
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 197-208.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240201
龚蒙萌1,2, 宋书锋2, 邱牡丹1,2, 董皓2, 张龙辉2, 李磊2, 李斌2, 谌伟军2, 李懿星2, 王天抗2, 雷东阳1,*( ), 李莉2,*(
), 李莉2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-01
修回日期:2024-03-21
出版日期:2025-03-10
发布日期:2025-03-19
通讯作者:
* email: leidongyang1980@126.com, lili@hhrrc.ac.cn基金资助:
GONG Mengmeng1,2, SONG Shufeng2, QIU Mudan1,2, DONG Hao2, ZHANG Longhui2, LI Lei2, LI Bin2, CHEN Weijun2, LI Yixing2, WANG Tiankang2, LEI Dongyang1,*( ), LI Li2,*(
), LI Li2,*( )
)
Received:2024-02-01
Revised:2024-03-21
Online:2025-03-10
Published:2025-03-19
Contact:
* email: leidongyang1980@126.com, lili@hhrrc.ac.cn摘要:
【目的】探究OsClpP6在叶绿体发育过程中的功能,为提高植物光合速率提供新的基因资源。【方法】对OsClpP6基因、蛋白进行生物信息学分析,通过实时定量PCR和亚细胞定位技术分析该基因的表达模式,利用CRISPR/Cas9技术对该基因进行定点编辑,通过透射电镜观察突变体叶肉细胞叶绿体结构,利用RNA-seq分析OsClpP6影响叶色途径。【结果】Clp基因家族在水稻叶绿体早期发育中起重要作用,且在植物进化过程中十分保守。OsClpP6是水稻Clps基因家族的重要成员之一。通过研究OsClpP6的时空表达模式发现OsClpP6主要在苗期地上部分及营养生长期的茎中表达,水稻原生质体亚细胞定位结果表明,OsClpP6定位在叶绿体。在华占水稻背景下构建了OsClpP6的CRISPR/Cas9敲除突变株系clpp6-6s-ko-1、clpp6-6s-ko-2,突变体较WT株高降低、叶色变浅、千粒重减少。对WT、clpp6-6s-ko-1和clpp6-6s-ko-2灌浆期剑叶叶片进行透射电镜观察叶肉细胞的叶绿体微观结构发现,突变体叶肉细胞叶绿体结构、类囊体片层结构和淀粉粒积累明显少于WT。通过对突变体和WT进行转录组分析发现差异基因主要富集在光合作用通路,多个叶绿体发育的关键蛋白表达出现显著变化。【结论】OsClpP6通过参与叶绿体发育影响水稻源库的平衡,进而影响千粒重。
龚蒙萌, 宋书锋, 邱牡丹, 董皓, 张龙辉, 李磊, 李斌, 谌伟军, 李懿星, 王天抗, 雷东阳, 李莉. 水稻叶色基因OsClpP6的功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 197-208.
GONG Mengmeng, SONG Shufeng, QIU Mudan, DONG Hao, ZHANG Longhui, LI Lei, LI Bin, CHEN Weijun, LI Yixing, WANG Tiankang, LEI Dongyang, LI Li. Functional Characterization of Rice Leaf Color Gene OsClpP6[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 197-208.

图1 Clp基因家族分析 A为Clp基因家族在水稻、小麦、玉米、拟南芥、大豆和烟草中的系统进化树,外圈显示结构域,不同颜色代表不同类型;B为从A中五种不同类型中各选取一个基因进行序列比对;C为水稻中ClpP基因家族的时空表达热图。
Fig. 1. Analysis of Clp family A represents the phylogenetic tree of the Clp gene family in rice, wheat, maize, Arabidopsis thaliana, soybean, and tobacco. The outer ring displays the domains, with different colors indicating different types; B shows the sequence alignment of one gene selected from each of the five different types in A; C shows the heatmap of the spatiotemporal expression of the ClpP gene family in rice.
