
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 16-28.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220503
裴峰1, 王广达1, 高鹏1, 冯志明1,2, 胡珂鸣1,2, 陈宗祥1,2, 陈红旗3, 崔傲4, 左示敏1,2,5( )
)
收稿日期:2022-05-06
修回日期:2022-07-31
出版日期:2023-01-10
发布日期:2023-01-10
通讯作者:
左示敏
基金资助:
PEI Feng1, WANG Guangda1, GAO Peng1, FENG Zhiming1,2, HU Keming1,2, CHEN Zongxiang1,2, CHEN Hongqi3, CUI Ao4, ZUO Shimin1,2,5( )
)
Received:2022-05-06
Revised:2022-07-31
Online:2023-01-10
Published:2023-01-10
Contact:
ZUO Shimin
摘要: 目的 探究在粳稻中敲除OsNramp5基因对镉等金属元素积累、产量和品质的影响,为科学高效地生产优质健康粳米提供新材料和理论参考。方法 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术,在优良食味高产粳稻品种南粳46背景下对OsNramp5进行基因敲除,结合标记辅助选择,获得了无外源基因的OsNramp5敲除突变系,考查其产量和品质性状变化特征,以及在不同镉含量土壤中和锌肥、硒肥喷施后的籽粒镉、锰、硒等七种金属元素的含量变化。结果 在T0代获得了5种OsNramp5不同变异类型的转基因植株,设计开发了其中3种突变型的特异分子标记,进而结合标记辅助选择,在各植株的T2代中获得不含潮霉素选择标记基因和CAS9蛋白基因的纯合敲除系。与野生型相比,无论在高浓度还是低浓度镉含量土壤中,敲除系整株包括籽粒中的镉含量和地上部组织中锰含量均显著低于南粳46;敲除系的株高略微下降,穗粒数显著降低并导致其单株产量明显下降,但在低分蘖肥处理中产量下降未达显著。敲除系稻米外观总体好于对照,蛋白质和直链淀粉含量明显高于对照,导致其食味值明显降低。敲除系籽粒中铜、锰和硒的含量显著低于对照,但在施用锌肥和硒肥后可以显著提高锌和硒的含量,同时有利于进一步降低籽粒镉的含量。施硒有利于改善稻米外观但施锌则相反,喷施两种肥料都会降低稻米食味值,不利于食味品质提升。敲除系在极端高/低温条件下的结实率变化与对照无异,但对纹枯病的抗性显著降低。结论 在优质高产粳稻品种中获得了无标记OsNramp5基因敲除系,证明其在生产低镉富硒富锌安全营养健康型稻米中具有重要价值,但在产量和食味品质上则有不同程度的下降。
裴峰, 王广达, 高鹏, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 陈红旗, 崔傲, 左示敏. 敲除OsNramp5基因创制低镉优质粳稻新材料的应用评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 16-28.
PEI Feng, WANG Guangda, GAO Peng, FENG Zhiming, HU Keming, CHEN Zongxiang, CHEN Hongqi, CUI Ao, ZUO Shimin. Evaluation of New japonica Rice Lines with Low Cadmium Accumulation and Good Quality Generated by Knocking Out OsNramp5[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 16-28.
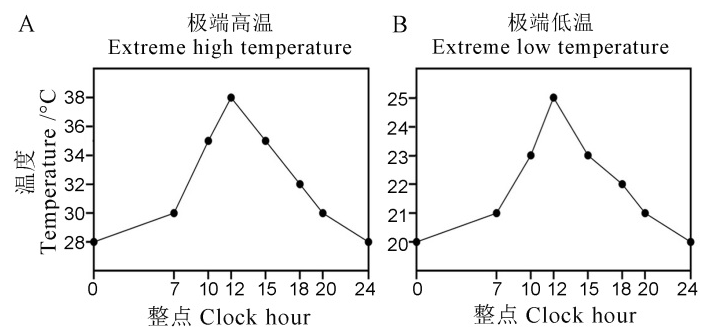
图1 极端温度条件的温度变化曲线 A―极端高温的日温度变化曲线;B―极端低温的日温度变化曲线。
Fig. 1. Temperature curves for extreme temperature conditions. A, Diurnal temperature curve of extreme high temperature; B, Diurnal temperature curve of extreme low temperature.
