
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 290-302.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230910
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
WEI Qianqian1, WANG Yulei2, KONG Haimin2, XU Qingshan1, YAN Yulian1, PAN Lin1, CHI Chunxin1, KONG Yali1, TIAN Wenhao1, ZHU Lianfeng1, CAO Xiaochuang1, ZHANG Junhua1,*( ), ZHU Chunqun1,*(
), ZHU Chunqun1,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-20
Revised:2023-11-22
Online:2024-05-10
Published:2024-05-13
Contact:
*email:zhangjunhua@caas.cn;
zhuchunquan@caas.cn
魏倩倩1, 汪玉磊2, 孔海民2, 徐青山1, 颜玉莲1, 潘林1, 迟春欣1, 孔亚丽1, 田文昊1, 朱练峰1, 曹小闯1, 张均华1,*( ), 朱春权1,*(
), 朱春权1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
*email:zhangjunhua@caas.cn;
zhuchunquan@caas.cn
基金资助:WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302.
魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230910
| 基因Gene | 序列Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| OsHistone-R | AACCGCAAAATCCAAAGAACG |
| OsHistone-F | GGTCAACTTGTTGATTCCCCTCT |
| OsALS1-F | GGTCGTCAGTCTCTGCCTTCTCO |
| OsALS1-R | CCTCCCCATCATTTTCATTTGT |
| OsSTAR1-F | TCGCATTGGCTCGCACCCT |
| OsSTAR1-R | TCGTCTTCTTCAGCCGCACGAT |
| OsSTAR2-F | ACCTCTTCATGGTCACCGTCG |
| OsSTAR2-R | CCTCAGCTTCTTCATCGTCACC |
Table 1. Primers selected for this study and their sequences
| 基因Gene | 序列Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| OsHistone-R | AACCGCAAAATCCAAAGAACG |
| OsHistone-F | GGTCAACTTGTTGATTCCCCTCT |
| OsALS1-F | GGTCGTCAGTCTCTGCCTTCTCO |
| OsALS1-R | CCTCCCCATCATTTTCATTTGT |
| OsSTAR1-F | TCGCATTGGCTCGCACCCT |
| OsSTAR1-R | TCGTCTTCTTCAGCCGCACGAT |
| OsSTAR2-F | ACCTCTTCATGGTCACCGTCG |
| OsSTAR2-R | CCTCAGCTTCTTCATCGTCACC |

Fig. 1. Changes of H2S content in rice under different treatments Different letters in the figure mean significant difference in the results by the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the values are mean ± standard deviation (n=3). TS, Tillering stage; HS, Full heading stage; MS, Mature stage. CK, 0.12 g/kg KCl; CK+S, KCl was replaced by 0.12 g/kg K2SO4;CK+NaHS, 0.12 g/kg KCl; 10 mL 10 μmol/L NaHS per week, Al, 2.5 g/kg AlCl3 was mixed with soil; 0.12 g/kg KCl, Al+S: 2.5 g/kg AlCl3 was mixed with soil; KCl was replaced by 0.12 g/kg K2SO4; Al+NaHS, 2.5 g/kg AlCl3 + 0.12 g/kg KCl(mixed with soil); 10 mL 10 μmol/L NaHS was applied per week. The same below.
| 处理 Treatment | 根总长 Total root length(cm) | 根平均直径 Average root diameter(mm) | 根总面积 Total root area(cm²) | 根总体积 Total volume of roots(cm3) | 根尖计数 Total root tip counts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5326.61±67.90 b | 1.48±0.16 a | 1779.40±80.11 b | 49.37±7.015 b | 33449±412 ab |
| CK+S | 5363.48±7.31 b | 1.37±0.16 ab | 1775.80±81.29 b | 53.21±3.95 b | 29847±603 b |
| CK+NaHS | 5373.04±79.76 b | 1.30±0.04 abc | 1526.82±93.32 c | 43.98±3.56 b | 30219±175 b |
