
中国水稻科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 535-543.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.231004
唐伟杰1,2, 陈海元1,2, 张所兵1,2, 唐骏1,2, 林静1,2, 方先文1,2, 张抒南4, 肖宁5, 吴云雨5, 李爱宏5, 张云辉1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-09
修回日期:2023-11-14
出版日期:2024-09-10
发布日期:2024-09-10
通讯作者:
*email: zyhrice@163.com
基金资助:
TANG Weijie1,2, CHEN Haiyuan1,2, ZHANG Suobing1,2, TANG Jun1,2, LIN Jing1,2, FANG Xianwen1,2, ZHANG Shunan4, XIAO Ning5, WU Yunyu5, LI Aihong5, ZHANG Yunhui1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-10-09
Revised:2023-11-14
Online:2024-09-10
Published:2024-09-10
Contact:
*email: zyhrice@163.com
摘要:
【目的】江苏省是水稻氮肥施用量较高的区域,且水稻品种选育历史悠久,种质来源广泛;为了鉴定江苏水稻品种的氮响应相关性状以及氮响应相关基因,筛选氮高效品系,最终降低氮肥用量。【方法】利用76份不同地区、不同选育时间育成的江苏粳稻品种为试验材料,利用GATK4等软件获取群体变异信息,并用Admixture软件分析群体结构,以三个不同氮肥处理水平,调查成熟期氮响应相关性状并分析氮响应相关位点。【结果】筛选到了华粳5号和宁粳5号等氮钝感品种;利用关联分析,发现了已知或已报道的氮相关基因(OsAMT1.2,OsNRT2.4和Fd-GOGAT1等)邻近位点;进一步分析了位点的优异变异和携带优异位点的品种。【结论】鉴定了江苏育成粳稻品种的氮响应差异和携带的优异位点,可为选育不同氮响应品种提供参考。
唐伟杰, 陈海元, 张所兵, 唐骏, 林静, 方先文, 张抒南, 肖宁, 吴云雨, 李爱宏, 张云辉. 江苏粳稻育成品种氮响应相关性状位点分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 535-543.
TANG Weijie, CHEN Haiyuan, ZHANG Suobing, TANG Jun, LIN Jing, FANG Xianwen, ZHANG Shunan, XIAO Ning, WU Yunyu, LI Aihong, ZHANG Yunhui. Analysis of Nitrogen-response Related Loci in japonica Rice Varieties from Jiangsu Province[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 535-543.
| 审定年份 Approval year | 品种数 Number of varieties | 代表品种 Representative varieties | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1983−1990 | 2 | 盐粳2号、武育粳2号 Yanjing 2, Wuyujing 2 | |
