
中国水稻科学 ›› 2026, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 61-71.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2026.250211
收稿日期:2025-02-25
修回日期:2025-03-21
出版日期:2026-01-10
发布日期:2026-01-21
通讯作者:
*email: ricebreeding_cnrri@163.com基金资助:
HUANG Qina, JIANG Hongrui, YANG Jie, YU Kunyu, YANG Changdeng, LIANG Yan*( )
)
Received:2025-02-25
Revised:2025-03-21
Online:2026-01-10
Published:2026-01-21
摘要:
【目的】水稻收获前穗发芽严重制约产量与品质形成,该性状主要受种子休眠基因调控。解析种子休眠分子机制对改良水稻穗萌抗性具有重要理论价值与育种意义。【方法】综合运用生物信息学分析、分子标记开发及标记辅助选择技术,系统解析种子休眠基因Sdr4(Seed dormancy 4)的生物学功能,探究其分子标记在多基因型种质改良中的应用潜力。【结果】Sdr4启动子区含TATA-box等核心元件及ABA响应元件等多种顺式作用元件,其编码蛋白为低稳定性疏水蛋白(101~150氨基酸区段磷酸化修饰占比25.93%),三级结构以α-螺旋(15.50%)、β-折叠(15.50%)和无规则卷曲(66.37%)为主。3K单倍型数据库与AlphaFold分析表明Sdr4基因具有6种功能性突变的单倍型,且在强休眠种质Kasalath与弱休眠种质日本晴(Nipponbare)的Sdr4氨基酸序列存在多个位点差异。系统发育分析显示Sdr4在非洲栽培稻(Oryza glaberrima)与沼生菰(Zizania palustris)中具有高度保守性。通过Kasalath与日本晴的Sdr4等位变异,开发了Sdr4-KF/KR与Sdr4-PF/PR两对功能标记,可精准区分种子休眠强度。基于25个水稻品种的分子检测筛选出休眠性显著差异的种质,并利用上述标记成功创制了强休眠型中组18改良系。【结论】Sdr4通过调控种子休眠深度影响水稻穗萌抗性。分子标记筛选表明20个主栽品种均呈种子弱休眠表型,利用Sdr4特异性标记选育的K17与K88新品系具有显著穗萌抗性。本研究为Sdr4功能解析及水稻抗穗萌分子育种提供了理论支撑与技术储备。
黄奇娜, 姜鸿瑞, 杨婕, 于坤宇, 杨长登, 梁燕. 种子休眠基因Sdr4的生物信息学分析与分子标记开发和应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 61-71.
HUANG Qina, JIANG Hongrui, YANG Jie, YU Kunyu, YANG Changdeng, LIANG Yan. Bioinformatics Analysis, Development and Application of Molecular Markers for Seed Dormancy Gene Sdr4 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2026, 40(1): 61-71.
| 引物名称 Primer | 引物序列(5’-3’) Sequence(5’-3’) | 片段长度 Length(bp) | 基因组位点 Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sdr4-F | CTTCTTAACCCCACCACCCC | 1161 | 引物5’端距离ATG上游102 bp 102 bp upstream of ATG |
| Sdr4-R | TTTGCTCCGGCTTGATGCATC | 引物3’端距离TGA下游27 bp 27 bp downstream of TGA | |
| Sdr4-KF | AAGGTCATCTCGCCGCGCG | 197 | 距离ATG 493~511 bp编码区 Coding region 493-511 bp from ATG |
| Sdr4-KR | GTTGCTGGAGTCCGAGACC | 距离ATG 702~720 bp编码区 Coding region 702-720 bp from ATG | |
| Sdr4-PF | AAGCTGCTGGAGCCG TGG | 227 | 距离ATG 493~509 bp编码区(画横线为引入的错配碱基) Coding region 493-509 bp from ATG (underlined bases are introduced mismatches) |
| Sdr4-PR | CTTGTACGCGTCGTTCACC | 距离ATG 672~690 bp编码区 Coding region 672-690 bp from ATG |
表1 Sdr4全基因组扩增引物与开发的分子标记
Table 1. Whole-genome amplification primers for Sdr4 and functionally validated molecular markers
| 引物名称 Primer | 引物序列(5’-3’) Sequence(5’-3’) | 片段长度 Length(bp) | 基因组位点 Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sdr4-F | CTTCTTAACCCCACCACCCC | 1161 | 引物5’端距离ATG上游102 bp 102 bp upstream of ATG |
| Sdr4-R | TTTGCTCCGGCTTGATGCATC | 引物3’端距离TGA下游27 bp 27 bp downstream of TGA | |
| Sdr4-KF | AAGGTCATCTCGCCGCGCG | 197 | 距离ATG 493~511 bp编码区 Coding region 493-511 bp from ATG |