| Al | 3356.06±105.96 d | 1.06±0.03 c | 1052.38±7.75 d | 27.03±7.10 c | 20640±448 c |
| Al+S | 6107.49±21.07 a | 1.17±0.15 bc | 2480.62±165.94 a | 71.50±7.90 a | 35210±4190 a |
| Al+NaHS | 3559.97±139.96 c | 1.43±0.06 ab | 1779.40±80.11 b | 45.27±3.82 b | 23117±881 c |
Table 2. Effects of S fertilizer application on rice root growth
| 处理 Treatment | 根总长 Total root length(cm) | 根平均直径 Average root diameter(mm) | 根总面积 Total root area(cm²) | 根总体积 Total volume of roots(cm3) | 根尖计数 Total root tip counts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5326.61±67.90 b | 1.48±0.16 a | 1779.40±80.11 b | 49.37±7.015 b | 33449±412 ab |
| CK+S | 5363.48±7.31 b | 1.37±0.16 ab | 1775.80±81.29 b | 53.21±3.95 b | 29847±603 b |
| CK+NaHS | 5373.04±79.76 b | 1.30±0.04 abc | 1526.82±93.32 c | 43.98±3.56 b | 30219±175 b |
| Al | 3356.06±105.96 d | 1.06±0.03 c | 1052.38±7.75 d | 27.03±7.10 c | 20640±448 c |
| Al+S | 6107.49±21.07 a | 1.17±0.15 bc | 2480.62±165.94 a | 71.50±7.90 a | 35210±4190 a |
| Al+NaHS | 3559.97±139.96 c | 1.43±0.06 ab | 1779.40±80.11 b | 45.27±3.82 b | 23117±881 c |
| 处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Pn(µmol·m−2s−1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci(mmol·mol−1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr(μmol·m−2s−1) | 气孔导度 Gs(μmol·m−2s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 13.51±0.30 a | 325.08±3.55 ab | 9.80±0.42 a | 384.64±21.84 a |
| CK+S | 13.19±0.87 a | 315.18±5.36 bc | 9.21±0.70 a | 361.63±14.37 b |
| CK+NaHS | 12.98±1.00 a | 313.5±0.02 bc | 9.50±0.53 a | 355.15±6.50 b |
| Al | 6.66±0.13 d | 284.75±7.54 c | 3.64±0.31 d | 223.69±2.11 d |
| Al+S | 8.44±0.05 c | 304.69±3.24 b | 4.94±0.63 c | 251.93±10.34 c |
| Al+NaHS | 12.51±0.06 a | 334.13±6.60 a | 6.73±1.06 b | 356.34±3.11 b |
Table 3. Effects of S fertilizer application on photosynthetic indexes of rice
| 处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Pn(µmol·m−2s−1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci(mmol·mol−1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr(μmol·m−2s−1) | 气孔导度 Gs(μmol·m−2s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 13.51±0.30 a | 325.08±3.55 ab | 9.80±0.42 a | 384.64±21.84 a |
| CK+S | 13.19±0.87 a | 315.18±5.36 bc | 9.21±0.70 a | 361.63±14.37 b |
| CK+NaHS | 12.98±1.00 a | 313.5±0.02 bc | 9.50±0.53 a | 355.15±6.50 b |
| Al | 6.66±0.13 d | 284.75±7.54 c | 3.64±0.31 d | 223.69±2.11 d |
| Al+S | 8.44±0.05 c | 304.69±3.24 b | 4.94±0.63 c | 251.93±10.34 c |
| Al+NaHS | 12.51±0.06 a | 334.13±6.60 a | 6.73±1.06 b | 356.34±3.11 b |
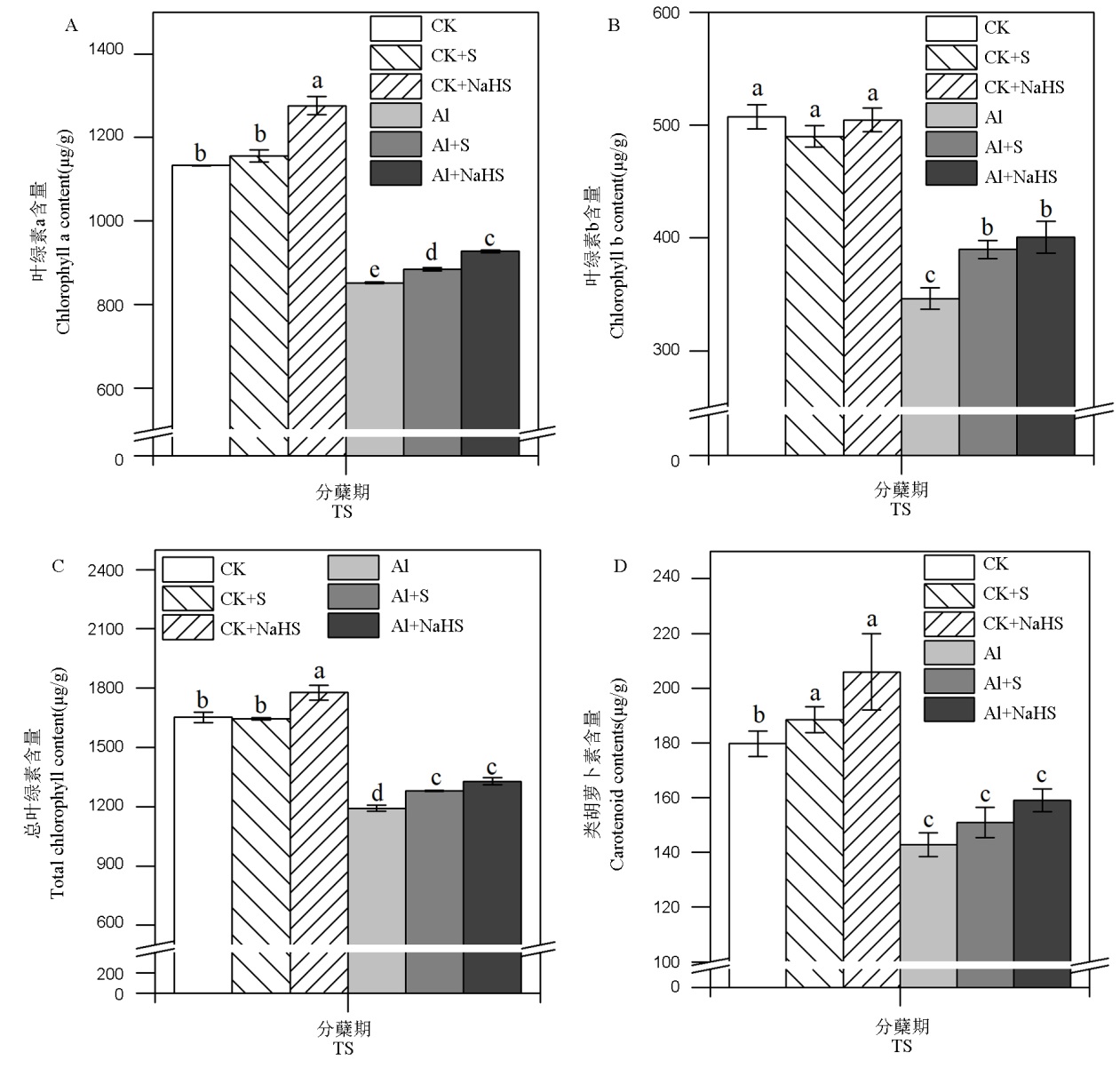
Fig. 2. Effects of S fertilizer application on photosynthetic pigment contents in rice Different letters in the figure mean significant difference in the results by the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the values are mean ± standard deviation (n=3). TS, Tillering stage.
