
中国水稻科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 185-197.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230803
杨永刚1, 袁晓娟1, 曹云1, 陈雪芳1, 尹慧来1, 王志强1, 文艳芳1, 杨志远1, 孙园园2, 贾现文3, 马均1, 孙永健1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-08
修回日期:2023-09-20
出版日期:2024-03-10
发布日期:2024-03-14
通讯作者:
* email:yongjians1980@163.com
基金资助:
YANG Yonggang1, YUAN Xiaojuan1, CAO Yun1, CHEN Xuefang1, YIN Huilai1, WANG Zhiqiang1, WEN Yanfang1, YANG Zhiyuan1, SUN Yuanyuan2, JIA Xianwen3, MA Jun1, SUN Yongjian1,*( )
)
Received:2023-08-08
Revised:2023-09-20
Online:2024-03-10
Published:2024-03-14
Contact:
* email:yongjians1980@163.com
摘要:
【目的】明确机械旱直播水稻品种和播种量对抑制杂草生长的效果,为实现机直播稻优质高产绿色高效栽培提供理论依据。【方法】以三系杂交稻川康优6308(C1)和两系杂交稻晶两优534(C2)为试材,设15 kg/hm2(S1)、22.5 kg/hm2(S2)、37.5 kg/hm2(S3)三个播种量,研究其对稻田主要杂草与水稻关键生育时期干物质累积、养分累积及转运的影响,并探讨品种和播种量互作下水稻与杂草养分竞争的关系。【结果】1) 直播后29 d时,稻田杂草密度较水稻显著增加39.29%~47.16%,且杂草与水稻群体干质量比及养分累积比均高于1∶1,据此进行了一次必要性除草。2) 除草前,品种C1较C2杂草密度显著降低91.34%~96.54%,水稻干物质累积量增加19.21%~30.24%,氮、磷、钾累积提高7.17%~34.59%;同一品种提高播种量,杂草量显著降低,相对S1,S2和S3处理杂草量显著降低21.95%~109.69%,水稻干物质累积量增加39.78%~94.52%,氮、磷、钾累积量提高10.11%~50.79%。3) 除草后,直播43 d,杂草数量显著降低,品种C1较C2干物质累积量增加54.12%~66.97%,氮、磷、钾养分提高15.56%~47.45%;同一品种下,S2和S3较S1处理水稻密度显著提高14.94%~32.34%,干物质累积量增加24.45%~85.07%,氮、磷、钾养分提高21.62%~98.34%;但随播种量的增加,结实期氮、磷、钾养分转运量与转运率,以及稻谷产量均呈先增加后降低趋势,以S2处理最高。【结论】综合抑制杂草生长和稻谷产量,机械旱直播水稻以选用川康优6308配套22.5 kg/hm2播种量,并依据稻田杂草总密度高于水稻且杂草与水稻群体干质量比及养分比1∶1时为最佳除草时机,可发挥水稻品种与播种量互作的优势控制杂草生长,减少除草剂使用,提高产量。
杨永刚, 袁晓娟, 曹云, 陈雪芳, 尹慧来, 王志强, 文艳芳, 杨志远, 孙园园, 贾现文, 马均, 孙永健. 品种和播种量互作对机械旱直播水稻与杂草养分竞争的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 185-197.
YANG Yonggang, YUAN Xiaojuan, CAO Yun, CHEN Xuefang, YIN Huilai, WANG Zhiqiang, WEN Yanfang, YANG Zhiyuan, SUN Yuanyuan, JIA Xianwen, MA Jun, SUN Yongjian. Effects of Variety and Seeding Rate Interaction on Nutrient Competition Between Mechanized Dry Direct Seeded Rice and Weeds[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(2): 185-197.
| 年份 Year | 全氮 Total N(g/kg) | 有机质 Organic matter(g/kg) | 速效养分 Available nutrient(mg/kg) | pH值 pH value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | ||||
| 2022 | 1.97 | 24.8 | 106.02 | 28.1 | 81.3 | 6.22 |
| 2023 | 2.06 | 26.1 | 110.40 | 25.6 | 96.2 | 5.90 |
表1 耕层土壤(0-20 cm)基础理化性质
Table 1. Basic physicochemical properties of topsoil(0-20 cm)
| 年份 Year | 全氮 Total N(g/kg) | 有机质 Organic matter(g/kg) | 速效养分 Available nutrient(mg/kg) | pH值 pH value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | ||||
| 2022 | 1.97 | 24.8 | 106.02 | 28.1 | 81.3 | 6.22 |
| 2023 | 2.06 | 26.1 | 110.40 | 25.6 | 96.2 | 5.90 |
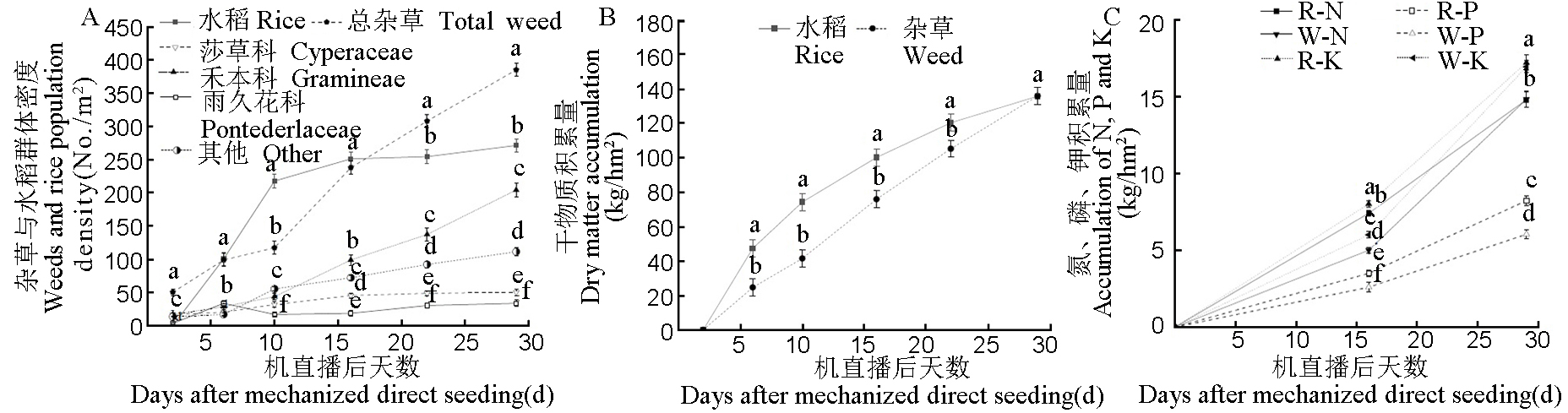
图1 稻田杂草与水稻群体密度(A)、干物质积累量(B)及氮磷钾积累量(C)动态变化 R-N:水稻氮含量;R-P:水稻磷含量;R-K:水稻钾含量;W-N:杂草氮含量;W-P:杂草磷含量;W-K:杂草钾含量。
Fig. 1. Dynamic changes in weed and rice population density (A), dry matter accumulation (B), and N, P, and K accumulation (C) in paddy fields R-N, N content in rice; R-P, P content in rice; R-K, K content in rice; W-N, N content in weed; W-P, P content in weed; W-K, K content in weed.
