
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 322-330.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240304
黄涛1, 魏兆根1, 陈玘1, 程泽1, 刘欣1, 王广达1, 胡珂鸣1,2, 谢文亚1,2, 陈宗祥1,2,3, 冯志明1,2,3,*( ), 左示敏1,2,3,*(
), 左示敏1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-04
修回日期:2024-05-06
出版日期:2025-05-10
发布日期:2025-05-21
通讯作者:
*email: fengzm@yzu.edu.cn;smzuo@yzu.edu.cn基金资助:
HUANG Tao1, WEI Zhaogen1, CHENG Qi1, CHENG Ze1, LIU Xin1, WANG Guangda1, HU Keming1,2, XIE Wenya1,2, CHEN Zongxiang1,2,3, FENG Zhiming1,2,3,*( ), ZUO Shimin1,2,3,*(
), ZUO Shimin1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2024-03-04
Revised:2024-05-06
Online:2025-05-10
Published:2025-05-21
Contact:
*email: fengzm@yzu.edu.cn;smzuo@yzu.edu.cn
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】类病斑突变体(Lesion mimic mutant, LMM)是研究植物细胞死亡和抗病机制的理想材料,可为作物抗病育种提供新的分子靶点和育种材料。【方法】利用图位克隆技术对水稻类病斑突变体lm52的突变基因进行了定位,并利用CRISPR/Cas9敲除技术对候选基因进行了功能验证,同时鉴定了lm52对水稻对主要病害(稻瘟病、纹枯病和白叶枯病)的抗性,并分析其抗性机制。【结果】突变体lm52从4叶期开始逐渐出现褐色点状病斑,成熟期病斑扩展至全叶;ATP酶基因LOC_Os06g03940上的单碱基突变(G1440A)是lm52产生类病斑表型的原因;lm52显著增强了对水稻三大主要病害(稻瘟病、纹枯病和白叶枯病)的抗性,且这与突变体中活氧性(ROS)的过度积累和防御基因的激活表达有关。【结论】ATP酶基因LM52的突变增强了水稻对不同类型病原菌的抗性,为水稻抗病分子育种提供潜在的靶标基因。
黄涛, 魏兆根, 陈玘, 程泽, 刘欣, 王广达, 胡珂鸣, 谢文亚, 陈宗祥, 冯志明, 左示敏. 水稻类病斑突变体lm52的基因克隆及其广谱抗病性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 322-330.
HUANG Tao, WEI Zhaogen, CHENG Qi, CHENG Ze, LIU Xin, WANG Guangda, HU Keming, XIE Wenya, CHEN Zongxiang, FENG Zhiming, ZUO Shimin. Gene Cloning and Broad-spectrum Disease Resistance Analysis of Rice Lesion Mimic Mutant lm52[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 322-330.

图1 野生型(日本晴)与突变体lm52表型对比 A: 野生型(日本晴)与突变体lm52叶片;B: 野生型与lm52整株对比;C: 野生型与lm52穗部对比。Nip: 日本晴。
Fig. 1. Comparison between wild type(Nipponbare) and mutant lm52 A, Leaf phenotypes of wild type (Nipponbare) and lm52 mutant; B, Comparison between wild type and lm52; C, Comparison of panicle of wild type and lm52. Nip, Niponbare.
