
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 751-759.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240709
陶士博1,2, 许娜1, 徐正进1, 刘畅1,*( ), 徐铨1,*(
), 徐铨1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-13
修回日期:2024-08-20
出版日期:2025-11-10
发布日期:2025-11-19
通讯作者:
* email:liuchang@syau.edu.cn,kobexu34@syau.edu.cn
基金资助:
TAO Shibo1,2, XU Na1, XU Zhengjin1, LIU Chang1,*( ), XU Quan1,*(
), XU Quan1,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-13
Revised:2024-08-20
Online:2025-11-10
Published:2025-11-19
Contact:
* email:liuchang@syau.edu.cn,kobexu34@syau.edu.cn
摘要:
【目的】挖掘鉴定水稻耐冷基因,创制耐冷种质。【方法】对粳稻品种笹锦进行了甲基磺酸乙酯(EMS)诱变,筛选发芽期耐冷性显著提高的突变体,通过遗传分析、精细定位、转基因验证、表达模式分析和单倍型分析对候选基因进行克隆和功能分析。【结果】筛选到一个发芽期耐冷性显著提高的突变体M34。遗传分析表明耐冷性状由隐性单基因控制,精细定位将目标基因锁定为Cold6。通过CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑构建Cold6敲除突变体验证Cold6参与发芽期耐冷性调控。Cold6在水稻各组织器官均有表达,其中穗部表达最高,编码SNF2等多个结构域。进化树分析显示Cold6可能存在籼粳分化,单倍型分析鉴定出Cold6可分为10个单倍型,其中单倍型Ⅰ~Ⅲ为主要单倍型,单倍型Ⅰ主要为粳稻,单倍型Ⅱ和Ⅲ主要为籼稻。【结论】本研究克隆了Cold6,一个新的水稻发芽期耐冷性调控位点,编码SNF2蛋白,对Cold6分子机理的研究不但可以加深水稻中SNF2家族基因功能的认知,还可为北方粳稻耐冷分子育种提供理论线索和种质资源。
陶士博, 许娜, 徐正进, 刘畅, 徐铨. 水稻发芽期耐冷基因Cold6的克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 751-759.
TAO Shibo, XU Na, XU Zhengjin, LIU Chang, XU Quan. Cloning of Cold6 Conferring Cold Tolerance in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 751-759.
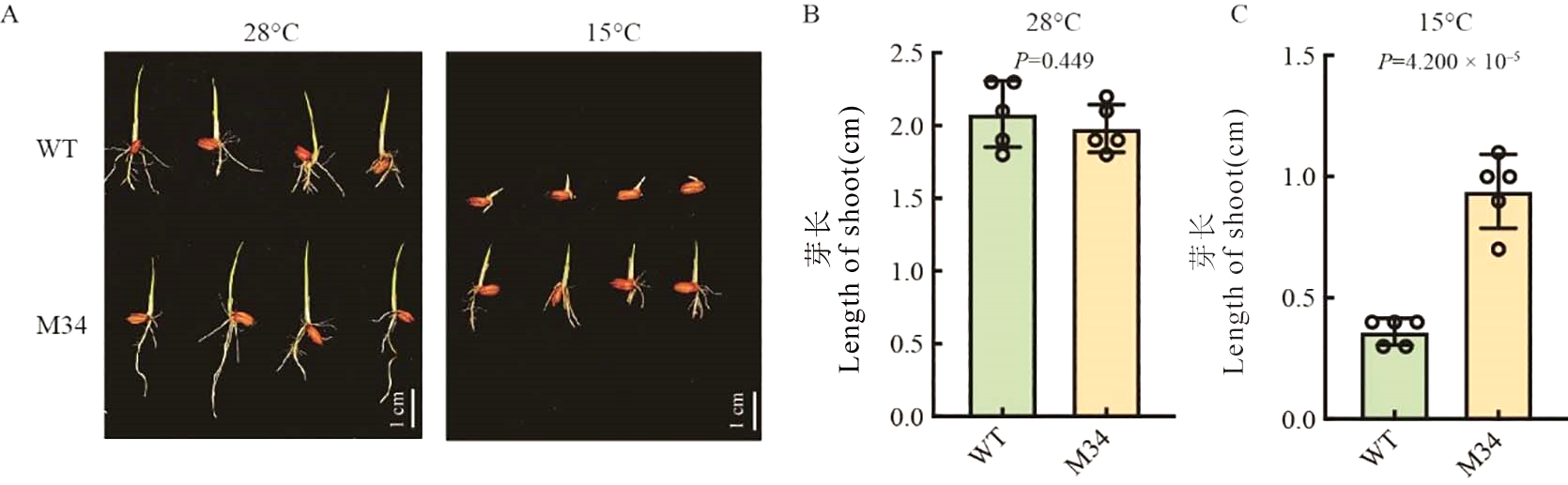
图1 WT和M34突变体28℃和15℃下表型 A:WT和M34突变体28℃和15℃下播种后5 d表型。标尺=1 cm;B:WT和M34突变体28℃下播种后5 d芽长;C:WT和M34突变体15℃下播种后5 d芽长。数据用平均值±标准差(n=5)。
Fig. 1. Phenotype of WT and M34 under 28 ℃ and 15℃ A, WT and M34 5 d after sowing under 28℃ and 15 ℃, bar = 1 cm. B, Length of shoot 5 d after sowing under 28 ℃. C, Length of shoot 5 d after sowing under 15 ℃. Data are mean ± SE (n = 5).
