
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 335-344.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.7007 335
• Orginal Article • Next Articles
Tingting XU1, Ning YU1, Yingxin ZHANG1, Zhenzhen BI1, Weixun WU1, Yongrun CAO1, Beifang WANG1, Yue ZHANG1, Dandan XUAN1, Daibo CHEN1, Xiaodeng ZHAN1, Shihua CHENG1,*, Liyong CAO1,2,*
Received:2016-01-13
Revised:2017-02-23
Online:2017-07-25
Published:2017-07-10
Contact:
Shihua CHENG, Liyong CAO
徐婷婷1, 余宁1, 张迎信1, 毕真真1, 吴玮勋1, 曹永润1,2, 王备芳1, 张越1, 轩丹丹1, 陈代波1, 占小登1, 程式华1,*, 曹立勇1,2,*
通讯作者:
程式华,曹立勇
基金资助:Tingting XU, Ning YU, Yingxin ZHANG, Zhenzhen BI, Weixun WU, Yongrun CAO, Beifang WANG, Yue ZHANG, Dandan XUAN, Daibo CHEN, Xiaodeng ZHAN, Shihua CHENG, Liyong CAO. Identification of Rice Blast Resistance Mutant lmm326 and Preliminary Analysis of Its Regulatory Pathway[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(4): 335-344.
徐婷婷, 余宁, 张迎信, 毕真真, 吴玮勋, 曹永润, 王备芳, 张越, 轩丹丹, 陈代波, 占小登, 程式华, 曹立勇. 水稻抗稻瘟病突变体lmm326的鉴定与调控通路初步分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(4): 335-344.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.7007 335
| 标记 | 前引物 | 后引物 |
|---|---|---|
| Marker | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| RD0115 | GTTGTAGATGTGATTGGAGAA | GACTATGTATGGCACTGTTGA |
| RM5310 | TAGACAAAGCAACGGGTTCC | CGGAAGCAGGAGAATCGTAG |
| RM3362 | AAGTTGAAGCAGTCGCCAAC | GAATTGCGTGGGATATGGAC |
| ZH4 ZH7 | TCCACGAACAAAGACGAG GACTCCGAGCCAGCAAAA | ACGGCACATTATCAACAACA GTCTCCGTGCCCTTGTGC |
| ZH8 | ATGGAGTCGCCTTGTTGA | AAATGTGGCTGGCTGATC |
| ZH11 | TTCGTCTCATTAGCAGCAT | CATTTATTCACTTGCCACAT |
| Qpr10 | GTCCGGGCACCATCTACACC | CAAGCTTCGTCTCCGTCGAGT |
| Qpal1 | TTCAACGCCGACACCT | GTAGAGCGGATACGACCTG |
| Qaos2 | AAGCTGCTGCAATACGTGTACTGG | CGACGAGCAACAGCCTTCCG |
| WRKY45 | GCCGACGACCAGCACGATCACC | ACGAGCCGACGCCGCCCTC |
| PR1a | CGTGTCGGCGTGGGTGT | GGCGAGTAGTTGCAGGTGATG |
| PR1b Actin | TACGCCAGCCAGAGGAGC CAGGCCGTCCTCTCTCTGTA | GCCGAACCCCAGAAGAGG AAGGATAGCATGGGGGAGAG |
Table 1 Sequence of primers used for fine mapping and qRT-PCR.