| Sdr4-KR | GTTGCTGGAGTCCGAGACC | 距离ATG 702~720 bp编码区 Coding region 702-720 bp from ATG | |
| Sdr4-PF | AAGCTGCTGGAGCCG TGG | 227 | 距离ATG 493~509 bp编码区(画横线为引入的错配碱基) Coding region 493-509 bp from ATG (underlined bases are introduced mismatches) |
| Sdr4-PR | CTTGTACGCGTCGTTCACC | 距离ATG 672~690 bp编码区 Coding region 672-690 bp from ATG |
| 类别 Type | 顺式作用元件 cis-acting element | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Number | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 激素相关作用元件Hormone-related response elements | ABRE | ACGTG/CACGTG | 11 | 脱落酸响应元件 Abscisic acid response element |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 1 | 水杨酸途径响应元件 Salicylic acid pathway response element | |
| CGTCA/TGACG-motif | CGTCA | 10 | 茉莉酸甲酯调控元件 Methyl jasmonate regulatory element | |
| 逆境相关作用元件 Stress-related response elements | ARE | AAACCA | 3 | 厌氧诱导调控元件 Anaerobic induction regulatory element |
| MYB/MYC | CAACCA/CATGTG | 4 | 干旱诱导响应元件 Drought-induced response element | |
| 生长发育相关作用元件Growth and development- related response elements | RY-element | CATGCATG | 4 | 种子特异性调控元件 Seed-specific regulatory element |
| Sp1 | GGGCGG | 7 | 光照响应元件 Light-responsive element |
表2 Sdr4基因启动子顺式作用元件
Table 2. cis-acting elements in the promoter region of Sdr4
| 类别 Type | 顺式作用元件 cis-acting element | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Number | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 激素相关作用元件Hormone-related response elements | ABRE | ACGTG/CACGTG | 11 | 脱落酸响应元件 Abscisic acid response element |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 1 | 水杨酸途径响应元件 Salicylic acid pathway response element | |
| CGTCA/TGACG-motif | CGTCA | 10 | 茉莉酸甲酯调控元件 Methyl jasmonate regulatory element | |
| 逆境相关作用元件 Stress-related response elements | ARE | AAACCA | 3 | 厌氧诱导调控元件 Anaerobic induction regulatory element |
| MYB/MYC | CAACCA/CATGTG | 4 | 干旱诱导响应元件 Drought-induced response element | |
| 生长发育相关作用元件Growth and development- related response elements | RY-element | CATGCATG | 4 | 种子特异性调控元件 Seed-specific regulatory element |
| Sp1 | GGGCGG | 7 | 光照响应元件 Light-responsive element |

图2 Sdr4序列比对与蛋白结构预测 A: 差异位点DNA序列比对与分子标记前引物Sdr4-KF和Sdr4-PF(绿色部分)的位点; B: Kasalath和日本晴中Sdr4氨基酸序列比对结果; C: Kasalath和日本晴中Sdr4二级结构预测; D: AlphaFold分析Kasalath和日本晴的Sdr4蛋白结构.
Fig. 2. Sequence alignment and protein structure prediction of Sdr4 A, Alignment of DNA sequences at different sites and the location of the forward primer F (highlighted in green) for molecular marker development; B, Alignment of the Sdr4 amino acid sequences in Kasalath and Nipponbare; C, Prediction of the secondary structure of Sdr4 in Kasalath and Nipponbare; D, AlphaFold analysis of the three-dimensional structure of Sdr4 in Kasalath and Nipponbare.
