
中国水稻科学 ›› 2026, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 85-94.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2026.240718
刘亚萍1,#, 董译词1,#, 郑君妍1, 邱绚1, 刘鹏程1, 叶亚峰2, 刘斌美2,*( ), 陈析丰1,*(
), 陈析丰1,*( ), 马伯军1,*(
), 马伯军1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-25
修回日期:2024-09-27
出版日期:2026-01-10
发布日期:2026-01-21
通讯作者:
*email: liubm@ipp.ac.cn;作者简介:第一联系人:共同第一作者
基金资助:
LIU Yaping1,#, DONG Yici1,#, ZHENG Junyan1, QIU Xuan1, LIU Pengcheng1, YE Yafeng2, LIU Binmei2,*( ), CHEN Xifeng1,*(
), CHEN Xifeng1,*( ), MA Bojun1,*(
), MA Bojun1,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-25
Revised:2024-09-27
Online:2026-01-10
Published:2026-01-21
About author:First author contact:These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要:
【目的】研究水稻防御反应和叶片早衰相关基因的分子机理。【方法】从粳稻武运粳7号诱变库中筛选出一个类病变早衰突变体lmes7 (lesion mimic and early senescence 7)。调查统计了该突变体的主要农艺性状,对其叶片中的光合色素含量进行测定,利用图位克隆技术对目的基因进行精细定位和测序鉴定,并对其编码蛋白进行分析与序列比对。【结果】突变体叶片中的光合色素含量比WT极显著降低,且细胞中存在活性氧(reactive oxygen species, ROS)的过量积累;突变体植株的生长发育受到严重影响,有效分蘖数、株高、剑叶长、剑叶宽、穗长、每穗粒数、结实率及单株产量等均显著下降,但粒厚显著增加;遗传分析表明,lmes7的突变表型受单隐性核基因控制;利用图位克隆技术将目的基因精细定位在水稻12号染色体上RM28486和RM28489之间的90 kb区域内;PCR测序分析表明,lmes7突变体中一个编码ATP-柠檬酸裂解酶的目标基因OsACL-A2发生了7个碱基缺失,导致该基因发生移码突变,蛋白翻译提前终止;对水稻OsACL-A2蛋白的进化分析与序列比对可知,lmes7突变位点发生在琥珀酰辅酶A合成酶结构域,lmes7是OsACL-A2新的等位变异。
刘亚萍, 董译词, 郑君妍, 邱绚, 刘鹏程, 叶亚峰, 刘斌美, 陈析丰, 马伯军. 水稻类病变早衰突变体lmes7的鉴定与基因精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 85-94.
LIU Yaping, DONG Yici, ZHENG Junyan, QIU Xuan, LIU Pengcheng, YE Yafeng, LIU Binmei, CHEN Xifeng, MA Bojun. Phenotypic Identification and Gene Fine Mapping of the Lesion Mimic and Early Senescence Mutant lmes7 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 85-94.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物 Former primer(5’ →3’) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5’ →3’) |
|---|---|---|
| Indel1 | CGATTTCTCGTCGAGGTTCC | TCCTTCAAGAATCTCCATCTGC |
| lmes7-1 | CGCTGCCTCACTAACGCCTAT | ACCTCCGAGTCCAAAACA |
| lmes7-2 | TTAGGTCACGGAATCAAC | TCCAGAATGGGAGAAAAG |
| lmes7-3 | GGAGAACTGGGATAAGGT | TTAGACTTACAGTATCAGCAT |
| lmes7-4 | GGTTGGAGATTTGGGAT | TCTTTGAGTTTGGTGGAT |
表1 本研究用到的PCR分子标记引物
Table 1. PCR molecular marker primers used in this study