| 标记 | 前引物 | 后引物 |
|---|---|---|
| Marker | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| RD0115 | GTTGTAGATGTGATTGGAGAA | GACTATGTATGGCACTGTTGA |
| RM5310 | TAGACAAAGCAACGGGTTCC | CGGAAGCAGGAGAATCGTAG |
| RM3362 | AAGTTGAAGCAGTCGCCAAC | GAATTGCGTGGGATATGGAC |
| ZH4 ZH7 | TCCACGAACAAAGACGAG GACTCCGAGCCAGCAAAA | ACGGCACATTATCAACAACA GTCTCCGTGCCCTTGTGC |
| ZH8 | ATGGAGTCGCCTTGTTGA | AAATGTGGCTGGCTGATC |
| ZH11 | TTCGTCTCATTAGCAGCAT | CATTTATTCACTTGCCACAT |
| Qpr10 | GTCCGGGCACCATCTACACC | CAAGCTTCGTCTCCGTCGAGT |
| Qpal1 | TTCAACGCCGACACCT | GTAGAGCGGATACGACCTG |
| Qaos2 | AAGCTGCTGCAATACGTGTACTGG | CGACGAGCAACAGCCTTCCG |
| WRKY45 | GCCGACGACCAGCACGATCACC | ACGAGCCGACGCCGCCCTC |
| PR1a | CGTGTCGGCGTGGGTGT | GGCGAGTAGTTGCAGGTGATG |
| PR1b Actin | TACGCCAGCCAGAGGAGC CAGGCCGTCCTCTCTCTGTA | GCCGAACCCCAGAAGAGG AAGGATAGCATGGGGGAGAG |
| 性状 Trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 lmm326 |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height/cm | 101.6±1.8 | 63.1±4.0** |
| 每株有效分蘖数No. of productive panicles per plant | 11.7±2.4 | 3.1±0.4** |
| 每穗总粒数No. of spikelets per panicle | 147.1±17.0 | 46.9±9.1** |
| 结实率Seed-setting rate/% | 85.5±0.0 | 77.4±0.0* |
| 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 23.7±0.9 | 18.7±0.7** |
Table 2 Comparison of agronomic traits between wild type Zhonghua 11 and the mutant lmm326(mean ±SD, n=10).
| 性状 Trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 lmm326 |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height/cm | 101.6±1.8 | 63.1±4.0** |
| 每株有效分蘖数No. of productive panicles per plant | 11.7±2.4 | 3.1±0.4** |
| 每穗总粒数No. of spikelets per panicle | 147.1±17.0 | 46.9±9.1** |
| 结实率Seed-setting rate/% | 85.5±0.0 | 77.4±0.0* |
| 千粒重1000-grain weight/g | 23.7±0.9 | 18.7±0.7** |
| 编号 Code | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 Mutant |
|---|---|---|
| 12-26-49-2 | 4.26±0.08 | 0.79±0.07** |
| 12-128-12-1 | 3.89±0.05 | 0.82±0.08** |
| 12-901-48-1 | 4.45±0.14 | 0.83±0.08** |
| 13-600-33-2 | 4.56±0.08 | 0.81±0.03** |
Table 3 Resistance identification of lmm326 and Zhonghua 11 to rice blast(mean±SD, n=3). cm
| 编号 Code | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 Mutant |
|---|---|---|
| 12-26-49-2 | 4.26±0.08 | 0.79±0.07** |
| 12-128-12-1 | 3.89±0.05 | 0.82±0.08** |
| 12-901-48-1 | 4.45±0.14 | 0.83±0.08** |
| 13-600-33-2 | 4.56±0.08 | 0.81±0.03** |
| 杂交组合 Hybrid combination | F2 | χ2(3∶1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型植株数 | 突变表型植株数 | ||||
| No. of normal plants | No. of mutant plants | ||||
| 中花11/lmm326 ZH11/lmm326 | 1761 | 629 | 2.21 | ||
| Dular/lmm326 | 1936 | 674 | 0.94 | ||
Table 4 Genetic analysis of mutant lmm326.