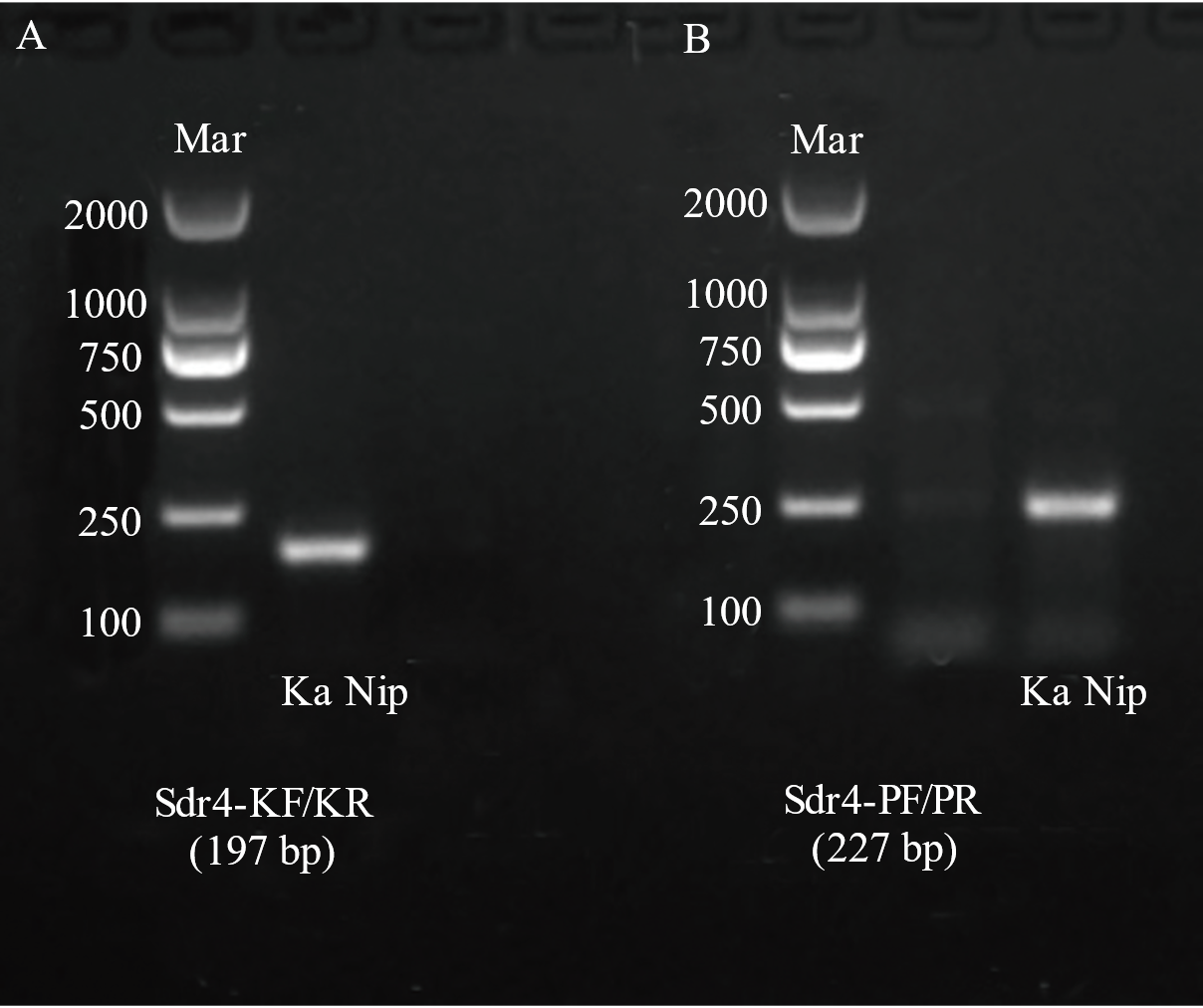
图3 分子标记Sdr4-KF/KR(A)与Sdr4-PF/PR(B)检测结果分析
Fig. 3. Analysis of detection results of molecular markers Sdr4-KF/KR (A) and Sdr4-PF/PR (B) Ka, Kasalath; Nip, Nipponbare; Mar, Easy 2K DNA marker.