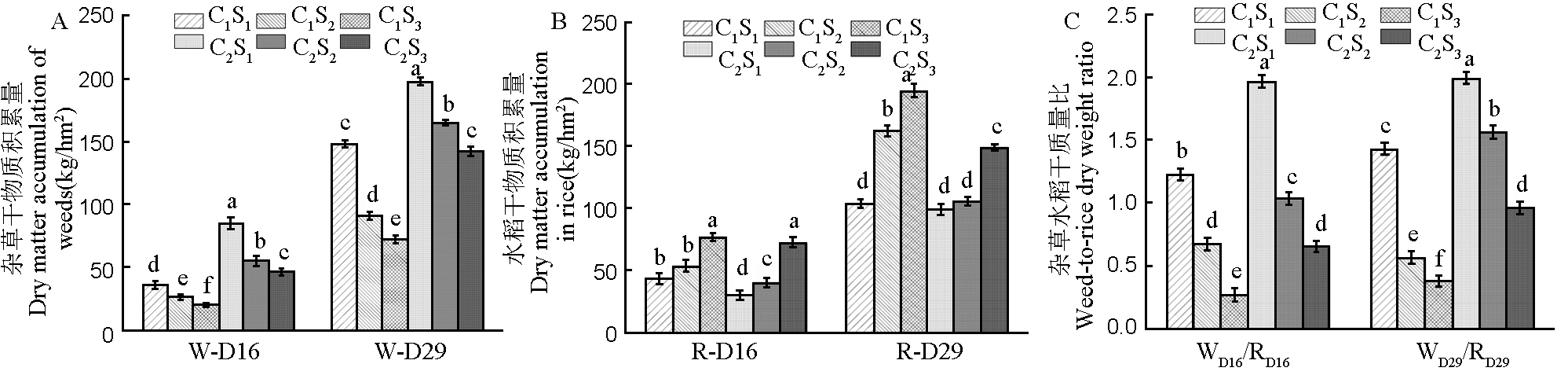
图2 除草前品种和播种量对杂草干物质积累量(A)、水稻干物质积累量(B)及杂草水稻干质量比(C)的影响 W-D16:直播后16 d杂草干物质累积量;W-D29:直播后29 d杂草干物质累积量;R-D16:直播后16 d水稻干物质累积量;R-D29:直播后29 d水稻干物质累积量。WD16/RD16:直播后16 d杂草水稻干质量比;WD29/RD29:直播后29 d杂草与水稻干质量比。C1:川康优6308;C2:晶两优534;S1、S2、S3:播种量15 kg/hm2、22.5 kg/hm2、37.5 kg/hm2。同一时期下不同处理间标注的不同字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 2. Effects of pre-weeding varieties and sowing rates on weed dry matter accumulation (A), rice dry matter accumulation (B), and weed-to-rice dry weight ratio (C) W-D16, Cumulant of dry matter of weeds at 16 days after direct seeding; W-D29, Cumulant of dry matter of weeds at 29 days after direct seeding; R-D16, Cumulant of dry matter of rice at 16 days after direct seeding; R-D29, Cumulant of dry matter of rice at 29 days after direct seeding. WD16/RD16, Weed-to-rice dry weight ratio at 16 days after direct seeding; WD29/RD29, Weed-to-rice dry weight ratio at 29 days after direct seeding. C1, Chuankangyou 6308; C2, Jingliangyou 534; S1, S2, S3, Sowing rates of 15 kg/hm2, 22.5 kg/hm2, 37.5 kg/hm2. Different letters between different treatments during the same period indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05).
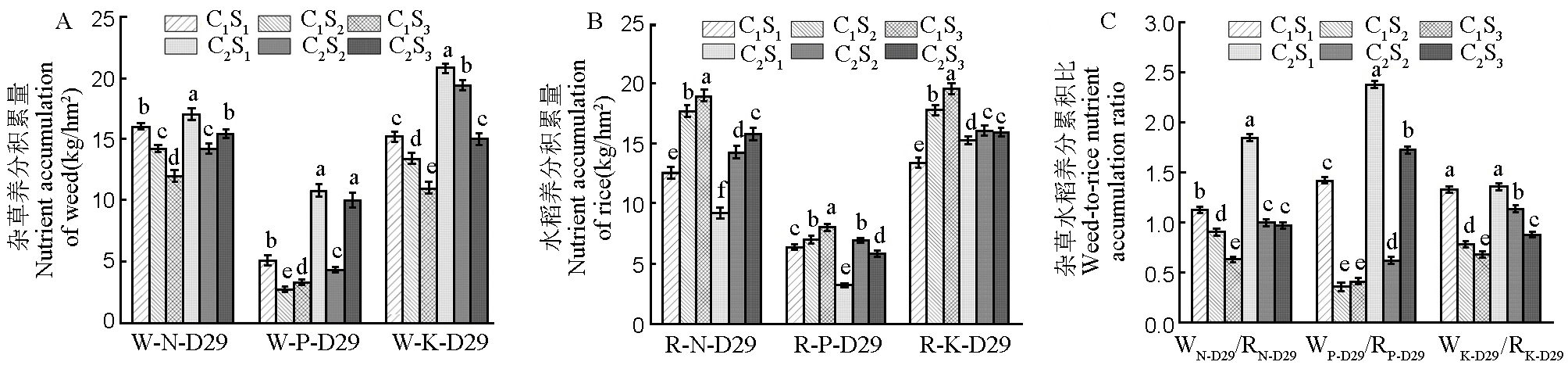
图3 除草前品种和播种量对杂草养分积累量(A)、水稻养分积累量(B)及杂草水稻养分累积比(C) W-N-D29:直播后29 d杂草氮累积量;W-P-D29:直播后29 d杂草磷累积量;W-K-D29:直播后29 d杂草钾累积量;R-N-D29:直播后29 d水稻氮累积量;R-P-D29:直播后29 d水稻磷累积量;R-K-D29:直播后29 d水稻钾累积量。WN-D29/RN-D29:直播29 d后杂草水稻氮养分累积比;WP-D29/RP-D29:直播29 d后杂草水稻磷养分累积比;WK-D29/RK-D29:直播29 d后杂草水稻钾养分累积比。C1:川康优6308;C2:晶两优534;S1、S2、S3:播种量15 kg/hm2、22.5 kg/hm2、37.5 kg/hm2。同一养分下不同处理间标注的不同字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 3. Effects of pre-weeding varieties and sowing rates on weed nutrient accumulation (A), rice nutrient accumulation (B), and weed-to-rice nutrient accumulation ratio (C) W-N-D29, Cumulant of weed N at 29 days after direct seeding; W-P-D29, Cumulant of weed P at 29 days after direct seeding; W-K-D29, Cumulant of weed K at 29 days after direct seeding; R-N-D29, Cumulant of N rice at 29 days after direct seeding; R-P-D29, Cumulant of P in rice at 29 days after direct seeding; R-K-D29, Cumulant of K in rice at 29 days after direct seeding. WN-D29/RN-D29: Weed-to-rice N accumulation ratio at 29 days after direct seeding;WP-D29/RP-D29: Weed-to-rice P accumulation ratio at 29 days after direct seeding; WK-D29/RK-D29: Weed-to-rice K accumulation at 29 days after direct seeding. C1, Chuankangyou 6308; C2, Jingliangyou 534; S1, S2, S3: Sowing rates of 15 kg/hm2, 22.5 kg/hm2, 37.5 kg/hm2. Different letters between different treatments during the same period indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05).