| 杂交组合 Hybrid combination | F2 | χ2(3∶1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型植株数 | 突变表型植株数 | ||||
| No. of normal plants | No. of mutant plants | ||||
| 中花11/lmm326 ZH11/lmm326 | 1761 | 629 | 2.21 | ||
| Dular/lmm326 | 1936 | 674 | 0.94 | ||
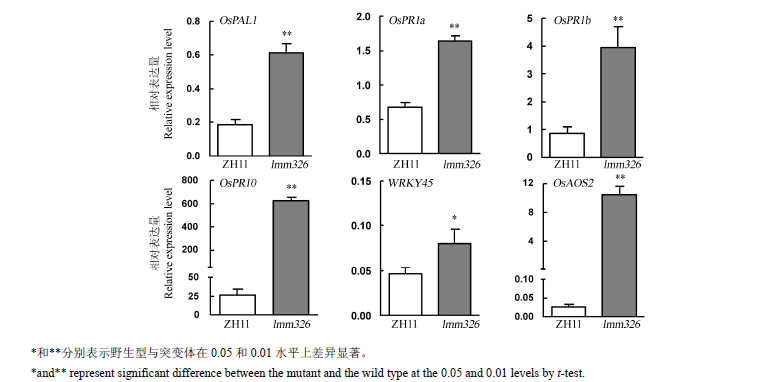
Fig. 6. Real-time PCR analysis of relative expression level of genes associated with defense response in the wild type(ZH11) and lmm326 mutant(mean±SD, n=3).
| [1] | Heath M C.Hypersensitive response-related death.Plant Mol Biol, 2000, 44: 321-334. |
| [2] | Wang S H, Lim J H, Kim S S, Cho S H, Yoo S C, Koh H J, Sakuraba Y, Paek N C.Mutation of SPOTTEDLEAF3 (SPL3) impairs abscisic acid-responsive signaling and delays leaf senescence in rice, J Exp Bot, 2015, 66(22): 7045-7059. |
| [3] | Gray J, Close P S, Briggs S P, Johal G S.A novel suppressor of cell death in plants encoded by the lls1 gene of maize. Cell, 1997, 89: 25-31. |
| [4] | Dietrich R A, Richberg M H, Schmidt R, Dean C, Dangl J L.A novel zinc finger protein is encoded by the Arabidopsis LSD1 gene and functions as a negative regulator of plant cell death. Cell, 1997, 88: 685-694. |
| [5] | Buschges R, Hollricher K, Panstruga R, Simons G, Wolter M,Frijters A, van Daelen R, van der Lee T, Diergaarde P, Groenendijk J, Töpsch S, Vos P, Salamini F, Schulze-Lefert P. The barley mol gene: A novel control element of plant pathogen resistance.Cell, 1997, 88: 695-705. |
| [6] | Brodersen P, Petersen M, Pike H M, Olszak B, Skov S, Odum N, Jørgensen L B, Brown R E, Mundy J.Knockout of Arabidopsis accelerated-cell-death11 encoding a sphingosine transfer protein causes activation of programmed cell death and defense. Genes Dev, 2002, 16: 490-502. |
| [7] | Wu C J, Bordeos A, Madamba M R, Baraoidan M, Ramos M, Wang G L, Leach J E, Leung H.Rice lesion mimic mutants with enhanced resistance to diseases.Mol Genet Genom, 2008, 279: 605-619. |
| [8] | Dangl J L, Dietrich R A, Richberg M H.Death don’t have no mercy: Cell death programs in plant-microbe interactions.Plant cell, 1996, 8(10):1793. |
| [9] | Neuffer M G, Calvert O H.Dominant disease lesion mimics in maize.J Hered, 1975, 6(5): 265-270. |
| [10] | Shirasu K, Chuize-Lefert P.Regulators of cell death in disease resistance. Plant Mol Biol, 2000, 44(3): 371-385. |
| [11] | Li Z, Zhang Y X, Liu L, Liu Q E, Bi Z Z, Yu N, Cheng S H, Cao L Y.Fine mapping of the lesion mimic and early senescence 1(lmes1) in rice(Oryza sativa). Plant Physiol Biochem, 2014, 80: 300-307. |
| [12] | Thomma B P, Penninckx I A, Broekaert W F, Cammue B P.The complexity of disease signaling in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Immunol, 2001, 13(1): 63-68. |
| [13] | Yoshioka K, Kachroo P, Tsui F, Sharma S B, Shah J, Klessig D F.Environmentally sensitive, SA-dependent defense responses in the cpr22 mutant of Arabidopsis. Plant J, 2001, 26(4): 447-459. |
| [14] | Weymann K, Hunt M, Uknes S, Neuenschwander U, Lawton K, Steiner H Y, Ryals J.Suppression and restoration of lesion formation in Arabidopsis Isd mutants. Plant Cell, 1995, 7(12): 2013-2022. |
| [15] | Lu H, Salimian S, Gamelin E, Wang G Y, Fedorowski J, LaCourse W, Greenberg J T. Genetic analysis of acd6-1 reveals complex defense networks and leads to identification of novel defense genes inArabidopsis. Plant J, 2009, 58(3): 401-412. |
