
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 516-528.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.250105
董立强1,2, 张义凯2,*( ), 杨铁鑫1, 冯莹莹1,3, 马亮1, 梁潇4, 张玉屏2, 李跃东1,*(
), 杨铁鑫1, 冯莹莹1,3, 马亮1, 梁潇4, 张玉屏2, 李跃东1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-08
修回日期:2025-02-17
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2025-07-21
通讯作者:
*email: zhangyikai@caas.cn,daozuosuo@126.com基金资助:
DONG Liqiang1,2, ZHANG Yikai2,*( ), YANG Tiexin1, FENG Yingying1,3, MA Liang1, LIANG Xiao4, ZHANG Yuping2, LI Yuedong1,*(
), YANG Tiexin1, FENG Yingying1,3, MA Liang1, LIANG Xiao4, ZHANG Yuping2, LI Yuedong1,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-08
Revised:2025-02-17
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-07-21
Contact:
*email: zhangyikai@caas.cn,daozuosuo@126.com摘要:
【目的】研究密播乳苗对机插水稻秧苗质量及取秧特性的影响,探明其对水稻育秧及机插效率的提升作用。【方法】于2024年以辽粳419为试材,以农户常规播种水平100 g/盘(长×宽为58 cm×28 cm, CK)为对照,设置125 g/盘(ISR1)、150 g/盘(ISR2)、175 g/盘(ISR3)、200 g/盘(ISR4)共4个密播处理,进行育苗试验,探究不同播种量对水稻秧苗质量及机插取秧特性的影响,阐明密播乳苗的秧苗生理生化特性与机插作业质量的关系。【结果】水稻秧苗整盘生物量随着播种量提高显著增加,在175 g/盘(ISR3)达到最大,且秧苗的根系盘结力显著提高,分别平均增加了35.6%和29.1%。高播种量处理下水稻秧苗个体生物量显著下降,秧苗抗氧化酶活性、可溶性糖含量降低,抗逆相关基因的表达受到影响。株高均匀度和茎基宽均匀度在ISR1~ISR3下较对照分别降低了1.3%~2.6%和0.6%~3.7%,ISR4分别显著降低了7.2%和9.3%;机插伤苗率与播种量呈线性正关系,在ISR1~ISR3下平均伤苗率为4.1%,ISR4下为9.8%,ISR2~ISR3处理维持较高的秧苗充实度、壮苗指数和较低的伤苗率。机插实际用秧盘数ISR1~ISR4较CK降低了53.2~148.1盘/hm2,机插人工操作效率显著提升17.2%~40.2%。【结论】密播乳苗育秧提高了整盘秧苗生物量和根系盘结力,150~175 g/盘播种量可以维持较高的个体秧苗质量,显著降低秧盘用量36.2%,极大提升了机插作业效率,可作为北方粳稻地区高质高效机插秧作业选择。
董立强, 张义凯, 杨铁鑫, 冯莹莹, 马亮, 梁潇, 张玉屏, 李跃东. 北方粳稻密苗机插育秧对秧苗素质及取秧特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 516-528.
DONG Liqiang, ZHANG Yikai, YANG Tiexin, FENG Yingying, MA Liang, LIANG Xiao, ZHANG Yuping, LI Yuedong. Effect of Dense Sowing Nursery on Seedling Quality and Picking Characteristics for Mechanized Transplanting in Northern japonica Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(4): 516-528.
