
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 152-160.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.5113
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yong-tao CUI, Li-wen WU, Shi-kai HU, De-yong REN, Chang-wei GE, Wei-jun YE, Guo-jun DONG, Long-biao GUO*( ), Xing-ming HU*(
), Xing-ming HU*( )
)
Received:2015-07-13
Revised:2015-10-18
Online:2016-03-10
Published:2016-03-10
Contact:
Long-biao GUO, Xing-ming HU
崔永涛, 吴立文, 胡时开, 任德勇, 葛常伟, 叶卫军, 董国军, 郭龙彪*( ), 胡兴明*(
), 胡兴明*( )
)
通讯作者:
郭龙彪,胡兴明
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yong-tao CUI, Li-wen WU, Shi-kai HU, De-yong REN, Chang-wei GE, Wei-jun YE, Guo-jun DONG, Long-biao GUO, Xing-ming HU. Phenotypical Analysis and Fine Mapping of a Semi-dominant Dwarfism Gene Si-dd1 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(2): 152-160.
崔永涛, 吴立文, 胡时开, 任德勇, 葛常伟, 叶卫军, 董国军, 郭龙彪, 胡兴明. 水稻半显性矮秆基因Si-dd1的表型分析和精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(2): 152-160.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.5113
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height /cm | 分蘖数 Tiller number | 一次枝梗 Number of primary rachis branches | 二次枝梗 Number of secondary rachis branches | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 总粒数 Total grain number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型WT | 83.8 a | 18.7 | 8.0 | 9.0 a | 88.8 a | 72.7 a |
| 半矮秆Si-dd1(Aa) | 60.6 b | 16.7 | 8.0 | 16.3 b | 61.3 b | 90.7 b |
| 矮秆Si-dd1(AA) | 43.7 c | 16.3 | 9.6 | 16.3 b | 1.1 c | 97.3 b |
Table 1 Comparison of tiller, plant height and panicle traits among wild type, Si-dd1(Aa) and Si-dd1(AA).
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height /cm | 分蘖数 Tiller number | 一次枝梗 Number of primary rachis branches | 二次枝梗 Number of secondary rachis branches | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 总粒数 Total grain number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型WT | 83.8 a | 18.7 | 8.0 | 9.0 a | 88.8 a | 72.7 a |
| 半矮秆Si-dd1(Aa) | 60.6 b | 16.7 | 8.0 | 16.3 b | 61.3 b | 90.7 b |
| 矮秆Si-dd1(AA) | 43.7 c | 16.3 | 9.6 | 16.3 b | 1.1 c | 97.3 b |
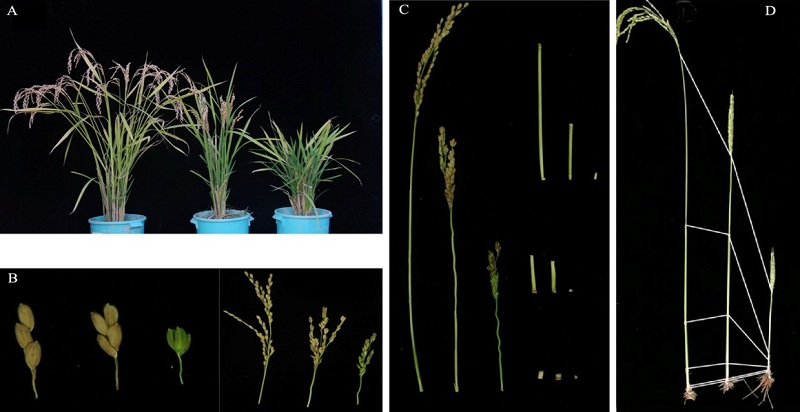

Fig. 1. Phenotypes of Si-dd1 at maturation stage. A, Whole plant; B, Panicle; C, Internode; D, Comparison of every internode. From left to right,wild type, Si-dd1(Aa) and Si-dd1(AA) in turn.
