
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (6): 595-605.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.200820
孙园园1,2,#, 张桥1,#, 孙永健1,*( ), 唐源1, 郭长春1, 刘芳艳1, 武云霞1, 杨志远1, 马均1
), 唐源1, 郭长春1, 刘芳艳1, 武云霞1, 杨志远1, 马均1
收稿日期:2020-08-28
修回日期:2021-03-30
出版日期:2021-11-10
发布日期:2021-11-10
通讯作者:
孙永健
基金资助:
Yuanyuan SUN1,2,#, Qiao ZHANG1,#, Yongjian SUN1,*( ), Yuan TANG1, Changchun GUO1, Fangyan LIU1, Yunxia WU1, Zhiyuan YANG1, jun MA1
), Yuan TANG1, Changchun GUO1, Fangyan LIU1, Yunxia WU1, Zhiyuan YANG1, jun MA1
Received:2020-08-28
Revised:2021-03-30
Online:2021-11-10
Published:2021-11-10
Contact:
Yongjian SUN
摘要:
【目的】氮素的吸收利用决定着水稻物质积累和产量的形成。随着农村劳动力的减少,机插稻迅速发展, 但针对机插稻育秧环节与插秧机具融合对机插稻氮素吸收利用特征影响的研究较少。以机插稻农机农艺首要融合点“育秧-机插”关键环节为研究对象,探究育秧方式配合不同插秧机具对机插稻氮素吸收利用的影响。【方法】以杂交籼稻F优498为试验材料,采用三因素随机区组试验,设置2种育秧方式:营养土育秧和稀泥育秧;3个播种量:65 g/盘,85 g/盘,105 g/盘;2种插秧机具:4行手扶式插秧机,6行乘坐式高速插秧机。【结果】育秧方式、播种量以及插秧机具对机插稻结实期不同营养器官氮素吸收转运、剑叶SPAD值以及氮素收获指数、氮素稻谷生产效率与产量影响显著或极显著,且互作效应显著或极显著。营养土育秧处理下机插稻氮素积累以及氮素利用效率较稀泥育秧优势明显,植株各器官氮素转运量、转运率、贡献率以及穗部氮素增加量均一定程度高于稀泥育秧处理,平均提高了21.12%、15.20%、10.03%、6.45%;随着播种量的增加,机插稻稻谷产量、结实期氮素吸收转运量、氮素干物质生产效率以及氮肥偏生产力呈先上升后下降的趋势,尤其播种量为85 g/盘时机插稻成熟期植株中氮素的积累量相较于65 g/盘、105 g/盘播量平均增加了16.19%,28.14%;6行乘坐式高速插秧机处理下机插稻产量以及构成因素、结实期干物质量、植株氮素吸收量和转运量、氮干物质生产效率以及氮肥偏生产力显著高于4行手扶式插秧机。【结论】综合氮素积累量和氮素转运量、机插稻结实期穗部氮素积累量、产量及其构成因素考虑,运用营养土育秧,播量85 g/盘配合6行乘坐式高速插秧机能有效提高机插稻氮素吸收利用,促进产量的形成。
孙园园, 张桥, 孙永健, 唐源, 郭长春, 刘芳艳, 武云霞, 杨志远, 马均. 不同育秧方式下播种量和插秧机具对机插稻氮素利用和产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 595-605.
Yuanyuan SUN, Qiao ZHANG, Yongjian SUN, Yuan TANG, Changchun GUO, Fangyan LIU, Yunxia WU, Zhiyuan YANG, jun MA. Effects of Seeding Quantity and Transplanting Machine Type on Nitrogen Utilization and Yield of Mechanically transplanted Rice in Different Seedling Raising Ways[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(6): 595-605.
| 年份 Year | 全氮 Total N/(g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | pH值 pH value | 速效养分 Available nutrient/(mg·kg-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | ||||
| 2018 | 2.16 | 24.9 | 4.62 | 101.3 | 57.9 | 102.5 |
| 2019 | 2.08 | 23.8 | 4.65 | 94.8 | 46.3 | 100.1 |
表1 试验田耕层土壤(0–20 cm)理化性状
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of soil (0-20 cm) in the experiments.
| 年份 Year | 全氮 Total N/(g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | pH值 pH value | 速效养分 Available nutrient/(mg·kg-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | ||||
| 2018 | 2.16 | 24.9 | 4.62 | 101.3 | 57.9 | 102.5 |
| 2019 | 2.08 | 23.8 | 4.65 | 94.8 | 46.3 | 100.1 |
| 年份 Year | 育秧方式 Seedling raising mode | 播种日期(月-日) Sowing date (Month-Day) | 移栽日期(月-日) Transplanting date (Month-Day) | 生育时期(月-日) Growth stage (Month-Day) 齐穗期 成熟期 Full heading stage Maturity stage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 营养土育秧 Seedling raised by nutrient soil | 04-04 | 05-04 | 07-22 | 09-02 |
| 稀泥育秧 Slime-raised seedling | 04-04 | 05-04 | 07-22 | 09-02 | |
| 2019 | 营养土育秧 Seedling raised by nutrient soil | 04-06 | 05-07 | 07-25 | 09-03 |
| 稀泥育秧 Slime-raised seedling | 04-06 | 05-07 | 07-25 | 09-03 | |
表2 不同育秧方式水稻主要生育时期
Table 2 Main growth periods of rice seedlings raised by different ways.
| 年份 Year | 育秧方式 Seedling raising mode | 播种日期(月-日) Sowing date (Month-Day) | 移栽日期(月-日) Transplanting date (Month-Day) | 生育时期(月-日) Growth stage (Month-Day) 齐穗期 成熟期 Full heading stage Maturity stage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 营养土育秧 Seedling raised by nutrient soil | 04-04 | 05-04 | 07-22 | 09-02 |
| 稀泥育秧 Slime-raised seedling | 04-04 | 05-04 | 07-22 | 09-02 | |
| 2019 | 营养土育秧 Seedling raised by nutrient soil | 04-06 | 05-07 | 07-25 | 09-03 |
| 稀泥育秧 Slime-raised seedling | 04-06 | 05-07 | 07-25 | 09-03 | |
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising ways | 插秧机具 Transplanting machine | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number /(×104·hm-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 总颖花数 Total spikelet number /(×106·hm-2) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 稻谷产量 Grain yield/(kg·hm-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | ||||||||||
| 营养土育秧(A1) Raised by nutrient soil | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 184.44 d | 192.30 c | 354.33 e | 31.11 a | 89.03 a | 11 001.2 c | 10 040.5 d | ||
| C2 | 192.61 b | 196.87 a | 378.81 b | 30.76 a | 88.84 a | 11 115.8 bc | 10 833.6 b | ||||
| C3 | 178.85 e | 191.47 c | 342.46 f | 30.67 a | 88.57 a | 9 909.9 d | 9 856.8 d | ||||
| 平均 Average | 185.30 | 193.55 | 358.53 | 30.85 | 88.81 | 10 675.6 | 10 243.6 | ||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 191.51 bc | 190.36 d | 364.57 c | 31.29 a | 89.64 a | 11 512.5 ab | 10 359.0 c | |||
| C2 | 204.62 a | 194.84 b | 398.68 a | 30.88 a | 88.74 a | 11 740.7 a | 11 376.3 a | ||||
| C3 | 188.50 c | 190.42 c | 358.94 d | 30.38 a | 88.19 a | 10 279.9 d | 10 341.2 c | ||||
| 平均 Average | 194.88 | 191.88 | 374.07 | 30.85 | 88.86 | 11 177.7 | 10 692.2 | ||||
| 稀泥育秧(A2) Slime-raised seedling | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 182.65 d | 190.37 b | 347.70 d | 30.71 a | 88.99 a | 10 501.2 b | 9 743.2 c | ||
| C2 | 186.71 c | 192.87 a | 360.12 b | 30.39 a | 88.36 a | 10 713.7 b | 10 323.8 b | ||||
| C3 | 178.55 e | 188.97 bc | 337.41 e | 30.28 a | 88.03 a | 10 093.4 c | 9 279.4 d | ||||
| 平均 Average | 182.63 | 190.74 | 348.41 | 30.46 | 88.46 | 10 436.1 | 9 782.1 | ||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 190.34 b | 187.88 c | 351.76 c | 30.80 a | 88.96 a | 11 303.2 a | 10 324.0 b | |||
| C2 | 202.58 a | 190.07 b | 380.62 a | 30.54 a | 88.62 a | 11 589.8 a | 11 000.2 a | ||||
| C3 | 179.31 e | 184.81 d | 340.82 e | 30.23 a | 88.54 a | 10 470.3 b | 9 140.3 d | ||||
| 平均 Average | 190.74 | 187.59 | 357.73 | 30.52 | 88.71 | 11 054.4 | 10 154.8 | ||||
| F值 F value | A | 25.37** | 182.91** | 219.90** | 0.07 | 1.25 | 37.82** | 57.82** | |||
| B | 293.72** | 128.36** | 135.60** | 0.09 | 0.58 | 679.13** | 120.78** | ||||
| C | 325.03** | 183.71** | 353.52** | 1.46 | 1.49 | 885.58** | 148.02** | ||||
| A×B | 11.63** | 15.09** | 39.66** | 0.07 | 0.26 | 20.00** | 9.97** | ||||
| A×C | 20.92** | 11.17** | 28.50** | 0.24 | 0.16 | 54.88** | 29.03** | ||||
| B×C | 49.50** | 0.48 | 49.61** | 0.78 | 0.13 | 23.46** | 12.84** | ||||
| A×B×C | 9.30** | 3.31 | 16.14** | 0.19 | 1.26 | 4.24* | 5.44* | ||||
表3 不同育秧方式下播种量和插秧机具对机插稻产量及其构成因素的影响
Table 3 Effects of seeding quantity and transplanting machines on yield and its components of mechanically transplanted rice under different seedling raising ways.