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward sequence (5'-3') | 反向引物 Reverse sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Actin-OS-GAPDH | TACAGCTCTCGCGTTGTTGA | CATCATGCGAAAAGCCAGCA |
| OsLPXC | TGAAAAATTGCGTTCTGCTG | GCAAGAAGCGAGAAATCACC |
| OsSPX1 | AGCAGCAGGAACTGTGGAAT | CCCGGTACTATCTCCAGCAA |
表1 本研究所用引物及其序列
Table 1. Primers used in the study
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward sequence (5'-3') | 反向引物 Reverse sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Actin-OS-GAPDH | TACAGCTCTCGCGTTGTTGA | CATCATGCGAAAAGCCAGCA |
| OsLPXC | TGAAAAATTGCGTTCTGCTG | GCAAGAAGCGAGAAATCACC |
| OsSPX1 | AGCAGCAGGAACTGTGGAAT | CCCGGTACTATCTCCAGCAA |
| 处理 Treatment | 横向取苗 Horizontal seedling width (mm) | 纵向取苗 Vertical seedling length(mm) | 取苗面积 Seedling area (mm2) | 理论取苗株数 Theoretical seedling number | 单盘理论取苗次数 Theoretical hill number per tray | 理论用苗盘数 Theoretical tray number(No./hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 14 | 14 | 196 | 4.43 | 828.57 | 251.45 |
| ISR1 | 14 | 12 | 168 | 4.62 | 966.67 | 215.53 |
| ISR2 | 14 | 10 | 140 | 4.43 | 1160.00 | 179.61 |
| ISR3 | 11 | 11 | 121 | 4.46 | 1370.91 | 151.97 |
| ISR4 | 11 | 10 | 110 | 4.74 | 1508.00 | 138.16 |
表2 机插取秧特性理论参数
Table 2. Theoretical parameters of seedling picking characteristics for mechanical transplanting
| 处理 Treatment | 横向取苗 Horizontal seedling width (mm) | 纵向取苗 Vertical seedling length(mm) | 取苗面积 Seedling area (mm2) | 理论取苗株数 Theoretical seedling number | 单盘理论取苗次数 Theoretical hill number per tray | 理论用苗盘数 Theoretical tray number(No./hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 14 | 14 | 196 | 4.43 | 828.57 | 251.45 |
| ISR1 | 14 | 12 | 168 | 4.62 | 966.67 | 215.53 |
| ISR2 | 14 | 10 | 140 | 4.43 | 1160.00 | 179.61 |
| ISR3 | 11 | 11 | 121 | 4.46 | 1370.91 | 151.97 |
| ISR4 | 11 | 10 | 110 | 4.74 | 1508.00 | 138.16 |
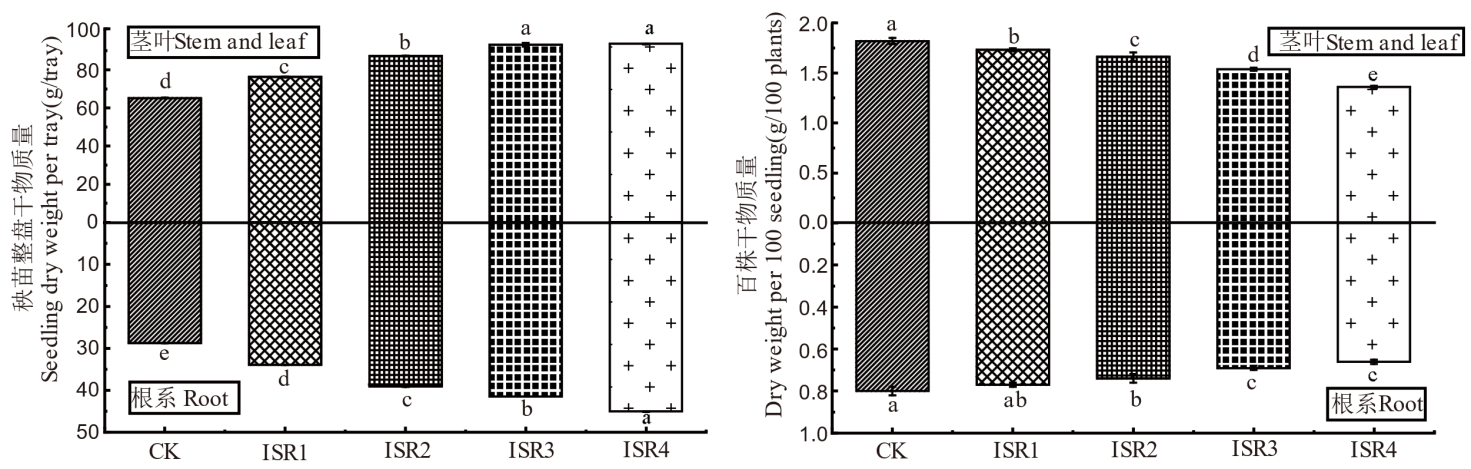
图2 不同播种量下水稻秧苗生物量积累 相同小写字母表示处理间差异未达0.05显著水平。下同。
Fig. 2. Biomass accumulation of rice seedlings under different sowing rates The same lowercase letters indicate that the difference between treatments is not significant at 0.05 level. The same as in the figures below.
