
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 246-255.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230907
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
MIAO Jun1,2, RAN Jinhui1, XU Mengbin1,3, BO Liubing1, WANG Ping1, LIANG Guohua1,2,*( ), ZHOU Yong1,2,*(
), ZHOU Yong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-14
Revised:2023-12-08
Online:2024-05-10
Published:2024-05-13
Contact:
*email: ricegb@yzu.edu.cn;
zhouyong@yzu.edu.cn
缪军1,2, 冉金晖1, 徐梦彬1,3, 卜柳冰1, 王平1, 梁国华1,2,*( ), 周勇1,2,*(
), 周勇1,2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
*email: ricegb@yzu.edu.cn;
zhouyong@yzu.edu.cn
基金资助:MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255.
缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230907
| 引物名称 | 前引物 | 后引物 |
|---|---|---|
| Primer name | Forward (5’-3’) | Reverse (5’-3’) |
| RGG2-BD | AAAGAATTCATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAACGGGGAGG | AAAGGATCCCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGATGCC |
| RGG2-AD | gccatggaggccagtgaattcATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAAC | cagctcgagctcgatggatccCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGA |
| RGB1-AD | AAACCCGGGTATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAGCTCA | AAAGGATCCTCAAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCGCTGAA |
| RGB1-BD | atggccatggaggccgaattcATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAG | ccgctgcaggtcgacggatccTCAAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCG |
| RGG2-cLUC | tacgcgtcccggggcggtaccATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAAC | acgaaagctctgcaggtcgacCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGA |
| RGB1-nLUC | acgggggacgagctcggtaccATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAG | cgcgtacgagatctggtcgacAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCGCT |
| OsActin-qPCR | GATGACCCAGATCATGTTTG | GGGCGATGTAGGAAAGC |
| RGG2-qPCR | GCAGGATGAACTGAACGAGC | GGATGCCCACCATTTGTTA |
| OsLEA3-qPCR | GCCGTGAATGATTTCCCTTTG | CACACCCGTCAGAAATCCTCC |
| OsRAB16A-qPCR | CATGGACAAGATCAAGGAGAAGC | CTTATTATTCAGGAAGGTGACGTGG |
| OsNCED4-qPCR | GATTGCACGGCACCTTCATT | CTCTGTAATTTGATTTTTCACTGGCTAAT |
| OsLIP9-qPCR | TGGAATTTGGAAGTGTTTGGC | CCCACACGAAACACAAACTTC |
| OsNAC6-qPCR | CGAGAAGACCAACTGGAT | CAACCTGAGGCTGTTCTT |
| OsABIL3-qPCR | GAGCGGGCAAGGATT | CCGTGGAACGACCATAAC |
Table 1. Primers used in this study
| 引物名称 | 前引物 | 后引物 |
|---|---|---|
| Primer name | Forward (5’-3’) | Reverse (5’-3’) |
| RGG2-BD | AAAGAATTCATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAACGGGGAGG | AAAGGATCCCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGATGCC |