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising ways | 插秧机具 Transplanting machine | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number /(×104·hm-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 总颖花数 Total spikelet number /(×106·hm-2) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 稻谷产量 Grain yield/(kg·hm-2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | ||||||||||
| 营养土育秧(A1) Raised by nutrient soil | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 184.44 d | 192.30 c | 354.33 e | 31.11 a | 89.03 a | 11 001.2 c | 10 040.5 d | ||
| C2 | 192.61 b | 196.87 a | 378.81 b | 30.76 a | 88.84 a | 11 115.8 bc | 10 833.6 b | ||||
| C3 | 178.85 e | 191.47 c | 342.46 f | 30.67 a | 88.57 a | 9 909.9 d | 9 856.8 d | ||||
| 平均 Average | 185.30 | 193.55 | 358.53 | 30.85 | 88.81 | 10 675.6 | 10 243.6 | ||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 191.51 bc | 190.36 d | 364.57 c | 31.29 a | 89.64 a | 11 512.5 ab | 10 359.0 c | |||
| C2 | 204.62 a | 194.84 b | 398.68 a | 30.88 a | 88.74 a | 11 740.7 a | 11 376.3 a | ||||
| C3 | 188.50 c | 190.42 c | 358.94 d | 30.38 a | 88.19 a | 10 279.9 d | 10 341.2 c | ||||
| 平均 Average | 194.88 | 191.88 | 374.07 | 30.85 | 88.86 | 11 177.7 | 10 692.2 | ||||
| 稀泥育秧(A2) Slime-raised seedling | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 182.65 d | 190.37 b | 347.70 d | 30.71 a | 88.99 a | 10 501.2 b | 9 743.2 c | ||
| C2 | 186.71 c | 192.87 a | 360.12 b | 30.39 a | 88.36 a | 10 713.7 b | 10 323.8 b | ||||
| C3 | 178.55 e | 188.97 bc | 337.41 e | 30.28 a | 88.03 a | 10 093.4 c | 9 279.4 d | ||||
| 平均 Average | 182.63 | 190.74 | 348.41 | 30.46 | 88.46 | 10 436.1 | 9 782.1 | ||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 190.34 b | 187.88 c | 351.76 c | 30.80 a | 88.96 a | 11 303.2 a | 10 324.0 b | |||
| C2 | 202.58 a | 190.07 b | 380.62 a | 30.54 a | 88.62 a | 11 589.8 a | 11 000.2 a | ||||
| C3 | 179.31 e | 184.81 d | 340.82 e | 30.23 a | 88.54 a | 10 470.3 b | 9 140.3 d | ||||
| 平均 Average | 190.74 | 187.59 | 357.73 | 30.52 | 88.71 | 11 054.4 | 10 154.8 | ||||
| F值 F value | A | 25.37** | 182.91** | 219.90** | 0.07 | 1.25 | 37.82** | 57.82** | |||
| B | 293.72** | 128.36** | 135.60** | 0.09 | 0.58 | 679.13** | 120.78** | ||||
| C | 325.03** | 183.71** | 353.52** | 1.46 | 1.49 | 885.58** | 148.02** | ||||
| A×B | 11.63** | 15.09** | 39.66** | 0.07 | 0.26 | 20.00** | 9.97** | ||||
| A×C | 20.92** | 11.17** | 28.50** | 0.24 | 0.16 | 54.88** | 29.03** | ||||
| B×C | 49.50** | 0.48 | 49.61** | 0.78 | 0.13 | 23.46** | 12.84** | ||||
| A×B×C | 9.30** | 3.31 | 16.14** | 0.19 | 1.26 | 4.24* | 5.44* | ||||
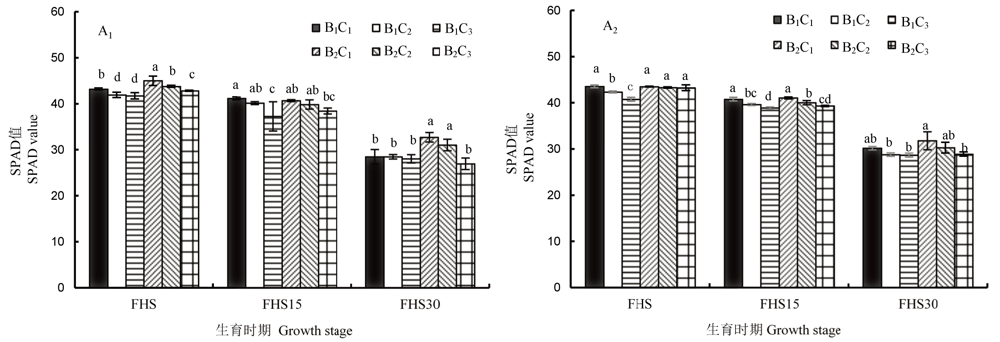
图1 不同育秧方式下播种量和插秧机具对剑叶SPAD值的影响(2018) 柱上的小写字母表示在P<0.05水平上差异显著。FHS–齐穗期;FHS15–齐穗后15 d;FHS30–齐穗后30 d。A1–营养土育秧;A2–稀泥育秧;B1–4行手扶式插秧机;B2–6行乘坐式高速插秧机;C1、C2、C3分别表示播种量为65 g/盘、85 g/盘、105 g/盘。
Fig. 1. Effects of seeding quantity and transplanting machine on SPAD of flag leaves under different seedling raising methods (2018). The lowercase letters on the column indicate that there is a significant difference at P<0.05 level. FHS, Full heading stage; FHS15, 15 d after full heading stage; FHS30, 30 d after full heading stage. A1, Seedling raised by nutrient soil; A2, Slime raised seedling; B1, Four-row walking transplanter; B2, 6-row riding high -speed rice transplanter. C1, C2 and C3 indicate seeding rates of 65 g/plate, 85 g/plate and 105 g/plate, respectively.
