
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 285-294.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220810
Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Xiaolong1, WANG Biao2, WANG Benfu1, ZHANG Zhisheng1, ZHANG Zuolin1, YANG Lantian1, CHENG Jianping1,*( ), LI Yang1,*(
), LI Yang1,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-29
Revised:2023-01-06
Online:2023-05-10
Published:2023-05-16
Contact:
*email: chjp609@163.com;liylcy163.com
杨晓龙1, 王彪2, 汪本福1, 张枝盛1, 张作林1, 杨蓝天1, 程建平1,*( ), 李阳1,*(
), 李阳1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
*email: chjp609@163.com;liylcy163.com
基金资助:YANG Xiaolong, WANG Biao, WANG Benfu, ZHANG Zhisheng, ZHANG Zuolin, YANG Lantian, CHENG Jianping, LI Yang. Effects of Different Water Management on Yield and Rice Quality of Dry-seeded Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 285-294.
杨晓龙, 王彪, 汪本福, 张枝盛, 张作林, 杨蓝天, 程建平, 李阳. 不同水分管理方式对旱直播水稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 285-294.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220810
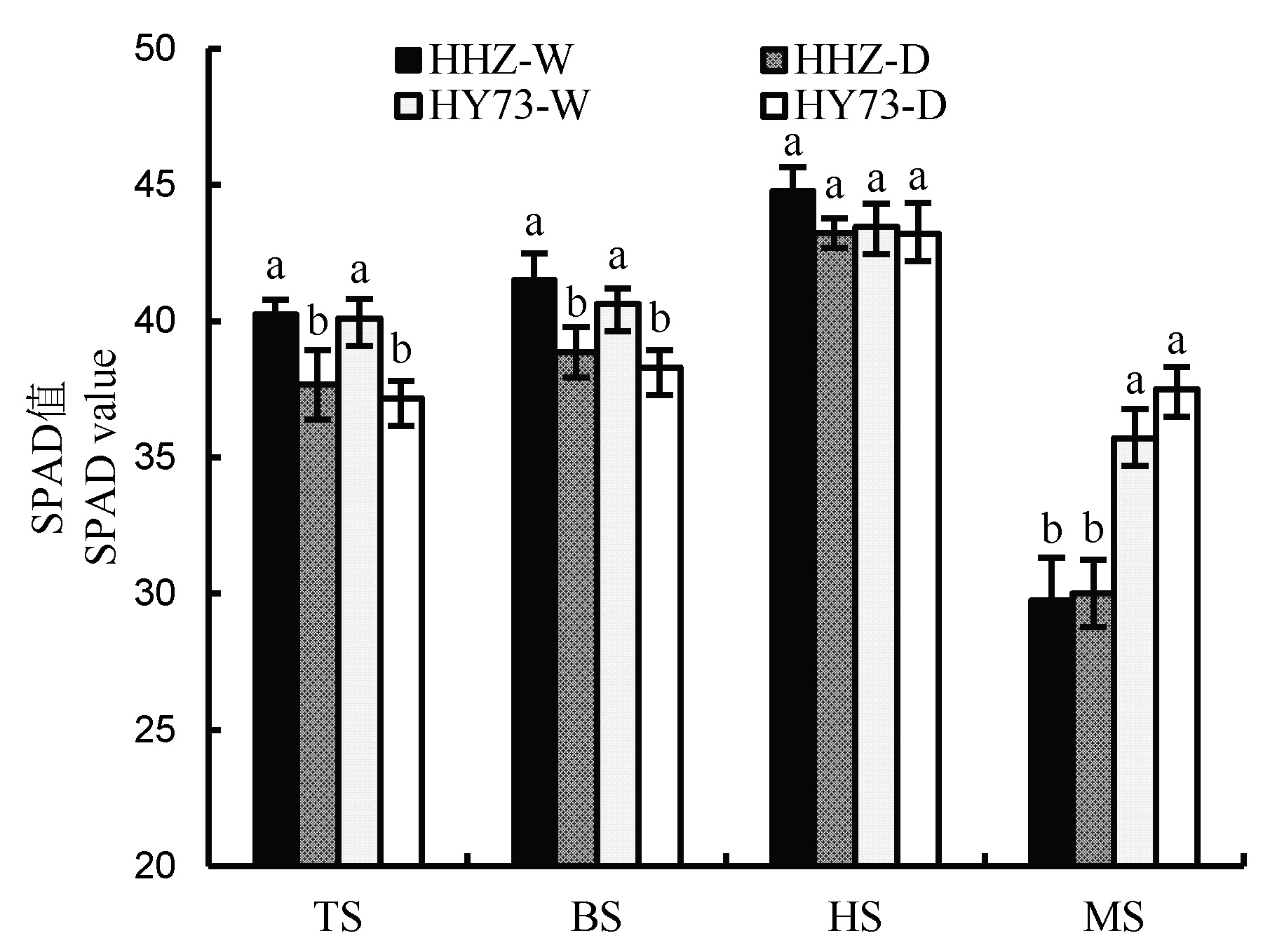
Fig. 1. SPAD value of flag leaf of rice at heading stage under different water management modes. HHZ, Huanghuazhan; HY73, Hanyou 73; W, Traditional flooding; D, Dry cultivation; TS, Tillering stage; BS, Booting stage; HS, Heading stage; MS, Maturity stage. Different letters above the column indicate statistical significance at P=0.05 level. The same below.
