
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 278-294.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.211003
张小祥1, 邵士梅2, 赵步洪1,*( ), 张耗2,*(
), 张耗2,*( ), 季红娟1, 肖宁1, 潘存红1, 李育红1, 吴云雨1, 蔡跃1, 刘建菊1, 吉春明1, 张秀琴1, 刘广青1, 周长海1, 黄年生1, 李爱宏1
), 季红娟1, 肖宁1, 潘存红1, 李育红1, 吴云雨1, 蔡跃1, 刘建菊1, 吉春明1, 张秀琴1, 刘广青1, 周长海1, 黄年生1, 李爱宏1
收稿日期:2021-10-13
修回日期:2022-01-11
出版日期:2022-05-10
发布日期:2022-05-11
通讯作者:
赵步洪,张耗
基金资助:
ZHANG Xiaoxiang1, SHAO Shimei2, ZHAO Buhong1,*( ), ZHANG Hao2,*(
), ZHANG Hao2,*( ), JI Hongjuan1, XIAO Ning1, PAN Cunhong1, LI Yuhong1, WU Yunyu1, CAI Yue1, LIU Jianju1, JI Chunming1, ZHANG Xiuqin1, LIU Guangqing1, ZHOU Changhai1, HUANG Niansheng1, LI Aihong1
), JI Hongjuan1, XIAO Ning1, PAN Cunhong1, LI Yuhong1, WU Yunyu1, CAI Yue1, LIU Jianju1, JI Chunming1, ZHANG Xiuqin1, LIU Guangqing1, ZHOU Changhai1, HUANG Niansheng1, LI Aihong1
Received:2021-10-13
Revised:2022-01-11
Online:2022-05-10
Published:2022-05-11
Contact:
ZHAO Buhong, ZHANG Hao
摘要:
【目的】阐明氮肥减施关键时期和适宜减施量对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻的产量及氮肥吸收利用的影响。【方法】以大穗型品种(丰粳3227)、中穗型品种(淮稻5号)和小穗型品种(扬辐粳8号)为材料,设置12种氮肥处理模式,即不施氮(0N)、当地常规施氮(CN,300 kg/hm2)、基肥减总氮10%与20%(BN10、BN20)、分蘖肥减总氮10%与20%(TN10、TN20)、促花肥减总氮10%与20%(SPN10、SPN20)、保花肥减总氮10%与20%(SNN10、SNN20)和均衡减氮10%与20%(AN10、AN20)。【结果】减氮处理下大穗型品种丰粳3227、中穗型品种淮稻5号和小穗型品种扬辐粳8号产量整体降幅分别为6.17%、7.67%和7.81%,尤以减氮20%降幅最大,其中,丰粳3227、淮稻5号和扬辐粳8号在SPN10、AN10和SSN10处理下产量降幅分别为0.17%、0.79%和0.23%,与CN相比略有下降但差异不显著。在相同减氮模式下,产量降幅最高的为小穗型品种,其次是中穗型品种,最后则为大穗型品种。减氮降低了单位面积有效穗数和每穗粒数,但提高了结实率。减氮处理后有效穗数对大穗型品种丰粳3227的产量促进作用最大,每穗粒数则对中穗型品种淮稻5号和小穗型品种扬辐粳8号产量的贡献最大。减氮处理降低了氮素转运量和穗部氮素积累量,提高了氮素吸收利用率和氮肥偏生产力。减氮模式下大穗型品种丰粳3227、中穗型品种淮稻5号、小穗型品种扬辐粳8号分别在SPN10、AN10、SSN10处理下的氮肥利用效率指标总体优于其他处理。【结论】大穗型品种在促花肥适量减氮、小穗型品种在保花肥适量减氮及中穗型品种均衡减氮处理下达到减氮不减产并提高氮肥吸收利用率。适量减氮能够调节不同穗型水稻群体的生长特性以实现产量稳定,但过量减氮使水稻群体自身的产量调节效应变弱。
张小祥, 邵士梅, 赵步洪, 张耗, 季红娟, 肖宁, 潘存红, 李育红, 吴云雨, 蔡跃, 刘建菊, 吉春明, 张秀琴, 刘广青, 周长海, 黄年生, 李爱宏. 氮肥减施模式对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 278-294.
ZHANG Xiaoxiang, SHAO Shimei, ZHAO Buhong, ZHANG Hao, JI Hongjuan, XIAO Ning, PAN Cunhong, LI Yuhong, WU Yunyu, CAI Yue, LIU Jianju, JI Chunming, ZHANG Xiuqin, LIU Guangqing, ZHOU Changhai, HUANG Niansheng, LI Aihong. Effects of Nitrogen Reduction Model on Yield and Nitrogen Absorption and Utilization of Late-maturing Mid-japonica Rice with Different Panicle Types[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 278-294.
| 减施处理 Nitrogen reduction treatment | 总氮量 Total nitrogen level /(kg·hm-2) | 基肥 Basal fertilizer level /(kg·hm-2) | 分蘖肥 Tillering fertilizer level /(kg·hm-2) | 促花肥 Spikelet-promoting fertilizer level /(kg·hm-2) | 保花肥 Spikelet-sustaining fertilizer level /(kg·hm-2) | 运筹比例 Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施氮 0N | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0﹕0﹕0﹕0 |
| 当地常规施氮 CN | 300 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 4﹕2﹕2﹕2 |
| 基肥减氮10% BN10 | 270 | 90 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 3.33﹕2.22﹕2.22﹕2.22 |
| 分蘖肥减氮10% TN10 | 270 | 120 | 30 | 60 | 60 | 4.44﹕1.11﹕2.22﹕2.22 |
| 促花肥减氮10% SPN10 | 270 | 120 | 60 | 30 | 60 | 4.44﹕2.22﹕1.11﹕2.22 |
| 保花肥减氮10% SSN10 | 270 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 30 | 4.44﹕2.22﹕2.22﹕1.11 |
| 均衡减氮10% AN10 | 270 | 112.5 | 52.5 | 52.5 | 52.5 | 4.17﹕1.94﹕1.94﹕1.94 |
| 基肥减氮20% BN20 | 240 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 2.5﹕2.5﹕2.5﹕2.5 |
| 分蘖肥减氮20% TN20 | 240 | 120 | 0 | 60 | 60 | 5﹕0﹕2.5﹕2.5 |
| 促花肥减氮20% SPN20 | 240 | 120 | 60 | 0 | 60 | 5﹕2.5﹕0﹕2.5 |
| 保花肥减氮20% SSN20 | 240 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 0 | 5﹕2.5﹕2.5﹕0 |
| 均衡减氮20% AN20 | 240 | 105 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 4.375﹕1.875﹕1.875﹕1.875 |
表1 氮肥减施量与减施时期
Table 1. Amount and application period of nitrogen fertilizer reduction in this study.
| 减施处理 Nitrogen reduction treatment | 总氮量 Total nitrogen level /(kg·hm-2) | 基肥 Basal fertilizer level /(kg·hm-2) | 分蘖肥 Tillering fertilizer level /(kg·hm-2) | 促花肥 Spikelet-promoting fertilizer level /(kg·hm-2) | 保花肥 Spikelet-sustaining fertilizer level /(kg·hm-2) | 运筹比例 Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施氮 0N | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0﹕0﹕0﹕0 |
| 当地常规施氮 CN | 300 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 4﹕2﹕2﹕2 |
| 基肥减氮10% BN10 | 270 | 90 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 3.33﹕2.22﹕2.22﹕2.22 |
| 分蘖肥减氮10% TN10 | 270 | 120 | 30 | 60 | 60 | 4.44﹕1.11﹕2.22﹕2.22 |
| 促花肥减氮10% SPN10 | 270 | 120 | 60 | 30 | 60 | 4.44﹕2.22﹕1.11﹕2.22 |
| 保花肥减氮10% SSN10 | 270 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 30 | 4.44﹕2.22﹕2.22﹕1.11 |
| 均衡减氮10% AN10 | 270 | 112.5 | 52.5 | 52.5 | 52.5 | 4.17﹕1.94﹕1.94﹕1.94 |
| 基肥减氮20% BN20 | 240 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 2.5﹕2.5﹕2.5﹕2.5 |
| 分蘖肥减氮20% TN20 | 240 | 120 | 0 | 60 | 60 | 5﹕0﹕2.5﹕2.5 |
| 促花肥减氮20% SPN20 | 240 | 120 | 60 | 0 | 60 | 5﹕2.5﹕0﹕2.5 |
| 保花肥减氮20% SSN20 | 240 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 0 | 5﹕2.5﹕2.5﹕0 |
| 均衡减氮20% AN20 | 240 | 105 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 4.375﹕1.875﹕1.875﹕1.875 |
| 品种/处理Cultivar/treatment | 穗数 Panicle number /(×104 hm-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||
| 0N | 265.66±1.50 c | 133.94±2.65 c | 90.5±1.98 a | 26.65±0.13 a | 8.58±0.18 f |
| CN | 318.92±28.43 a | 162.14±7.25 a | 86.7±2.20 bc | 25.58±0.77 bc | 11.47±0.12 a |
| BN10 | 298.43±5.57 ab | 161.53±6.12 a | 88.0±2.34 ab | 25.93±0.44 abc | 11.00±0.01 b |
| TN10 | 295.45±3.91 ab | 161.79±5.91 a | 88.5±2.93 ab | 26.01±0.70 abc | 11.00±0.03 b |
| SPN10 | 317.98±14.02 a | 156.23±4.31 ab | 88.6±2.81 ab | 26.01±0.92 abc | 11.45±0.07 a |
| SSN10 | 319.15±10.00 a | 162.07±5.82 a | 83.9±1.66 cd | 25.19±0.47 c | 10.93±0.08 b |
| AN10 | 304.64±8.89 ab | 159.48±4.41 a | 87.1±1.38 b | 25.65±0.18 bc | 10.86±0.09 bc |
| BN20 | 285.66±19.62 bc | 160.69±7.28 a | 88.1±2.24 ab | 26.08±0.07 ab | 10.54±0.06 cde |
| TN20 | 278.42±12.78 bc | 162.33±2.00 a | 88.3±2.33 ab | 26.07±0.14 ab | 10.40±0.16 de |
| SPN20 | 317.77±12.74 a | 145.31±6.73 b | 88.6±1.50 ab | 26.08±0.24 ab | 10.67±0.17 bcd |
| SSN20 | 316.37±8.54 a | 162.79±5.52 a | 82.0±1.10 d | 24.18±0.48 d | 10.20±0.13 e |
| AN20 | 299.15±8.78 ab | 156.79±5.43 a | 86.2±0.99 bc | 25.54±0.28 bc | 10.32±0.40 de |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||
| 0N | 277.75±3.47 c | 99.69±4.10 d | 94.6±0.84 a | 29.52±0.21 a | 7.73±0.25 f |
| CN | 323.45±17.36 a | 130.07±4.95 a | 91.6±0.40 abc | 28.21±0.51 b | 10.87±0.04 a |
| BN10 | 310.11±9.72 ab | 129.09±5.25 a | 92.0±1.69 ab | 28.40±0.08 b | 10.46±0.02 bc |
| TN10 | 309.29±10.56 ab | 129.22±3.18 a | 92.1±1.48 ab | 28.40±0.28 b | 10.46±0.08 bc |
| SPN10 | 322.48±8.70 a | 117.03±6.58 bc | 92.1±1.30 ab | 28.45±0.21 b | 9.89±0.29 d |
| SSN10 | 324.03±28.20 a | 130.61±9.18 a | 90.2±1.10 bc | 27.37±0.65 cd | 10.45±0.05 bc |
| AN10 | 316.44±8.74 ab | 129.76±3.70 a | 92.2±1.20 ab | 28.49±0.18 b | 10.78±0.08 ab |
| BN20 | 293.79±11.13 bc | 129.97±4.20 a | 92.9±0.97 ab | 28.51±0.29 b | 10.11±0.11 cd |
| TN20 | 293.24±9.73 bc | 130.35±3.23 a | 93.2±1.15 ab | 28.60±0.22 b | 10.19±0.09 cd |
| SPN20 | 323.33±3.51 a | 110.31±5.11 cd | 93.2±0.35 ab | 28.61±0.31 b | 9.51±0.26 e |
| SSN20 | 322.85±7.72 a | 128.03±2.70 a | 88.8±1.49 c | 26.79±0.33 d | 9.83±0.40 de |
| AN20 | 311.04±11.27 ab | 123.19±4.62 ab | 91.5±0.86 bc | 28.16±0.75 bc | 9.88±0.34 de |
| 扬辐粳8号Yangfujing 8 | |||||
| 0N | 291.82±8.34 c | 91.86±4.28 c | 91.4±1.64 a | 26.98±0.89 a | 6.61±0.49 e |
| CN | 342.79±15.22 a | 112.27±4.44 a | 88.9±2.12 ab | 25.74±0.15 b | 8.80±0.08 a |
| BN10 | 322.14±15.69 ab | 112.42±9.25 a | 89.5±1.73 a | 25.79±0.63 b | 8.36±0.02 b |
| TN10 | 321.50±43.88 ab | 112.82±14.85 a | 89.5±0.76 a | 25.78±0.79 b | 8.37±0.00 b |
| SPN10 | 342.16±4.96 a | 102.24±2.95 abc | 89.9±1.10 a | 25.81±0.19 b | 8.11±0.28 b |
| SSN10 | 342.96±12.40 a | 112.73±5.25 a | 88.5±0.47 ab | 25.68±0.19 b | 8.78±0.08 a |
| AN10 | 330.99±11.11 ab | 109.36±4.16 a | 89.5±1.30 a | 25.87±0.36 b | 8.38±0.01 b |
| BN20 | 310.31±6.10 bc | 112.00±6.36 a | 89.9±0.82 a | 25.83±0.35 b | 8.07±0.16 bc |
| TN20 | 307.15±7.06 bc | 112.84±5.12 a | 90.3±0.73 a | 25.85±0.41 b | 8.09±0.14 b |
| SPN20 | 342.06±2.50 a | 95.54±3.79 bc | 90.4±2.54 a | 25.85±0.20 b | 7.64±0.23 d |
| SSN20 | 341.58±6.66 a | 112.09±5.78 a | 85.9±2.05 b | 24.69±0.15 c | 8.12±0.08 b |
| AN20 | 318.20±4.48 abc | 106.30±5.87 ab | 88.7±1.16 ab | 25.68±0.46 b | 7.70±0.28 cd |
| F值F-value | |||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 47.022** | 185.485** | 18.904** | 114.049** | 1442.01** |
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 8.338** | 14.835** | 7.425** | 11.58** | 79.032** |
| V×N | 0.062ns | 0.253ns | 0.344ns | 0.42ns | 3.87** |
表2 氮肥减施对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻产量及其构成因素的影响(2020年)
Table 2. Effects of different nitrogen reduction treatments on the yield and its components of late-maturing japonica rice with different panicle types(2020).