| 1991−2000 | 11 | 武育粳3号、镇稻88、淮稻5号、泗稻11 Wuyujing 3, Zhendao 88, Huaidao 5, Sidao 11 | |
| 2001−2010 | 45 | 徐稻3号、华粳5号、连粳4号、南粳46 Xudao 3, Huadao 5, Lianjing 4, Nanjing 46 | |
| 2011−2014 | 18 | 宁粳5号、扬粳805、南粳49、连粳11 Ningjing 5, Yangjing 805, Nanjing 49, Lianjing 11 | |
表1 供试品种审定年份、品种数和代表性品种
Table 1. Variety approval year, number of varieties, and representative varieties
| 审定年份 Approval year | 品种数 Number of varieties | 代表品种 Representative varieties | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1983−1990 | 2 | 盐粳2号、武育粳2号 Yanjing 2, Wuyujing 2 | |
| 1991−2000 | 11 | 武育粳3号、镇稻88、淮稻5号、泗稻11 Wuyujing 3, Zhendao 88, Huaidao 5, Sidao 11 | |
| 2001−2010 | 45 | 徐稻3号、华粳5号、连粳4号、南粳46 Xudao 3, Huadao 5, Lianjing 4, Nanjing 46 | |
| 2011−2014 | 18 | 宁粳5号、扬粳805、南粳49、连粳11 Ningjing 5, Yangjing 805, Nanjing 49, Lianjing 11 | |
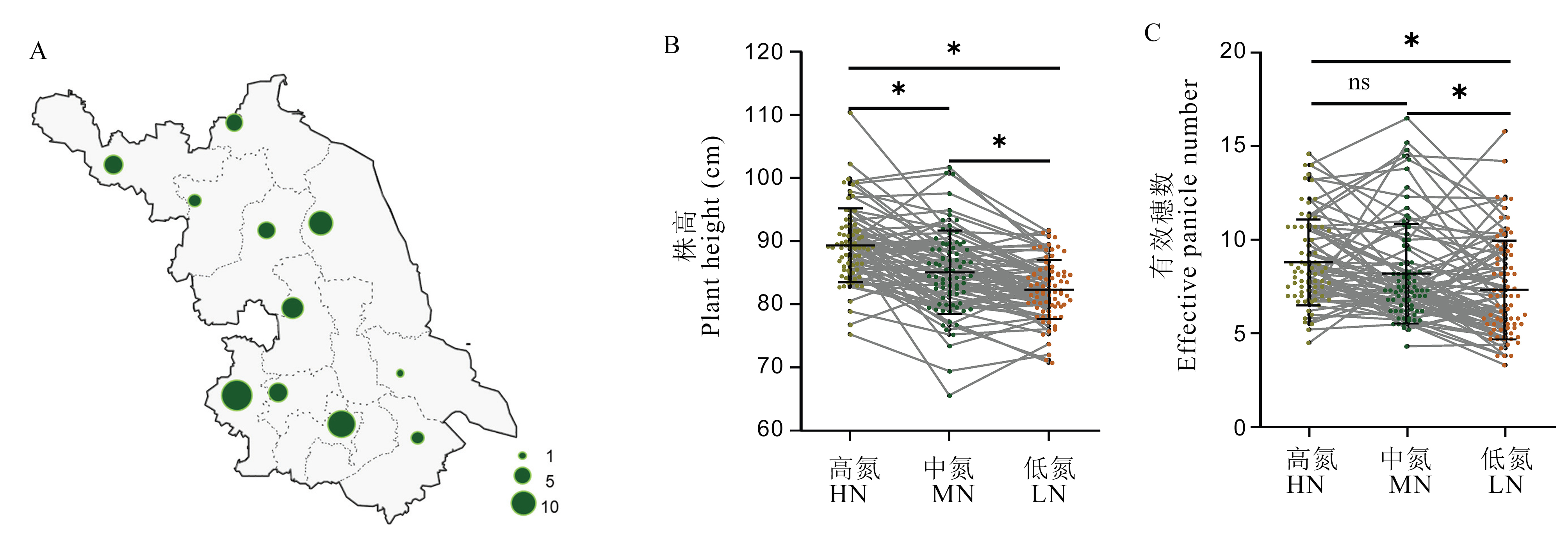
图1 76份江苏粳稻育成品种地域分布和不同氮肥处理下的株高和有效穗数统计 A: 76份品种在江苏的分布情况。B, C: 高、中和低氮处理下株高和有效穗数。n = 76。*P < 0.05; ns, P≥0.05(Duncan多重极差检验)。
Fig. 1. Geographical distribution of 76 japonica varieties from Jiangsu Province and plant height and effective panicle number under different nitrogen treatments A, Geographical distribution of 76 varieties in Jiangsu Province. B and C, Plant height and effective panicle number under high, medium, and zero nitrogen treatments. NH, High nitrogen; MN, Medium nitrogen; LN, Zero nitrogen; n = 76. * P < 0.05; ns, P≥0.05(Duncan’s multiple range test).