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising way | 插秧机具 Transplanting machine | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 穗 Panicle | 植株 Plant | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FHS | MS | FHS | MS | FHS | MS | FHS | MS | ||||||||
| 营养土育秧(A1) Seedling raised by nutrient soil (A1) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 52.81 d | 33.21 c | 91.47 c | 23.58 d | 25.72 d | 126.51 d | 169.99 cd | 183.30 d | |||||
| C2 | 59.71 b | 36.93 b | 103.08 b | 30.67 b | 29.67 b | 144.78 b | 192.46 b | 212.38 b | |||||||
| C3 | 39.60 f | 24.50 e | 88.07 d | 17.78 e | 23.46 e | 119.40 e | 152.47 e | 161.67 e | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 50.70 | 31.55 | 94.21 | 24.01 | 26.28 | 130.23 | 171.20 | 185.78 | |||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 56.82 c | 35.16 bc | 90.56 cd | 27.31 c | 26.60 d | 137.37 c | 173.98 c | 199.66 c | ||||||
| C2 | 63.78 a | 39.46 a | 115.83 a | 34.95 a | 32.53 a | 158.24 a | 212.13 a | 232.65 a | |||||||
| C3 | 46.57 e | 29.03 d | 91.88 c | 30.59 b | 28.10 c | 126.64 d | 166.55 d | 186.26 d | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 55.72 | 34.55 | 99.42 | 30.95 | 29.07 | 140.75 | 180.89 | 206.19 | |||||||
| 稀泥育秧(A2) Slime-raised seedling(A2) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 44.60 d | 33.25 c | 81.16 d | 24.33 d | 24.31 d | 121.68 d | 150.08 d | 179.26 d | |||||
| C2 | 49.54 b | 36.84 b | 97.34 b | 28.92 b | 28.62 b | 133.45 b | 175.49 b | 199.21 b | |||||||
| C3 | 36.70 f | 27.90 d | 70.82 e | 24.02 d | 24.87 d | 117.77 e | 132.39 e | 169.69 d | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 43.61 | 32.66 | 83.11 | 25.76 | 25.93 | 124.30 | 152.65 | 182.72 | |||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 38.43 e | 32.13 c | 84.52 c | 25.25 cd | 26.62 c | 131.71 c | 147.57 d | 189.09 c | ||||||
| C2 | 56.26 a | 38.34 a | 102.95 a | 32.55 a | 31.07 a | 136.70 a | 190.27 a | 207.59 a | |||||||
| C3 | 47.02 c | 32.23 c | 82.36 cd | 26.43 c | 26.84 c | 118.43 e | 156.21 c | 177.09 d | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 47.24 | 34.23 | 89.94 | 28.08 | 28.17 | 128.95 | 164.68 | 191.26 | |||||||
| F值 F value | A | 585.20** | 441.23** | 25.04** | 167.37** | 5.09* | 3.05 | 314.69** | 231.88** | ||||||
| B | 179.96** | 129.01** | 130.59** | 76.87** | 362.35** | 206.35** | 230.44** | 704.43** | |||||||
| C | 729.44** | 713.59** | 294.79** | 197.53** | 892.78** | 214.93** | 701.96** | 1064.92** | |||||||
| A×B | 4.70* | 50.45** | 10.05** | 12.12** | 136.35** | 51.31** | 34.53** | 155.83** | |||||||
| A×C | 119.78** | 59.12** | 7.73** | 32.34** | 326.29** | 25.36** | 57.40** | 148.87** | |||||||
| B×C | 78.76** | 17.85** | 18.20** | 108.40** | 3.84* | 4.34* | 14.68** | 2.73 | |||||||
| A×B×C | 46.68** | 21.18** | 3.64* | 39.11** | 124.02** | 9.71** | 7.50** | 25.91** | |||||||
表4 不同育秧方式下播种量和插秧机具对机插稻结实期氮素积累的影响(2018)
Table 4 Effects of seeding quantity and transplanting machines on N accumulation in seed setting stage of machine transplanted rice under different seeding ways (2018). kg/hm2
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising way | 插秧机具 Transplanting machine | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 穗 Panicle | 植株 Plant | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FHS | MS | FHS | MS | FHS | MS | FHS | MS | ||||||||
| 营养土育秧(A1) Seedling raised by nutrient soil (A1) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 52.81 d | 33.21 c | 91.47 c | 23.58 d | 25.72 d | 126.51 d | 169.99 cd | 183.30 d | |||||
| C2 | 59.71 b | 36.93 b | 103.08 b | 30.67 b | 29.67 b | 144.78 b | 192.46 b | 212.38 b | |||||||
| C3 | 39.60 f | 24.50 e | 88.07 d | 17.78 e | 23.46 e | 119.40 e | 152.47 e | 161.67 e | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 50.70 | 31.55 | 94.21 | 24.01 | 26.28 | 130.23 | 171.20 | 185.78 | |||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 56.82 c | 35.16 bc | 90.56 cd | 27.31 c | 26.60 d | 137.37 c | 173.98 c | 199.66 c | ||||||
| C2 | 63.78 a | 39.46 a | 115.83 a | 34.95 a | 32.53 a | 158.24 a | 212.13 a | 232.65 a | |||||||
| C3 | 46.57 e | 29.03 d | 91.88 c | 30.59 b | 28.10 c | 126.64 d | 166.55 d | 186.26 d | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 55.72 | 34.55 | 99.42 | 30.95 | 29.07 | 140.75 | 180.89 | 206.19 | |||||||
| 稀泥育秧(A2) Slime-raised seedling(A2) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 44.60 d | 33.25 c | 81.16 d | 24.33 d | 24.31 d | 121.68 d | 150.08 d | 179.26 d | |||||
| C2 | 49.54 b | 36.84 b | 97.34 b | 28.92 b | 28.62 b | 133.45 b | 175.49 b | 199.21 b | |||||||
| C3 | 36.70 f | 27.90 d | 70.82 e | 24.02 d | 24.87 d | 117.77 e | 132.39 e | 169.69 d | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 43.61 | 32.66 | 83.11 | 25.76 | 25.93 | 124.30 | 152.65 | 182.72 | |||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 38.43 e | 32.13 c | 84.52 c | 25.25 cd | 26.62 c | 131.71 c | 147.57 d | 189.09 c | ||||||
| C2 | 56.26 a | 38.34 a | 102.95 a | 32.55 a | 31.07 a | 136.70 a | 190.27 a | 207.59 a | |||||||
| C3 | 47.02 c | 32.23 c | 82.36 cd | 26.43 c | 26.84 c | 118.43 e | 156.21 c | 177.09 d | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 47.24 | 34.23 | 89.94 | 28.08 | 28.17 | 128.95 | 164.68 | 191.26 | |||||||
| F值 F value | A | 585.20** | 441.23** | 25.04** | 167.37** | 5.09* | 3.05 | 314.69** | 231.88** | ||||||
| B | 179.96** | 129.01** | 130.59** | 76.87** | 362.35** | 206.35** | 230.44** | 704.43** | |||||||
| C | 729.44** | 713.59** | 294.79** | 197.53** | 892.78** | 214.93** | 701.96** | 1064.92** | |||||||
| A×B | 4.70* | 50.45** | 10.05** | 12.12** | 136.35** | 51.31** | 34.53** | 155.83** | |||||||
| A×C | 119.78** | 59.12** | 7.73** | 32.34** | 326.29** | 25.36** | 57.40** | 148.87** | |||||||
| B×C | 78.76** | 17.85** | 18.20** | 108.40** | 3.84* | 4.34* | 14.68** | 2.73 | |||||||
| A×B×C | 46.68** | 21.18** | 3.64* | 39.11** | 124.02** | 9.71** | 7.50** | 25.91** | |||||||
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising way | 插秧机具 Transplanter | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 穗 Panicle | 植株 Plant | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FHS | MS | FHS | MS | FHS | MS | FHS | MS | ||||||||
| 营养土育秧 (A1) Seedling raising by nutrient soil (A1) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 48.03 d | 26.24 c | 67.45 cd | 27.49 c | 38.32 bc | 118.39 c | 153.80 e | 172.12 d | |||||
| C2 | 63.67 a | 28.12 b | 82.79 b | 30.12 b | 43.49 a | 133.23 a | 189.96 b | 191.46 b | |||||||
| C3 | 45.44 d | 25.46 cd | 66.61 d | 25.22 d | 37.12 c | 117.89 c | 149.17 f | 168.56 d | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 52.38 | 26.61 | 72.28 | 27.61 | 39.64 | 123.17 | 164.31 | 177.38 | |||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 51.14 c | 24.17 d | 70.92 c | 24.52 d | 37.93 bc | 129.81 b | 159.99 d | 178.50 c | ||||||
| C2 | 64.94 a | 29.71 a | 89.85 a | 34.08 a | 43.90 a | 136.59 a | 198.74 a | 200.38 a | |||||||
| C3 | 55.63 b | 26.10 c | 79.69 b | 29.81 b | 40.24 b | 126.91 b | 172.56 c | 182.81 c | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 57.24 | 26.66 | 80.15 | 29.47 | 40.691 | 130.83 | 177.10 | 187.23 | |||||||
| 稀泥育秧 (A2) Slime seedling raising(A2) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 42.14 d | 24.59 d | 62.76 c | 27.27 b | 34.93 b | 114.41 d | 139.83 d | 167.27 c | |||||