| 品种/处理Cultivar/treatment | 穗数 Panicle number /(×104 hm-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||
| 0N | 265.66±1.50 c | 133.94±2.65 c | 90.5±1.98 a | 26.65±0.13 a | 8.58±0.18 f |
| CN | 318.92±28.43 a | 162.14±7.25 a | 86.7±2.20 bc | 25.58±0.77 bc | 11.47±0.12 a |
| BN10 | 298.43±5.57 ab | 161.53±6.12 a | 88.0±2.34 ab | 25.93±0.44 abc | 11.00±0.01 b |
| TN10 | 295.45±3.91 ab | 161.79±5.91 a | 88.5±2.93 ab | 26.01±0.70 abc | 11.00±0.03 b |
| SPN10 | 317.98±14.02 a | 156.23±4.31 ab | 88.6±2.81 ab | 26.01±0.92 abc | 11.45±0.07 a |
| SSN10 | 319.15±10.00 a | 162.07±5.82 a | 83.9±1.66 cd | 25.19±0.47 c | 10.93±0.08 b |
| AN10 | 304.64±8.89 ab | 159.48±4.41 a | 87.1±1.38 b | 25.65±0.18 bc | 10.86±0.09 bc |
| BN20 | 285.66±19.62 bc | 160.69±7.28 a | 88.1±2.24 ab | 26.08±0.07 ab | 10.54±0.06 cde |
| TN20 | 278.42±12.78 bc | 162.33±2.00 a | 88.3±2.33 ab | 26.07±0.14 ab | 10.40±0.16 de |
| SPN20 | 317.77±12.74 a | 145.31±6.73 b | 88.6±1.50 ab | 26.08±0.24 ab | 10.67±0.17 bcd |
| SSN20 | 316.37±8.54 a | 162.79±5.52 a | 82.0±1.10 d | 24.18±0.48 d | 10.20±0.13 e |
| AN20 | 299.15±8.78 ab | 156.79±5.43 a | 86.2±0.99 bc | 25.54±0.28 bc | 10.32±0.40 de |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||
| 0N | 277.75±3.47 c | 99.69±4.10 d | 94.6±0.84 a | 29.52±0.21 a | 7.73±0.25 f |
| CN | 323.45±17.36 a | 130.07±4.95 a | 91.6±0.40 abc | 28.21±0.51 b | 10.87±0.04 a |
| BN10 | 310.11±9.72 ab | 129.09±5.25 a | 92.0±1.69 ab | 28.40±0.08 b | 10.46±0.02 bc |
| TN10 | 309.29±10.56 ab | 129.22±3.18 a | 92.1±1.48 ab | 28.40±0.28 b | 10.46±0.08 bc |
| SPN10 | 322.48±8.70 a | 117.03±6.58 bc | 92.1±1.30 ab | 28.45±0.21 b | 9.89±0.29 d |
| SSN10 | 324.03±28.20 a | 130.61±9.18 a | 90.2±1.10 bc | 27.37±0.65 cd | 10.45±0.05 bc |
| AN10 | 316.44±8.74 ab | 129.76±3.70 a | 92.2±1.20 ab | 28.49±0.18 b | 10.78±0.08 ab |
| BN20 | 293.79±11.13 bc | 129.97±4.20 a | 92.9±0.97 ab | 28.51±0.29 b | 10.11±0.11 cd |
| TN20 | 293.24±9.73 bc | 130.35±3.23 a | 93.2±1.15 ab | 28.60±0.22 b | 10.19±0.09 cd |
| SPN20 | 323.33±3.51 a | 110.31±5.11 cd | 93.2±0.35 ab | 28.61±0.31 b | 9.51±0.26 e |
| SSN20 | 322.85±7.72 a | 128.03±2.70 a | 88.8±1.49 c | 26.79±0.33 d | 9.83±0.40 de |
| AN20 | 311.04±11.27 ab | 123.19±4.62 ab | 91.5±0.86 bc | 28.16±0.75 bc | 9.88±0.34 de |
| 扬辐粳8号Yangfujing 8 | |||||
| 0N | 291.82±8.34 c | 91.86±4.28 c | 91.4±1.64 a | 26.98±0.89 a | 6.61±0.49 e |
| CN | 342.79±15.22 a | 112.27±4.44 a | 88.9±2.12 ab | 25.74±0.15 b | 8.80±0.08 a |
| BN10 | 322.14±15.69 ab | 112.42±9.25 a | 89.5±1.73 a | 25.79±0.63 b | 8.36±0.02 b |
| TN10 | 321.50±43.88 ab | 112.82±14.85 a | 89.5±0.76 a | 25.78±0.79 b | 8.37±0.00 b |
| SPN10 | 342.16±4.96 a | 102.24±2.95 abc | 89.9±1.10 a | 25.81±0.19 b | 8.11±0.28 b |
| SSN10 | 342.96±12.40 a | 112.73±5.25 a | 88.5±0.47 ab | 25.68±0.19 b | 8.78±0.08 a |
| AN10 | 330.99±11.11 ab | 109.36±4.16 a | 89.5±1.30 a | 25.87±0.36 b | 8.38±0.01 b |
| BN20 | 310.31±6.10 bc | 112.00±6.36 a | 89.9±0.82 a | 25.83±0.35 b | 8.07±0.16 bc |
| TN20 | 307.15±7.06 bc | 112.84±5.12 a | 90.3±0.73 a | 25.85±0.41 b | 8.09±0.14 b |
| SPN20 | 342.06±2.50 a | 95.54±3.79 bc | 90.4±2.54 a | 25.85±0.20 b | 7.64±0.23 d |
| SSN20 | 341.58±6.66 a | 112.09±5.78 a | 85.9±2.05 b | 24.69±0.15 c | 8.12±0.08 b |
| AN20 | 318.20±4.48 abc | 106.30±5.87 ab | 88.7±1.16 ab | 25.68±0.46 b | 7.70±0.28 cd |
| F值F-value | |||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 47.022** | 185.485** | 18.904** | 114.049** | 1442.01** |
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 8.338** | 14.835** | 7.425** | 11.58** | 79.032** |
| V×N | 0.062ns | 0.253ns | 0.344ns | 0.42ns | 3.87** |
| 品种/处理Cultivar/treatment | 穗数 Panicle number /(×104 hm-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||
| 0N | 262.00±5.36 d | 130.78±1.08 f | 90.15±0.85 a | 26.28±0.09 a | 8.12±0.24 g |
| CN | 329.49±20.28 a | 157.56±1.84 abc | 86.83±1.27 cd | 25.59±0.71 bc | 11.51±0.11 a |
| BN10 | 301.76±10.46 b | 157.38±1.02 abc | 87.41±0.82 cd | 25.92±0.44 abc | 10.75±0.12 cd |
| TN10 | 306.00±8.69 b | 157.92±2.59 ab | 86.24±0.77 de | 25.89±0.22 abc | 10.78±0.14 cd |
| SPN10 | 309.75±3.49 ab | 158.59±1.26 a | 87.67±1.24 cd | 26.08±0.27 abc | 11.23±0.27 ab |
| SSN10 | 312.54±5.29 ab | 157.69±342 abc | 86.24±0.55 de | 25.49±0.55 c | 10.83±0.16 cd |
| AN10 | 307.69±5.56 b | 158.27±1.00 ab | 87.45±0.69 cd | 25.66±0.10 abc | 10.93±0.28 bc |
| BN20 | 300.47±4.16 b | 153.03±1.70 cde | 87.51±0.82 cd | 26.15±0.10 ab | 10.52±0.15 de |
| TN20 | 281.98±6.38 c | 157.55±2.00 abc | 89.35±0.57 ab | 26.11±0.15 abc | 10.36±0.18 ef |
| SPN20 | 312.40±8.76 ab | 148.88±2.62 e | 88.30±0.80 bc | 26.12±0.12 ab | 10.72±0.07 cd |
| SSN20 | 309.60±4.62 ab | 153.64±1.72 bcd | 84.15±0.83 f | 25.84±0.25 abc | 10.34±0.05 ef |
| AN20 | 300.50±8.60 b | 152.72±2.19 de | 85.11±1.12 ef | 25.71±0.12 abc | 10.04±0.11 f |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||
| 0N | 287.59±7.34 d | 98.69±2.69 g | 92.41±0.94 ab | 28.95±0.20 a | 7.59±0.08 g |
| CN | 317.49±8.73 abc | 130.07±4.95 a | 91.17±0.20 bc | 28.50±0.07 ab | 10.72±0.11 a |
| BN10 | 315.74±7.45 abc | 125.11±2.92 bcd | 91.08±0.51 bc | 28.49±0.13 ab | 10.25±0.05 bcd |
| TN10 | 310.42±2.67 bc | 125.90±1.22 abc | 91.74±0.59 abc | 28.51±0.13 ab | 10.22±0.12 bcd |
| SPN10 | 320.78±5.34 abc | 123.54±2.70 cde | 91.44±0.82 abc | 28.45±0.05 ab | 10.31±0.09 bc |
| SSN10 | 332.39±10.80 a | 124.04±2.47 cde | 91.01±0.18 bc | 27.02±0.32 c | 10.13±0.09 cde |
| AN10 | 315.17±4.60 abc | 129.57±1.48 ab | 91.00±0.60 bc | 28.42±0.14 ab | 10.56±0.06 ab |
| BN20 | 312.65±9.99 abc | 121.02±1.34 de | 92.37±0.71 ab | 28.35±0.11 ab | 9.90±0.11 def |
| TN20 | 301.80±6.61 cd | 122.01±1.37 cde | 92.91±0.41 a | 28.52±0.16 ab | 9.75±0.08 f |
| SPN20 | 333.92±11.57 a | 113.79±2.60 f | 90.71±0.55 bc | 28.52±0.12 ab | 9.83±0.45 ef |
| SSN20 | 330.56±8.61 ab | 120.13±1.20 e | 90.14±0.50 c | 27.29±0.26 c | 9.76±0.15 f |
| AN20 | 316.25±7.30 abc | 121.06±1.35 de | 90.81±0.51 bc | 28.18±0.17 b | 9.79±0.13 ef |
| 扬辐粳8号Yangfujing 8 | |||||
| 0N | 315.19±9.54 de | 89.93±1.92 e | 91.31±0.60 a | 26.57±0.31 a | 6.88±0.25 f |
| CN | 334.98±6.43 bcd | 111.63±1.96 a | 90.38±0.67 abcd | 25.84±0.24 b | 8.73±0.16 a |
| BN10 | 327.02±2.21 cde | 110.12±1.97 ab | 89.64±0.41 abcd | 25.79±0.34 b | 8.32±0.15 bc |
| TN10 | 329.65±5.74 bcd | 108.84±1.29 ab | 89.27±0.78 cd | 25.78±0.79 b | 8.25±0.18 bc |
| SPN10 | 350.12±8.95 ab | 102.24±2.95 d | 90.48±0.64 abc | 25.71±0.05 b | 8.32±0.11 bc |
| SSN10 | 332.20±6.49 bcd | 112.14±1.43 a | 89.20±0.60 cd | 25.80±0.05 b | 8.57±0.12 ab |
| AN10 | 329.38±2.91 bcd | 106.90±1.85 bc | 88.91±0.52 cd | 26.01±0.29 b | 8.14±0.06 cd |
| BN20 | 307.28±3.12 e | 112.43±1.92 a | 89.50±0.44 bcd | 26.14 ±0.14 ab | 8.08±0.04 cde |
| TN20 | 316.66±18.23 de | 110.25±3.98 ab | 91.01±0.32 ab | 25.80±0.32 b | 8.18±0.07 cd |
| SPN20 | 345.03±12.13 abc | 99.13±1.12 d | 88.68±1.20 de | 26.01±0.16 b | 7.88±0.15 de |
| SSN20 | 359.67±19.52 a | 103.70±4.13 cd | 87.18±1.71 e | 24.82±0.10 c | 8.05±0.09 cde |
| AN20 | 335.34±9.03 bcd | 100.22±2.19 d | 89.08±0.32 cd | 25.96±0.10 b | 7.77±0.15 e |
| F值F-value | |||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 760.85** | 2202.77** | 108.45** | 264.60* | 1934.99** |
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 12.59** | 71.21** | 12.95** | 9.80* | 112.32** |
| V×N | 1.75** | 3.62** | 1.80* | 2.53** | 5.33** |
表3 氮肥减施对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻产量及产量构成因素的影响(2019年)
Table 3. Effects of different nitrogen reduction treatments on the yield and its components of late-maturing japonica rice with different panicle types(2019).