| 基因名 Gene name | 登录号 Locus ID | 长度 CDS length(bp) | 氨基酸数 Amino acids | 等电点 PI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsClp1 | LOC_Os01g16530.1 | 897 | 298 | 9.37 |
| OsClp2 | LOC_Os01g32350.1 | 945 | 314 | 8.78 |
| OsClp3 | LOC_Os02g42290.1 | 897 | 298 | 7.25 |
| OsClpP5 | LOC_Os03g19510.1 | 849 | 282 | 8.46 |
| OsClp5 | LOC_Os03g22430.1 | 1026 | 341 | 9.85 |
| OsClpP6 | LOC_Os03g29810.1 | 780 | 259 | 7.94 |
| OsClp7 | LOC_Os04g44400.1 | 930 | 309 | 7.30 |
| OsClp8 | LOC_Os05g51450.1 | 1161 | 386 | 9.30 |
| OsClp9 | LOC_Os06g04530.1 | 894 | 297 | 9.50 |
| OsClp10 | LOC_Os06g39712.1 | 651 | 216 | 4.38 |
| / | LOC_Os08g15270.1 | 651 | 216 | 4.38 |
| / | LOC_Os10g21300.1 | 651 | 216 | 4.38 |
| OsClp11 | LOC_Os10g43050.1 | 882 | 293 | 4.69 |
| OsClp13 | LOC_Os12g10590.1 | 651 | 216 | 4.49 |
表1 水稻Clp家族基因信息
Table 1. Information for Clp family in rice
| 基因名 Gene name | 登录号 Locus ID | 长度 CDS length(bp) | 氨基酸数 Amino acids | 等电点 PI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsClp1 | LOC_Os01g16530.1 | 897 | 298 | 9.37 |
| OsClp2 | LOC_Os01g32350.1 | 945 | 314 | 8.78 |
| OsClp3 | LOC_Os02g42290.1 | 897 | 298 | 7.25 |
| OsClpP5 | LOC_Os03g19510.1 | 849 | 282 | 8.46 |
| OsClp5 | LOC_Os03g22430.1 | 1026 | 341 | 9.85 |
| OsClpP6 | LOC_Os03g29810.1 | 780 | 259 | 7.94 |
| OsClp7 | LOC_Os04g44400.1 | 930 | 309 | 7.30 |
| OsClp8 | LOC_Os05g51450.1 | 1161 | 386 | 9.30 |
| OsClp9 | LOC_Os06g04530.1 | 894 | 297 | 9.50 |
| OsClp10 | LOC_Os06g39712.1 | 651 | 216 | 4.38 |
| / | LOC_Os08g15270.1 | 651 | 216 | 4.38 |
| / | LOC_Os10g21300.1 | 651 | 216 | 4.38 |
| OsClp11 | LOC_Os10g43050.1 | 882 | 293 | 4.69 |
| OsClp13 | LOC_Os12g10590.1 | 651 | 216 | 4.49 |

图2 OsClpP6表达模式分析 A为OsClpP6在水稻中的组织表达模式;B为OsClpP6蛋白的亚细胞定位,GFP为GFP荧光,Chloroplast为叶绿体荧光,Bright为明场,Merge为融合场。P3、P8分别代表幼穗分化第3、8期的幼穗。
Fig. 2. Analysis of expression pattern of OsClpP6 A represents the tissue expression pattern of OsClpP6 in rice, and B represents the subcellular localization of the OsClpP6 protein. P3 and P8 represent young panicles at the 3rd and 8th stages of panicle differentiation, respectively.