| C2 | 61.69 b | 31.91 b | 74.56 a | 29.25 ab | 37.78 a | 119.99 c | 174.03 b | 183.15 b | |||||||
| C3 | 48.52 c | 29.22 c | 60.62 c | 24.11 c | 27.19 d | 109.70 e | 134.32 e | 163.04 c | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 50.78 | 28.57 | 65.98 | 26.87 | 32.97 | 114.04 | 149.44 | 171.16 | |||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 42.54 d | 28.94 b | 67.16 b | 29.10 b | 31.74 c | 119.51 b | 141.44 d | 177.56 b | ||||||
| C2 | 65.45 a | 32.30 a | 76.06 a | 32.05 a | 38.12 a | 127.85 a | 179.63 a | 193.19 a | |||||||
| C3 | 50.81 c | 29.36 b | 60.71 c | 27.86 b | 36.49 ab | 119.55 b | 148.01 c | 176.76 b | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 52.95 | 30.20 | 67.98 | 28.67 | 35.45 | 122.30 | 156.36 | 182.50 | |||||||
| F值 F value | A | 70.01** | 0.64 | 103.20** | 198.19** | 9.76** | 297.48** | 79.62** | 80.91** | ||||||
| B | 57.56** | 113.64** | 136.64** | 40.11** | 40.66** | 685.46** | 87.37** | 179.25** | |||||||
| C | 94.28** | 279.56** | 138.96** | 223.37** | 17.97** | 475.45** | 107.30** | 420.16** | |||||||
| A×B | 33.99** | 1.20 | 0.56 | 9.74** | 11.12** | 5.37* | 8.74** | 4.85* | |||||||
| A×C | 41.41** | 294.58** | 48.47** | 67.15** | 73.26** | 43.37** | 21.52** | 46.60** | |||||||
| B×C | 3.96* | 132.19** | 0.44 | 94.02** | 44.57** | 162.71** | 1.91 | 132.84** | |||||||
| A×B×C | 13.08** | 38.15** | 24.85** | 26.15** | 45.09** | 84.38** | 22.65** | 16.51** | |||||||
表5 不同育秧方式下播种量和插秧机具对机插稻结实期氮素积累的影响(2019)
Table 5 Effects of seeding quantity and transplanting machines on N accumulation in grain filling stage of machine transplanted rice under different seeding ways (2019). kg/hm2
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising way | 插秧机具 Transplanter | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 穗 Panicle | 植株 Plant | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FHS | MS | FHS | MS | FHS | MS | FHS | MS | ||||||||
| 营养土育秧 (A1) Seedling raising by nutrient soil (A1) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 48.03 d | 26.24 c | 67.45 cd | 27.49 c | 38.32 bc | 118.39 c | 153.80 e | 172.12 d | |||||
| C2 | 63.67 a | 28.12 b | 82.79 b | 30.12 b | 43.49 a | 133.23 a | 189.96 b | 191.46 b | |||||||
| C3 | 45.44 d | 25.46 cd | 66.61 d | 25.22 d | 37.12 c | 117.89 c | 149.17 f | 168.56 d | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 52.38 | 26.61 | 72.28 | 27.61 | 39.64 | 123.17 | 164.31 | 177.38 | |||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 51.14 c | 24.17 d | 70.92 c | 24.52 d | 37.93 bc | 129.81 b | 159.99 d | 178.50 c | ||||||
| C2 | 64.94 a | 29.71 a | 89.85 a | 34.08 a | 43.90 a | 136.59 a | 198.74 a | 200.38 a | |||||||
| C3 | 55.63 b | 26.10 c | 79.69 b | 29.81 b | 40.24 b | 126.91 b | 172.56 c | 182.81 c | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 57.24 | 26.66 | 80.15 | 29.47 | 40.691 | 130.83 | 177.10 | 187.23 | |||||||
| 稀泥育秧 (A2) Slime seedling raising(A2) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 42.14 d | 24.59 d | 62.76 c | 27.27 b | 34.93 b | 114.41 d | 139.83 d | 167.27 c | |||||
| C2 | 61.69 b | 31.91 b | 74.56 a | 29.25 ab | 37.78 a | 119.99 c | 174.03 b | 183.15 b | |||||||
| C3 | 48.52 c | 29.22 c | 60.62 c | 24.11 c | 27.19 d | 109.70 e | 134.32 e | 163.04 c | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 50.78 | 28.57 | 65.98 | 26.87 | 32.97 | 114.04 | 149.44 | 171.16 | |||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 42.54 d | 28.94 b | 67.16 b | 29.10 b | 31.74 c | 119.51 b | 141.44 d | 177.56 b | ||||||
| C2 | 65.45 a | 32.30 a | 76.06 a | 32.05 a | 38.12 a | 127.85 a | 179.63 a | 193.19 a | |||||||
| C3 | 50.81 c | 29.36 b | 60.71 c | 27.86 b | 36.49 ab | 119.55 b | 148.01 c | 176.76 b | |||||||
| 平均 Average | 52.95 | 30.20 | 67.98 | 28.67 | 35.45 | 122.30 | 156.36 | 182.50 | |||||||
| F值 F value | A | 70.01** | 0.64 | 103.20** | 198.19** | 9.76** | 297.48** | 79.62** | 80.91** | ||||||
| B | 57.56** | 113.64** | 136.64** | 40.11** | 40.66** | 685.46** | 87.37** | 179.25** | |||||||
| C | 94.28** | 279.56** | 138.96** | 223.37** | 17.97** | 475.45** | 107.30** | 420.16** | |||||||
| A×B | 33.99** | 1.20 | 0.56 | 9.74** | 11.12** | 5.37* | 8.74** | 4.85* | |||||||
| A×C | 41.41** | 294.58** | 48.47** | 67.15** | 73.26** | 43.37** | 21.52** | 46.60** | |||||||
| B×C | 3.96* | 132.19** | 0.44 | 94.02** | 44.57** | 162.71** | 1.91 | 132.84** | |||||||
| A×B×C | 13.08** | 38.15** | 24.85** | 26.15** | 45.09** | 84.38** | 22.65** | 16.51** | |||||||
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising way | 插秧机具 Transplanting machine | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 氮转运量 N translocation amount /(kg·hm-2) | 氮转运率 N translocation efficiency /% | 氮贡献率 N contribution rate /% | 穗氮增加量 N increment in panicle /(kg·hm-2) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | ||||||||
| 营养土育秧(A1) Seedling raising by nutrient soil (A1) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 19.59 c | 67.89 c | 37.06 a | 74.22 a | 15.50 a | 47.61 b | 100.80 d | ||||
| C2 | 22.77 ab | 72.41 b | 38.15 a | 70.26 b | 15.73 a | 50.23 a | 115.11 b | ||||||
| C3 | 15.12 e | 60.29 e | 38.12 a | 68.46 bc | 12.66 b | 49.99 a | 95.94 e | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 19.16 | 66.86 | 37.78 | 70.98 | 14.63 | 49.27 | 103.95 | ||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 21.66 b | 63.26 d | 38.10 a | 69.85 c | 15.41 a | 46.07 c | 110.78 c | |||||
| C2 | 24.39 a | 80.88 a | 38.24 a | 69.83 bc | 15.75 a | 51.11 a | 125.71 a | ||||||
| C3 | 17.54 d | 61.29 e | 37.70 a | 66.71 d | 13.85 b | 48.40 b | 98.54 de | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 21.20 | 68.48 | 38.01 | 68.80 | 15.01 | 48.53 | 111.68 | ||||||
| 稀泥育秧(A2) Slime seedling raising(A2) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 11.36 c | 56.83 c | 25.46 b | 70.13 a | 9.33 b | 46.97 bc | 97.37 b | ||||
| C2 | 12.70 c | 68.43 a | 25.63 b | 70.08 a | 9.52 b | 50.77 a | 104.84 a | ||||||
| C3 | 8.80 d | 42.80 d | 23.94 b | 66.86 b | 7.49 c | 36.35 d | 92.90 c | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 10.95 | 56.02 | 25.01 | 69.02 | 8.78 | 44.70 | 98.37 | ||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 6.30 e | 59.27 b | 16.37 c | 70.11 a | 4.78 d | 44.99 c | 105.09 a | |||||
| C2 | 17.92 a | 70.40 a | 31.85 a | 68.38 a | 13.11 a | 51.50 a | 105.63 a | ||||||
| C3 | 15.45 b | 55.92 c | 31.44 a | 68.16 a | 12.49 a | 47.78 b | 91.60 c | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 13.22 | 61.86 | 26.55 | 68.88 | 10.13 | 48.09 | 100.77 | ||||||
| F值 F value | A | 566.16** | 310.51** | 370.73** | 10.35** | 377.31** | 44.22** | 243.76** | |||||
| B | 35.16** | 51.52** | 1.99 | 8.82** | 9.74** | 12.35** | 88.76** | ||||||
| C | 96.68** | 458.69** | 17.30** | 41.63** | 22.71** | 75.94** | 376.75** | ||||||
| A×B | 10.18* | 13.37** | 1.08 | 12.07** | 3.08 | 30.14** | 24.52** | ||||||
| A×C | 37.10** | 1.74 | 13.22** | 1.53 | 34.65** | 38.65** | 41.66** | ||||||
| B×C | 26.79** | 27.71** | 15.30** | 4.31* | 31.99** | 26.63** | 17.73** | ||||||
| A×B×C | 26.76** | 25.72** | 20.83** | 7.16** | 27.33** | 34.70** | 4.55* | ||||||
表6 不同育秧方式下播种量和插秧机具对机插稻结实期氮素转运的影响(2018)
Table 6 Effects of seeding quantity and transplanting machines on N transport during grain filling stage of machine transplanted rice under different seeding ways (2018).
