
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 779-788.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.250208
侯桂花1, 周立国2, 雷建国1, 陈虹1, 聂元元1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-24
修回日期:2025-03-28
出版日期:2025-11-10
发布日期:2025-11-19
通讯作者:
* email:happynyy@163.com
基金资助:
HOU Guihua1, ZHOU Liguo2, LEI Jianguo1, CHEN Hong1, NIE Yuanyuan1,*( )
)
Received:2025-02-24
Revised:2025-03-28
Online:2025-11-10
Published:2025-11-19
Contact:
* email:happynyy@163.com
摘要:
【目的】干旱是影响水稻生产的重要因素,避旱性是作物抗旱最重要的机制。研究水稻避旱性候选基因OsRDR5的作用机制,可以为水稻避旱性的改良提供理论依据。【方法】利用NCBI数据库对OsRDR5核酸序列、蛋白结构域和系统进化关系进行分析;采用qRT-PCR进行组织表达模式分析;通过CRISPR/Cas9系统构建OsRDR5基因敲除突变体;采用“篮子法”评价OsRDR5对水稻深根比的影响。【结果】OsRDR5具有一个Coa3_cc结构域,属于细胞色素c氧化酶组装因子3基因家族,定位于内质网,在水稻根、茎、叶等主要组织中均有表达。深根比表型鉴定发现,野生型深根比为53.7%,突变体株系深根比分别为63.3%和64.9%,显著高于野生型。根系转录组分析共鉴定到1434个差异表达基因。GO富集分析表明,这些基因显著富集到响应缺水、脱落酸、活性氧等与干旱胁迫相关的通路。在缺水通路中,多个与干旱胁迫相关的NAC基因(OsNAC016、OsNAC45等)上调表达。【结论】OsRDR5基因敲除影响了水稻深根比,在水稻避旱性中发挥重要作用。
侯桂花, 周立国, 雷建国, 陈虹, 聂元元. 水稻OsRDR5基因功能及作用机制初步解析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 779-788.
HOU Guihua, ZHOU Liguo, LEI Jianguo, CHEN Hong, NIE Yuanyuan. Preliminary Analysis of Function and Mechanism of OsRDR5 Gene in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 779-788.
| 用途 Purpose | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene cloning | OsRDR5-1F | ATGGACGACGACGACCATG |
| OsRDR5-1R | TTAGGATCCCGCGGTGGA | |
| 转基因鉴定 Identification of transgenes | OsRDR5-2F | TATGTTTGTCCGCCCCTCTG |
| OsRDR5-2R | GAGAGAGTGGGGTGGAGGAA | |
| 组织表达模式分析 Analysis of tissue expression patterns | OsRDR5-qRT-3F | CCCTCTATACTGAACCGATGAC |
| OsRDR5-qRT-3R | TAAAACTGCAATCCAACTCTGC | |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | OsRDR5-4F | ATGGACGACGACGACCATGACC |
| OsRDR5-4R | AGATCCTCCTCCAGATCCTCCTC | |
| 内参基因Actin1 Reference gene Actin1 | Actin1-F | CATCTATGAAGGATATGCTCTC |
| Actin1-R | CCGTTGTGGTGAATGAGT | |