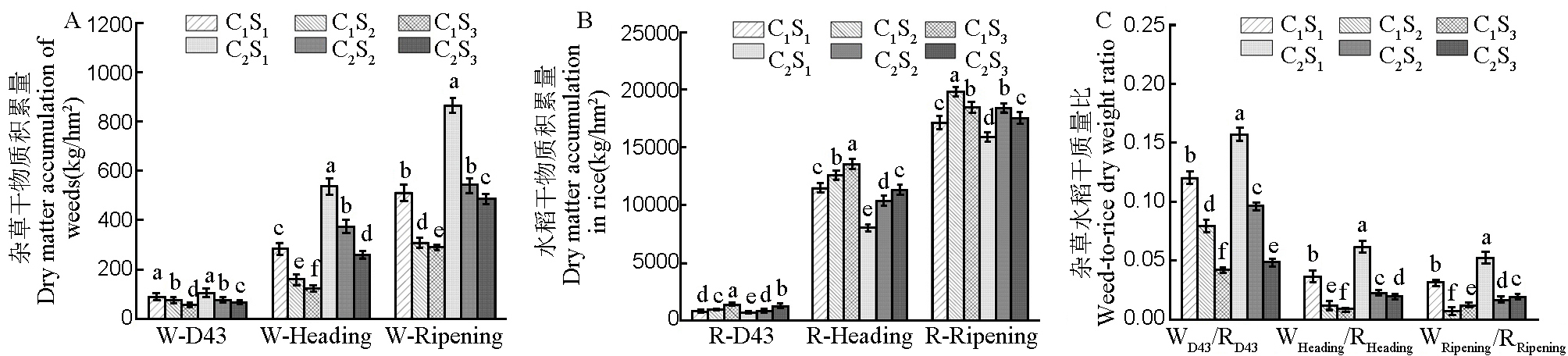
图4 除草后品种和播种量对杂草干物质积累量(A)、水稻干物质积累量(B)及杂草水稻干质量比(C) W-D43:直播43 d杂草干物质积累量;W-Heading:抽穗期杂草干物质积累量;W-Ripening:成熟期杂草干物质积累量;R-D43: 直播43 d水稻干物质积累量;R-Heading:抽穗期水稻干物质积累量;R-Ripening:成熟期水稻干物质积累量。WD43/RD43:直播43 d后杂草水稻干物质积累量比;WHeading/RHeading:抽穗期杂草水稻干物质积累量比;WRipening/RRipening:成熟期杂草水稻干物质积累量比。C1:川康优6308;C2:晶两优534;S1、S2、S3:播种量15 kg/hm2、22.5 kg/hm2、37.5 kg/hm2。同一时期下不同处理间标注的不同字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 4. Effects of weed varieties and sowing amount on weed dry matter accumulation (A), rice dry matter accumulation (B), and weed-to-rice dry weight ratio (C) after weeding W-D43, Dry matter accumulation of weed at 43 days after direct seeding; W-Heading, Dry matter accumulation of weeds during heading; W-Ripening, Dry matter accumulation of weeds during ripening; R-D43, Dry matter accumulation of rice at 43 days after direct seeding; R-Heading, Dry matter accumulation of rice during heading; R-Ripening, Dry matter accumulation of rice during ripening. WD43/RD43: Weed-to-rice dry matter accumulation ratio at 43 days after direct seeding; WHeading/RHeading: Weed-to-rice dry matter accumulation ratio during the heading stage; WRipening/RRipening: Weed-to-rice dry matter accumulation ratio during the ripening stage; C1, Chuankangyou 6308; C2, Jingliangyou 534; S1, S2, S3, Sowing rates of 15 kg/hm2, 22.5 kg/hm2, 37.5 kg/hm2. Different letters between different treatments during the same period indicate significant differences between treatments (P<0.05).
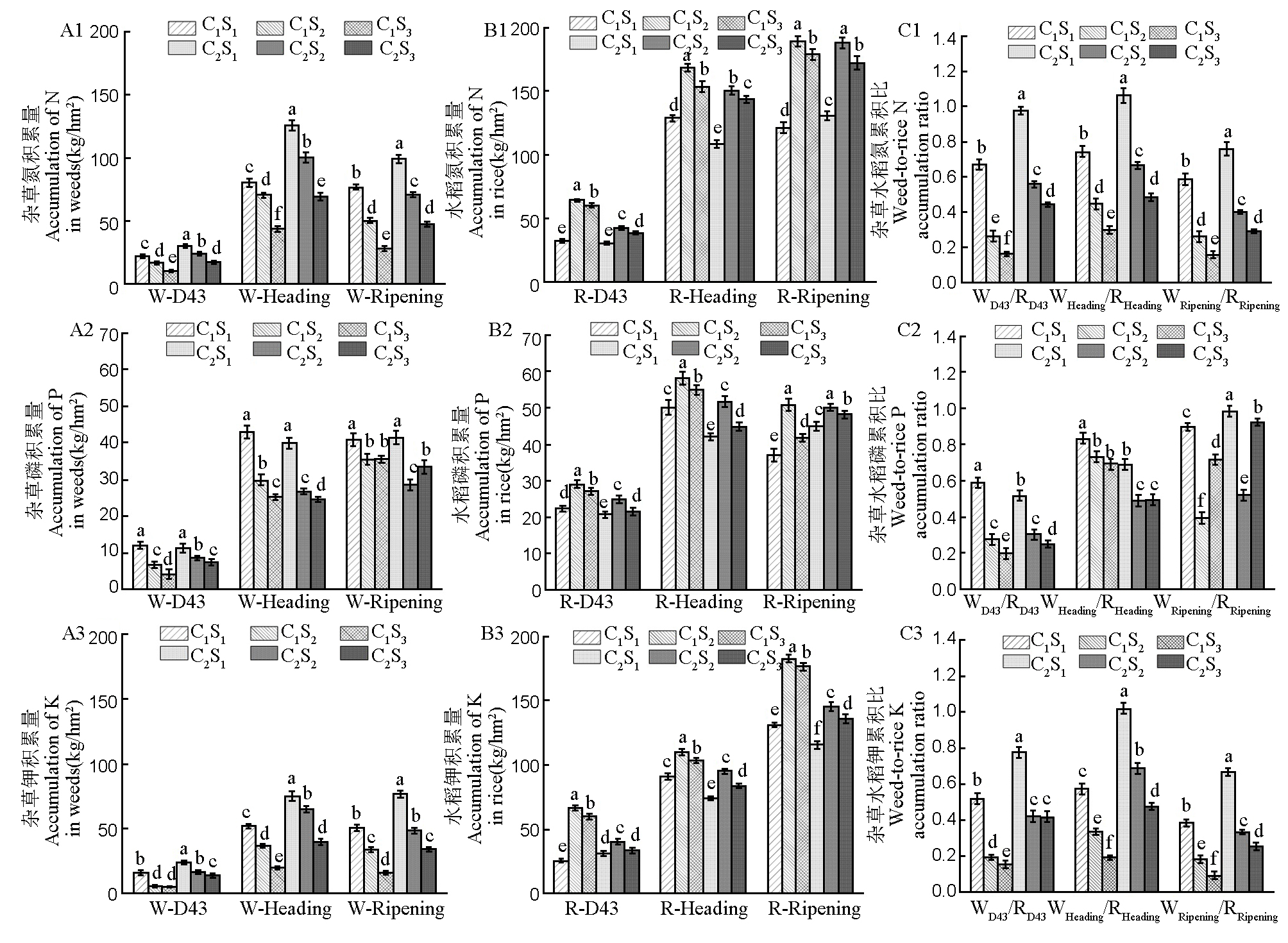
图5 除草后品种和播种量对杂草养分积累量、水稻养分积累量及杂草水稻养分累积比 W-D43:直播后43 d杂草氮(磷/钾)含量;W-Heading:抽穗期杂草氮(磷/钾)含量;W-Ripening:成熟期杂草氮(磷/钾)含量;R-D43:直播后43 d水稻氮(磷/钾)含量;R-Heading:抽穗期水稻氮(磷/钾)含量;R-Ripening:成熟期水稻氮(磷/钾)含量。WD43/RD43:直播43 d后杂草水稻氮(磷/钾)养分累积比;WHeading/RHeading:抽穗期杂草水稻氮(磷/钾)养分累积比;WRipening/RRipening:成熟期杂草水稻氮(磷/钾)养分累积比。C1:川康优 6308;C2:晶两优534;S1、S2、S3:播种量15 kg/hm2、22.5 kg/hm2、37.5 kg/hm2。同一时期下不同处理间标注的不同字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Fig. 5. Effects of weeding varieties and sowing rates on weed nutrient accumulation, rice nutrient accumulation, and weed-to- rice nutrient accumulation ratio W-D43, Weed nitrogen (P/K) content at 43 days after direct seeding; W-Heading, Nitrogen (P/K) content of weeds during heading period; W-Ripening, Nitrogen (P/K) content in ripening weeds; R-D43, Rice nitrogen (P/K) content at 43 days after of direct seeding; R-Heading, Nitrogen (P/K) content of rice during heading period; R-Ripening, Nitrogen (P/K) content in ripening rice. WD43/RD43: Weed-to-rice N (P/K) accumulation ratio at 43 days after direct seeding; WHeading/RHeading: Weed-to-rice of N (P/K) accumulation ratio during heading stage. WRipening/RRipening: Weed-to-rice of N (P/K) accumulation ratio during ripening stage. C1, Chuankangyou 6308; C2, Jingliangyou 534; S1, S2, S3, Sowing rates of 15 kg/hm2, 22.5 kg /hm2, 37.5 kg/hm2. Different letters labeled between different treatments during the same period indicate significant differences (P<0.05).
| 处理 Treatment | 氮N | 磷P2O5 | 钾K2O | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 品种 Cultivar | 播种量 Seeding rate | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | |||
| 川康优6308 Chuankangyou 6308 | S1 | 32.80 ab | 61.62 c | 35.42 a | 65.90 b | 20.77 b | 28.39 c | |||
| S2 | 20.72 d | 53.31 e | 18.57 c | 54.82 d | 14.74 c | 17.58 e | ||||
| S3 | 13.70 d | 57.70 d | 24.04 b | 59.58 c | 10.65 d | 21.79 d | ||||
| 平均 Average | 22.41 | 57.54 | 26.01 | 60.10 | 15.39 | 22.59 | ||||
| 晶两优534 Jingliangyou 534 | S1 | 36.80 a | 77.62 a | 21.35 bc | 73.12 a | 30.25 a | 50.65 a | |||
| S2 | 30.37 b | 67.35 b | 10.95 d | 43.41 e | 20.67 b | 32.34 b | ||||
| S3 | 18.90 c | 63.44 c | 16.43 c | 63.06 bc | 15.22 c | 25.55 c | ||||
| 平均 Average | 28.69 | 69.47 | 16.24 | 59.86 | 22.05 | 36.18 | ||||
| F值 F value | C | 82.07** | 182.73** | 326.29** | 46.00** | 0.41 | 265.94** | |||
| S | 111.01** | 55.41** | 146.95** | 25.91** | 68.90** | 229.13** | ||||
| C×S | 22.44** | 5.35** | 3.28 | 266.37** | 178.47** | 311.48** | ||||
表2 品种和播种量互作对机械旱直播稻结实期杂草氮(N)、磷(P2O5)、钾素(K2O)转运的影响
Table 2. Effects of rice variety and sowing rate interaction on nitrogen(N), phosphorus((P2O5), and potassium(K2O) transport of weeds during the seeding stage under mechanized dry direct seeding
| 处理 Treatment | 氮N | 磷P2O5 | 钾K2O | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 品种 Cultivar | 播种量 Seeding rate | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | |||
| 川康优6308 Chuankangyou 6308 | S1 | 32.80 ab | 61.62 c | 35.42 a | 65.90 b | 20.77 b | 28.39 c | |||
| S2 | 20.72 d | 53.31 e | 18.57 c | 54.82 d | 14.74 c | 17.58 e | ||||