| RGG2-AD | gccatggaggccagtgaattcATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAAC | cagctcgagctcgatggatccCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGA |
| RGB1-AD | AAACCCGGGTATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAGCTCA | AAAGGATCCTCAAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCGCTGAA |
| RGB1-BD | atggccatggaggccgaattcATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAG | ccgctgcaggtcgacggatccTCAAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCG |
| RGG2-cLUC | tacgcgtcccggggcggtaccATGAGGGGGGAGGCGAAC | acgaaagctctgcaggtcgacCTAGGAAAAATCTGAGCCTTTGGA |
| RGB1-nLUC | acgggggacgagctcggtaccATGGCGTCCGTGGCGGAG | cgcgtacgagatctggtcgacAACTATTTTCCGGTGTCCGCT |
| OsActin-qPCR | GATGACCCAGATCATGTTTG | GGGCGATGTAGGAAAGC |
| RGG2-qPCR | GCAGGATGAACTGAACGAGC | GGATGCCCACCATTTGTTA |
| OsLEA3-qPCR | GCCGTGAATGATTTCCCTTTG | CACACCCGTCAGAAATCCTCC |
| OsRAB16A-qPCR | CATGGACAAGATCAAGGAGAAGC | CTTATTATTCAGGAAGGTGACGTGG |
| OsNCED4-qPCR | GATTGCACGGCACCTTCATT | CTCTGTAATTTGATTTTTCACTGGCTAAT |
| OsLIP9-qPCR | TGGAATTTGGAAGTGTTTGGC | CCCACACGAAACACAAACTTC |
| OsNAC6-qPCR | CGAGAAGACCAACTGGAT | CAACCTGAGGCTGTTCTT |
| OsABIL3-qPCR | GAGCGGGCAAGGATT | CCGTGGAACGACCATAAC |
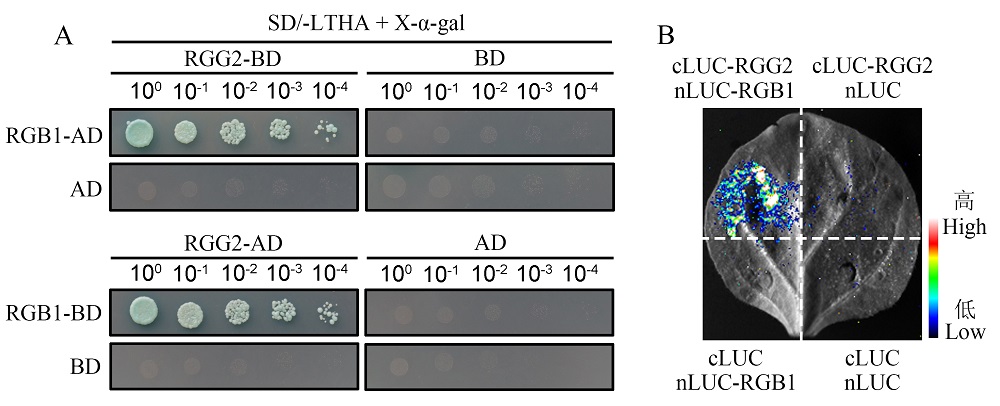
Fig. 1. Interaction analysis between RGG2 and RGB1 proteins A, Yeast two-hybrid analysis of RGG2 and RGB1. RGG2 was cloned into pGBKT7 (BD) or pGADT7 (AD) vectors, respectively. RGB1 was cloned into AD and BD vectors, respectively. Yeast was grown on the medium lacking Trp, Leu, His, and Ade to analyze protein interactions; B, Split-LUC analysis of RGG2 and RGB1. RGG2 was linked to the C-terminal fragment of luciferase (cLUC) and RGB1 was linked to the N-terminal fragment of luciferase (nLUC), respectively. Luciferase activity was detected after infestation of N. benthamiana leaves for 2 days.
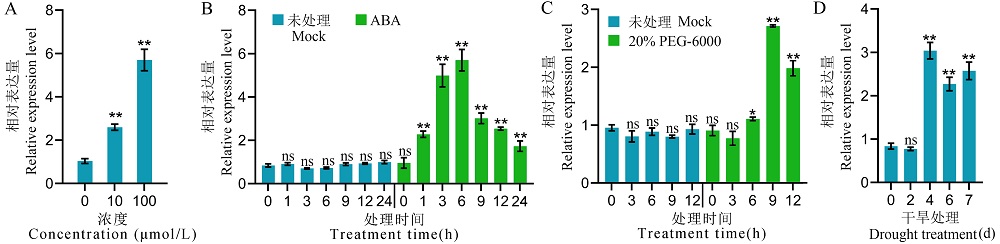
Fig. 2. ABA, PEG-6000 and drought treatment induce the expression of RGG2 A, The expression levels of RGG2 after the treatment with ABA at various concentrations. 2-week-old Nipponbare seedlings were treated with 10 and 100 μmol/L ABA, then the samples were collected at 6 h after treatment for expression analysis; B, The expression levels of RGG2 at different times after treatment with and without 100 μmol/L ABA. C, The expression levels of RGG2 at different times after treatment with and without 20% PEG-6000. D, The expression levels of RGG2 at different times after drought treatment. Values represent the mean ± SD (n=3). t-test: ns, Not significant; *, P ≤ 0.05;**, P ≤ 0.01.