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物 Former primer(5’ →3’) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5’ →3’) |
|---|---|---|
| Indel1 | CGATTTCTCGTCGAGGTTCC | TCCTTCAAGAATCTCCATCTGC |
| lmes7-1 | CGCTGCCTCACTAACGCCTAT | ACCTCCGAGTCCAAAACA |
| lmes7-2 | TTAGGTCACGGAATCAAC | TCCAGAATGGGAGAAAAG |
| lmes7-3 | GGAGAACTGGGATAAGGT | TTAGACTTACAGTATCAGCAT |
| lmes7-4 | GGTTGGAGATTTGGGAT | TCTTTGAGTTTGGTGGAT |

图1 水稻类病变早衰突变体lmes7的鉴定 A: 植株在分蘖期的表型,标尺=10 cm;B: 植株在成熟期的表型,标尺=20 cm;C: 剑叶表型,标尺=2 cm;D: 染色前的野生型和lmes7的叶片表型;E: 叶片的NBT染色;F: 叶片的DAB染色,标尺=1 cm;G: 叶片光合色素含量;H~J: WT和突变体lmes7籽粒的长度、宽度和厚度的照片,标尺=1 cm。
Fig. 1. Phenotype of the lesion mimic and early senescence mutant lmes7 A, Phenotype of plants during the tillering stage, bar=10 cm; B, Phenotype of plants at maturity, bar=20 cm; C, Flag leaf phenotype, bar=2 cm; D, WT and lmes7 leaf phenotype before staining; E, NBT staining of leaves; F, DAB staining of leaves, bar=1 cm; G, Content of photosynthetic pigments in leaves. H and J, Grain length, grain width and grain thickness of WT and lmes7, bar=1 cm.
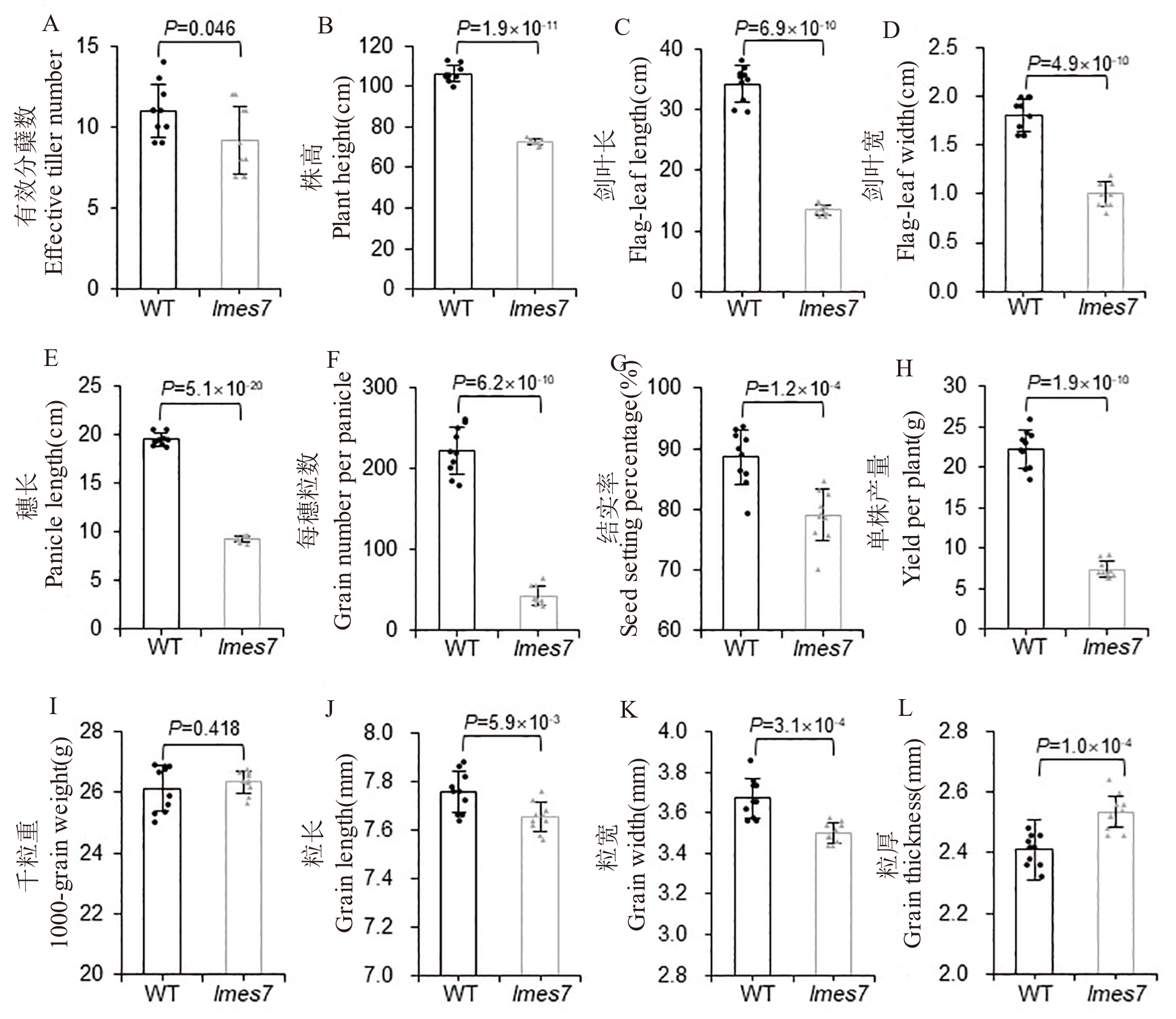
图2 水稻突变体lmes7与WT的大田农艺性状比较 A:有效分蘖数;B:株高;C:剑叶长;D:剑叶宽;E:穗长;F:每穗粒数;G:结实率;H:单株产量;I:千粒重;J:粒长;K:粒宽;L:粒厚。t检验存在显著性差异(P< 0.05)和极显著性差异(P< 0.01)。
Fig. 2. Comparison of agronomic traits between WT and rice mutant lmes7 A, Effective tiller number; B, Plant height; C, Flag-leaf length; D, Flag-leaf width; E, Panicle length; F, Grain number per panicle; G, Setting percentage; H, Yield per plant; I, 1000-grain weight; J, Grain length; K, Grain width; L, Grain thickness. t-test showed significant difference (P< 0.05) and extremely significant difference (P< 0.01).
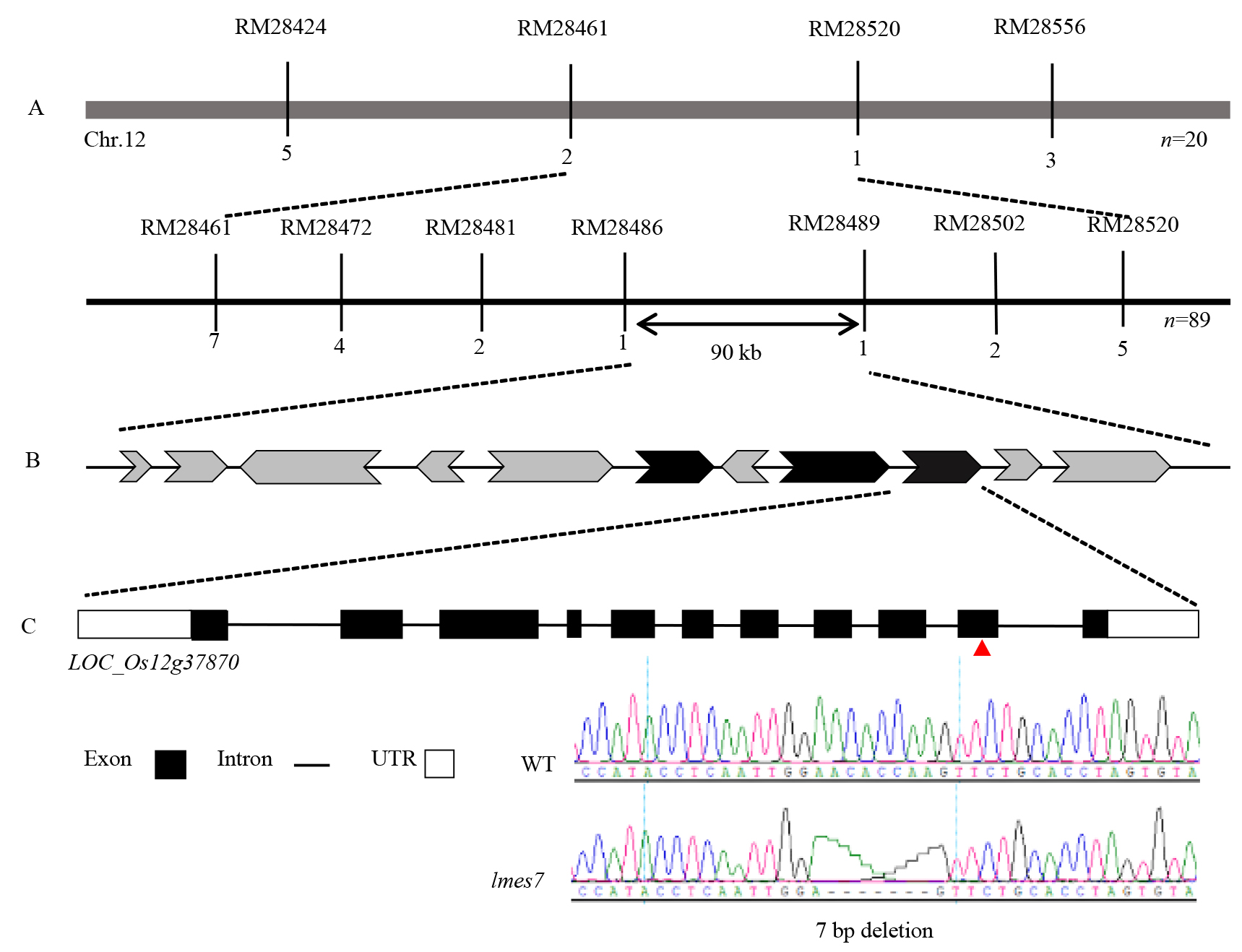
图3 水稻lmes7基因的精细定位与候选基因测序分析 A: lmes7基因精细定位的遗传图谱,“n”为定位分析所用到F2突变单株数,标记下的数字为该标记检测到的重组数; B: 定位区间内注释基因;C: 候选基因LOC_Os12g37870突变位点的测序结果。
Fig. 3. Fine mapping and candidate gene sequencing of rice lmes7 A, Genetic map of the lmes7 gene by fine mapping, ‘n’ refers to the number of F2 mutants used for mapping, the number under each marker represents the number of recombination detected by the corresponding marker; B, Annotation genes in the localization interval; C, Sequencing results of candidate gene LOC_Os12g37870 in the mutation sites.
