
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 352-364.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240502
韦新宇1,2,#, 曾跃辉1,2,#, 肖长春1,2, 黄建鸿1,2, 阮宏椿4, 杨旺兴2,3, 邹文广2,3, 许旭明2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-30
修回日期:2024-07-23
出版日期:2025-05-10
发布日期:2025-05-21
通讯作者:
*email: fj63xxm@sina.com作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
WEI Xinyu1,2,#, ZENG Yuehui1,2,#, XIAO Changchun1,2, HUANG Jianhong1,2, RUAN Hongchun4, YANG Wangxing2,3, ZOU Wenguang2,3, XU Xuming2,3,*( )
)
Received:2024-04-30
Revised:2024-07-23
Online:2025-05-10
Published:2025-05-21
Contact:
*email: fj63xxm@sina.com
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】稻瘟病是一种由丝状子囊菌稻瘟病菌(Magnaporthe oryzae)引起的世界性真菌病害,严重影响水稻的品质和产量,培育和种植抗性品种是控制稻瘟病发生最经济有效的措施,而抗性基因的挖掘和利用是选育抗病品种的基础和关键。本研究以三明市农业科学研究院选育且具有广谱抗性的优质籼型杂交稻保持系康丰B (KFB)为研究材料,对其抗稻瘟病基因Pi-kf2(t)进行抗谱分析、克隆和功能验证。【方法】利用来自全国不同地区的100个稻瘟病菌株对KFB[Pi-kf2(t)]、75-1-127 (Pi9)、C101A51 (Pi2)、IRBLzt-T (Piz-t)、EBZ (Pi50)和GM 4 (Pigm) 3~4叶期幼苗进行喷雾接菌;结合半定量PCR (RT-PCR)和实时荧光定量PCR (qRT-PCR)技术对Pi-kf2(t)两个候选基因Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2和Pi-kf2(t)-NBS4进行表达模式分析;采用同源克隆技术并构建系统进化树对Pi-kf2(t)基因进行克隆以及分析Pi-kf2(t)与Pi9、Pi2、Piz-t、Pi50和Pigm之间的进化关系;通过转基因互补试验对Pi-kf2(t)候选基因进行功能验证。【结果】Pi-kf2(t)与Pi9、Pi2、Piz-t、Pi50和Pigm存在明显的抗谱差异,其抗谱分别为93%、90%、91%、78%、95%和96%;候选基因Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2在KFB苗期叶片具有较高的表达水平且不受稻瘟病菌诱导,属于组成型表达,而Pi-kf2(t)-NBS4表达量极低;多重氨基酸序列比对分析表明,Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2与Pi9、Pi2、Piz-t、Pi50和Pigm蛋白分别存在45、31、34、2和2个氨基酸的差异;系统进化树分析表明,Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2与Pi50和Pigm具有更近的亲缘关系和更高的同源性;另外,转基因互补试验进一步验证了候选基因Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2即为Pi-kf2(t)抗稻瘟病基因。【结论】Pi-kf2(t)为Pi2/Pi9基因家族中一个新的稻瘟病抗性基因,本研究为Pi-kf2(t)后期抗病机理研究提供了理论基础,同时为选育抗稻瘟病水稻新品种提供了重要种质资源。
韦新宇, 曾跃辉, 肖长春, 黄建鸿, 阮宏椿, 杨旺兴, 邹文广, 许旭明. 水稻康丰B抗稻瘟病基因Pi-kf2(t)的克隆与功能验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 352-364.
WEI Xinyu, ZENG Yuehui, XIAO Changchun, HUANG Jianhong, RUAN Hongchun, YANG Wangxing, ZOU Wenguang, XU Xuming. Cloning and Functional Verification of Rice-Blast Resistance Gene Pi-kf2(t) in Kangfeng B[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 352-364.
| 编号Number | 菌种名称Isolate | 来源 Origin | 编号Number | 菌种名称Isolate | 来源 Origin | 编号Number | 菌种名称Isolate | 来源 Origin | 编号Number | 菌种名称 Isolate | 来源 Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J01 | 2022075 | 福建福州 | J26 | 2021146 | 广东惠州 | J51 | 2021137 | 福建沙县 | J76 | 2022027 | 福建武夷山 |
| J02 | 2021024 | 福建武夷山 | J27 | 2021021 | 广东惠州 | J52 | 2022026 | 福建武夷山 | J77 | 2021033 | 江西婺源 |
| J03 | 2022048 | 湖北恩施 | J28 | 2021119 | 福建连城 | J53 | 2021048 | 福建将乐 | J78 | 2022037 | 福建浦城 |
| J04 | 2022036 | 湖北恩施 | J29 | 2021013 | 福建尤溪 | J54 | 2021018 | 江西婺源 | J79 | 2021036 | 福建宁化 |
| J05 | 2022024 | 福建建阳 | J30 | 2021121 | 福建连城 | J55 | 2021032 | 江西婺源 | J80 | 2023020 | 湖北恩施 |
| J06 | 2023090 | 福建柘荣 | J31 | 2020117 | 安徽肥西 | J56 | 2023112 | 福建宁化 | J81 | 2022006 | 福建上杭 |
| J07 | 2021017 | 江苏扬州 | J32 | 2022072 | 安徽肥西 | J57 | 2022005 | 福建上杭 | J82 | 2023019 | 江苏扬州 |
| J08 | 2020062 | 江苏扬州 | J33 | 2021001 | 福建福州 | J58 | 2020114 | 安徽肥西 | J83 | 2020156 | 江苏扬州 |
| J09 | 2021085 | 福建上杭 | J34 | 2023104 | 江西婺源 | J59 | 2020059 | 安徽肥西 | J84 | 2022044 | 湖北宜昌 |
| J11 | 2020010 | 福建宁化 | J36 | 2021078 | 湖北宜昌 | J61 | 2023131 | 福建将乐 | J86 | 2022063 | 福建莆田 |
| J12 | 2021068 | 福建莆田 | J37 | 2022065 | 湖北恩施 | J62 | 2020107 | 福建松溪 | J87 | 2021031 | 福建松溪 |
| J13 | 2021092 | 福建福安 | J38 | 2022021 | 福建建阳 | 163 | 2023034 | 江苏扬州 | J88 | 2020017 | 江西井冈山 |