图2 江苏76份育成品种株高和有效穗数不同氮处理比值频数分布
Fig. 2. Frequency distribution of plant height ratio and effective panicle number ratios(EPNR) between nitrogen treatments
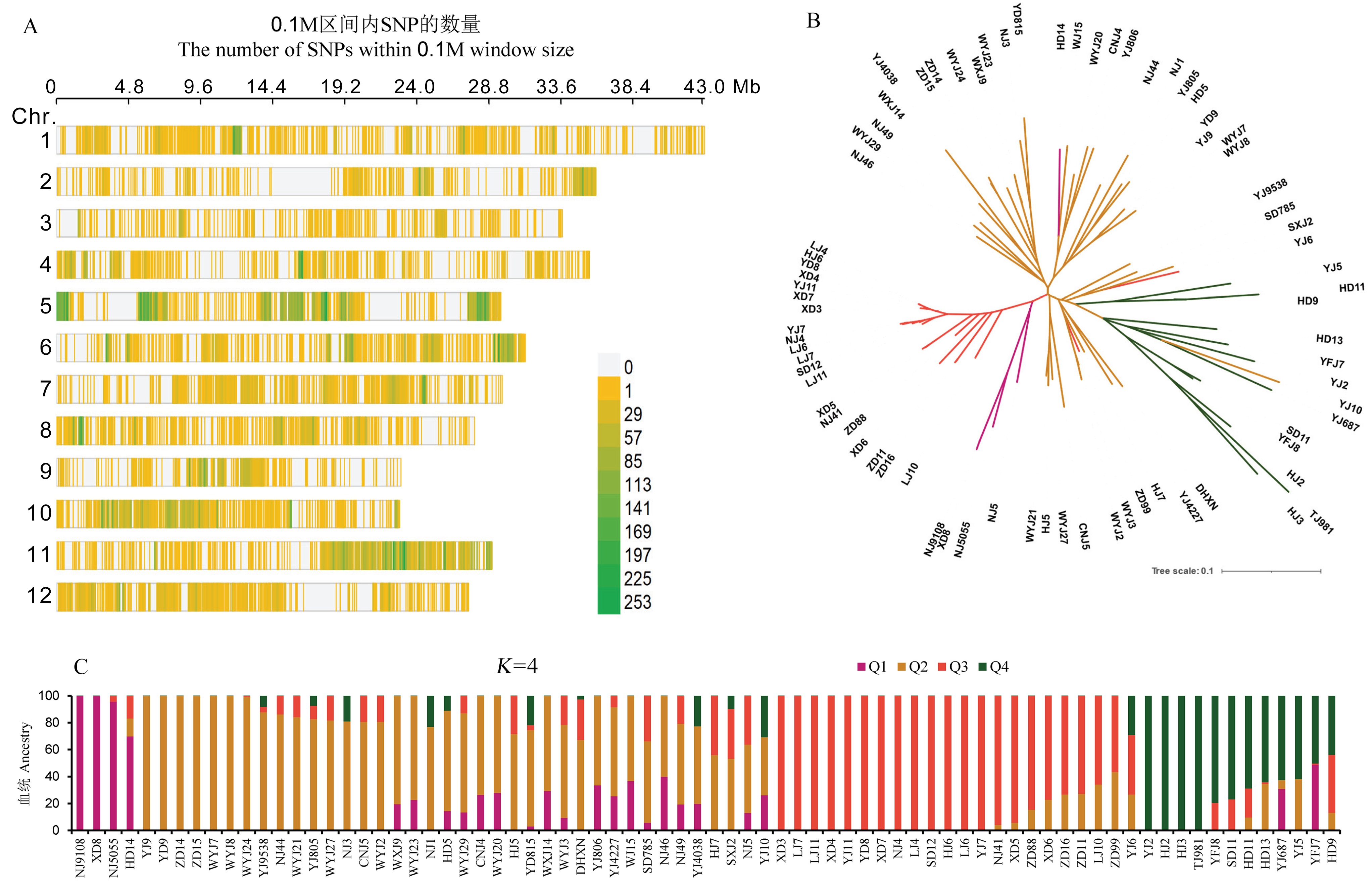
图3 江苏76份育成粳稻品种的群体结构分析 A: 76份育成品种SNP在12条染色体上的分布;B: Neighbor-joining群体进化树分析,每个分支代表一个品种;C: 群体结构分析,Admixture软件计算的每个水稻品种属于4个亚群的后验概率,每个竖条表示一个品种,每个竖条内的彩色部分表示加入不同聚类的隶属系数(Q)。
Fig. 3. Population structure analysis of 76 japonica rice varieties A, Distribution of SNPs in 76 varieties on 12 chromosomes; B, Neighbor-joining population evolutionary tree analysis. Each branch represents a variety; C, Population structure analysis. Posterior probabilities of a variety belonging to four subpopulations were calculated by Admixture software. Each accession is represented by a vertical bar. The colored subsections within each vertical bar indicate membership coefficient (Q) of the accession to different clusters.