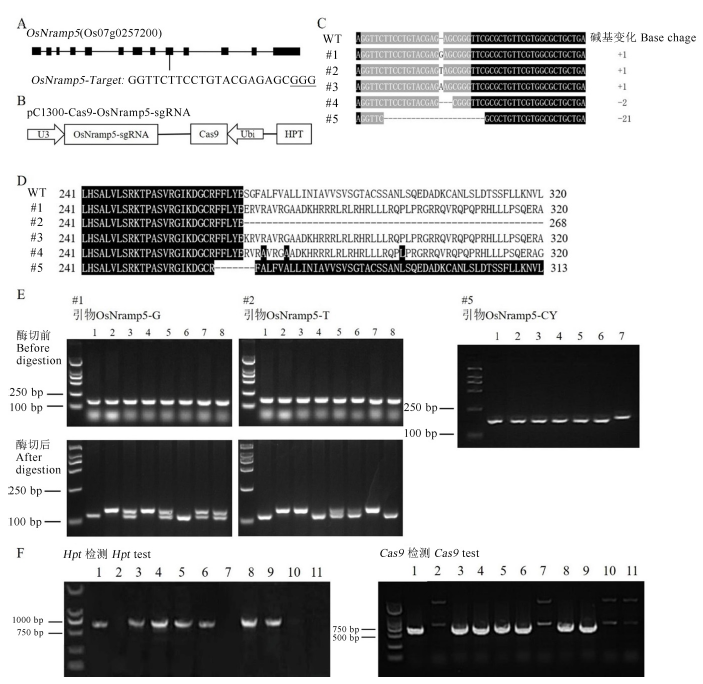
图2 OsNramp5敲除系的构建和基因型检测 A―靶点序列在OsNramp5上的位置。B―pC1300-Cas9-OsNramp5-sgRNA表达载体的结构。C―T0代植株与野生型的基因序列比对分析。黑色阴影为相同序列,灰色阴影为靶点序列,“+”表示插入,“-”表示缺失,“WT”表示野生型。D―T0代植株与野生型的氨基酸比对分析。序列左侧和右侧数字表示该氨基酸序列在蛋白中的位置;黑色阴影为与野生型相同序列,“-”表示缺失,“WT”表示野生型。E―各突变型的特异分子标记开发及PCR检测。图上方分别标注有检测的家系号和使用的特异PCR标记名称;#1和#2号系均是开发的CAPS标记,泳道1为经过测序确认的纯合突变型,泳道2为野生型,泳道3-8分别表示T2世代的不同单株,其中双带表示杂合基因型;#5号系开发的是InDel标记,电泳图中泳道1-6为纯合突变型,泳道7为野生型;使用的分子量标记为DL 2000(下同)。F―部分纯合突变型株系的转基因成分检测。泳道1和2分别为阳性和阴性对照,泳道3~11为不同株系的检测结果,其中泳道7、10和11分别对应nramp5ko-1、-2和-3。
Fig. 2. Construction and genotyping of OsNramp5 knockout lines. Note: (A) Position of the target sequence in OsNramp5; (B) Construction of the vector of pC1300-Cas9-OsNramp5-sgRNA;(C) Comparative analysis of gene sequences between T0 generation plants and wild type. Black shadows represent the same sequences, gray shadows represent the target sequence, ‘+’ Insertion, ‘-’ Deletion, ‘WT’ Wild type;(D) Comparative analysis of amino acids between T0 generation plants and wild type. The numbers to the left and right of the sequence indicate the position of the amino acid sequence in the protein. The black shadows represent the same sequences as the wild type, ‘-’ Deletion, ‘WT’ Wild type ;(E) Development of molecular markers specific to three different variants lines. Different mutant lines and their specific markers were marked at the top of the figure. CAPS markers were developed for mutant lines #1 and #2, and in their electrophoretic picture, the lane 1 represents homozygous mutant that was confirmed by sequencing. The lane 2 indicates the wild type and remaining lanes 3~8 represent different individual plants from T2 population. InDel marker was developed for genotyping mutant lines #5, and the lane 7 and the remaining lanes indicate wild type and different individual T2 plants, respectively. DL 2000 was used as the molecular marker (Same as below). (F) Detection of transgenic components for some homozygous mutant plant lines. Lanes 1 and 2 are positive and negative controls, respectively. Lanes 3~11 represent different homozygous mutant plant lines, and among them, lanes 7, 10 and 11 correspond to nramp5ko-1, -2 and -3 respectively.
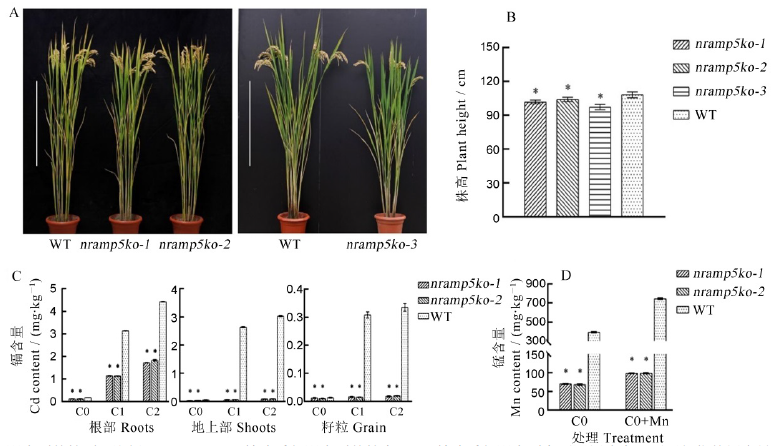
图3 OsNramp5敲除系植株的株型及镉和锰的含量分析 A―敲除系与野生型的株型。比例尺=50 cm;B―敲除系与野生型的株高;C―敲除系与野生型在不同镉浓度下不同部位的镉含量。C0为对照,C1为1.2 mg/kg外源镉,C2为2.0 mg/kg外源镉;D―敲除系与野生型在不同处理下地上部的锰含量。C0为对照,C0+Mn为喷施锰肥处理。数据为平均数±标准差(n=3)。*代表与WT有显著性差异(P<0.05)(t检验)。
Fig. 3. Whole plant and analysis of cadmium and manganese contents in OsNramp5 knockout lines. A,Whole plant of the wild type and homozygous mutant lines. Scale = 50 cm. B, Plant height of knockout lines and wild type. C, Cadmium content in different parts of knockout lines and wild type under different cadmium concentrations. ‘C0’,control; ‘C1’, 1.2 mg/kg cadmium; ‘C2’, 2.0 mg/kg cadmium; D, Manganese content in shoots of knockout lines and wild type under different treatments. ‘C0’, control; ‘C0+Mn’, spraying manganese fertilizer treatment. Data are shown as means ± SD(n=3). * represent a significant difference from WT (P<0.05) (t-test).