| J14 | 2022078 | 福建漳州 | J39 | 2021037 | 福建宁化 | J64 | 2022032 | 福建浦城 | J89 | 2021016 | 江西井冈山 |
| J15 | 2021122 | 福建连城 | J40 | 2023018 | 江西婺源 | J65 | 2020061 | 福建将乐 | J90 | 2023035 | 江苏扬州 |
| J16 | 2022074 | 福建福州 | J41 | 2022049 | 福建福安 | J66 | 2020041 | 福建上杭 | J91 | 2021084 | 福建上杭 |
| J17 | 2021034 | 江西井冈山 | J42 | 2021138 | 福建沙县 | J67 | 2022045 | 湖北宜昌 | J92 | 2022085 | 福建南靖 |
| J18 | 2022008 | 江西井冈山 | J43 | 2021049 | 福建将乐 | J68 | 2022081 | 福建漳州 | J93 | 2021081 | 福建三明 |
| J19 | 2021080 | 福建三明 | J44 | 2021027 | 福建武夷山 | J69 | 2023029 | 江苏徐州 | J94 | 2022007 | 福建将乐 |
| J20 | 2021040 | 福建将乐 | J45 | 2021035 | 江西井冈山 | J70 | 2023004 | 福建福州 | J95 | 2023037 | 江西井冈山 |
| J21 | 2021009 | 福建沙县 | J46 | 2021020 | 江苏扬州 | J71 | 2021141 | 福建沙县 | J96 | 2020143 | 福建浦城 |
| J22 | 2022046 | 湖北恩施 | J47 | 2022015 | 江苏扬州 | J72 | 2023003 | 江苏徐州 | J97 | 2020105 | 福建松溪 |
| J23 | 2022011 | 湖北宜昌 | J48 | 2021014 | 福建尤溪 | J73 | 2023031 | 江苏徐州 | J98 | 2020039 | 福建上杭 |
| J24 | 2023014 | 福建三明 | J49 | 2023041 | 福建建阳 | J74 | 2021149 | 广东惠州 | J99 | 2022004 | 福建上杭 |
| J25 | 2022018 | 福建三明 | J50 | 2021072 | 福建莆田 | J75 | 2021005 | 广东惠州 | J100 | 2023042 | 江苏徐州 |
表1 来自全国不同地区的100个稻瘟病菌株
Table 1. 100 Magnaporthe oryzae isolates originated from different regions of China
| 编号Number | 菌种名称Isolate | 来源 Origin | 编号Number | 菌种名称Isolate | 来源 Origin | 编号Number | 菌种名称Isolate | 来源 Origin | 编号Number | 菌种名称 Isolate | 来源 Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J01 | 2022075 | 福建福州 | J26 | 2021146 | 广东惠州 | J51 | 2021137 | 福建沙县 | J76 | 2022027 | 福建武夷山 |
| J02 | 2021024 | 福建武夷山 | J27 | 2021021 | 广东惠州 | J52 | 2022026 | 福建武夷山 | J77 | 2021033 | 江西婺源 |
| J03 | 2022048 | 湖北恩施 | J28 | 2021119 | 福建连城 | J53 | 2021048 | 福建将乐 | J78 | 2022037 | 福建浦城 |
| J04 | 2022036 | 湖北恩施 | J29 | 2021013 | 福建尤溪 | J54 | 2021018 | 江西婺源 | J79 | 2021036 | 福建宁化 |
| J05 | 2022024 | 福建建阳 | J30 | 2021121 | 福建连城 | J55 | 2021032 | 江西婺源 | J80 | 2023020 | 湖北恩施 |
| J06 | 2023090 | 福建柘荣 | J31 | 2020117 | 安徽肥西 | J56 | 2023112 | 福建宁化 | J81 | 2022006 | 福建上杭 |
| J07 | 2021017 | 江苏扬州 | J32 | 2022072 | 安徽肥西 | J57 | 2022005 | 福建上杭 | J82 | 2023019 | 江苏扬州 |
| J08 | 2020062 | 江苏扬州 | J33 | 2021001 | 福建福州 | J58 | 2020114 | 安徽肥西 | J83 | 2020156 | 江苏扬州 |
| J09 | 2021085 | 福建上杭 | J34 | 2023104 | 江西婺源 | J59 | 2020059 | 安徽肥西 | J84 | 2022044 | 湖北宜昌 |
| J11 | 2020010 | 福建宁化 | J36 | 2021078 | 湖北宜昌 | J61 | 2023131 | 福建将乐 | J86 | 2022063 | 福建莆田 |
| J12 | 2021068 | 福建莆田 | J37 | 2022065 | 湖北恩施 | J62 | 2020107 | 福建松溪 | J87 | 2021031 | 福建松溪 |
| J13 | 2021092 | 福建福安 | J38 | 2022021 | 福建建阳 | 163 | 2023034 | 江苏扬州 | J88 | 2020017 | 江西井冈山 |
| J14 | 2022078 | 福建漳州 | J39 | 2021037 | 福建宁化 | J64 | 2022032 | 福建浦城 | J89 | 2021016 | 江西井冈山 |
| J15 | 2021122 | 福建连城 | J40 | 2023018 | 江西婺源 | J65 | 2020061 | 福建将乐 | J90 | 2023035 | 江苏扬州 |
| J16 | 2022074 | 福建福州 | J41 | 2022049 | 福建福安 | J66 | 2020041 | 福建上杭 | J91 | 2021084 | 福建上杭 |
| J17 | 2021034 | 江西井冈山 | J42 | 2021138 | 福建沙县 | J67 | 2022045 | 湖北宜昌 | J92 | 2022085 | 福建南靖 |
| J18 | 2022008 | 江西井冈山 | J43 | 2021049 | 福建将乐 | J68 | 2022081 | 福建漳州 | J93 | 2021081 | 福建三明 |
| J19 | 2021080 | 福建三明 | J44 | 2021027 | 福建武夷山 | J69 | 2023029 | 江苏徐州 | J94 | 2022007 | 福建将乐 |
| J20 | 2021040 | 福建将乐 | J45 | 2021035 | 江西井冈山 | J70 | 2023004 | 福建福州 | J95 | 2023037 | 江西井冈山 |
| J21 | 2021009 | 福建沙县 | J46 | 2021020 | 江苏扬州 | J71 | 2021141 | 福建沙县 | J96 | 2020143 | 福建浦城 |
| J22 | 2022046 | 湖北恩施 | J47 | 2022015 | 江苏扬州 | J72 | 2023003 | 江苏徐州 | J97 | 2020105 | 福建松溪 |
| J23 | 2022011 | 湖北宜昌 | J48 | 2021014 | 福建尤溪 | J73 | 2023031 | 江苏徐州 | J98 | 2020039 | 福建上杭 |
| J24 | 2023014 | 福建三明 | J49 | 2023041 | 福建建阳 | J74 | 2021149 | 广东惠州 | J99 | 2022004 | 福建上杭 |