| [1] | Hammond-Kosack K E, Jones J D. Resistance gene-dependent plant defense responses[J]. The Plant Cell, 1996, 8(10): 1773-1791. |
| [2] | 刘宝玉, 刘军化, 杜丹, 闫萌, 郑丽媛, 吴雪, 桑贤春, 张长伟. 水稻类病斑突变体spl34的鉴定与基因精细定位[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(3): 332-342. |
| Liu B Y, Liu J H, Du D, Yan M, Zheng L Y, Wu X, Sang X C, Zhang C W. Identification and gene mapping of a lesion mimic mutant spl34 in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 332-342. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 王建军, 朱旭东, 王林友, 张利华, 薛庆中, 何祖华. 水稻类病斑突变体的生理与遗传分析[J]. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2004, 30(3): 331-338. |
| Wang J J, Zhu X D, Wang L Y, Zhang L H, Xue Q Z, He Z H. Physiological and genetic analysis of lesion resembling disease mutants (lrd) of Oryza sativa L.[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology and Molecular Biology, 2004, 30(3): 331-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Zou T, Li G W, Liu M M, Liu R, Yang S Y, Wang K, Lu L H, Ye Q Y, Liu J X, Liang J, Deng Q M, Wang S Q, Zhu J, Liang Y Y, Liu H N, Yu X M, Sun C H, Li P, Li S C. A ubiquitin-specific protease functions in regulating cell death and immune responses in rice[J]. Plant Cell Environment, 2023, 46(4): 1312-1326. |
| [5] | Chen X F, Hao L, Pan J W, Zheng X X, Jiang G H, Jin Y, Gu Z M, Qian Q, Zhai W X, Ma B J. SPL5, a cell death and defense-related gene, encodes a putative splicing factor 3b subunit 3 (SF3b3) in rice[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2012, 30(2): 939-949. |
| [6] | Lorrain S, Lin B Q, Auriac M C, Kroj T, Saindrenan P, Nicole M, Balagué C, Roby D. Vascular associated death1, a novel GRAM domain containing protein, is a regulator of cell death and defense responses in vascular tissues[J]. The Plant Cell, 2004, 16(8): 2217-2232. |
| [7] | Yamanouchi U, Yano M, Lin H X, Ashikari M, Yamada K. A rice spotted leaf gene, Spl7, encodes a heat stress transcription factor protein[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(11): 7530-7535. |