| 品种/处理Cultivar/treatment | 穗数 Panicle number /(×104 hm-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Yield/(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||
| 0N | 262.00±5.36 d | 130.78±1.08 f | 90.15±0.85 a | 26.28±0.09 a | 8.12±0.24 g |
| CN | 329.49±20.28 a | 157.56±1.84 abc | 86.83±1.27 cd | 25.59±0.71 bc | 11.51±0.11 a |
| BN10 | 301.76±10.46 b | 157.38±1.02 abc | 87.41±0.82 cd | 25.92±0.44 abc | 10.75±0.12 cd |
| TN10 | 306.00±8.69 b | 157.92±2.59 ab | 86.24±0.77 de | 25.89±0.22 abc | 10.78±0.14 cd |
| SPN10 | 309.75±3.49 ab | 158.59±1.26 a | 87.67±1.24 cd | 26.08±0.27 abc | 11.23±0.27 ab |
| SSN10 | 312.54±5.29 ab | 157.69±342 abc | 86.24±0.55 de | 25.49±0.55 c | 10.83±0.16 cd |
| AN10 | 307.69±5.56 b | 158.27±1.00 ab | 87.45±0.69 cd | 25.66±0.10 abc | 10.93±0.28 bc |
| BN20 | 300.47±4.16 b | 153.03±1.70 cde | 87.51±0.82 cd | 26.15±0.10 ab | 10.52±0.15 de |
| TN20 | 281.98±6.38 c | 157.55±2.00 abc | 89.35±0.57 ab | 26.11±0.15 abc | 10.36±0.18 ef |
| SPN20 | 312.40±8.76 ab | 148.88±2.62 e | 88.30±0.80 bc | 26.12±0.12 ab | 10.72±0.07 cd |
| SSN20 | 309.60±4.62 ab | 153.64±1.72 bcd | 84.15±0.83 f | 25.84±0.25 abc | 10.34±0.05 ef |
| AN20 | 300.50±8.60 b | 152.72±2.19 de | 85.11±1.12 ef | 25.71±0.12 abc | 10.04±0.11 f |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||
| 0N | 287.59±7.34 d | 98.69±2.69 g | 92.41±0.94 ab | 28.95±0.20 a | 7.59±0.08 g |
| CN | 317.49±8.73 abc | 130.07±4.95 a | 91.17±0.20 bc | 28.50±0.07 ab | 10.72±0.11 a |
| BN10 | 315.74±7.45 abc | 125.11±2.92 bcd | 91.08±0.51 bc | 28.49±0.13 ab | 10.25±0.05 bcd |
| TN10 | 310.42±2.67 bc | 125.90±1.22 abc | 91.74±0.59 abc | 28.51±0.13 ab | 10.22±0.12 bcd |
| SPN10 | 320.78±5.34 abc | 123.54±2.70 cde | 91.44±0.82 abc | 28.45±0.05 ab | 10.31±0.09 bc |
| SSN10 | 332.39±10.80 a | 124.04±2.47 cde | 91.01±0.18 bc | 27.02±0.32 c | 10.13±0.09 cde |
| AN10 | 315.17±4.60 abc | 129.57±1.48 ab | 91.00±0.60 bc | 28.42±0.14 ab | 10.56±0.06 ab |
| BN20 | 312.65±9.99 abc | 121.02±1.34 de | 92.37±0.71 ab | 28.35±0.11 ab | 9.90±0.11 def |
| TN20 | 301.80±6.61 cd | 122.01±1.37 cde | 92.91±0.41 a | 28.52±0.16 ab | 9.75±0.08 f |
| SPN20 | 333.92±11.57 a | 113.79±2.60 f | 90.71±0.55 bc | 28.52±0.12 ab | 9.83±0.45 ef |
| SSN20 | 330.56±8.61 ab | 120.13±1.20 e | 90.14±0.50 c | 27.29±0.26 c | 9.76±0.15 f |
| AN20 | 316.25±7.30 abc | 121.06±1.35 de | 90.81±0.51 bc | 28.18±0.17 b | 9.79±0.13 ef |
| 扬辐粳8号Yangfujing 8 | |||||
| 0N | 315.19±9.54 de | 89.93±1.92 e | 91.31±0.60 a | 26.57±0.31 a | 6.88±0.25 f |
| CN | 334.98±6.43 bcd | 111.63±1.96 a | 90.38±0.67 abcd | 25.84±0.24 b | 8.73±0.16 a |
| BN10 | 327.02±2.21 cde | 110.12±1.97 ab | 89.64±0.41 abcd | 25.79±0.34 b | 8.32±0.15 bc |
| TN10 | 329.65±5.74 bcd | 108.84±1.29 ab | 89.27±0.78 cd | 25.78±0.79 b | 8.25±0.18 bc |
| SPN10 | 350.12±8.95 ab | 102.24±2.95 d | 90.48±0.64 abc | 25.71±0.05 b | 8.32±0.11 bc |
| SSN10 | 332.20±6.49 bcd | 112.14±1.43 a | 89.20±0.60 cd | 25.80±0.05 b | 8.57±0.12 ab |
| AN10 | 329.38±2.91 bcd | 106.90±1.85 bc | 88.91±0.52 cd | 26.01±0.29 b | 8.14±0.06 cd |
| BN20 | 307.28±3.12 e | 112.43±1.92 a | 89.50±0.44 bcd | 26.14 ±0.14 ab | 8.08±0.04 cde |
| TN20 | 316.66±18.23 de | 110.25±3.98 ab | 91.01±0.32 ab | 25.80±0.32 b | 8.18±0.07 cd |
| SPN20 | 345.03±12.13 abc | 99.13±1.12 d | 88.68±1.20 de | 26.01±0.16 b | 7.88±0.15 de |
| SSN20 | 359.67±19.52 a | 103.70±4.13 cd | 87.18±1.71 e | 24.82±0.10 c | 8.05±0.09 cde |
| AN20 | 335.34±9.03 bcd | 100.22±2.19 d | 89.08±0.32 cd | 25.96±0.10 b | 7.77±0.15 e |
| F值F-value | |||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 760.85** | 2202.77** | 108.45** | 264.60* | 1934.99** |
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 12.59** | 71.21** | 12.95** | 9.80* | 112.32** |
| V×N | 1.75** | 3.62** | 1.80* | 2.53** | 5.33** |
| 品种 Cultivar | 产量构成因素 Yield components | Y效应 Effect on Y (Pi-Y) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X2 | X3 | X4 | Y(Yield) | ||
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||
| 单位面积有效穗数Panicle number(X1) | 0.011ns | -0.540** | -0.491** | 0.547** | 1.015 |
| 每穗粒数Spikelet number per panicle(X2) | -0.298ns | -0.381* | 0.651** | 0.917 | |
| 结实率Full-filled grain rate(X3) | 0.519** | -0.112ns | 0.478 | ||
| 千粒重1000-grain weight(X4) | -0.153ns | 0.447 | |||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||
| 单位面积有效穗数Panicle number(X1) | -0.007ns | -0.409* | -0.560** | 0.460** | 0.756 |
| 每穗粒数Spikelet number per panicle(X2) | -0.500** | -0.406* | 0.800** | 1.064 | |
| 结实率Full-filled grain rate(X3) | 0.722** | -0.354* | 0.335 | ||
| 千粒重1000-grain weight(X4) | -0.344* | 0.245 | |||
| 扬辐粳8号 Yangfujing 8 -0.322ns | |||||
| 单位面积有效穗数Panicle number(X1) | -0.243ns | -0.214ns | -0.322ns | 0.458** | 0.925 |
| 每穗粒数Spikelet number per panicle(X2) | -0.515** | -0.429** | 0.665** | 1.192 | |
| 结实率Full-filled grain rate(X3) | 0.432** | -0.368* | 0.356 | ||
| 千粒重1000-grain weight(X4) | -0.327ns | 0.289 | |||
表4 氮肥减施对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻产量与产量构成因素间的相关性与直接通径分析
Table 4. Correlation and path coefficients between the yield and its components of different panicles type late-maturing japonica rice under reduced nitrogen treatments.
| 品种 Cultivar | 产量构成因素 Yield components | Y效应 Effect on Y (Pi-Y) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X2 | X3 | X4 | Y(Yield) | ||
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||
| 单位面积有效穗数Panicle number(X1) | 0.011ns | -0.540** | -0.491** | 0.547** | 1.015 |
| 每穗粒数Spikelet number per panicle(X2) | -0.298ns | -0.381* | 0.651** | 0.917 | |
| 结实率Full-filled grain rate(X3) | 0.519** | -0.112ns | 0.478 | ||
| 千粒重1000-grain weight(X4) | -0.153ns | 0.447 | |||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||
| 单位面积有效穗数Panicle number(X1) | -0.007ns | -0.409* | -0.560** | 0.460** | 0.756 |
| 每穗粒数Spikelet number per panicle(X2) | -0.500** | -0.406* | 0.800** | 1.064 | |
| 结实率Full-filled grain rate(X3) | 0.722** | -0.354* | 0.335 | ||
| 千粒重1000-grain weight(X4) | -0.344* | 0.245 | |||
| 扬辐粳8号 Yangfujing 8 -0.322ns | |||||
| 单位面积有效穗数Panicle number(X1) | -0.243ns | -0.214ns | -0.322ns | 0.458** | 0.925 |
| 每穗粒数Spikelet number per panicle(X2) | -0.515** | -0.429** | 0.665** | 1.192 | |
| 结实率Full-filled grain rate(X3) | 0.432** | -0.368* | 0.356 | ||
| 千粒重1000-grain weight(X4) | -0.327ns | 0.289 | |||
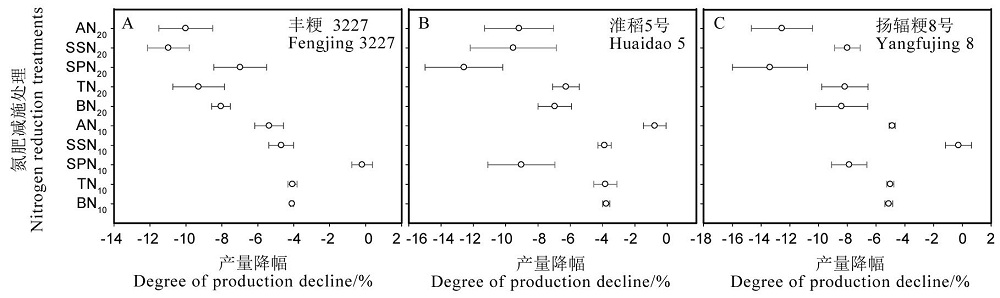
图1 氮肥减施处理下不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻产量的降幅
Fig. 1. Reduction in the yield of late-maturing medium japonica rice with different panicle types under nitrogen fertilizer reduction treatments.