Fig. 3. Overexpression of RGG2 in the Nipponbare background increases rice sensitivity to ABA A, Seed germination of NIP and RGG2 overexpression lines exposed to different concentrations of ABA. Scale bars = 1 cm. B-F, Seed germination rates of NIP and RGG2 overexpression lines under 0 μmol/L (B), 1 μmol/L (C), 2 μmol/L (D), 5 μmol/L (E), 10 μmol/L (F) ABA treatment. G, Seed germination rates of NIP and RGG2 overexpression lines with various ABA concentrations treatment for 84 h. H, Root length of NIP and RGG2 overexpression lines under different concentrations of ABA. Values are mean ± SD (n = 4). t-test: ns, not significant; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01. NIP, Nipponbare. NIP-OE1 and NIP-OE2 represent the overexpression lines of RGG2 in the background of Nipponbare.
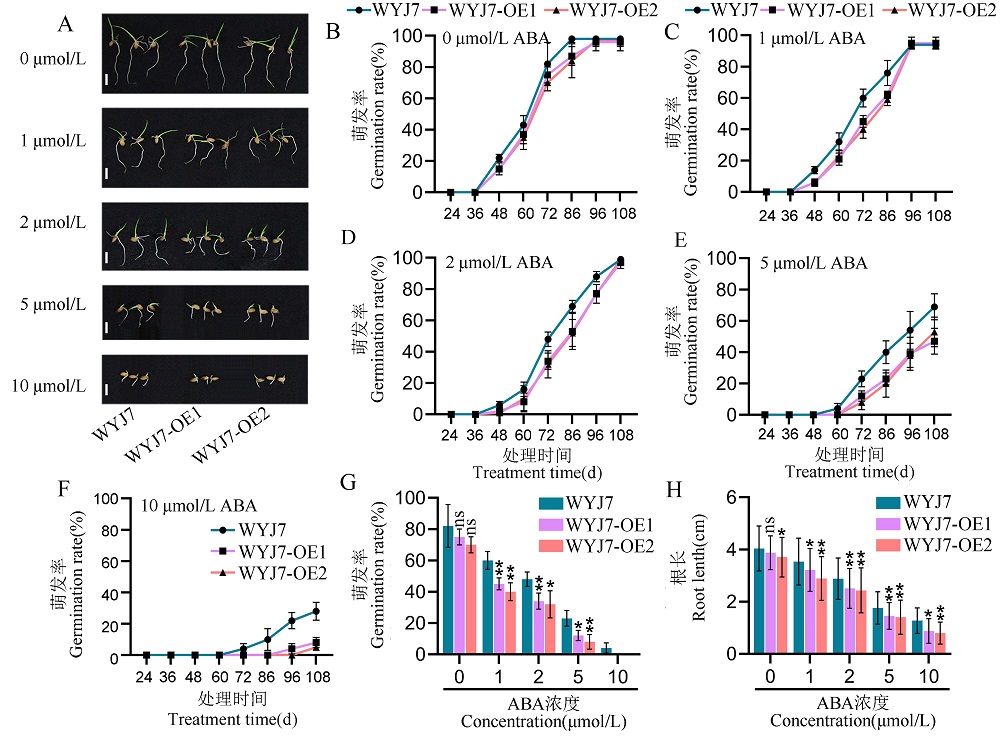
Fig. 4. Overexpression of RGG2 in the Wuyunjing 7 background increases rice sensitivity to ABA A, Seed germination of WYJ7 and RGG2 overexpression lines (WYJ7-OE1, WYJ7-OE2) at different concentrations of ABA. Scale bars = 1 cm. B-F, Seed germination rates of WYJ7 and RGG2 overexpression lines under 0 μmol/L (B), 1 μmol/L (C), 2 μmol/L (D), 5 μmol/L (E), 10 μmol/L (F) ABA treatment. G, Seed germination rates of WYJ7 and RGG2 overexpression lines under various ABA concentrations treatment for 84h. H, Root length of WYJ7 and RGG2 overexpression lines at different concentrations of ABA. Values represent the mean ± SD (n = 4). t-test: ns, not significant; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01. WYJ7, Wuyunjing 7. WYJ7-OE1 and WYJ7-OE2 represent the overexpression lines of RGG2 in the background of Wuyunjing 7.