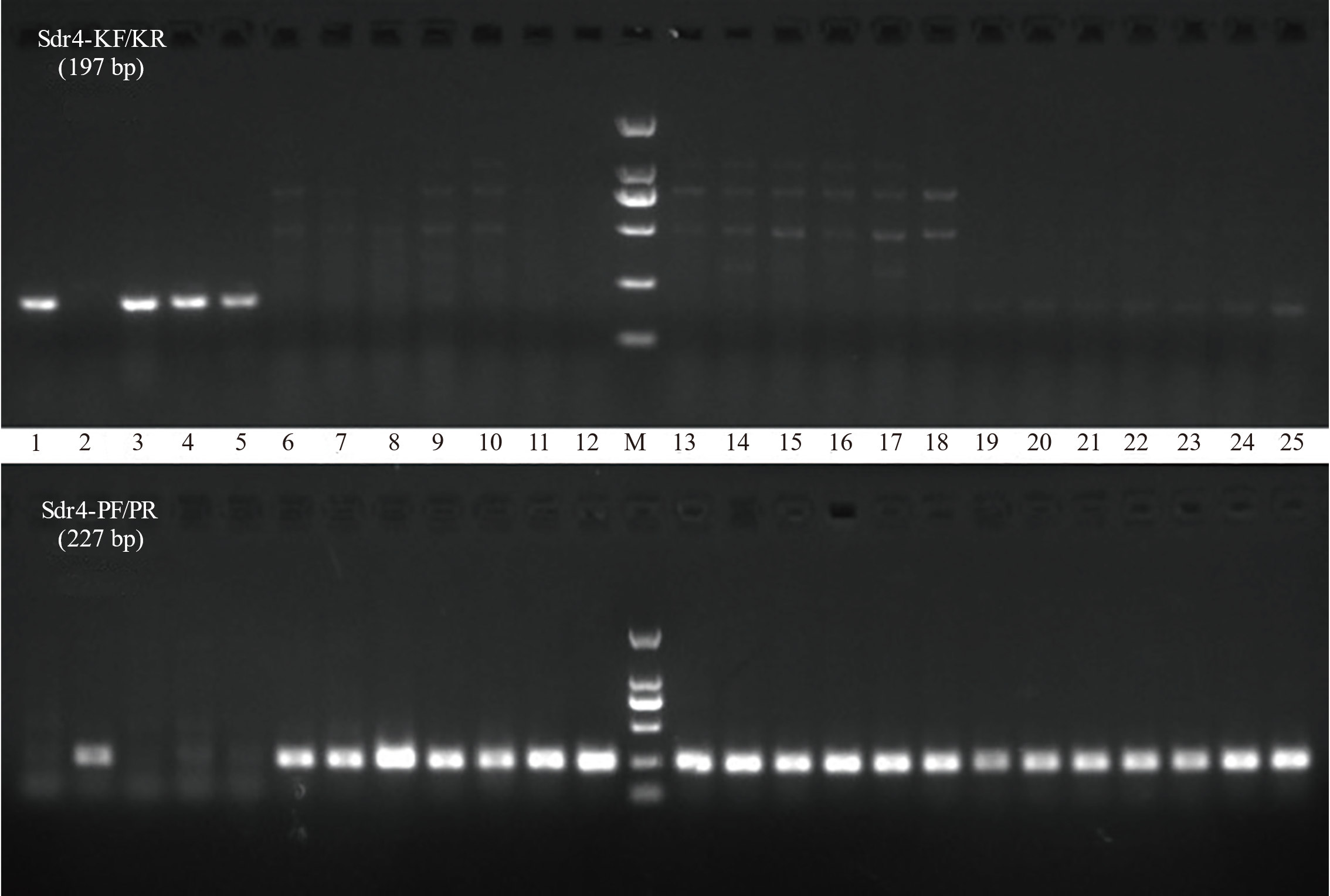
图4 不同水稻资源分子标记检测结果 1 : Kasalath; 2: Nip; 3: IR24; 4: IR36; 5: IR64; 6: 中组1号; 7: 中组3号; 8: 中组9号; 9: 中早22; 10: 中早35; 11: 中早39; 12: 中组18; 13: 中冷23; 14: 中佳早10号; 15: 浙106; 16: 浙农131; 17: 浙农135; 18: 甬籼15; 19: 甬籼57; 20: 甬籼378; 21: 温723; 22: 台早502; 23: 台早816; 24: 金早47; 25: 早籼310; M: Easy 2K DNA marker。
Fig. 4. Analysis of molecular marker detection results in diverse rice varieties 1, Kasalath; 2, Nip; 3, IR24; 4, IR36; 5, IR64; 6, Zhongzu 1; 7, Zhongzu 3; 8, Zhongzu 9; 9, Zhongzao 22; 10, Zhongzao 35; 11, Zhongzao 39; 12, Zhongzu 18; 13, Zhongleng 23; 14, Zhongjiazao 10; 15, Zhe 106; 16, Zhenong 131; 17, Zhenong 135; 18, Yongxian 15; 19, Yongxian 57; 20, Yongxian 378; 21, Wen 723; 22, Taizao 502; 23, Taizao 816; 24, Jinzao 47; 25, Zaoxian 310; M, Easy 2K DNA marker.
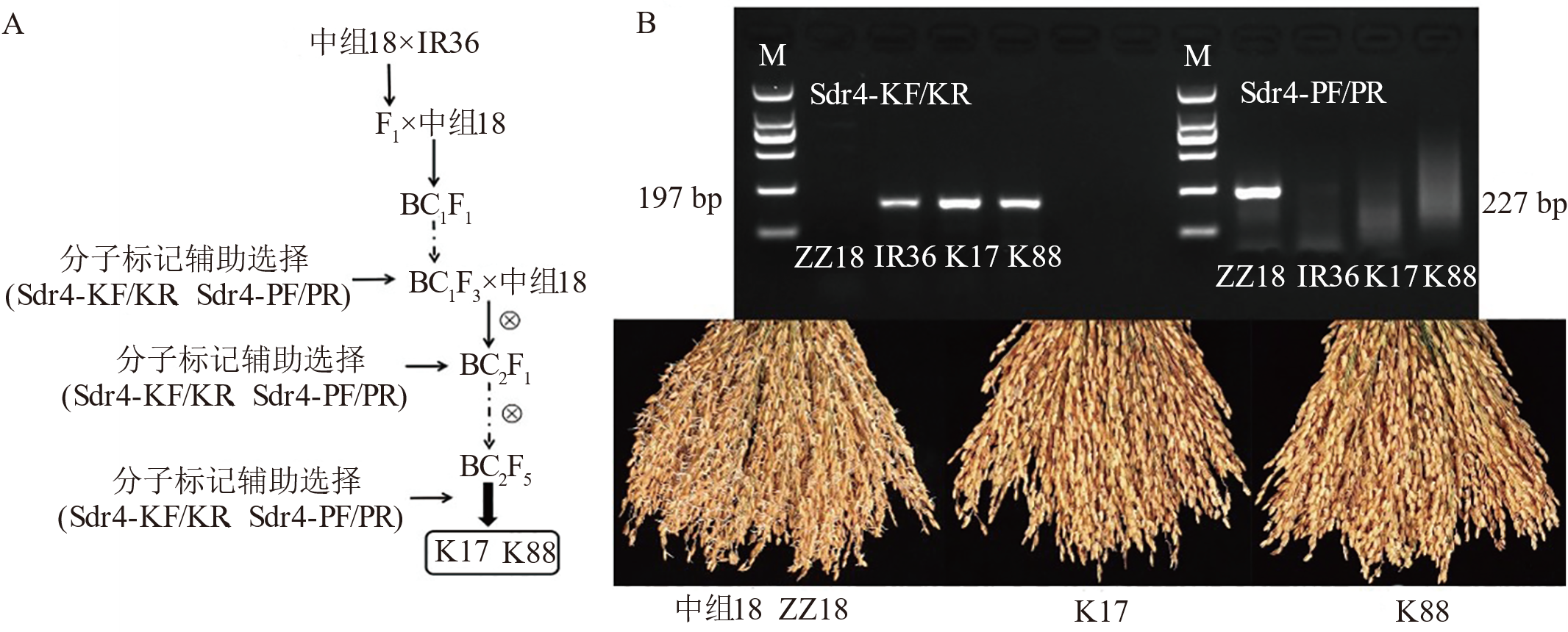

图6 抗穗萌新材料选育过程(A)和分子标记检测结果及其表型(B) 运用Sdr4-KF/KR(197 bp)与Sdr4-PF/PR(227 bp)引物分别扩增中组18(ZZ18)、IR36、K17与K88基因组DNA。将中组18、K17与K88水稻材料种子分别室温浸种48 h,35℃催芽萌发48 h后,进行表型鉴定并拍照记录。M: 标记。
Fig. 6. Breeding process of new materials resistant to panicle sprouting (A), molecular marker detection results and their phenotypes (B) Genomic DNA from the rice varieties ZZ18, IR36, K17, and K88 was amplified using the Sdr4-KF/KR (197 bp) and Sdr4-PF/PR (227 bp) primers, respectively. Seeds of ZZ18, K17, and K88 were soaked for 48 at room temperature and subsequently incubated at 37℃ for 48 h to promote germination. Following germination, phenotypic characterization was performed, and images were captured for documentation. M, Marker.
| [1] | Finch-savage W E, Leubner-metzger G. Seed dormancy and the control of germination[J]. New Phytologist, 2006, 171: 501-523. |
| [2] | Sohn S I, Pandian S, Kumar T S, Zoclanclounon Y A B, Muthuramalingam P, Shilpha J, Satish L, Ramesh M. Seed dormancy and pre-harvest sprouting in rice: An updated overview[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(21): 11804. |
| [3] | Finkelstein R, Reeves W, Ariizumi T, Steber C. Molecular aspects of seed dormancy[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2008, 59: 387-415. |