| 品种/减施处理Cultivar/treatment | 施氮量 Total nitrogen level/(t·hm-2) | 拔节期 Jointing period | 抽穗期 Heading date | 成熟期 Maturity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | ||||
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 81.46±5.18 e | 1.82±0.02 e | 97.93±1.26 g | 1.23±0.00 e | 137.74±4.45 f | 0.87±0.02 b | ||
| CN | 300 | 135.43±3.75 a | 2.28±0.04 a | 199.80±0.46 a | 1.89±0.01 a | 243.95±0.74 a | 1.17±0.02 a | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 120.80±5.28 b | 2.19±0.06 ab | 186.89±5.45 b | 1.85±0.02 ab | 238.55±2.83 c | 1.16±0.01 a | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 118.58±1.98 bc | 2.19±0.04 ab | 183.46±2.73 bc | 1.81±0.02 bc | 235.38±1.66 cd | 1.16±0.00 a | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 130.61±3.92 a | 2.26±0.07 a | 198.66±4.27 a | 1.89±0.01 a | 243.34±2.44 ab | 1.17±0.01 a | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 117.28±1.64 bc | 2.14±0.03 bc | 178.89±3.18 cd | 1.81±0.01 bc | 239.23±1.95 bc | 1.17±0.01 a | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 115.88±2.67 bc | 2.18±0.03 ab | 179.92±2.24 cd | 1.79±0.01 cd | 239.58±2.39 abc | 1.17±0.00 a | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 99.86±4.88 d | 1.96±0.04 d | 175.37±6.27 de | 1.77±0.05 cd | 232.19±2.14 de | 1.15±0.01 a | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 111.12±3.16 c | 2.12±0.03 bc | 169.86±3.04 ef | 1.75±0.03 cd | 233.92±1.08 de | 1.16±0.00 a | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 112.96±3.13 bc | 2.13±0.02 bc | 171.37±5.35 e | 1.74±0.04 d | 232.09±0.91 de | 1.14±0.01 a | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 111.48±6.14 c | 2.08±0.09 bc | 164.40±4.15 f | 1.79±0.02 bcd | 230.66±1.83 de | 1.14±0.01 a | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 103.37±2.26 d | 2.06±0.06 c | 173.74±2.70 de | 1.78±0.02 cd | 230.37±1.46 e | 1.15±0.01 a | ||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 87.74±0.81 d | 1.93±0.01 e | 104.00±0.68 f | 1.32±0.01 f | 131.07±2.18 d | 0.90±0.00 e | ||
| CN | 300 | 140.39±1.17 a | 2.43±0.02 a | 208.85±3.67 a | 2.03±0.01 a | 238.11±1.25 a | 1.15±0.01 cd | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 122.35±5.64 b | 2.31±0.12 bc | 183.08±2.81 bc | 1.91±0.02 b | 233.83±1.30 ab | 1.18±0.01 ab | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 121.14±1.04 b | 2.24±0.02 cd | 180.15±7.07 bc | 1.88±0.01 bc | 230.12±4.07 b | 1.15±0.01 cd | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 120.71±2.70 b | 2.23±0.04 cd | 185.45±1.98 b | 1.92±0.02 b | 235.83±1.95 a | 1.16±0.03 bcd | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 122.58±2.16 b | 2.16±0.01 d | 181.45±3.19 bc | 1.85±0.03 c | 234.69±1.03 a | 1.18±0.00 ab | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 136.21±3.55 a | 2.39±0.02 ab | 202.95±3.00 a | 2.02±0.02 a | 238.02±1.21 a | 1.20±0.00 a | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 116.73±4.38 bc | 2.21±0.03 cd | 172.06±4.01 de | 1.83±0.01 cd | 220.60±2.03 c | 1.14±0.00 d | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 116.58±1.78 bc | 2.27±0.01 cd | 177.63±3.83 cd | 1.92±0.04 b | 219.97±2.42 c | 1.16±0.01 bcd | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 111.94±3.92 c | 2.16±0.06 d | 171.75±0.98 de | 1.83±0.03 cd | 220.11±1.09 c | 1.15±0.00 cd | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 109.48±3.55 c | 2.17±0.05 d | 173.00±1.66 de | 1.77±0.03 e | 219.68±1.42 c | 1.15±0.00 cd | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 110.33±1.17 c | 2.19±0.02 d | 170.02±0.68 e | 1.78±0.02 de | 223.22±0.89 c | 1.17±0.00 abc | ||
| 扬辐粳8号Yangfujing 8 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 71.98±2.20 f | 1.78±0.01 g | 91.97±2.94 g | 1.18±0.02 f | 129.37±4.81 c | 0.81±0.02 e | ||
| CN | 300 | 127.30±3.30 a | 2.30±0.06 a | 184.54±1.17 a | 1.85±0.02 a | 233.01±1.53 a | 1.20±0.01 a | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 112.78±5.99 cd | 2.26±0.03 ab | 166.04±2.58 bc | 1.77±0.01 bc | 230.40±1.86 a | 1.18±0.01 a | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 114.85±3.13 bc | 2.22±0.04 abc | 168.84±3.99 b | 1.81±0.03 ab | 230.15±1.81 a | 1.19±0.02 a | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 114.03±1.74 bc | 2.19±0.04 bcd | 162.23±0.35 bcd | 1.74±0.02 cd | 230.29±0.71 a | 1.18±0.01 a | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 120.79±2.24 ab | 2.27±0.05 ab | 179.23±0.45 a | 1.82±0.01 ab | 232.93±1.35 a | 1.18±0.01 a | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 114.12±0.53 bc | 2.21±0.05 abcd | 161.66±5.19 cde | 1.73±0.03 cd | 229.10±3.12 a | 1.12±0.05 bc | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 101.68±2.86 e | 2.03±0.02 f | 157.83±2.00 def | 1.73±0.02 cd | 220.79±0.65 b | 1.15±0.01 b | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 104.94±1.53 de | 2.12±0.06 def | 154.48±1.85 ef | 1.71±0.03 de | 219.97±0.47 b | 1.12±0.01 bc | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 105.35±6.88 de | 2.08±0.08 ef | 156.85±3.96 def | 1.72±0.05 cde | 220.27±1.86 b | 1.08±0.03 d | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 105.72±1.16 de | 2.09±0.01 ef | 151.48±2.25 f | 1.66±0.05 e | 220.93±2.63 b | 1.12±0.01 c | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 105.42±5.61 de | 2.15±0.10 cde | 157.12±2.19 cde | 1.71±0.02 de | 219.55±1.44 b | 1.10±0.01 cd | ||
| F值F-value | |||||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 142.204** | 19.829** | 198.183** | 178.999** | 224.359** | 6.562ns | |||
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 82.725** | 41.964** | 328.554** | 245.86** | 1058.211** | 266.323** | |||
| V×N | 3.497** | 2.484** | 7.805** | 5.992** | 2.107** | 7.927** | |||
表5 氮肥减施对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻几个重要时期水稻氮素吸收的影响(2020年)
Table 5. Effects of different nitrogen reduction treatments on nitrogen absorption of late-maturing japonica rice with different panicle types during important growth stages (2020).
| 品种/减施处理Cultivar/treatment | 施氮量 Total nitrogen level/(t·hm-2) | 拔节期 Jointing period | 抽穗期 Heading date | 成熟期 Maturity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | ||||
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 81.46±5.18 e | 1.82±0.02 e | 97.93±1.26 g | 1.23±0.00 e | 137.74±4.45 f | 0.87±0.02 b | ||
| CN | 300 | 135.43±3.75 a | 2.28±0.04 a | 199.80±0.46 a | 1.89±0.01 a | 243.95±0.74 a | 1.17±0.02 a | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 120.80±5.28 b | 2.19±0.06 ab | 186.89±5.45 b | 1.85±0.02 ab | 238.55±2.83 c | 1.16±0.01 a | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 118.58±1.98 bc | 2.19±0.04 ab | 183.46±2.73 bc | 1.81±0.02 bc | 235.38±1.66 cd | 1.16±0.00 a | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 130.61±3.92 a | 2.26±0.07 a | 198.66±4.27 a | 1.89±0.01 a | 243.34±2.44 ab | 1.17±0.01 a | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 117.28±1.64 bc | 2.14±0.03 bc | 178.89±3.18 cd | 1.81±0.01 bc | 239.23±1.95 bc | 1.17±0.01 a | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 115.88±2.67 bc | 2.18±0.03 ab | 179.92±2.24 cd | 1.79±0.01 cd | 239.58±2.39 abc | 1.17±0.00 a | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 99.86±4.88 d | 1.96±0.04 d | 175.37±6.27 de | 1.77±0.05 cd | 232.19±2.14 de | 1.15±0.01 a | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 111.12±3.16 c | 2.12±0.03 bc | 169.86±3.04 ef | 1.75±0.03 cd | 233.92±1.08 de | 1.16±0.00 a | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 112.96±3.13 bc | 2.13±0.02 bc | 171.37±5.35 e | 1.74±0.04 d | 232.09±0.91 de | 1.14±0.01 a | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 111.48±6.14 c | 2.08±0.09 bc | 164.40±4.15 f | 1.79±0.02 bcd | 230.66±1.83 de | 1.14±0.01 a | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 103.37±2.26 d | 2.06±0.06 c | 173.74±2.70 de | 1.78±0.02 cd | 230.37±1.46 e | 1.15±0.01 a | ||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 87.74±0.81 d | 1.93±0.01 e | 104.00±0.68 f | 1.32±0.01 f | 131.07±2.18 d | 0.90±0.00 e | ||
| CN | 300 | 140.39±1.17 a | 2.43±0.02 a | 208.85±3.67 a | 2.03±0.01 a | 238.11±1.25 a | 1.15±0.01 cd | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 122.35±5.64 b | 2.31±0.12 bc | 183.08±2.81 bc | 1.91±0.02 b | 233.83±1.30 ab | 1.18±0.01 ab | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 121.14±1.04 b | 2.24±0.02 cd | 180.15±7.07 bc | 1.88±0.01 bc | 230.12±4.07 b | 1.15±0.01 cd | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 120.71±2.70 b | 2.23±0.04 cd | 185.45±1.98 b | 1.92±0.02 b | 235.83±1.95 a | 1.16±0.03 bcd | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 122.58±2.16 b | 2.16±0.01 d | 181.45±3.19 bc | 1.85±0.03 c | 234.69±1.03 a | 1.18±0.00 ab | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 136.21±3.55 a | 2.39±0.02 ab | 202.95±3.00 a | 2.02±0.02 a | 238.02±1.21 a | 1.20±0.00 a | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 116.73±4.38 bc | 2.21±0.03 cd | 172.06±4.01 de | 1.83±0.01 cd | 220.60±2.03 c | 1.14±0.00 d | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 116.58±1.78 bc | 2.27±0.01 cd | 177.63±3.83 cd | 1.92±0.04 b | 219.97±2.42 c | 1.16±0.01 bcd | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 111.94±3.92 c | 2.16±0.06 d | 171.75±0.98 de | 1.83±0.03 cd | 220.11±1.09 c | 1.15±0.00 cd | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 109.48±3.55 c | 2.17±0.05 d | 173.00±1.66 de | 1.77±0.03 e | 219.68±1.42 c | 1.15±0.00 cd | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 110.33±1.17 c | 2.19±0.02 d | 170.02±0.68 e | 1.78±0.02 de | 223.22±0.89 c | 1.17±0.00 abc | ||
| 扬辐粳8号Yangfujing 8 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 71.98±2.20 f | 1.78±0.01 g | 91.97±2.94 g | 1.18±0.02 f | 129.37±4.81 c | 0.81±0.02 e | ||