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height(cm) | 分蘖数 Number of tillers | 穗长 Panicle length(cm) | 一次枝梗数 Primary rachis branch number | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 千粒重 1000-grain weight(g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT lm52 | 102.70±3.35 85.75±1.21** | 13.8±1.0 10.4±0.5** | 22.20±1.23 20.30±0.46** | 9.5±1.3 8.8±0.9 | 134.5±6.1 91.1±5.1** | 24.40±0.26 21.33±0.31** |
表1 野生型(日本晴)和突变体lm52的农艺性状
Table 1. Agronomic traits of wild type(Nipponbare, WT) and lm52
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height(cm) | 分蘖数 Number of tillers | 穗长 Panicle length(cm) | 一次枝梗数 Primary rachis branch number | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 千粒重 1000-grain weight(g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT lm52 | 102.70±3.35 85.75±1.21** | 13.8±1.0 10.4±0.5** | 22.20±1.23 20.30±0.46** | 9.5±1.3 8.8±0.9 | 134.5±6.1 91.1±5.1** | 24.40±0.26 21.33±0.31** |
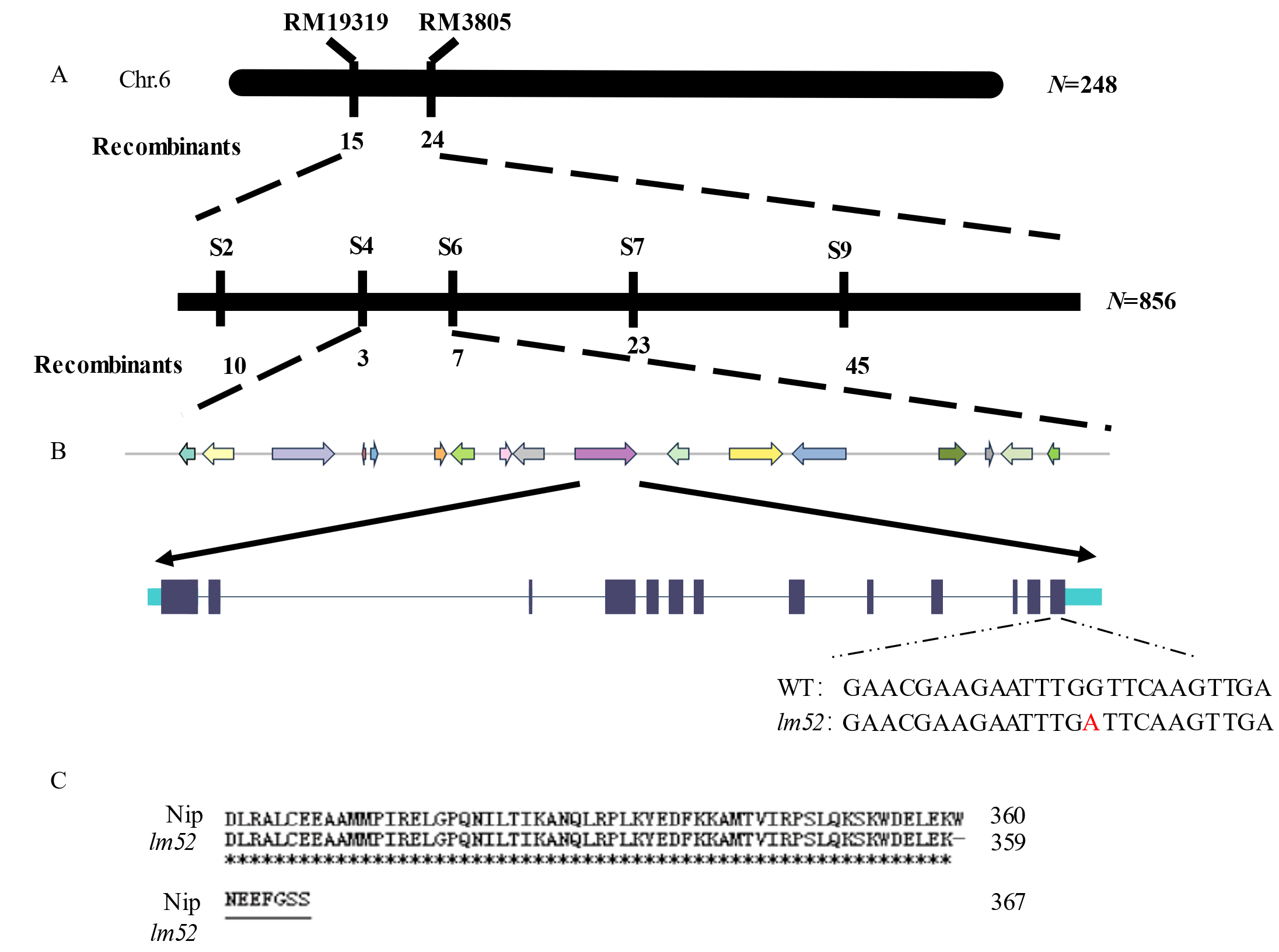
图2 lm52的图位克隆 A:在6号染色体上通过RM19319和RM3805两个标记进行初步定位,定位在S4和S6之间,物理距离分别为1.54 Mb和1.64 Mb;B:17个候选基因分布情况,在LOC_Os06g03940上发现突变位点;C:lm52与野生型氨基酸序列比对。*表示比对结果一致。
Fig. 2. Map-based cloning of lm52 A, LM52 was preliminarily located between S4 and S6 on chromosome 6 with RM19319 and RM3805, with a physical distance of 1.54 Mb and 1.64 Mb, respectively; B, Distribution of 17 candidate genes, and mutation sites on LOC_Os06g03940; C, lm52 and wild-type amino acid sequence comparison. * indicates that the comparison results are consistent.
