
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 143-151.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.5154
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zheng-fu YANG1, Ying-xin ZHANG1, Lian-ping SUN1,2, Pei-pei ZHANG1, Dan-dan XUAN1, Ling LIU1,3, Xia HU1, Zi-he LI1, Xiao-deng ZHAN1, Wei-xun WU1, Li-yong CAO1,*( ), Shi-hua CHENG1,*(
), Shi-hua CHENG1,*( )
)
Received:2015-10-19
Revised:2015-12-11
Online:2016-03-10
Published:2016-03-10
Contact:
Li-yong CAO, Shi-hua CHENG
About author:# These authors contributed equally to this work;
杨正福1, 张迎信1, 孙廉平1,2, 张沛沛1, 轩丹丹1, 刘嶺1,3, 胡霞1, 李紫荷1, 占小登1, 吴玮勋1, 曹立勇1,*( ), 程式华1,*(
), 程式华1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
曹立勇,程式华
作者简介:# 共同第一作者;
基金资助:CLC Number:
Zheng-fu YANG, Ying-xin ZHANG, Lian-ping SUN, Pei-pei ZHANG, Dan-dan XUAN, Ling LIU, Xia HU, Zi-he LI, Xiao-deng ZHAN, Wei-xun WU, Li-yong CAO, Shi-hua CHENG. Identification and Gene Mapping of Male Sterile Mutant gamyb5 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(2): 143-151.
杨正福, 张迎信, 孙廉平, 张沛沛, 轩丹丹, 刘嶺, 胡霞, 李紫荷, 占小登, 吴玮勋, 曹立勇, 程式华. 水稻雄性不育突变体gamyb5的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(2): 143-151.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.5154
| 引物名称 Primer name | 上游引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 下游引物 Reverse primer (5'-3') | 实验目的 Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD0114 | GCTTGTGGCAATTGGG | CGCCTGATGGATGTCG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-26 | GATCATACCATCATCAGAAGCAGT | CAAGCAGCCCACATCACAGC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-28 | TCTCGCTCCTCTTCGCCCAAAC | ACCCGCACCAGTACGTGACCC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-29 | GGCAGCAGCAATCACAACAC | TCGGCACTTTCTTTACTCAACT | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-31 | CAGCCAGGCACCGCAGCAAA | AAGAAAGGCAGAGCAAGAAGG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-32 | GCACGCTTCTCGCTACGCTAT | GCTCCAGGAACACCACCAACTC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-38 | TGGGTGCGAGGTTTCTGTGA | AATGAATGCGTGTTTCCTGT | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| InDel15 | CAACCCCTCCAAATACCTGA | ACCGTGTTCATGCCTTTCAC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| GAMYB5 | ACTGGAGCACTGCTGATCTTC | GCACATCTTCTCAGTTGCCAG | gamyb5位点检测gamyb5 deletion site detection |
| cDNA | CCCCTGCGAGTCCAATCTAC | ACCGGCTTATCTCCATGCAC | cDNA测序cDNA sequencing |
Table 1 Makers used for fine mapping and sequencing.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 上游引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 下游引物 Reverse primer (5'-3') | 实验目的 Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD0114 | GCTTGTGGCAATTGGG | CGCCTGATGGATGTCG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-26 | GATCATACCATCATCAGAAGCAGT | CAAGCAGCCCACATCACAGC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-28 | TCTCGCTCCTCTTCGCCCAAAC | ACCCGCACCAGTACGTGACCC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-29 | GGCAGCAGCAATCACAACAC | TCGGCACTTTCTTTACTCAACT | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-31 | CAGCCAGGCACCGCAGCAAA | AAGAAAGGCAGAGCAAGAAGG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-32 | GCACGCTTCTCGCTACGCTAT | GCTCCAGGAACACCACCAACTC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-38 | TGGGTGCGAGGTTTCTGTGA | AATGAATGCGTGTTTCCTGT | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| InDel15 | CAACCCCTCCAAATACCTGA | ACCGTGTTCATGCCTTTCAC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| GAMYB5 | ACTGGAGCACTGCTGATCTTC | GCACATCTTCTCAGTTGCCAG | gamyb5位点检测gamyb5 deletion site detection |
| cDNA | CCCCTGCGAGTCCAATCTAC | ACCGGCTTATCTCCATGCAC | cDNA测序cDNA sequencing |
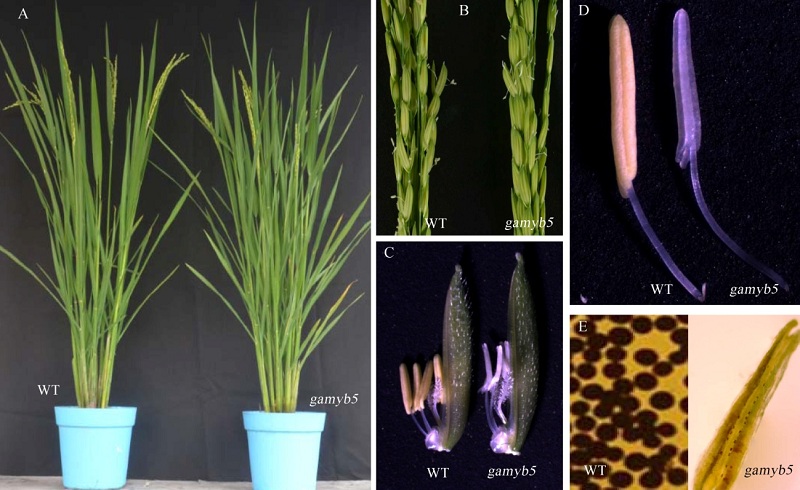

Fig. 1. Phenotypic comparison of wild type Zhonghui 8015(WT)and gamyb5 . A, Plant of Zhonghui 8015 and the gamyb5 mutant at the heading stage; B, Panicle of Zhonghui 8015 and the gamyb5 mutant; C, Spikelet of the wild type Zhonghui 8015 and gamyb5 ; D, Anther of Zhonghui 8015 and gamyb5 mutant; E, Pollen fertility of Zhonghui 8015 and gamyb5.
| 组合 Cross | Seed-setting rate of F1 /% | F2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型植株数 Number of wild type plants | 突变体植株数 Number of mutant plants | ||||
| gamyb5/02428 | 86.8 | 1895 | 642 | 0.14 | 3.84 |
| gamyb5/中恢8015 gamyb5/Zhonghui 8015 | 87.2 | 234 | 70 | 0.63 | |
| 中恢8015/02428 Zhonghui 8015/02428 | 87.6 | 960 | 0 | - | |
Table 2 Genetic analysis of the gamyb5 mutant.
| 组合 Cross | Seed-setting rate of F1 /% | F2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型植株数 Number of wild type plants | 突变体植株数 Number of mutant plants | ||||
| gamyb5/02428 | 86.8 | 1895 | 642 | 0.14 | 3.84 |
| gamyb5/中恢8015 gamyb5/Zhonghui 8015 | 87.2 | 234 | 70 | 0.63 | |
| 中恢8015/02428 Zhonghui 8015/02428 | 87.6 | 960 | 0 | - | |

Fig.2. Positional cloning of the gamyb5 mutated gene. A, Preliminary mapping of gamyb5; B, Fine mapping of gamyb5; C, Prediction of the candidate gene within the fine-mapped region; D, The structure of candidate gene LOC_Os01g0812000 and the mutation site in gamyb5 mutant (8 bases deleted).
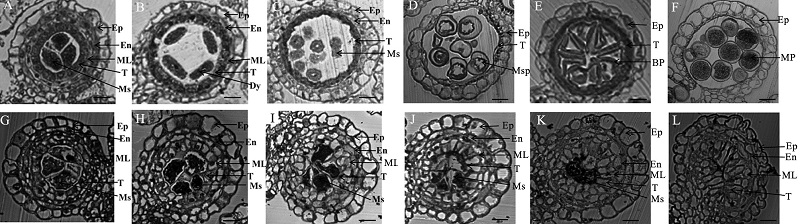
Fig. 3. Transverse section analyses of the wild type and gamyb5 anthers in various of developmental stages. A to E, Wild type; G to L, The gamyb5 mutant. A and G, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 7; B and H, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 8; C and I, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 9; D and J, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 10; E and K, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 11; F and L, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 12. Ep, Epidermis; En, Endothecium; ML, Middle layer; T, Tapetum; Ms, Microsporocyte; Dy, Dyad cell; Msp, Microspore; BP, Biceullar pollen; MP, Mature pollen. Bars = 20 μm.