| J25 | 2022018 | 福建三明 | J50 | 2021072 | 福建莆田 | J75 | 2021005 | 广东惠州 | J100 | 2023042 | 江苏徐州 |

图1 康丰B(KFB)抗稻瘟病基因Pi-kf2(t)的抗谱分析 A: KFB、75-1-127、C101A51、IRBLzt-T、EBZ和GM-4对100个稻瘟病菌株的抗性反应; 其中, J01-J100代表来自全国不同地区100个稻瘟病菌株, R%代表抗谱, R、MR、MS、S和HS分别表示为抗、中抗、中感、感和高感稻瘟病; B, C, D: KFB、75-1-127、C101A51、IRBLzt-T、EBZ和GM-4对稻瘟病菌株J71 (B)、J91 (C)和J93 (D)的抗性反应。1: KFB; 2: 75-1-127; 3: C101A51; 4: IRBLzt-T; 5: EBZ; 6: GM-4。
Fig. 1. Resistance spectrum analysis of rice blast resistance gene Pi-kf2(t) in KFB A, Reaction of KFB, 75-1-127, C101A51, IRBLzt-T, EBZ, and GM-4 to 100 isolates of Magnaporthe oryzae. J01-J100, The 100 isolates were collected from different regions of China. R%, Resistance spectrum. R, MR, MS, S, and HS represent resistance, mid-resistance, mid-susceptibility, susceptibility, and high-susceptibility to rice blast, respectively; B, C, D, Reaction of KFB, 75-1-127, C101A51, IRBLzt-T, EBZ, and GM-4 to J71(B), J91(C), and J93(D), where 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 represent KFB, 75-1-127, C101A51, IRBLzt-T, EBZ, and GM-4, respectively.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5'-3') | 用途 Usage | 预测PCR产物大小 Excepted PCR product size(bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NBS2-Q-F | CTGCTAATGTACAGTGACCGA | NBS-LRR2基因qPCR检测 | 111 |
| NBS2-Q-R | AGTGACTGATCCTTCGGCAT | qPCR detection for NBS-LRR2 | |
| NBS4-Q-F | TGATCACGACCTTGCTTGTG | NBS-LRR4基因qPCR检测 | 122 |
| NBS4-Q-R | CTGACCTGTTGTTCGACGTC | qPCR detection for NBS-LRR4 | |
| HPT-F | ATTTGTGTACGCCCGACAGT | 鉴定HPT | 577 |
| HPT-R | GTGCTTGACATTGGGGAGTT | PCR detection for HPT | |
| NBS2Seq-01F | CCCAAGTGAGGATGCAAAACA | NBS-LRR2基因测序 | 803 |
| NBS2Seq-01R | TGACATGCAAGAAACGGGTG | Sequencing for NBS-LRR2 | |
| NBS2Seq-02F | TGGCTAGGCTTACGTTTTGG | NBS-LRR2基因测序 | 2219 |
| NBS2Seq-02R | ACAACGAAGAGTATGCAGACA | Sequencing for NBS-LRR2 | |
| NBS2Seq-03F | AGGATGTTACGGGTCTTGGA | NBS-LRR2基因测序 | 2107 |
| NBS2Seq-03R | AACAACTGCAGGCCAAACAA | Sequencing for NBS-LRR2 | |
| OsActin-F | ACCTTCAACACCCCTGCTAT | 内参基因OsActin qPCR检测 | 105 |
| OsActin-R | CACCATCACCAGAGTCCAAC | qPCR detection for OsActin (as internal standard) |
表2 本研究所使用的引物序列
Table 2. Sequences of primers used in this study
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5'-3') | 用途 Usage | 预测PCR产物大小 Excepted PCR product size(bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NBS2-Q-F | CTGCTAATGTACAGTGACCGA | NBS-LRR2基因qPCR检测 | 111 |
| NBS2-Q-R | AGTGACTGATCCTTCGGCAT | qPCR detection for NBS-LRR2 | |
| NBS4-Q-F | TGATCACGACCTTGCTTGTG | NBS-LRR4基因qPCR检测 | 122 |
| NBS4-Q-R | CTGACCTGTTGTTCGACGTC | qPCR detection for NBS-LRR4 | |
| HPT-F | ATTTGTGTACGCCCGACAGT | 鉴定HPT | 577 |
| HPT-R | GTGCTTGACATTGGGGAGTT | PCR detection for HPT | |
| NBS2Seq-01F | CCCAAGTGAGGATGCAAAACA | NBS-LRR2基因测序 | 803 |
| NBS2Seq-01R | TGACATGCAAGAAACGGGTG | Sequencing for NBS-LRR2 | |
| NBS2Seq-02F | TGGCTAGGCTTACGTTTTGG | NBS-LRR2基因测序 | 2219 |
| NBS2Seq-02R | ACAACGAAGAGTATGCAGACA | Sequencing for NBS-LRR2 | |
| NBS2Seq-03F | AGGATGTTACGGGTCTTGGA | NBS-LRR2基因测序 | 2107 |
| NBS2Seq-03R | AACAACTGCAGGCCAAACAA | Sequencing for NBS-LRR2 | |
| OsActin-F | ACCTTCAACACCCCTGCTAT | 内参基因OsActin qPCR检测 | 105 |
| OsActin-R | CACCATCACCAGAGTCCAAC | qPCR detection for OsActin (as internal standard) |
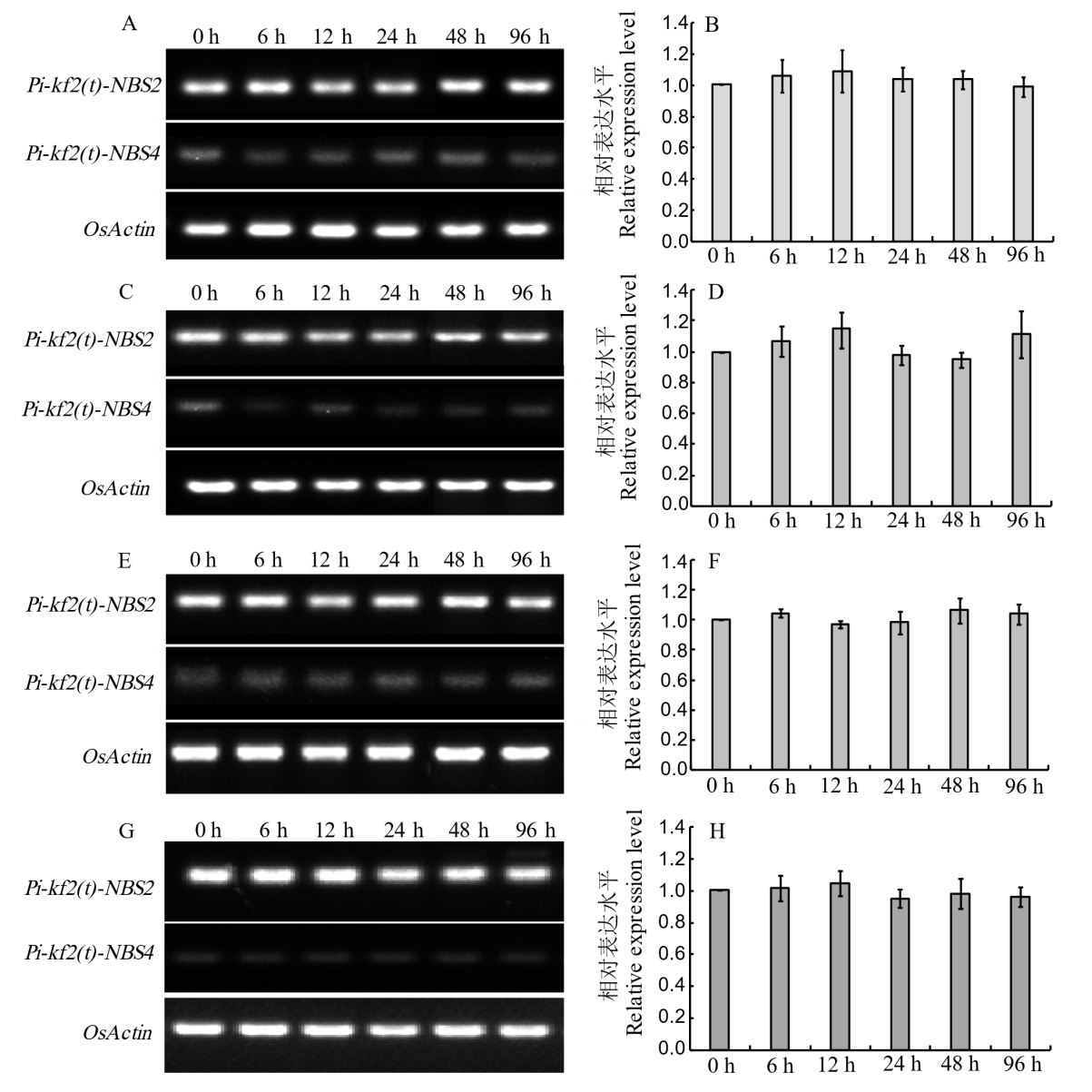