| [4] | Chen W, Wang W, Lyu Y, Wu Y, Huang P, Hu S, Wei X, Jiao G, Sheng Z, Tang S, Shao G, Luo J. OsVP1 activates Sdr4 expression to control rice seed dormancy via the ABA signaling pathway[J]. The Crop Journal, 2021, 9: 68-78. |
| [5] | He D, Yang P. Proteomics of rice seed germination[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2013, 4: 246. |
| [6] | Liu S, Sehgal S K, Li J, Lin M, Trick H N, Yu J, Gill B S, Bai G. Cloning and characterization of a critical regulator for preharvest sprouting in wheat[J]. Genetics, 2013, 195(1): 263-273. |
| [7] | Shu K, Meng Y J, Shuai H W, Liu W G, Du J B, Liu J, Yang W Y. Dormancy and germination: How does the crop seed decide?[J]. Plant Biology, 2015, 17(6): 1104-1112. |
| [8] | Falade K O, Semon O M, Fadairo O S, Oladunjoye A O, Orou K K. Functional and physico-chemical properties of flours and starches of African rice cultivars[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2014, 39: 41-50. |
| [9] | Lee H S, Choi M G, Hwang W H, Jeong J H, Lee C G. Occurrence of rice preharvest sprouting varies greatly depending on past weather conditions during grain filling[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 264: 108087. |
| [10] | 胡伟民, 马华升, 樊龙江, 阮松林. 杂交水稻制种不育系穗上发芽特性[J]. 作物学报, 2003, 29(3): 441-446. |
| Hu W M, Ma H S, Fan L J, Ruan S L. Characteristics of pre-harvest sprouting in sterile lines in hybrid rice seeds production[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2003, 29(3): 441-446. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Liao Y, Bai Q, Xu P, Wu T, Guo D, Peng Y, Zhang H, Deng X, Chen X, Luo M, Ali A, Wang W, Wu X. Mutation in rice abscisic Acid2 results in cell death, enhanced disease-resistance, altered seed dormancy and development[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 405. |
| [12] | Nakamura S, Abe F, Kawahigashi H, Nakazono K, Tagiri A, Matsumoto T, Utsugi S, Ogawa T, Handa H, Ishida H, Mori M, Kawaura K, Ogihara Y, Miura H. A wheat homolog of MOTHER OF FT AND TFL1 acts in the regulation of germination[J]. Plant Cell, 2011, 23(9): 3215-3229. |