| 处理 Treatment | 叶龄 Leaf age | SPAD | 株高 Plant height(cm) | 茎基宽 Stem base width(mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.78±0.04 a | 29.26±0.56 a | 14.80±0.18 a | 2.17±0.03 a |
| ISR1 | 2.54±0.03 b | 28.70±0.19 a | 14.48±0.19 ab | 1.79±0.02 b |
| ISR2 | 2.47±0.03 bc | 28.44±0.69 a | 14.15±0.18 b | 1.72±0.02 c |
| ISR3 | 2.44±0.03 c | 28.35±0.42 a | 13.19±0.17 c | 1.66±0.02 c |
| ISR4 | 2.16±0.03 d | 28.05±0.38 a | 12.11±0.16 d | 1.58±0.02 d |
表3 不同播种量下水稻秧苗个体形态特征
Table 3. Individual morphological characteristics of rice seedlings under different sowing rates
| 处理 Treatment | 叶龄 Leaf age | SPAD | 株高 Plant height(cm) | 茎基宽 Stem base width(mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.78±0.04 a | 29.26±0.56 a | 14.80±0.18 a | 2.17±0.03 a |
| ISR1 | 2.54±0.03 b | 28.70±0.19 a | 14.48±0.19 ab | 1.79±0.02 b |
| ISR2 | 2.47±0.03 bc | 28.44±0.69 a | 14.15±0.18 b | 1.72±0.02 c |
| ISR3 | 2.44±0.03 c | 28.35±0.42 a | 13.19±0.17 c | 1.66±0.02 c |
| ISR4 | 2.16±0.03 d | 28.05±0.38 a | 12.11±0.16 d | 1.58±0.02 d |
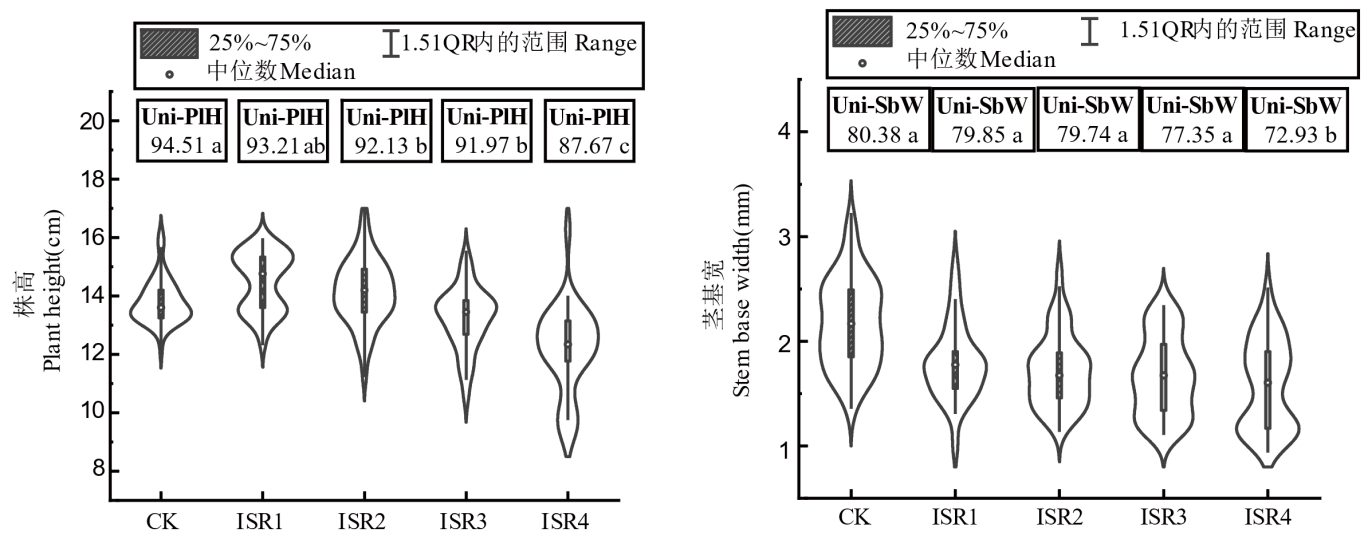
图5 不同播种量下水稻秧苗株高和茎基宽均匀度 Uni-PIH: 株高均匀度(%); Uni-SbW: 茎基宽均匀度(%)。
Fig. 5. Uniformity of plant height and stem base width under different sowing rates Uni-PIH, Uniformity of plant height(%); Uni-SbW, Uniformity of stem base width(%).