| LOC_Os01g01430 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | TACTGCTGGGCGTGAAGAAG |
| qRT-R | GCGTCTGCGGCTCAAATATG | |
| LOC_Os03g04070 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | AGTGGTACTTCTTCGTGCCG |
| qRT-R | CGTGACGTCTGCTTCTTCCT | |
| LOC_Os11g03370 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | TATGGAGGCAGCAGCAACAA |
| qRT-R | AGCTACAGGAGGAGGTGGAG | |
| LOC_Os08g37370 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | GAAGTGGACCCAGGAGAACG |
| qRT-R | ATGAACCCCTTGTACAGCGC | |
| LOC_Os11g05614 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | ATCTCCTCCGCCACAAACAG |
| qRT-R | GCCATGATCCGACGATGCTA | |
| LOC_Os01g64310 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | ATTCACCACGAGATGCTGGG |
| qRT-R | GCCACCTTGATCCATCAGCT | |
| LOC_Os02g26720 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | CCTCCAGGAGTTCGTCAACC |
| qRT-R | TTAGACCGATACCCAGCCCA |
表1 本研究使用的引物
Table 1. Primers used in this study
| 用途 Purpose | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene cloning | OsRDR5-1F | ATGGACGACGACGACCATG |
| OsRDR5-1R | TTAGGATCCCGCGGTGGA | |
| 转基因鉴定 Identification of transgenes | OsRDR5-2F | TATGTTTGTCCGCCCCTCTG |
| OsRDR5-2R | GAGAGAGTGGGGTGGAGGAA | |
| 组织表达模式分析 Analysis of tissue expression patterns | OsRDR5-qRT-3F | CCCTCTATACTGAACCGATGAC |
| OsRDR5-qRT-3R | TAAAACTGCAATCCAACTCTGC | |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | OsRDR5-4F | ATGGACGACGACGACCATGACC |
| OsRDR5-4R | AGATCCTCCTCCAGATCCTCCTC | |
| 内参基因Actin1 Reference gene Actin1 | Actin1-F | CATCTATGAAGGATATGCTCTC |
| Actin1-R | CCGTTGTGGTGAATGAGT | |
| LOC_Os01g01430 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | TACTGCTGGGCGTGAAGAAG |
| qRT-R | GCGTCTGCGGCTCAAATATG | |
| LOC_Os03g04070 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | AGTGGTACTTCTTCGTGCCG |
| qRT-R | CGTGACGTCTGCTTCTTCCT | |