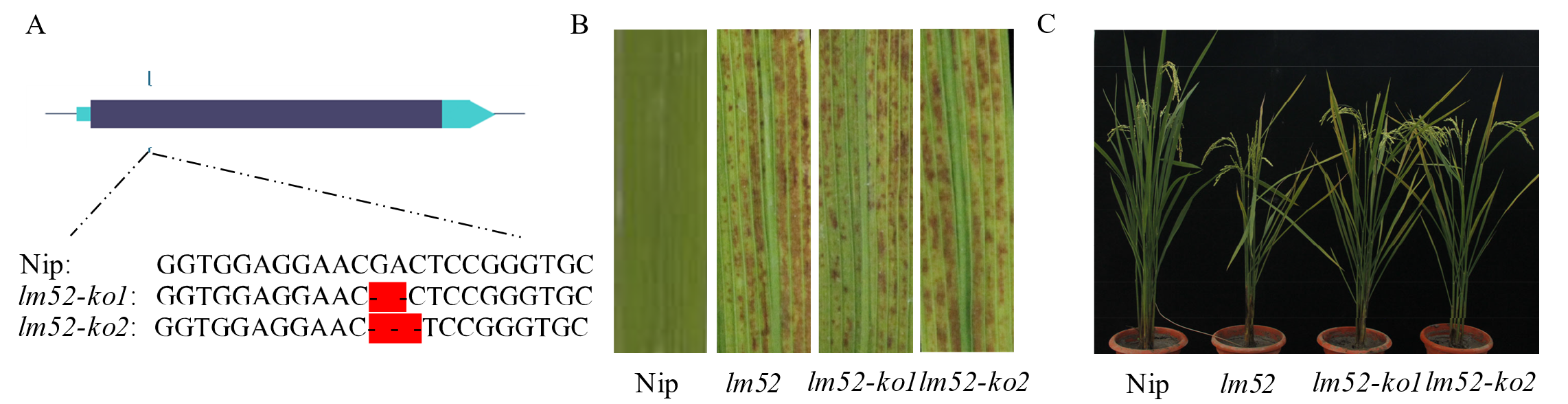
图3 候选基因的功能验证 A: Nip与lm52-ko1和lm52-ko2 LOC_Os06g03940基因上的cDNA序列比对;B: 野生型Nip、突变体lm52、敲除系lm52-ko1和敲除系lm52-ko2叶片对比;C: 野生型Nip、突变体lm52、敲除系lm52-ko1和敲除系lm52-ko2整株对比。Nip: 日本晴。
Fig. 3. Functional verification of candidate genes A, cDNA sequence comparison between Nip and lm52-ko1 (lm52-ko2) on LOC_Os06g03940 gene; B, Comparison of leaves of wild-type Nip, mutant lm52, and knockout lines lm52-ko1 and lm52-ko2; C, Comparison of wild-type Nip, mutant lm52, and knockout lines lm52-ko1 and lm52-ko2.