| 处理 Treatment | 总根长 Total root length(cm) | 根总表面积 Total root surface area(cm2) | 根总体积 Total volume of roots(mm3) | 平均直径 Average diameter(mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 79.33±1.80 a | 7.80±0.18 a | 57.99±1.31 a | 0.87±0.02 a |
| ISR1 | 76.71±1.04 ab | 7.56±0.10 ab | 57.13±0.78 a | 0.84±0.01 ab |
| ISR2 | 76.55±1.58 ab | 7.44±0.15 bc | 55.44±1.15 a | 0.83±0.02 ab |
| ISR3 | 75.04±0.85 b | 7.19±0.08 c | 52.01±0.59 b | 0.83±0.01 b |
| ISR4 | 70.82±1.21 c | 6.62±0.11 d | 48.63±0.83 c | 0.82±0.01 b |
表4 不同播种量下水稻秧苗根系性状
Table 4. Root traits of rice seedlings under different sowing rates
| 处理 Treatment | 总根长 Total root length(cm) | 根总表面积 Total root surface area(cm2) | 根总体积 Total volume of roots(mm3) | 平均直径 Average diameter(mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 79.33±1.80 a | 7.80±0.18 a | 57.99±1.31 a | 0.87±0.02 a |
| ISR1 | 76.71±1.04 ab | 7.56±0.10 ab | 57.13±0.78 a | 0.84±0.01 ab |
| ISR2 | 76.55±1.58 ab | 7.44±0.15 bc | 55.44±1.15 a | 0.83±0.02 ab |
| ISR3 | 75.04±0.85 b | 7.19±0.08 c | 52.01±0.59 b | 0.83±0.01 b |
| ISR4 | 70.82±1.21 c | 6.62±0.11 d | 48.63±0.83 c | 0.82±0.01 b |
| 处理 Treatment | SOD活性 SOD activity (U/g) | POD活性 POD activity (U/g) | CAT活性 CAT activity (U·g/min) | MDA活性 MDA activity (nmol/g) | 可溶性糖 Soluble protein content (U·g/g) | 可溶性蛋白 Soluble sugar content (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 350.36±7.94 a | 12.10±0.27 a | 45.25±1.03 a | 0.45±0.01 d | 1.36±0.03 a | 17.61±0.40 a |
| ISR1 | 343.29±4.66 a | 11.79±0.16 a | 44.46±0.60 a | 0.46±0.01 d | 1.32±0.02 ab | 17.59±0.24 a |
| ISR2 | 340.37±7.03 a | 10.79±0.22 b | 44.14±0.91 ab | 0.49±0.01 c | 1.28±0.03 bc | 16.99±0.35 ab |
| ISR3 | 320.18±3.61 b | 9.57±0.11 c | 42.35±0.48 bc | 0.52±0.01 b | 1.25±0.01 c | 16.60±0.19 b |
| ISR4 | 302.31±5.18 c | 8.99±0.15 d | 41.25±0.71 c | 0.56±0.01 a | 1.24±0.02 c | 15.46±0.26 c |
表5 不同播种量下水稻秧苗叶片抗氧化相关酶活性
Table 5. Antioxidant enzyme activities in rice seedling leaves under different sowing rates
| 处理 Treatment | SOD活性 SOD activity (U/g) | POD活性 POD activity (U/g) | CAT活性 CAT activity (U·g/min) | MDA活性 MDA activity (nmol/g) | 可溶性糖 Soluble protein content (U·g/g) | 可溶性蛋白 Soluble sugar content (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 350.36±7.94 a | 12.10±0.27 a | 45.25±1.03 a | 0.45±0.01 d | 1.36±0.03 a | 17.61±0.40 a |
| ISR1 | 343.29±4.66 a | 11.79±0.16 a | 44.46±0.60 a | 0.46±0.01 d | 1.32±0.02 ab | 17.59±0.24 a |
| ISR2 | 340.37±7.03 a | 10.79±0.22 b | 44.14±0.91 ab | 0.49±0.01 c | 1.28±0.03 bc | 16.99±0.35 ab |
| ISR3 | 320.18±3.61 b | 9.57±0.11 c | 42.35±0.48 bc | 0.52±0.01 b | 1.25±0.01 c | 16.60±0.19 b |
| ISR4 | 302.31±5.18 c | 8.99±0.15 d | 41.25±0.71 c | 0.56±0.01 a | 1.24±0.02 c | 15.46±0.26 c |
| [1] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| Guan Y Q, E Z G, Wang L, Shen H F. An empirical study on the factors influencing the development of rice production outsourcing in China: From the perspective of population effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 徐春春, 纪龙, 陈中督, 方福平. 2023年我国水稻产业形势分析及2024年展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2024, 30(2): 1-4. |
| Xu C C, Ji L, Chen Z D, Fang F P. Analysis of China’s rice industry in 2023 and the outlook for 2024[J]. China Rice, 2024, 30(2): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 覃朝晖, 汪晓婉, 余威震, 丁志国. 中国水稻种植要素配置效率测度与收敛性分析[J/OL]. 中国农业资源与区划, https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3513.s.20241128.1443.018. |
| Qin Z H, Wang X W, Yu W Z, Ding Z G. Allocation efficiency of rice planting factors in China and its convergence analysis[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3513.s.20241128.1443.018. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 杨思雨, 李伟. 农机社会化服务对农业劳动生产率的影响研究[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2023, 44(11): 151-162. |