| LOC_Os11g03370 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | TATGGAGGCAGCAGCAACAA |
| qRT-R | AGCTACAGGAGGAGGTGGAG | |
| LOC_Os08g37370 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | GAAGTGGACCCAGGAGAACG |
| qRT-R | ATGAACCCCTTGTACAGCGC | |
| LOC_Os11g05614 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | ATCTCCTCCGCCACAAACAG |
| qRT-R | GCCATGATCCGACGATGCTA | |
| LOC_Os01g64310 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | ATTCACCACGAGATGCTGGG |
| qRT-R | GCCACCTTGATCCATCAGCT | |
| LOC_Os02g26720 qRT-PCR | qRT-F | CCTCCAGGAGTTCGTCAACC |
| qRT-R | TTAGACCGATACCCAGCCCA |

图2 OsRDR5基因结构域分析 粉红色方块代表单跨膜区;蓝色方块代表结构域。
Fig. 2. Analysis of the domain of OsRDR5 gene Pink squares indicate single transmembrane regions; Blue squares indicate domains.

图3 RDR5同源蛋白的氨基酸序列多重比对 粳稻:Oryza_sativa_Japonica;大麦:Hordeum_vulgare;画眉草:Eragrostis_curvula;柳枝稷:Panicum_virgatum;黍: Panicum_miliaceum;乌拉尔图小麦:Triticum_urartu;白福尼奥米:Digitaria_exilis;芦苇:Phragmites_australis;穇子: Eleusine_coracana_subsp._coracana ;谷子: Setaria_italica;玉米:Zea_mays;扫帚黍:Dichanthelium_oligosanthes。
Fig. 3. Multiple alignment of amino acid sequences of RDR5 homologous proteins
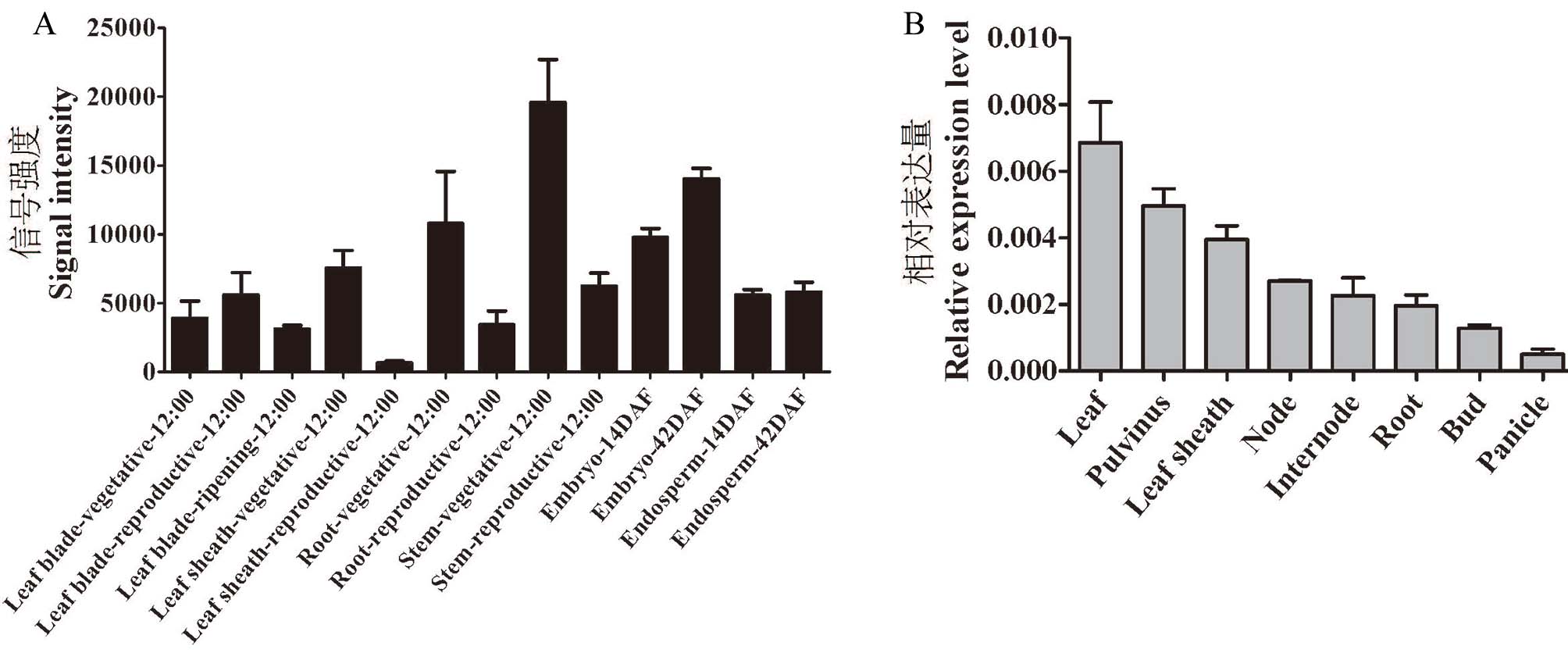
图5 OsRDR5 的组织表达模式 A:OsRDR5芯片数据表达量;OsRDR5基因信号强度:Signal intensity;营养生长期:Vegetative;生殖生长期:Reproductive;成熟期:Ripening;叶片:Leaf blade;叶鞘:Leaf sheath;根:Root;茎:Stem;胚:Embryo;胚乳:Endosperm;14DAF、42DAF分别代表发育14 d 和42 d的胚和胚乳;12:00表示组织取样时间;B:以Actin1作为内参基因,数值为含标准误差的平均值,3次生物学重复。
Fig. 5. Tissue-specific expression of OsRDR5 A, OsRDR5 chip data expression level; Signal intensity, OsRDR5 gene signal intensity; Vegetative, Vegetative growth period; Reproductive, Reproductive growth period; Ripening, Ripening period; 14DAF and 42DAF represent embryos and endosperms after 14 days and 42 days of development, respectively; 12:00 indicates tissue sampling time; B, Actin1 gene was used as an internal control. Values are means±SE, n = 3.