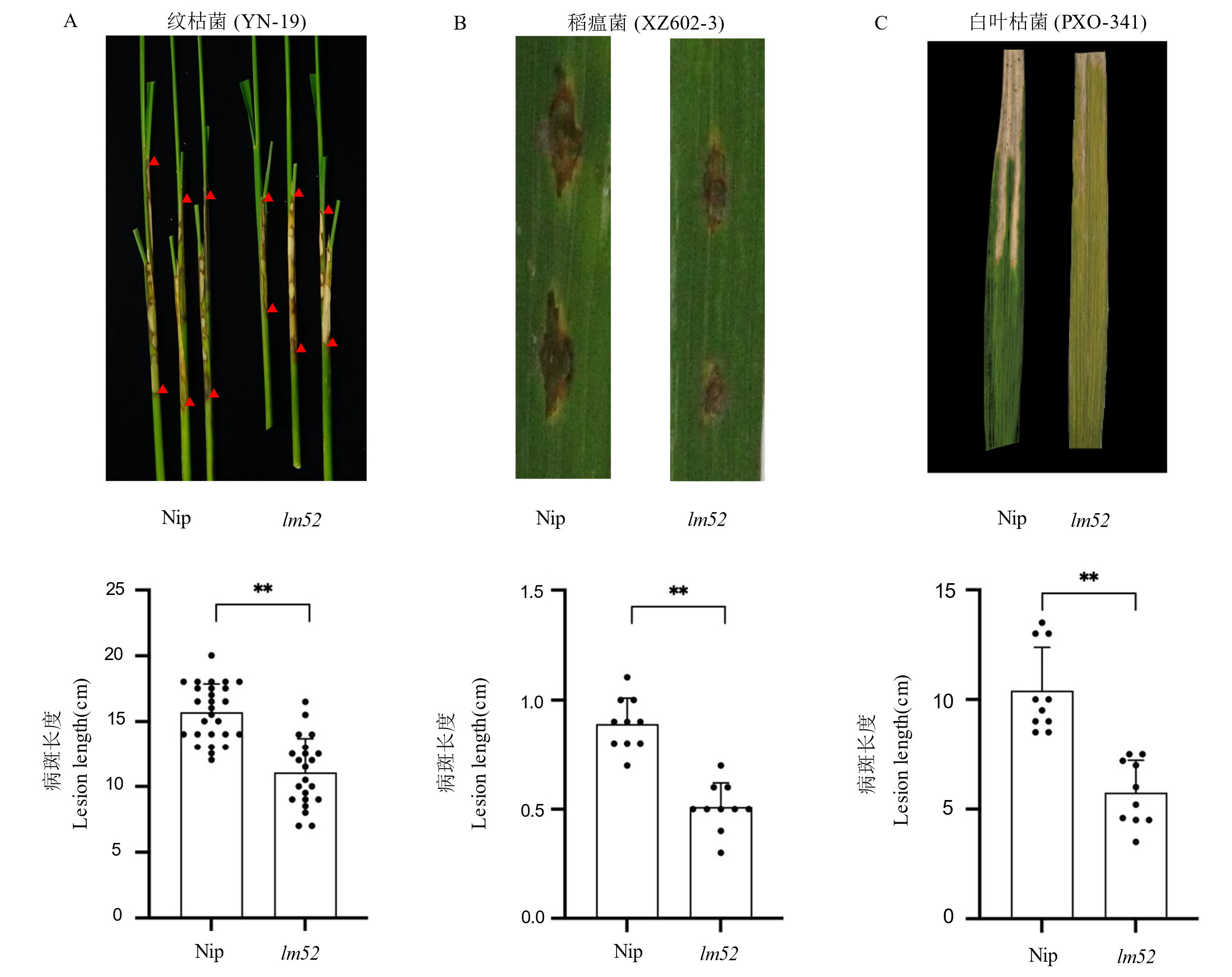
图4 lm52对不同病原菌的抗性 A: 日本晴与lm52的纹枯病表型和相应病级; B:日本晴与lm52的稻瘟病表型和相应病级; C:日本晴与lm52的白叶枯病表型和相应病级。
Fig. 4. Resistance of lm52 to diverse pathogens A, Sheath blight symptoms and corresponding disease grade histogram of Nipponbare and lm52; B, Rice blast symptoms and corresponding disease grade histogram of Nipponbare and lm52; C, Bacterial blight symptoms and disease grades of Nipponbare and lm52.