| Yang S Y, Li W. Study on the influence of agricultural machinery socialization service on agricultural labor productivity[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2023, 44(11): 151-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 陈梦涵, 吕晓, Sergey Y S, Tatsiana V S. 农村劳动力转移对耕地利用可持续集约化的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2024, 40(20): 241-249. |
| Chen M H, Lü X, Sergey Y S, Tatsiana V S. Impact of rural labor transfer on the sustainable intensification of cultivated land use[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2024, 40(20): 241-249. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 易小兰, 颜琰, 张彤彤. 劳动力价格上涨、粮食生产机械化及其产出效应[J]. 华中农业大学学报(社会科学版), 2023, 25(6): 14-25. |
| Yi X L, Yan Y, Zhang T T. Rising labor price, mechanization of grain production, and its output effect[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University(Social Sciences Edition), 2023, 25(6): 14-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 王亚梁, 朱德峰, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 徐一成, 张义凯. 杂交稻低播量精量播种育秧及机插取秧特性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 332-338. |
| Wang Y L, Zhu D F, Xiang J, Chen H Z, Zhang Y P, Xu Y C, Zhang Y K. Characteristics of seedling raising and mechanized transplanting of hybrid rice with a low seeding rate by precise seeding method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(4): 332-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 王亚梁, 朱德峰, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 徐一成, 张义凯. 杂交稻低播量精量播种育秧及机插取秧特性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 332-338. |
| Wang Y L, Zhu D F, Xiang J, Chen H Z, Zhang Y P, Xu Y C, Zhang Y K. Characteristics of seedling raising and mechanized transplanting of hybrid rice with a low seeding rate by precise seeding method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(4): 332-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Dong L Q, Yang T X, Li R, Ma L, Feng Y Y, Li Y D. Grain yield, rice seedlings and transplanting quantity in response to decreased sowing rate under precision drill sowing[J]. Agriculture, 2024, 14(10): 1745. |
| [10] | 谢冬梅, 汪希成, 伍骏骞. 农业机械化水平对中国粮食生产技术效率的空间溢出效应研究:基于农机跨区作业视角[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2023, 44(3): 223-231. |
| Xie D M, Wang X C, Wu J Q. Research on the spatial spillover effect of the level of agricultural mechanization on the technical efficiency of grain production in China: Based on the perspective of agricultural machinery cross regional operation[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2023, 44(3): 223-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 俞高红, 王磊, 孙良, 赵雄, 叶秉良. 大田机械化移栽技术与装备研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报, 2022, 53(9): 1-20. |
| Yu G H, Wang L, Sun L, Zhao X, Ye B L. Advancement of mechanized transplanting technology and equipment for field crops[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(9): 1-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 李睿, 董立强, 商文奇, 马亮, 王先俱, 王铮, 李跃东. 育秧基质和喷水间隔处理对机插秧苗素质及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 59-68. |
| Li R, Dong L Q, Shang W Q, Ma L, Wang X J, Wang Z, Li Y D. Effects of seedling-raising substrate and water spraying interval on seedling quality and grain yield of mechanically transplanted rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(1): 59-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 李跃东, 董立强, 隋国民, 柴振军, 徐婷婷. 辽宁省水稻生产现状分析及技术优化建议[J]. 中国稻米, 2022, 28(6): 98-101. |
| Li Y D, Dong L Q, Sui G M, Chai Z J, Xu T T. Analysis on the status of rice production in Liaoning Province and suggestions for technical optimization[J]. China Rice, 2022, 28(6): 98-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 董立强, 杨铁鑫, 李睿, 商文奇, 马亮, 李跃东, 隋国民. 株行距配置对超高产田水稻产量及根系形态生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 392-404. |