| 分蘖肥处理 Tillering fertilizer level | 株系 Line | 有效穗 Effective panicle | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/ % | 千粒重 1000-grain weight / g | 理论产量Theoretical yield/(kg·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低肥 Low (37.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 9.6±1.1 b | 125.4±3.9 e | 96.12±0.96 a | 24.36±0.15 bc | 8541.75 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 9.9±2.1 ab | 123.2±3.3 e | 96.59±0.98 a | 24.47±0.47 abc | 8735.70 | |
| WT | 7.8±1.1 c | 156.0±4.9 b | 95.71±0.95 a | 24.82±0.05 a | 8759.25 | |
| 正常 Normal (112.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 9.9±1.1 ab | 138.4±1.9 cd | 91.27±1.43 c | 24.42±0.03 abc | 9254.10 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 9.6±1.9 b | 141.4±2.1 cd | 92.69±1.73 bc | 24.41±0.07 abc | 9306.90 | |
| WT | 9.9±1.6 ab | 163.8±4.2 a | 95.44±0.77 a | 24.73±0.04 ab | 11 598.15 | |
| 高肥 High (187.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 11.2±1.0 a | 137.0±1.7 d | 92.15±2.60 bc | 23.02±0.08 d | 9863.40 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 11.1±1.8 ab | 141.8±2.3 c | 91.33±3.39 c | 23.19±0.03 d | 10 101.75 | |
| WT | 10.8±1.6 ab | 165.2±3.2 a | 93.52±1.23 b | 24.23±0.09 c | 12 251.25 |
表1 OsNramp5敲除系与对照在不同分蘖肥处理间的理论产量及其构成因素比较
Table 1. Comparison of theoretical yield and its components between OsNramp5 knockout lines and control at different tillering fertilizer levels.
| 分蘖肥处理 Tillering fertilizer level | 株系 Line | 有效穗 Effective panicle | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/ % | 千粒重 1000-grain weight / g | 理论产量Theoretical yield/(kg·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低肥 Low (37.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 9.6±1.1 b | 125.4±3.9 e | 96.12±0.96 a | 24.36±0.15 bc | 8541.75 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 9.9±2.1 ab | 123.2±3.3 e | 96.59±0.98 a | 24.47±0.47 abc | 8735.70 | |
| WT | 7.8±1.1 c | 156.0±4.9 b | 95.71±0.95 a | 24.82±0.05 a | 8759.25 | |
| 正常 Normal (112.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 9.9±1.1 ab | 138.4±1.9 cd | 91.27±1.43 c | 24.42±0.03 abc | 9254.10 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 9.6±1.9 b | 141.4±2.1 cd | 92.69±1.73 bc | 24.41±0.07 abc | 9306.90 | |
| WT | 9.9±1.6 ab | 163.8±4.2 a | 95.44±0.77 a | 24.73±0.04 ab | 11 598.15 | |
| 高肥 High (187.5 kg/hm2) | nramp5ko-1 | 11.2±1.0 a | 137.0±1.7 d | 92.15±2.60 bc | 23.02±0.08 d | 9863.40 |
| nramp5ko-2 | 11.1±1.8 ab | 141.8±2.3 c | 91.33±3.39 c | 23.19±0.03 d | 10 101.75 | |
| WT | 10.8±1.6 ab | 165.2±3.2 a | 93.52±1.23 b | 24.23±0.09 c | 12 251.25 |
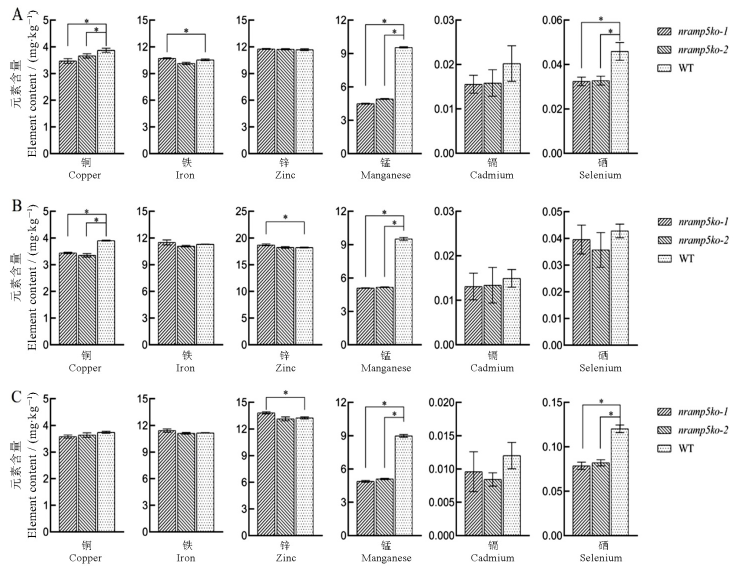
图4 三种施肥处理下OsNramp5敲除系和野生型籽粒中的元素含量 A、B和C分别是正常施肥、增施锌肥和增施硒肥条件下的籽粒中铜、铁、锌、锰、镉和硒元素的含量。数据为平均数±标准差(n=3)。 *代表连线之间具有显著性差异(P<0.05)(t检验)。
Fig. 4. Element contents in grains of OsNramp5 knockout lines and wild type under three fertilization treatments. A, B and C were contents of copper, iron, zinc, manganese, cadmium and selenium in grains under normal fertilization, zinc fertilization and selenium fertilization respectively. Data are shown as means ± SD(n=3). * represents significant differences between lines(P<0.05) (t-test).