| [13] | Nakamura S, Pourkheirandish M, Morishige H, Kubo Y, Nakamura M, Ichimura K, Seo S, Kanamori H, Wu J, Ando T, Hensel G, Sameri M, Stein N, Sato K, Matsumoto T, Yano M, Komatsuda T. Mitogen-activated protein Kinase Kinase 3 regulates seed dormancy in barley[J]. Current Biology, 2016, 26(6): 775-781. |
| [14] | Sato K, Yamane M, Yamaji N, Kanamori H, Tagiri A, Schwerdt J G, Fincher G B, Matsumoto T, Takeda K, Komatsuda T. Alanine aminotransferase controls seed dormancy in barley[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 11625. |
| [15] | Bentsink L, Jowett J, Hanhart C J, Koornneef M. Cloning of DOG1, a quantitative trait locus controlling seed dormancy in Arabidopsis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(45): 17042-17047. |
| [16] | Cao H, Han Y, Li J, Ding M, Li Y, Li X, Chen F, Soppe W J, Liu Y. Arabidopsis thaliana SEED DORMAN-CY 4-LIKE regulates dormancy and germination by mediating the gibberellin pathway[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2020, 71(3): 919-933. |
| [17] | Carrillo-barral N, Rodríguez-gacio M D C, Matilla A J. Delay of germination-1 (DOG1): A key to understanding seed dormancy[J]. Plants (Basel), 2020, 9(4): 480. |
| [18] | Liu F, Zhang H, Ding L, Soppe W J J, Xiang Y. RE-VERSAL OF RDO5 1, a homolog of rice seed dormancy4, interacts with bHLH57 and controls ABA biosynthesis and seed dormancy in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2020, 32(6): 1933-1948. |
| [19] | Hattori T, Terada T, Hamasuna S T. Sequence and functional analyses of the rice gene homologous to the maize Vp1[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 1994, 24: 805-810. |
| [20] | Zhao B, Zhang H, Chen T, Ding L, Zhang L, Ding X, Zhang J, Qian Q, Xiang Y. Sdr4 dominates pre-harvest sprouting and facilitates adaptation to local climatic condition in Asian cultivated rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2022, 64(6): 1246-1263. |
| [21] | Fan X, Gao F, Liu Y, Huang W, Yang Y, Luo Z, Zhang J, Qi F, Lü J, Su X, Wang L, Song S, Ren G, Xing Y. The transcription factor CCT30 promotes rice preharvest sprouting by regulating sugar signalling to inhibit the ABA-mediated pathway[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2025, 23(2): 579-591. |