| Dong L Q, Yang T X, Li R, Shang W Q, Ma L, Li Y D, Sui G M. Effect of plant-row spacing on rice yield and root morphological and physiological characteristics in super high yield field[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 392-404. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 赵羽涵, 丁俊杰, 杨晓贺, 姚亮亮, 邱磊, 张茂明, 王自杰, 高雪冬, 黄成亮, 崔士泽, 张家智. “双免密苗”技术对寒地水稻秧苗素质及酶活性的影响[J/OL]. 作物杂志, 2025(2): 109-114. |
| Zhao Y H, Ding J J, Yang X H, Yao L L, Qiu L, Zhang M M, Wang Z J, Gao X D, Huang C L, Cui S Z, Zhang J Z. Effects of “double free dense seedling” technique on seedling quality and enzyme activity of rice in cold region[J/OL]. Crops, 2025(2): 109-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| Lian J J, Tang L Y, Zhang Y N, Zheng J X, Zhu C Y, Ye Y H, Wang Y X, Shang W N, Fu Z H, Xu X X, Wu R C, Lu M, Wang C C, Rao Y C. Genetic locus mining and candidate gene analysis of antioxidant traits in rice[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Islam F, Khan M S S, Ahmed S, Abdullah M, Hannan F, Chen J. OsLPXC negatively regulates tolerance to cold stress via modulating oxidative stress, antioxidant defense and JA accumulation in rice[J]. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 2023, 199: 2-16. |
| [18] | 朱春权, 徐青山, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 孔亚丽, 金千瑜, 张均华. 不同属性特征基质对早稻秧苗耐低温的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 503-512. |
| Zhu C Q, Xu Q S, Cao X C, Zhu L F, Kong Y L, Jin Q Y, Zhang J H. Effects of different attribute characteristic substrates on low temperature tolerance of early rice seedlings[J]. China Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 503-512. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 张昌爱, 于秀英, 杨力, 林海涛, 辛淑荣. 肥包埋置测定包膜尿素在土壤中氮素释放的方法及应用[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(9): 2055-2061. |
| Zhang C A, Yu X Y, Yang L, Lin H T, Xin S R. Determination of nitrogen release from coated urea in soils using buried fertilizer packet and its application[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(9): 2055-2061. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000: 167-169. |
| Li H S. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological and Biochemical Experiments[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000: 167-169. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 张治安. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2004: 26-34. |
| Zhang Z A. Plant Physiology Experiment Guide[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2004: 26-34. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 李玲. 植物生理学模块实验指导[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 95-97. |
| Li L. Plant Physiology Module Experiment Guide[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 95-97. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 宋云生, 张洪程, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 朱聪聪, 孙圳, 杨大柳, 王惟清, 刘俊, 吴爱国. 水稻钵苗机插秧苗素质的调控[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(22): 11-22. |
| Song Y S, Zhang H C, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Zhu C C, Sun Z, Yang D L, Wang W Q, Liu J, Wu A G. Seedling quality regulation of rice potted-seedling in mechanical transplanting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(22): 11-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 李泽华, 马旭, 李秀昊, 陈林涛, 李宏伟, 袁志成. 水稻栽植机械化技术研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(5): 1-20. |
| Li Z H, Ma X, Li X H, Chen L T, Li H W, Yuan Z C. Research progress of rice transplanting mechanization[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(5): 1-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 李泽华, 马旭, 李宏伟, 郭林杰, 刘朝东, 傅荣富, 杨明祥, 梁振宇. 低播种量下杂交稻不同机械化种植方式的产量构成及特征[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2020, 41(4): 22-29. |