图2 Pi-kf2(t)候选基因的表达模式分析 A、C、E: 通过RT-PCR分析康丰B苗期叶片在接种稻瘟病菌株J71(A)、J91(C)和J93(E)后0、6、12、24、48和96 h候选基因Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2和Pi-kf2(t)-NBS4的表达模式;B、D、F: 通过qRT-PCR分析KFB苗期叶片在接种稻瘟病菌株J71(B)、J91(D)和J93(F)后0、6、12、24、48和96 h候选基因Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2的表达模式;G: 通过RT-PCR分析KFB苗期叶片在模拟接菌后0、6、12、24、48和96 h候选基因Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2和Pi-kf2(t)-NBS4的表达模式;H: 通过qRT-PCR分析KFB苗期叶片在模拟接菌后0、6、12、24、48和96 h候选基因Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2的表达模式。
Fig. 2. Expression pattern analysis of Pi-kf2(t) candidate gene A, C, E, Expression patterns of candidate genes Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2 and Pi-kf2(t)-NBS4 in KFB seedling leaves at 0, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 96 h after inoculation with the isolates J71(A), J91(C), and J93(E), determined by RT-PCR; B, D, F, Expression patterns of candidate genes Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2 in KFB seedling leaves at 0, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 96 h after inoculation with the isolates J71(B), J91(D), and J93(F), determined by qRT-PCR;G, Expression patterns of candidate genes Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2 and Pi-kf2(t)-NBS4 in KFB seedling leaves at 0, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 96 h after mock inoculation, determined by RT-PCR; H, The expression patterns of candidate genes Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2 in KFB seedling leaves at 0, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 96 h after mock inoculation, determined by qRT-PCR.

图3 Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2与Pi9、Pi2、Piz-t/Pizh、Pi50和Pigm氨基酸序列比对分析 深蓝色突出显示的是相同氨基酸,粉红色和淡蓝色突出显示的是相似氨基酸,红色矩形表示LRR区域富含亮氨酸重复(xxLxLxx)基序。
Fig. 3. Amino-acid sequences alignment of Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2 with Pi9, Pi2, Piz-t/Pizh, Pi50, and Pigm Dark blue highlights identical residues, while similar residues are marked in pink or light blue, and red rectangles indicate the xxLxLxx motifs of LRR domain.
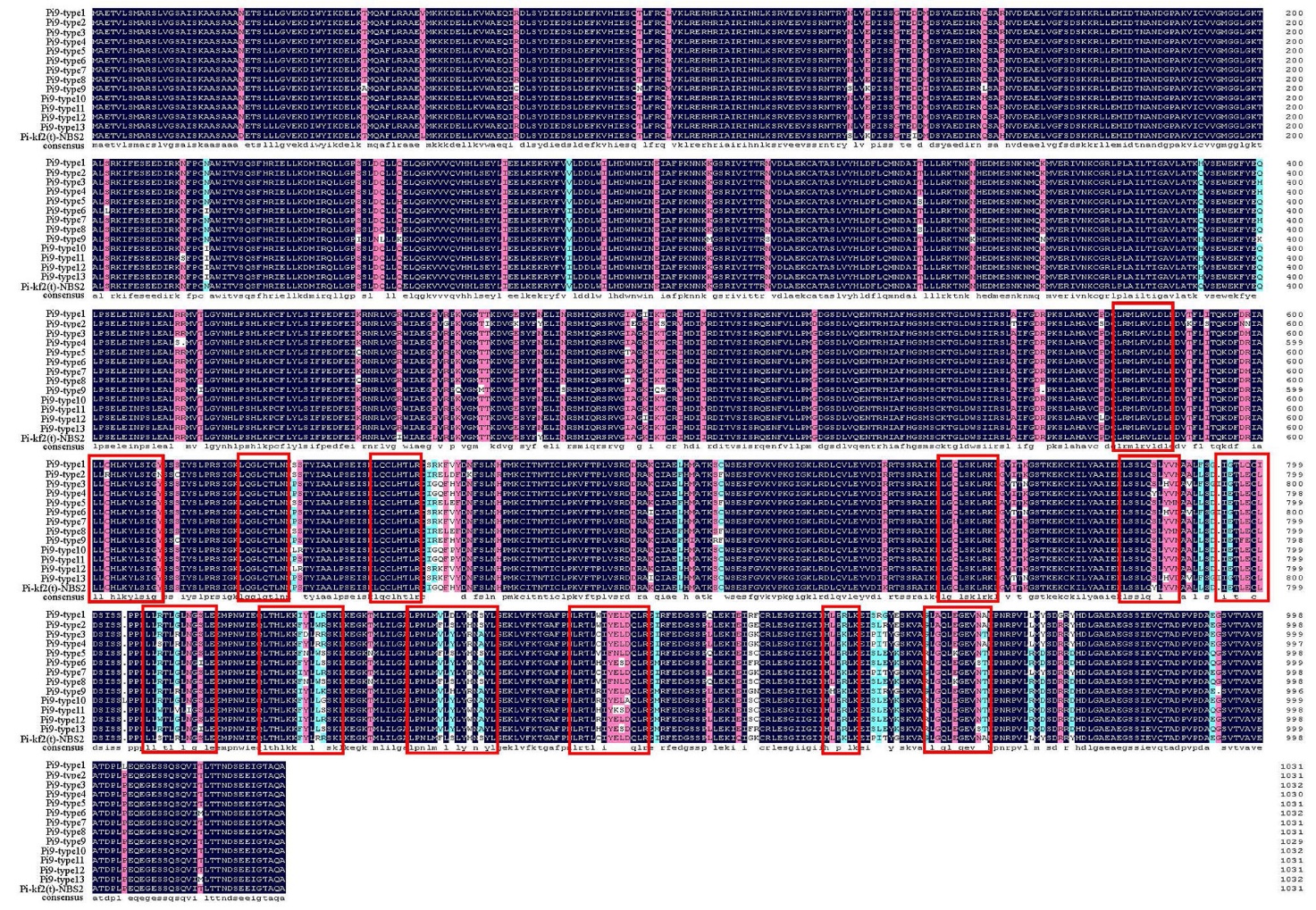
图4 Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2与Pi9-type1~Pi9-type13氨基酸序列比对分析 深蓝色突出显示的是相同氨基酸,粉红色和淡蓝色突出显示的是相似氨基酸,红色矩形表示LRR区域富含亮氨酸重复(xxLxLxx)基序。
Fig. 4. Amino-acid sequences alignment of Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2 with Pi9-type1-Pi9-type13 Dark blue highlights identical residues, while similar residues are marked in pink or light blue, and red rectangles indicate the xxLxLxx motifs of LRR domain.
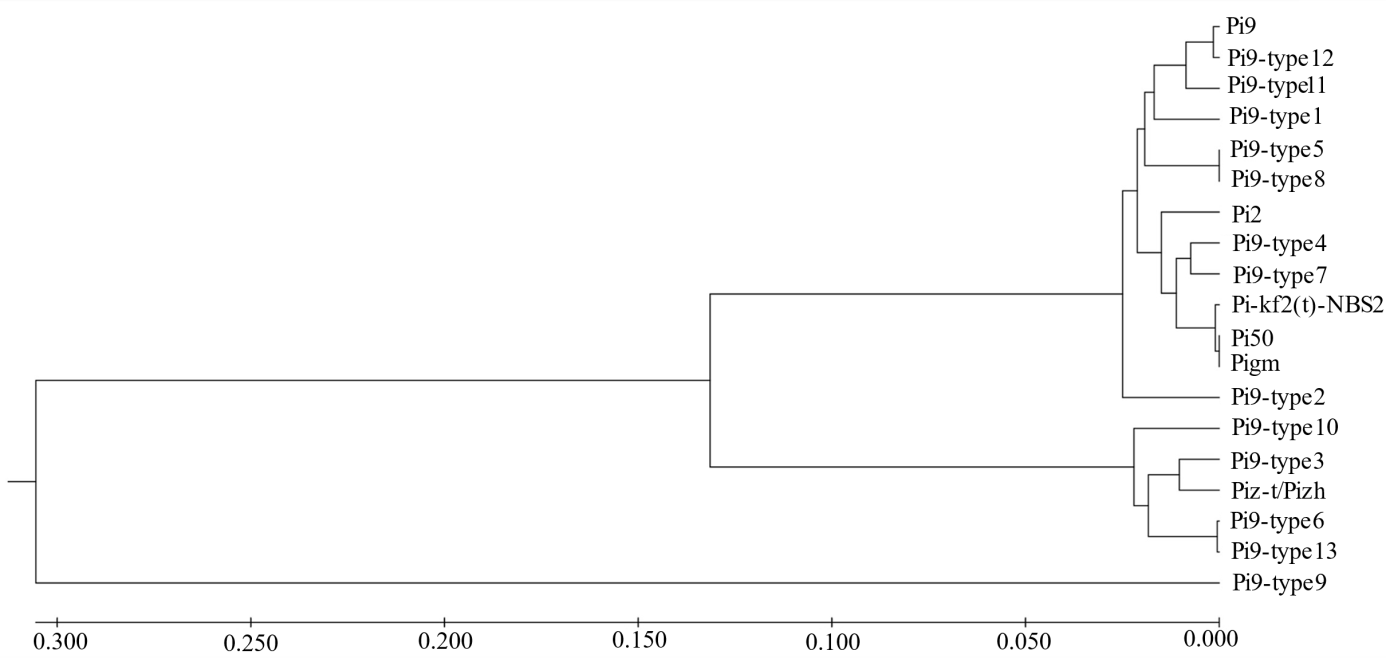
图5 Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2与Pi9、Pi2、Piz-t/Pizh、Pi50、Pigm和Pi9-type1~Pi9-type13蛋白序列系统进化树分析
Fig. 5. A phylogenetic tree representing the alignment of Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2 and protein sequences of Pi9, Pi2, Piz-t/Pizh, Pi50, Pigm, and Pi9-type1-Pi9-type13
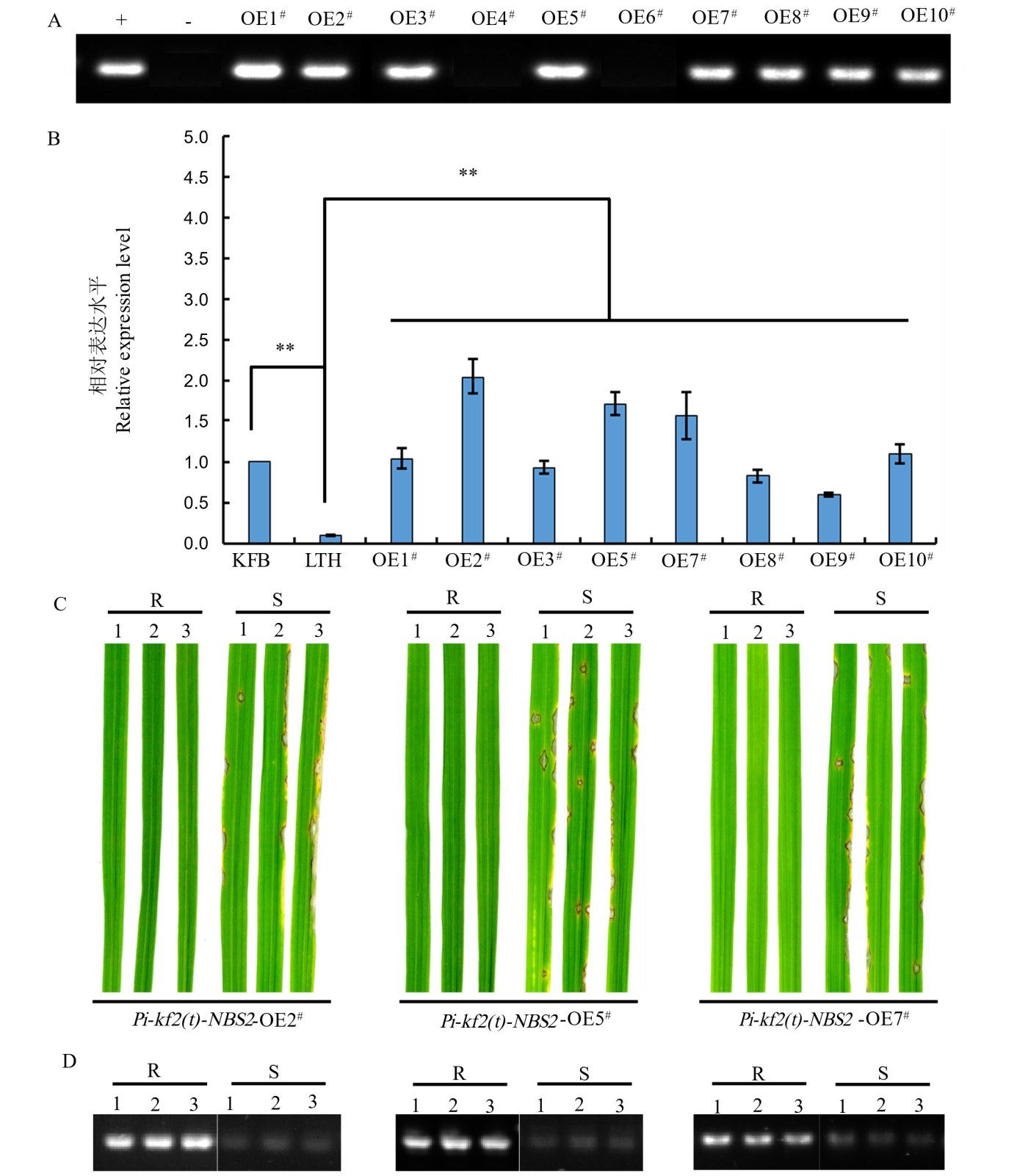
图6 候选基因Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2的功能验证 A: 利用潮霉素抗性标记引物HPT-F/R鉴定T0代阳性转基因单株,其中“+”和“−”分别表示阳性对照和阴性对照;B: qRT-PCR分析过表达转基因株系中候选基因Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2的表达水平,其中“**”代表在0.01水平上的极显著差异,误差线表示标准差(SD);C: 过表达转基因株系T1代单株接种稻瘟病菌株(J71,J91和J93)的抗性反应,其中“R”和“S”分别代表抗病和感病,Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2-OE2#、Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2-OE5#和Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2-OE7#株系分别接种稻瘟病菌株J71、J91和J93;D: RT-PCR分析T1代转基因株系单株中候选基因Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2的表达。
