
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 365-373.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7130
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ruicai HAN1, Ruqi SU1, Jianlin WAN2, Qizhang LONG2, Yongjun ZENG1, Xiaohua PAN1, Qinghua SHI1, Ziming WU1,*( )
)
Online:2018-07-10
Published:2018-07-10
Contact:
Ziming WU
韩瑞才1, 苏如奇1, 万建林2, 龙启樟2, 曾勇军1, 潘晓华1, 石庆华1, 吴自明1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
吴自明
基金资助:CLC Number:
Ruicai HAN, Ruqi SU, Jianlin WAN, Qizhang LONG, Yongjun ZENG, Xiaohua PAN, Qinghua SHI, Ziming WU. Protective Roles of Over-expression of OsXDH in Rice Seedlings Under High Temperature Stress[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(4): 365-373.
韩瑞才, 苏如奇, 万建林, 龙启樟, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 吴自明. 高温胁迫下黄嘌呤脱氢酶基因超表达对水稻幼苗的保护作用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 365-373.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7130
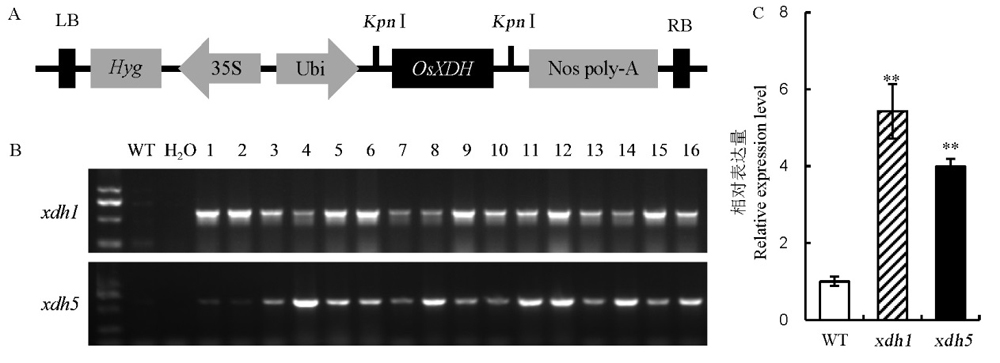
Fig. 1. Construction of OsXDH over-expression vector, PCR analysis of OsXDH gene in T2 transgenic plants and expression analysis of OsXDH in over-expressed lines. A, Structure of OsXDH over-expression vector. LB, Left border of T-DNA; Hyg, Hygromycin gene; 35S, 35S promoter of CaMV; Ubi, Promoter of ubiqutin; Kpn I, Restriction enzyme cutting site; RB, Right border of T-DNA. B, PCR identification of the T2 transgenic plants. WT, Wild type; 1–16, 16 randomly selected T2 transgenic plants. C, Relative expression level of OsXDH in transgenic plants. xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Values are shown as mean±SD (n=3). **, Significant difference at P<0.01 level by LSD.
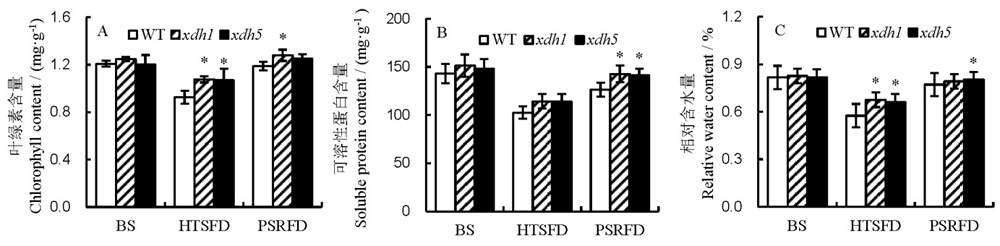
Fig. 2. Effects of high temperature stress on chlorophyll content, soluble protein content and relative water content in rice leaves. A, Chlorophyll content; B, Soluble protein content; C, Relative water content. BS, Before high temperature stress; HTSFD, High temperature stress for 5 days; PSRFD, Post-stress recovery for 5 days. WT, Wild type; xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Values are shown as mean±SD (n=3). *, Significant difference at P<0.05 level by LSD.