图4 不同氮肥处理间的株高比和有效穗数比的关联分析 A~C:不同氮肥处理株高比关联分析(A: 低氮/高氮; B: 低氮/中氮; C: 中氮/高氮);D~F:不同氮肥处理有效穗数比关联分析(D: 低氮/高氮; E: 低氮/中氮; F: 中氮/高氮)。
Fig. 4. Association analysis of plant height ratio and effective panicle number ratio between nitrogen fertilizer treatments A, B and C, Association analysis of plant height ratio under different nitrogen treatments(A, Zero nitrogen/High nitrogen; B, Zero nitrogen/Medium nitrogen; C, Medium nitrogen/High nitrogen); D, E and F, Association analysis of effective panicle number ratio under different nitrogen treatments(D, Zero nitrogen/High nitrogen; E, Zero nitrogen/Medium nitrogen; F, Medium nitrogen/High nitrogen).

图5 距离已知氮素利用相关基因相近显著位点变异分析 REF:与参考基因组一致位点;ALT:变异位点。差异采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)计算。
Fig. 5. Analysis of significant loci adjacent to known nitrogen utilization related genes REF, Reference site; ALT, Mutation site. The differences were calculated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
| 品种Variety | S6_6595563 | S2_24640294 | S8_7618813 | S7_9740940 | S1_20637066 | S7_27706813 | S12_293167 | 合计Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 镇稻11号 Zhendao 11 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 |
| 南粳44 Nanjing 44 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 |
| 华粳5号 Huajing 5 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | 6 |
| 苏香粳2号 Suxiangjing 2 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | 6 |
| 盐稻815 Yandao 815 | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | 5 |
| 徐稻6号 Xudao 6 | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 5 |
| 镇稻16号 Zhendao 16 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | NA | Y | 5 |
| 武运粳21 Wuyunjing 21 | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | 5 |
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | 5 |
| 武育粳20 Wuyujing 20 | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | 5 |
表2 氮响应相关显著位点数量统计
Table 2. Statistics of the number of nitrogen-response loci
| 品种Variety | S6_6595563 | S2_24640294 | S8_7618813 | S7_9740940 | S1_20637066 | S7_27706813 | S12_293167 | 合计Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 镇稻11号 Zhendao 11 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 |
| 南粳44 Nanjing 44 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 |
| 华粳5号 Huajing 5 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | 6 |
| 苏香粳2号 Suxiangjing 2 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | 6 |
| 盐稻815 Yandao 815 | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | 5 |
| 徐稻6号 Xudao 6 | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 5 |
| 镇稻16号 Zhendao 16 | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | NA | Y | 5 |
| 武运粳21 Wuyunjing 21 | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | 5 |
| 武运粳24 Wuyunjing 24 | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | 5 |
| 武育粳20 Wuyujing 20 | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | 5 |
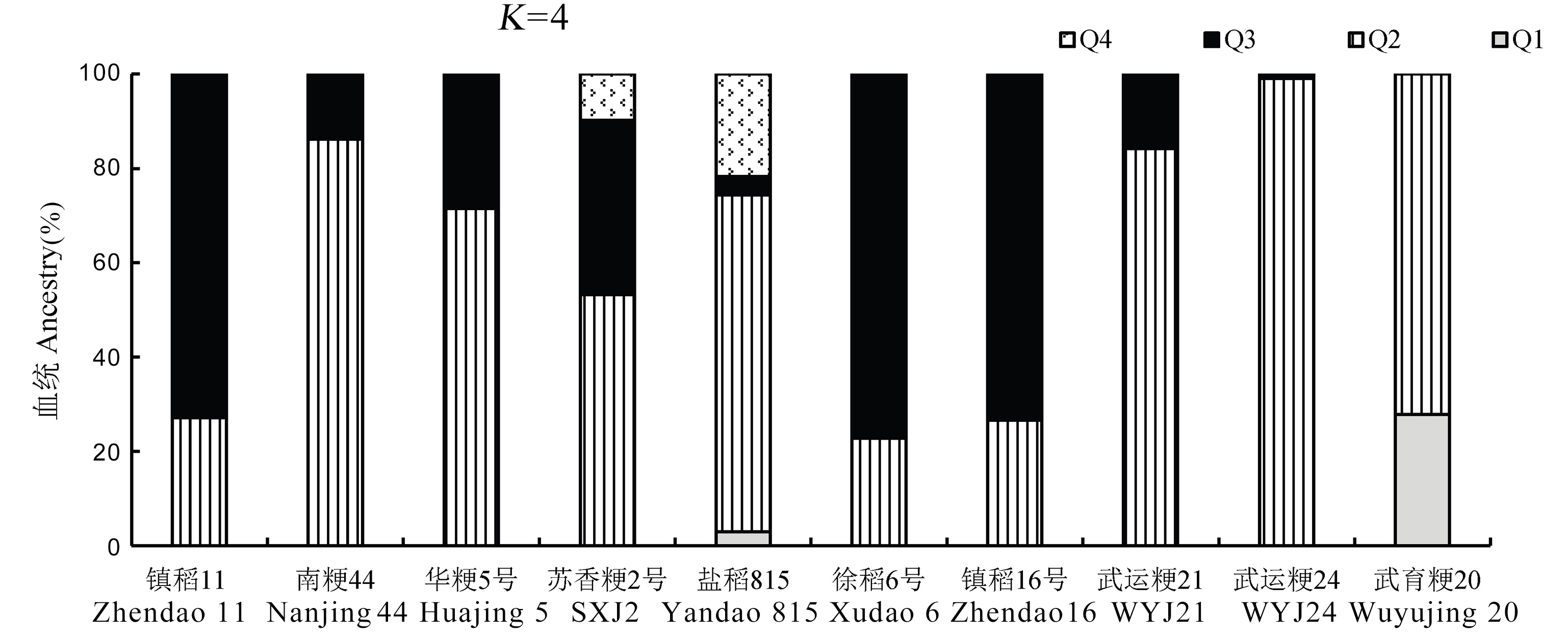
图6 不同品种优异位点数量和群体结构分析 Admixture软件计算的10个水稻品种属于4个亚群的后验概率,每个竖条内的部分表示加入不同聚类的隶属系数(Q)。
Fig. 6. Analysis of the number of superior site and population structure in different varieties Posterior probabilities of each variety belonging to 4 subpopulations calculated by Admixture. Each accession is represented by a vertical bar. The subsections within a column indicate membership coefficient (Q) of the accession to clusters. SXJ2, Suxiangjing 2; WYJ21, Wuyunjing 21; WYJ24, Wuyunjing 24.