Fig. 6. Functional verification of candidate gene Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2 A, PCR identification of the positive transgenic plants in the overexpressed lines of T0 generation with HPT-F/R, where “+” and “−” indicate the positive control and negative control, respectively; B, Expression levels of Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2 candidate gene in the overexpressed transgenic lines, determined by qRT-PCR, where “**” indicates significant differences at 0.01 level and error bars represent the standard deviation (SD); C, Reaction of T1 transgenic lines inoculated with the isolates J71, J91, and J93, where “R” and “S” represent resistance and susceptibility to rice blast, respectively. Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2-OE2#, Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2-OE5#, and Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2-OE7# were inoculated with isolates J71, J91, and J81, respectively; D, Expression analysis of Pi-kf2(t)-NBS2 candidate gene in the individual plant of T1 transgenic lines, determined by RT-PCR.
| [1] | Valent B, Chumley F G. Molecular genetic analysis of the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 1991, 29: 443-467. |
| [2] | Oliveira-Garcia E, Yan X, Oses-Ruiz M, de Paula S, Talbot N J. Effector-triggered susceptibility by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. The New Phytologist, 2024, 241(3): 1007-1020. |
| [3] | 杨婕, 杨长登, 曾宇翔, 侯雨萱, 陈天晓, 梁燕. 水稻稻瘟病抗性基因挖掘与利用研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 5: 591-603. |
| Yang J, Yang C D, Zeng Y X, Hou Y X, Chen T X, Liang Y. Research progress on mining and utilization of rice blast resistance genes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2024, 38(6): 591-603. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 殷得所, 夏明元, 李进波, 万丙良, 查中萍, 杜雪树, 戚华雄. 抗稻瘟病基因Pi9的STS连锁标记开发及在分子标记辅助育种中的应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(1): 2: 25-30. |
| Yin D S, Xia M Y, Li J B, Wan B L, Zha Z P, Du X S, Qi H X. Development ofof STS marker linked to rice blast resistance gene Pi9 in marker-assisted selection breeding[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(1): 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Zhu X Y, Chen S, Yang J Y, Zhou S C, Zeng L X, Han J L, Su J, Wang L, Pan Q H. The identification of Pi50(t), a new member of the rice blast resistance Pi2/Pi9 multigene family[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2012, 124: 1295-1304. |
| [6] | Hulbert S H W, Webb C A S, Smith S M S, Sun Q. Resistance gene complexes: E: Evolution and utilization[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2001, 39:285-312. |
| [7] | 华丽霞, 汪文娟, 陈深, 汪聪颖, 曾烈先, 杨健源, 朱小源, 苏菁. 抗稻瘟病Pi2/9/z-t基因特异性分子标记的开发[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(3): 3: 305-310. |
| Hua L X, Wang W J, Chen S, Wang C Y, Zeng L X, Yang J Y, Zhu X Y, Su J. Development of specific DNA markers for detecting the rice blast resistance gene alleles Pi2/9/z-t[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2015, 29(3): 305-310. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Deng Y W, Zhu X D, Shen Y, He Z H. Genetic characterization and fine mapping of the blast resistance locus Pigm(t) tightly linked to Pi2 and Pi9in a broad-spectrum resistant Chinese variety[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 113(4): 705-713. |
| [9] | Wang Z X, Yano M, Yamanouchi U, Iwamoto M, Monna L, Hayasaka H, Katayose Y, Sasaki T. The Pib gene for rice blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes[J]. The Plant Journal, 1999, 19(1): 55-64. |
| [10] | Qu S L, Liu G Z, Zhou B, Bellizzi M Z, Zeng L D, Dai L H, Han B W, Wang G L. The broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a multigene family in rice[J]. Genetics, 2006, 172(3): 1: 1901-1914. |