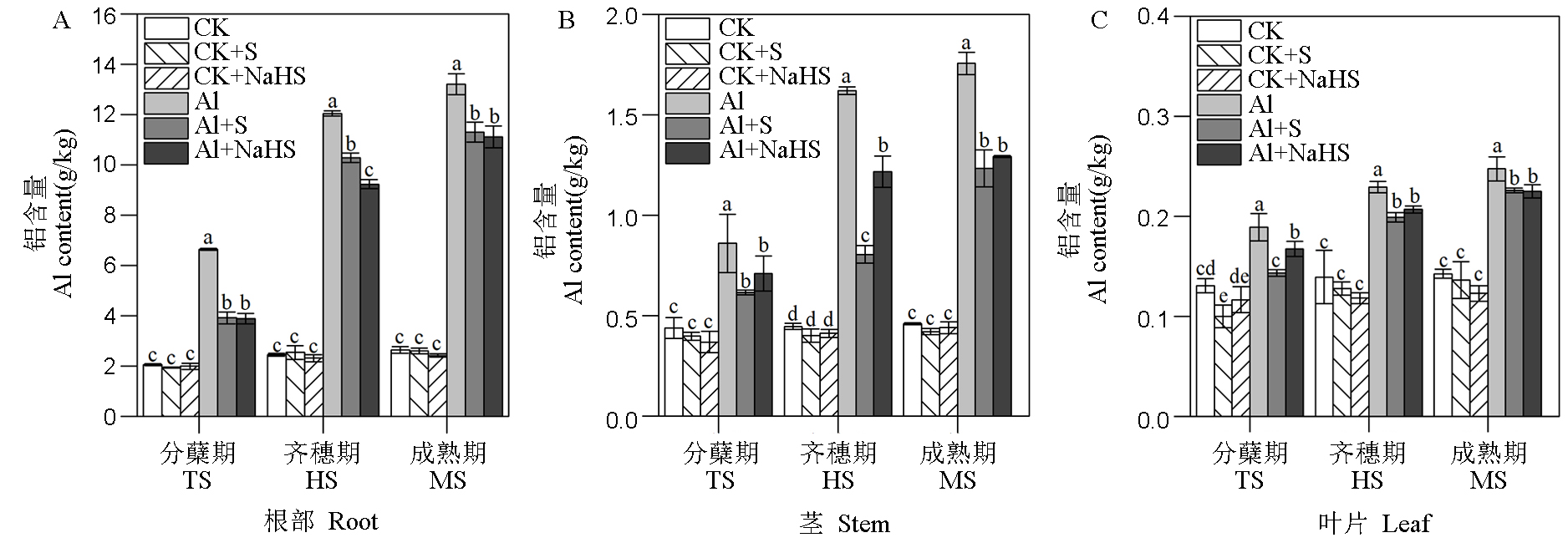
Fig. 3. Effects of S fertilizer application on Al contents in roots, stems and leaves of rice at different growth stages Different letters in the figure mean significant difference in the results by the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the values are mean ± standard deviation (n=3). TS, Tillering stage; HS, Full heading stage; MS, Mature stage.