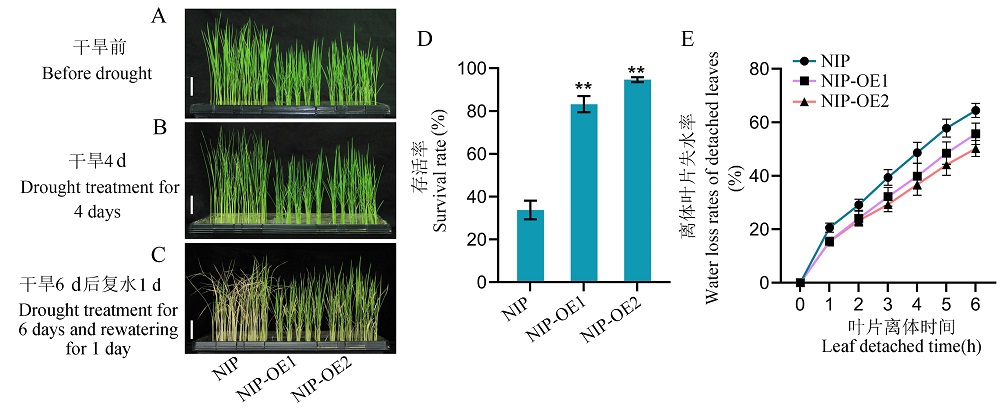
Fig. 5. Overexpression of RGG2 increases the tolerance to drought in rice A, The 3-week-old plants of NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2 grown under normal conditions. Scale bar = 5 cm. B, The plants of NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2 after drought treatment for 4 days. Scale bar = 5 cm. C, The plants of NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2 after drought treatment for 6 days and rewatering for 1 day. Scale bar = 5 cm. D, Survival rates of NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2 after drought treatment and rewatering. Values represent mean ± SD (n = 3). E, Water loss rates of detached leaves of NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2. Values represent mean ± SD (n = 10). t-test: **, P ≤ 0.01. NIP, Nipponbare. NIP-OE1 and NIP-OE2 represent the overexpression lines of RGG2 in the background of Nipponbare.

Fig. 6. RGG2 promotes the expression of ABA- and drought stress-related genes The expression levels of OsLEA3, OsRAB16A, OsNCED4, OsLIP9, OsNAC6, and OsABIL3 were detected in NIP and overexpression lines of RGG2 under drought treatment for 0, 4, and 6 days, respectively. Values represent mean ± SD (n = 3). t-test: ns, not significant; **, P ≤ 0.01. NIP, Nipponbare. NIP-OE1 and NIP-OE2 represent the overexpression lines of RGG2 in the background of Nipponbare.
| [1] | Trusov Y, Rookes J E, Chakravorty D, Armour D, Schenk P M, Botella J R. Heterotrimeric G proteins facilitate Arabidopsis resistance to necrotrophic pathogens and are involved in jasmonate signaling[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 140(1): 210-220. |
| [2] | Urano D, Chen J G, Botella J R, Jones A M. Heterotrimeric G protein signalling in the plant kingdom[J]. Open Biology, 2013, 3(3): 120186. |
| [3] | Trusov Y, Rookes J E, Tilbrook K, Chakravorty D, Mason M G, Anderson D, Chen J G, Jones A M, Botella J R. Heterotrimeric G protein gamma subunits provide functional selectivity in Gβγ dimer signaling in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(4): 1235-1250. |
| [4] | Liu J M, Ding P T, Sun T J, Nitta Y, Dong O, Huang X C, Yang W, Li X, Botella J R, Zhang Y L. Heterotrimeric G proteins serve as a converging point in plant defense signaling activated by multiple receptor-like kinases[J]. Plant Physiology, 2013, 161(4): 2146-2158. |
| [5] | Anderson D J, Botella J R. Expression analysis and subcellular localization of the Arabidopsis thaliana G-protein beta-subunit AGB1[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2007, 26(9): 1469-1480. |
| [6] | Brenya E, Trusov Y, Dietzgen R G, Botella J R. Heterotrimeric G-proteins facilitate resistance to plant pathogenic viruses in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2016, 11(8): e1212798. |
| [7] | Trusov Y, Sewelam N, Rookes J E, Kunkel M, Nowak E, Schenk P M, Botella J R. Heterotrimeric G proteins- mediated resistance to necrotrophic pathogens includes mechanisms independent of salicylic acid-, jasmonic acid/ethylene- and abscisic acid-mediated defense signaling[J]. Plant Journal, 2009, 58(1): 69-81. |
| [8] | Subramaniam G, Trusov Y, Lopez-Encina C, Hayashi S, Batley J, Botella J R. Type B heterotrimeric G protein γ-subunit regulates auxin and ABA signaling in tomato[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170(2): 1117-1134. |