| [11] | Hassan B, Peng Y T, Li S, Yin X X, Chen C, Gulzar F, Zhou S X, Pu M, Ji Y P, Wang Y P, Zhao W S, Huang F, Peng Y L, Zhao Z X, Wang W M. Identification of the blast resistance genes in three elite restorer lines of hybrid rice[J]. Phytopathology Research, 2022, 4(1): 15. |
| [12] | Martin G B, Bogdanove A J, Sessa G. Understanding the functions of plant disease resistance proteins[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2003, 54: 23-61. |
| [13] | Belkhadir Y, Subramaniam R, Dangl J L. Plant disease resistance protein signaling: NBS-LRR proteins and their partners[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2004, 7(4): 391-399. |
| [14] | Zhou B Q, Qu S H L, Liu G F D, Dolan M S, Sakai H L, Lu G D, Bellizzi M W, Wang G L. The eight amino-acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2006, 19( 11):1216-1228. |
| [15] | Tamura M, Tachida H. Evolution of the number of LRRs in plant disease resistance genes[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2011, 285(5): 393-402. |
| [16] | Dodds P N L, Lawrence G J E, Ellis J G. Six amino acid changes confined to the leucine-rich repeat beta-strand/beta-turn motif determine the difference between the P and P2 rust resistance specificities in flax[J]. The Plant Cell, 2001, 13(1):163-178. |
| [17] | Wu J L, Fan Y Y, Li D B, Zheng K L, Leung H, Zhuang J Y. Genetic control of rice blast resistance in the durably resistant cultivar Gumei 2 against multiple isolates[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2005, 111(1): 50-56. |
| [18] | Jeung J U, Kim B R, Cho Y C, Han S S, Moon H P, Lee Y T, Jena K K. A novel gene, Pi40(t), linked to the DNA markers derived from NBS-LRR motifs confers broad spectrum of blast resistance in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2007, 115(8): 1163-1177. |
| [19] | Jiang N, Li Z Q, Wu J, Wang Y, Wu L Q, Wang S H, Wang D, Wen T, Liang Y, Sun P Y, Liu J L, Dai L Y, Wang Z L, Wang C, Luo M Z, Liu X L, Wang G L. Molecular mapping of the Pi2/9 allelic genePi2-2 conferring broad-spectrum resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae in the rice cultivar Jefferson[J]. Rice, 2012, 5(1): 29. |
| [20] | Su J, Wang W J, Han J L, Chen S, Wang C Y, Zeng L X, Feng A Q, Yang J Y, Zhou B, Zhu X Y. Functional divergence of duplicated genes results in a novel blast resistance gene Pi50 at the Pi2/9 locus[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2015, 128(11): 2213-2225. |
| [21] | Deng Y W, Zhai K R, Xie Z, Yang D Y, Zhu X D, Liu J Z, Wang X, Qin P, Yang Y Z, Zhang G M, Li Q, Zhang J F, Wu S Q, Milazzo J, Mao B Z, Wang E, Xie H A, Tharreau D, He Z H. Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328): 962-965. |
| [22] | Xie Z Y, Yan B X S, Shou J Y T, Tang J W, Wang X Z, Zhai K R L, Liu J Y L, Li Q L, Luo M Z D, Deng Y W H, He Z H. A nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat receptor pair confers broad-spectrum disease resistance through physical association in rice[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B-Biological Sciences, 2019,374(1767): 20180308. |
| [23] | Lü Q M, Xu X, Shang J J, Jiang G H, Pang Z Q, Zhou Z Z, Wang J, Liu Y, Li T, Li X B, Xu J C, Cheng Z K, Zhao X F, Li S G, Zhu L H. Functional analysis of Pid3-A4, an ortholog of rice blast resistance gene Pid3 revealed by allele mining in common wild rice[J]. Phytopathology, 2013, 103: 594-599. |
| [24] | Zhou Y, Lei F, Wang Q, He W C, Yuan B, Yuan W Y. Identification of novel alleles of the rice blast-resistance gene Pi9 through sequence-based allele mining[J]. Rice, 2020, 13: 80. |