| Li Z, Ma X, Li H, Guo L, Liu C, Fu R, Yang M, Liang Z. Yield components and characteristics of hybrid rice with different mechanical transplanting methods under low sowing rate[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2020, 41(4): 22-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 吕伟生, 曾勇军, 石庆华, 潘晓华, 黄山, 商庆银, 谭雪明, 李木英, 胡水秀. 机插早稻分蘖成穗特性及基本苗公式参数研究[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(03): 427-436. |
| Lü W S, Zeng Y J, Shi Q H, Pan X H, Huang S, Shang Q Y, Tan X M, Li M Y, Hu S X. Tillering and panicle formation characteristics of machine-transplanted early rice and its parameters of basic population formulae[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(3): 427-436. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 滕飞, 陈惠哲, 朱德峰, 蔡雪青, 向镜, 徐一成, 张正凯. 播种量对水稻机插秧苗成毯性及素质的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2015, 37(3): 398-403. |
| Teng F, Chen H Z, Zhu D F, Cai X Q, Xiang J, Xu Y C, Zhang Z K. Effects of sowing rates on seedling root entwining and seedling quality of machine-transplanted rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2015, 37(3): 398-403. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 胡海涛, 郭龙彪. 植物核黄素的生物合成及其功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 638-655. |
| Hu H T, Guo L B. Progress in the research on riboflavin biosynthesis and function in plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 638-655. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| Hou X Q, Wang Y, Yu B, Fu W M, Feng B H, Shen Y C, Xie H J, Wang H R, Xu Y Q, Wu Z H, Wang J J, Tao L X, Fu G F. Mechanisms behind the role of potassium fulvic acid in enhancing salt tolerance in rice seedlings[J]. China Journal of Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 毋翔, 张义凯, 张鹏, 马昕伶, 陈玉林, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 向镜, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 李良涛. 2, 4-表油菜素内酯对生物炭基质育秧水稻秧苗根系生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 685-694. |
| Wu X, Zhang Y K, Zhang P, Ma X L, Chen Y L, Chen H Z, Zhang Y P, Xiang J, Wang Y L, Wang Z G, Li L T. Effects of 2, 4-epibrassinolide on root growth and physiological characteristics of rice seedlings raised in biochar substrate[J]. China Journal of Rice Science, 2024, 38(6): 685-694. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 廖莎, 谭雪明, 李木英, 胡凯, 潘晓华, 石庆华. 芸薹素内酯对稻草基质育秧水稻秧苗生理特性及栽后生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 181-190. |
| Liao S, Tan X M, Li M Y, Hu K, Pan X H, Shi Q H. Effects of brassinolide on physiological characteristics and growth of straw substrate-cultured rice seedlings after transplanting[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(2): 181-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Zhang Z G, Zhang Q, Wu J X, Zheng X, Zheng S, Sun X H, Qiu Q S, Lu T G. Gene knockout study reveals that cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase 2 (OsAPX2) plays a critical role in growth and reproduction in rice under drought, salt and cold stresses[J]. PloS One, 2013, 8(2): e57472 |
| [33] | 朱德峰, 张玉屏, 陈惠哲, 向镜, 张义凯. 中国水稻高产栽培技术创新与实践[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(17): 3404-3414. |
| Zhu D F, Zhang Y P, Chen H Z, Xiang J, Zhang Y K. Innovation and Practice of High-Yield Rice Cultivation Technology in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(17): 3404-3414. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 王亚梁, 朱德峰, 陈若霞, 方文英, 王晶卿, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 谌江华. 杂交稻低播量精准条播育秧机插提高群体均匀度和产量的效应分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(4): 666-679. |