图4 OsClpP6基因突变体表型观察 A为WT、clpp6-6s-ko-1和clpp6-6s-ko-2成熟期的表型;B为WT、clpp6-6s-ko-1和clpp6-6s-ko-2的剑叶叶片;C-H为WT、clpp6-6s-ko-1和clpp6-6s-ko-2叶片的透射电镜图;I为株高统计图;J为剑叶叶绿素b含量统计图;K为剑叶叶绿素a含量统计图;Cw表示细胞壁;S表示淀粉粒;Og表示嗜锇小体;Thy表示类囊体。
Fig. 4. Phenotypic observation of OsClpP6 mutants A shows the phenotypic images of WT, clpp6-6s-ko-1, and clpp6-6s-ko-2 at the mature stage; B shows the flag leaves of WT, clpp6-6s-ko-1, and clpp6-6s-ko-2; C-H are the transmission electron microscopy images of the leaves of WT, clpp6-6s-ko-1, and clpp6-6s-ko-2; I is the statistical chart of plant height; J is the statistical chart of chlorophyll b content in the flag leaf; K is the statistical chart of chlorophyll a content in the flag leaf; Cw stands for cell wall; S stands for starch granules; Og stands for osmiophilic globules; Thy stands for thylakoids.

图5 OsClpP6基因突变体穗部表型观察 A为WT、clpp6-6s-ko-1和clpp6-6s-ko-2的穗部表型;B、C为WT、clpp6-6s-ko-1和clpp6-6s-ko-2的粒型对比;D-I为农艺性状统计图。
Fig. 5. Observation of panicle phenotypes of OsClpP6 mutants A shows the panicle phenotypes of WT, clpp6-6s-ko-1, and clpp6-6s-ko-2; B and C show comparison of grain shape among WT, clpp6-6s-ko-1, and clpp6-6s-ko-2; D-I are statistical charts of agronomic traits.

图6 转录组测序质量检测 A为比对到参考基因组上的Reads数目;B为比对到参考基因组唯一位置的Reads数目;C为挑选20个上调基因和20个下调基因进行qRT-PCR验证转录组结果;D为WT和clpp6-6s-ko-1突变体中叶绿体发育及光合作用相关基因的qRT-PCR结果。数据表示为均数±标准差(n = 3)。** P < 0.01。
Fig. 6. RNA-seq quality assessment A represents the number of reads aligned to the reference genome; B indicates the number of reads aligned to unique locations in the reference genome; C refers to the selection of 20 up- and 20 down-regulated genes for qRT-PCR validation of transcriptome results; D represents the qRT-PCR analysis results of genes related to chloroplast development and photosynthesis in WT and the mutants. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). ** P < 0.01.
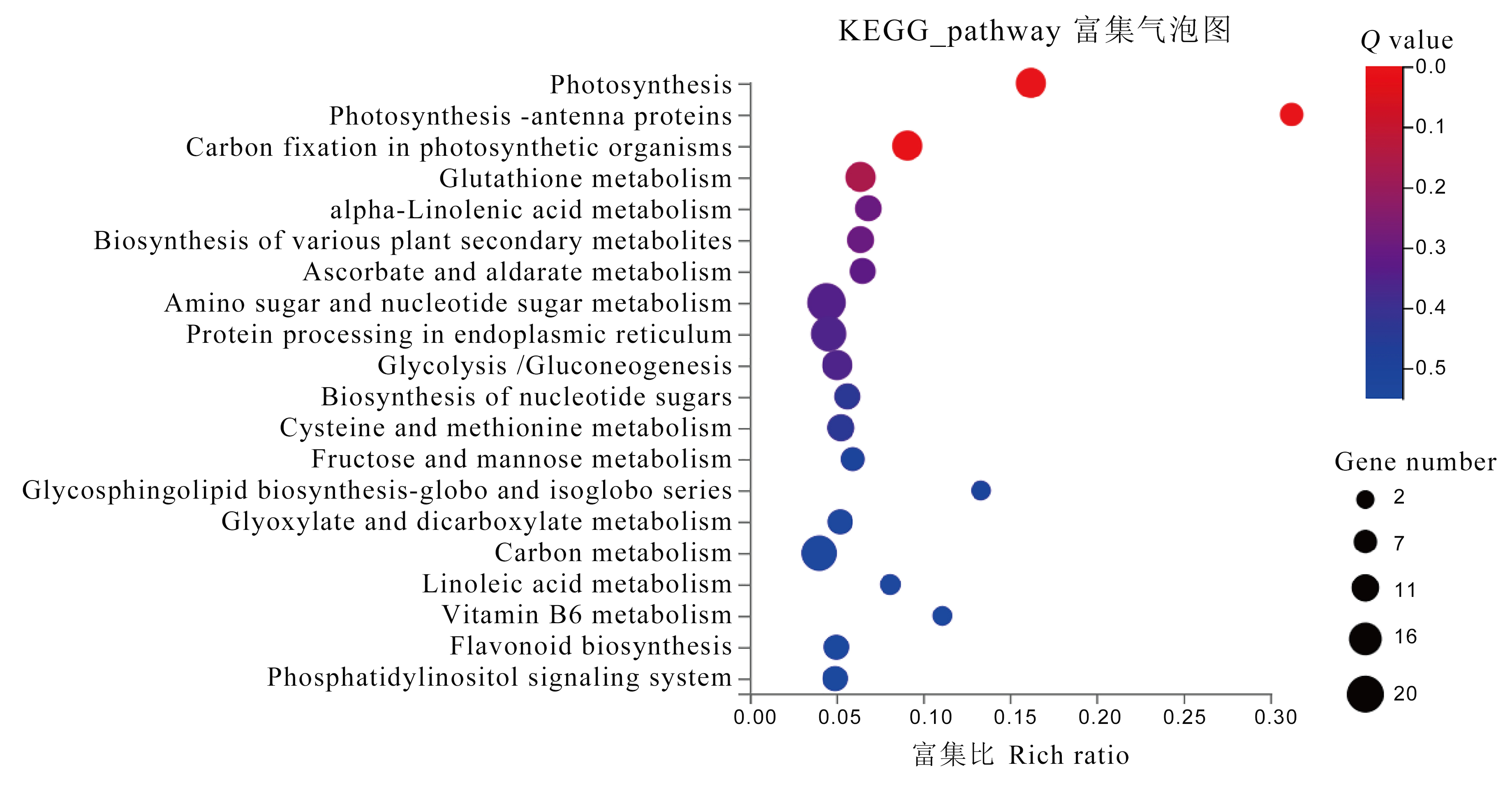
图7 转录组测序结果分析 富集显著性q值小于0.05,气泡大小代表通路基因数。
Fig. 7. Analysis of RNA-seq result The enrichment significance q-value less than 0.05, and the bubble size representing the number of genes in the pathway.
| KEGG通路 KEGG pathway | 基因编号 Gene ID | 基因 Gene | log2(FC_clpp6-6s-ko/WT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 光合作用Photosynthesis | Os01g0773700 | −1.8675 | |
| Os02g0103800 | OsLFNR1 | −2.5355 | |
| Os02g0103850 | −2.5179 | ||
| Os02g0578400 | −3.1080 | ||
| Os06g0107700 | OsLFNR2 | −1.2132 | |
| Os07g0148900 | −2.7024 | ||
| Os08g0119800 | −2.0123 | ||
| Os09g0481200 | −2.2606 | ||
| Os10g0355800 | 2.1703 | ||
| Os12g0189400 | −2.0962 | ||
| Os12g0420400 | −1.8026 | ||
| Os04g0414700 | −1.8744 | ||
| 光合作用-天线蛋白Photosynthesis-antenna proteins | Os01g0600900 | −2.0603 | |
| Os02g0197600 | −1.2470 | ||
| Os06g0320500 | −1.8205 | ||
| Os08g0435900 | Lhca4 | −1.9374 | |