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising way | 插秧机具 Transplanting machine | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 氮转运量 N translocation amount /(kg·hm-2) | 氮转运率 N translocation efficiency /% | 氮贡献率 N contribution rate /% | 穗氮增加量 N increment in panicle /(kg·hm-2) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | ||||||||
| 营养土育秧(A1) Seedling raising by nutrient soil (A1) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 19.59 c | 67.89 c | 37.06 a | 74.22 a | 15.50 a | 47.61 b | 100.80 d | ||||
| C2 | 22.77 ab | 72.41 b | 38.15 a | 70.26 b | 15.73 a | 50.23 a | 115.11 b | ||||||
| C3 | 15.12 e | 60.29 e | 38.12 a | 68.46 bc | 12.66 b | 49.99 a | 95.94 e | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 19.16 | 66.86 | 37.78 | 70.98 | 14.63 | 49.27 | 103.95 | ||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 21.66 b | 63.26 d | 38.10 a | 69.85 c | 15.41 a | 46.07 c | 110.78 c | |||||
| C2 | 24.39 a | 80.88 a | 38.24 a | 69.83 bc | 15.75 a | 51.11 a | 125.71 a | ||||||
| C3 | 17.54 d | 61.29 e | 37.70 a | 66.71 d | 13.85 b | 48.40 b | 98.54 de | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 21.20 | 68.48 | 38.01 | 68.80 | 15.01 | 48.53 | 111.68 | ||||||
| 稀泥育秧(A2) Slime seedling raising(A2) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 11.36 c | 56.83 c | 25.46 b | 70.13 a | 9.33 b | 46.97 bc | 97.37 b | ||||
| C2 | 12.70 c | 68.43 a | 25.63 b | 70.08 a | 9.52 b | 50.77 a | 104.84 a | ||||||
| C3 | 8.80 d | 42.80 d | 23.94 b | 66.86 b | 7.49 c | 36.35 d | 92.90 c | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 10.95 | 56.02 | 25.01 | 69.02 | 8.78 | 44.70 | 98.37 | ||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 6.30 e | 59.27 b | 16.37 c | 70.11 a | 4.78 d | 44.99 c | 105.09 a | |||||
| C2 | 17.92 a | 70.40 a | 31.85 a | 68.38 a | 13.11 a | 51.50 a | 105.63 a | ||||||
| C3 | 15.45 b | 55.92 c | 31.44 a | 68.16 a | 12.49 a | 47.78 b | 91.60 c | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 13.22 | 61.86 | 26.55 | 68.88 | 10.13 | 48.09 | 100.77 | ||||||
| F值 F value | A | 566.16** | 310.51** | 370.73** | 10.35** | 377.31** | 44.22** | 243.76** | |||||
| B | 35.16** | 51.52** | 1.99 | 8.82** | 9.74** | 12.35** | 88.76** | ||||||
| C | 96.68** | 458.69** | 17.30** | 41.63** | 22.71** | 75.94** | 376.75** | ||||||
| A×B | 10.18* | 13.37** | 1.08 | 12.07** | 3.08 | 30.14** | 24.52** | ||||||
| A×C | 37.10** | 1.74 | 13.22** | 1.53 | 34.65** | 38.65** | 41.66** | ||||||
| B×C | 26.79** | 27.71** | 15.30** | 4.31* | 31.99** | 26.63** | 17.73** | ||||||
| A×B×C | 26.76** | 25.72** | 20.83** | 7.16** | 27.33** | 34.70** | 4.55* | ||||||
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising way | 插秧机具 Transplanting machine | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 氮转运量 N translocation amount /(kg·hm-2) | 氮转运率 N translocation efficiency /% | 氮贡献率 N contribution rate /% | 穗氮增加量 N increment in panicle /(kg·hm-2) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | ||||||||
| 营养土育秧(A1) Seedling raising by nutrient soil (A1) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 21.79 d | 39.96 d | 45.37 c | 59.24 b | 18.41 c | 33.75 c | 80.07 c | ||||
| C2 | 35.55 a | 52.67 b | 55.83 a | 63.62 ab | 26.68 a | 39.53 a | 89.74 ab | ||||||
| C3 | 19.98 d | 41.39 d | 43.97 c | 62.14 b | 16.95 c | 35.11 b | 80.77 c | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 25.77 | 44.67 | 48.39 | 61.67 | 20.68 | 36.13 | 83.53 | ||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 26.97 c | 46.40 c | 52.74 b | 62.43 b | 20.78 b | 35.74 b | 91.88 a | |||||
| C2 | 35.23 a | 55.77 a | 54.25 ab | 65.07 a | 25.79 a | 40.83 a | 92.69 a | ||||||
| C3 | 29.53 b | 49.88 b | 53.08 b | 62.59 b | 23.27 b | 39.30 a | 86.67 b | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 30.58 | 50.68 | 53.36 | 63.36 | 23.28 | 38.63 | 90.41 | ||||||
| 稀泥育秧(A2) Slime seedling raising(A2) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 17.55 d | 35.49 c | 41.65 c | 56.55 b | 15.34 c | 32.44 c | 74.48 d | ||||
| C2 | 29.78 b | 45.31 a | 48.27 b | 60.77 a | 24.61 a | 39.06 a | 78.21 c | ||||||
| C3 | 19.30 cd | 36.51 bc | 39.78 c | 60.23 a | 17.59 b | 34.87 b | 77.51 c | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 22.21 | 39.10 | 43.23 | 59.18 | 19.18 | 35.46 | 76.73 | ||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 13.60 e | 38.06 b | 31.97 d | 56.67 b | 11.38 d | 31.85 c | 87.77 a | |||||
| C2 | 33.15 a | 44.01 a | 50.65 a | 57.86 b | 25.93 a | 34.42 b | 89.73 a | ||||||
| C3 | 21.45 c | 32.85 d | 42.22 c | 54.11 c | 17.94 b | 27.48 d | 83.06 b | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 22.73 | 38.31 | 41.61 | 56.21 | 18.42 | 31.25 | 86.85 | ||||||
| F值 F value | A | 134.41** | 126.76** | 78.59** | 33.25** | 61.71** | 39.58** | 29.91** | |||||
| B | 15.74** | 28.11** | 12.19** | 12.79** | 4.15* | 4.21* | 385.04** | ||||||
| C | 31.54** | 5.09* | 5.18* | 188.91** | 4.06* | 19.21** | 485.91** | ||||||
| A×B | 33.94** | 5.21* | 24.35** | 0.61 | 34.41** | 0.29 | 0.19 | ||||||
| A×C | 17.41** | 10.34** | 7.09* | 72.12** | 10.61** | 2.45 | 1.05 | ||||||
| B×C | 13.76** | 2.28 | 16.88** | 11.07** | 20.89** | 9.39** | 138.87** | ||||||
| A×B×C | 18.97** | 36.52** | 17.71** | 78.42** | 8.34** | 21.44** | 24.15** | ||||||
表7 不同育秧方式下播种量和插秧机具对机插稻结实期氮素转运的影响(2019)
Table 7 Effects of seeding quantity and transplanting machines on N transport during grain filling stage of machine transplanted rice under different seeding ways (2019).