| S3 | 13.70 d | 57.70 d | 24.04 b | 59.58 c | 10.65 d | 21.79 d | ||||
| 平均 Average | 22.41 | 57.54 | 26.01 | 60.10 | 15.39 | 22.59 | ||||
| 晶两优534 Jingliangyou 534 | S1 | 36.80 a | 77.62 a | 21.35 bc | 73.12 a | 30.25 a | 50.65 a | |||
| S2 | 30.37 b | 67.35 b | 10.95 d | 43.41 e | 20.67 b | 32.34 b | ||||
| S3 | 18.90 c | 63.44 c | 16.43 c | 63.06 bc | 15.22 c | 25.55 c | ||||
| 平均 Average | 28.69 | 69.47 | 16.24 | 59.86 | 22.05 | 36.18 | ||||
| F值 F value | C | 82.07** | 182.73** | 326.29** | 46.00** | 0.41 | 265.94** | |||
| S | 111.01** | 55.41** | 146.95** | 25.91** | 68.90** | 229.13** | ||||
| C×S | 22.44** | 5.35** | 3.28 | 266.37** | 178.47** | 311.48** | ||||
| 处理 Treatment | 氮N | 磷P2O5 | 钾K2O | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 品种 Cultivar | 播种量 Seeding rate | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | |||
| 川康优6308 Chuankangyou 6308 | S1 | 17.88 d | 22.06 d | 7.91 c | 31.31 e | 9.25 bc | 12.02 c | |||
| S2 | 37.96 a | 59.00 a | 17.15 a | 84.43 a | 13.17 a | 19.11 a | ||||
| S3 | 27.29 c | 49.98 b | 13.94 b | 68.55 b | 8.68 c | 12.68 c | ||||
| 平均 Average | 27.71 | 43.68 | 13.00 | 76.49 | 10.37 | 14.60 | ||||
| 晶两优534 Jingliangyou 534 | S1 | 8.59 e | 17.09 e | 12.76 b | 44.06 d | 11.15 b | 14.82 b | |||
| S2 | 32.05 b | 36.98 c | 18.31 a | 51.64 c | 13.91 a | 15.49 b | ||||
| S3 | 17.19 d | 23.38 d | 5.69 c | 34.08 e | 4.96 d | 6.47 d | ||||
| 平均 Average | 24.62 | 30.18 | 12.25 | 47.85 | 10.01 | 12.26 | ||||
| F值 F value | C | 93.92** | 44.34** | 4.29* | 4.14* | 29.11** | 32.48** | |||
| S | 35.21** | 12.65** | 17.85** | 38.62** | 133.45** | 228.06** | ||||
| C×S | 52.54** | 29.42** | 4.57* | 75.10** | 102.51** | 58.21** | ||||
表3 品种和播种量互作对机械旱直播稻结实期氮(N)、磷(P2O5)、钾素(K2O)转运的影响
Table 3. Effects of variety and sowing rate interaction on nitrogen(N), phosphorus(P2O5), and potassium(K2O) transport during seed setting stage of mechanized dry direct seeded rice
| 处理 Treatment | 氮N | 磷P2O5 | 钾K2O | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 品种 Cultivar | 播种量 Seeding rate | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | 转运量 Transit volume (kg/hm2) | 转运率 Transit rate (%) | |||
| 川康优6308 Chuankangyou 6308 | S1 | 17.88 d | 22.06 d | 7.91 c | 31.31 e | 9.25 bc | 12.02 c | |||
| S2 | 37.96 a | 59.00 a | 17.15 a | 84.43 a | 13.17 a | 19.11 a | ||||
| S3 | 27.29 c | 49.98 b | 13.94 b | 68.55 b | 8.68 c | 12.68 c | ||||
| 平均 Average | 27.71 | 43.68 | 13.00 | 76.49 | 10.37 | 14.60 | ||||
| 晶两优534 Jingliangyou 534 | S1 | 8.59 e | 17.09 e | 12.76 b | 44.06 d | 11.15 b | 14.82 b | |||
| S2 | 32.05 b | 36.98 c | 18.31 a | 51.64 c | 13.91 a | 15.49 b | ||||
| S3 | 17.19 d | 23.38 d | 5.69 c | 34.08 e | 4.96 d | 6.47 d | ||||
| 平均 Average | 24.62 | 30.18 | 12.25 | 47.85 | 10.01 | 12.26 | ||||
| F值 F value | C | 93.92** | 44.34** | 4.29* | 4.14* | 29.11** | 32.48** | |||
| S | 35.21** | 12.65** | 17.85** | 38.62** | 133.45** | 228.06** | ||||
| C×S | 52.54** | 29.42** | 4.57* | 75.10** | 102.51** | 58.21** | ||||
| 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 播种量 Seeding rate | 有效穗 Effective panicles (×104/hm2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelets No per panicle | 总颖花数 Total spikelets (×106/hm2) | 结实率 Seed setting rate(%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight(g) | 产量 Grain yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 川康优6308 Chuankangyou 6308 | S1 | 166.96 c | 181.78 ab | 340.82 c | 81.24 a | 32.55 a | 8333.79 bc |
| S2 | 200.81 b | 189.52 a | 401.16 a | 79.00 b | 32.38 a | 9582.00 a | ||
| S3 | 173.87 c | 160.98 c | 325.78 d | 81.10 a | 32.54 a | 7936.17 c | ||
| 平均 Average | 180.55 | 177.43 | 355.92 | 80.45 | 32.49 | 8617.32 | ||
| 晶两优534 Jingliangyou 534 | S1 | 209.79 b | 162.57 c | 316.41 d | 78.04 c | 30.59 a | 7932.07 c | |
| S2 | 237.24 a | 177.49 b | 356.21 b | 75.33 d | 30.36 a | 8573.81 b | ||
| S3 | 216.47 b | 154.84 d | 315.85 d | 77.78 c | 30.52 a | 7850.35 c | ||
| 平均 Average | 221.17 | 164.97 | 329.49 | 77.05 | 30.49 | 8118.74 | ||
| F值 F | C | 123.22** | 125.71** | 54.55** | 320.33** | 10.78** | 11.22** | |
| F value | S | 42.66** | 10.53** | 102.64** | 30.33** | 0.42 | 23.60** | |
| C×S | 5.34* | 0.39* | 8.06** | 4.33* | 0.01 | 3.31* | ||
| 2023 | 川康优6308 Chuankangyou 6308 | S1 | 228.39 c | 182.95 a | 397.47 b | 81.07 a | 31.09 a | 8338.78 c |
| S2 | 240.29 bc | 178.52 a | 407.72 a | 80.65 a | 31.03 a | 9979.11 a | ||
| S3 | 184.49 e | 161.25 b | 337.52 c | 78.81 b | 30.76 a | 8714.03 bc | ||
| 平均 Average | 217.72 | 174.24 | 380.90 | 80.18 | 30.96 | 9010.64 | ||
| 晶两优534 Jingliangyou 534 | S1 | 199.97 d | 164.81 b | 329.57 c | 74.02 c | 30.15 b | 7223.48 d | |