| CN | 300 | 127.30±3.30 a | 2.30±0.06 a | 184.54±1.17 a | 1.85±0.02 a | 233.01±1.53 a | 1.20±0.01 a | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 112.78±5.99 cd | 2.26±0.03 ab | 166.04±2.58 bc | 1.77±0.01 bc | 230.40±1.86 a | 1.18±0.01 a | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 114.85±3.13 bc | 2.22±0.04 abc | 168.84±3.99 b | 1.81±0.03 ab | 230.15±1.81 a | 1.19±0.02 a | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 114.03±1.74 bc | 2.19±0.04 bcd | 162.23±0.35 bcd | 1.74±0.02 cd | 230.29±0.71 a | 1.18±0.01 a | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 120.79±2.24 ab | 2.27±0.05 ab | 179.23±0.45 a | 1.82±0.01 ab | 232.93±1.35 a | 1.18±0.01 a | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 114.12±0.53 bc | 2.21±0.05 abcd | 161.66±5.19 cde | 1.73±0.03 cd | 229.10±3.12 a | 1.12±0.05 bc | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 101.68±2.86 e | 2.03±0.02 f | 157.83±2.00 def | 1.73±0.02 cd | 220.79±0.65 b | 1.15±0.01 b | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 104.94±1.53 de | 2.12±0.06 def | 154.48±1.85 ef | 1.71±0.03 de | 219.97±0.47 b | 1.12±0.01 bc | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 105.35±6.88 de | 2.08±0.08 ef | 156.85±3.96 def | 1.72±0.05 cde | 220.27±1.86 b | 1.08±0.03 d | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 105.72±1.16 de | 2.09±0.01 ef | 151.48±2.25 f | 1.66±0.05 e | 220.93±2.63 b | 1.12±0.01 c | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 105.42±5.61 de | 2.15±0.10 cde | 157.12±2.19 cde | 1.71±0.02 de | 219.55±1.44 b | 1.10±0.01 cd | ||
| F值F-value | |||||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 142.204** | 19.829** | 198.183** | 178.999** | 224.359** | 6.562ns | |||
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 82.725** | 41.964** | 328.554** | 245.86** | 1058.211** | 266.323** | |||
| V×N | 3.497** | 2.484** | 7.805** | 5.992** | 2.107** | 7.927** | |||
| 品种/减施处理Cultivar/treatment | 施氮量 Total nitrogen level/(t·hm-2) | 拔节期 Jointing period | 抽穗期 Heading date | 成熟期 Maturity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | ||||
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 76.44±2.30 f | 1.73±0.04 g | 86.63±1.78 f | 1.21±0.01 f | 129.49±4.96 g | 0.82±0.02 d | ||
| CN | 300 | 133.99±3.01 a | 2.32±0.03 a | 190.36±1.67 a | 1.87±0.01 a | 234.08±0.89 a | 1.17±0.03 a | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 120.48±1.39 b | 2.21±0.03 bc | 175.15±2.42 c | 1.82±0.01 ab | 228.85±1.47 bc | 1.14±0.00 bc | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 118.79±3.05 b | 2.18±0.03 cd | 182.17±7.00 b | 1.80±0.02 b | 228.27±2.34 bcd | 1.14±0.01 bc | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 129.90±4.80 a | 2.26±0.02 ab | 186.10±5.35 ab | 1.82±0.01 ab | 230.48±2.10 ab | 1.16±0.02 ab | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 118.04±2.98 b | 2.15±0.04 cde | 162.29±3.23 d | 1.71±0.02 c | 227.76±1.93 bcd | 1.14±0.01 bc | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 116.00±0.37 bc | 2.14±0.01 cde | 169.60±2.38 c | 1.79±0.02 b | 229.43±1.41 bc | 1.16±0.01 ab | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 106.57±1.86 de | 2.07±0.04 e | 144.01±1.54 e | 1.61±0.03 e | 224.26±0.31 def | 1.12±0.00 c | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 106.80±2.41 de | 2.14±0.02 cde | 144.11±6.43 e | 1.62±0.04 e | 225.03±2.50 cde | 1.14±0.01 bc | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 108.17±3.40 de | 2.10±0.06 de | 147.73±5.15 e | 1.64±0.02 de | 219.94±1.44 f | 1.14±0.01 bc | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 111.12±3.86 cd | 2.07±0.04 e | 146.52±3.46 e | 1.68 ±0.02 cd | 222.00±3.07 ef | 1.12±0.02 c | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 103.97±1.30 e | 1.99±0.04 f | 147.13±2.68 e | 1.69±1.69 cd | 221.50±0.82 ef | 1.12±0.01 c | ||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 82.97±0.79 e | 1.88±0.01 f | 85.70±3.89 f | 1.32±0.05 f | 126.91±2.29 d | 0.91±0.01 e | ||
| CN | 300 | 136.65±1.94 a | 2.40±0.02 a | 188.39±4.03 a | 1.94±0.01 a | 230.87±1.42 a | 1.15±0.01 abc | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 119.31±3.14 b | 2.32±0.02 bc | 166.66±3.73 bc | 1.88±0.03 bc | 227.76±1.62 ab | 1.16±0.01 a | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 120.68±0.50 b | 2.32±0.01 bc | 168.69±0.94 b | 1.85±0.03 c | 225.74±2.05 b | 1.13±0.01 cd | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 121.88±3.05 b | 2.29±0.07 c | 160.82±1.22 cd | 1.78±0.01 d | 226.58±2.05 ab | 1.16±0.01 ab | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 122.61±3.69 b | 2.28±0.04 c | 158.50±3.47 d | 1.68±0.02 e | 226.91±2.89 ab | 1.16±0.01 abc | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 132.96±0.79 a | 2.38±0.01 ab | 186.11±1.74 a | 1.92±0.03 ab | 228.51±0.64 ab | 1.14±0.02 abcd | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 108.88±3.82 cd | 2.10±0.03 e | 141.23±5.62 e | 1.65±0.02 e | 218.47±2.00 c | 1.12±0.01 d | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 112.28±1.32 c | 2.24±0.03 cd | 141.14±5.10 e | 1.68±0.07 e | 219.51±0.61 c | 1.13±0.00 bcd | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 107.43±7.05 cd | 2.17±0.06 de | 141.63±1.75 e | 1.69±0.00 e | 219.61±0.89 c | 1.14±0.01 abcd | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 105.68±2.47 d | 2.11±0.03 e | 144.35±1.34 e | 1.67±0.02 e | 218.66±1.04 c | 1.13±0.01 cd | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 109.82±0.66 cd | 2.16±0.01 e | 140.57±3.17 e | 1.65±0.02 e | 220.31±1.95 c | 1.14±0.01 abcd | ||
| 扬辐粳8号Yangfujing 8 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 65.37±1.59 d | 1.67±0.03 e | 87.93±2.24 g | 1.20±0.02 e | 123.01±2.29 d | 0.81±0.01 f | ||
| CN | 300 | 125.57±2.52 a | 2.26±0.02 a | 181.52±2.58 a | 1.82±0.03 a | 228.32±1.63 a | 1.18±0.01 a | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 111.61±1.24 b | 2.23±0.05 ab | 164.08±2.97 cd | 1.73±0.04 bc | 220.08±1.86 b | 1.14±0.01 cd | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 107.11±1.74 b | 2.16±0.02 bc | 166.32±1.23 c | 1.75±0.01 b | 220.44±1.22 b | 1.17±0.00 ab | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 108.42±1.50 b | 2.13±0.06 c | 160.78±2.82 cd | 1.69±0.03 c | 221.36±2.43 b | 1.17±0.02 ab | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 124.55±2.63 a | 2.29±0.06 a | 174.14±2.83 b | 1.76±0.02 b | 224.18±1.73 b | 1.16±0.01 bc | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 111.69±1.92 b | 2.17±0.01 bc | 157.76±1.21 d | 1.73±0.00 bc | 221.66±2.60 b | 1.13±0.02 cde | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 98.97±1.41 c | 2.03±0.04 d | 143.33±3.39 e | 1.61±0.02 d | 210.67±0.72 c | 1.11±0.01 de | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 97.80±3.48 c | 2.03±0.07 d | 142.26±2.41 ef | 1.59±0.01 d | 213.42±1.00 c | 1.12±0.01 de | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 97.91±4.50 c | 2.00±0.03 d | 136.52±1.46 ef | 1.61±0.02 d | 212.71±3.63 c | 1.11±0.01 e | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 99.82±1.45 c | 2.04±0.01 d | 135.38±5.52 f | 1.57±0.04 d | 213.16±2.31 c | 1.11±0.01 de | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 97.37±1.53 c | 2.01±0.03 d | 141.99±2.64 ef | 1.61±0.01 d | 211.99±2.11 c | 1.11±0.01 de | ||
| F值F-value | |||||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 206.24** | 67.22** | 37.84** | 94.63** | 117.06** | 2.71ns | |||
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 158.75** | 97.61** | 334.41** | 245.55** | 1130.05** | 296.47** | |||
| V×N | 4.94** | 3.48** | 7.83** | 5.156** | 1.09ns | 5.63** | |||
表6 氮肥减施对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻几个重要时期水稻氮素吸收的影响(2019年)
Table 6. Effects of different nitrogen reduction treatments on nitrogen absorption of late-maturing japonica rice with different panicle types at important stages (2019).
| 品种/减施处理Cultivar/treatment | 施氮量 Total nitrogen level/(t·hm-2) | 拔节期 Jointing period | 抽穗期 Heading date | 成熟期 Maturity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | 植株氮积累量Nitrogen accumulation /(kg·hm-2) | 植株含氮率Nitrogen content /% | ||||
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 76.44±2.30 f | 1.73±0.04 g | 86.63±1.78 f | 1.21±0.01 f | 129.49±4.96 g | 0.82±0.02 d | ||
| CN | 300 | 133.99±3.01 a | 2.32±0.03 a | 190.36±1.67 a | 1.87±0.01 a | 234.08±0.89 a | 1.17±0.03 a | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 120.48±1.39 b | 2.21±0.03 bc | 175.15±2.42 c | 1.82±0.01 ab | 228.85±1.47 bc | 1.14±0.00 bc | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 118.79±3.05 b | 2.18±0.03 cd | 182.17±7.00 b | 1.80±0.02 b | 228.27±2.34 bcd | 1.14±0.01 bc | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 129.90±4.80 a | 2.26±0.02 ab | 186.10±5.35 ab | 1.82±0.01 ab | 230.48±2.10 ab | 1.16±0.02 ab | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 118.04±2.98 b | 2.15±0.04 cde | 162.29±3.23 d | 1.71±0.02 c | 227.76±1.93 bcd | 1.14±0.01 bc | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 116.00±0.37 bc | 2.14±0.01 cde | 169.60±2.38 c | 1.79±0.02 b | 229.43±1.41 bc | 1.16±0.01 ab | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 106.57±1.86 de | 2.07±0.04 e | 144.01±1.54 e | 1.61±0.03 e | 224.26±0.31 def | 1.12±0.00 c | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 106.80±2.41 de | 2.14±0.02 cde | 144.11±6.43 e | 1.62±0.04 e | 225.03±2.50 cde | 1.14±0.01 bc | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 108.17±3.40 de | 2.10±0.06 de | 147.73±5.15 e | 1.64±0.02 de | 219.94±1.44 f | 1.14±0.01 bc | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 111.12±3.86 cd | 2.07±0.04 e | 146.52±3.46 e | 1.68 ±0.02 cd | 222.00±3.07 ef | 1.12±0.02 c | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 103.97±1.30 e | 1.99±0.04 f | 147.13±2.68 e | 1.69±1.69 cd | 221.50±0.82 ef | 1.12±0.01 c | ||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 82.97±0.79 e | 1.88±0.01 f | 85.70±3.89 f | 1.32±0.05 f | 126.91±2.29 d | 0.91±0.01 e | ||
| CN | 300 | 136.65±1.94 a | 2.40±0.02 a | 188.39±4.03 a | 1.94±0.01 a | 230.87±1.42 a | 1.15±0.01 abc | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 119.31±3.14 b | 2.32±0.02 bc | 166.66±3.73 bc | 1.88±0.03 bc | 227.76±1.62 ab | 1.16±0.01 a | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 120.68±0.50 b | 2.32±0.01 bc | 168.69±0.94 b | 1.85±0.03 c | 225.74±2.05 b | 1.13±0.01 cd | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 121.88±3.05 b | 2.29±0.07 c | 160.82±1.22 cd | 1.78±0.01 d | 226.58±2.05 ab | 1.16±0.01 ab | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 122.61±3.69 b | 2.28±0.04 c | 158.50±3.47 d | 1.68±0.02 e | 226.91±2.89 ab | 1.16±0.01 abc | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 132.96±0.79 a | 2.38±0.01 ab | 186.11±1.74 a | 1.92±0.03 ab | 228.51±0.64 ab | 1.14±0.02 abcd | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 108.88±3.82 cd | 2.10±0.03 e | 141.23±5.62 e | 1.65±0.02 e | 218.47±2.00 c | 1.12±0.01 d | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 112.28±1.32 c | 2.24±0.03 cd | 141.14±5.10 e | 1.68±0.07 e | 219.51±0.61 c | 1.13±0.00 bcd | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 107.43±7.05 cd | 2.17±0.06 de | 141.63±1.75 e | 1.69±0.00 e | 219.61±0.89 c | 1.14±0.01 abcd | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 105.68±2.47 d | 2.11±0.03 e | 144.35±1.34 e | 1.67±0.02 e | 218.66±1.04 c | 1.13±0.01 cd | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 109.82±0.66 cd | 2.16±0.01 e | 140.57±3.17 e | 1.65±0.02 e | 220.31±1.95 c | 1.14±0.01 abcd | ||