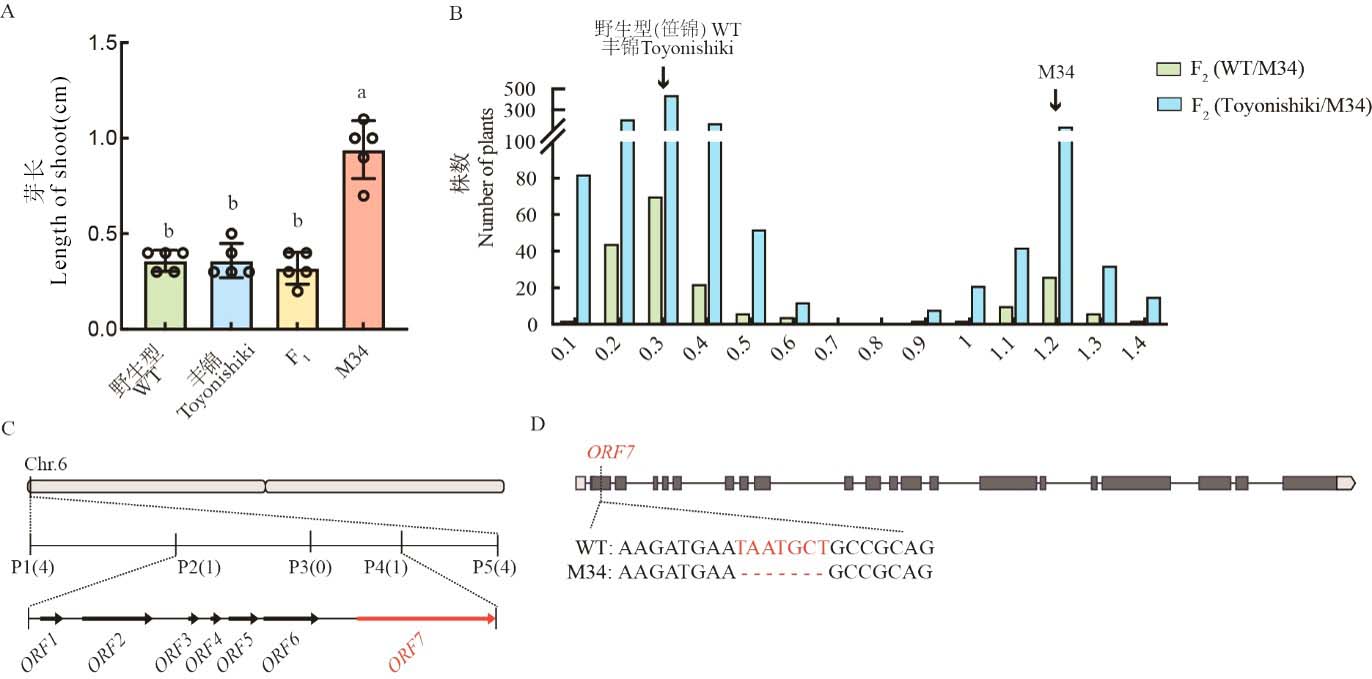
图2 候选基因Cold6的图位克隆 A:15℃下播种5 d后WT、M34及其F1芽长。数据为平均值±标准差(n=5);不同字母代表在0.05水平上差异显著;B:F2群体15℃下播种后5 d的芽长分布;C:候选基因的精细定位;D:候选基因在WT和M34之间的序列差异。
Fig. 2. Map-based cloning of candidate gene Cold6 A, Length of shoot of WT, M34, and F1 plants 5 d after sowing under 15℃. Data are mean ± SE (n = 5). Different letters denote significant differences (P < 0.05) by Duncan’s multiple range test; B, Distribution of shoot length of F2 population under 15℃ 5 d after sowing; C, Fine mapping of candidate gene; D, Sequence difference between WT and M34 in ORF7.
