病斑突变体lm52的基因克隆及其广谱抗病性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 322-330. |
| [9] | 马顺婷, 胡运高, 高方远, 刘利平, 牟昌铃, 吕建群, 苏相文, 刘松, 梁毓玉, 任光俊, 郭鸿鸣. 水稻真核翻译起始因子OseIF6.2调控粒型的功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 331-342. |
| [10] | 张彬涛, 刘聪聪, 郭明亮, 杨绍华, 吴世强, 郭龙彪, 朱义旺. 水稻OsDR8基因的稻瘟病抗性评价及优异单倍型鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 343-351. |
| [11] | 韦新宇, 曾跃辉, 肖长春, 黄建鸿, 阮宏椿, 杨旺兴, 邹文广, 许旭明. 水稻康丰B抗稻瘟病基因Pi-kf2(t)的克隆与功能验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 352-364. |
| [12] | 李文奇, 许扬, 王芳权, 朱建平, 陶亚军, 李霞, 范方军, 蒋彦婕, 陈智慧, 杨杰. 广谱抗稻瘟病基因PigmR的KASP标记开发及应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 365-372. |
| [13] | 韦还和, 汪璐璐, 马唯一, 张翔, 左博源, 耿孝宇, 朱旺, 朱济邹, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 戴其根. 盐−旱复合胁迫下粳稻品种南粳9108籽粒灌浆特性及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 373-386. |
| [14] | 沈智达, 余秋华, 张斌, 曹玉东, 王少华, 王红飞, 伍永清, 戴志刚, 李小坤. 磷肥施用量对湖北省直播水稻产量、磷素积累及利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 399-411. |
| [15] | 何勇, 张诗骞, 王志成, 詹逍康, 丁一可, 刘晓瑞, 马素素, 田志宏. 印度梨形孢与复合肥组合施用对水稻机插秧秧苗素质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 412-422. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||