| [9] | Jiang K, Frick-Cheng A, Trusov Y, Delgado-Cerezo M, Rosenthal D M, Lorek J, Panstruga R, Booker F L, Botella J R, Molina A, Ort D R, Jones A M. Dissecting arabidopsis Gβ signal transduction on the protein surface[J]. Plant Physiology, 2012, 159(3): 975-983. |
| [10] | Klopffleisch K, Phan N, Augustin K, Bayne R S, Booker K S, Botella J R, Carpita N C, Carr T, Chen J G, Cooke T R, Frick-Cheng A, Friedman E J, Fulk B, Hahn M G, Jiang K, Jorda L, Kruppe L, Liu C, Lorek J, McCann M C, Molina A, Moriyama E N, Mukhtar M S, Mudgil Y, Pattathil S, Schwarz J, Seta S, Tan M, Temp U, Trusov Y, Urano D, Welter B, Yang J, Panstruga R, Uhrig J F, Jones A M. Arabidopsis G-protein interactome reveals connections to cell wall carbohydrates and morphogenesis[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2011, 7: 532. |
| [11] | Miao J, Yang Z F, Zhang D P, Wang Y Z, Xu M B, Zhou L H, Wang J, Wu S J, Yao Y J, Du X, Gu F F, Gong Z Y, Gu M H, Liang G H, Zhou Y. Mutation of RGG2, which encodes a type B heterotrimeric G protein γ subunit, increases grain size and yield production in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(3): 650-664. |
| [12] | Gao Y, Gu H W, Leburu M, Li X H, Wang Y, Sheng J Y, Fang H M, Gu M H, Liang G H. The heterotrimeric G protein β subunit RGB1 is required for seedling formation in rice[J]. Rice, 2019, 12(1): 53. |
| [13] | Utsunomiya Y, Samejima C, Takayanagi Y, Izawa Y, Yoshida T, Sawada Y, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Iwasaki Y. Suppression of the rice heterotrimeric G protein β-subunit gene, RGB1, causes dwarfism and browning of internodes and lamina joint regions[J]. Plant Journal, 2011, 67(5): 907-916. |
| [14] | Tao Y J, Miao J, Wang J, Li W Q, Xu Y, Wang F Q, Jiang Y J, Chen Z H, Fan F J, Xu M B, Zhou Y, Liang G H, Yang J. RGG1, involved in the cytokinin regulatory pathway, controls grain size in rice[J]. Rice, 2020, 13(1): 76. |
| [15] | Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Mao H L, Lu T T, Han B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F. GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 112(6): 1164-1171. |
| [16] | Huang X Z, Qian Q, Liu Z B, Sun H Y, He S Y, Luo D, Xia G M, Chu C C, Li J Y, Fu X D. Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2009, 41(4): 494-497. |
| [17] | Zhou Y, Zhu J Y, Li Z Y, Yi C D, Liu J, Zhang H G, Tang S Z, Gu M H, Liang G H. Deletion in a quantitative trait gene qPE9-1 associated with panicle erectness improves plant architecture during rice domestication[J]. Genetics, 2009, 183(1): 315-324. |
| [18] | Urano D, Jones A M. Heterotrimeric G protein-coupled signaling in plants[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2014, 65: 365-384. |
| [19] | Pandey S. Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling in plants: conserved and novel mechanisms[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2019, 70: 213-238. |
| [20] | Wang Y J, Wang Y L, Deng D X. Multifaceted plant G protein: Interaction network, agronomic potential, and beyond[J]. Planta, 2019, 249(5): 1259-1266. |
| [21] | Mao H L, Sun S Y, Yao J L, Wang C R, Yu S B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F. Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(45): 19579-19584. |
| [22] | Sun S Y, Wang L, Mao H L, Shao L, Li X H, Xiao J H, Ouyang Y D, Zhang Q F. A G-protein pathway determines grain size in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 851. |