图6 OsRDR5的亚细胞定位分析 从左到右依次为荧光通道、标记通道、可见光通道、叠加图像;eGFP:RDR5-eGFP绿色荧光蛋白;ER:内质网, ER marker:SPER-mKATE红色荧光蛋白;Bright field:可见光通道;Merged:叠加图像;比例尺=10 μm。
Fig. 6. Subcellular localization of OsRDR5 From left to right, the fluorescence channel, marker channel, bright field and overlay images are shown; eGFP, RDR5-eGFP green fluorescent protein; ER, Endoplasmic reticulum; ER marker, SPER-mKATE red fluorescent protein; Bright field, Photographs captured under bright lighting conditions; Merged, An image of the superposition of three channels: eGFP, ER marker and Bright field; Scale bar =10 μm.

图7 OsRDR5基因序列分析 A:OsRDR5基因结构及突变位点分析。OsRDR5基因序列中黑色线条代表内含子,黑色条块代表外显子,黑色线条框代表UTR;WT为野生型,rdr5-1和rdr5-2为两个突变体;显示的序列均为靶位点及PAM位点;突变体序列中红色横线表示碱基缺失;B:蛋白质序列比对分析。WT编码185个氨基酸,rdr5-1编码35个氨基酸,rdr5-2编码24个氨基酸,完全相同的氨基酸用蓝色阴影表示。
Fig. 7. Sequence analysis of OsRDR5 gene A, Analysis of OsRDR5 gene structure and mutation sites. In the OsRDR5 gene sequence, black lines indicate introns, black blocks indicate exons, and black boxes indicate UTRs; WT was the wild type, rdr5-1 and rdr5-2 were two mutants; All the sequences displayed were the target sites and PAM sites; Red horizontal lines in the mutant sequence indicate base deletions; B, Protein sequence alignment analysis. WT encodes 185 amino acids, rdr5-1 encodes 35 amino acids, and rdr5-2 encodes 24 amino acids. Identical amino acids are shaded in blue.
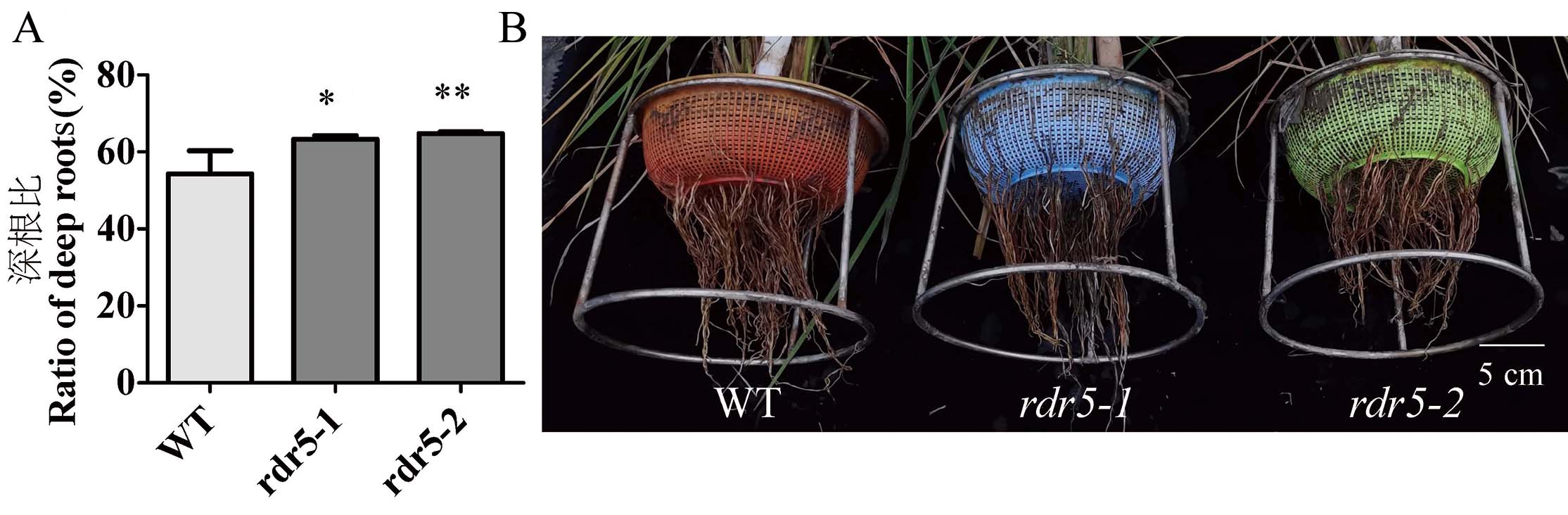

图8 WT和rdr5突变体的深根比
Fig. 8. Ratios of deep rooting of WT and rdr5 mutants A, Deep root ratio and root distribution map of WT and rdr5 lines. The deep root ratio = Number of deep roots/total number of roots; Data are shown as mean ± SD, (n = 12); *,** indicate significance at levels of 0.05, 0.01 by independent t-test, respectively.