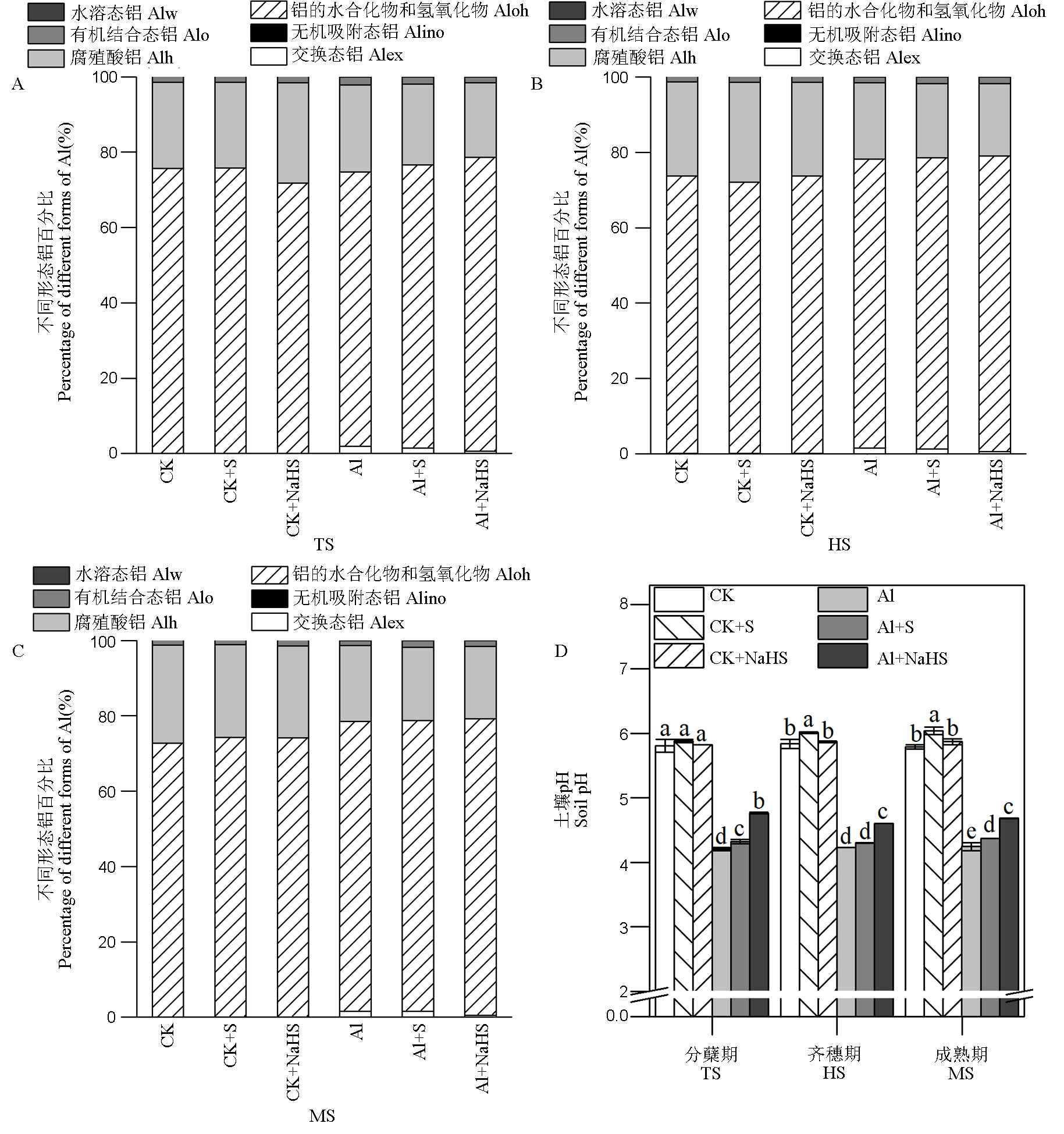
Fig. 4. Effects of S application on the changes of Al form and pH in rhizosphere soil Different letters in the figure mean significant difference in the results by the analysis of variance (p<0.05), and the values are mean ± standard deviation (n=3). TS, Tillering stage, HS, Full heading stage, MS, Mature stage. Alw,Water soluble aluminum; Alo, Organic combined aluminum; Alh, Humic acid aluminum; Aloh,Aluminum of hydrous oxide and hydroxide; Alino, Inorganic adsorption aluminum; Alex, Exchangeable aluminum.