| S2 | 246.22 ab | 168.28 b | 414.34 a | 73.13 d | 30.65 ab | 9268.93 b | ||
| S3 | 257.22 a | 152.10 c | 391.23 b | 71.64 e | 30.61 ab | 8270.98 c | ||
| 平均 Average | 234.47 | 161.73 | 378.38 | 72.93 | 30.47 | 8254.46 | ||
| F值 | C | 15.51** | 18.48** | 2.28 | 1281.33** | 12.28* | 11.73** | |
| F value | S | 81.96** | 15.11** | 108.52** | 97.00** | 0.54 | 23.62** | |
| C×S | 2.27* | 0.95* | 2.55* | 6.33* | 0.55 | 0.78* | ||
表4 品种和播种量互作对机械旱直播稻产量及其构成的影响
Table 4. Effects of the Interaction between varieties and seeding rates on the yield and its components of mechanized dry direct seeded rice
| 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 播种量 Seeding rate | 有效穗 Effective panicles (×104/hm2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelets No per panicle | 总颖花数 Total spikelets (×106/hm2) | 结实率 Seed setting rate(%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight(g) | 产量 Grain yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 川康优6308 Chuankangyou 6308 | S1 | 166.96 c | 181.78 ab | 340.82 c | 81.24 a | 32.55 a | 8333.79 bc |
| S2 | 200.81 b | 189.52 a | 401.16 a | 79.00 b | 32.38 a | 9582.00 a | ||
| S3 | 173.87 c | 160.98 c | 325.78 d | 81.10 a | 32.54 a | 7936.17 c | ||
| 平均 Average | 180.55 | 177.43 | 355.92 | 80.45 | 32.49 | 8617.32 | ||
| 晶两优534 Jingliangyou 534 | S1 | 209.79 b | 162.57 c | 316.41 d | 78.04 c | 30.59 a | 7932.07 c | |
| S2 | 237.24 a | 177.49 b | 356.21 b | 75.33 d | 30.36 a | 8573.81 b | ||
| S3 | 216.47 b | 154.84 d | 315.85 d | 77.78 c | 30.52 a | 7850.35 c | ||
| 平均 Average | 221.17 | 164.97 | 329.49 | 77.05 | 30.49 | 8118.74 | ||
| F值 F | C | 123.22** | 125.71** | 54.55** | 320.33** | 10.78** | 11.22** | |
| F value | S | 42.66** | 10.53** | 102.64** | 30.33** | 0.42 | 23.60** | |
| C×S | 5.34* | 0.39* | 8.06** | 4.33* | 0.01 | 3.31* | ||
| 2023 | 川康优6308 Chuankangyou 6308 | S1 | 228.39 c | 182.95 a | 397.47 b | 81.07 a | 31.09 a | 8338.78 c |
| S2 | 240.29 bc | 178.52 a | 407.72 a | 80.65 a | 31.03 a | 9979.11 a | ||
| S3 | 184.49 e | 161.25 b | 337.52 c | 78.81 b | 30.76 a | 8714.03 bc | ||
| 平均 Average | 217.72 | 174.24 | 380.90 | 80.18 | 30.96 | 9010.64 | ||
| 晶两优534 Jingliangyou 534 | S1 | 199.97 d | 164.81 b | 329.57 c | 74.02 c | 30.15 b | 7223.48 d | |
| S2 | 246.22 ab | 168.28 b | 414.34 a | 73.13 d | 30.65 ab | 9268.93 b | ||
| S3 | 257.22 a | 152.10 c | 391.23 b | 71.64 e | 30.61 ab | 8270.98 c | ||
| 平均 Average | 234.47 | 161.73 | 378.38 | 72.93 | 30.47 | 8254.46 | ||
| F值 | C | 15.51** | 18.48** | 2.28 | 1281.33** | 12.28* | 11.73** | |
| F value | S | 81.96** | 15.11** | 108.52** | 97.00** | 0.54 | 23.62** | |
| C×S | 2.27* | 0.95* | 2.55* | 6.33* | 0.55 | 0.78* | ||
| [1] | 于居龙, 张国, 朱阿秀, 张新凤, 王红春, 赵来成, 张建华, 姚克兵, 娄远来, 束兆林. 江苏丘陵地区旱直播水稻田杂草化除技术[J]. 杂草学报, 2022, 40(1): 34-41. |
| Yu J L, Zhang G, Zhu A X, Zhang X F, Wang H C, Zhao L C, Zhang J H, Yao K B, Lou Y L, Shu Z L. Weed control technology in dry direct seeding rice fields in hilly areas of Jiangsu Province[J]. Acta Weedica Sinica, 2022, 40 (1): 34-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 孔祥男, 张一, 丁伟. 3种除草剂对水稻旱直播阔叶杂草防效及安全性研究[J]. 植物保护, 2021, 47(5): 302-309. |
| Kong X N, Zhang Y, Ding W. Study on the control effect and safety of three herbicides on dry direct seeding broad-leaved weeds in rice[J]. Plant Protection, 2021, 47 (5): 302-309. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 李绍平, 邢志鹏, 田晋钰, 程爽, 胡群, 胡雅杰, 郭保卫, 魏海燕, 张洪程. 机械旱直播方式对水稻产量和光合物质生产特征的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(7): 1-9. |
| Li S P, Xing Z P, Tian J Y, Cheng S, Hu Q, Hu Y J, Guo B W, Wei H Y, Zhang H C. The effect of mechanical dry direct seeding on rice yield and photosynthetic material production characteristics[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2022, 38(7): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 罗锡文, 王在满, 曾山, 臧英, 杨文武, 张明华. 水稻机械化直播技术研究进展[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2019, 40(5): 1-13. |
| Luo X W, Wang Z M, Zeng S, Zang Y, Yang W Y, Zhang M H. Research progress in mechanized direct seeding technology for rice[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2019, 40(5): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 陈雪飞, 唐艳萍, 谢英杰, 李尚, 楚建波, 敖方源, 彭维钦, 李海山, 万玉华. 我国机械化直播水稻生产技术研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2018, 24(4): 9-15. |
| Chen X F, Tang Y P, Xie Y J, Li S, Chu J B, Ao F Y, Peng W Q, Li H S, Wan Y H. Research progress on mechanized direct seeding rice production technology in China[J]. China Rice, 2018, 24(4): 9-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 孙永健, 郑洪帧, 徐徽, 杨志远, 贾现文, 程洪彪, 马均. 机械旱直播方式促进水稻生长发育提高产量[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(20): 10-18. |