图9 WT和rdr5突变体根系转录组分析 A:差异基因设置条件:P ≤ 0.05 和 |log2FC| ≥ 1;红色代表上调基因,蓝色代表下调基因;B:差异表达基因的qRT-PCR验证分析;rdr5-1和rdr5-2株系的qRT-PCR和RNA-Seq数值均以WT为校验标准,其中转录组测序数据计算公式为rdr5-1(FC)=rdr5-1(FPKM)/WT(FPKM), rdr5-2(FC)=rdr5-2(FPKM)/WT(FPKM);C:GO富集分析;D:KEGG富集分析。横坐标代表相应条目中基因占该条目所有基因的比例,纵坐标代表不同的基因功能条目;圆圈大小代表富集在相应条目中的基因数目,圆圈越大,代表富集在该通路中的基因越多;颜色代表富集显著性,圆圈表示该基因功能既关联到上调基因,也关联到下调基因,上三角形表示仅关联到上调基因,下三角形表示仅关联到下调基因,颜色代表富集显著性。
Fig. 9. Transcriptome analysis of WT and rdr5 mutant roots A, Differentially expressed genes: P≤0.05 and |log2FC|≥1; Red represents up-regulated genes and blue represents down-regulated genes; B, qRT-PCR verification analysis of differentially expressed genes; The qRT-PCR and RNA-Seq values of the rdr5-1 and rdr5-2 lines were measured using WT as the calibration standard, where the transcriptome sequencing data were calculated using the formula: rdr5-1(FC)=rdr5-1(FPKM)/WT(FPKM), rdr5-2(FC)=rdr5-2(FPKM)/WT(FPKM); C, GO enrichment analysis; D, KEGG enrichment analysis. The abscissa represents the proportion of genes in the corresponding item in all genes of the item, and the ordinate represents different gene function items; The size of the circle represents the number of genes enriched in the corresponding entry, and the larger the circle, the more genes enriched in the pathway; The color represents enrichment significance, the circle indicates that the gene function is associated with both up-regulated and down-regulated genes, the upper triangle indicates that it is only associated with up-regulated genes, the lower triangle indicates that it is only associated with down-regulated genes, and the color represents enrichment significance.