| [16] | Chong J L, Pierrel M A, Atanassova R, Werck-Reichhart D, Fritig B, Saindrenan P.Free and conjugated benzoic acid in tobacco plants and cell cultures. Induced accumulation upon elicitation of defense responses and role as salicylic acid precursors. Plant Physiol, 2001, 125: 318-328. |
| [17] | Lu H, Rate D N, Song J T, Greenberg J T.ACD6, a novel ankyrin protein, is a regulator and an effector of salicylic acid signaling in the Arabidopsis defense response. Plant Cell, 2003, 15(10): 2408-2420. |
| [18] | Yu D Q, Chen C H, Chen Z X.Evidence for an important role of WRKY DNA binding proteins in the regulation of NPR1 gene expression. Plant Cell, 2001, 13(7): 1527-1540. |
| [19] | Despré s C, De Long C, Glaze S, Liu E W, Fobert P R. The Arabidopsis NPR1 NIM1 protein enhances the DNA binding activity of a subgroup of the TGA family of bZIP transcription factors. Plant Cell, 2000, 12: 279-290. |
| [20] | Chen X F, Hao L, Pan J W, Zheng X X, Jiang G H, Jin Y, Gu Z M, Qian Q, Zhai W X, Ma B J.SPL5, a cell death and defense related gene, encodes a putative splicing factor 3b subunit 3(SF3b3) in rice. Mol Breeding, 2012, 30(2): 939-949. |
| [21] | Yamanouchi U, Yano M, Lin H, Ashikari M, Yamada K.A rice spotted leaf gene,SPL7, encodes a heat stress transcription factor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2002, 99: 7530-7535. |
| [22] | Zeng L R, Qu S H, Bordeos A, Yang C, Baraoidan M, Yan H, Xie Q, Nahm B H, Leung H, Wang G L.Spotted leaf 11, a negative regulator of plant cell death and defense, encodes a ubox/armadillo repeat protein endowed with E3 ubiquitinligase activity. Plant Cell, 2004, 16: 2795-2808. |
| [23] | Mori M, Tomita C, Sugimoto K, Hasegawa M, Hayashi N, Dubouzet J G, Ochiai H, Sekimoto H, Hirochika H, Kikuchi S.Isolation and molecular characterization of aSpotted leaf 18 mutant by modified activation-tagging in rice. Plant Mol Biol, 2007, 63: 847-860. |
| [24] | Qiao Y L, Jiang W Z, Lee J, Park B, Choi M S, Piao R H, Woo M O, Roh J H, Han L Z, Paek N C, Seo H S, Koh H J.SPL28 encodes a clathrin-associated adaptor protein complex 1, medium subunitu1(AP1M1) and early senescence in rice(Oryza sativa). New Phytol, 2010, 185(1): 258-274. |
| [25] | Fekih R, Tamiru M, Kanzaki H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kanzaki E, Saitoh H, Takagi H, Natsume S, Undan J R, Undan J, Terauchi R.The rice(Oryza sativa L.) LESION MIMIC RESEMBLING, which encodes an AAA-type ATPase, is implicated in defense response. Mol Genet Genom, 2015, 290: 611-622 . |
| [26] | Yin Z C, Chen J, Zeng L R, Goh M, Leung H, Khush G S, Wang G L.Characterizing rice lesion mimic mutants and identifying a mutant with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight.Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 2000, 13(8): 869-876. |
| [27] | Wang L J, Pei Z Y, Tian Y C, He C Z.OsLSD1, a rice zinc finger protein, regulates programmed cell death and callus differentiation. Mol Plant Microb Interact, 2005, 18: 375-384. |
| [28] | Sun C H, Liu L C, Tang J Y, Lin A H, Zhang F T, Fang J, Zhang G F, Chu C C.RLIN1,encoding a putative coproporphyrinogen III oxidase, is involved in lesion initiation in rice. J Genet Genomics, 2011, 38: 29-37. |