| [1] | 应兴华, 曹立勇, 胡培松, 程式华. 加快水稻科技创新保障国家粮食安全[J]. 农业科研经济管理, 2016(2): 6-9. |
| Ying X H, Cao L Y, Hu P S, Cheng S H. Accelerate rice science and technology innovation to protect national food security[J]. Management for Economy in Agricultural Scientific Research, 2016(2): 6-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 杜永林. 江苏省水稻品种选育利用现状与发展对策[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2010(1): 9-13. |
| Du Y L. Current situation and development counter- measures of rice variety bred and utilization in Jiangsu Province[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2010(1): 9-13. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 鄂志国, 孙红伟, 林海, 王磊, 童汉华, 陈红旗, 朱练峰. 浙江育成和审定水稻品种分析(1980―2019)[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2020, 21(3): 542-548. |
| E Z G, Sun H W, Lin H, Wang L, Tong H H, Chen H Q, Zhu L F. Analysis of rice varieties bred and certified in Zhejiang Province, China(1980-2019)[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2020, 21(3): 542-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 杜文婷, 雷肖肖, 卢慧宇, 王云凤, 徐佳星, 罗彩霞, 张树兰. 氮肥减量施用对我国三大粮食作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(24): 4863-4878. |
| Du W T, Lei X X, Lu H Y, Wang Y F, Xu J X, Luo C X, Zhang S L. Effects of reducing nitrogen application rate on the yields of three major cereals in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(24): 4863-4878. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Lu Y, Jenkins A, Ferrier R C, Bailey M, Gordon I J, Song S, Huang J, Jia S, Zhang F, Liu X. Addressing China’s grand challenge of achieving food security while ensuring environmental sustainability[J]. Science Advances, 2015, 1(1): e1400039. |
| [6] | 陶小龙, 徐磊, 夏磊, 金细莲, 涂良瑛. 农业面源污染中农田氮污染对水体的危害及防治措施[J]. 农业灾害研究, 2022, 12(6): 161-163. |
| Tao X L, Xu L, Xia L, Jin X L, Tu L Y. Harm of farmland nitrogen pollution to water body in agricultural non-point source pollution and its control measures. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 2022, 12(6): 161-163. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Sun H, Qian Q, Wu K, Luo J, Wang S, Zhang C, Ma Y, Liu Q, Huang X, Yuan Q. Heterotrimeric G proteins regulate nitrogen-use efficiency in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2014, 46(6): 652. |
| [8] | Liu Y, Wang H, Jiang Z, Wang W, Xu R, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Li A, Liang Y, Ou S, Liu X, Cao S, Tong H, Wang Y, Zhou F, Liao H, Hu B, Chu C. Genomic basis of geographical adaptation to soil nitrogen in rice[J]. Nature, 2021, 590(7847): 600-605. |
| [9] | Tang W J, Ye J, Yao X M, Zhao P Z, Xuan W, Tian Y L, Zhang Y Y, Xu S, An H Z, Chen G M, Yu J, Wu W, Ge Y W, Liu X L, Li J, Zhang H Z, Zhao Y Q, Peng C, Zhou C, Terzaghi W, Wang C M, Wan J M. Genome-wide associated study identifies NAC42-activated nitrate transporter conferring high nitrogen use efficiency in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5279. |
| [10] | Yu J, Xuan W, Tian Y, Fan L, Sun J, Tang W, Chen G, Wang B, Liu Y, Wu W, Liu X, Jiang X, Zhou C, Dai Z, Xu D, Wang C, Wan J. Enhanced OsNLP4-OsNiR cascade confers nitrogen use efficiency by promoting tiller number in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19(1): 167-176. |