| [23] | Kunihiro S, Saito T, Matsuda T, Inoue M, Kuramata M, Taguchi-Shiobara F, Youssefian S, Berberich T, Kusano T. Rice DEP1, encoding a highly cysteine-rich G protein γ subunit, confers cadmium tolerance on yeast cells and plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(14): 4517-4527. |
| [24] | Zhang D P, Zhou Y, Yin J F, Yan X J, Lin S, Xu W F, Baluška F, Wang Y P, Xia Y J, Liang G H, Liang J S. Rice G-protein subunits qPE9-1 and RGB1 play distinct roles in abscisic acid responses and drought adaptation[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(20): 6371-6384. |
| [25] | Liu Q, Han R X, Wu K, Zhang J Q, Ye Y F, Wang S S, Chen J F, Pan Y J, Li Q, Xu X P, Zhou J W, Tao D Y, Wu Y J, Fu X D. G-protein βγ subunits determine grain size through interaction with MADS-domain transcription factors in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 852. |
| [26] | Wang Y Y, Lv Y, Yu H P, Hu P, Wen Y, Wang J G, Tan Y Q, Wu H, Zhu L X, Wu K X, Chai B Z, Liu J L, Zeng D L, Zhang G H, Zhu L, Gao Z Y, Dong G J, Ren D Y, Shen L, Zhang Q, Li Q, Guo L B, Xiong G S, Qian Q, Hu J. GR5 acts in the G-protein pathway to regulate grain size in rice[J]. Plant Communications, 2023: 100673. |
| [27] | Swain D M, Sahoo R K, Srivastava V K, Tripathy B C, Tuteja R, Tuteja N. Function of heterotrimeric G-protein γ subunit RGG1 in providing salinity stress tolerance in rice by elevating detoxification of ROS[J]. Planta, 2017, 245(2): 367-383. |
| [28] | Yadav D K, Islam S M, Tuteja N. Rice heterotrimeric G-protein gamma subunits (RGG1 and RGG2) are differentially regulated under abiotic stress[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2012, 7(7): 733-740. |
| [29] | Kan Y, Mu X R, Zhang H, Gao J, Shan J X, Ye W W, Lin H X. TT2 controls rice thermotolerance through SCT1-dependent alteration of wax biosynthesis[J]. Nature Plants, 2022, 8(1): 53-67. |
| [30] | Zhang H L, Yu F F, Xie P, Sun S Y, Qiao X H, Tang S Y, Chen C X, Yang S, Mei C, Yang D K, Wu Y R, Xia R, Li X, Lu J, Liu Y X, Xie X W, Ma D M, Xu X, Liang Z W, Feng Z H, Huang X H, Yu H, Liu G F, Wang Y C, Li J Y, Zhang Q F, Chen C, Ouyang Y D, Xie Q. A Gγ protein regulates alkaline sensitivity in crops[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6638): eade8416. |
| [31] | Golldack D, Lüking I, Yang O. Plant tolerance to drought and salinity: Stress regulating transcription factors and their functional significance in the cellular transcriptional network[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2011, 30(8): 1383-1391. |
| [32] | Ferrero-Serrano Á, Assmann S M. The α-subunit of the rice heterotrimeric G protein, RGA1, regulates drought tolerance during the vegetative phase in the dwarf rice mutant d1[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(11): 3433-3443. |
| [33] | Jangam A P, Pathak R R, Raghuram N. Microarray analysis of rice d1 (RGA1) mutant reveals the potential role of G-protein alpha subunit in regulating multiple abiotic stresses such as drought, salinity, heat, and cold[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 11. |
| [34] | Swain D M, Sahoo R K, Chandan R K, Ghosh S, Kumar R, Jha G, Tuteja N. Concurrent overexpression of rice G-protein β and γ subunits provide enhanced tolerance to sheath blight disease and abiotic stress in rice[J]. Planta, 2019, 250(5): 1505-1520. |
| [35] | Suharsono U, Fujisawa Y, Kawasaki T, Iwasaki Y, Satoh H, Shimamoto K. The heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunit acts upstream of the small GTPase Rac in disease resistance of rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(20): 13307-13312. |