图5 lm52体内ROS富集情况 A,B分别为日本晴和lm52 DAB染色前(A)后(B)对比;C:过氧化氢(H2O2)活性含量检测与超氧阴离子含量检测。
Fig. 5. ROS accumulation in lm52 A and B, Comparison between Nipponbare and lm52 before (A) and after (B) DAB-staining; C, Detection of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content and superoxide anion content.
| [1] | Greenberg J T. Programmed cell death in plant-pathogen interactions[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 1997, 48: 525-545. |
| [2] | 沈旺鑫, 史小品, 杜海波, 冯志明, 陈宗祥, 胡珂鸣, 范江波, 左示敏. 水稻类病斑突变体基因克隆及发生机制研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(3): 837-848. |
| Shen W X, Shi X P, Du H B, Feng Z M, Chen Z X, Hu K M, Fan J B, Zuo S M. Research advances in gene cloning and occurrence mechanism of rice lesion mimic mutants[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 38(3): 837-848. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Zhu X B, Ze M, Mawsheng C, Chen X W, Wang J. Deciphering rice lesion mimic mutants to understand molecular network governing plant immunity and growth[J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(4): 278-288. |
| [4] | Qiu T, Zhao X, Feng H, Qi L, Yang J, Peng Y, Zhao A, Kong L, Zhou Y, Xu J, Li S, Zhu W. OsNBL3, a mitochondrion-localized pentatricopeptide repeat protein, is involved in splicing nad5 intron 4 and its disruption causes lesion mimic phenotype with enhanced resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19(11): 2277-2290. |
| [5] | Qiao Y, Jiang W, Lee J, Park B, Choi M S, Piao R, Woo M O, Roh J H, Han L, Paek N C, Seo H S, Koh H J. SPL28 encodes a clathrin-associated adaptor protein complex 1, medium subunit μ1 (AP1M1) and is responsible for spotted leaf and early senescence in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. New Phytologist, 2010, 185(1): 258-274. |
| [6] | Gao M, He Y, Yin X, Zhong X, Yan B, Wu Y, Chen J, Li X, Zhai K, Huang Y, Gong X, Chang H, Xie S, Liu J, Yue J, Xu J, Zhang G, Deng Y, Wang E, Tharreau D, Wang G L, Yang W, He Z. Ca(2+) sensor-mediated ROS scavenging suppresses rice immunity and is exploited by a fungal effector[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(21): 5391-5404.e17. |
| [7] | Zou T, Li G, Liu M, Liu R, Yang S, Wang K, Lu L, Ye Q, Liu J, Liang J, Deng Q, Wang S, Zhu J, Liang Y, Liu H, Yu X, Sun C, Li P, Li S. A ubiquitin-specific protease functions in regulating cell death and immune responses in rice[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2023, 46(4): 1312-1326. |
| [8] | Kiyosawa S. Inheritance of a particular sensitivity of the rice variety, Sekiguchi Asahi, to pathogens and chemicals, and linkage relationship with blast resistance genes[J]. Nogyo Gijutsu Kenkyusho Hokoku, 1970(21): 61-71. |
| [9] | Qian J, Liu F, Qu C, Wang J, Zhou Y, Yang Q, Li Y, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Zhu X. Research progress on cloning and mechanism of rice lesion mimic mutation gene[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 19(10): 3274-3280. |
| [10] | Zeng L R, Qu S, Bordeos A, Yang C, Baraoidan M, Yan H, Xie Q, Nahm B H, Leung H, Wang G L. Spotted leaf11, a negative regulator of plant cell death and defense, encodes a U-box/Armadillo repeat protein endowed with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity[J]. The Plant Cell, 2004, 16(10): 2795-2808. |
| [11] | Liu Q, Ning Y, Zhang Y, Yu N, Zhao C, Zhan X, Wu W, Chen D, Wei X, Wang G L, Cheng S, Cao L. OsCUL3a negatively regulates cell death and immunity by degrading OsNPR1 in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29(2): 345-359. |