| [1] | McCormick S. Male gametophyte development.Plant Cell,1993, 5: 1265-1275. |
| [2] | Scott R J, Spielman M, Dickinson H G.Stamen structure and function.Plant Cell, 2004,16(Suppl): 46-60. |
| [3] | Ma H.Molecular genetic analyses of microsporogenesis and microgametogenesis in flowering plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2005, 56: 393-434. |
| [4] | Zhang D B, Wilson Z A.Stamen specification and anther development in rice.Chin Sci Bull, 2009, 54: 2342-2353. |
| [5] | Zhang D B, Luo X, Zhu L, et al.Cytological analysis and genetic control of rice anther development.J Genet Genom, 2011, 38: 379-390. |
| [6] | Zhang D B, Yang L.Specification of tapetum and microsporocyte cells within the anther.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2014, 17C: 49-55. |
| [7] | 马西青, 方才臣, 邓联武, 等. 水稻隐性核雄性不育基因研究进展及育种应用探讨. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(5): 511-520. |
| Ma X Q, Fang C C, Deng L W, et al.Research progress and breeding application of recessive genic male sterility genes in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2012, 26(5): 511-520. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Nonomura K, Miyoshi K.The MSP1 gene is necessary to restrict the number of cells entering into male and female sporogenesis and to initiate anther wall formation in rice.Plant Cell, 2003, 15(8): 1728-1739. |
| [9] | Ken-Ichi N, Mutsuko N, Toshiyuki F, et al.The novel gene HOMOLOGOUS PAIRING ABERRATION IN RICE MEIOSIS1 of rice encodes a putative coiled-coil protein required for homologous chromosome pairing in meiosis.Plant J, 2004, 16(4): 1008-1020. |
| [10] | Nonomura K I, Nakano M, Murata K, et al.An insertional mutation in the rice PAIR2 gene, the ortholog of Arabidopsis ASY1, results in a defect in homologous chromosome pairing during meiosis.Mol Genet Genom, 2004, 271(2): 121-129. |
| [11] | Yuan W Y, Li X W, Chang Y X, et al.Mutation of the rice gene PAIR3 results in lack of bivalent formation in meiosis.Plant J, 2009, 59(2): 303-315. |
| [12] | Sandra N Ol, Elizabeth S D, Rudy D.ABA regulates apoplastic sugar transport and is a potential signal for cold-induced pollen sterility in rice.Plant Cell Physiol, 2007, 48(9): 1319-1330. |
| [13] | Ken-Ichi N, Akane M, Mutsuko N, et al.A germ cell-specific gene of the ARGONAUTE family is essential for the progression of premeiotic mitosis and meiosis during sporogenesis in rice.Plant Cell, 2007, 19(8): 2583-2594. |
| [14] | Wang C, Huang W, Ying Y H, et al.Functional characterization of the rice SPX-MFS family reveals a key role of OsSPX-MFS1 in controlling phosphate homeostasis in leaves.New Phytol, 2012, 196(1): 139-148. |
| [15] | Li L, Li Y X, Song S F.An anther development F-box (ADF) protein regulated by tapetum degeneration retardation (TDR) controls rice anther development.Planta, 2015, 241(1): 157-166. |
| [16] | Jung K H, Han M J, Lee Y S.Rice undeveloped tapetum1 is a major regulator of early tapetum development.Plant Cell, 2005, 17(10): 2705-2722. |
| [17] | Liu Z H, Bao W J.Identification of gamyb-4 and analysis of the regulatory role of GAMYB in rice anther development.J Integ Plant Biol, 2010, 52(7): 670-678. |
| [18] | Li H, Yuan Z.PERSISTENT TAPETAL CELL1 Encodes a PHD-finger protein that is required for tapetal cell death and pollen development in rice.Plant Physiol, 2011, 156(2): 615-630. |
| [19] | Li X W, Gao X Q.Rice APOPTOSIS INHIBITOR5 coupled with two DEAD-box adenosine 5'-triphosphate-dependent RNA helicases regulates tapetum degeneration.Plant Cell, 2011, 23(4): 1416-1434. |
| [20] | Jung K H, Han M J.Wax-deficient anther1 is involved in cuticle and wax production in rice anther walls and is required for pollen development.Plant Cell, 2006, 18(11): 3015-3032. |
| [21] | Shi J, Tan H X.Defective pollen wall is required for anther and microspore development in rice and encodes a fatty acyl carrier protein reductase.Plant Cell, 2011, 23(6): 2225-2246. |