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因符号 Gene symbol | 表达量差异倍数 log2FC | P值 P-value | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os01g01430 | OsNAC016 | 1.20 | 0.031 | 负调控水稻抗旱性Negative regulation of rice drought resistance |
| LOC_Os03g04070 | ONAC022 | 1.40 | 0.0002 | 正调控水稻抗旱性Positive regulation of rice drought resistance |
| LOC_Os11g03370 | OsNAC45 | 1.10 | 9.26E-06 | 正调控水稻抗旱性Positive regulation of rice drought resistance |
| LOC_Os01g64310 | ENAC1 | 3.32 | 1.87E-12 | 干旱诱导表达基因Drought-induced expression gene |
表2 响应干旱胁迫的差异表达基因
Table 2. Differentially expressed genes in response to drought stress
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因符号 Gene symbol | 表达量差异倍数 log2FC | P值 P-value | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os01g01430 | OsNAC016 | 1.20 | 0.031 | 负调控水稻抗旱性Negative regulation of rice drought resistance |
| LOC_Os03g04070 | ONAC022 | 1.40 | 0.0002 | 正调控水稻抗旱性Positive regulation of rice drought resistance |
| LOC_Os11g03370 | OsNAC45 | 1.10 | 9.26E-06 | 正调控水稻抗旱性Positive regulation of rice drought resistance |
| LOC_Os01g64310 | ENAC1 | 3.32 | 1.87E-12 | 干旱诱导表达基因Drought-induced expression gene |
| [1] | Luo L J. Breeding for water-saving and drought-resistance rice (WDR) in China[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010, 61(13): 3509-3517. |
| [2] | Pandey V, Shukla A. Acclimation and tolerance strategies of rice under drought stress[J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(4): 147-161. |
| [3] | Gupta A, Rico-Medina A, Canõ-Delgado A I. The physiology of plant responses to drought[J]. Science, 2020, 368: 266-269. |
| [4] | 罗利军. 水旱稻分化与节水抗旱稻[J]. 自然杂志, 2022, 44(5): 339-346. |
| Luo L J. Differentiation of lowland-upland rice and development of water-saving and drought-resistant rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2022, 44(5): 339-346. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Farooq M, Wahid A, Lee D J, Ito O, Siddique K H M. Advances in drought resistance of rice[J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2009, 28: 199-217. |
| [6] | Henry A, Cal A J, Batoto T C, Torres R O, Serraj R. Root attributes affecting water uptake of rice (Oryza sativa) under drought[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63: 4751-4763. |
| [7] | Kim Y, Chung Y S, Lee E, Tripathi P, Heo S, Kim K H. Root response to drought stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21: 1513. |
| [8] | Chen Y, Shen J, Zhang L, Qi H Y, Yang L J, Wang H Y, Wang J X, Wang Y X, Du H, Tao Z, Zhao T, Deng P C, Shu Q Y, Qian Q, Yu H, Song S Y. Nuclear translocation of OsMFT1 that is impeded by OsFTIP1 promotes drought tolerance in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14: 1297-1311. |
| [9] | Kong X Z, Yu S H, Xiong Y L, Song X Y, Nevescanin-Moreno L, Wei X Q, Rao J L, Zhou H, Bennett M J, Pandey B K, Huang G Q. Root hairs facilitate rice root penetration into compacted layers[J]. Current Biology, 2024, 34: 2039-2048. |
| [10] | Han S C, Wang Y L, Li Y X, Zhu R, Gu Y S, Li J, Guo H F, Ye W, Nabi H G, Yang T, Wang Y M, Liu P L, Duan J Z, Sun X M, Zhang Z Y, Zhang H L, Li Z C, Li J J. The OsNAC41-RoLe1-OsAGAP module promotes root development and drought resistance in upland rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2024, 17: 1573-1593. |
| [11] | O’Toole J C, Bland W L. Genotypic variation in crop plant root systems[J]. Advances in Agronomy, 1987, 41: 91-145. |
| [12] | Kato Y, Abe J, Kamoshita A, Yamagishi J. Genotypic variation in root growth angle in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and its association with deep root development in upland fields with different water regimes[J]. Plant Soil, 2006, 287: 117-129. |