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising way | 插秧机具 Transplanting machine | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 氮转运量 N translocation amount /(kg·hm-2) | 氮转运率 N translocation efficiency /% | 氮贡献率 N contribution rate /% | 穗氮增加量 N increment in panicle /(kg·hm-2) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶片 Leaf | ||||||||
| 营养土育秧(A1) Seedling raising by nutrient soil (A1) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 21.79 d | 39.96 d | 45.37 c | 59.24 b | 18.41 c | 33.75 c | 80.07 c | ||||
| C2 | 35.55 a | 52.67 b | 55.83 a | 63.62 ab | 26.68 a | 39.53 a | 89.74 ab | ||||||
| C3 | 19.98 d | 41.39 d | 43.97 c | 62.14 b | 16.95 c | 35.11 b | 80.77 c | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 25.77 | 44.67 | 48.39 | 61.67 | 20.68 | 36.13 | 83.53 | ||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 26.97 c | 46.40 c | 52.74 b | 62.43 b | 20.78 b | 35.74 b | 91.88 a | |||||
| C2 | 35.23 a | 55.77 a | 54.25 ab | 65.07 a | 25.79 a | 40.83 a | 92.69 a | ||||||
| C3 | 29.53 b | 49.88 b | 53.08 b | 62.59 b | 23.27 b | 39.30 a | 86.67 b | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 30.58 | 50.68 | 53.36 | 63.36 | 23.28 | 38.63 | 90.41 | ||||||
| 稀泥育秧(A2) Slime seedling raising(A2) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 17.55 d | 35.49 c | 41.65 c | 56.55 b | 15.34 c | 32.44 c | 74.48 d | ||||
| C2 | 29.78 b | 45.31 a | 48.27 b | 60.77 a | 24.61 a | 39.06 a | 78.21 c | ||||||
| C3 | 19.30 cd | 36.51 bc | 39.78 c | 60.23 a | 17.59 b | 34.87 b | 77.51 c | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 22.21 | 39.10 | 43.23 | 59.18 | 19.18 | 35.46 | 76.73 | ||||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 13.60 e | 38.06 b | 31.97 d | 56.67 b | 11.38 d | 31.85 c | 87.77 a | |||||
| C2 | 33.15 a | 44.01 a | 50.65 a | 57.86 b | 25.93 a | 34.42 b | 89.73 a | ||||||
| C3 | 21.45 c | 32.85 d | 42.22 c | 54.11 c | 17.94 b | 27.48 d | 83.06 b | ||||||
| 平均 Average | 22.73 | 38.31 | 41.61 | 56.21 | 18.42 | 31.25 | 86.85 | ||||||
| F值 F value | A | 134.41** | 126.76** | 78.59** | 33.25** | 61.71** | 39.58** | 29.91** | |||||
| B | 15.74** | 28.11** | 12.19** | 12.79** | 4.15* | 4.21* | 385.04** | ||||||
| C | 31.54** | 5.09* | 5.18* | 188.91** | 4.06* | 19.21** | 485.91** | ||||||
| A×B | 33.94** | 5.21* | 24.35** | 0.61 | 34.41** | 0.29 | 0.19 | ||||||
| A×C | 17.41** | 10.34** | 7.09* | 72.12** | 10.61** | 2.45 | 1.05 | ||||||
| B×C | 13.76** | 2.28 | 16.88** | 11.07** | 20.89** | 9.39** | 138.87** | ||||||
| A×B×C | 18.97** | 36.52** | 17.71** | 78.42** | 8.34** | 21.44** | 24.15** | ||||||
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising way | 插秧机具 Transplanter | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氮收获 指数 NHI /% | 氮干物质 生产效率 NMPE /(kg·kg-1) | 氮稻谷 生产效率 NGPE /(kg·kg-1) | 氮肥 偏生产力 NPP /(kg·kg-1) | 氮收获 指数 NHI /% | 氮干物质 生产效率 NMPE /(kg·kg-1) | 氮稻谷 生产效率 NGPE /(kg·kg-1) | 氮肥 偏生产力 NPP /(kg·kg-1) | ||||||
| 营养土育秧 (A1) Seedling raising by nutrient soil (A1) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 69.02 b | 94.29 ab | 60.02 b | 73.21 c | 68.51 b | 98.40 c | 62.32 a | 66.94 d | |||
| C2 | 68.28 b | 95.00 ab | 52.43 d | 73.97 bc | 68.35 b | 98.48 c | 56.00 c | 72.22 b | |||||
| C3 | 75.72 a | 91.23 b | 62.86 a | 65.93 d | 68.83 b | 98.01 c | 60.63 a | 65.71 d | |||||
| 平均 Average | 71.01 | 93.51 | 58.44 | 71.04 | 68.56 | 98.30 | 59.65 | 68.29 | |||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 67.62 c | 96.76 a | 56.69 c | 76.62 ab | 72.72 a | 103.08 b | 58.03 bc | 69.06 c | ||||
| C2 | 67.44 c | 98.05 a | 49.87 e | 77.87 a | 68.17 b | 110.94 a | 56.57 c | 75.84 a | |||||
| C3 | 68.62 b | 97.57 a | 55.70 c | 68.40 d | 69.42 b | 101.14 b | 56.77 c | 68.94 c | |||||
| 平均 Average | 67.89 | 97.46 | 54.09 | 74.30 | 70.10 | 105.05 | 57.12 | 71.28 | |||||
| 稀泥育秧(A2) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 69.97 a | 93.18 c | 60.39 a | 69.87 b | 65.41 b | 102.32 b | 58.99 b | 64.95 c | |||
| Slime seedling raising(A2) | C2 | 66.99 b | 97.59 a | 55.83 d | 71.29 b | 63.33 c | 103.29 a | 56.38 c | 68.83 b | ||||
| C3 | 67.29 b | 94.99 b | 57.67 c | 67.16 c | 63.82 c | 97.63 d | 56.56 c | 61.86 d | |||||
| 平均 Average | 68.08 | 95.25 | 57.96 | 69.44 | 64.18 | 101.58 | 57.31 | 65.21 | |||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 69.66 a | 94.52 bc | 59.78 ab | 75.22 a | 72.00 a | 103.94 a | 60.18 a | 68.83 b | ||||
| C2 | 65.85 c | 97.86 a | 53.78 e | 77.13 a | 65.50 c | 104.72 a | 56.35 c | 73.33 a | |||||
| C3 | 67.13 b | 94.35 bc | 59.35 b | 69.67 bc | 65.69 c | 100.36 c | 54.81 d | 60.94 d | |||||
| 平均 Average | 67.55 | 95.58 | 57.63 | 74.01 | 67.73 | 103.01 | 57.11 | 67.70 | |||||
| F值 F value | A | 148.41** | 0.17 | 70.66** | 13.21* | 20.71** | 17.11** | 17.98** | 52.69** | ||||
| B | 184.50** | 14.96** | 81.93** | 60.87** | 46.99** | 49.38** | 24.94** | 94.98** | |||||
| C | 130.53** | 9.07** | 492.32** | 79.57** | 118.05** | 65.74** | 39.29** | 148.02** | |||||
| A×B | 91.96** | 10.57** | 216.90** | 1.70 | 13.62** | 18.02** | 6.01* | 2.96 | |||||
| A×C | 193.05** | 2.31 | 49.32** | 14.91* | 29.87** | 6.29* | 4.93* | 29.03** | |||||
| B×C | 45.24** | 0.43 | 16.13** | 10.09* | 113.86** | 14.89** | 1.89 | 12.84** | |||||
| A×B×C | 68.39** | 2.43 | 24.46** | 11.40* | 9.87** | 13.79** | 5.43* | 14.43** | |||||
表8 不同育秧方式下播种量和插秧机具对机插稻氮素利用的影响
Table 8 Effects of seeding quantity and transplanting machines on N utilization in machine transplanted rice under different seedling raising ways.