| [22] | Li H, Pinot F.Cytochrome P450 family member CYP704B2 catalyzes the ω -Hydroxylation of fatty acids and is required for anther cutin biosynthesis and pollen exine formation in rice.Plant Cell, 2010, 22(1): 173-190. |
| [23] | Yang X J, Wu D. rice CYP703A3, a cytochrome P450 hydroxylase, is essential for development of anther cuticle and pollen exine.J Integ Plant Biol, 2014, 56(10): 979-994. |
| [24] | Zhu Q H, Ramm K, Shivakkumar R, et al.The ANTHER INDEHISCENCE1 gene encoding a single MYB domain protein is involved in anther development in rice.Plant Physiol, 2004, 135(3): 1514-1525. |
| [25] | 初明光, 李双成, 王世全, 等. 一个水稻雄性不育突变体的遗传分析和基因定位. 作物学报, 2009, 35(6): 1151-1155. |
| Chu G M, Li S C, Wang S Q, et al.Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of a male sterile mutant in rice.Crop J, 2004, 135(3): 1514-1525. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 卢扬江, 郑康乐. 提取水稻DNA 的一种简易方法. 中国水稻科学, 1992, 6(1): 47-48. |
| Lu Y J, Zheng K L.A simple method for isolation of rice DNA.Chin J Rice Sci, 1992, 6(1): 47-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Orjuela J, Garavito A, Bouniol M.A universal core genetic map for rice.Theor Appl Genet, 2010,120,563-572. |
| [28] | Rychlik W.Oligo primer analysis software version 7.0. 2nd ed. Molecular Biology Insights, Inc, Cascade, Co, 2008. |
| [29] | Aya K, Miyako Ueguchi-Tanaka M. Gibberellin modulates anther development in rice via the transcriptional regulation of GAMYB.Plant Cell, 2009, 21(5): 1453-1472. |
| [30] | Gocal, Sheldon G F. GAMYB-like genes, flowering and gibberellin signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 2001,127, 1682-1693. |
| [31] | Gubler F, Kalla R, Roberts J K, et al.Gibberellin-regulated expression of a MYB gene in barley aleurone cells: Evidence for Myb transactivation of a high-pI α-amylase gene promoter.Plant Cell, 1995, 7: 1879-1891. |
| [32] | Fiona J, Woodger A M, Murray F, et al.The role of GAMYB transcription factors in GA-regulated gene expression.J Plant Growth Regul, 2003, 22, 176-184. |
| [33] | Kaneko M, Inukai Y, Ueguchi-Tanaka M. loss-of-function mutations of the rice GAMYB gene impair α-amylase expression in aleurone and flower development.Plant Cell, 2004,16:1473-1487. |
| [34] | Aya K, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Kondo M, et al.Gibberellin modulates anther development in rice via the transcriptional regulation of GAMYB.Plant Cell, 2009, 21:1453-1472. |
| [35] | Wang Y, Wang Y F, Zhang D B.Identification of the rice (Oryza sativa L.) mutant msp1-4 and expression analysis of its UDT1 and GAMYB genes.J Plant Physiol Mol Biol, 2006 , 32: 527-534. |
| [36] | Morant M, Jorgensen K, Schaller H.CYP703 is an ancient cytochrome P450 in land plants catalyzing in-chain hydroxylation of lauric acid to provide building blocks for sporopollenin synthesis in pollen.Plant Cell, 2007, 19:1473-1487. |
| [37] | Dobritsa A A, Shrestha J, Morant M.CYP704B1 is a long-chain fatty acid ω-hydroxylase essential for sporopollenin synthesis in pollen of Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol, 2009, 151: 574-589. |
| [38] | Bouquin L, Pinot R, Benveniste F, et al.Cloning and functional characterization of CYP94A2, a medium chain fatty acid hydroxylase from Vicia sativa. Biochem. Biophys.Res Commun, 1999, 261: 156-162. |
| [39] | Kurdyukov S, Faust A, Trenkamp S.Genetic and biochemical evidence for involvement of HOTHEAD in the biosynthesis of long-chain alpha-omega-dicarboxylic fatty acids and formation of extracellular matrix.Planta, 2006, 224: 315-329. |
| [40] | Kandel S, Sauveplane V, Compagnon V.Characterization of a methyl jasmonate and wounding-responsive cytochrome P450 of Arabidopsis thaliana catalyzing dicarboxylic fatty acid formation in vitro.FEBS J, 2007, 274: 5116-5127. |
| [41] | Sauveplane V, Kandel S, Kastner P E.Arabidopsis thaliana CYP77A4 is the first cytochrome P450 able to catalyze the epoxidation of free fatty acids in plants.FEBS J, 2009, 276: 719-735. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||