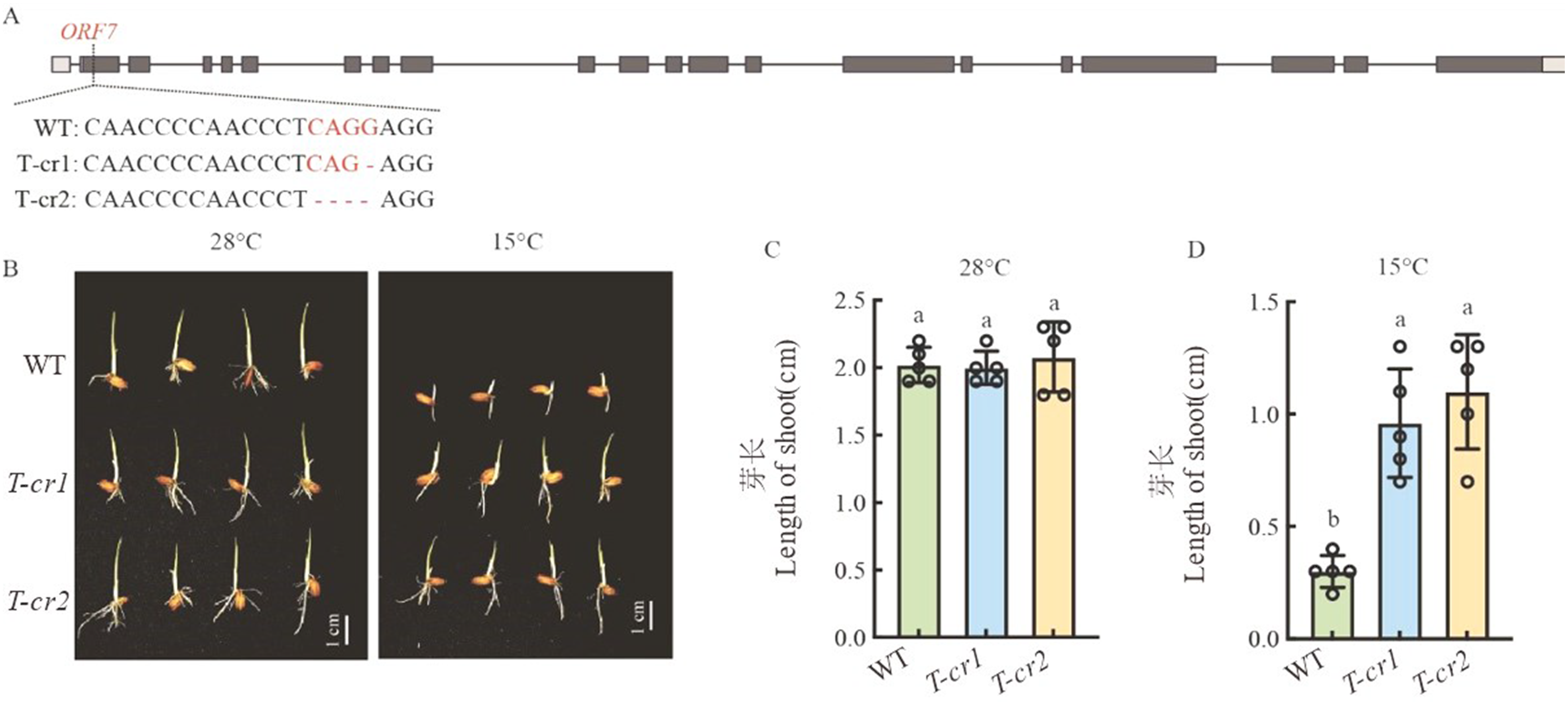
图3 Cold6的CRISPR/Cas9基因敲除突变体构建和表型调查 A:Cold6的基因编辑靶点和突变体序列;B:WT和基因编辑植株在28 ℃和15 ℃下播种5 d后的芽长;C:WT和基因编辑植株在28 ℃下播种5 d 后的芽长,标尺=1 cm;D:WT和基因编辑植株在15 ℃下播种5 d 后的芽长。数据为平均值±标准差(n=5),不同字母代表在0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3. CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing of Cold6 and phenotypic investigation A, Target sites and mutation sequences of Cold6 gene; B, WT and gene edited plants under 28 ℃ and 15℃ 5 d after sowing, scale bar = 1 cm; C, Shoot length of WT and gene edited plants under 28 ℃ 5 d after sowing; D, Shoot length of WT and gene edited plants under 15 ℃ 5 d after sowing. Data are mean ± SE (n = 5). Different letters denote significant differences (P < 0.05) by Duncan’s multiple range test.