| [25] | Li L Y W, Wang L J, Jing J X L, Li Z Q L, Lin F H, Huang L F P, Pan Q H. The Pikm gene, c, conferring stable resistance to isolates of Magnaporthe oryzae,was finely mapped in a crossover-cold region on rice chromosome 11[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2007, 20:179-188. |
| [26] | Kovi B, Sakai T, Abe A, Kanzaki E, Terauchi R, Shimizu M. Isolation of Pikps, an allele of Pik, from the aus rice cultivar Shoni[J]. Genes and Genetic Systems, 2023, 97(5): 229-235. |
| [27] | 黄衍焱, 李燕, 王贺, 王文明. 水稻小种特异性抗稻瘟病基因的等位性变异研究进展[J]. 植物病理学报, 2023, 53(5):753-768. |
| Huang Y Y L, Li Y W, Wang H W, Wang W M, Allelic variation in the race-specific blast resistance genes in rice[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2023, 53(5):753-768. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Rybka K M, Miyamoto M A, Ando I S, Saito A K, Kawasaki S. High resolution mapping of the indica-derived rice blast resistance genes:II. Pi-ta2 and Pi-ta and a consideration of their origin[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 1997, 10(4):517-524. |
| [29] | Liu X Q, Yang Q Z, Lin F, Hua L X, Wang C T, Wang L, Pan Q H. Identification and fine mapping of Pi39(t), a major gene conferring the broad-spectrum resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2007, 278(4): 403-410. |
| [30] | 吴俊, 刘雄伦, 戴良英, 王国梁. 水稻广谱抗稻瘟病基因研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2007, 19(2):233-238. |
| Wu J, Liu X L, Dai L Y, Wang G L. Advances on the identification and characterization of broad-spectrum blast resistance genes in rice[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Science, 2007, 19(2): 233-238. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Sallaud C, Lorieux M, Roumen E, Tharreau D, Berruyer R, Svestasrani P, Garsmeur O, Ghesquiere A, Notteghem J L. Identification of five new blast resistance genes in the highly blast-resistant rice variety IR64 using a QTL mapping strategy[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2003, 106: 794-803. |
| [32] | Liu B, Zhang S H, Zhu X Y, Yang Q Y, Wu S Z, Mei M T, Mauleon R, Leach J, Mew T, Leung H. Candidate defense genes as predictors of quantitative blast resistance in rice[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2004, 17: 1146-1152. |
| [33] | 韦新宇, 许旭明, 张锐, 陈美莲, 马彬林, 邹文广, 杨旺兴, 卓伟, 王宗华, 梁康迳. 籼粳交新种质康丰A对稻瘟病抗性的遗传[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2014, 15(5):1133-1137. |
| Wei X Y, Xu X M, Zhang R, Chen M L, Ma B L, Zou W G, Yang W X, Zhuo W, Wang Z H, Liang K J. Inheritance of blast resistance in new germplasm Kangfeng A from indica-japonica crosses[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2014, 15(5):1133-1137. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | Wei X Y Z, Zeng Y H Z, Zhang R H, Huang J H Y, Yang W X Z, Zou W G X, Xu X M. Fine mapping and identification of the rice blast-resistance locus Pi-kf2(t) as a new member of the Pi2/Pi9 multigene family[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2019,39:108. |
| [35] | Bonman J M, Khush G S, N, Nelson R J. Breeding rice for resistance to pests[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 1992, 30:507-528. |
| [36] | 韦新宇, 曾跃辉, 杨旺兴, 肖长春, 候新坡, 黄建鸿, 邹文广, 许旭明. 利用CRISPR-Cas9技术编辑Badh2基因创制优质香型籼稻三系不育系[J]. . 作物学报, 2023, 49(8):2144-2159. |