| [12] | Matsui H, Takahashi A, Hirochika H. Rice immune regulator, OsPti1a, is specifically phosphorylated at the plasma membrane[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2015, 10(3): 369-399. |
| [13] | 孙志广, 代慧敏, 陈庭木, 李景芳, 迟铭, 周振玲, 刘艳, 刘金波, 徐波, 邢运高, 杨波, 李健, 卢百关, 方兆伟, 王宝祥, 徐大勇. 水稻类病斑突变体lmm7的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 357-366. |
| Sun Z G, Dai H M, Chen T L, Li J F, Chi M, Zhou Z L, Liu Y, Liu J B, Xu B, Xing Y G, Yang B, Li J, Lu B G, Fang Z W, Wang B X, Xu D Y. Identification and gene mapping of rice spot-like mutant lmm7[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(4): 357-366. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Ma H, Li J, Ma L, Wang P, Xue Y, Yin P, Xiao J, Wang S. Pathogen-inducible OsMPKK10.2-OsMPK6 cascade phosphorylates the Raf-like kinase OsEDR1 and inhibits its scaffold function to promote rice disease resistance[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(4): 620-632. |
| [15] | Sakuraba Y, Rahman M L, Cho S H, Kim Y S, Koh H J, Yoo S C, Paek N C. The rice faded green leaf locus encodes protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase B and is essential for chlorophyll synthesis under high light conditions[J]. The Plant Journal, 2013, 74(1): 122-133. |
| [16] | Fekih R, Tamiru M, Kanzaki H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kanzaki E, Saitoh H, Takagi H, Natsume S, Undan J R, Undan J, Terauchi R. The rice(Oryza sativa L) lesion mimic resembling, which encodes an AAA-type ATPase, is implicated in defense response[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2015, 290(2): 611-622. |
| [17] | Zhao X, Qiu T, Feng H, Yin C, Zheng X, Yang J, Peng Y L, Zhao W. A novel Glycine-rich domain protein, GRDP1, functions as a critical feedback regulator for controlling cell death and disease resistance in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2021, 72(2): 608-622. |
| [18] | 徐欢, 周涛, 孙悦, 王木妹, 杨亚春, 马卉, 李浩, 徐大伟, 周海, 杨剑波, 倪金龙. 水稻颖壳类病斑突变体glmm1的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 497-506. |
| Xu H, Zhou T, Sun Y, Wang M M, Yang Y C, M H, Li H, Xu D W, Zhou H, Yang J B, Ni J L. Identification and gene mapping of glmm1 mutant in rice glumes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 497-506. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Sha G, Sun P, Kong X, Han X, Sun Q, Fouillen L, Zhao J, Li Y, Yang L, Wang Y, Gong Q, Zhou Y, Zhou W, Jain R, Gao J, Huang R, Chen X, Zheng L, Zhang W, Qin Z, Zhou Q, Zeng Q, Xie K, Xu J, Chiu T Y, Guo L, Mortimer J C, Boutté Y, Li Q, Kang Z, Ronald P C, Li G. Genome editing of a rice CDP-DAG synthase confers multipathogen resistance[J]. Nature, 2023, 618(7967): 1017-1023. |
| [20] | 贺闽, 尹俊杰, 冯志明, 朱孝波, 赵剑华, 左示敏, 陈学伟. 水稻稻瘟病和纹枯病抗性鉴定方法[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. |
| He M, Yin J J, Feng Z M, Zhu X B, Zhou J H, Zuo S M, Chen X W. Identification of blast and sheath blight resistance in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 马海港, 袁猛. 水稻白叶枯病菌及细菌性条斑病菌培养及接种[J]. Bio-protocol, 2018, 8(20): e1010180. |
| Ma H G, Yuan M. Cultivation of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, Xoo and inuculation of rice[J]. Bio-protocol, 2018, 8(20): e1010180. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Zhu X, Yin J, Liang S, Liang R, Zhou X, Chen Z, Zhao W, Wang J, Li W, He M, Yuan C, Miyamoto K, Ma B, Wang J, Qin P, Chen W, Wang Y, Wang W, Wu X, Yamane H, Zhu L, Li S, Chen X. The multivesicular bodies (MVBs)-localized AAA ATPase LRD6- 6 inhibits immunity and cell death likely through regulating MVBs-mediated vesicular trafficking in rice[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2016, 12(9): e1006311. |