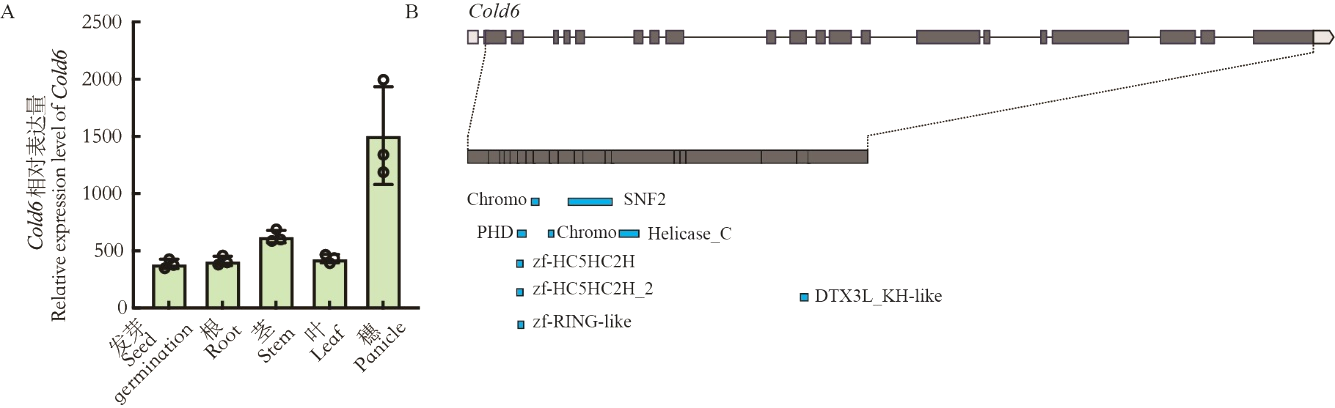
图4 Cold6的表达模式和结构域分析 A:植株不同组织中Cold6的相对表达量,数据为平均值±标准差(n=3);B:Cold6结构域预测。
Fig. 4. Expression pattern and motif domain prediction of Cold6 A, Relative expression of Cold6 in different organs of plants, data are mean ± SE (n = 3); B, Prediction of motif in Cold6.
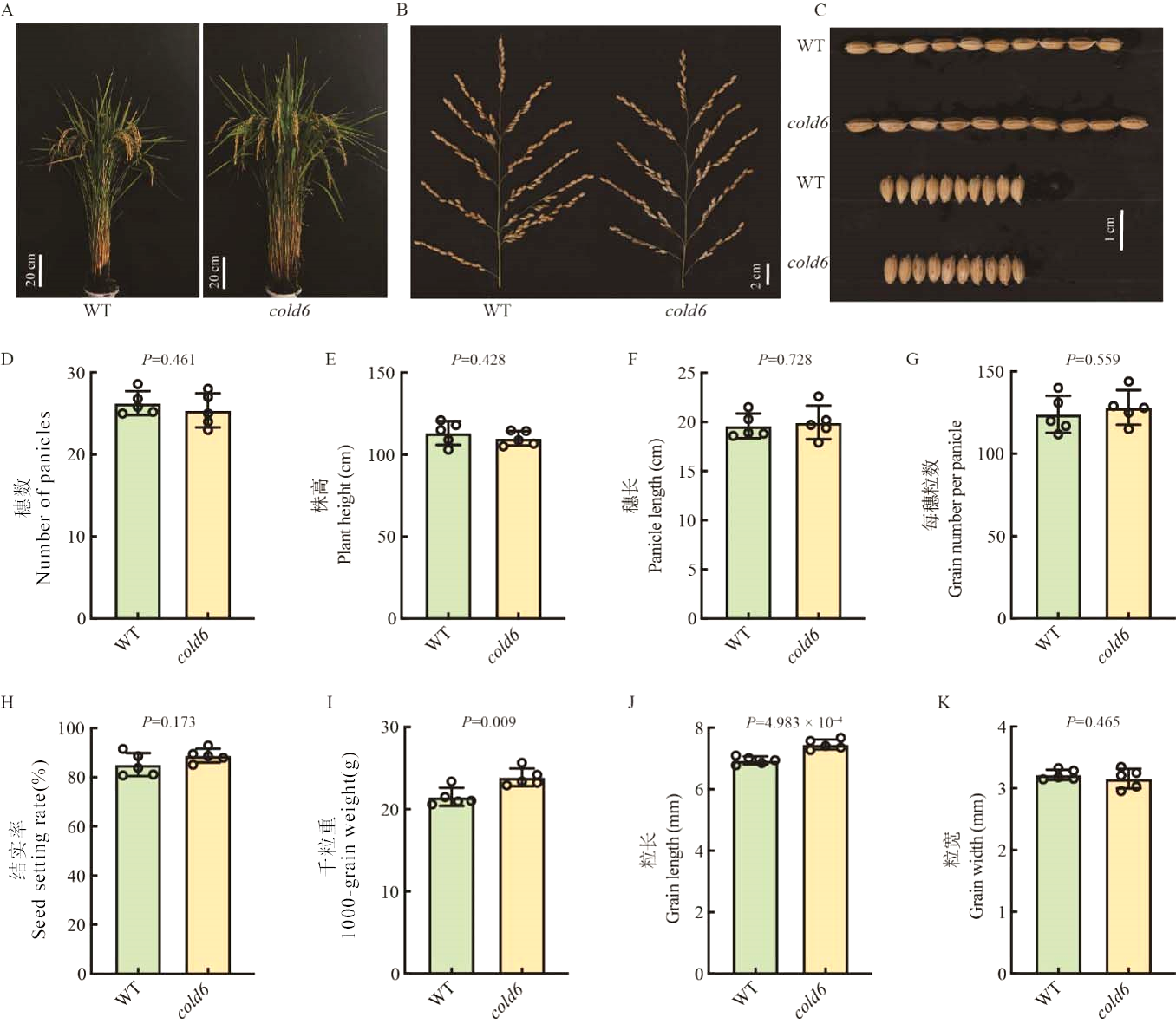
图5 Cold6对水稻主要农艺性状的影响 A:WT和cold6突变体的株型,标尺=20 cm;B:WT和cold6突变体的穗型,标尺=2 cm;C:WT和cold6突变体的粒形,标尺=1 cm;D-K:WT和cold6突变体的穗数、株高、穗长、每穗粒数、结实率、千粒重、粒长和粒宽,数据为平均值±标准差(n=5)。
Fig. 5. Effect of Cold6 on agronomic traits in rice A, Plant architecture of WT and cold6 mutant, scale bar = 20 cm; B, Panicle architecture of WT and cold6 mutant, scale bar = 2 cm; C, Grain shape of WT and cold6 mutant, scale bar = 1 cm; D-K, Number of panicles, plant height, panicle length, grain number per panicle, seed setting rate, 1,000-grain weight, grain length, and grain width of WT and cold6 mutant. Data are mean ± SE (n = 5).
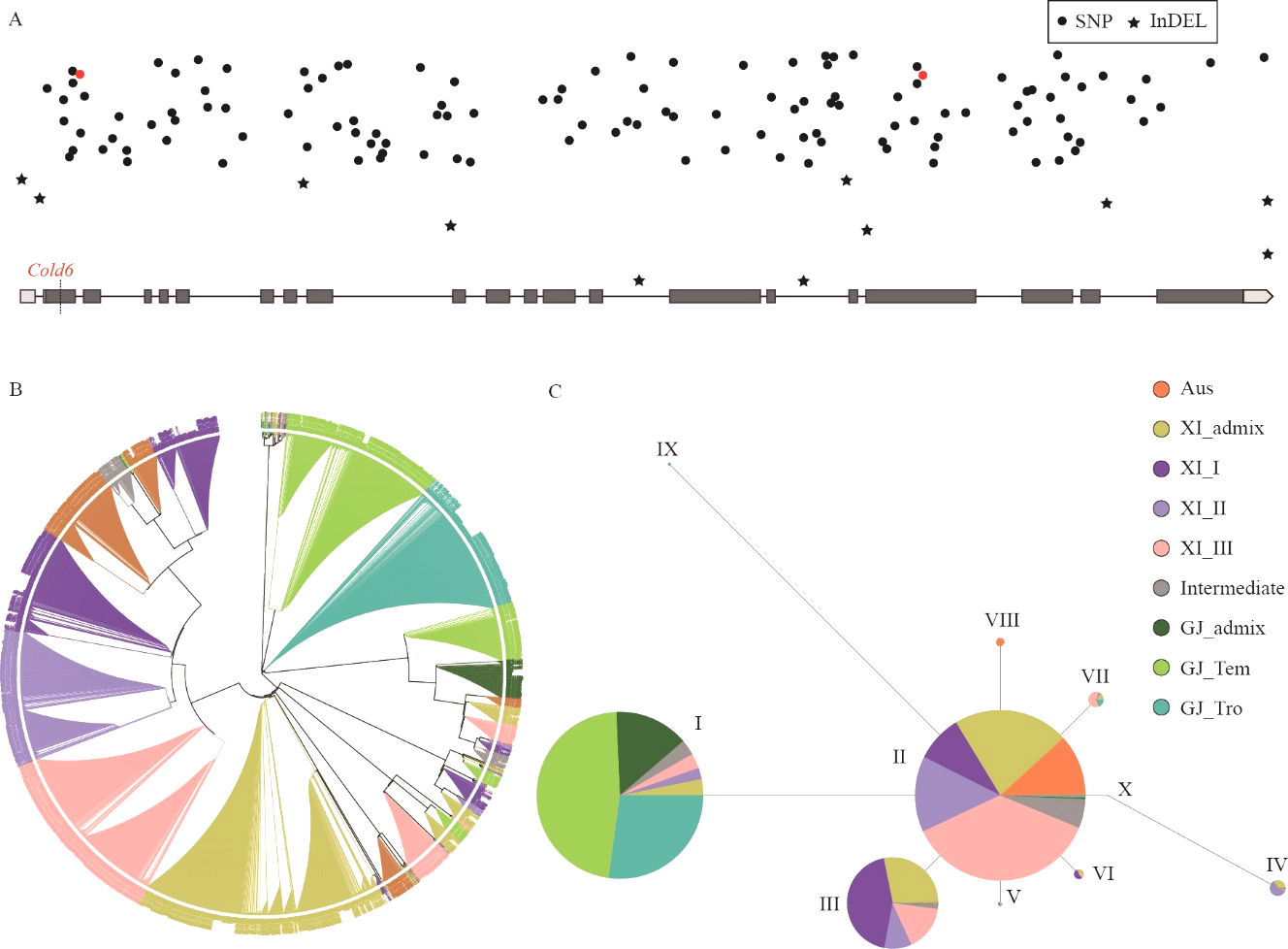
图6 Cold6的进化和单倍型分析 A:Cold6中SNP和InDel的多态性分布,红色为PloyPhen-2预测的可能引起蛋白功能变化的SNP;B:Cold6的进化树分析;C:Cold6的单体型分析。
Fig. 6. Phylogenetic and haplotype analysis of Cold6 A, Distribution of SNP and InDel on Cold6. Red color indicates the SNP causing the change of protein function predicted by PloyPhen-2; B, Phylogenetic analysis of Cold6; C, Haplotype analysis of Cold6.
| [1] | Qian Q. Genomics-assisted germplasm improvement[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2018, 60(2): 82-84. |
| [2] | Zhang Z, Li J, Pan Y, Zhou L, Shi H, Zeng Y, Guo H, Yang S, Zheng W, Yu J, Sun X, Li G, Ding Y, Ma L, Shen S, Dai L, Zhang H, Guo Y, Li Z. Natural variation in CTB4a enhances rice adaptation to cold habitats[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14788. |
| [3] | Lu G, Wu F Q, Wu W, Wang H T, Zheng X M, Zhang Y, Chen X, Zhou K, Jin M, Cheng Z, Li X, Jiang L, Wang H, Wan J. Rice LTG1 is involved in adaptive growth and fitness under low ambient temperature[J]. The Plant Journal, 2014, 78: 468-480. |
| [4] | Liu C T, Wang W, Mao B G, Chu C C. Cold stress tolerance in rice: Physiological changes, molecular mechanism, and future prospects[J]. Yi Chuan, 2018, 40: 171-185. |