| 施肥方式Fertilization treatment | 株系 Line | 糙米率 Brown rice rate /% | 精米率 Milled rice rate /% | 整精米率 Head milled rice rate /% | 垩白粒率 Chalky rice rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常 Conventional | nramp5ko-1 | 84.89±0.17 b | 72.20±0.50 b | 67.29±0.70 b | 6.6±0.2 f | 2.0±0.1 d |
| nramp5ko-2 | 85.12±0.27 ab | 73.44±1.97 ab | 67.31±1.59 b | 7.7±0.2 e | 1.9±0.1 d | |
| WT | 84.91±0.23 ab | 73.86±0.83 a | 69.49±0.74 ab | 8.7±0.1 c | 2.3±0.1 c | |
| 锌肥 +Zn | nramp5ko-1 | 84.91±0.29 ab | 71.95±0.39 b | 67.63±1.58 b | 9.4±0.3 b | 2.7±0.2 b |
| nramp5ko-2 | 84.95±0.08 ab | 72.92±0.86 ab | 67.61±1.15 b | 8.2±0.1 d | 2.5±0.1 bc | |
| WT | 84.82±0.26 b | 73.38±1.00 ab | 69.85±1.99 a | 11.8±0.2 a | 3.4±0.2 a | |
| 硒肥 +Se | nramp5ko-1 | 85.24±0.15 a | 73.10±1.69 ab | 67.72±1.17 b | 4.3±0.1 h | 1.1±0.1 e |
| nramp5ko-2 | 85.22±0.18 a | 72.53±0.26 ab | 67.66±2.85 b | 4.6±0.1 h | 1.2±0.1 e | |
| WT | 84.94±0.27 ab | 73.30±0.68 ab | 70.08±0.42 a | 5.5±0.2 g | 1.4±0.1 e |
表2 OsNramp5-ko敲除系在不同施肥处理中的稻米加工和品质相关指标差异比较
Table 2. Comparison of rice processing and quality related indexes of OsNramp5-ko knockout lines under different fertilization treatments.
| 施肥方式Fertilization treatment | 株系 Line | 糙米率 Brown rice rate /% | 精米率 Milled rice rate /% | 整精米率 Head milled rice rate /% | 垩白粒率 Chalky rice rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常 Conventional | nramp5ko-1 | 84.89±0.17 b | 72.20±0.50 b | 67.29±0.70 b | 6.6±0.2 f | 2.0±0.1 d |
| nramp5ko-2 | 85.12±0.27 ab | 73.44±1.97 ab | 67.31±1.59 b | 7.7±0.2 e | 1.9±0.1 d | |
| WT | 84.91±0.23 ab | 73.86±0.83 a | 69.49±0.74 ab | 8.7±0.1 c | 2.3±0.1 c | |
| 锌肥 +Zn | nramp5ko-1 | 84.91±0.29 ab | 71.95±0.39 b | 67.63±1.58 b | 9.4±0.3 b | 2.7±0.2 b |
| nramp5ko-2 | 84.95±0.08 ab | 72.92±0.86 ab | 67.61±1.15 b | 8.2±0.1 d | 2.5±0.1 bc | |
| WT | 84.82±0.26 b | 73.38±1.00 ab | 69.85±1.99 a | 11.8±0.2 a | 3.4±0.2 a | |
| 硒肥 +Se | nramp5ko-1 | 85.24±0.15 a | 73.10±1.69 ab | 67.72±1.17 b | 4.3±0.1 h | 1.1±0.1 e |
| nramp5ko-2 | 85.22±0.18 a | 72.53±0.26 ab | 67.66±2.85 b | 4.6±0.1 h | 1.2±0.1 e | |
| WT | 84.94±0.27 ab | 73.30±0.68 ab | 70.08±0.42 a | 5.5±0.2 g | 1.4±0.1 e |
| 施肥方式 Fertilization treatment | 株系 Line | 蛋白质含量 Protein content / % | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency /mm | 硬度Hardness | 黏度viscosity | 平衡度Balance | 食味值 Taste value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常 Conventional | nramp5ko-1 | 7.55±0.02 a | 9.35±0.00 d | 75.5±0.5 a | 6.1±0.1 a | 7.3±0.1 d | 7.3±0.1 e | 74.6±0.9 de |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.24±0.01 b | 9.87±0.00 c | 75.5±0.5 a | 5.8±0.0 c | 7.9±0.3 abc | 7.9±0.2 bcd | 77.9±1.4 bcd | |
| WT | 6.82±0.01 c | 10.20±0.04 b | 77.5±0.5 a | 5.6±0.0 d | 8.4±0.1 a | 8.4±0.1 a | 81.4±0.8 a | |