| 扬辐粳8号Yangfujing 8 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 65.37±1.59 d | 1.67±0.03 e | 87.93±2.24 g | 1.20±0.02 e | 123.01±2.29 d | 0.81±0.01 f | ||
| CN | 300 | 125.57±2.52 a | 2.26±0.02 a | 181.52±2.58 a | 1.82±0.03 a | 228.32±1.63 a | 1.18±0.01 a | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 111.61±1.24 b | 2.23±0.05 ab | 164.08±2.97 cd | 1.73±0.04 bc | 220.08±1.86 b | 1.14±0.01 cd | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 107.11±1.74 b | 2.16±0.02 bc | 166.32±1.23 c | 1.75±0.01 b | 220.44±1.22 b | 1.17±0.00 ab | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 108.42±1.50 b | 2.13±0.06 c | 160.78±2.82 cd | 1.69±0.03 c | 221.36±2.43 b | 1.17±0.02 ab | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 124.55±2.63 a | 2.29±0.06 a | 174.14±2.83 b | 1.76±0.02 b | 224.18±1.73 b | 1.16±0.01 bc | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 111.69±1.92 b | 2.17±0.01 bc | 157.76±1.21 d | 1.73±0.00 bc | 221.66±2.60 b | 1.13±0.02 cde | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 98.97±1.41 c | 2.03±0.04 d | 143.33±3.39 e | 1.61±0.02 d | 210.67±0.72 c | 1.11±0.01 de | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 97.80±3.48 c | 2.03±0.07 d | 142.26±2.41 ef | 1.59±0.01 d | 213.42±1.00 c | 1.12±0.01 de | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 97.91±4.50 c | 2.00±0.03 d | 136.52±1.46 ef | 1.61±0.02 d | 212.71±3.63 c | 1.11±0.01 e | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 99.82±1.45 c | 2.04±0.01 d | 135.38±5.52 f | 1.57±0.04 d | 213.16±2.31 c | 1.11±0.01 de | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 97.37±1.53 c | 2.01±0.03 d | 141.99±2.64 ef | 1.61±0.01 d | 211.99±2.11 c | 1.11±0.01 de | ||
| F值F-value | |||||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 206.24** | 67.22** | 37.84** | 94.63** | 117.06** | 2.71ns | |||
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 158.75** | 97.61** | 334.41** | 245.55** | 1130.05** | 296.47** | |||
| V×N | 4.94** | 3.48** | 7.83** | 5.156** | 1.09ns | 5.63** | |||
| 品种/减施处理 Cultivar/treatment | 施氮量 Total nitrogen level/(t·hm-2) | 抽穗期至成熟期氮素转运量 Nitrogen transport/(kg·hm-2) | 抽穗期至成熟期氮素转运率 Nitrogen transfer rate/% | 成熟期穗部氮素增加量 Increase of nitrogen/(kg·hm-2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | ||||
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 38.22±2.28 e | 46.13±1.27 g | 52.20±2.13 a | 55.29±1.13 b | 81.09±3.92 e | 85.94±4.37 f | ||
| CN | 300 | 87.80±2.07 a | 105.45±1.57 a | 53.83±1.20 a | 60.37±0.59 a | 131.52±3.43 a | 149.60±1.93 a | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 75.37±3.85 b | 87.73±4.14 bc | 50.34±2.08 a | 53.42±1.29 bcd | 129.06±2.61 ab | 139.39±1.42 b | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 82.04±8.70 ab | 80.18±3.03 cd | 52.02±2.63 a | 49.95±1.37 cde | 128.14±1.64 abc | 132.10±1.20 cde | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 84.22±2.91 ab | 94.90±2.35 b | 53.01±0.91 a | 54.59±0.86 bc | 128.61±4.37 abc | 139.58±4.95 b | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 61.66±1.93 c | 77.40±1.39 de | 44.83±0.56 b | 49.46±1.73 de | 127.13±1.52 abc | 137.74±2.38 bc | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 64.39±2.77 c | 73.47±4.48 def | 43.90±1.06 bc | 46.46±2.70 e | 124.21±1.23 bc | 133.13±1.80 cde | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 47.18±3.02 d | 77.13±9.80 de | 38.59±2.30 cde | 50.10±4.45 cde | 127.42±3.32 abc | 133.94±2.59 cd | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 47.31±6.40 d | 69.53±4.66 ef | 38.05±3.40 de | 46.69±2.31 e | 128.23±1.11 abc | 133.59±3.11 cd | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 49.79±5.98 d | 69.41±6.81 ef | 39.04±3.16 cde | 46.13±2.97 e | 122.00±2.13 cd | 130.06±0.75 de | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 51.18±1.80 d | 65.10±4.53 f | 39.69±0.40 bcd | 45.43±2.05 e | 126.67±1.31 abc | 131.37±0.60 de | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 43.12±2.74 de | 70.94±1.56 ef | 33.68±1.69 e | 46.31±0.53 e | 117.48±3.23 d | 127.56±2.90 e | ||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 33.67±5.78 e | 49.83±0.85 d | 45.53±5.53 a | 55.45±1.52 a | 74.88±1.89 c | 76.91±0.99 f | ||
| CN | 300 | 69.90±3.78 a | 95.21±5.97 a | 42.83±13.8 ab | 51.29±2.44 ab | 112.38±1.16 ab | 124.47±4.64 ab | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 53.36±2.87 bc | 68.93±6.45 bc | 36.64±1.12 cd | 42.06±3.61 c | 114.46±1.45 ab | 119.68±2.48 bc | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 58.70±1.93 b | 69.44±6.45 b | 39.84±1.17 bc | 43.17±2.66 c | 115.74±3.05 a | 119.41±4.27 bc | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 48.87±3.69 c | 66.32±3.26 bc | 34.70±2.28 cde | 39.82±1.61 c | 114.63±1.39 ab | 116.69±2.96 c | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 45.08±3.01 cd | 65.82±3.15 bc | 32.86±1.67 def | 40.84±1.08 c | 113.48±5.29 ab | 119.06±2.02 bc | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 70.72±4.81 a | 90.14±3.77 a | 43.57±2.51 ab | 49.66±1.48 b | 113.11±3.09 ab | 125.20±1.06 a | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 32.83±5.92 e | 61.65±2.72 bc | 26.06±3.60 gh | 40.22±0.95 c | 110.07±0.90 ab | 110.18±2.59 de | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 29.39±6.33 e | 66.62±3.31 bc | 23.49±4.19 h | 41.85±2.06 c | 107.77±3.29 b | 108.96±2.25 de | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 35.28±1.72 de | 59.83±1.14 c | 28.07±1.01 fgh | 39.07±0.65 c | 113.27±2.07 ab | 108.19±2.00 e | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 37.59±0.94 de | 64.11±1.74 bc | 29.57±0.76 efg | 41.49±0.99 c | 111.90±2.32 ab | 110.79±1.00 de | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 33.14±3.89 e | 61.39±4.44 bc | 26.71±2.50 gh | 40.46±2.71 c | 112.89±1.52 ab | 114.40±3.79 cd | ||
| 扬辐粳8号Yangfujing 8 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 33.46±2.36 cd | 28.67±1.48 c | 44.16±1.98 a | 36.75±1.19 a | 68.54±2.74 c | 66.07±2.65 c | ||
| CN | 300 | 53.58±2.93 a | 52.43±3.08 a | 33.55±1.64 b | 32.35±1.61 b | 100.38±1.33 ab | 100.89±3.89 ab | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 40.33±5.55 bc | 36.65±4.27 bc | 27.70±3.21 cde | 24.76±2.61 d | 96.34±1.09 b | 101.02±1.34 ab | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 46.50±1.72 ab | 39.76±1.49 b | 31.30±0.93 bc | 26.47±0.38 d | 100.62±1.48 ab | 101.07±0.87 ab | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 41.32±7.18 bc | 35.27±1.85 bc | 28.71±4.47 bcd | 24.42±1.24 d | 101.90±8.08 ab | 103.33±2.78 a | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 48.96±4.68 ab | 49.62±2.88 a | 31.90±2.79 bc | 31.31±1.78 bc | 99.00±2.13 ab | 103.33±4.00 a | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 40.25±2.76 bc | 35.01±7.17 bc | 28.30±1.67 bcd | 24.70±5.19 d | 104.15±4.42 a | 102.45±5.78 a | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 30.21±4.53 de | 36.13±2.02 bc | 23.39±2.90 def | 25.90±1.34 d | 97.55±1.56 ab | 99.08±1.06 ab | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 32.61±4.17 cd | 37.85±6.01 bc | 25.37±2.69 de | 27.62±4.06 cd | 103.78±1.39 a | 103.34±3.77 a | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 21.24±0.99 e | 35.68±4.07 bc | 17.38±0.93 g | 25.43±2.15 d | 97.41±3.62 ab | 99.10±1.71 ab | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 22.89±7.26 e | 30.88±0.63 bc | 18.62±5.11 fg | 22.90±0.64 d | 100.66±1.38 ab | 100.33±2.09 ab | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 28.77±3.00 de | 33.00±1.76 bc | 22.55±1.96 efg | 23.78±1.14 d | 98.78±0.72 ab | 95.43±1.09 b | ||
| F值F-value | |||||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 326.78** | 842.881** | 390.92** | 654.203** | 1230.22** | 191.522** | |||
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 57.33** | 36.976** | 42.1* | 20.663** | 87.06** | 144.074** | |||
| V×N | 6.28** | 7.275** | 3.85** | 3.779** | 2.82** | 5.864** | |||
表7 氮肥减施对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻在抽穗期至成熟期关键阶段氮素转运的影响
Table 7. Effects of different nitrogen reduction treatments on nitrogen translocation of late-maturing Japonica rice with different panicle types.
| 品种/减施处理 Cultivar/treatment | 施氮量 Total nitrogen level/(t·hm-2) | 抽穗期至成熟期氮素转运量 Nitrogen transport/(kg·hm-2) | 抽穗期至成熟期氮素转运率 Nitrogen transfer rate/% | 成熟期穗部氮素增加量 Increase of nitrogen/(kg·hm-2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | ||||
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 38.22±2.28 e | 46.13±1.27 g | 52.20±2.13 a | 55.29±1.13 b | 81.09±3.92 e | 85.94±4.37 f | ||
| CN | 300 | 87.80±2.07 a | 105.45±1.57 a | 53.83±1.20 a | 60.37±0.59 a | 131.52±3.43 a | 149.60±1.93 a | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 75.37±3.85 b | 87.73±4.14 bc | 50.34±2.08 a | 53.42±1.29 bcd | 129.06±2.61 ab | 139.39±1.42 b | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 82.04±8.70 ab | 80.18±3.03 cd | 52.02±2.63 a | 49.95±1.37 cde | 128.14±1.64 abc | 132.10±1.20 cde | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 84.22±2.91 ab | 94.90±2.35 b | 53.01±0.91 a | 54.59±0.86 bc | 128.61±4.37 abc | 139.58±4.95 b | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 61.66±1.93 c | 77.40±1.39 de | 44.83±0.56 b | 49.46±1.73 de | 127.13±1.52 abc | 137.74±2.38 bc | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 64.39±2.77 c | 73.47±4.48 def | 43.90±1.06 bc | 46.46±2.70 e | 124.21±1.23 bc | 133.13±1.80 cde | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 47.18±3.02 d | 77.13±9.80 de | 38.59±2.30 cde | 50.10±4.45 cde | 127.42±3.32 abc | 133.94±2.59 cd | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 47.31±6.40 d | 69.53±4.66 ef | 38.05±3.40 de | 46.69±2.31 e | 128.23±1.11 abc | 133.59±3.11 cd | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 49.79±5.98 d | 69.41±6.81 ef | 39.04±3.16 cde | 46.13±2.97 e | 122.00±2.13 cd | 130.06±0.75 de | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 51.18±1.80 d | 65.10±4.53 f | 39.69±0.40 bcd | 45.43±2.05 e | 126.67±1.31 abc | 131.37±0.60 de | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 43.12±2.74 de | 70.94±1.56 ef | 33.68±1.69 e | 46.31±0.53 e | 117.48±3.23 d | 127.56±2.90 e | ||