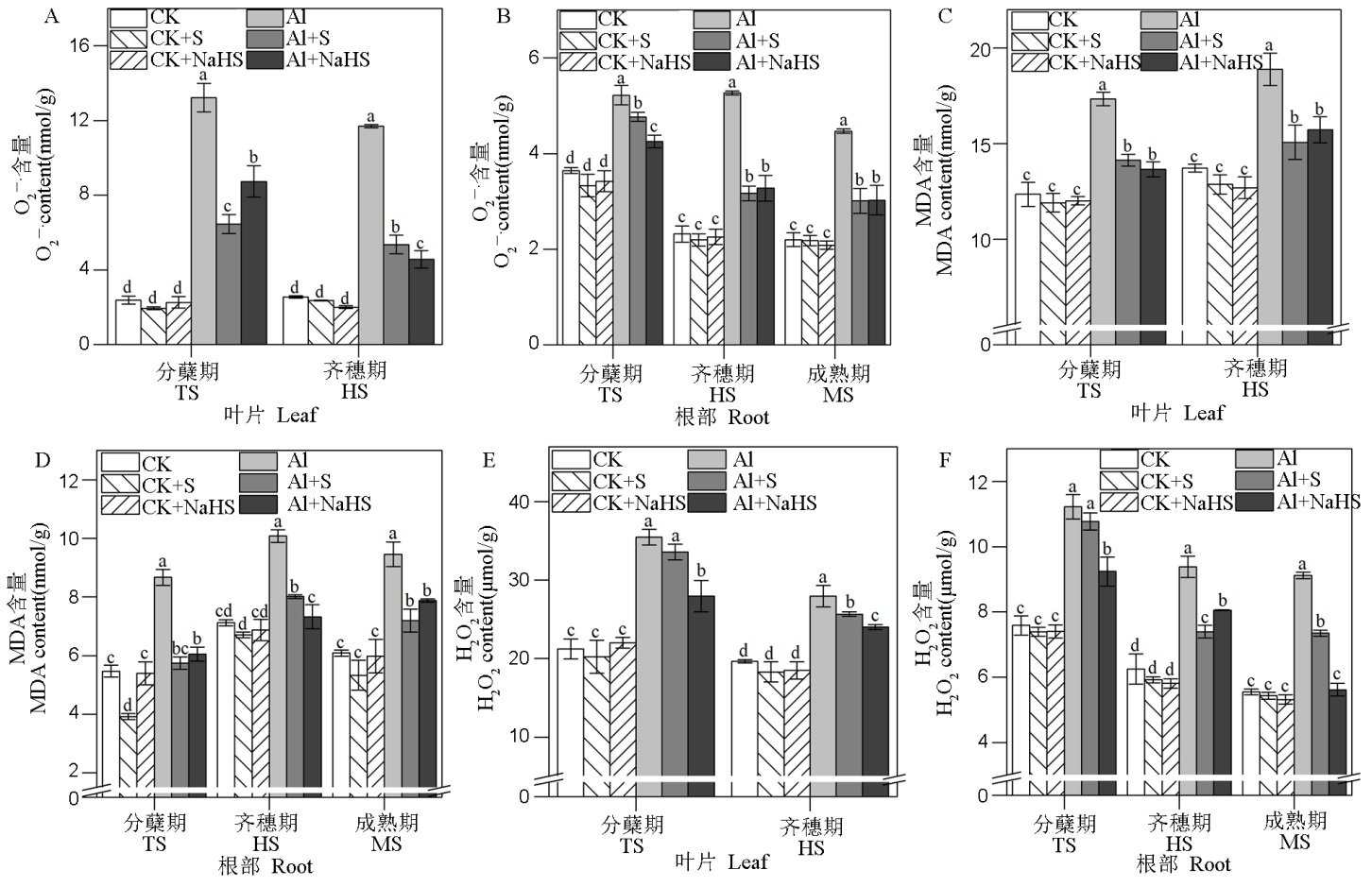
Fig. 5. Effects of S fertilizer application on contents of O2−·, MDA and H2O2 in roots and leaves of rice at different growth stages Different letters in the figure indicate significant difference in the results by the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the values are mean ± standard deviation (n=3). TS, Tillering stage; HS, Full heading stage; MS, Mature stage.
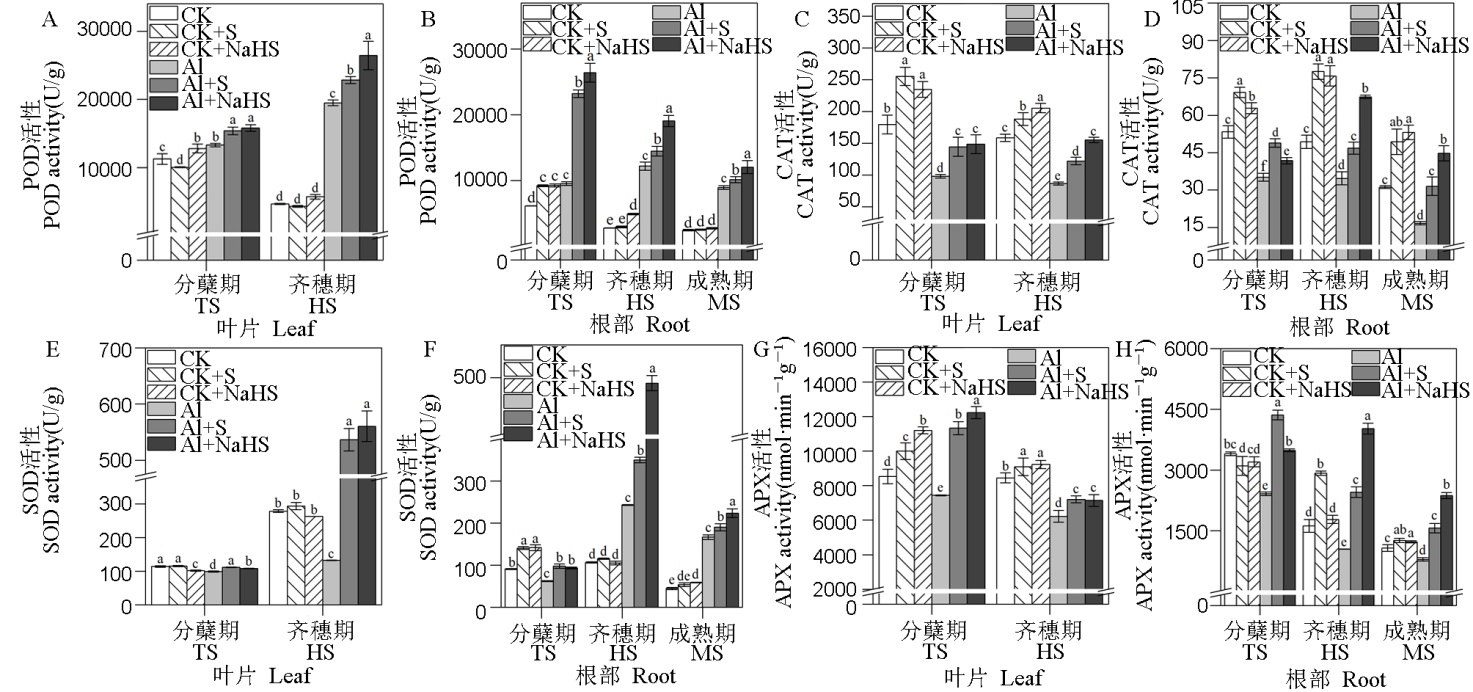
Fig. 6. Effects of S fertilizer on the activities of antioxidant enzymes in root and leaf of rice at different growth stages Different letters in the figure indicate significant difference in the results by the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the values are mean ± standard deviation (n=3). TS, Tillering stage, HS, Full heading stage, MS, Mature stage.