| 育秧方式 Seedling raising way | 插秧机具 Transplanter | 播种量 Seeding quantity | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氮收获 指数 NHI /% | 氮干物质 生产效率 NMPE /(kg·kg-1) | 氮稻谷 生产效率 NGPE /(kg·kg-1) | 氮肥 偏生产力 NPP /(kg·kg-1) | 氮收获 指数 NHI /% | 氮干物质 生产效率 NMPE /(kg·kg-1) | 氮稻谷 生产效率 NGPE /(kg·kg-1) | 氮肥 偏生产力 NPP /(kg·kg-1) | ||||||
| 营养土育秧 (A1) Seedling raising by nutrient soil (A1) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 69.02 b | 94.29 ab | 60.02 b | 73.21 c | 68.51 b | 98.40 c | 62.32 a | 66.94 d | |||
| C2 | 68.28 b | 95.00 ab | 52.43 d | 73.97 bc | 68.35 b | 98.48 c | 56.00 c | 72.22 b | |||||
| C3 | 75.72 a | 91.23 b | 62.86 a | 65.93 d | 68.83 b | 98.01 c | 60.63 a | 65.71 d | |||||
| 平均 Average | 71.01 | 93.51 | 58.44 | 71.04 | 68.56 | 98.30 | 59.65 | 68.29 | |||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 67.62 c | 96.76 a | 56.69 c | 76.62 ab | 72.72 a | 103.08 b | 58.03 bc | 69.06 c | ||||
| C2 | 67.44 c | 98.05 a | 49.87 e | 77.87 a | 68.17 b | 110.94 a | 56.57 c | 75.84 a | |||||
| C3 | 68.62 b | 97.57 a | 55.70 c | 68.40 d | 69.42 b | 101.14 b | 56.77 c | 68.94 c | |||||
| 平均 Average | 67.89 | 97.46 | 54.09 | 74.30 | 70.10 | 105.05 | 57.12 | 71.28 | |||||
| 稀泥育秧(A2) | 4行机(B1) 4-row transplanter | C1 | 69.97 a | 93.18 c | 60.39 a | 69.87 b | 65.41 b | 102.32 b | 58.99 b | 64.95 c | |||
| Slime seedling raising(A2) | C2 | 66.99 b | 97.59 a | 55.83 d | 71.29 b | 63.33 c | 103.29 a | 56.38 c | 68.83 b | ||||
| C3 | 67.29 b | 94.99 b | 57.67 c | 67.16 c | 63.82 c | 97.63 d | 56.56 c | 61.86 d | |||||
| 平均 Average | 68.08 | 95.25 | 57.96 | 69.44 | 64.18 | 101.58 | 57.31 | 65.21 | |||||
| 6行机(B2) 6-row transplanter | C1 | 69.66 a | 94.52 bc | 59.78 ab | 75.22 a | 72.00 a | 103.94 a | 60.18 a | 68.83 b | ||||
| C2 | 65.85 c | 97.86 a | 53.78 e | 77.13 a | 65.50 c | 104.72 a | 56.35 c | 73.33 a | |||||
| C3 | 67.13 b | 94.35 bc | 59.35 b | 69.67 bc | 65.69 c | 100.36 c | 54.81 d | 60.94 d | |||||
| 平均 Average | 67.55 | 95.58 | 57.63 | 74.01 | 67.73 | 103.01 | 57.11 | 67.70 | |||||
| F值 F value | A | 148.41** | 0.17 | 70.66** | 13.21* | 20.71** | 17.11** | 17.98** | 52.69** | ||||
| B | 184.50** | 14.96** | 81.93** | 60.87** | 46.99** | 49.38** | 24.94** | 94.98** | |||||
| C | 130.53** | 9.07** | 492.32** | 79.57** | 118.05** | 65.74** | 39.29** | 148.02** | |||||
| A×B | 91.96** | 10.57** | 216.90** | 1.70 | 13.62** | 18.02** | 6.01* | 2.96 | |||||
| A×C | 193.05** | 2.31 | 49.32** | 14.91* | 29.87** | 6.29* | 4.93* | 29.03** | |||||
| B×C | 45.24** | 0.43 | 16.13** | 10.09* | 113.86** | 14.89** | 1.89 | 12.84** | |||||
| A×B×C | 68.39** | 2.43 | 24.46** | 11.40* | 9.87** | 13.79** | 5.43* | 14.43** | |||||
| [1] | 施能浦. 近期我国稻谷(米)供求趋势分析及发展预测与对策[J]. 中国稻米, 2015, 21(1): 1-5. |
| Shi N P.Analysis and development strategy on rice production & marketing trend in China[J]. China Rice, 2015, 21(1): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Chen J, Cao F, Yin X, Huang M, Zou Y.Yield performance of early-season rice cultivars grown in the late season of double-season crop production under machine-transplanted conditions[J/OL].PloS ONE, 2019, 14(3): e0213075. |
| [3] | 李旭毅, 孙永健, 程宏彪, 郑洪帧, 杨志远, 贾现文, 刘树金, 胡蓉, 马均. 氮肥运筹和栽培方式对杂交籼稻Ⅱ优498 结实期群体光合特性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2011, 37(9): 1650-1659. |
| Li X Y, Sun Y J, Cheng H B, Zheng H Z, Yang Z Y, Jia X W, Liu S J, Hu R, Ma J.Effects of nitrogen application strategy and cultivation model on the performances of canopy apparent photosynthesis of indica hybrid rice Er you 498 during filling stage[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2011, 37(9): 1650-1659. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 李旭毅, 孙永健, 程洪彪, 郑宏祯, 刘树金, 胡蓉, 马均. 两种生态条件下氮素调控对不同栽培方式水稻干物质积累和产量的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(4): 773-781. |
| Li X Y, Sun Y J, Cheng H B, Zheng H Z, Liu S J, Hu R, Ma J.Effects of nitrogen regulation on dry matter accumulation and grain yield of rice under different cultivation models and two kinds of ecological conditions[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(4): 773-781. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 魏海燕, 张洪程, 杭杰, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 张胜飞, 马群, 张庆, 张军. 不同氮素利用效率基因型水稻氮素积累与转移的特性[J]. 作物学报, 2008, 34(1): 119-125. |
| Wei H Y, Zhang H C, Hang J, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Zhang S F, Ma Q, Zhang Q, Zhang J.Characteristics of N accumulation and translocation in rice genotypes with different N use efficiencies[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008, 34(1): 119-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 赵敏, 胡剑锋, 钟晓媛, 张强, 周虹, 任万军. 不同基因型机插稻植株氮素积累运转特性[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(2): 277-287. |
| Zhao M, Hu J F, Zhong X Y, Zhang Q, Zhou H, Ren W J.Differences in N accumulation and translocation in the machine-transplanted rice genotypes[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2015, 21(2): 277-287. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Chen S, Liu S W, Yin M, Zheng X, Chu G, Xu C N, Wang D Y, Zhang X F.Seasonal changes in crop growth and grain yield of different japonica rice cultivars in Southeast China.Agronomy Journal, 2020, 112: 215-227. |
| [8] | 王海月, 蒋明金, 孙永健, 郭长春, 殷尧翥, 何艳, 严田蓉, 杨志远, 徐徽, 马均. 常规氮肥与缓释氮肥配施对不同株距机插杂交稻磷素吸收、转运及分配特征的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(1): 115-125. |
| Wang H Y, Jiang M J, Sun Y J, Guo C C,Yin Y Z, He Y, Yan T R, Yang Z Y, Xu H, Ma J.Effects of conventional urea combined with slow-release urea application on phosphorus uptake, translocation and distribution in mechanically transplanted rice with different plant spacings[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(1): 115-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 王海月, 李玥, 孙永健, 李应洪, 蒋明金, 王春雨, 赵建红, 孙园园, 徐徽, 严奉君, 马均. 不同施氮水平下缓释氮肥配施对机插稻氮素利用特征及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(1): 50-64. |
| Wang H Y, Li Y, Sun Y J, Li Y H, Jiang M J, Wang C Y, Zhao J H, Sun Y Y, Xu H, Yan F J, Ma J.Effects of slow-release urea on nitrogen utilization and yield in mechanically-transplanted rice under different nitrogen application rates[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(1): 50-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 李玥, 李应洪, 赵建红, 孙永健, 徐徽, 严奉君, 谢华英, 马均. 缓控释氮肥对机插稻氮素利用特征及产量的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2015, 41(6): 673-684. |
| Li Y, Li Y H, Zhao J H, Sun Y J, Xu H, Yan F J, Xie H Y, Ma J.Effects of slow and controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen utilization characteristics and yield of machine-transplanted rice[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture & Life Sciences), 2015, 41(6): 673-684. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 张绍文, 何巧林, 王海月, 蒋明金, 李应洪, 严奉君, 杨志远, 孙永健, 郭翔, 马均. 控制灌溉条件下施氮量对杂交籼稻F优498氮素利用效率及产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(1): 82-94. |
| Zhang S W, He Q L, Wang H Y, Jiang M J, Li Y H, Yan F J, Yang Z Y, Sun Y J, Guo X, Ma J.Effects of nitrogen application rates on nitrogen use efficiency and grain yield of indica hybrid rice F you 498 under controlled intermittent irrigation[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2018, 24(1): 82-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 孙永健, 马均, 孙园园, 徐徽, 严奉君, 代邹, 蒋明金, 李玥. 水氮管理模式对杂交籼稻冈优527群体质量和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(10): 2047-2061. |
| Sun Y J, Ma J, Sun Y Y, Xu H, Yan F J, Dai Z, Jiang M J, Li Y.Effects of water and nitrogen management patterns on population quality and yield of hybrid rice gangyou 527[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2014, 47(10): 2047-2061. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | He H, You C, Wu H, Zhu D, Yang R, He Q, Wu L.Effects of nursery tray and transplanting methods on rice yield[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2018, 110(1): 104. |