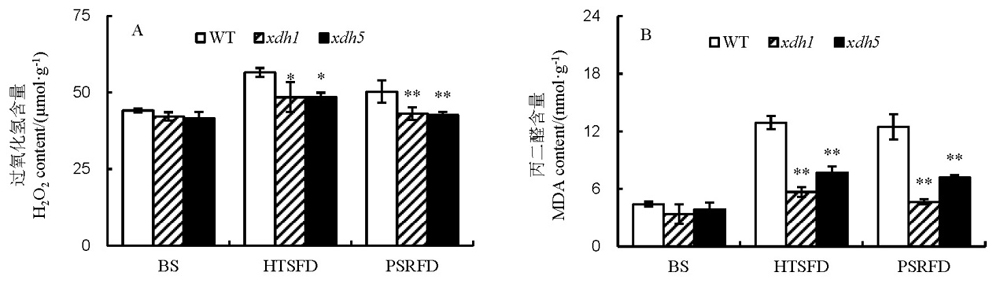
Fig. 3. Effects of high temperature stress on H2O2 and Malondialdehyde(MDA) content in rice leaves. A, H2O2 content; B, MDA content. BS, Before high temperature stress; HTSFD, High temperature stress for 5 days; PSRFD, Post-stress recovery for 5 days. WT, Wild type; xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Values are shown as mean±SD (n=3). * and **, Significant difference at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels by LSD, respectively.
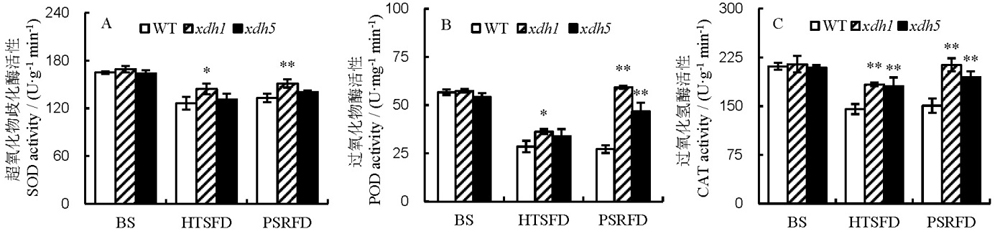
Fig. 4. Effects of high temperature stress on activities of superoxide dismutase(SOD), peroxidase(POD) and catalase(CAT) in rice leaves. A, SOD activity; B, POD activity; C, CAT activity. BS, Before high temperature stress; HTSFD, High temperature stress for 5 days; PSRFD, Post-stress recovery for 5 days. WT, Wild type; xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Values are shown as mean±SD (n=3). * and **, Significant difference at P<0.05 and P<0.01 level by LSD, respectively.
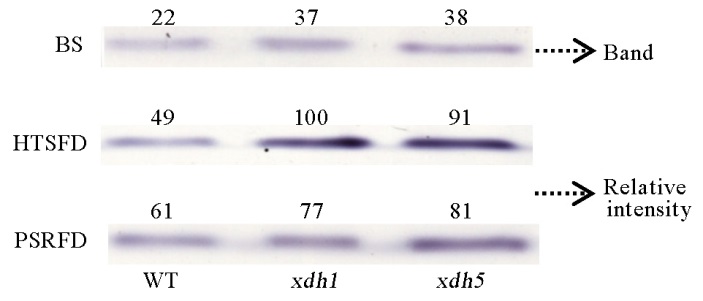
Fig. 5. Effects of high temperature stress on xanthine dehydrogenase(XDH) activity in rice leaves. BS, Before high temperature stress; HTSFD, High temperature stress for 5 days; PSRFD, Post-stress recovery for 5 days. WT, Wild type; xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Each lane in the gel was loaded with equal content soluble protein. XDH activity was detected in gel with hypoxanthine as substrate. Numbers above the lanes indicate relative intensity obtained by scanning the formazan bands with a computing laser densitometer using ImageJ2x software.