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 33.67±5.78 e | 49.83±0.85 d | 45.53±5.53 a | 55.45±1.52 a | 74.88±1.89 c | 76.91±0.99 f | ||
| CN | 300 | 69.90±3.78 a | 95.21±5.97 a | 42.83±13.8 ab | 51.29±2.44 ab | 112.38±1.16 ab | 124.47±4.64 ab | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 53.36±2.87 bc | 68.93±6.45 bc | 36.64±1.12 cd | 42.06±3.61 c | 114.46±1.45 ab | 119.68±2.48 bc | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 58.70±1.93 b | 69.44±6.45 b | 39.84±1.17 bc | 43.17±2.66 c | 115.74±3.05 a | 119.41±4.27 bc | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 48.87±3.69 c | 66.32±3.26 bc | 34.70±2.28 cde | 39.82±1.61 c | 114.63±1.39 ab | 116.69±2.96 c | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 45.08±3.01 cd | 65.82±3.15 bc | 32.86±1.67 def | 40.84±1.08 c | 113.48±5.29 ab | 119.06±2.02 bc | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 70.72±4.81 a | 90.14±3.77 a | 43.57±2.51 ab | 49.66±1.48 b | 113.11±3.09 ab | 125.20±1.06 a | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 32.83±5.92 e | 61.65±2.72 bc | 26.06±3.60 gh | 40.22±0.95 c | 110.07±0.90 ab | 110.18±2.59 de | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 29.39±6.33 e | 66.62±3.31 bc | 23.49±4.19 h | 41.85±2.06 c | 107.77±3.29 b | 108.96±2.25 de | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 35.28±1.72 de | 59.83±1.14 c | 28.07±1.01 fgh | 39.07±0.65 c | 113.27±2.07 ab | 108.19±2.00 e | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 37.59±0.94 de | 64.11±1.74 bc | 29.57±0.76 efg | 41.49±0.99 c | 111.90±2.32 ab | 110.79±1.00 de | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 33.14±3.89 e | 61.39±4.44 bc | 26.71±2.50 gh | 40.46±2.71 c | 112.89±1.52 ab | 114.40±3.79 cd | ||
| 扬辐粳8号Yangfujing 8 | |||||||||
| 0N | 0 | 33.46±2.36 cd | 28.67±1.48 c | 44.16±1.98 a | 36.75±1.19 a | 68.54±2.74 c | 66.07±2.65 c | ||
| CN | 300 | 53.58±2.93 a | 52.43±3.08 a | 33.55±1.64 b | 32.35±1.61 b | 100.38±1.33 ab | 100.89±3.89 ab | ||
| BN10 | 270 | 40.33±5.55 bc | 36.65±4.27 bc | 27.70±3.21 cde | 24.76±2.61 d | 96.34±1.09 b | 101.02±1.34 ab | ||
| TN10 | 270 | 46.50±1.72 ab | 39.76±1.49 b | 31.30±0.93 bc | 26.47±0.38 d | 100.62±1.48 ab | 101.07±0.87 ab | ||
| SPN10 | 270 | 41.32±7.18 bc | 35.27±1.85 bc | 28.71±4.47 bcd | 24.42±1.24 d | 101.90±8.08 ab | 103.33±2.78 a | ||
| SSN10 | 270 | 48.96±4.68 ab | 49.62±2.88 a | 31.90±2.79 bc | 31.31±1.78 bc | 99.00±2.13 ab | 103.33±4.00 a | ||
| AN10 | 270 | 40.25±2.76 bc | 35.01±7.17 bc | 28.30±1.67 bcd | 24.70±5.19 d | 104.15±4.42 a | 102.45±5.78 a | ||
| BN20 | 240 | 30.21±4.53 de | 36.13±2.02 bc | 23.39±2.90 def | 25.90±1.34 d | 97.55±1.56 ab | 99.08±1.06 ab | ||
| TN20 | 240 | 32.61±4.17 cd | 37.85±6.01 bc | 25.37±2.69 de | 27.62±4.06 cd | 103.78±1.39 a | 103.34±3.77 a | ||
| SPN20 | 240 | 21.24±0.99 e | 35.68±4.07 bc | 17.38±0.93 g | 25.43±2.15 d | 97.41±3.62 ab | 99.10±1.71 ab | ||
| SSN20 | 240 | 22.89±7.26 e | 30.88±0.63 bc | 18.62±5.11 fg | 22.90±0.64 d | 100.66±1.38 ab | 100.33±2.09 ab | ||
| AN20 | 240 | 28.77±3.00 de | 33.00±1.76 bc | 22.55±1.96 efg | 23.78±1.14 d | 98.78±0.72 ab | 95.43±1.09 b | ||
| F值F-value | |||||||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 326.78** | 842.881** | 390.92** | 654.203** | 1230.22** | 191.522** | |||
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 57.33** | 36.976** | 42.1* | 20.663** | 87.06** | 144.074** | |||
| V×N | 6.28** | 7.275** | 3.85** | 3.779** | 2.82** | 5.864** | |||
| 品种/减施处理 Cultivar/treatment | 氮素吸收利用率 Nitrogen apparent recovery efficiency/% | 氮肥偏生产力 Partial factor productivity of nitrogen/(kg·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | ||
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||
| CN | 34.95±0.30 e | 35.16±0.15 d | 38.37±0.35 f | 38.23±0.40 d | |
| BN10 | 36.90±0.54 cd | 37.55±0.79 bc | 39.81±0.44 e | 40.74±0.04 c | |
| TN10 | 36.69±0.86 d | 36.08±0.65 cd | 39.94±0.53 e | 40.75±0.11 c | |
| SPN10 | 37.50±0.78 bcd | 39.63±0.65 a | 41.59±0.99 cd | 42.40±0.24 b | |
| SSN10 | 36.50±0.72 d | 37.70±0.94 b | 40.10±0.60 e | 40.49±0.29 c | |
| AN10 | 37.12±0.52 bcd | 37.88±0.59 b | 40.49±1.04 de | 40.20±0.34 c | |
| BN20 | 39.60±0.13 a | 39.07±1.15 ab | 43.83±0.61 ab | 43.94±0.25 ab | |
| TN20 | 39.92±1.04 a | 39.85±0.66 a | 43.17±0.73 b | 43.35±0.69 ab | |
| SPN20 | 37.80±0.60 bcd | 39.68±0.51 a | 44.68±0.30 a | 44.46±0.70 a | |
| SSN20 | 38.66±1.28 ab | 38.30±1.03 ab | 43.08±0.21 b | 42.55±0.55 b | |
| AN20 | 38.45±0.34 abc | 38.60±0.40 ab | 41.82±0.48 c | 43.01±1.67 ab | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||
| CN | 34.82±0.47 d | 35.32±0.25 c | 35.72±0.37 d | 36.24±0.12 d | |
| BN10 | 37.54±0.60 abc | 37.91±0.70 ab | 37.95±0.18 bc | 38.74±0.09 c | |
| TN10 | 36.79±0.76 c | 36.59±1.68 bc | 37.86±0.46 bc | 38.72±0.29 c | |
| SPN10 | 37.10±0.76 bc | 38.25±0.69 ab | 38.17±0.32 bc | 36.62±1.08 d | |
| SSN10 | 37.22±1.07 bc | 38.02±0.80 ab | 37.52±0.35 c | 38.70±0.17 c | |
| AN10 | 37.82±0.24 abc | 38.92±0.63 a | 39.11±0.23 b | 39.94±0.28 bc | |
| BN20 | 38.36±0.84 abc | 37.08±0.25 b | 41.26±0.44 a | 42.14±0.47 a | |
| TN20 | 38.79±0.25 ab | 36.90±0.93 bc | 40.64±0.35 a | 42.45±0.37 a | |
| SPN20 | 38.84±0.37 ab | 36.75±0.56 bc | 40.96±1.89 a | 39.59±1.09 bc | |
| SSN20 | 38.44±0.43 abc | 36.74±0.65 bc | 40.68±0.61 a | 40.98±1.66 ab | |
| AN20 | 39.13±0.81 a | 38.32±0.63 ab | 40.81±0.55 a | 41.14±1.42 ab | |
| 扬辐粳8号 Yangfujing 8 | |||||
| CN | 34.91±0.54 d | 34.82±0.37 c | 29.11±0.55 e | 29.36±0.28 d | |
| BN10 | 37.82±0.69 c | 37.44 ±0.80 ab | 30.82±0.55 d | 30.96±0.09 bc | |
| TN10 | 37.95±0.45 bc | 37.66 ±0.91 ab | 30.57±0.67 d | 31.00±0.02 bc | |
| SPN10 | 38.29±0.90 abc | 37.19 ±0.22 ab | 30.81±0.41 d | 30.06±1.05 cd | |
| SSN10 | 39.34±0.64 abc | 38.79 ±0.70 a | 31.75±0.44 cd | 32.54±0.29 ab | |
| AN10 | 38.40±0.96 abc | 38.38 ±0.31 ab | 30.67±0.37 d | 33.63±0.67 a | |
| BN20 | 38.62±0.30 abc | 36.79 ±0.70 b | 33.67±0.16 ab | 31.04±0.04 bc | |
| TN20 | 39.77±0.42 a | 38.15 ±0.28 ab | 34.07±0.31 a | 33.71±0.59 a | |
| SPN20 | 39.47±1.51 abc | 38.08 ±0.75 ab | 32.85±0.62 abc | 31.79±0.96 b | |
| SSN20 | 39.66±0.96 ab | 38.44 ±0.93 ab | 33.54±0.36 ab | 33.77±0.33 a | |
| AN20 | 39.17±0.88 abc | 38.08±0.30 ab | 32.36±0.62 bc | 32.10±1.15 b | |
| F值F-value | |||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 16.2* | 22.224** | 3170.17** | 1568.163** | |
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 17.2* | 10.481** | 46.25** | 31.383** | |
| V×N | 1.19ns | 3.036** | 1.89* | 3.722** | |
表8 氮肥减施对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻氮素利用的影响
Table 8. Effects of reduced nitrogen fertilizer application on nitrogen utilization of late-maturing japonica rice with different panicle types.
| 品种/减施处理 Cultivar/treatment | 氮素吸收利用率 Nitrogen apparent recovery efficiency/% | 氮肥偏生产力 Partial factor productivity of nitrogen/(kg·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | ||
| 丰粳3227 Fengjing 3227 | |||||
| CN | 34.95±0.30 e | 35.16±0.15 d | 38.37±0.35 f | 38.23±0.40 d | |
| BN10 | 36.90±0.54 cd | 37.55±0.79 bc | 39.81±0.44 e | 40.74±0.04 c | |
| TN10 | 36.69±0.86 d | 36.08±0.65 cd | 39.94±0.53 e | 40.75±0.11 c | |
| SPN10 | 37.50±0.78 bcd | 39.63±0.65 a | 41.59±0.99 cd | 42.40±0.24 b | |
| SSN10 | 36.50±0.72 d | 37.70±0.94 b | 40.10±0.60 e | 40.49±0.29 c | |
| AN10 | 37.12±0.52 bcd | 37.88±0.59 b | 40.49±1.04 de | 40.20±0.34 c | |
| BN20 | 39.60±0.13 a | 39.07±1.15 ab | 43.83±0.61 ab | 43.94±0.25 ab | |
| TN20 | 39.92±1.04 a | 39.85±0.66 a | 43.17±0.73 b | 43.35±0.69 ab | |
| SPN20 | 37.80±0.60 bcd | 39.68±0.51 a | 44.68±0.30 a | 44.46±0.70 a | |
| SSN20 | 38.66±1.28 ab | 38.30±1.03 ab | 43.08±0.21 b | 42.55±0.55 b | |
| AN20 | 38.45±0.34 abc | 38.60±0.40 ab | 41.82±0.48 c | 43.01±1.67 ab | |
| 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 | |||||
| CN | 34.82±0.47 d | 35.32±0.25 c | 35.72±0.37 d | 36.24±0.12 d | |
| BN10 | 37.54±0.60 abc | 37.91±0.70 ab | 37.95±0.18 bc | 38.74±0.09 c | |
| TN10 | 36.79±0.76 c | 36.59±1.68 bc | 37.86±0.46 bc | 38.72±0.29 c | |
| SPN10 | 37.10±0.76 bc | 38.25±0.69 ab | 38.17±0.32 bc | 36.62±1.08 d | |
| SSN10 | 37.22±1.07 bc | 38.02±0.80 ab | 37.52±0.35 c | 38.70±0.17 c | |
| AN10 | 37.82±0.24 abc | 38.92±0.63 a | 39.11±0.23 b | 39.94±0.28 bc | |
| BN20 | 38.36±0.84 abc | 37.08±0.25 b | 41.26±0.44 a | 42.14±0.47 a | |
| TN20 | 38.79±0.25 ab | 36.90±0.93 bc | 40.64±0.35 a | 42.45±0.37 a | |
| SPN20 | 38.84±0.37 ab | 36.75±0.56 bc | 40.96±1.89 a | 39.59±1.09 bc | |
| SSN20 | 38.44±0.43 abc | 36.74±0.65 bc | 40.68±0.61 a | 40.98±1.66 ab | |
| AN20 | 39.13±0.81 a | 38.32±0.63 ab | 40.81±0.55 a | 41.14±1.42 ab | |
| 扬辐粳8号 Yangfujing 8 | |||||
| CN | 34.91±0.54 d | 34.82±0.37 c | 29.11±0.55 e | 29.36±0.28 d | |
| BN10 | 37.82±0.69 c | 37.44 ±0.80 ab | 30.82±0.55 d | 30.96±0.09 bc | |
| TN10 | 37.95±0.45 bc | 37.66 ±0.91 ab | 30.57±0.67 d | 31.00±0.02 bc | |
| SPN10 | 38.29±0.90 abc | 37.19 ±0.22 ab | 30.81±0.41 d | 30.06±1.05 cd | |
| SSN10 | 39.34±0.64 abc | 38.79 ±0.70 a | 31.75±0.44 cd | 32.54±0.29 ab | |
| AN10 | 38.40±0.96 abc | 38.38 ±0.31 ab | 30.67±0.37 d | 33.63±0.67 a | |
| BN20 | 38.62±0.30 abc | 36.79 ±0.70 b | 33.67±0.16 ab | 31.04±0.04 bc | |
| TN20 | 39.77±0.42 a | 38.15 ±0.28 ab | 34.07±0.31 a | 33.71±0.59 a | |
| SPN20 | 39.47±1.51 abc | 38.08 ±0.75 ab | 32.85±0.62 abc | 31.79±0.96 b | |
| SSN20 | 39.66±0.96 ab | 38.44 ±0.93 ab | 33.54±0.36 ab | 33.77±0.33 a | |
| AN20 | 39.17±0.88 abc | 38.08±0.30 ab | 32.36±0.62 bc | 32.10±1.15 b | |
| F值F-value | |||||
| 品种Variety(V) | 16.2* | 22.224** | 3170.17** | 1568.163** | |
| 氮肥处理Nitrogen(N) | 17.2* | 10.481** | 46.25** | 31.383** | |
| V×N | 1.19ns | 3.036** | 1.89* | 3.722** | |
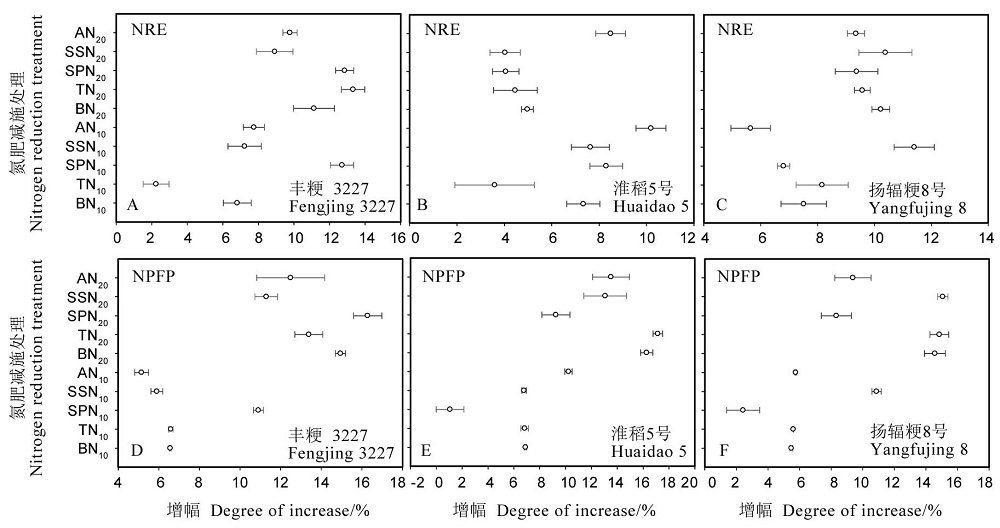
图2 氮肥减施对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻氮肥吸收利用率(NRE)和氮肥偏生产力(NPFP)的影响
Fig. 2. Increase in the nitrogen apparent recovery efficiency (NRE) and partial factor productivity of nitrogen (NPFP) of late-maturing medium japonica rice with different panicle types under nitrogen fertilizer reduction.