| [8] | Büschges R, Hollricher K, Panstruga R, Simons G, Wolter M, Frijters A, van Daelen R, van der Lee T, Diergaarde P, Groenendijk J, Töpsch S, Vos P, Salamini F, Schulze-Lefert P. The barley Mlo gene: A novel control element of plant pathogen resistance[J]. Cell, 1997, 88(5): 695-705. |
| [9] | Gray J, Close P S, Briggs S P, Johal G S. A novel suppressor of cell death in plants encoded by the Lls1 gene of maize[J]. Cell, 1997, 89(1): 25-31. |
| [10] | Ma H G, Li J, Ma L, Wang P L, Xue Y, Yin P, Xiao J H, Wang S P. Pathogen inducible OsMPKK10.2-OsMPK6 cascade phosphorylates the Raf like kinase OsEDR1 and inhibits its scaffold function to promote rice disease resistance[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(4): 620-632. |
| [11] | Undan J R, Tamiru M, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Takagi H, Yoshida K, Kanzaki H, Saitoh H, Fekih R, Sharma S, Undan J, Yano M, Terauchi R. Mutation in OsLMS, a gene encoding a protein with two double-stranded RNA binding motifs, causes lesion mimic phenotype and early senescence in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Genes & Genetic Systems, 2012, 87(3): 169-179. |
| [12] | Qiao Y L, Jiang W Z, Lee J, Park B, Choi M, Piao R, Woo M, Roh J, Han L, Paek N, Seo H S, Koh H. SPL28 encodes a clathrin-associated adaptor protein complex 1, medium subunit micro 1 (AP1M1) and is responsible for spotted leaf and early senescence in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. The New Phytologist, 2010, 185(1): 258-274. |
| [13] | 余瑶, 王紫瑶, 周思睿, 刘鹏程, 叶亚峰, 马伯军, 刘斌美, 陈析丰. 水稻类病变突变体lms1的表型鉴定与抗病分子机制分析[J]. 作物学报, 2024, 50(4): 857-870. |
| Yu Y, Wang Z Y, Zhou S R, Liu P C, Ye Y F, Ma B J, Liu B M, Chen X F. Phenotypic identification and disease resistance mechanism analysis of rice lesion mutant lms1[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2024, 50(4): 857-870. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 王小虎. 水稻类病变早衰基因LMES3和LMES4的克隆与功能研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2018. |
| Wang X H. Map-based cloning and function analysis of two lesion mimic and early senescence gene LMES3 and LMES4 in rice[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Quirino B F, Reiter W D, Amasino R D. One of two tandem Arabidopsis genes homologous to monosaccharide transporters is senescence-associated[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2001, 46(4): 447-457. |