| Os09g0346500 | OsCAB1R | −1.2537 | |
| 光合组织中的碳固定作用Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms | Os02g0601300 | 1.1576 | |
| Os04g0682100 | −4.7302 | ||
| Os06g0133800 | −1.9227 | ||
| Os06g0608700 | OsAld-Y | −2.7748 | |
| Os10g0390500 | FLO12 | 1.6028 | |
| Os11g0171300 | AldP | −1.9355 | |
| Os12g0169600 | −3.9710 | ||
| Os12g0291066 | −3.1725 | ||
| Os12g0291100 | OsRBCS3 | −3.6935 | |
| Os12g0291400 | OsRBCS5 | −3.5781 | |
| Os12g0292301 | −5.1414 | ||
| Os12g0292400 | OsRBCS4 | −4.3509 |
表3 光合作用相关通路中的差异表达基因
Table 3. Differentially expressed genes in photosynthesis-related pathways
| KEGG通路 KEGG pathway | 基因编号 Gene ID | 基因 Gene | log2(FC_clpp6-6s-ko/WT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 光合作用Photosynthesis | Os01g0773700 | −1.8675 | |
| Os02g0103800 | OsLFNR1 | −2.5355 | |
| Os02g0103850 | −2.5179 | ||
| Os02g0578400 | −3.1080 | ||
| Os06g0107700 | OsLFNR2 | −1.2132 | |
| Os07g0148900 | −2.7024 | ||
| Os08g0119800 | −2.0123 | ||
| Os09g0481200 | −2.2606 | ||
| Os10g0355800 | 2.1703 | ||
| Os12g0189400 | −2.0962 | ||
| Os12g0420400 | −1.8026 | ||
| Os04g0414700 | −1.8744 | ||
| 光合作用-天线蛋白Photosynthesis-antenna proteins | Os01g0600900 | −2.0603 | |
| Os02g0197600 | −1.2470 | ||
| Os06g0320500 | −1.8205 | ||
| Os08g0435900 | Lhca4 | −1.9374 | |
| Os09g0346500 | OsCAB1R | −1.2537 | |
| 光合组织中的碳固定作用Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms | Os02g0601300 | 1.1576 | |
| Os04g0682100 | −4.7302 | ||
| Os06g0133800 | −1.9227 | ||
| Os06g0608700 | OsAld-Y | −2.7748 | |
| Os10g0390500 | FLO12 | 1.6028 | |
| Os11g0171300 | AldP | −1.9355 | |
| Os12g0169600 | −3.9710 | ||
| Os12g0291066 | −3.1725 | ||
| Os12g0291100 | OsRBCS3 | −3.6935 | |
| Os12g0291400 | OsRBCS5 | −3.5781 | |
| Os12g0292301 | −5.1414 | ||
| Os12g0292400 | OsRBCS4 | −4.3509 |
| [1] | 于红燕, 刘世义. 我国水稻产业发展现状、趋势及对策[J]. 农村经济与科技, 2016, 27(9): 7-9. |
| Yu H Y, Liu S Y. Current situation, trends and countermeasures of the rice industry[J]. Rural Economy and Science-Technology, 2016, 27(9): 7-9. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 魏颖娟, 赵杨, 邹应斌. 不同穗型超级稻品种籽粒灌浆特性[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(10): 1516-1529. |
| Wei Y J, Zhao Y, Zou Y B. Grain-filling characteristics in super rice with different panicle types[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1516-1529. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Toshiyuki T, Yoshimichi F, Tatsuhiko S, Takeshi H. Time-related mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling grain-filling in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2005, 56(418): 2107-2118. |
| [4] | 赵宏亮, 陈凯, 张强, 徐建龙, 黎志康. 应用主成分分析和聚类分析的水稻源库特性研究[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2015, 46(2): 135-141. |