| [22] | Sugimoto K, Takeuchi Y, Ebana K, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Hara N, Ishiyama K, Kobayashi M, Ban Y, Hattori T, Yano M. Molecular cloning of Sdr4, a regulator involved in seed dormancy and domestication of rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(13): 5792-5797. |
| [23] | Du L, Xu F, Fang J, Gao S, Tang J, Fang S, Wang H, Tong H, Zhang F, Chu J, Wang G, Chu C. Endosperm sugar accumulation caused by mutation of PHS8/ ISA1 leads to pre-harvest sprouting in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2018, 95(3): 545-556. |
| [24] | Magwa R A, Zhao H, Xing Y. Genome-wide association mapping revealed a diverse genetic basis of seed dormancy across subpopulations in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. BMC Genetics, 2016, 17: 1-13. |
| [25] | Meyer R S, Purugganan M D. Evolution of crop species: Genetics of domestication and diversification[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2013, 14(12): 840-852. |
| [26] | Edwards K, Johnstone C, Thompson C. A simple and rapid method for the preparation of plant genomic DNA for PCR analysis[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1991, 19(6): 1349. |
| [27] | Hilhorst H W M, Karssen C M. Seed dormancy and germination: The role of abscisic acid and gibberellins and the importance of hormone mutants[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 1992, 11: 225-238. |
| [28] | Omoarelojie L O, Kulkarni M G, Finnie J F, van Staden J. Smoke-derived cues in the regulation of seed germination: Are Ca2+-dependent signals involved?[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2022, 97(2): 343-355. |
| [29] | 张毛宁. 基于花生RIL群体的鲜种子发芽性状QTL定位及分子标记开发[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2022. |
| Zhang M N. QTL mapping for fresh seed germination traits based on a peanut RIL population and molecular marker development[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 李兴沂, 陈玲, 邵建韬, 肖素勤, 李金璐, 付惠仙, 殷富有, 张建红, 程在全, 刘丽. 水稻产量与淀粉品质协同调控的分子遗传研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 1-17. |