| [5] | Yonemaru J I, Yamamoto T, Fukuoka S, Uga Y, Hori K, Yano M J R. Q-TARO: QTL Annotation Rice Online Database[J]. Rice, 2010, 3: 194-203. |
| [6] | Fujino K, Sekiguchi H, Matsuda Y, Sugimoto K, Ono K, Yano M. Molecular identification of a major quantitative trait locus, qLTG3-1, controlling low-temperature germinability in rice [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105: 12623-12628. |
| [7] | Wang X, Zou B, Shao Q, Cui Y, Lu S, Zhang Y, Huang Q, Huang J, Hua J. Natural variation reveals that OsSAP16 controls low-temperature germination in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2018, 69: 413-421. |
| [8] | Ma Y, Dai X, Xu Y, Luo W, Zheng X, Zeng D, Pan Y, Lin X, Liu H, Zhang D. COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice[J]. Cell, 2015, 160: 1209-1221. |
| [9] | Zhao J, Zhang S, Dong J, Yang T, Mao X, Liu Q, Wang X, Liu B. A novel functional gene associated with cold tolerance at the seedling stage in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15: 1141-1148. |
| [10] | Liu C, Schläppi M R, Mao B, Wang W, Wang A, Chu C. The bZIP73 transcription factor controls rice cold tolerance at the reproductive stage[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17: 1834-1849. |
| [11] | Liu C, Ou S, Mao B, Tang J, Wang W, Wang H, Cao S, Schläppi M R, Zhao B, Xiao G, Wang X, Chu C. Early selection of bZIP73 facilitated adaptation of japonica rice to cold climates[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3302. |
| [12] | Mao D, Xin Y, Tan Y, Hu X, Bai J, Liu Z, Yu Y, Li L, Peng C, Fan T, Zhu Y, Guo Y, Wang S, Lu D, Xing Y, Yuan L, Chen C. Natural variation in the HAN1 gene confers chilling tolerance in rice and allowed adaptation to a temperate climate[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116: 3494-3501. |
| [13] | Saito K, Hayano-Saito Y, Kuroki M, Sato Y J P. Map-based cloning of the rice cold tolerance gene Ctb1[J]. Plant Science, 2010, 179: 97-102. |