| Zhao H L, Chen K, Zhang Q, Xu J L, Li Z K. Application of principal component analysis and cluster analysis of source-sink characteristics of rice[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2015, 46(2): 135-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 吕川根, 李霞, 陈国祥. 超级杂交稻两优培九高产的光合特性及其生理基础[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(21): 4055-4070. |
| Lü C G, Li X, Chen G X. Photosynthetic characteristics and its physiological basis of super high-yielding hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(21): 4055-4070. | |
| [6] | Meskauskiene R, Nater M, Goslings D A M, Kessler F, Opden C R, Apel K. FLU: A negative regulator of chlorophyll biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2001, 98: 12826-12831. |
| [7] | Boekema E J, van Roon H, van Breemen J F, Dekker J P. Supramolecular organization of photosystem II and its light-harvesting antenna in partially solubilized photosystem II membranes[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1999, 266(2): 444-452. |
| [8] | 李保珠, 赵孝亮, 彭雷. 植物叶绿体发育及调控研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(3): 337-345. |
| Li B Z, Zhao X L, Peng L. Research advances in the development and regulation of plant chloroplasts[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2014, 49(3): 337-345. | |
| [9] | Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Tozawa Y, Yazaki J, Kishimoto N, Kikuchi S, Iba K. The virescent-2 mutation inhibits translation of plastid transcripts for the plastid genetic system at an early stage of chloroplast differentiation[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2004, 45(8): 985-996. |
| [10] | Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Noguchi K, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Iba K. The rice nuclear gene, VIRESCENT 2, is essential for chloroplast development and encodes a novel type of guanylate kinase targeted to plastids and mitochondria[J]. The Plant Journal, 2007, 52(3): 512. |
| [11] | Lee S, Kim J H, Yoo E S, Lee C H, Hirochika H, An G. Differential regulation of chlorophyll a oxygenase genes in rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2005, 57: 805-818. |
| [12] | Wang P, Gao J, Wan C, Zhang F T, Xu Z J, Huang X Q, Sun X Q, Deng X J. Divinyl chlorophyll(ide) a can be converted to monovinyl chlorophyll(ide) a by a divinyl reductase in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 153(3): 994. |
| [13] | Sakuraba Y, Rahman M L, Cho S H, Kim Y S, Koh H J, Yoo S C, Paek N C. The rice faded green leaf locus encodes protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase B and is essential for chlorophyll synthesis under high light conditions[J]. Plant Journal, 2013, 74(1): 122-133. |