| 锌肥 +Zn | nramp5ko-1 | 7.30±0.00 b | 10.38±0.00 ab | 77.5±0.5 a | 5.9±0.1 bc | 8.2±0.2 ab | 8.2±0.3 ab | 79.8±1.9 ab |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.47±0.02 a | 10.60±0.08 a | 77.0±1.0 a | 5.9±0.1 bc | 8.1±0.2 ab | 8.0±0.1 abc | 78.5±1.0 abc | |
| WT | 6.89±0.04 c | 10.72±0.18 a | 78.5±0.5 a | 5.8±0.1 c | 7.7±0.3 bcd | 7.8±0.2 bcde | 77.3±1.7 bcde | |
| 硒肥 +Se | nramp5ko-1 | 7.22±0.04 b | 10.42±0.11 ab | 69.0±1.0 b | 6.0±0.2 ab | 7.4±0.5 cd | 7.4±0.5 de | 75.2±3.0 de |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.27±0.04 b | 10.53±0.15 ab | 69.5±1.5 b | 6.1±0.0 a | 7.4±0.2 cd | 7.3±0.1 e | 74.4±0.7 e | |
| WT | 7.25±0.02 b | 10.42±0.04 ab | 69.0±1.0 b | 5.9±0.0 bc | 7.5±0.1 cd | 7.5±0.0 cde | 75.8±0.2 cde |
表3 OsNramp5-ko敲除系在不同施肥处理中的稻米营养品质和食味品质相关指标差异比较
Table 3. Comparison of OsNramp5-ko knockout lines in rice nutritional quality and food quality indexes under different fertilization treatments.
| 施肥方式 Fertilization treatment | 株系 Line | 蛋白质含量 Protein content / % | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 胶稠度 Gel consistency /mm | 硬度Hardness | 黏度viscosity | 平衡度Balance | 食味值 Taste value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常 Conventional | nramp5ko-1 | 7.55±0.02 a | 9.35±0.00 d | 75.5±0.5 a | 6.1±0.1 a | 7.3±0.1 d | 7.3±0.1 e | 74.6±0.9 de |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.24±0.01 b | 9.87±0.00 c | 75.5±0.5 a | 5.8±0.0 c | 7.9±0.3 abc | 7.9±0.2 bcd | 77.9±1.4 bcd | |
| WT | 6.82±0.01 c | 10.20±0.04 b | 77.5±0.5 a | 5.6±0.0 d | 8.4±0.1 a | 8.4±0.1 a | 81.4±0.8 a | |
| 锌肥 +Zn | nramp5ko-1 | 7.30±0.00 b | 10.38±0.00 ab | 77.5±0.5 a | 5.9±0.1 bc | 8.2±0.2 ab | 8.2±0.3 ab | 79.8±1.9 ab |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.47±0.02 a | 10.60±0.08 a | 77.0±1.0 a | 5.9±0.1 bc | 8.1±0.2 ab | 8.0±0.1 abc | 78.5±1.0 abc | |
| WT | 6.89±0.04 c | 10.72±0.18 a | 78.5±0.5 a | 5.8±0.1 c | 7.7±0.3 bcd | 7.8±0.2 bcde | 77.3±1.7 bcde | |
| 硒肥 +Se | nramp5ko-1 | 7.22±0.04 b | 10.42±0.11 ab | 69.0±1.0 b | 6.0±0.2 ab | 7.4±0.5 cd | 7.4±0.5 de | 75.2±3.0 de |
| nramp5ko-2 | 7.27±0.04 b | 10.53±0.15 ab | 69.5±1.5 b | 6.1±0.0 a | 7.4±0.2 cd | 7.3±0.1 e | 74.4±0.7 e | |
| WT | 7.25±0.02 b | 10.42±0.04 ab | 69.0±1.0 b | 5.9±0.0 bc | 7.5±0.1 cd | 7.5±0.0 cde | 75.8±0.2 cde |
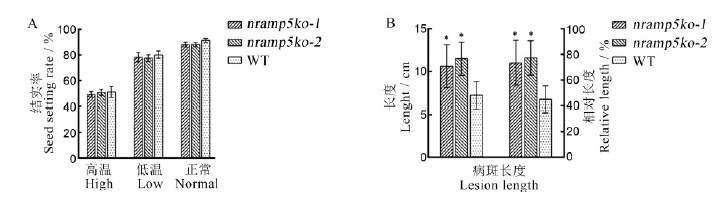
图6 OsNramp5敲除系在极端温度及纹枯病菌接种处理下与野生型的抗逆性差异 A―敲除系和野生型在极端高温和低温胁迫下的结实率;B―敲除系和野生型的离体接种纹枯病的发病情况。数据为平均数±标准差(n=3)。*代表与WT有显著性差异(P<0.05)(t检验)。
Fig 6. Stress resistance difference between OsNramp5 knockout lines and wild-type under extreme high and low temperature and rice sheath blight inoculation. A, Seed setting rate of knockout lines and wild type under extreme high and low temperature stress; B, Incidence of rice sheath blight of knockout lines and wild type after inoculation in vitro. Data are shown as means ± SD(n=3). * represents a significant difference from WT(P<0.05) (t-test).