| 组合 Cross | F1 | F2 | χ2(1:2:1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总株数 Total of plants | 正常高秆 Normal plants | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 矮秆 Dwarf | |||
| Si-dd1(AA)/9311 | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 184 | 48 | 94 | 42 | 0.478 |
| Si-dd1(AA)/NJ06 | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 243 | 62 | 122 | 59 | 0.078 |
| NJ06/Si-dd1(AA) | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 193 | 47 | 100 | 46 | 0.264 |
| 9311/Si-dd1(AA) | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 290 | 72 | 150 | 68 | 0.455 |
Table 2 Genetice analysis of F2 population of Si-dd1(AA) / NJ06(9311).
| 组合 Cross | F1 | F2 | χ2(1:2:1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总株数 Total of plants | 正常高秆 Normal plants | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 矮秆 Dwarf | |||
| Si-dd1(AA)/9311 | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 184 | 48 | 94 | 42 | 0.478 |
| Si-dd1(AA)/NJ06 | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 243 | 62 | 122 | 59 | 0.078 |
| NJ06/Si-dd1(AA) | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 193 | 47 | 100 | 46 | 0.264 |
| 9311/Si-dd1(AA) | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 290 | 72 | 150 | 68 | 0.455 |
| 组合 Cross | 野生型 Wild type | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 总株数 Total | χ2(1:1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si-dd1(Aa)/ 9311 | 54 | 48 | 102 | 0.353 |
| Si-dd1(Aa)/ NJ06 | 59 | 54 | 113 | 0.220 |
| 9311 /Si-dd1(Aa) | 52 | 45 | 97 | 0.505 |
| NJ06 /Si-dd1(Aa) | 52 | 48 | 100 | 0.160 |
Table 3 Genetice analysis of F1 population of Si-dd1(Aa) /NJ06 and Si-dd1(Aa) /9311.
| 组合 Cross | 野生型 Wild type | 半矮秆 Semi-dwarf | 总株数 Total | χ2(1:1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si-dd1(Aa)/ 9311 | 54 | 48 | 102 | 0.353 |
| Si-dd1(Aa)/ NJ06 | 59 | 54 | 113 | 0.220 |
| 9311 /Si-dd1(Aa) | 52 | 45 | 97 | 0.505 |
| NJ06 /Si-dd1(Aa) | 52 | 48 | 100 | 0.160 |
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Forward primer(5'-3') | 引物序列(5'-3') Reverse primer(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | CAGTCTTGCTCCGTTTGTTG | CTGTGACTGACTTGGTCATAGG |