| [1] | 杨建昌, 杜永, 吴长付, 刘立军, 王志琴, 朱庆森. 超高产粳型水稻生长发育特性的研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2006, 39(7): 1336-1345. |
| Yang J C, Du Y, Wu C F, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Zhu Q S. Growth and development characteristics of super-high- yielding mid-season japonica rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2006, 39(7): 1336-1345. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Fan M S, Shen J B, Yuan L X, Jiang R F, Chen X P, Davies W J, Zhang F S. Improving crop productivity and resource use efficiency to ensure food security and environmental quality in China[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63(1): 13-24. |
| [3] | Chen Y L, Xiao C X, Chen X C, Li Q, Zhang J, Chen F J, Yuan L X, Mi G H. Characterization of the plant traits contributed to high grain yield and high grain nitrogen concentration in maize[J]. Field Crops Research, 2014, 159: 1-9. |
| [4] | Xue YG, Duan H, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Zhang J H. An improved crop management increases grain yield and nitrogen and water use efficiency in rice[J]. Crop Science, 2013, 53(1): 271-284. |
| [5] | Liu L J, Chen T T, Wang Z Q, Zhang H, Yang J C, Zhang J H. Combination of site-specific nitrogen management and alternate wetting and drying irrigation increases grain yield and nitrogen and water use efficiency in super rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 154: 226-235. |
| [6] | Peng S B, Buresh R J, Huang J L, Zhong X H, Zou Y B, Yang J C, Wang G H, Liu Y Y, Tang Q Y, Cui K H, Zhang F S, Dobermann A. Improving nitrogen fertilization in rice by site-specific N management: A review[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2010, 30(3): 649-656. |
| [7] | Hussain S, Peng S B, Fahad S, Khaliq A, Huang J L, Cui K H, Nie L X. Rice management interventions to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions: A review[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(5): 3342-3360. |
| [8] | 刘红江, 郑建初, 郭智, 陈留根, 张岳芳, 王鑫. 太湖地区氮肥减量对水稻氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(11): 2960-2965. |
| Liu H J, Zheng J C, Guo Z, Chen L G, Zhang Y F, Wang X. Effects of reduced nitrogen application on nitrogen uptake and use efficiency of rice in Taihu area[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(11): 2960-2965. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 王绍华, 曹卫星, 丁艳锋, 田永超, 姜东. 水氮互作对水稻氮吸收与利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2004, 37(4): 497-501. |
| Wang S H, Cao W X, Ding Y F, Tian Y C, Jiang D. Interactions of water management and nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen absorption and utilization in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2004, 37(4): 497-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 汤国平, 熊强强, 钟蕾, 陈小荣, 朱昌兰, 彭小松, 贺浩华. 双季早稻氮素亏缺补偿效应的形成及其生理机制初探[J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(8): 1585-1593. |
| Tang G P, Xiong Q Q, Zhong L, Chen X R, Zhu C L, Peng X S, He H H. Primary research on the formation and its physiological mechanism of nitrogen deficiency compensatory effects in double-season early rice[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(8): 1585-1593. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 龙瑞平, 张朝钟, 戈芹英, 李贵勇, 夏琼梅, 朱海平, 马淑琴, 万卫东, 王勤, 杨从党. 不同轮作模式下基于机插粳稻稳产和氮肥高效的氮肥运筹方式[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(4): 646-656. |
| Long R P, Zhang C Z, Ge Q Y, Li G Y, Xia Q M, Zhu H P, Ma S Q, Wan W D, Wang Q, Yang C D. Nitrogen management in machinery transplanted japonica rice under different rotation systems for stable grain yield and higher nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(4): 646-656. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Yang J C, Zhang J H, Liu K. Involvement of polyamines in the drought resistance of rice. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2007, 61: 3177-3189. |
| [13] | 方林发, 张宇亭, 谢军, 黄兴成, 赵亚南, 杨林生, 石孝均. 氮肥用量和运筹对冷浸田水稻产量和氮素利用率的影响. 西南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 42(3): 53-60. |
| Fang L F, Zhang Y T, Xie J, Huang X C, Zhao Y N, Yang L S, Shi X J. Effects of nitrogen rate and application regime on rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency in cold waterlogged paddy fields[J]. Journal of Southwest University: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 42(3): 53-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 李俊周, 邵鹏, 彭廷, 张静, 孙红正, 赵全志. 施氮量对杂交水稻Y两优886产量、稻米品质及氮肥吸收利用的影响[J]. 杂交水稻, 2017, 32(6): 50-54. |
| Li J Z, Shao P, Peng T, Zhang J, Sun H Z, Zhao Q Z. Effects of nitrogen rate on grain yield,quality and nitrogen uptake and utilization of hybrid rice Y liangyou 886[J]. Hybrid rice, 2017, 32(6): 50-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 孙永健, 孙园园, 严奉君, 杨志远, 徐徽, 李玥, 王海月, 马均. 氮肥后移对不同减氮效率水稻花后碳氮代谢的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 44(3): 407-419. |
| Sun Y J, Sun Y Y, Yan F J, Yang Z Y, Xu H, Li Y, Wang H Y, Ma J. Effects of postponing nitrogen top dressing on post-anthesis carbon and nitrogen metabolism in rice cultivars with different nitrogen use efficiencies[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 407-419. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 刘立军, 王康君, 卞金龙, 熊溢伟, 陈璐, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 水稻产量对氮肥响应的品种间差异及其与根系形态生理的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2014, 40(11): 1999-2007. |
| Liu L J, Wang K J, Bian J L, Xiong Y W, Chen L, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Differences in yield response to nitrogen fertilizer among rice cultivars and their relationship with root morphology and physiology[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(11): 1999-2007. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 张洪程, 马群, 杨雄, 李敏, 葛梦婕, 李国业, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 高辉, 刘艳阳. 水稻品种氮肥群体最高生产力及其增长规律[J]. 作物学报, 2012, 38(1): 86-98. |
| Zhang H C, Ma Q, Yang X, Li M, Ge M J, Li G Y, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Gao H, Liu Y Y. The highest population productivity of nitrogen fertilization and its variation rules in rice cultivars[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(1): 86-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 张自常, 李鸿伟, 曹转勤, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 施氮量和灌溉方式的交互作用对水稻产量和品质影响[J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(1): 84-92. |
| Zhang Z C, Li H W, Cao Z Q, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Effect of interaction between nitrogen rate and irrigation regime on grain yield and quality of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(1): 84-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 邹应斌, 敖和军, 夏冰, 唐启源, 彭少兵, Roland J Buresh. 不同氮肥施用对杂交稻产量及其氮素利用效率的影响[J]. 作物研究, 2008, 22(4): 214-219. |
| Zou Y B, Ao H J, Xia B, Tang Q Y, Peng S B, Roland J B. Effects of different nitrogen application on the yield and nitrogen use efficiency in hybrid rice[J]. Crop Research, 2008, 22(4): 214-219. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Zhang X X, Zhou J, Huang N S, Mo L J, Lv M J, Gao Y B, Chen C, Yin S Y, Ju J, Dong G C, Zhou Y, Yang Z F, Li A H, Wang Y L, Huang J Y, Yao Y L. Transcriptomic and co-expression network profiling of shoot apical meristem reveal contrasting response to nitrogen rate between indica and japonica rice subspecies[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(23): 5922. |
| [21] | 蒋鹏, 熊洪, 张林, 朱永川, 周兴兵, 刘茂, 郭晓艺, 徐富贤. 不同生态条件下施氮量和移栽密度对杂交稻氮、磷、钾吸收积累的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(2): 342-350. |
| Jiang P, Xiong H, Zhang L, Zhu Y C, Zhou X B, Liu M, Guo X Y, Xu F X. Effects of N rate and planting density on nutrient uptake and utilization of hybrid rice under different ecological conditions[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2017, 23(2): 342-350. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 吴培, 陈天晔, 袁嘉琦, 黄恒, 邢志鹏, 胡雅杰, 朱明, 李德剑, 刘国林, 张洪程. 施氮量和直播密度互作对水稻产量形成特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 269-281. |
| Wu P, Chen T Y, Yuan J Q, Huang H, Xing Z P, Hu Y J, Zhu M, Li D J, Liu G L, Zhang H C. Effects of interaction between nitrogen application rate and direct-sowing density on yield formation characteristics of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(3): 269-281. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 李俊峰, 杨建昌. 水分与氮素及其互作对水稻产量和水肥利用效率的影响研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(3): 327-334. |
| Li J F, Yang J C. Research advances in the effects of water, nitrogen and their interaction on the yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(3): 327-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 朱相成, 张振平, 张俊, 邓艾兴, 张卫建. 增密减氮对东北水稻产量、氮肥利用效率及温室效应的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(2): 453-461. |
| Zhu X C, Zhang Z P, Zhang J, Deng A X, Zhang W J. Effects of increased planting density with reduced nitrogen fertilizer application on rice yield, N use efficiency and greenhouse gas emission in northeast China[J], Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(2): 453-461. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 李敏, 罗德强, 江学海, 蒋明金, 姬广梅, 李立江, 周维佳. 控水增密模式对杂交籼稻减氮后产量形成的调控效应[J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(9): 1430-1447. |
| Li M, Luo D Q, Jiang X H, Jiang M J, Ji G M, Li L J, Zhou W J. Regulations of controlled irrigations and increased densities on yield formation of hybrid indica rice under nitrogen-reduction conditions[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(9): 1430-1447. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Zhang H, Jing W J, Zhao B H, Wang W L, Xu Y J, Zhang W Y, Gu J F, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Alternative fertilizer and irrigation practices improve rice yield and resource use efficiency by regulation source- sink relationships[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 265: 108124 |
| [27] | 凌启鸿. 作物群体质量[M]. 上海: 上海科学出版社, 2000: 45-220. |
| Ling Q H. Crop Population Quality[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2000: 45-220. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 张敏, 赵淼, 田玉华, 尹斌, 朱兆良. 太湖地区高产高效措施下水稻氮淋溶和径流损失的研究[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(1): 35-42. |
| Zhang M, Zhao M, Tian Y H, Yin B, Zhu Z L. Study on N leaching and runoff under integrated high yield and high efficiency practices in paddy fields of Taihu Lake region[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(1): 35-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 霍中洋, 杨雄, 张洪程, 葛梦婕, 马群, 李敏, 戴其根, 许轲, 魏海燕, 李国业, 朱聪聪, 王亚江, 颜希亭. 不同氮肥群体最高生产力水稻品种各器官的干物质和氮素的积累与转运[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(5): 1035-1045. |
| Huo Z Y, Yang X, Zhang H C, Ge M J, Ma Q, Li M, Dai Q G, Xu K, Wei H Y, Li G Y, Zhu C C, Wang Y J, Yan X T. Accumulation and translocation of dry matter and nitrogen nutrition in organs of rice cultivars with different productivity levels[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2012, 18(5): 1035-1045. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 陈佳娜, 曹放波, 谢小兵, 单双吕, 高伟, 李志斌, 黄敏, 邹应斌. 机插条件下低氮密植栽培对“早晚兼用”双季稻产量和氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(8): 1176-1187. |
| Chen J N, Cao F B, Xie X B, Shan S L, Gao W, Li Z B, Huang M, Zou Y B. Effect of low nitrogen rate combined with high plant density on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of machine-transplanted early-late season double cropping rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(8): 1176-1187. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 乔月, 朱建强, 吴启侠, 黄思情, 李明辉. 氮肥运筹下不同种植方式水稻对氮素的吸收、转运和利用[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019, 12(6): 1-8. |
| Qiao Y, Zhu J Q, Wu Q X, Huang S Q, Li M H. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer management on nitrogen absorption, translocation and utilization of rice in different planting methods[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2019, 12(6): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 金树权, 陈若霞, 汪峰, 姚红燕, 谌江华. 不同氮肥运筹模式对稻田田面水氮浓度和水稻产量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(1): 242-248. |
| Jin S Q, Chen R X, Wang F, Yao H Y, Chen J H. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer application modes on the variation of nitrogen concentration in paddy field surface water and the yield of rice[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(1): 242-248. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 吴立鹏, 张士荣, 娄金华, 魏立兴, 孙泽强, 刘盛林, 丁效东. 秸秆还田与优化施氮对稻田土壤碳氮含量及产量的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(4): 158-166. |
| Wu L P, Zhang S R, Lou J H, Wei L X, Sun Z Q, Liu S L, Ding X D. Effects of straw returning and nitrogen fertilizer on soil C and N content and yield of rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2019, 34(4): 158-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 仇景涛, 吴壮, 蒋天昊, 刘飞, 张祖建. 不同生育时期氮肥减施对水稻群体生产特征的影响及减肥策略初步分析[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2020, 41(3): 52-58+65. |
| Qiu J T, Wu Z, Jiang T H, Liu F, Zhang Z J. Effects of nitrogen reduction at different growth stages on rice population production characteristics and preliminary analysis of nitrogen reduction strategies[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition), 2020, 41(3): 52-58+65. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [4] | 赵艺婷, 谢可冉, 高逖, 崔克辉. 水稻分蘖期干旱锻炼对幼穗分化期高温下穗发育和产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [5] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [6] | 彭显龙, 董强, 张辰, 李鹏飞, 李博琳, 刘智蕾, 于彩莲. 不同土壤条件下秸秆还田量对土壤还原性物质及水稻生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [7] | 朱旺, 张翔, 耿孝宇, 张哲, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 戴其根, 许轲, 朱广龙, 周桂生, 孟天瑶. 盐-旱复合胁迫下水稻根系的形态和生理特征及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [8] | 吴玉红, 李艳华, 王吕, 秦宇航, 李杉杉, 郝兴顺, 张庆路, 崔月贞, 肖飞. 陕南稻区紫云英稻草联合还田配施减量氮肥协同提升水稻产量与稻米品质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 628-641. |
| [9] | 邹宇傲, 吴启侠, 周乾顺, 朱建强, 晏军. 孕穗期杂交中稻对淹涝胁迫的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| [10] | 兰金松, 庄慧. 水稻株型的分子机理研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 449-458. |
| [11] | 袁沛, 周旋, 杨威, 尹凌洁, 靳拓, 彭建伟, 荣湘民, 田昌. 化肥减氮配施对洞庭湖区双季稻产量和田面水氮磷流失风险的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 518-528. |
| [12] | 肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [13] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [14] | 高欠清, 任孝俭, 翟中兵, 郑普兵, 吴源芬, 崔克辉. 头季穗肥和促芽肥对再生稻再生芽生长及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 405-414. |
| [15] | 王文婷, 马佳颖, 李光彦, 符卫蒙, 李沪波, 林洁, 陈婷婷, 奉保华, 陶龙兴, 符冠富, 秦叶波. 高温下不同施肥量对水稻产量品质形成的影响及其与能量代谢的关系分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 253-264. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||