| [16] | Kumar D, Yusuf M A, Singh P, Sardar M, Sarin N B. Histochemical detection of superoxide and H2O2 accumulation in Brassica juncea seedlings[J]. Bio-protocol, 2014, 4(8): 1108-1111. |
| [17] | Thordal-Christensen H, Zhang Z G, Wei Y D, Collinge D B. Subcellular localization of H2O2 in plants: H2O2 accumulation in papillae and hypersensitive response during the barley-powdery mildew interaction[J]. Plant Journal, 1997, 11: 1187-1194. |
| [18] | 甘婷. 水稻类病斑突变体spl30的表型鉴定与基因功能分析[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2014. |
| Gan T. Phenotypic characterization and gene function analysis of a lesion mimic mutant spl30 in rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 赵晨晨, 黄福灯, 龚盼, 杨茜, 程方民, 潘刚. 水稻叶片早衰突变体osled的生理特征与基因定位[J]. 作物学报, 2014, 40(11): 1946-1955. |
| Zhao C C, Huang F D, Gong P, Yang X, Cheng F M, Pan G. Physiological characteristics and gene mapping of a leaf early senescence mutant osled in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(11): 1946-1955. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 陈析丰, 刘亚萍, 马伯军. 图位克隆技术新型遗传学实验教学项目的设计与实践[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 797-803. |
| Chen X F, Liu Y P, Ma B J. Design and practice of a new teaching project of the map-based cloning experiment in genetics[J]. Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 797-803. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Sasaki T. The map-based sequence of the rice genome[J]. Nature, 2005, 436(7052): 793-800. |
| [22] | Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA 7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2016, 33(7): 1870-1874. |
| [23] | Danon A, Miersch O, Felix G, Camp R G L, Apel K. Concurrent activation of cell death-regulating signaling pathways by singlet oxygen in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant Journal, 2005, 41(1): 68-80. |
| [24] | 凌凤珠. 柠檬酸转运蛋白和柠檬酸裂解酶对高山被孢霉脂质积累的影响[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021. |