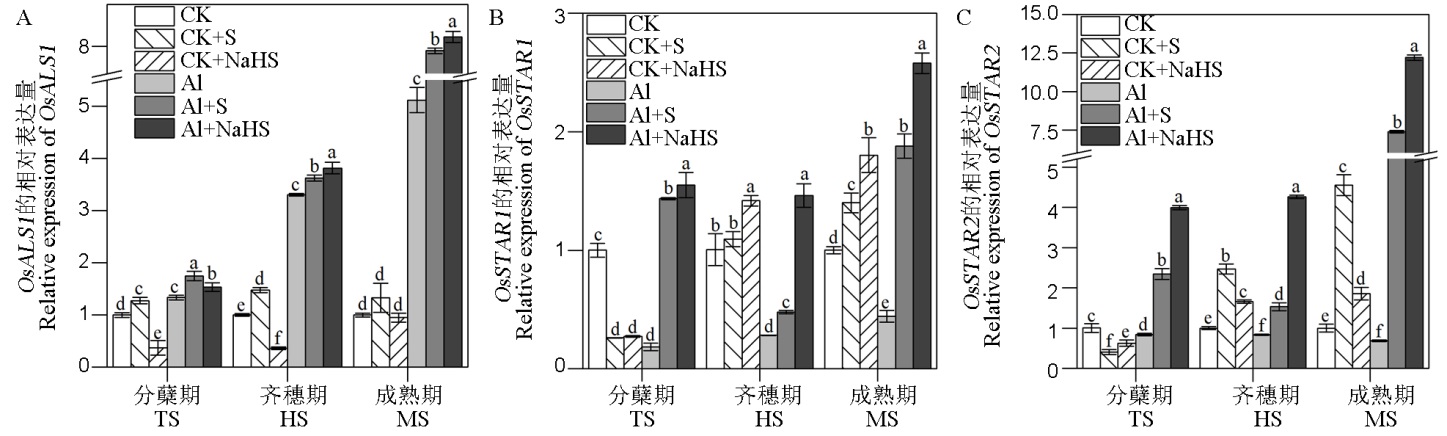
Fig. 7. Effects of exogenous application of S fertilizer on the relative expression levels of OsALS1, OsSTAR1 and OsSTAR2 in rice at different growth stages Different letters indicate significant difference by the analysis of variance (P<0.05), and the values are mean ± standard deviation (n=3). TS, Tillering stage; HS, Full heading stage; MS, Mature stage.