| [1] | 陈璐, 刘黎瑶, 丛方地. 我国粮食安全的挑战性问题分析及应对策略探讨[J]. 粮油与饲料科技, 2021(6): 1-5. |
| Chen L, Liu L Y, Cong F D. Analysis on the challenging problems of China’s food security and discussion on the countermeasures[J]. Grain Oil and Feed Technology, 2021(6): 1-5. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 徐春春, 纪龙, 陈中督, 方福平. 2020年我国水稻产业形势分析及2021年展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2021, 27(2): 1-4. |
| Xu C C, Ji L, Chen Z D, Fang F P. Analysis of China’s rice industry in 2020 and the outlook for 2021[J]. China Rice, 2021, 27(2): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 陈印军, 方琳娜, 杨俊彦. 我国农田土壤污染状况及防治对策[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2014, 35(4): 1-5. |
| Chen Y J, Fang L N, Yang J Y. The cropland pollution in China: Status and countermeaures[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2014, 35(4): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 周启星, 宋玉芳. 污染土壤修复原理与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. |
| Zhou Q X, Song Y F. Principles and Methods of Contaminated Soil Remediation[M]. Beijing: China Science Press, 2004. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 宋伟, 陈百明, 刘琳. 中国耕地土壤重金属污染概况[J]. 水土保持研究, 2013, 20(2): 293-298. |
| Song W, Chen B M, Liu L. Soil heavey meatal pollution of cultivated land in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2013, 20(2): 293-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 蔡美芳, 李开明, 谢丹平, 吴仁人. 我国耕地土壤重金属污染现状与防治对策研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2014, 37(S2): 223-230. |
| Cai M F, Li K M, Xie D P, Wu R R. The status and protection strategy of farmland soils polluted by heavy metals[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 37(S2): 223-230. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] |
Bertin G, Averbeck D. Cadmium: Cellular effects, modifications of biomolecules, modulation of DNA repair and genotoxic consequences[J]. Biochimie, 2006, 88(11): 1549-1559.
PMID |
| [8] |
Nawrot T, Plusquin M, Hogervorst J, Roels H A, Staessen J A. Environmental exposure to cadmium and risk of cancer: A prospective population-based study[J]. Lancet Oncology, 2006, 7(2): 119-126.
PMID |
| [9] |
Kumar S, Sharma A. Cadmium toxicity: Effects on human reproduction and fertility[J]. Reviews on Environmental Health, 2019, 34(4): 327-338.
PMID |
| [10] | Genchi G, Sinicropi M S, Lauria G, Carocci A, Catalano A. The effects of cadmium toxicity[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(11): 3782. |
| [11] | Codex Alimentarius Commission, Joint FAO. Codex Alimentarius Commission: Procedural Manual[M]. Codex Alimentarius, 2007. |
| [12] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局.食品安全国家标准食品中污染物限量:GB 2762-2017[Z]. 2017: 24. |
| State Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration.National Food Safety Standard Limit of Pollutants in Food:GB 2762-2017[Z]. 2017: 24. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] |
Colangelo E P, Guerinot M L. Put the metal to the petal: metal uptake and transport throughout plants[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2006, 9(3): 322-330.
PMID |
| [14] | Xia J, Yamaji N, Kasai T, Jian F M. Plasma membrane-localized transporter for aluminum in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010, 107(43): 18381-18385. |
| [15] | Nevo Y, Nelson N. The NRAMP family of metal-ion transporters[J]. Molecular Cell Research, 2006, 1763(7): 609-620. |
| [16] |
Akimasa S, Naoki Y, Kengo Y, Feng M J. Nramp5 is a major transporter responsible for manganese and cadmium uptake in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(5): 2155-2167.
PMID |
| [17] | Ishimaru Y, Takahashi R, Bashir K, Shimo H, Nishizawa N K. Characterizing the role of rice NRAMP5 in manganese, iron and cadmium transport[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2(6071): 286. |
| [18] | Ishimaru Y, Bashir K, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa N K. OsNRAMP5, a major player for constitutive iron and manganese uptake in rice[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2012, 7(7): 763-766. |
| [19] | Ishikawa S, Ishimaru Y, Igura M, Kuramata M, Abe T, Senoura T, Hase Y, Arao T, Nishizawa N K, Nakanishi H. Ion-beam irradiation, gene identification, and marker-assisted breeding in the development of low-cadmium rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(47): 19166-19171. |
| [20] | Ryuichi T, Yasuhiro I, Hugo S, Khurram B, Takeshi S, Kazuhiko S, Kazuko O, Nobuo S, Naoki K, Satomi I. From laboratory to field: OsNRAMP5-knockdown rice is a promising candidate for Cd phytoremediation in paddy fields[J]. PloS ONE, 2014, 9(6): e98816. |
| [21] | Wang T K, Li Y X, Fu Y F. Mutation at different sites of metal transporter gene OsNramp5 affects Cd accumulation and related agronomic traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 1081-1092. |
| [22] |
Tang L, Mao B G, Li Y K, Lv Q M, Zhang L P, Chen C Y, He H J, Wang W P, Zeng X F, Shao Y, Pan Y L, Hu Y Y, Peng Y, Li H Q, Xia S T, Zhao B R. Knockout of OsNramp5 using the CRISPR/Cas9 system produces low Cd-accumulating indica rice without compromising yield[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 14438.