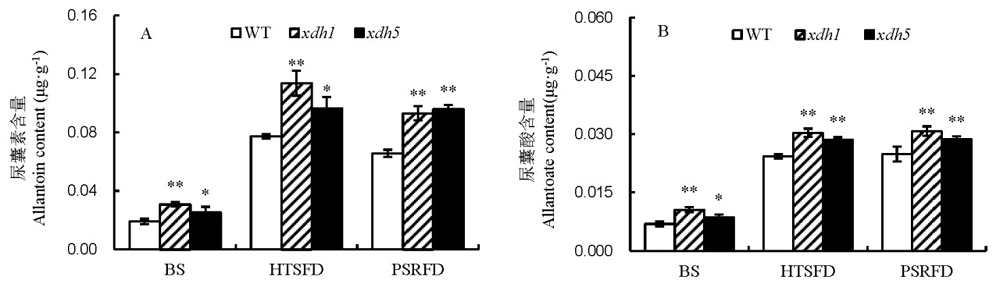
Fig. 6. Effects of high temperature stress on allantoin and allantoate contents in rice leaves. A, Allantoin content. B, Allantoate content. BS, Before high temperature stress; HTSFD, High temperature stress for 5 days; PSRFD, Post-stress recovery for 5 days. WT, Wild type; xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Values are shown as mean±SD (n=3). *, and **, Significant difference at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels by LSD, respectively.
| [1] | Challinor A J, Ewert F, Arnold S, Simelton E, Fraser E.Crops and climate change: Progress, trends, and challenges in simulating impacts and informing adaptation.J Exp Bot, 2009, 60(10): 2775-2789. |
| [2] | Maestri E, Klueva N, Perrotta C, Gulli M, Nguyen H T, Marmiroli N.Molecular genetics of heat tolerance and heat shock proteins in cereals.Plant Mol Biol, 2002, 48(5-6): 667-681. |
| [3] | 段骅, 杨建昌. 高温对水稻的影响及其机制的研究进展. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(4): 393-400. |
| Duan Y, Yang J C.Research advances in the effect of high temperature on rice and its mechanism. Chin J Rice Sci, 2012, 26(4): 393-400.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 曹云英, 赵华. 高温胁迫下油菜素内酯对水稻幼苗的保护作用. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(5):525-529. |
| Cao Y Y, Zhao H.Protective Roles of brassinolide in rice seedlings under heat stress. Chin J Rice Sci, 2007, 21(5): 525-529. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 周伟辉, 薛大伟, 张国平. 高温胁迫下水稻叶片的蛋白响应及其基因型和生育期差异. 作物学报, 2011, 37(5): 820-831. |
| Zhou W Hui, Xue D W, Zhang G P.Protein response of rice leaves to high temperature stress and its difference of genotypes at different growth stage.Acta Agron Sin, 2011, 37(5): 820-831.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 曹云英, 段骅, 杨立年, 王志琴, 周少川, 杨建昌. 减数分裂期高温胁迫对耐热性不同水稻品种产量的影响及其生理原因. 作物学报, 2008, 34(12): 2134-2142. |
| Cao Y Y, Duan H, Yang L N, Wang Z Q, Zhou S C, Yang J C.Effect of heat-stress during meiosis on grain yield of rice cultivars differing in heat-tolerance and its physiological mechanism.Acta Agron Sin, 2008, 34(12): 2134-2142. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 张桂莲, 张顺堂, 王力, 肖应辉, 唐文帮, 陈光辉, 陈立云. 抽穗结实期不同时段高温对稻米品质的影响. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(14): 2869-2879. |
| Zhang G L, Zhang S T, Wang L, Xiao Y H, Tang W B, Chen G H, Chen L Y.Effects of high temperature at different times during the heading and filling periods on rice quality.Sci Agric Sin, 2013, 46(14): 2869-2879.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Werner A K, Witte C P.The biochemistry of nitrogen mobilization: purine ring catabolism.Trends Plant Sci, 2011, 16(7): 381-387. |
| [9] | Yesbergenova Z, Yang G H, Oron E, Soffer D, Fluhr R, Sagi M.The plant Mo-hydroxylases aldehyde oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenase have distinct reactive oxygen species signatures and are induced by drought and abscisic acid. Plant J, 2005, 42(6): 862-876. |
| [10] | Zdunek-Zastocka E, Lips H S.Is xanthine dehydrogenase involved in response of pea plants (Pisum sativum L.) to salinity or ammonium treatment? Acta Physiol Plant, 2003, 25(4): 395-401. |
| [11] | Barabás N K, Omarov R T, Erdei L, Lips S H.Distribution of the Mo-enzymes aldehyde oxidase, xanthine dehydrogenase and nitrate reductase in maize (Zea mays L.) nodal roots as affected by nitrogen and salinity. Plant Sci, 2000, 155(1): 49-58. |