| [1] | Kochian L V, Hoekenga O A, Piñeros M A. How do crop plants tolerate acid soils: Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance and phosphorous efficiency[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2004, 55: 459-493. |
| [2] | Zhu C Q, Zhang J H, Sun LM, Zhu L F, Abliz B, Hu W J, Zhong C, Bai Z G, Sajid H, Cao X C, Jin Q Y. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity via decreasing apoplast and symplast Al contents in rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 294 |
| [3] | Yan L, Riaz M, Liu J Y, Min Y, Jiang C C. The aluminum tolerance and detoxification mechanisms in plants: Recent advances and prospects[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 6: 1491-1527. |
| [4] | Ma J F, Hiradate S, Matsumoto H. High aluminum resistance in buckwheat: Ⅱ. Oxalic acid detoxifies aluminum internally[J]. Plant Physiology, 1998, 117: 753-759. |
| [5] | Wang W, Zhao X Q, Chen R F, Dong X Y, Lan P, Ma J F, Shen R F. Altered cell wall properties are responsible for ammonium-reduced aluminium accumulation in rice roots[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 2015, 38: 1382-1390. |
| [6] | Huang C F, Yamaji N, Chen Z, Ma J F. A tonoplast-localized half-size ABC transporter is required for internal detoxification of aluminum in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2011, 69(5): 857-867. |
| [7] | 魏倩倩, 朱春权, 黄晶, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 孔亚丽, 刘佳, 金千瑜, 项兴佳, 张均华. 硫化氢调控植物重金属胁迫耐性机制研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2022, 58(8): 1412-1422. |
| Wei Q Q, Zhu C Q, Huang J, Cao X C, Zhu L F, Kong Y L, Liu J, Jin Q Y, Xiang X J, Zhang J H. Advances in the mechanism of hydrogen sulfide regulating tolerance for heavy metal stress in plants[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2022, 58(8): 1412-1422. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 裴雁曦. 植物中的气体信号分子硫化氢: 无香而立, 其臭如兰[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2016, 32(7): 721-733. |
| Pei Y X. Gasotransmitter hydrogen sulfide in plants: Stinking to high heaven, but refreshing to fine life[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2016, 32(7): 721-733. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Wang Y, Li L, Cui W, Xu S, Shen W B, Wang R. Hydrogen sulfide enhances alfalfa tolerance against salinity during seed germination by nitric oxide pathway[J]. Plant and Soil, 2012, 351(1-2): 107-119. |
| [10] | Zhang H, Tang J, Liu X, Wang Y, Yu W, Peng W Y, Fang F, Ma D F, Wei Z J, Hu L Y. Hydrogen Sulfide Promotes Root Organogenesis inIpomoea batatas, Salix matsudana andGlycine max[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2009, 51(12): 1086-1094. |
| [11] | Li Y J, Shi Z Q, Gan L J, Chen J, Li Y J, Shi A Q, Gan L J, Chen J. Hydrogen sulfide is a novel gasotransmitter with pivotal role in regulating lateral root formation in plants[J]. Plant Signaling Behavior, 2014(9): e29127. |
| [12] | Chen J, Wu F H, Wang W H, Zheng C J, Lin G H, Dong X J, He J X, Pei Z M, Zheng H L. Hydrogen sulphide enhances photosynthesis through promoting chloroplast biogenesis, photosynthetic enzyme expression, and thiol redox modification in Spinacia oleracea seedlings[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(13): 4481-4493. |
| [13] | Wang H H, Ji F, Zhang Y Y, Hou J J, Liu W W, Huang J J, Liang W H. Interactions between hydrogen sulphide and nitric oxide regulate two soybean citrate transporters during the alleviation of aluminium toxicity[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 2019, 42(8): 2340-2356. |
| [14] | Kushwaha B K, Singh V P. Mitigation of chromium (VI) toxicity by additional sulfur in some vegetable crops involves glutathione and hydrogen sulfide[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2020, 155: 952-964. |
| [15] | 张艳萍, 宗良纲, 史艳芙. 茶园土壤pH变化对土壤中铝特性的影响[J]. 土壤, 2019, 51(4): 746-751. |
| Zhang Y P, Zong L G, Shi Y F. Effects of soil pH on characteristics of soil Al in tea plantations[J]. Soils, 2019, 51(4): 746-751. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Asgher M, Khan M I, Anjum N A, Khan N A. Minimising toxicity of cadmium in plants role of plant growth regulators[J]. Protoplasma, 2015, 252(2): 399-413. |
| [17] | Jia H, Wang X F, Dou Y H, Liu D, Si W T, Fang H, Zhao C, Chen S L, Xi J J, Li L S. Hydrogen sulfide-cysteine cycle system enhances cadmium tolerance through alleviating cadmium induced oxidative stress and ion toxicity in Arabidopsis roots[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 397025. |
| [18] | Chen Z J, Liu C Y, Cao B L, Xu K. A hydrogen sulfde application can alleviate the toxic effects of cadmium on ginger (Zingiber ofcinale Roscoe)[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 22(1): 68422-68431. |
| [19] | Zhang C F, Jiang D, Liu F L, Dai T B, Liu W C, Jing Q, Cao W X. Exogenous nitric oxide improves seed germination in wheat against mitochondrial oxidative damage induced by high salinity[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2009, 67: 222-227. |
| [20] | Yan L, Riaz M, Du C Q, Liu Y L, Zeng Y, Jiang C C. Ameliorative role of boron to toxicity of aluminum in trifoliate orange roots[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 179(15): 212-221. |
| [21] | Zhu C Q, Wei Q Q, Hu W J, Kong Y L, Xiang X J, Zhang H, Cao X C, Zhu L F, Liu J, Tian W H, Jin Q Y, Zhang J H. Unearthing the alleviatory mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide in aluminum toxicity in rice[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2022, 182: 133-144. |