| [13] | Uga Y, Okuno K, Yano M. Dro1, a major QTL involved in deep rooting of rice under upland field conditions[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62: 2485-2494. |
| [14] | Uga Y, Sugimoto K, Ogawa S, Rane J, Ishitani M, Hara N, Kitomi Y, Inukai Y, Ono K, Kanno N, Inoue H, Takehisa H, Motoyama R, Nagamura Y, Wu J, Matsumoto T, Takai T, Okuno K, Yano M. Control of root system architecture by DEEPER ROOTING 1 increases rice yield under drought conditions[J]. Nature Genetics, 2013, 45: 1097-1102. |
| [15] | Kitomi Y, Kanno N, Kawai S, Mizubayashi T, Fukuoka S, Uga Y. QTLs underlying natural variation of root growth angle among rice cultivars with the same functional allele of DEEPER ROOTING 1[J]. Rice, 2015, 8: 16. |
| [16] | Uddin N, Fukuta Y. A region on chromosome 7 related to differentiation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) between lowland and upland ecotypes[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 1135. |
| [17] | Lou Q J, Chen L, Mei H W, Wei H B, Feng F J, Wang P, Xia H, Li T F, Luo L J. Quantitative trait locus mapping of deep rooting by linkage and association analysis in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66: 4749-4757. |
| [18] | Lou Q J, Chen L, Mei H W, Xu K, Wei H B, Feng F J, Li T F, Pang X, Shi C, Luo L J, Zhong Y. Root transcriptomic analysis revealing the importance of energy metabolism to the development of deep roots in rice (Oryza sativa L)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1314. |
| [19] | Xu K, Lou Q J, Wang D, Li T M, Chen S J, Li T F, Luo L J, Chen L. Overexpression of a novel small auxin-up RNA gene, OsSAUR11, enhances rice deep rootedness[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2023, 23: 319. |
| [20] | Zhou L G, Liu Z C, Liu Y H, Kong D Y, Li T F, Yu S W, Mei H W, Xu X Y, Liu H Y, Chen L, Luo L J. A novel gene OsAHL1 improves both drought avoidance and drought tolerance in rice[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 30264. |
| [21] | 聂元元. 东乡野生稻遗传多样性评价与避旱优异基因资源挖掘[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2022. |
| Nie Y Y. Evaluation of genetic diversity and mining of excellent drought avoidance genes in Dongxiang wild rice[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Ma X, Zhang Q, Zhu Q, Liu W, Chen Y, Qiu R, Wang B, Yang Z, Li H, Lin Y, Xie Y, Shen R, Chen S, Wang Z, Chen Y, Guo J, Chen L, Zhao X, Dong Z, Liu Y G. A robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(8): 1274-1284. |
| [23] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method[J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [24] | Peralta S, Clemente P, Sánchez-Martínez A, Calleja m, Hernández-Sierra R, Matsushima Y, Adán C, Ugalde C, Fernández-Moreno M A, Kaguni L S. Coiled coil domain-containing protein 56 (CCDC56) is a novel mitochondrial protein essential for cytochrome c oxidase function[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2012, 287(29): 24174-24185. |
| [25] | Wikström M, Krab K, Sharma V. Oxygen activation and energy conservation by cytochrome c oxidase[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(5): 2469-2490. |
| [26] | Kadenbach B, Hüttemann M. The subunit composition and function of mammalian cytochrome c oxidase[J]. Mitochondrion, 2015, 24: 64-76. |
| [27] | Kondo M, Pablico P P, Aragones D V, Agbisit R, Abe J, Morita S, Courtois B. Genotypic and environmental variations in root morphology in rice genotypes under upland field conditions[J]. Plant and Soil, 2003, 255: 189-200. |
| [28] | 谢建坤, 胡标林, 万勇, 张弢, 李霞, 刘如龙, 黄运红, 戴亮芳, 罗向东. 东乡普通野生稻与栽培稻苗期抗旱性的比较[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(06). |