| [11] | 马立珩, 张莹, 隋标, 刘彩玲, 王萍, 顾琐娣, 沈其荣, 徐茂, 郭世伟. 江苏省水稻过量施肥的影响因素分析[J]. 扬州大学学报, 2011, 32(2): 48-52. |
| Ma L H, Zhang Y, Sui B, Liu C L, Wang P, Gu S D, Shen Q R, Xu M, Guo S W. The impact factors of excessive fertilization in Jiangsu Province[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University, 2011, 32(2): 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 马群, 李国业, 顾海永, 杨雄, 张洪程. 我国水稻氮肥利用现状及对策[J]. 广东农业科学, 2010, 37(11): 126. |
| Ma Q, Li G Y, Gu H Y, Yang X, Zhang H C. Current situation and countermeasures of rice nitrogen fertilizer utilization in China[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 37(11): 126. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | Good A G, Shrawat A K, Muench D G. Can less yield more? Is reducing nutrient input into the environment compatible with maintaining crop production?[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2004, 9(12): 597-605. |
| [14] | 周新伟, 王建平, 陈益海, 朱勇良, 乔中英, 朱兴连, 谢裕林. 江苏省主栽粳稻品种亲本选配分析及选育策略[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2003(3): 4-7. |
| Zhou X W, Wang J P, Chen Y H, Zhu Y L, Qiao Z Y, Zhu X L, Xie Y L. Analysis of parent selection and breeding strategies for major japonica rice cultivars in Jiangsu Province[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2003(3): 4-7. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | Tang W, Lin J, Wang Y, An H, Chen H, Pan G, Zhang S, Guo B, Yu K, Li H, Fang X, Zhang Y. Selection and Validation of 48 KASP markers for variety identification and breeding guidance in conventional and hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Rice (NY), 2022, 15(1): 48. |
| [16] | Huang X, Feng Q, Qian Q, Zhao Q, Wang L, Wang A, Guan J, Fan D, Weng Q, Huang T, Dong G, Sang T, Han B. High-throughput genotyping by whole-genome resequencing[J]. Genome Research, 2009, 19(6): 1068. |
| [17] | Xiao N, Pan C, Li Y, Wu Y, Cai Y, Lu Y, Wang R, Yu L, Shi W, Kang H, Zhu Z, Huang N, Zhang X, Chen Z, Liu J, Yang Z, Ning Y, Li A. Genomic insight into balancing high yield, good quality, and blast resistance of japonica rice[J]. Genome Biology, 2021, 22(1): 283. |
| [18] | Alexander D H, Shringarpure S S, Novembre J, Lange K. Admixture 1.3 Software Manual[EB/OL]. (2015-11-28) https://vcru.wisc.edu/simonlab/bioinformatics/programs/admixture/admixture-manual.pdf |
| [19] | Bradbury P J, Zhang Z, Kroon D E, Casstevens T M, Ramdoss Y, Buckler E S. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples[J]. Bioinformatics, 2007, 23(19): 2633-2635. |
| [20] | Wang Q, Su Q, Nian J, Zhang J, Guo M, Dong G, Hu J, Wang R, Wei C, Li G, Wang W, Guo H S, Lin S, Qian W, Xie X, Qian Q, Chen F, Zuo J. The Ghd7 transcription factor represses ARE1 expression to enhance nitrogen utilization and grain yield in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(6): 1012-1023. |
| [21] | Wei J, Zheng Y, Feng H, Qu H, Fan X, Yamaji N, Ma J F, Xu G. OsNRT2.4 encodes a dual-affinity nitrate transporter and functions in nitrate-regulated root growth and nitrate distribution in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2018, 69(5): 1095-1107. |
| [22] | Zeng D D, Qin R, Li M, Alamin M, Jin X L, Liu Y, Shi C H. The ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase (OsFd- GOGAT) participates in leaf senescence and the nitrogen remobilization in rice[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2016, 292(2): 385-395. |