| Wang Y L, Zhu D F, Chen R X, Fang W Y, Wang J Q, Xiang J, Chen H Z, Zhang Y P, Chen J H. Beneficial effects of precision drill sowing with low seeding rates in machine transplanting for hybrid rice to improve population uniformity and yield[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(4): 666-679. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 贾旋, 宋建农, 王继承, 曹晓林, 刘彩玲, 万里鹏程, 郑慧娜, 徐泽昕. 秧龄和基土比对机插大钵体毯状苗晚稻群体质量和产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(12): 1-11. |
| Jia X, Song J N, Wang J C, Cao X L, Liu C L, Wan L P C, Zheng H N, Xu Z X. Effects of seedling age and substrate soil ratio on the population quality and yield of late rice of machine-transplanted large-pot carpet seedlings[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(12): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 孙巧玉, 刘依琳, 杨洪福, 陈雪, 范先鹏, 孙文涛, 王玉峰, 杨越超, 侯立刚, 刘宏斌. 育秧期钵盘施用全量控释肥显著降低稻田氮素损失风险[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(3): 566-574. |
| Sun Q Y, Liu Y L, Yang H F, Chen X, Fan X P, Sun W T, Wang Y F, Yang Y C, Hou L G, Liu H B. Applying control-released fertilizer of whole growth duration in seedling-raising pot to effectively decrease the risk of N loss in the paddy field[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(3): 566-574. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 徐静, 熊世豪, 张倩. 资源环境约束下中国水稻生产效率及提升路径[J]. 资源科学, 2024, 46(7): 1330-1345. |
| Xu J, Xiong S H, Zhang Q. Efficiency and improvement path of rice production in China under resource and environmental constraints[J]. Resources Science, 2024, 46(7): 1330-1345. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 唐承翰, 陈惠哲, 怀燕, 孙良, 张玉屏, 向镜, 张义凯, 王志刚, 徐逸文, 王亚梁. 杂交稻钵毯苗机插质量及产量形成对钵深的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 491-500. |
| [2] | 朱鹏, 凌溪铁, 王金彦, 张保龙, 杨郁文, 许轲, 裘实. 机直播条件下不同控草方式对抗除草剂水稻产量和品质差异性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 501-515. |
| [3] | 周洋, 叶凡, 刘立军. 典型促生微生物提高盐胁迫水稻抗性的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 529-542. |
| [4] | 朱建平, 李霞, 李文奇, 许扬, 王芳权, 陶亚军, 蒋彦婕, 陈智慧, 范方军, 杨杰. 水稻粉质胚乳突变体we1的表型分析与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 543-551. |
| [5] | 黄福灯, 吴春艳, 郝媛媛, 韩一飞, 张小斌, 孙会锋, 潘刚. 不同氮肥水平下水稻倒二叶叶鞘的转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 563-574. |
| [6] | 卢椰子, 邱结华, 蒋楠, 寇艳君, 时焕斌. 稻瘟病菌效应子研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 287-294. |
| [7] | 王超瑞, 周宇琨, 温雅, 张瑛, 法晓彤, 肖治林, 张耗. 秸秆还田方式对稻田土壤特性和温室气体排放的影响及其水肥互作调控[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 295-305. |
| [8] | 王雅宣, 王新峰, 杨后红, 刘芳, 肖晶, 蔡玉彪, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊. 稻飞虱适应水稻抗性机制的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 306-321. |
| [9] | 黄涛, 魏兆根, 陈玘, 程泽, 刘欣, 王广达, 胡珂鸣, 谢文亚, 陈宗祥, 冯志明, 左示敏. 水稻类病斑突变体lm52的基因克隆及其广谱抗病性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 322-330. |
| [10] | 马顺婷, 胡运高, 高方远, 刘利平, 牟昌铃, 吕建群, 苏相文, 刘松, 梁毓玉, 任光俊, 郭鸿鸣. 水稻真核翻译起始因子OseIF6.2调控粒型的功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 331-342. |
| [11] | 张彬涛, 刘聪聪, 郭明亮, 杨绍华, 吴世强, 郭龙彪, 朱义旺. 水稻OsDR8基因的稻瘟病抗性评价及优异单倍型鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 343-351. |
| [12] | 韦新宇, 曾跃辉, 肖长春, 黄建鸿, 阮宏椿, 杨旺兴, 邹文广, 许旭明. 水稻康丰B抗稻瘟病基因Pi-kf2(t)的克隆与功能验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 352-364. |
| [13] | 李文奇, 许扬, 王芳权, 朱建平, 陶亚军, 李霞, 范方军, 蒋彦婕, 陈智慧, 杨杰. 广谱抗稻瘟病基因PigmR的KASP标记开发及应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 365-372. |
| [14] | 韦还和, 汪璐璐, 马唯一, 张翔, 左博源, 耿孝宇, 朱旺, 朱济邹, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 戴其根. 盐−旱复合胁迫下粳稻品种南粳9108籽粒灌浆特性及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 373-386. |
| [15] | 沈智达, 余秋华, 张斌, 曹玉东, 王少华, 王红飞, 伍永清, 戴志刚, 李小坤. 磷肥施用量对湖北省直播水稻产量、磷素积累及利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 399-411. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||