| Xie J K, Hu B L, Wan Y, Zhang T, Li X, Liu R L, Huang Y H, Dai L F, Luo X D. Comparison of drought resistance between common wild rice and cultivated rice at seedling stage in Dongxiang[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(06). (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Zhou S X, Tian F, Zhu Z F, Fu Y C, Wang X K, Sun C Q. Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling drought tolerance at seedling stage in Chinese Dongxiang common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.)[J]. Acta Genetica Sinica, 2006, 33(6): 551-8. |
| [30] | Zhang F T, Cui F L, Zhang L X, Wen X F, Luo X D, Zhou Y, Li X, Wan Y, Zhang J, Xie J K. Development and identification of a introgression line with strong drought resistance at seedling stage derived from Oryza sativa L. mating with Oryza rufipogon Griff[J]. Euphytica, 2014, 200(1): 1-7. |
| [31] | 王会民, 唐秀英, 龙起樟, 黄永兰, 芦明, 万建林. 一个东乡野生稻苗期耐旱主效QTL-qDR7的分离鉴定[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(5): 1569-1577. |
| Wang H M, Tang X Y, Long Q Z, Huang Y L, Lu M, Wan J L. Isolation and identification of a major drought tolerance QTL-qDR7 in Dongxiang wild rice at seedling stage[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(5): 1569-1577. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Uga Y Yamamoto, Kanno N, Kawai S, Mizubayashi T, Fukuoka S. A major QTL controlling deep rooting on rice chromosome 4[J]. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3: 3040. |
| [1] | 王娟, 吴丽娟, 洪海波, 姚志文, 王磊, 鄂志国. 水稻泛素结合酶E2的生物学功能研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 744-750. |
| [2] | 陶士博, 许娜, 徐正进, 刘畅, 徐铨. 水稻发芽期耐冷基因Cold6的克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 751-759. |
| [3] | 陈伟, 叶元妹, 赵剑华, 冯志明, 陈宗祥, 胡珂鸣, 左示敏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术改良南粳46抽穗期[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 760-770. |
| [4] | 陆帅, 陶涛, 刘冉, 周文玉, 曹蕾, 杨青青, 张明秋, 任鑫哲, 杨芝笛, 徐福祥, 环海东, 龚远航, 张皓程, 金素奎, 蔡秀玲, 高继平, 冷语佳. 水稻长护颖小粒突变体lsg8的表型鉴定与基因克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 813-824. |
| [5] | 邓欢, 刘亚培, 王春连, 郭威, 陈析丰, 纪志远. 水稻抗白叶枯病新基因Xa49(t)的定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 825-831. |
| [6] | 郝雯倩, 蔡兴菁, 杨海东, 吴宇阳, 滕轩, 薛超, 龚志云. 不同类型组蛋白修饰在水稻响应非生物胁迫中的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 575-585. |
| [7] | 王镜博, 苏畅, 冯晶, 姜思旭, 徐海, 崔志波, 赵明辉. 水稻OsAlR1基因耐铝性功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 615-623. |
| [8] | 韶也, 胡远艺, 彭彦, 毛毕刚, 刘慧敏, 唐婵娟, 雷斌, 唐丽, 余丽霞, 李文建, 罗武中, 罗治斌, 袁远涛, 李曜魁, 张丹, 周利斌, 柏连阳, 唐文帮, 赵炳然. 基于M1TDS靶向筛选技术的重离子束诱变定向改良杂交水稻卓两优1126性状的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 624-634. |
| [9] | 徐群, 王珊, 袁筱萍, 金石桥, 晋芳, 郝万军, 吴小碧, 冯跃, 余汉勇, 孙燕飞, 杨窑龙, 魏兴华. 用于水稻品种真实性验证的SNP位点评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 635-642. |
| [10] | 张海鹏, 李莞意, 廖福兴, 马美子, 张洪程, 杨艳菊. 纳米钼对水稻根系形态生理和硝态氮吸收的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 650-664. |
| [11] | 刘钰婷, 周星, 何辰延, 李秋萍, 艾小凤, 袁玉洁, 刘睿, 杨景文, 刘婷婷, 王丽, 程红, 黄蓉, 李奥运, 胡文, 胡忠, 任万军, 邓飞. 不同光照条件下减穴稳苗配置对水稻茎鞘干物质积累转运特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 665-678. |
| [12] | 杨行洲, 崔苗苗, 魏利辉, 顾爱国, 李东霞, 乐秀虎, 冯辉. 外源miR3979处理水稻对拟禾本科根结线虫趋性、侵染和发育的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 703-710. |
| [13] | 朱鹏, 凌溪铁, 王金彦, 张保龙, 杨郁文, 许轲, 裘实. 机直播条件下不同控草方式对抗除草剂水稻产量和品质差异性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 501-515. |
| [14] | 董立强, 张义凯, 杨铁鑫, 冯莹莹, 马亮, 梁潇, 张玉屏, 李跃东. 北方粳稻密苗机插育秧对秧苗素质及取秧特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 516-528. |
| [15] | 周洋, 叶凡, 刘立军. 典型促生微生物提高盐胁迫水稻抗性的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 529-542. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||