PMID |
| [23] | 吕爱清, 罗天相, 刘沐生. 隐性饥饿的研究现状与应对策略[J]. 中国食物与营养, 2017, 23(6): 5-8. |
| Lü A Q, Luo T X, Liu M S. Research advancements and coping strategies on hidden hunger[J]. Food and Nutrition in China, 2017, 23(6): 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] |
Guilbert J J. The world health report 2002: Reducing risks, promoting healthy life[J]. Education for Health, 2003, 16(2): 230.
PMID |
| [25] | 中国营养学会. 中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量[J]. 营养学报, 2001, 23(3): 193-196. |
| Chinese Nutrition Society. Chinese Dietary Reference Intakes, DRIs[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 2001, 23(3): 193-196. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 梅忠, 王治学, 梅沙, 蒋宙蕾, 梅淑芳, 舒小丽, 吴殿星. 高锌水稻研究进展[J]. 核农学报, 2016, 30(8): 1515-1523. |
| Mei Z, Wang Z X, Mei S, Jiang Z L, Mei S F, Shu X L, Wu D X. Study on rice high in zinc content[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 30(8): 1515-1523. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Gao J, Liu Y, Huang Y, Lin Z Q, Bañuelos G S, Lam M H W, Yin X. Daily selenium intake in a moderate selenium deficiency area of Suzhou, China[J]. Food Chemistry, 2011, 126(3): 1088-1093. |
| [28] | Rayman M P. Food-chain selenium and human health: Emphasis on intake[J]. British Journal of Nutrition, 2008, 100(2): 254-268. |
| [29] | 李海蓉, 杨林生, 谭见安, 王五一, 侯少范, 李永华, 虞江萍, 韦炳干. 我国地理环境硒缺乏与健康研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5): 381-386. |
| Li H R, Yang L R, Tan J A, Wang W Y, Hou S F, Li Y H, Yu J P, Wei B G. Progress on selenium deficiency in geographical environment and its health impacts in China[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5): 381-386. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 向敏, 黄鹤春. 功能性稻米研究进展[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2016, 55(12): 2997-3000. |
| Xiang M, Huang H C. Progress of functional rice research[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 55(12): 2997-3000. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 胡时开, 胡培松. 功能稻米研究现状与展望[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 311-325. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| Hu S K, Hu P S. Research progress and prospect of functional rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 311-325. | |
| [32] | 张云慧, 杜平, 秦晓鹏. 不同浓度锌处理下水稻幼苗对镉的累积效应[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(3): 761-768. |
| Zhang Y H, Du P, Qin X P. Accumulation of cadmium in rice seedlings after treatment with different concentrations of zinc[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(3): 761-768. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | 李小秀, 吕启明, 袁定阳. OsNramp5基因变异影响水稻重要农艺性状的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 562-571. |
| Li X X, Lü Q M, Yuan D Y. Research progress on the effects of OsNramp5 mutation on important agronomic traits in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 562-571. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 梁欢婷, 何冰, 顾明华, 王学礼, 吕梦婷, 韦燕燕. 施硒对镉污染稻米中镉,硒含量的影响及其膳食风险评估[J]. 食品工业, 2021, 42(3): 331-335. |
| Liang H T, He B, Gu M H, Wang X L, Lü M T, Wei Y Y. Foliar selenium application on the concentrations of selenium and cadmium in rice grain and health risk assessment[J]. The Food Industry, 2021, 42(3): 331-335. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 刘永贤, 潘丽萍, 黄雁飞, 农梦玲, 鹿士杨, 赵于莹, 梁潘霞, 熊柳梅, 李科冰, 兰秀. 外源喷施硒与硅对水稻籽粒镉累积的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30(7): 1588-1592. |
| Liu Y X, Pan L P, Huang Y F, Nong M L, Lu S Y, Zhao Y Y, Liang P X, Xiong L M, Li K B, Lan X. Effects of selenium or silicon foliar fertilizer on cadmium accumulation in rice[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 30(7): 1588-1592. (in Chinese with English abstract)1 | |
| [36] |
Huang QQ, Liu YY,Qin X,Zhao LJ,Liang XF,Xu YM. Selenite mitigates cadmium-induced oxidative stress and affects Cd uptake in rice seedlings under different water management systems[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 168: 486-494.