| [12] | You S H, Zhu B, Wang F B, Han H J, Sun M, Zhu H W, Peng R H, Yao Q H.A Vitis vinifera xanthine dehydrogenase gene, VvXDH, enhances salinity tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol Rep, 2017, 11(4): 247. |
| [13] | Hofmann N R.Opposing functions for plant xanthine dehydrogenase in response to powdery mildew infection: production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species.Plant Cell, 2016, 28(5): 1001. |
| [14] | 孙学成, 胡承孝. 高等植物含钼酶与钼营养. 植物生理学通讯, 2005, 6(3): 395-399. |
| Sun X C, Hu C X.Molybdoenzymes and Molybdenum Nutrition in Higher Plants.Plant Physiol Commun, 2005, 6(3): 395-399. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Taylor N J, Cowan A K.Xanthine dehydrogenase and aldehyde oxidase impact plant hormone homeostasis and affect fruit size in ‘Hass’ avocado.J Plant Res, 2004, 117(2): 121-130. |
| [16] | Lichtenthaler H K, Wellbuen A R.Determinations of total caroten oids and chlorophylls a and b leaf extracts in different solvents.Biochem Soc Trans, 1983, 11(5): 591-592. |
| [17] | 张志良. 植物生理学实验指导. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1991: 183-184. |
| Zhang Z L.Experimental Guidance on Plant Physiology. 2nd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1991: 183-184. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 李合生, 孙群, 赵世杰, 章文华. 植物生理生化实验原理与技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. |
| Li H S, Sun Q, Zhao S J, Zhang W H.The Experiment Principle and Technique on Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | Lin C C, Kao C H.Abscisic acid induced changes in cell wall peroxidase activity and hydrogen peroxide level in roots of rice seedlings.Plant Sci, 2001, 160: 323-329. |
| [20] | Sagi M, Omarov R T, Lips S H.The Mo-hydroxylases xanthine dehydrogenase and aldehyde oxidase in ryegrass as affected by nitrogen and salinity.Plant Sci, 1998, 135(2): 125-135. |
| [21] | 张桂莲, 陈立云, 雷东阳, 张顺堂. 水稻耐热性研究进展. 杂交水稻, 2005, 20(1): 1-5. |
| Zhang G L, Chen L Y, Lei D Y, Zhang S T.Research progress on heat resistance of rice. Hybrid Rice, 2005, 20(1): 1-5.(in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 李轶冰, 杨顺强, 任广鑫, 冯永忠, 张强, 李鹏. 低温处理下不同禾本科牧草的生理变化及其抗寒性比较. 生态学报, 2009, 29(3): 1341-1347. |
| Li T B, Yang S Q, Ren G X, Feng Y Z, Zhang Q, Li P.Changes analysis in physiological properties of several gram ineous grass species and cold-resistance comparison on under cold stress.Acta Ecol Sin, 2009, 29(3): 1341-1347. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 张顺堂, 张桂莲, 陈立云, 肖应辉. 高温胁迫对水稻剑叶净光合速率和叶绿素荧光参数的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(3): 335-338. |
| Zhang S T, Zhang G L, Chen L Y, Xiao Y H.Effects of high temperature stress on net photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of flag leaf in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2011, 25(3): 335-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Rang Z W, Jagadish S V K, Zhou Q M, Craufurd P Q, Heuer S. Effect of high temperature and water stress on pollen germination and spikelet fertility in rice.Environ Exp Bot, 2011, 70(1): 60-65. |
| [25] | Mehdy M C.Active oxygen species in plant defense against pathogens.Plant Physiol, 1994, 105(2): 467-472. |
| [26] | Gill S S, Tuteja N.Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants.Plant Physiol Bioch, 2010, 48(12): 909-930. |
| [27] | 王贺正, 马均, 李旭毅, 李艳, 张荣萍, 汪仁全. 水分胁迫对水稻结实期活性氧产生和保护系统的影响. 中国农业科学, 2007, 40(7): 1379-1387. |
| Wang H Z, Ma J, Li X Y, Li Y, Zhang R P, Wang R Q.Effects of Water Stress on Active Oxygen Generation and Protection System in Rice During Grain Filling Stage.Sci Agric Sin, 2007, 40(7): 1379-1387. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 杨淑慎, 高俊凤. 活性氧、自由基与植物的衰老. 西北植物学报, 2001, 21(2): 215-220. |