| [2] | 岳轩宇, 谢文亚, 冯志明, 陈宗祥, 胡珂鸣, 左示敏. OsERF93参与调控水稻纹枯病抗性的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 37-50. |
| [3] | 王轶欣, 林参, 马刘洋, 陈龙, 奉保华, 倪深, 魏祥进, 贺记外, 陈天晓. 谷丙转氨酶基因OsAlaAT4调控水稻氮素吸收和产量[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 51-60. |
| [4] | 程朝平, 何旎清, 白康呈, 林少俊, 黄凤凰, 刘军化, 程祖锌, 黄成志, 杨德卫. 聚合稻瘟病抗性基因Pigm-1和Pid2的水稻三系不育系福梦A的选育与利用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 72-84. |
| [5] | 刘亚萍, 董译词, 郑君妍, 邱绚, 刘鹏程, 叶亚峰, 刘斌美, 陈析丰, 马伯军. 水稻类病变早衰突变体lmes7的鉴定与基因精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 85-94. |
| [6] | 谢世民, 周誉株, 薛晓迪, 朱广飞, 孙良, 陈建能. 水稻钵苗取栽协同作业式移栽机构设计与试验[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2026, 40(1): 131-144. |
| [7] | 王娟, 吴丽娟, 洪海波, 姚志文, 王磊, 鄂志国. 水稻泛素结合酶E2的生物学功能研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 744-750. |
| [8] | 陶士博, 许娜, 徐正进, 刘畅, 徐铨. 水稻发芽期耐冷基因Cold6的克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 751-759. |
| [9] | 陈伟, 叶元妹, 赵剑华, 冯志明, 陈宗祥, 胡珂鸣, 左示敏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术改良南粳46抽穗期[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 760-770. |
| [10] | 侯桂花, 周立国, 雷建国, 陈虹, 聂元元. 水稻OsRDR5基因功能及作用机制初步解析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 779-788. |
| [11] | 陆帅, 陶涛, 刘冉, 周文玉, 曹蕾, 杨青青, 张明秋, 任鑫哲, 杨芝笛, 徐福祥, 环海东, 龚远航, 张皓程, 金素奎, 蔡秀玲, 高继平, 冷语佳. 水稻长护颖小粒突变体lsg8的表型鉴定与基因克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 813-824. |
| [12] | 邓欢, 刘亚培, 王春连, 郭威, 陈析丰, 纪志远. 水稻抗白叶枯病新基因Xa49(t)的定位分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 825-831. |
| [13] | 郝雯倩, 蔡兴菁, 杨海东, 吴宇阳, 滕轩, 薛超, 龚志云. 不同类型组蛋白修饰在水稻响应非生物胁迫中的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 575-585. |
| [14] | 王镜博, 苏畅, 冯晶, 姜思旭, 徐海, 崔志波, 赵明辉. 水稻OsAlR1基因耐铝性功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 615-623. |
| [15] | 韶也, 胡远艺, 彭彦, 毛毕刚, 刘慧敏, 唐婵娟, 雷斌, 唐丽, 余丽霞, 李文建, 罗武中, 罗治斌, 袁远涛, 李曜魁, 张丹, 周利斌, 柏连阳, 唐文帮, 赵炳然. 基于M1TDS靶向筛选技术的重离子束诱变定向改良杂交水稻卓两优1126性状的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 624-634. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||