| Sun Y J, Zheng H J, Xu H, Yang Z Y, Jia X W, Cheng H B, Ma J. The mechanical dry direct seeding method promotes the growth and development of rice and increases yield[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2014, 30(20): 10-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 周燕芝, 陈丽明, 王文霞, 李祖军, 曾勇军, 谭雪明, 胡水秀, 石庆华, 潘晓华, 曾研华. 不同直播方式与杂草防除时期对稻田杂草发生及早籼稻产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 132-140. |
| Zhou Y Z, Chen L M, Wang W X, Li Z J, Zeng Y J, Tan X M, Hu S X, Shi Q H, Pan X H, Zeng Y H. The effects of different direct seeding methods and weed control periods on weed occurrence and early indica rice yield in rice fields[J]. Acta Prataculturage Sinica, 2020, 29 (5): 132-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 吴爱民. 直播稻田杂草综合防除策略及除草剂安全性评析[J]. 杂草科学, 2006(2): 1-3. |
| Wu A M Comprehensive weed control strategies and safety evaluation of herbicides in direct seeding rice fields[J]. Weed Science, 2006(2): 1-3. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 赵海英, 卢兆成, 乔利, 杨黎明. 5种除草剂防除旱直播稻田杂草比较试验[J]. 杂草科学, 2012, 30(1): 48-50. |
| Zhao H Y, Lu Z C, Qiao L, Yang L M. Comparative experiment on 5 herbicides for controlling weeds in dry direct seeding rice fields[J]. Weed Science, 2012, 30(1): 48-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 刘建凤, 吉春明, 陆玉荣, 郭勋斌. 不同药剂对旱直播稻田茎叶杂草的防效[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2014(21): 41-43. |
| Liu J F, Ji C M, Lu Y R, Guo X B. The control effect of different pesticides on stem and leaf weeds in dry direct seeding rice fields[J]. Hunan Agricultural Science, 2014(21): 41-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 邓权权, 潘圣刚, 段美洋, 田华, 钟克友, 肖立中, 唐湘如. 除草剂对旱直播稻田杂草防效和水稻幼苗的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2015, 28(1): 131-135. |
| Deng Q Q, Pan S G, Duan M Y, Tian H, Zhong K Y, Xiao L Z, Tang X R. The effect of herbicides on weed control and rice seedlings in dry direct seeding rice fields[J]. Southwest Agricultural Journal, 2015, 28(1): 131-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Sanjoy S, Sushmita M, Sudhanshu S, Virender K, Kumar J H. Crop establishment and weed control options for sustaining dry direct seeded rice production in eastern India[J]. Agronomy, 2021, 11(2): 11020389. |
| [13] | 朱新云, 施慎年, 吴佳文. 水稻旱直播田47%氯吡·丙·异可湿性粉剂除草效果及安全性[J]. 杂草学报, 2016, 34(4): 39-42. |
| Zhu X Y, Shi S M, Wu J W. Herbicidal efficacy and safety of 47% chlorpyrifos propargyl isowettable powder in rice dry direct seeding fields[J]. Acta Weedica Sinica, 2016, 34(4): 39-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 沈浦, 高菊生, 徐明岗, 李冬初, 牛德奎, 秦道珠. 长期施用含硫和含氯化肥对稻田杂草生长动态的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(4): 992-998. |
| Shen P, Gao J S, Xu M G, Li D C, Niu D K, Qin D Z. The effect of long-term application of sulfur and chloride fertilizers on the growth dynamics of weeds in rice fields[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(4): 992-998. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 梁玉刚, 周晶, 余政军, 李静怡, 黄璜, 赵正洪. 稻鸭共育对直播水稻田间杂草群落组成及多样性的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2022, 37(2): 160-170. |
| Liang Y G, Zhou J, Yu Z J, Li J Y, Huang H, Zhao Z H. The effect of rice duck co cultivation on the composition and diversity of weed communities in direct seeding rice fields[J]. North China Agricultural Journal, 2022, 37(2): 160-170. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Chhokar R S, 禹盛苗. 不同耕作和种植方式对稻田杂草及水稻产量的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2016, 22(5): 48-52. |
| Chhokar R S, Yu S M. The effects of different tillage and planting methods on weeds and rice yield in rice fields[J]. China Rice, 2016, 22(5): 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 李阳, 林义月, 杨晓龙, 汪本福, 张枝盛, 张作林, 余振渊, 程建平. 水分管理和播种量对旱直播水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 节水灌溉, 2022(9): 87-92. |
| Li Y, Lin Y Y, Yang X L, Wang B F, Zhang Z S, Zhang Z L, Yu Z Y, Cheng J P. The effects of water management and sowing rate on the yield formation of dry direct seeding rice[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2022(9): 87-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 施林林, 沈明星, 蒋敏, 陆长婴, 王海侯, 吴彤东, 周新伟, 沈新平. 长期不同施肥方式对稻麦轮作田杂草群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(2): 310-316. |
| Shi L L, Shen M X, Jiang M, Lu C Y, Wang H H, Wu T D, Zhou X W, Shen X P. The effect of long-term different fertilization methods on weed communities in rice wheat rotation fields[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2013, 46 (2): 310-316. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 董春华, 马朝红, 胡柯鑫, 何云龙, 李万民, 褚飞, 杨曾平. 化肥氮钾优化施用及紫云英、秸秆协同还田下的双季稻生产效益[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2020(9): 19-23. |