| [14] | Sato Y, Morita R, Katsuma S, Nishimura M, Tanaka A, Kusaba M. Two short-chain dehydrogenase/reductases, NON-YELLOW COLORING 1 and NYC1-LIKE, are required for chlorophyll b and light-harvesting complex II degradation during senescence in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2009, 57(1): 120-131. |
| [15] | Kato Y, Sakamoto W. New insights into the types and function of proteases in plastids[J]. International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology, 2010, 280: 185-218. |
| [16] | 中国科学院植物研究所. 揭示叶绿体蛋白转运与质量控制的新机制[J]. 高科技与产业化, 2022, 28(6): 47. |
| Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Unveiling the new mechanisms of chloroplast protein transport and quality control[J]. High-Technology & Industrialization, 2022, 28(6): 47. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | Rodriguez-Concepcion M, D’Andrea L, Pulido P. Control of plastidial metabolism by the Clp protease complex[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(7): 2049-2058. |
| [18] | Adam Z, Rudella A, van Wijk K J. Recent advances in the study of Clp, FtsH and other proteases located in chloroplasts[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2006, 9(3): 234-240. |
| [19] | 陈晓, 孙朝辉, 李思远, 陈彦惠. 玉米ClpR2同源基因PL5L15的克隆及其在不同光周期处理下的表达分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2008(6): 1187-1192. |
| Chen X, Sun Z H, Li S Y, Chen Y H. Clone and transcription levels analysis of ortholog PL5L15 of ClpR2 in maize under different photoperiod control[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2008(6): 1187-1192. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Dong H, Fei G L, Wu C Y, Wu F Q, Sun Y Y, Chen M J, Ren Y L, Zhou K N, Cheng Z J, Wang J L, Jiang L, Zhang X, Guo X P, Lei C L, Su N, Wang H, Wan J M. A rice virescent-yellow leaf mutant reveals new insights into the role and assembly of plastid caseinolytic protease in higher plants[J]. Plant Physiology, 2013, 162: 1867. |
| [21] | 纪鸿飞, 彭振英, 马敬, 毕玉平. 花生Clp蛋白酶基因(AhClpP)的克隆与序列分析[J]. 华北农学报, 2010, 25(S2): 5-8. |
| Hong J F, Peng Z Y, Ma J, Bi Y P. Cloning and analyzing of caseinolytic protease gene from Arachis hypogaea L.[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2010, 25(S2): 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Kim J, Kimber M S, Nishimura K, Friso G, Schultz L, Ponnala L, van Wijk K J. Structures, functions, and interactions of ClpT1 and ClpT2 in the Clp protease system of Arabidopsis chloroplasts[J]. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(5): 1477-1496. |
| [23] | Kuroda H, Maliga P. The plastid clpP1 protease gene is essential for plant development[J]. Nature, 2003, 425: 86-89. |
| [24] | Tsugane K, Maekawa M, Takagi K, Takahara H, Qian Q, Eun C H, Iida S. An active DNA transposon nDart causing leaf variegation and mutable dwarfism and its related elements in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2006, 45(1): 46-57. |