| [23] | 邹江石, 江祺祥. 武育粳3号的培育构思及生产表现[J]. 江苏农业科学, 1994(6): 7-9. |
| Zhou J S, Jiang Q X. Cultivation concept and production performance of Wuyujing 3[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 1994(6): 7-9. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 胡春明, 林添资, 龚红兵, 刁立平, 景德道, 盛生兰. 中粳稻镇稻88育种实践的分析与启示[J]. 江西农业学报, 2008, 20(11): 47-49. |
| Hu C M, Lin T Z, Gong H B, Diao L P, Jing D D, Sheng S L. Analysis and enlightenment on the breeding practice of mid-season japonica Zhendao 88[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2008, 20(11): 47-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 任维晨, 常庆霞, 张亚军, 朱宽宇, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 不同氮利用率粳稻品种的碳氮积累与转运特征及其生理机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 586-600. |
| Ren W C, Chang Q X, Zhang Y J, Zhu K Y, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Characteristics and physiological mechanism of carbon and nitrogen accumulation and translocation of japonica rice varieties differing in nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 586-600. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 赵凌, 张勇, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 张亚东, 王才林. 南粳系列品种氮素利用效率初探[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(5): 1153-1161. |
| Zhao L, Zhang Y, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhang Y D, Wang C L. Study on nitrogen use efficiency of Nanjing series japonica rice varieties[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 38(5): 1153-1161. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Li C, Tang Z, Wei J, Qu H, Xie Y, Xu G. The OsAMT1.1 gene functions in ammonium uptake and ammonium- potassium homeostasis over low and high ammonium concentration ranges[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2016, 43(11): 639-649. |
| [28] | Wu X, Xie X, Yang S, Yin Q, Cao H, Dong X, Hui J, Liu Z, Jia Z, Mao C J P. OsAMT1;1 and OsAMT1;2 coordinate root morphological and physiological responses to ammonium for efficient nitrogen foraging in rice[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2022, 63(9): 1309. |
| [29] | Lee S, Marmagne A, Park J, Fabien C, Yim Y, Kim S J, Kim T H, Lim P O, Masclaux-Daubresse C, Nam H G J T P J. Concurrent activation of OsAMT1;2 and OsGOGAT1 in rice leads to enhanced nitrogen use efficiency under nitrogen limitation[J]. Plant Journal, 2020, 103(1): 7-20. |
| [30] | Yang G, Chen S, Chen L, Sun K, Huang C, Zhou D, Huang Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Chen Z, Guo T. Development of a core SNP arrays based on the KASP method for molecular breeding of rice[J]. Rice(NY), 2019, 12(1): 21. |
| [31] | Yang G L, Chen S P, Chen L K, Gao W W, Huang Y T, Huang C H, Zhou D H, Wang J F, Liu Y Z, Huang M, Xiao W M, Wang H, Guo T, Chen Z Q. Development and utilization of functional KASP markers to improve rice eating and cooking quality through MAS breeding[J]. Euphytica, 2019, 215(4): 254466210. |
| [1] | 剧成欣, 陈尧杰, 赵步洪, 刘立军, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 实地氮肥管理对不同氮响应粳稻品种产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(3): 237-246. |
| [2] | 徐云碧, 王建军, 申宗坦. 水稻亚种间的亲和性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1989, 3(3): 113-119 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||