| Dong C H, Ma C H, Hu K X, He Y L, Li W M, Chu F, Yang Z P. Optimal application of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers and synergistic return of purple vetch and straw to the field for the production efficiency of double cropping rice[J]. Hunan Agricultural science, 2020(9): 19-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 王卫, 谢小立, 谢永宏, 陈惟财. 不同施肥制度对双季稻氮吸收、净光合速率及产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(3): 752-757. |
| Wang W, Xie X L, Xie Y H, Chen W C. The effects of different fertilization systems on nitrogen absorption, net photosynthetic rate, and yield of double cropping rice[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2010, 16(3): 752-757. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 李香菊. 近年我国农田杂草防控中的突出问题与治理对策[J]. 植物保护, 2018, 44(5): 77-84. |
| Li X J. Outstanding problems and management strategies in weed prevention and control in farmland in China in recent years[J]. Plant Protection, 2018, 44(5): 77-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 袁晓娟, 孙知白, 杨永刚, 林郸, 郭长春, 文艳芳, 郭兴新, 杨志远, 陈宗奎, 徐富贤, 马均, 孙永健. 3种复种模式下秸秆还田对机插杂交籼稻产量形成及品质的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2022, 40(3): 319-330. |
| Yuan X J, Sun Z B, Yang Y G, Lin D, Guo C C, Wen Y F, Guo X X, Yang Z Y, Chen Z K, Xu F X, Ma J, Sun Y J. The effect of straw returning to the field on yield formation and quality of machine inserted hybrid indica rice under three multiple cropping modes[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2022, 40(3): 319-330. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 林郸, 李郁, 孙永健, 谌洁, 吕腾飞, 孙知白, 吕旭, 刘芳艳, 郭长春, 孙园园, 杨志远, 马均. 不同轮作模式下秸秆还田与氮肥运筹对杂交籼稻产量及米质的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(10): 1581-1590. |
| Lin D, Li Y, Sun Y J, Chen J, Lü T F, Sun Z B, Lü X, Liu F Y, Guo C C, Sun Y Y, Yang Z Y, Ma J. The effect of straw return and nitrogen fertilizer application on the yield and quality of hybrid indica rice under different rotation patterns[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecological Agriculture, 2020, 28(10): 1581-1590. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Guo C, Yuan X, Wen Y, Yang Y, Ma Y, Yan F, Li B, Wang Z, Xing M, Zhang R, Yang Z, Ma J, Sun Y. Common population characteristics of direct-seeded hybrid indica rice for high yield[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2023, 115(4): 1606-1621. |
| [25] | 李小艳, 孙宇, 贺建荣, 汪亚雄, 王红春, 娄远来. 水稻旱直播田全程草害化除技术[J]. 杂草科学, 2015, 33(4): 51-54. |
| Li X Y, Sun Y, He J R, Wang Y X, Wang H C, Lou Y L. The whole process grass pest control technology for dry direct seeding rice fields[J]. Weed Science, 2015, 33(4): 51-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 张勇, 王艳艳, 王梅, 周凤艳, 高同春. 不同除草剂对水稻水直播田杂草的防除效果及安全性评价[J]. 植物保护, 2016, 42(4): 230-235. |
| Zhang Y, Wang Y Y, Wang M, Zhou F Y, Gao T C. Evaluation of the control effect and safety of different herbicides on weeds in rice direct seeding fields[J]. Plant Protection, 2016, 42(4): 230-235. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Ahmed S, Alam M J, Hossain A, Islam A, Sabagh A E. Interactive effect of weeding regimes, rice cultivars, and seeding rates influence the rice-weed competition under dry direct-seeded condition[J]. Sustainability, 2021(13): 317. |
| [28] | 孙永健, 朱懿, 孙园园, 严奉君, 蒋明金, 杨志远, 许远明, 徐徽, 马均. 除草剂配施对机械旱直播稻田杂草控制及稻谷产量的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2018, 36(2): 131-137. |
| Sun Y J, Zhu Y, Sun Y Y, Yan F J, Jiang M J, Yang Z Y, Xu Y M, Xu H, Ma J. The effect of herbicide combination application on weed control and rice yield in mechanical dry direct seeding rice fields[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2018, 36(2): 131-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 董立尧, 沈晋良, 高同春, 周伯军, 张勇. 水直播稻田千金子的生态经济阈值及其防除临界期[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2003, 26(3): 5. |
| Dong L Y, Shen J L, Gao T C, Zhou B J, Zhang Y. Ecological and economic threshold and critical period for prevention and control of direct seeding rice field of Euphorbia paniculata[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2003, 26(3): 5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Chauhan B S, Abugho S B. Effects of water regime, nitrogen fertilization, and rice plant density on growth and reproduction of lowland weed Echinochloa crus-galli[J]. Crop Protection, 2013, 54: 142-147. |
| [31] | Sun L, Hussain S, Liu H, Peng S, Huang J, Cui K, Nie L. Implications of low sowing rate for hybrid rice varieties under dry direct-seeded rice system in Central China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2015, 175: 87-95. |