| [14] | Gu S, Zhang Z, Li J, Sun J, Cui Z, Li F, Zhuang J, Chen W, Su C, Wu L, Wang X, Guo Z, Xu H, Zhao M, Ma D, Chen W. Natural variation in OsSEC13 HOMOLOG 1 modulates redox homeostasis to confer cold tolerance in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2023, 193: 2180-2196. |
| [15] | Wu J, Liu H, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Li D, Liu S, Lu S, Wei L, Hua J, Zou B. A major gene for chilling tolerance variation in indica rice codes for a kinase OsCTK1 that phosphorylates multiple substrates under cold[J]. The New Phytologist, 2024, 242: 2077-2092. |
| [16] | Zu X, Luo L, Wang Z, Gong J, Yang C, Wang Y, Xu C, Qiao X, Deng X, Song X, Chen C, Tan B C, Cao X. A mitochondrial pentatricopeptide repeat protein enhances cold tolerance by modulating mitochondrial superoxide in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 6789. |
| [17] | Zhong Y, Luo Y, Sun J, Qin X, Gan P, Zhou Z, Qian Y, Zhao R, Zhao Z, Cai W, Luo J, Chen L L, Song J M. Pan-transcriptomic analysis reveals alternative splicing control of cold tolerance in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2024, 36: 2117-2139. |
| [18] | Li R, Song Y, Wang X, Zheng C, Liu B, Zhang H, Ke J, Wu X, Wu L, Yang R, Jiang M. OsNAC5 orchestrates OsABI5 to fine-tune cold tolerance in rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2024, 66: 660-682. |
| [19] | Shen Y, Cai X, Wang Y, Li W, Li D, Wu H, Dong W, Jia B, Sun M, Sun X Y. MIR1868 negatively regulates rice cold tolerance at both the seedling and booting stages[J]. The Crop Journal, 2024, 12: 375-383. |
| [20] | Jiang S, Yang C, Xu Q, Wang L, Yang X, Song X, Wang J, Zhang X, Li B, Li H, Li Z, Li W. Genetic dissection of germinability under low temperature by building a resequencing linkage map in japonica rice[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(4): 1284. |
| [21] | Wang Y, Li F, Zhang F, Wu L, Xu N, Sun Q, Chen H, Yu Z, Lu J, Jiang K, Wang X, Wen S, Zhou Y, Zhao H, Jiang Q, Wang J, Jia R, Sun J, Tang L, Xu H, Hu W, Xu Z, Chen W, Guo A, Xu Q. Time-ordering japonica/geng genomes analysis indicates the importance of large structural variants in rice breeding[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2023, 21: 202-218. |