| [14] | 王海月, 殷尧翥, 孙永健, 李应洪, 杨志远, 严奉君, 张绍文, 郭长春, 马均. 不同株距和缓释氮肥配施量下机插杂交稻的产量及光合特性[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(4): 843-855. |
| Wang H Y, Yin Y Z, Sun Y J, Li Y H, Yang Z Y, Yan F J, Zhang S W, Guo C C, Ma J.Yield and photosynthetic characteristics of mechanical-transplanted rice under different slow-release nitrogen fertilizer rates and plant population[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2017, 23(4): 843-855. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 张桥, 向开宏, 孙永健, 武云霞, 郭长春, 唐源, 刘芳艳, 马均. 不同育秧方式下播种量和插秧机具对水稻产量及群体质量的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(11): 227-238. |
| Zhang Q, Xiang K H, Sun Y J, Wu Y X,; Guo C C, Tang Y, Liu F Y, Ma J.Effects of seeding amount and transplanting machines on rice yield and population quality under different seedling raising methods[J]. Journal Nuclear Agricultural Science, 2020, 34(11): 227-238. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 孙永健, 孙园园, 蒋明金, 李应洪, 严奉君, 徐徽, 王海月, 马均. 施肥水平对不同氮效率水稻氮素利用特征及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(24): 4745-4756. |
| Sun Y J, Sun Y Y, Jiang M J, Li Y H, Yan F J, Xu H, Wang H Y, Ma J.Effects of fertilizer levels on nitrogen utilization characteristics and yield in rice cultivars with different nitrogen use efficiencies[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(24): 4745-4756. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 李应洪, 孙永健, 李玥, 吕腾飞, 蒋明金, 严奉君, 马均. 不同秧龄下机插方式与密度对杂交稻根系生长及氮素利用特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 599-610. |
| Li Y H, Sun Y J, Li Y, Lü T F, Jiang M J, Yan F J, Ma J.Effects of mechanical-transplanted modes and density on root growth and characteristics of nitrogen utilization in hybrid rice at different seedling-ages[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 599-610. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 戢林, 杨欢, 李廷轩, 张锡洲, 余海英. 氮高效利用基因型水稻干物质生产和氮素积累特性[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(6): 327-335. |
| Ji L, Yang H, Li T X, Zhang X Z, Yu H Y.Dry matter production and nitrogen accumulation of rice genotypes with different nitrogen use efficiencies[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(6): 327-335. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 陈明霞, 黄见良, 崔克辉, 聂立孝, 彭少兵. 不同氮效率基因型水稻植株氨挥发速率及其与氮效率的关系[J].作物学报, 2010, 36(5): 879-884. |
| Chen M X, Huan J L, Cui K H, Nie L X, Peng S B.Genotypic variation in ammonia volatilization rate of rice shoots and its relationship with nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2010, 36(5): 879-884. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 尹晓明, 李辰. 不同氮效率水稻品种叶片光合作用及氮利用特征的差异分析[J]. 作物杂志, 2019(1): 90-96. |
| Yi X M, Li C.Differences in leaf photosynthesis and assimilation of nitrogen between two rice cultivars differing in nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Crops, 2019(1): 90-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 彭玉, 孙永健, 蒋明金, 徐徽, 秦俭, 杨志远, 马均. 不同水分条件下缓/控释氮肥对水稻干物质量和氮素吸收、运转及分配的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2014, 40(5): 859-870. |
| Peng Y, Sun Y J, Jiang M J, Xu H, Qin J, Yang Z Y, Ma J.Effects of water management and slow/controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on biomass and nitrogen accumulation, translocation, and distribution in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(5): 859-870. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 许轲, 周兴涛, 曹利强, 张洪程, 郭保卫, 陈厚存, 吴中华, 朱聪聪, 杨岩. 不同类型钵苗及摆栽密度对粳型超级稻氮素吸收利用与转运特征的影响[J].中国农业科学, 2013, 46(23): 4876-4892. |
| Xu K, Zhou X T, Cao L H, Zhang H C, Guo B W, Chen H C, Wu Z H, Zhu C C, Yang Y.Effects of different types of bowl seedlings and densities on characteristics of nitrogen uptake, utilization and translocation of bowl transplanted japonica super rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 46(23): 4876-4892. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 侯玉. 不同栽培管理模式下水稻产量形成与氮肥利用效率的比较研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2014: 37. |
| Hou Y.Grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency under different crop management practices in single season rice[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014: 37. | |
| [24] | 彭龙龙. 氮肥运筹和播种量对双季稻群体发育及产量形成研究[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2016: 55-56. |
| Peng L L.The research on characteristics of nitrogen application and different seeding rate on double crop rice machine plug population development and yield formation[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2016: 55-56. | |
| [25] | 吴文革, 周永进, 陈刚, 蔡海涛, 吴然然, 李霞红, 孙如银. 不同育秧基质和水分管理对机插稻秧苗素质与产量的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2014, 22(9): 1057-1063. |
| Wu W G, Zhou Y J, Chen G, Cai H T, Wu R R, Li X H, Sun R Y.Effects of different seedling nursery substrates and water management modes on seedling quality and yield of mechanically transplanted rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2014, 22(9): 1057-1063. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 汪建军, 曾勇军, 易艳红, 章起明, 胡启星, 谭雪明, 黄山, 商庆银, 曾研华, 石庆华. 基于不同播种量的双季机插早稻均匀度对产量形成的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2018(2): 141-147. |
| Wang J J, Zeng Y J, Yi Y H, Zhang Q M, Hu Q X, Tan X M, Huang S, Shang Q Y, Zeng Y H, Shi Q H.The uniformity of mechanical-transplanted early-season rice under different seeding rates and its effects on the formation of grain yield[J]. Crops, 2018(2): 141-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 龙瑞平, 邓安凤, 刘冲发, 祁春, 夏琼梅, 李贵勇, 杨从党. 播种量对机插稻产量和生物学特性的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2013, 19(4): 109-110, 113. |
| Long Y P, Deng A F, Liu C F, Qi C, Xia Q M, Li G Y, Yang C D.Effects of seeding rate on yield and biological characteristics of mechanical transplanting rice[J]. China Rice, 2013, 19(4): 109-110, 113. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 何文洪, 陈惠哲, 朱德峰, 徐一成, 林贤青, 张玉屏. 不同播种量对水稻机插秧苗素质及产量的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2008, 14(3): 60-62. |
| He W H, Chen H Z, Zhu D F, Xu Y C, Lin X Q, Zhang Y P.Effects of different sowing quantity on quality and yield of rice transplanter seedlings[J]. China Rice, 2008, 14(3): 60-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 蒋鹏, 张林, 周兴兵, 郭晓艺, 朱永川, 刘茂, 郭长春, 熊洪, 徐富贤. 冬水田轻简化栽培杂交稻蓄留再生稻产量形成特点 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [2] | 熊家欢, 张义凯, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 姚坚, 张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [3] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [4] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [5] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [6] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [7] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [8] | 杨永刚, 袁晓娟, 曹云, 陈雪芳, 尹慧来, 王志强, 文艳芳, 杨志远, 孙园园, 贾现文, 马均, 孙永健. 品种和播种量互作对机械旱直播水稻与杂草养分竞争的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 185-197. |
| [9] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [10] | 朱旺, 张翔, 耿孝宇, 张哲, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根, 许轲, 朱广龙, 周桂生, 孟天瑶. 盐-旱复合胁迫下水稻根系的形态和生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [11] | 吴玉红, 李艳华, 王吕, 秦宇航, 李杉杉, 郝兴顺, 张庆路, 崔月贞, 肖飞. 陕南稻区紫云英稻草联合还田配施减量氮肥协同提升水稻产量与稻米品质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 628-641. |
| [12] | 邹宇傲, 吴启侠, 周乾顺, 朱建强, 晏军. 孕穗期杂交中稻对淹涝胁迫的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| [13] | 袁沛, 周旋, 杨威, 尹凌洁, 靳拓, 彭建伟, 荣湘民, 田昌. 化肥减氮配施对洞庭湖区双季稻产量和田面水氮磷流失风险的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 518-528. |
| [14] | 肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [15] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||