| [32] | Ni H, Robles M. Analysis of competition between wet-seeded rice and barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) using a response-surface model[J]. Weed Science, 2004, 52(1): 142-146. |
| [33] | Zhao D L, Atlin G N, Bastiaans L, Spiertz J. Developing selection protocols for weed competitiveness in aerobic rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2006, 97(2-3): 272-285. |
| [34] | 李木英, 陈志攀, 石庆华, 潘晓华, 谭雪明. 不同氮钾用量配比对直播稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2012, 34(6): 1071-1079. |
| Li M Y, Chen Z P, Shi Q H, Pan X H, Tan X M. The effect of different nitrogen and potassium dosage ratios on the yield and quality of direct seeding rice[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2012, 34(6): 1071-1079. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 孙永健, 郑洪帧, 杨志远, 王海月, 张绍文, 马均. 机械旱直播方式对水稻氮磷钾吸收转运及分配的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(3): 73-80. |
| Sun Y J, Zheng H J, Yang Z Y, Wang H Y, Zhang S W, Ma J. The effect of mechanical dry direct seeding on the absorption, transportation, and distribution of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in rice[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2017, 33(3): 73-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 王英, 刘汝亮, 周丽娜, 洪瑜, 王芳, 冒辛平, 孙权. 宁夏旱直播水稻氮、磷、钾养分吸收规律研究[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2022, 63(6): 10-13. |
| Wang Y, Liu R L, Zhou L N, Hong Y, Wang F, Mao X P, Sun Q. A study on the absorption patterns of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium nutrients in dry direct seeding rice in Ningxia[J]. Ningxia Agriculture and Forestry Technology, 2022, 63(6): 10-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 袁嫚嫚, 孙义祥, 钟成虎, 王家宝, 邬刚, 胡鹏, 张祥明, 王文军, 井玉丹. 控释复合肥和播种量对机械旱直播水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2022, 41(9): 1700-1707. |
| Yuan M M, Sun Y X, Zhong C H, Wang J B, Wu G, Hu P, Zhang X M, Wang W J, Jing Y D. The Effect of Controlled release compound fertilizer and sowing rate on the yield formation of mechanically dried rice[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2022, 41(9): 1700-1707. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 张建军, 刘红, 蒋小平, 李春元, 黄庆林, 张效瑕. 直播方式与播种量组合对水稻群体发育及产量构成的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(5): 1-7. |
| Zhang J J, Liu H, Jiang X P, Li C Y, Huang Q L, Zhang X X. The effect of the combination of direct seeding method and sowing amount on the population development and yield composition of rice[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 37(5): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 陈云, 李思宇, 朱安, 刘昆, 张亚军, 张耗, 顾骏飞, 张伟杨, 刘立军, 杨建昌. 播种量和穗肥施氮量对优质食味直播水稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(3): 656-666. |
| Chen Y, Li S Y, Zhu A, Liu K, Zhang Y J, Zhang H, Gu J F, Zhang W Y, Liu L J, Yang J C. The effects of sowing rate and nitrogen application rate on the yield and quality of high-quality taste direct seeding rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(3): 656-666. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 汪邑晨, 朱本顺, 周磊, 朱骏, 杨仲南. 光/温敏核不育系的不育机理及两系杂交稻的发展与展望 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 463-474. |
| [2] | 许用强, 徐军, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 王丹英, 曾宇翔, 符冠富. 水稻花粉管生长及其对非生物逆境胁迫的响应机理研究进展 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 495-506. |
| [3] | 何勇, 刘耀威, 熊翔, 祝丹晨, 王爱群, 马拉娜, 王廷宝, 张健, 李建雄, 田志宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑OsOFP30基因创制水稻粒型突变体 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [4] | 吕阳, 刘聪聪, 杨龙波, 曹兴岚, 王月影, 童毅, Mohamed Hazman, 钱前, 商连光, 郭龙彪. 全基因组关联分析(GWAS)鉴定水稻氮素利用效率候选基因 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 516-524. |
| [5] | 杨好, 黄衍焱, 王剑, 易春霖, 石军, 谭楮湉, 任文芮, 王文明. 水稻中八个稻瘟病抗性基因特异分子标记的开发及应用 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 525-534. |
| [6] | 唐伟杰, 陈海元, 张所兵, 唐骏, 林静, 方先文, 张抒南, 肖宁, 吴云雨, 李爱宏, 张云辉. 江苏粳稻育成品种氮响应相关性状位点分析 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 535-543. |
| [7] | 杨铭榆, 陈志诚, 潘美清, 张汴泓, 潘睿欣, 尤林东, 陈晓艳, 唐莉娜, 黄锦文. 烟-稻轮作下减氮配施生物炭对水稻茎鞘同化物转运和产量 形成的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 555-566. |
| [8] | 熊家欢, 张义凯, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 姚坚, 张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [9] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [10] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [11] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [12] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [13] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [14] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [15] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||