| M2 | ATCGCAGCAATGCCTCGTG | TGCGTTTGTGTTTGGCTCG |
| M3 | CTCAACGTTGACACCTCGTG | TCCTCCATCGAGCAGTATCA |
Table 4 Makers for primary mapping of Si-DD1.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Forward primer(5'-3') | 引物序列(5'-3') Reverse primer(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | CAGTCTTGCTCCGTTTGTTG | CTGTGACTGACTTGGTCATAGG |
| M2 | ATCGCAGCAATGCCTCGTG | TGCGTTTGTGTTTGGCTCG |
| M3 | CTCAACGTTGACACCTCGTG | TCCTCCATCGAGCAGTATCA |
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Forward primer(5'-3') | 引物序列(5'-3') Reverse primer(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | GGTCGCAGCTTGAATTAATGA | GCAATCTCATTTGTTGAGAACC |
| P2 | TGATGTTTGGCACATACTTGC | GCAAACTTTCTGATAAGGAATAG |
| P3 | CTCCAAAGCTGACAATGGTG | TGAGAAGGAGTAGGAAGCATAACA |
| P4 | GGTACTAACCATGTGATTGAG | CACCTGAATTACCGTATATG |
| P5 | CGTAGGAGTCGACGCTGTC | CCCAATCCGCTGTGGTTTT |
| P6 | GCAGGTTGTAATGGAGGTGAA | CGGCGAGCCATATTGTTTAT |
Table 5 Makers for fine mapping of Si-DD1.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Forward primer(5'-3') | 引物序列(5'-3') Reverse primer(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | GGTCGCAGCTTGAATTAATGA | GCAATCTCATTTGTTGAGAACC |
| P2 | TGATGTTTGGCACATACTTGC | GCAAACTTTCTGATAAGGAATAG |
| P3 | CTCCAAAGCTGACAATGGTG | TGAGAAGGAGTAGGAAGCATAACA |
| P4 | GGTACTAACCATGTGATTGAG | CACCTGAATTACCGTATATG |
| P5 | CGTAGGAGTCGACGCTGTC | CCCAATCCGCTGTGGTTTT |
| P6 | GCAGGTTGTAATGGAGGTGAA | CGGCGAGCCATATTGTTTAT |
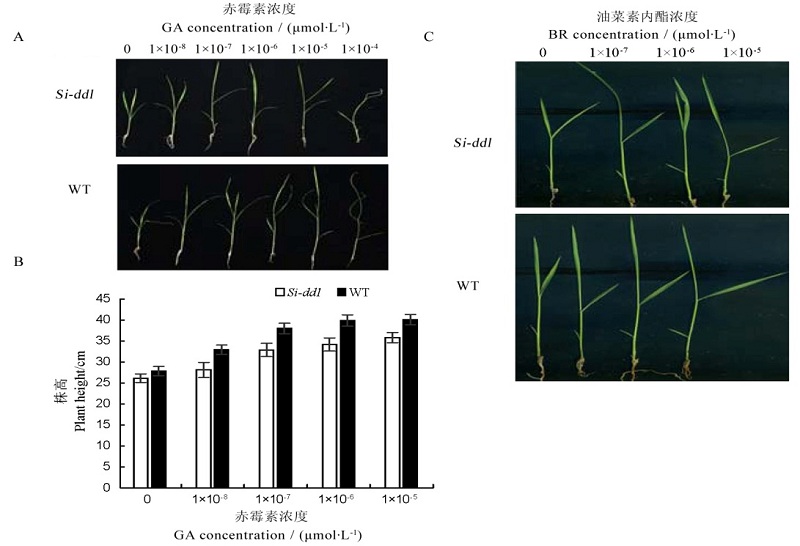
Fig. 3. Si-dd1 exposed to GA and BR. WT,Wild type; GA, Gibberellic acid; BR,Brassinolide. A, Plant phenotype after GA treatment at different concentrations; B, Plant height after GA treatment at different concentrations; C, Leaf angle after BR treatment at different concentrations.
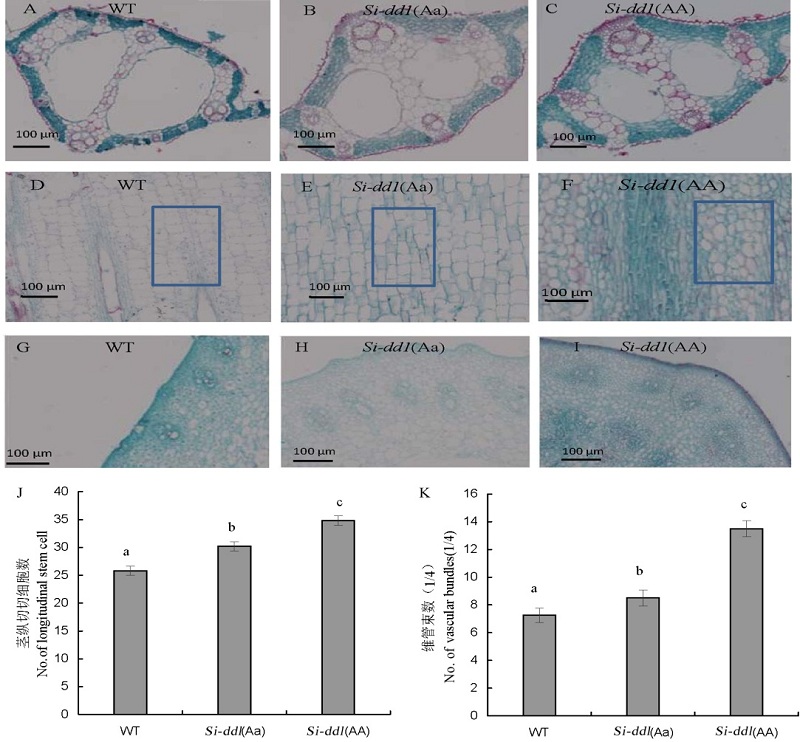
Fig. 5. Comparison of microscopic structure among WT, Si-dd1(Aa) and Si-dd1(AA). A,B,C, Cross sections of leaf main vein of WT, Si-dd1(Aa) and Si-dd1(AA); D,E,F, Longitudinal section of the second internode from the top of WT, Si-dd1(Aa) and Si-dd1(AA); G,H,I, Cross sections of the second internode from the top of WT, Si-dd1(Aa) and Si-dd1(AA). J,K, Numbers of vascular bundles and longitudinal stem cells.