| [25] | Li W, Wu C, Hu G C, Xing L, Qian W J, Si H M, Sun Z X, Wang X C, Fu Y P, Liu W Z. Characterization and fine mapping of a novel rice narrow leaf mutant nal9 [J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2013, 55(11): 1016. |
| [26] | 丁颖, 李乃铭, 徐雪宾. 水稻分蘖发育现象的观察[M]. 广州: 华南农学院, 1959. |
| Ding Y, Li N M, Xu X B. Observation on the Phenomenon of Rice Tillering Development[M]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural College, 1959. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 张立成, 李懿星, 王天抗, 邱牡丹, 宋书锋, 董皓, 李磊, 刘建丰, 李莉. 水稻抽穗期基因OsDof6功能的初步研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 397-405. |
| Zhang L C, Li Y X, Wang T K, Qiu M D, Song S F, Dong H, Li L, Liu J F, Li L. A preliminary study on the function of rice heading date gene OsDof6[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(5): 397-405. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 夏思奇, 杨汉树, 邱牡丹, 李磊, 李懿星, 宋书锋, 李莉, 王建龙. 水稻糖苷水解酶基因OsINV3影响花粉育性的研究[J]. 杂交水稻, 2024, 39(1): 35-43. |
| Xia S Q, Yang H S, Qiu M D, Li L, Li Y X, Song S F, Li L, Wang J L. Effects of rice glycoside hydrolase gene OsINV3 on pollen fertility[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2024, 39(1): 35-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Goh C H, Satoh K, Kikuchi S, Kim S C, Ko S M, Kang H G, Jeon J S, Kim C S, Park Y I. Mitochondrial activity in illuminated leaves of chlorophyll-deficient mutant rice (OsCHLH) seedlings[J]. Plant Biotechnology Reports, 2010, 4(4): 281-291. |
| [30] | Wang P, Wan C, Xu Z, Wang P, Wang W, Sun C, Ma X, Xiao Y, Zhu J, Gao X, Deng X. One divinyl reductase reduces the 8-vinyl groups in various intermediates of chlorophyll biosynthesis in a given higher plant species, but the isozyme differs between species[J]. Plant Physiology, 2013, 161(1): 521-534. |
| [31] | 杨海莲, 刘敏, 郭旻, 李荣德, 张宏根, 严长杰. 一个水稻黄绿叶突变体ygl10的遗传分析和基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(1): 41-48. |
| Yang H L, Liu M, Guo W, Li R D, Zhang H G, Yan C J. Genetic analysis and position cloning of a yellowgreen leaf 10(yel10) gene, responsible for leaf color in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(1): 41-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Sugiyama N, Izawa T, Oikawa T, Shimamoto K. Light regulation of circadian clock-controlled gene expression in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2001, 26(6): 607-615. |
| [33] | Yamatani H, Kohzuma K, Nakano M, Takami T, Kato Y, Hayashi Y, Monden Y, Okumoto Y, Abe T, Kumamaru T, Tanaka A, Sakamoto W, Kusaba M. Impairment of Lhca4, a subunit of LHCI, causes high accumulation of chlorophyll and the stay-green phenotype in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2018, 69: 1027-1035. |