| [22] | Adzhubei I A, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky V E, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov A S, Sunyaev S R. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations[J]. Nature Methods, 2010, 7: 248-249. |
| [23] | Saito K, Miura K, Nagano K, Hayano-Saito Y, Araki H, Kato A. Identification of two closely linked quantitative trait loci for cold tolerance on chromosome 4 of rice and their association with anther length[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2001, 103: 862-868. |
| [24] | Jiang N, Shi S, Shi H, Khanzada H, Wassan G, Zhu C, Peng X, Yu Q, Chen X, He X, Fu J, Hu L, Xu J, Ouyang L, Sun X, Zhou D, He H, Bian J. Mapping QTL for seed germinability under low temperature using a new high-density genetic map of rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1223. |
| [25] | Lee J, Lee W, Kwon S W. A quantitative shotgun proteomics analysis of germinated rice embryos and coleoptiles under low-temperature conditions[J]. Proteome Science, 2015, 13: 27. |
| [26] | Yang L M, Liu H L, Zhao H W, Wang J G, Sun J, Zheng H L, Lei L, Zou D T. Mapping quantitative trait loci and meta-analysis for cold tolerance in rice at booting stage[J]. Euphytica, 2019, 215 (5): 89 |
| [27] | 吴爱婷, 宋佳谕, 胡涛, 刘思彤, 高继平, 黄丽湘, 高银隆, 赵明辉. 超级稻沈农265苗期耐冷性QTL定位[J]. 核农学报, 2018, 32(8): 1477-1482. |
| Wu A T, Song J Y, Hu T, Liu S T, Gao J P, Huang L X, Gao Y L, Zhao M H. QTLs mapping for cold tolerance at seedling stage in super rice variety Shennong 265[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 32(8): 1477-1482. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Hu Y, Zhu N, Wang X, Yi Q, Zhu D, Lai Y, Zhao Y. Analysis of rice Snf2 family proteins and their potential roles in epigenetic regulation[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2013, 70: 33-42. |
| [29] | Hu Y, Liu D, Zhong X, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Zhou D X. CHD3 protein recognizes and regulates methylated histone H3 lysines 4 and 27 over a subset of targets in the rice genome[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109: 5773-5778. |