| [22] | 周小华, 谷照虎, 徐慧妮, 陈丽梅, 李昆志. 外源抗坏血酸AsA对铝胁迫下水稻光合特性的影响[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2015, 36: 73-78. |
| Zhou X H, Gu Z H, Xu H N, Chen L M, Li K Z. The effects of exogenous ascorbic acid on photosynthetic characteristics in Oryza sativa L. under aluminum stress[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition, 2015, 36: 73-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 李晓科, 武玉珍, 张谨华, 张义贤. H2S 对 Cd 胁迫下大麦幼苗逆境生理及光合作用的影响[J]. 福建农业学报, 2020, 35(10): 1131-1137. |
| Li X K, Wu Y Z, Zhang J H, Zhang Y X. Effects of hydrogen sulfide on physiology and photosynthesis of barley seedlings under Cd-stress[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 35(10): 1131-1137. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 赵晶, 冯文强, 秦鱼生, 喻华, 廖明兰, 甲卡拉铁, 程瑜, 王昌全, 涂仕华. 不同氮磷钾肥对土壤pH和镉有效性的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2017, 5(4): 17-19. |
| Zhao J, Feng W Q, Qin Y S, Yu H, Liao M L, Jia Ka L T, Cheng Y, Wang C Q, Tu S H. Effects of application of nitrogen phosphorus and potassium fertilizers on soil pH and cadmium availability[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2017, 5(4): 17-19. | |
| [25] | 宋晓培. 不同硫酸钾用量对土壤及烤烟矿质元素积累的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院: 8-9. |
| Song X P. Effects of different potassium sulfate levels on the soil and mineral accumulation of flue-cured tobacco[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science, 8-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 陈苏, 孙丽娜, 孙铁珩, 晁雷, 杨春璐. 钾肥对镉的植物有效性的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2007(1): 182-188. |
| Chen S, Sun L N, Sun T H, Zhao L, Yang C L. Influence of potassium fertilizer on the phytoavailability of cadmium[J]. Environmental Science, 2007(1): 182-188. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Clarkson D T. Interactions between aluminium and phosphorus on root surfaces and cell wall material[J]. Plant and Soil, 1967, 27(3): 347-356. |
| [28] | Shi H T, Ye T T, Chan Z L. Nitric oxide-activated hydrogen sulfide is essential for cadmium stress response in bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon (L). Pers.)[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 74: 99-107. |
| [29] | Claudio I B, Zed R, Miren A. Molecular and physiological strategies to increase aluminum resistance in plants[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2012, 39(3): 2069-2079. |
| [30] | Larsen P B, Cancel J, Rounds M, Ochoa V. Arabidopsis ALS1 encodes a root tip and stele localized half type ABC transporter require for root growth in an aluminum toxic environment[J]. Planta, 2007, 225(6): 1447-1458. |
| [31] | Ma H X, Bai G H, Carver B F, Zhou L L. Molecular mapping of a quantitative trait locus for aluminum tolerance in wheat cultivar Atlas 66[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2005, 112(1): 51-57. |
| [1] |
WANG Yichen, ZHU Benshun, ZHOU Lei, ZHU Jun, YANG Zhongnan.
Sterility Mechanism of Photoperiod/Thermo-sensitive Genic Male Sterile Lines and Development and Prospects of Two-line Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 463-474. |
| [2] |
XU Yongqiang XU Jun, FENG Baohua, XIAO Jingjing, WANG Danying, ZENG Yuxiang, FU Guanfu.
Research Progress of Pollen Tube Growth in Pistil of Rice and Its Response to Abiotic stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 495-506. |
| [3] |
HE Yong, LIU Yaowei, XIONG Xiang, ZHU Danchen, WANG Aiqun, MA Lana, WANG Tingbao, ZHANG Jian, LI Jianxiong, TIAN Zhihong.
Creation of Rice Grain Size Mutants by Editing OsOFP30 via CRISPR/Cas9 System [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [4] |
LÜ Yang, LIU Congcong, YANG Longbo, CAO Xinglan, WANG Yueying, TONG Yi, Mohamed Hazman, QIAN Qian, SHANG Lianguang, GUO Longbiao.
Identification of Candidate Genes for Rice Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 516-524. |
| [5] |
YANG Hao, HUANG Yanyan, WANG Jian, YI Chunlin, SHI Jun, TAN Chutian, REN Wenrui, WANG Wenming.
Development and Application of Specific Molecular Markers for Eight Rice Blast Resistance Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 525-534. |
| [6] |
JIANG Peng, ZHANG Lin, ZHOU Xingbing, GUO Xiaoyi, ZHU Yongchuan, LIU Mao, GUO Chanchun, XIONG Hong, XU Fuxian.
Yield Formation Characteristics of Ratooning Hybrid Rice Under Simplified Cultivation Practices in Winter Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [7] |
YANG Mingyu, CHEN Zhicheng, PAN Meiqing, ZHANG Bianhong, PAN Ruixin, YOU Lindong, CHEN Xiaoyan, TANG Lina, HUANG Jinwen.
Effects of Nitrogen Reduction Combined with Biochar Application on Stem and Sheath Assimilate Translocation and Yield Formation in Rice Under Tobacco-rice Rotation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 555-566. |
| [8] |
XIONG Jiahuan, ZHANG Yikai, XIANG Jing, CHEN Huizhe, XU Yicheng, WANG Yaliang, WANG Zhigang, YAO Jian, ZHANG Yuping .
Effect of Biochar-based Fertilizer Application on Rice Yield and Nitrogen Utilization in Film- mulched PaddyFields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [9] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [10] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [11] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [12] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [13] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [14] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [15] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||