| Ling F Z. Role of citrate carrier and ATP citrate lyase on lipid accumulation in Mortierella alpina[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Ruan B, Hua Z H, Zhao J, Zhang B, Ren D Y, Liu C L, Yang S L, Zhang A P, Jiang H Z, Yu H P, Hu J, Zhu L, Chen G, Shen L, Dong G J, Zhang G H, Zeng D L, Guo L B, Qian Q, Gao Z Y. OsACL-A2 negatively regulates cell death and disease resistance in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(7): 1344-1356. |
| [26] | Desikan R, Neill S J, Hancock J T. Hydrogen peroxide-induced gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2000, 28(5): 773-778. |
| [27] | 李长宁, 农倩, 谭秦亮, Srivastava M K, 杨丽涛, 李杨瑞. 甘蔗 ATP 柠檬酸裂解酶基因的克隆与表达分析[J]. 作物学报, 2012, 38(11): 2024-2033. |
| Li C N, Nong Q, Tan Q L, Srivastava M K, Yang L T, Li Y R. Cloning and expression analysis of ATP-citrate lyase genes from sugarcane[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(11): 2024-2033. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Fatland B L, Ke J, Anderson M D, Mentzen W I, Cui L W, Allred C C, Johnston J L, Nikolau B J, Wurtele E S. Molecular characterization of a heteromeric ATP-citrate lyase that generates cytosolic acetyl-coenzyme a in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2002, 130: 740-756. |
| [29] | Liu F J, Ma Z F, Cai S, Dai L J, Gao J B, Zhou B L. ATP-citrate lyase B (ACLB) negatively affects cell death and resistance to Verticillium wilt[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2022, 22: 443. |
| [30] | 郭玲霞. 柑橘ATP柠檬酸裂解酶(ACL)在柠檬酸和相关物质积累中的作用及其机制和影响因素研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2020. |
| Guo L X. Studying the role of citrus ATP-citrate lyase (ACL) in the accumulation of citrate and its relative metabolites, as well as ACL action mechanism and ACL-affecting factors[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 马芝凤. 沉默ATP-柠檬酸裂解酶基因(ACLB-2)引起棉花细胞程序性死亡的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2021. |
| Ma Z F. Silencing of ATP-citrate lyase gene (ACLB-2) leads to programmed cell death in cotton[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 熊振民, 孔繁林. 大粒型水稻品种的遗传动态及其选育[J]. 浙江农业科学, 1976(2): 26-29. |