| [1] | 王娟, 吴丽娟, 洪海波, 姚志文, 王磊, 鄂志国. 水稻泛素结合酶E2的生物学功能研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 744-750. |
| [2] | 陈伟, 叶元妹, 赵剑华, 冯志明, 陈宗祥, 胡珂鸣, 左示敏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术改良南粳46抽穗期[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 760-770. |
| [3] | 侯桂花, 周立国, 雷建国, 陈虹, 聂元元. 水稻OsRDR5基因功能及作用机制初步解析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 779-788. |
| [4] | 陆帅, 陶涛, 刘冉, 周文玉, 曹蕾, 杨青青, 张明秋, 任鑫哲, 杨芝笛, 徐福祥, 环海东, 龚远航, 张皓程, 金素奎, 蔡秀玲, 高继平, 冷语佳. 水稻长护颖小粒突变体lsg8的表型鉴定与基因克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 813-824. |
| [5] | 邓欢, 刘亚培, 王春连, 郭威, 陈析丰, 纪志远. 水稻抗白叶枯病新基因Xa49(t)的定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 825-831. |
| [6] | 郝雯倩, 蔡兴菁, 杨海东, 吴宇阳, 滕轩, 薛超, 龚志云. 不同类型组蛋白修饰在水稻响应非生物胁迫中的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 575-585. |
| [7] | 王镜博, 苏畅, 冯晶, 姜思旭, 徐海, 崔志波, 赵明辉. 水稻OsAlR1基因耐铝性功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 615-623. |
| [8] | 韶也, 胡远艺, 彭彦, 毛毕刚, 刘慧敏, 唐婵娟, 雷斌, 唐丽, 余丽霞, 李文建, 罗武中, 罗治斌, 袁远涛, 李曜魁, 张丹, 周利斌, 柏连阳, 唐文帮, 赵炳然. 基于M1TDS靶向筛选技术的重离子束诱变定向改良杂交水稻卓两优1126性状的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 624-634. |
| [9] | 徐群, 王珊, 袁筱萍, 金石桥, 晋芳, 郝万军, 吴小碧, 冯跃, 余汉勇, 孙燕飞, 杨窑龙, 魏兴华. 用于水稻品种真实性验证的SNP位点评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 635-642. |
| [10] | 张海鹏, 李莞意, 廖福兴, 马美子, 张洪程, 杨艳菊. 纳米钼对水稻根系形态生理和硝态氮吸收的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 650-664. |
| [11] | 刘钰婷, 周星, 何辰延, 李秋萍, 艾小凤, 袁玉洁, 刘睿, 杨景文, 刘婷婷, 王丽, 程红, 黄蓉, 李奥运, 胡文, 胡忠, 任万军, 邓飞. 不同光照条件下减穴稳苗配置对水稻茎鞘干物质积累转运特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 665-678. |
| [12] | 杨行洲, 崔苗苗, 魏利辉, 顾爱国, 李东霞, 乐秀虎, 冯辉. 外源miR3979处理水稻对拟禾本科根结线虫趋性、侵染和发育的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 703-710. |
| [13] | 朱鹏, 凌溪铁, 王金彦, 张保龙, 杨郁文, 许轲, 裘实. 机直播条件下不同控草方式对抗除草剂水稻产量和品质差异性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 501-515. |
| [14] | 董立强, 张义凯, 杨铁鑫, 冯莹莹, 马亮, 梁潇, 张玉屏, 李跃东. 北方粳稻密苗机插育秧对秧苗素质及取秧特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 516-528. |
| [15] | 周洋, 叶凡, 刘立军. 典型促生微生物提高盐胁迫水稻抗性的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 529-542. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||