| Yang S S, Gao J F.Influence of active oxygen and free radicals on plant senescence.Acta Bot Boreal, 2001, 21(2): 215-220. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Hung K T, Kao C H.Nitric oxide counteracts the senescence of rice leaves induced by abscisic acid.J Plant Physiol, 2003, 160(8): 871-879. |
| [30] | Nakagawa A, Sakamoto S, Takahashi M, Morikawa H, Sakamoto A.The RNAi-mediated silencing of xanthine dehydrogenase impairs growth and fertility and accelerates leaf senescence in transgenic Arabidopsis Plants. Plant Cell Physiol, 2007, 48(10): 1484-1495. |
| [31] | Brychkova G, Alikulov Z, Fluhr R, Sagi M.A critical role for ureides in dark and senescence-induced purine remobilization is unmasked in the Atxdh1 Arabidopsis mutant. Plant J, 2008, 54(3): 496-509. |
| [32] | Watanabe S, Nakagawa A, Izumi S, Shimada H, Sakamoto A.RNA interference-mediated suppression of xanthine dehydrogenase reveals the role of purine metabolism in drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett, 2010, 584(6): 1181-1186. |
| [33] | Pastori G M, del Rio L A. Natural senescence of pea leaves: an activated oxygen-mediated function for peroxisomes.Plant Physiol, 1997, 113(2): 411-418. |
| [34] | Yobi A, Wone B W, Xu W X, Alexander D C, Guo L N, Ryals J A, Oliver M J, Cushman J C.Metabolomic profling in Selaginella lepidophylla at various hydration states provides new insights into the mechanistic basis of desiccation tolerance. Mol Plant, 2013, 6(2): 369-385. |
| [35] | Brychkova G, Fluhr R, Sagi M.Formation of xanthine and the use of purine metabolites as a nitrogen source in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Signal & Behav, 2008, 3(11): 999-1001. |
| [36] | 郭培国, 李荣华. 夜间高温胁迫对水稻叶片光合机构的影响. 植物学报, 2000, 42(7): 673-678. |
| Guo P G, Li R H.Effects of high nocturnal temperature on photosynthetic organization in rice leaves.Acta Bot Sin, 2000, 42(7): 673-678. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Ma X F, Wang W M, Bittner F, Schmidt N, Berkey R, Zhang L L, King H, Zhang Y, Feng J Y, Wen Y Q, Tan L Q, Li Y, Zhang Q, Deng Z N, Xiong X Y, Xiao S Y.Dual and opposing roles of xanthine dehydrogenase in defense-associated reactive oxygen species metabolism in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2016, 28(5): 1108-1126. |
| [38] | Smith P M C, Atkins C A. Purine biosynthesis, big in cell division, even bigger in nitrogen assimilation.Plant Physiol, 2004, 128(3): 793-802. |
| [39] | Bittner F, Oreb M, Mendel R R.ABA3 is a molybdenum cofactor sulfurase required for activation of aldehyde oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenase in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(44): 40381-40384. |
| [40] | Watanabe S, Kounosu Y, Shimada H, Sakamoto A.Arabidopsis xanthine dehydrogenase mutants defective in purine degradation show a compromised protective response to drought and oxidative stress. Plant Biotechnol,2014, 31(2): 173-178. |
| [41] | Leydecker M T, Moureaux T, Kraepiel Y, Caboche M.Molybdenum cofactor mutants, specifically impaired in xanthine dehydrogenase activity and abscisic acid biosynthesis, simultaneously overexpress nitrate reductase. Plant Physiol, 1995, 107(4): 1427-1431. |
| [42] | Taylor N, Cowan K.Plant hormone homeostasis and the control of avocado fruit size.Plant Grow Regul, 2001, 35(3): 247-255. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||