| [23] | 亓璐, 张涛, 曾娟, 李春广, 李天娇, 赵艳丽, 闫硕. 近年我国水稻五大产区主要病害发生情况分析[J]. 中国植保导刊, 2021, 4(4): 37-42. |
| Qi L, Zhang T, Zeng J, Li C G, Li T J, Zhao Y L, Yan S. Analysis of main diseases in five major rice producing areas in China in recent years[J]. China Plant Protection Guide, 2021, 4(4): 37-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Zhang B, Van Aken O, Thatcher L, De Clercq I, Duncan O, Law S R, Murcha M W, van der Merwe M, Seifi H S, Carrie C, Cazzonelli C, Radomiljac J, Höfte M, Singh K B, Van Breusegem F, Whelan J. The mitochondrial outer membrane AAA ATPase AtOM66 affects cell death and pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. The Plant Journal, 2014, 80(4): 709-727. |
| [25] | Lee M H, Sano H. Suppression of salicylic acid signaling pathways by an ATPase associated with various cellular activities (AAA) protein in tobacco plants[J]. Plant Biotechnology, 2007, 24(2): 209-215. |
| [26] | Lee M H, Sano H. Attenuation of the hypersensitive response by an ATPase associated with various cellular activities (AAA) protein through suppression of a small GTPase, ADP ribosylation factor, intobacco plants[J]. The Plant Journal, 2007, 51(1): 127-139. |
| [1] | 卢椰子, 邱结华, 蒋楠, 寇艳君, 时焕斌. 稻瘟病菌效应子研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 287-294. |
| [2] | 王超瑞, 周宇琨, 温雅, 张瑛, 法晓彤, 肖治林, 张耗. 秸秆还田方式对稻田土壤特性和温室气体排放的影响及其水肥互作调控[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 295-305. |
| [3] | 王雅宣, 王新峰, 杨后红, 刘芳, 肖晶, 蔡玉彪, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊. 稻飞虱适应水稻抗性机制的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 306-321. |
| [4] | 马顺婷, 胡运高, 高方远, 刘利平, 牟昌铃, 吕建群, 苏相文, 刘松, 梁毓玉, 任光俊, 郭鸿鸣. 水稻真核翻译起始因子OseIF6.2调控粒型的功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 331-342. |
| [5] | 张彬涛, 刘聪聪, 郭明亮, 杨绍华, 吴世强, 郭龙彪, 朱义旺. 水稻OsDR8基因的稻瘟病抗性评价及优异单倍型鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 343-351. |
| [6] | 韦新宇, 曾跃辉, 肖长春, 黄建鸿, 阮宏椿, 杨旺兴, 邹文广, 许旭明. 水稻康丰B抗稻瘟病基因Pi-kf2(t)的克隆与功能验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 352-364. |
| [7] | 李文奇, 许扬, 王芳权, 朱建平, 陶亚军, 李霞, 范方军, 蒋彦婕, 陈智慧, 杨杰. 广谱抗稻瘟病基因PigmR的KASP标记开发及应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 365-372. |
| [8] | 韦还和, 汪璐璐, 马唯一, 张翔, 左博源, 耿孝宇, 朱旺, 朱济邹, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 戴其根. 盐−旱复合胁迫下粳稻品种南粳9108籽粒灌浆特性及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 373-386. |
| [9] | 沈智达, 余秋华, 张斌, 曹玉东, 王少华, 王红飞, 伍永清, 戴志刚, 李小坤. 磷肥施用量对湖北省直播水稻产量、磷素积累及利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 399-411. |
| [10] | 何勇, 张诗骞, 王志成, 詹逍康, 丁一可, 刘晓瑞, 马素素, 田志宏. 印度梨形孢与复合肥组合施用对水稻机插秧秧苗素质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 412-422. |
| [11] | 吴金水, 唐江英, 谭立, 过志强, 杨娟, 张鑫臻, 陈桂芳, 王建龙, 施婉菊. 水稻对砷的吸收与转运机理及农艺阻控策略[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 143-155. |
| [12] | 马唯一, 朱济邹, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 刁刘云, 汪璐璐, 孟天瑶, 高平磊, 陈英龙, 戴其根, 韦还和. 盐害和干旱对稻米品质形成的影响及生理机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 156-170. |
| [13] | 张来桐, 杨乐, 刘洪, 赵学明, 程涛, 徐振江. 水稻香味物质的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 171-186. |
| [14] | 冯涛, 张朝阳, 黄新妮, 王月, 钟旭志, 冯志明, 刘欣, 左示敏, 欧阳寿强. Osa-miR166i-3p介导活性氧积累途径正调控水稻纹枯病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 187-196. |
| [15] | 龚蒙萌, 宋书锋, 邱牡丹, 董皓, 张龙辉, 李磊, 李斌, 谌伟军, 李懿星, 王天抗, 雷东阳, 李莉. 水稻叶色基因OsClpP6的功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 197-208. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||