| Xiong Z M, Kong F L. Genetic dynamics and breeding of large-grain rice varieties[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 1976(2): 26-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 李兴沂, 陈玲, 邵建韬, 肖素勤, 李金璐, 付惠仙, 殷富有, 张建红, 程在全, 刘丽. 水稻产量与淀粉品质协同调控的分子遗传研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 1-17. |
| [2] | 岳轩宇, 谢文亚, 冯志明, 陈宗祥, 胡珂鸣, 左示敏. OsERF93参与调控水稻纹枯病抗性的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 37-50. |
| [3] | 王轶欣, 林参, 马刘洋, 陈龙, 奉保华, 倪深, 魏祥进, 贺记外, 陈天晓. 谷丙转氨酶基因OsAlaAT4调控水稻氮素吸收和产量[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 51-60. |
| [4] | 黄奇娜, 姜鸿瑞, 杨婕, 于坤宇, 杨长登, 梁燕. 种子休眠基因Sdr4的生物信息学分析与分子标记开发和应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 61-71. |
| [5] | 程朝平, 何旎清, 白康呈, 林少俊, 黄凤凰, 刘军化, 程祖锌, 黄成志, 杨德卫. 聚合稻瘟病抗性基因Pigm-1和Pid2的水稻三系不育系福梦A的选育与利用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 72-84. |
| [6] | 谢世民, 周誉株, 薛晓迪, 朱广飞, 孙良, 陈建能. 水稻钵苗取栽协同作业式移栽机构设计与试验[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 131-144. |
| [7] | 王娟, 吴丽娟, 洪海波, 姚志文, 王磊, 鄂志国. 水稻泛素结合酶E2的生物学功能研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 744-750. |
| [8] | 陶士博, 许娜, 徐正进, 刘畅, 徐铨. 水稻发芽期耐冷基因Cold6的克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 751-759. |
| [9] | 陈伟, 叶元妹, 赵剑华, 冯志明, 陈宗祥, 胡珂鸣, 左示敏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术改良南粳46抽穗期[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 760-770. |
| [10] | 侯桂花, 周立国, 雷建国, 陈虹, 聂元元. 水稻OsRDR5基因功能及作用机制初步解析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 779-788. |
| [11] | 陆帅, 陶涛, 刘冉, 周文玉, 曹蕾, 杨青青, 张明秋, 任鑫哲, 杨芝笛, 徐福祥, 环海东, 龚远航, 张皓程, 金素奎, 蔡秀玲, 高继平, 冷语佳. 水稻长护颖小粒突变体lsg8的表型鉴定与基因克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 813-824. |
| [12] | 邓欢, 刘亚培, 王春连, 郭威, 陈析丰, 纪志远. 水稻抗白叶枯病新基因Xa49(t)的定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 825-831. |
| [13] | 郝雯倩, 蔡兴菁, 杨海东, 吴宇阳, 滕轩, 薛超, 龚志云. 不同类型组蛋白修饰在水稻响应非生物胁迫中的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 575-585. |
| [14] | 王镜博, 苏畅, 冯晶, 姜思旭, 徐海, 崔志波, 赵明辉. 水稻OsAlR1基因耐铝性功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 615-623. |
| [15] | 韶也, 胡远艺, 彭彦, 毛毕刚, 刘慧敏, 唐婵娟, 雷斌, 唐丽, 余丽霞, 李文建, 罗武中, 罗治斌, 袁远涛, 李曜魁, 张丹, 周利斌, 柏连阳, 唐文帮, 赵炳然. 基于M1TDS靶向筛选技术的重离子束诱变定向改良杂交水稻卓两优1126性状的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 624-634. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||