| [29] | Sakuraba Y, Rahman M L, Cho S H, Kim Y S, Koh H J, Yoo S C, Paek N C.The rice faded green leaf locus encodes protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase B and is essential for chlorophyll synthesis under high light conditions.Plant J, 2013, 74: 122-133. |
| [30] | Thordal-Christansen H, Zhang Z G, Wei Y D.Subcellular localization of H2O2 in plants: H2O2 accumulation in papillae and hypersensitive response during the barley powdery mildew interaction. Plant J, 1997, 11: 1187-1194. |
| [31] | Kong X P, Li D Q.Hydrogen peroxide is not involved in HrpN from Erwinia amylovora-induced hypersensitive cell death in maize leaves. Plant Cell Rep, 2011, 30: 1273-1279. |
| [32] | Wellbuin A R.The spectral determination of chlorophyll a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometer of different resolution.J Plant Physiol, 1994, 144: 307-313. |
| [33] | Rogers S O, Bendich A J.Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol, 1985, 5: 69-76. |
| [34] | 陈析丰, 金杨, 马伯军. 水稻类病变突变体及抗病性的研究进展. 植物病理学报, 2011, 41(1): 1-9. |
| Chen X F, Jin Y, Ma B J.Progress on the studies of rice lesion mimics and their resistant mechanism to the pathogens.Acta Phytopathol Sin, 2011, 41(1): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | Jiao B B, Wang J J, Zhu X D, Zeng L J, Li Q, He Z H.A novel protein RLS1 with NB-ARM domains is involved in chloroplast degradation during leaf senescence in rice.Mol Plant, 2012, 5(1): 205-217. |
| [36] | Takahashi A, Agrawal G K, Yamazaki M, Onosato K, Miyao A, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K, Hirochika H.RicePti1a negatively regulates RAR1-dependent defense responses. Plant Cell, 2007, 19: 2940-2951. |
| [37] | Feng B H, Yang Y, Shi Y F, Shen H C, Wang H M, Huang Q N, Xu X, Lü X G, Wu J L.Characterization and genetic analysis of a novel rice spotted-leaf mutantHM47 with broad-spectrum resistance to Xanthomnas oryzae pv. oryzae. J Integr Plant Biol, 2013, 55(5): 473-483. |
| [38] | Liu X Q, Li F, Tang J Y, Wang W H, Zhang F X, Wang G D, Chu J F, Yan C Y, Wang T Q, Chu C C, Li C Y.Activation of the jasmonic acid pathway by depletion of the hydroxide lyaseOsHPL3 reveals crosstalk between the HPL and AOS branches of the oxylipin pathway in rice. Plos One, 2012, 7: e50089. |
| [39] | Jiang C J, Shimono M, Maeda S, Inoue H, Mori M, Hasegawa M, Sugano S, Takatsuji H.Suppression of the rice fatty-acid desaturase geneosssi2 enhances resistance to blast and leaf blight diseases in rice. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact, 2009, 22: 820-829. |
| [40] | Yang W, Dong R, Liu L, Hu Z B, Li J, Wang Y, Ding X H, Chu Z H.A novel mutant allele ofSSI2 confers a better balance between disease resistance and plant growth inhibition on Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol, 2016, 16: 208. |
| [41] | Song N, Hu Z R, Li Y H, Li C, Peng F X, Yao Y Y, Peng H R, Ni Z F, Xie C J, Sun Q X.Overexpression of a wheat stearoyl-ACP desaturase(SACPD) geneTaSSI2 in Arabidopsis ssi2 mutant compromise its resistance to powdery mildew. Gene, 2013, 524: 220-227. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||