| Wei X Y, Zeng Y H, Yang W X, Xiao C C, Hou X P, Huang J H, Zou W G, Xu X M. Development of high-quality fragrant indica CMS line by editing Badh2 gene using CRISPR-Cas9 technology in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 49(8):2144-2159. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Zeng Y H, Wei X Y, Xiao C C, Zhang R, Huang J H, Xu X M. Fine mapping and identification of a novel albino gene OsAL50 that is required for chlorophyll biosynthesis and chloroplast development in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2024, 103(2):389-407. |
| [38] | 曾跃辉, 韦新宇, 黄建鸿, 肖长春, 张锐, 尚伟, 许旭明. 不同来源特种稻香味和黑色种皮基因的鉴定与遗传特性分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2021, 22(4):951-962. |
| Zeng Y H, Wei X Y, Huang J H, Xiao C C, Zhang R, Shang W, Xu X M. Identification and genetic analysis of the genes for fragrance and black pericarp in special rice from different regions[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2021, 22(4):951-962. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 陈深, 苏菁, 华丽霞, 汪文娟, 汪聪颖, 杨健源, 曾烈先, 朱小源. 水稻恢复系华占抗稻瘟病遗传分析及基因鉴定[J]. 植物病理学报, 2015, 45(6):598-605. |
| Chen S, Su J, Hua L X, Wang W J, Wang C Y, Yang J Y, Zeng L X, Zhu X Y. Genetic analysis and gene identification of restorer line Huazhan against rice blast[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2015, 45(6):598-605. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | Ellis J, Dodds P, Pryor T. The generation of plant disease resistance gene specificities[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2000, 5(9):373-379. |
| [1] | 朱鹏, 凌溪铁, 王金彦, 张保龙, 杨郁文, 许轲, 裘实. 机直播条件下不同控草方式对抗除草剂水稻产量和品质差异性研究 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 501-515. |
| [2] | 董立强, 张义凯, 杨铁鑫, 冯莹莹, 马亮, 梁潇, 张玉屏, 李跃东. 北方粳稻密苗机插育秧对秧苗素质及取秧特性的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 516-528. |
| [3] | 周洋, 叶凡, 刘立军. 典型促生微生物提高盐胁迫水稻抗性的研究进展 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 529-542. |
| [4] | 朱建平, 李霞, 李文奇, 许扬, 王芳权, 陶亚军, 蒋彦婕, 陈智慧, 范方军, 杨杰. 水稻粉质胚乳突变体we1的表型分析与基因定位 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 543-551. |
| [5] | 黄福灯, 吴春艳, 郝媛媛, 韩一飞, 张小斌, 孙会锋, 潘刚. 不同氮肥水平下水稻倒二叶叶鞘的转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 563-571. |
| [6] | 卢椰子, 邱结华, 蒋楠, 寇艳君, 时焕斌. 稻瘟病菌效应子研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 287-294. |
| [7] | 王超瑞, 周宇琨, 温雅, 张瑛, 法晓彤, 肖治林, 张耗. 秸秆还田方式对稻田土壤特性和温室气体排放的影响及其水肥互作调控[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 295-305. |
| [8] | 王雅宣, 王新峰, 杨后红, 刘芳, 肖晶, 蔡玉彪, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊. 稻飞虱适应水稻抗性机制的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 306-321. |
| [9] | 黄涛, 魏兆根, 陈玘, 程泽, 刘欣, 王广达, 胡珂鸣, 谢文亚, 陈宗祥, 冯志明, 左示敏. 水稻类病斑突变体lm52的基因克隆及其广谱抗病性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 322-330. |
| [10] | 马顺婷, 胡运高, 高方远, 刘利平, 牟昌铃, 吕建群, 苏相文, 刘松, 梁毓玉, 任光俊, 郭鸿鸣. 水稻真核翻译起始因子OseIF6.2调控粒型的功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 331-342. |
| [11] | 张彬涛, 刘聪聪, 郭明亮, 杨绍华, 吴世强, 郭龙彪, 朱义旺. 水稻OsDR8基因的稻瘟病抗性评价及优异单倍型鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 343-351. |
| [12] | 李文奇, 许扬, 王芳权, 朱建平, 陶亚军, 李霞, 范方军, 蒋彦婕, 陈智慧, 杨杰. 广谱抗稻瘟病基因PigmR的KASP标记开发及应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 365-372. |
| [13] | 韦还和, 汪璐璐, 马唯一, 张翔, 左博源, 耿孝宇, 朱旺, 朱济邹, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 戴其根. 盐−旱复合胁迫下粳稻品种南粳9108籽粒灌浆特性及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 373-386. |
| [14] | 沈智达, 余秋华, 张斌, 曹玉东, 王少华, 王红飞, 伍永清, 戴志刚, 李小坤. 磷肥施用量对湖北省直播水稻产量、磷素积累及利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 399-411. |
| [15] | 何勇, 张诗骞, 王志成, 詹逍康, 丁一可, 刘晓瑞, 马素素, 田志宏. 印度梨形孢与复合肥组合施用对水稻机插秧秧苗素质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 412-422. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||