PMID |
| [37] | 王才林, 张亚东, 陈涛, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 赵凌, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 魏晓东, 路凯, 梁文化. 姊妹系间杂交快速培育优良食味半糯粳稻新品种的育种效果[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35 (5): 455-465. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Chen T, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Zhao L, Zhao C F, Zhou L H, Wei X D, Lu K, Liao W H. Rapid breeding of new semi-glutinous japonica rice varieties with good eating quality by crossing between sister lines[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35 (5): 455-465. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 王才林, 张亚东, 陈涛, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 赵春芳, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 魏晓东, 路凯, 梁文化. 地点和播期对半糯粳稻食味品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35 (4): 373-382. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Chen T, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Zhao C F, Yao S, Zhou L H, Zhao L, Wei X D, Lu K, Liao W H. Effect of location and sowing date on eating quality of semi-waxy japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 373-382. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] |
Miao J, Guo D S, Zhang J Z, Huang Q P, Qin G J, Zhang X, Wan J M, Gu H Y, Qu L J. Targeted mutagenesis in rice using CRISPR-Cas system[J]. Cell Research, 2013, 23(10): 1233-1236.
PMID |
| [40] | 王广达, 高鹏, 杨文艳, 崔傲, 赵剑华, 冯志明, 曹文磊, 陈宗祥, 左示敏. 金粳818抗咪唑啉酮类除草剂基因的功能标记开发与应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 316-324. |
| Wang G D, Gao P, Yang W Y, Cui A, Zhao J H, Feng Z M, Cao W L, Chen Z X, Zuo S M. Development and utilization of functional markers for imidazolinone herbicides resistance gene in japonica rice variety Jinjing 818[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(4): 316-324. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 贺闽, 尹俊杰, 冯志明, 朱孝波, 赵剑华, 左示敏, 陈学伟. 水稻稻瘟病和纹枯病抗性鉴定方法[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. |
| He M, Yin J J, Feng Z M, Zhu X B, Zhao J H, Zuo S M, Chen X W. Methods for evaluation of rice resistance to blast and sheath blight diseases[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. (in Chinese) | |
| [42] | 董家瑜, 吴天昊, 孙远涛, 何含杰, 李曜魁, 彭彦, 冀中英, 孟前程, 赵炳然, 唐丽. 不同锰浓度环境下OsNRAMP5突变对水稻耐热性和主要经济性状的影响[J]. 杂交水稻, 2021, 36(2): 79-88. |
| Dong J Y, Wu T H, Sun Y T, He H J, Li Y K, Peng Y, Ji Z Y, Meng Q C, Zhao B R, Tang L. Effects of OsNRAMP5 mutation on heat tolerance and main economic traits of rice under the conditions of different manganese concentration[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2021, 36(2): 79-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 龙起樟, 黄永兰, 唐秀英, 王会民, 芦明, 袁林峰, 万建林. 利用CRISPR/Cas9敲除OsNramp5基因创制低镉籼稻[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 407-420. |
| Long Q Z, Huang Y L, Tang X Y, Wang H M, Lu M, Yuan L F, Wan J L. Creation of low-Cd-accumulating indica rice by disruption of OsNramp5 gene via CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(5): 407-420. | |
| [44] | Gashu D, Nalivata P C, Amede T, Ander E L, Bailey E H, Botoman L, Chagumaira C, Gameda S, Haefele S M, Hailu K, Joy E J M, Kalimbira A A, Kumssa D B, Lark R M, Ligowe I S, Towett E K, Walsh M G, Wilson L, Young S D, Broadley M R. The nutritional quality of cereals varies geospatially in Ethiopia and Malawi[J]. Nature, 2021, 594: 71-76. |
| [1] | 何勇, 刘耀威, 熊翔, 祝丹晨, 王爱群, 马拉娜, 王廷宝, 张健, 李建雄, 田志宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑OsOFP30基因创制水稻粒型突变体 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [2] | 蒋鹏, 张林, 周兴兵, 郭晓艺, 朱永川, 刘茂, 郭长春, 熊洪, 徐富贤. 冬水田轻简化栽培杂交稻蓄留再生稻产量形成特点 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [3] | 熊家欢, 张义凯, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 姚坚, 张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [4] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [5] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [6] | 丁正权, 潘月云, 施扬, 黄海祥. 基于基因芯片的嘉禾系列长粒优质食味粳稻综合评价与比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [7] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [9] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [10] | 肖正午, 方升亮, 曹威, 胡丽琴, 黎星, 解嘉鑫, 廖成静, 康玉灵, 胡玉萍, 张珂骞, 曹放波, 陈佳娜, 黄敏. 米粉质构特性与稻米理化性状的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 316-323. |
| [11] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [12] | 梁楚炎, 巫明明, 黄凤明, 翟荣荣, 叶靖, 朱国富, 俞法明, 张小明, 叶胜海. 基因编辑及全基因组选择技术在水稻育种中的应用展望[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 1-12. |
| [13] | 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 王岩, 王旺, 王开, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 许轲, 张洪程. 穗分化末期-灌浆初期干旱胁迫对优质食味粳稻根系形态和叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [14] | 雍明玲, 叶苗, 张雨, 陶钰, 倪川, 康钰莹, 张祖建. 不同食味水稻品种稻米淀粉结构与理化特性及其对氮素响应的差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 57-71. |
| [15] | 易晓璇, 刘玮琦, 曾盖, 罗丽华, 肖应辉. 灌浆期高温胁迫对早籼稻品质性状的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 72-80. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||