| [36] | Komatsu S, Yang G, Hayashi N, Kaku H, Umemura K, Iwasaki Y. Alterations by a defect in a rice G protein α subunit in probenazole and pathogen-induced responses[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 2004, 27(7): 947-957. |
| [37] | Yang W S, Wu K, Wang B, Liu H H, Guo S Y, Guo X Y, Luo W, Sun S Y, Ouyang Y D, Fu X D, Chong K, Zhang Q F, Xu Y Y. The RING E3 ligase CLG1 targets GS3 for degradation via the endosome pathway to determine grain size in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(10): 1699-1713. |
| [38] | Xu D B, Chen M, Ma Y N, Xu Z S, Li L C, Chen Y F, Ma Y Z. A G-protein β subunit, AGB1, negatively regulates the ABA response and drought tolerance by down-regulating AtMPK6-related pathway in Arabidopsis[J]. PloS One, 2015, 10(1): e0116385. |
| [1] |
WANG Yichen, ZHU Benshun, ZHOU Lei, ZHU Jun, YANG Zhongnan.
Sterility Mechanism of Photoperiod/Thermo-sensitive Genic Male Sterile Lines and Development and Prospects of Two-line Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 463-474. |
| [2] |
XU Yongqiang XU Jun, FENG Baohua, XIAO Jingjing, WANG Danying, ZENG Yuxiang, FU Guanfu.
Research Progress of Pollen Tube Growth in Pistil of Rice and Its Response to Abiotic stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 495-506. |
| [3] |
HE Yong, LIU Yaowei, XIONG Xiang, ZHU Danchen, WANG Aiqun, MA Lana, WANG Tingbao, ZHANG Jian, LI Jianxiong, TIAN Zhihong.
Creation of Rice Grain Size Mutants by Editing OsOFP30 via CRISPR/Cas9 System [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [4] |
LÜ Yang, LIU Congcong, YANG Longbo, CAO Xinglan, WANG Yueying, TONG Yi, Mohamed Hazman, QIAN Qian, SHANG Lianguang, GUO Longbiao.
Identification of Candidate Genes for Rice Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 516-524. |
| [5] |
YANG Hao, HUANG Yanyan, WANG Jian, YI Chunlin, SHI Jun, TAN Chutian, REN Wenrui, WANG Wenming.
Development and Application of Specific Molecular Markers for Eight Rice Blast Resistance Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 525-534. |
| [6] |
JIANG Peng, ZHANG Lin, ZHOU Xingbing, GUO Xiaoyi, ZHU Yongchuan, LIU Mao, GUO Chanchun, XIONG Hong, XU Fuxian.
Yield Formation Characteristics of Ratooning Hybrid Rice Under Simplified Cultivation Practices in Winter Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [7] |
YANG Mingyu, CHEN Zhicheng, PAN Meiqing, ZHANG Bianhong, PAN Ruixin, YOU Lindong, CHEN Xiaoyan, TANG Lina, HUANG Jinwen.
Effects of Nitrogen Reduction Combined with Biochar Application on Stem and Sheath Assimilate Translocation and Yield Formation in Rice Under Tobacco-rice Rotation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 555-566. |
| [8] |
XIONG Jiahuan, ZHANG Yikai, XIANG Jing, CHEN Huizhe, XU Yicheng, WANG Yaliang, WANG Zhigang, YAO Jian, ZHANG Yuping .
Effect of Biochar-based Fertilizer Application on Rice Yield and Nitrogen Utilization in Film- mulched PaddyFields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [9] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [10] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [11] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [12] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [13] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [14] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [15] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||