| [34] | Hubbart S, Ajigboye O O, Horton P, Murchie E H. The photoprotective protein PsbS exerts control over CO2 assimilation rate in fluctuating light in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2012, 71(3): 402-412. |
| [35] | Yang C, Hu H, Ren H, Kong Y, Lin H, Guo J, Wang L, He Y, Ding X, Grabsztunowicz M, Mulo P, Chen T, Liu Y, Wu Z, Wu Y, Mao C, Wu P, Mo X. LIGHT- INDUCED RICE1 regulates light-dependent attachment of leaf-type ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase to the thylakoid membrane in rice and Arabidopsis [J]. The Plant Cell, 2016, 28(3): 712-728. |
| [36] | Zhang F, Zhang P, Zhang Y, Wang S, Qu L, Liu X, Luo J. Identification of a peroxisomal-targeted aldolase involved in chlorophyll biosynthesis and sugar metabolism in rice[J]. Plant Science, 2016, 250: 205-215. |
| [1] | 吴金水, 唐江英, 谭立, 过志强, 杨娟, 张鑫臻, 陈桂芳, 王建龙, 施婉菊. 水稻对砷的吸收与转运机理及农艺阻控策略[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 143-155. |
| [2] | 马唯一, 朱济邹, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 刁刘云, 汪璐璐, 孟天瑶, 高平磊, 陈英龙, 戴其根, 韦还和. 盐害和干旱对稻米品质形成的影响及生理机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 156-170. |
| [3] | 张来桐, 杨乐, 刘洪, 赵学明, 程涛, 徐振江. 水稻香味物质的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 171-186. |
| [4] | 冯涛, 张朝阳, 黄新妮, 王月, 钟旭志, 冯志明, 刘欣, 左示敏, 欧阳寿强. Osa-miR166i-3p介导活性氧积累途径正调控水稻纹枯病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 187-196. |
| [5] | 闫影, 王凯, 张丽霞, 胡泽军, 叶俊华, 杨航, 顾春军, 吴书俊. 利用分子聚合育种培育优质多抗粳稻新品种沪香粳216[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 209-219. |
| [6] | 徐月梅, 彭诗燕, 孙志伟, 王志琴, 朱宽宇, 杨建昌. 不同耐低磷水稻品种的内源激素水平差异及其与产量和磷利用率的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 231-244. |
| [7] | 随晶晶, 赵桂龙, 金欣, 卜庆云, 唐佳琦. 水稻孕穗期耐冷调控的分子及生理机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 1-10. |
| [8] | 任宁宁, 孙永建, 申聪聪, 朱双兵, 李慧菊, 张志远, 陈凯. 水稻中胚轴研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 11-23. |
| [9] | 张丰勇, 应晓平, 张健, 杨隆维, 应杰政. 半矮秆基因sd1调控水稻重要农艺性状的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 24-32. |
| [10] | 陈智慧, 陶亚军, 范方军, 许扬, 王芳权, 李文奇, 古丽娜尔·巴合提别克, 蒋彦婕, 朱建平, 李霞, 杨杰. 水稻抽穗期调控基因Hd6功能标记的开发及应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 47-54. |
| [11] | 胡风越, 王健, 王春, 王克剑, 刘朝雷. 水稻DMP1、DMP2、DMP3基因突变体的创制及其单倍体诱导能力鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 55-66. |
| [12] | 陈书融, 朱练峰, 秦碧蓉, 王婕, 朱旭华, 田文昊, 朱春权, 曹小闯, 孔亚丽, 张均华, 金千瑜. 增氧灌溉下配施硝化抑制剂对水稻生长、产量和氮肥利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 92-100. |
| [13] | 吴猛, 倪川, 康钰莹, 毛雨欣, 叶苗, 张祖建. 水稻分蘖早发特性的品种间差异及其氮素响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 101-114. |
| [14] | 王晓茜, 蔡创, 宋练, 周伟, 杨雄, 顾歆悦, 朱春梧. 开放式大气CO2浓度升高和温度升高对扬稻6号稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 115-127. |
| [15] | 江敏, 王广伦, 李明璐, 苗波, 李明煊, 石春林. 基于模型的水稻高温热害风险评估与动态预警[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 128-142. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||