| [1] | Spielmeyer W, Ellis M H, Chandler P M.Semidwarf (sd-1), “green revolution” rice, contains a defective gibberellin 20-oxidase gene.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99: 9043-9048. |
| [2] | Yin H F, Gao P, Liu C W, et al.SUI-family genes encode phosphatidylserine synthases and regulate stem development in rice.Planta, 2013, 237: 15-27. |
| [3] | Komorisono M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Aichi I, et al.Analysis of the rice mutant dwarf and gladius leaf 1 , aberrant katanin-mediated microtubule organization causes up-regulation of gibberellin biosynthetic genes independently of gibberellin signaling.Plant Physiol, 2005, 138: 1982-1993. |
| [4] | Iwamoto M, Kiyota S, Hanada A, et al.The multiple contributions of phytochromes to the control of internode elongation in rice.Plant Physiol, 2011, 157: 1187-1195. |
| [5] | Toyomasu T, Kagahara T, Hirose Y, et al.Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding ent-copalyl diphosphate synthases in wheat: Insight into the evolution of rice phytoalexin biosynthetic genes.Biosc Biotech Biochem, 2009, 73: 772-775. |
| [6] | Hirano K, Asano K, Tsuji H, et al.Characterization of the molecular mechanism underlying gibberellin perception complex formation in rice.Plant Cell, 2010, 22: 2680-2696. |
| [7] | Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Nakajima M, Katoh E, et al.Molecular interactions of a soluble gibberellin receptor, GID1, with a rice DELLA protein, SLR1, and gibberellin.Plant Cell, 2007, 19: 2140-2155. |
| [8] | Oikawa T, Koshioka M, Kojima K, et al.A role of OsGA20ox1, encoding an isoform of gibberellin 20-oxidase, for regulation of plant stature in rice.Plant Mol Biol, 2004, 55: 687-700. |
| [9] | Hirano K, Kouketu E, Katoh H, et al.The suppressive function of the rice DELLA protein SLR1 is dependent on its transcriptional activation activity.Plant J, 2012, 71: 443-453. |
| [10] | Yang M F, Qi W W, Sun F, et al.Overexpression of rice LRK1 restricts internode elongation by down-regulating OsKO2.Biotech Lett, 2013, 35: 121-128. |
| [11] | Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Fujisawa Y, Kobayashi M, et al.Rice dwarf mutant d1, which is defective in the α subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein, affects gibberellin signal transduction.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2000, 97: 11638-11643. |
| [12] | Wang L, Xu Y, Ma Q, et al.Heterotrimeric G protein α subunit is involved in rice brassinosteroid response.Cell Res, 2006, 16: 916-922. |
| [13] | Hu X, Qian Q, Xu T, et al.The U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase TUD1 functions with a heterotrimeric G α subunit to regulate brassinosteroid-mediated growth in rice.PLoS Gene, 2013, 9: e1003391. |
| [14] | Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Inukai Y, et al.Auxin signal transcription factor regulates expression of the brassinosteroid receptor gene in rice.Plant J, 2013, 73: 676-688. |
| [15] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Umemura K, et al.A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450.Plant Cell, 2003, 15: 2900-2910. |
| [16] | Zhi H, Miyako U, Shozo F, et al.The rice brassinosteroid-deficient dwarf2 Mutant, defective in the rice homolog of Arabidopsis DIMINUTO/DWARF1, is rescued by the endogenously accumulated alternative bioactive brassinosteroid, dolichosterone.Plant Cell, 2005, 17(8): 2243-2254. |
| [17] | Thirumurugan T, Ito Y, Kubo T, et al.Identification, characterization and interaction of HAP family genes in rice.Mol Genet Genom, 2008, 279: 279-289. |
| [18] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Shimizu-Sato S, et al.Loss-of-function of a rice brassinosteroid biosynthetic enzyme, C-6 oxidase, prevents the organized arrangement and polar elongation of cells in the leaves and stem.Plant J, 2002, 32: 495-508. |
| [19] | Tanabe S, Ashikari M, Fujioka S, et al.A novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant, dwarf11, with reduced seed length.Plant Cell, 2005, 17: 776-790. |
| [20] | Bai M Y, Zhang L Y, Gampala S S, et al.Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104: 13839-13844. |
| [21] | Sang D J, Chen D Q, Liu G F, et al.Strigolactones regulate rice tiller angle by attenuating shoot gravitropism through inhibiting auxin biosynthesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111: 11199-11204. |
| [22] | Ito S, Kitahata N, Umehara M, et al.A new lead chemical for strigolactone biosynthesis inhibitors.Plant Cell Physiol, 2010, 51: 1143-1150. |
| [23] | Arite T, Umehara M, Ishikawa S, et al.d14, a strigolactone-insensitive mutant of rice, shows an accelerated outgrowth of tillers.Plant Cell Physiol, 2009, 50: 1416-1424. |
| [24] | Zou J H, Zhang S Y, Zhang W P, et al.The rice HIGH-TILLERING DWARF1 encoding an ortholog of Arabidopsis MAX3 is required for negative regulation of the outgrowth of axillary buds.Plant J, 2006, 48: 687-696. |
| [25] | Jiang L, Liu X, Xiong G S, et al.DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice.Nature, 2014, 506: 401-405. |
| [26] | Liu W, Kohlen W, Lillo A, et al.Strigolactone biosynthesis in medicago truncatula and rice requires the symbiotic GRAS-type transcription factors NSP1 and NSP2.Plant Cell, 2011, 23: 3853-3865. |
| [27] | Guo S Y, Xu Y Y, Liu H H, et al.The interaction between OsMADS57 and OsTB1 modulates rice tillering via DWARF14.Nat Comm, 2013, 4(3): 1566. |
| [28] | Du H, Wu N, Fu J, et al.A GH3 family member, OsGH3-2, modulates auxin and abscisic acid levels and differentially affects drought and cold tolerance in rice.J Exp Bot, 2012, 63: 6467-6480. |
| [29] | Sazuka T, Kamiya N, Nishimura T, et al.A rice tryptophan deficient dwarf mutant, tdd1, contains a reduced level of indole acetic acid and develops abnormal flowers and organless embryos.Plant J, 2009, 60: 227-241. |
| [30] | Sato-Izawa K, Nakaba S, Tamura K, et al.DWARF50 (D50), a rice (Oryza sativa L.) gene encoding inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase, is required for proper development of intercalary meristem.Plant Cell Environ, 2012, 35: 2031-2044. |
| [31] | Zhang B C, Liu X L, Qian Q, et al.Golgi nucleotide sugar transporter modulates cell wall biosynthesis and plant growth in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108: 5110-5115. |
| [32] | Luan W J, Liu Y Q, Zhang F X, et al.OsCD1 encodes a putative member of the cellulose synthase-like D sub-family and is essential for rice plant architecture and growth.Plant Biotech J, 2011, 9: 513-524. |
| [33] | Rogers S O, Bendich A J.Extraction of DNA from milligram amountsof fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues.Plant Mol Biol, 1985, 5: 69-76. |
| [34] | Huang L M, Sun Q W, Qin F J, et al.Down-regulation of a SILENT INFORMATION REGULATOR2-related histone deacetylase gene, OsSRT1, induces DNA fragmentation and cell death in rice.Plant Physiol, 2007, 144: 1508-1519. |
| [35] | Zhang Q, Xu J, Li Y, et al.Morphological, anatomical and genetic analysis for a rice mutant with abnormal hull.J Genet Genom, 2007, 34: 519-526. |
| [36] | Yang D L, Li Q, Deng Y W, et al.Altered disease development in the eui mutants and Eui overexpressors indicates that gibberellins negatively regulate rice basal disease resistane.Mol Plant, 2008, 1: 528-537. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||