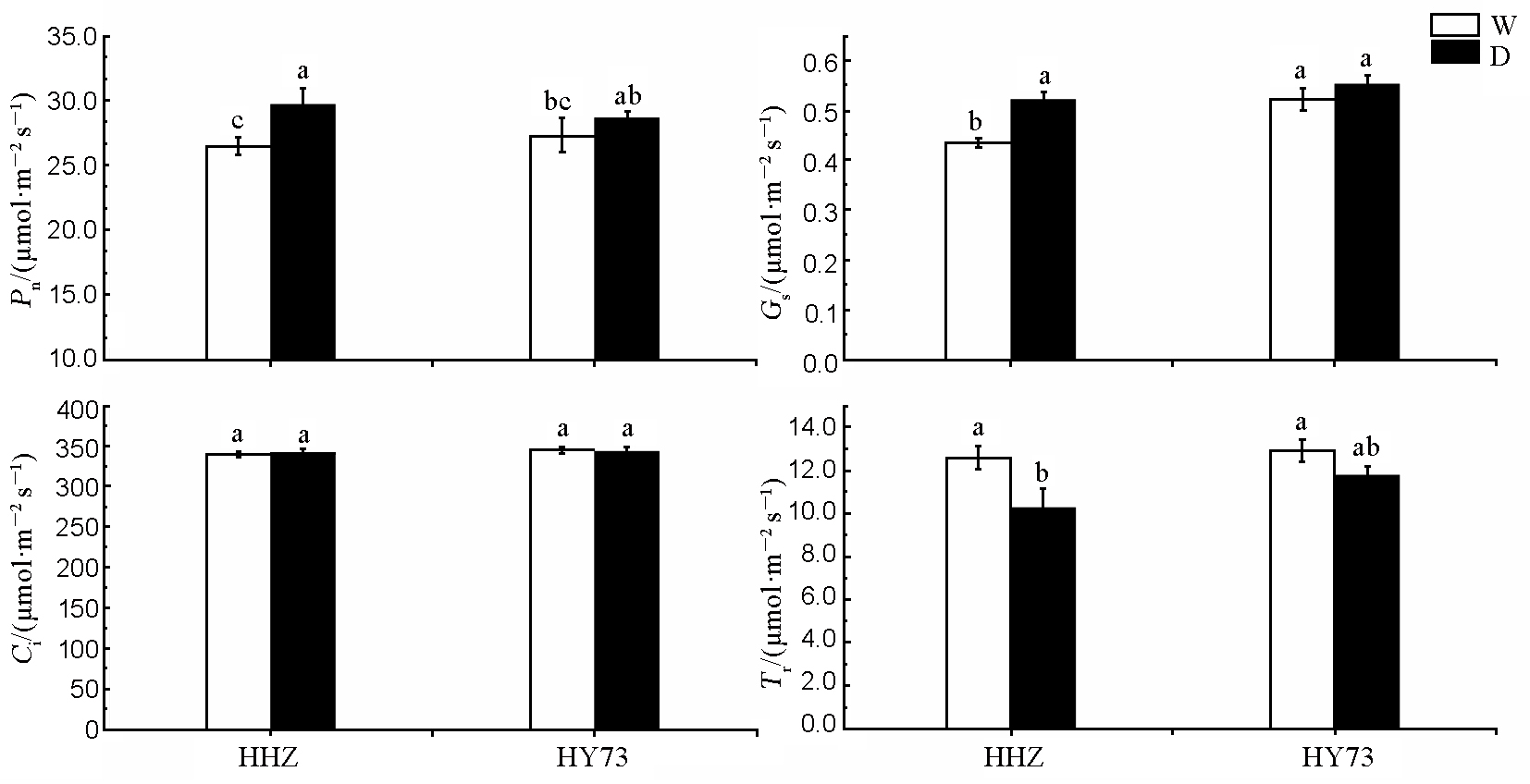
Fig. 2. Photosynthetic parameters of flag leaf of rice at heading stage under different water management modes. HHZ, Huanghuazhan; HY73, Hanyou 73; W, Traditional flooding; D, Dry cultivation. Different letters above the column indicate statistical significance at P=0.05 level. The same as below.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 茎秆 Culm | 叶片 Leaf | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 转运量 Translocation amount/(kg·hm−2) | 转运率 Translocation rate/% | 转运贡献率 Contribution rate of translocation/% | 转运量 Translocation amount/(kg·hm−2) | 转运率 Translocation rate/% | 转运贡献率 Contribution rate of translocation/% | |||
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 419.1±30.2 b | 12.39±1.61 b | 17.57±2.97 b | 305.3±18.15 c | 22.13±1.18 b | 12.70±0.81 b | |
| D | 696.7±57.7 a | 20.55±1.63 a | 25.00±5.05 a | 496.7±29.05 a | 27.89±2.07 a | 17.76±2.84 a | ||
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 303.3±17.4 c | 9.02±0.19 c | 13.38±2.39 b | 250.6±7.25 d | 19.57±2.65 b | 10.98±1.13 b | |
| D | 791.8±77.3 a | 17.94±1.99 a | 27.39±5.45 a | 426.8±21.97 b | 25.83±2.49 a | 14.72±2.20 a | ||
Table 1. Dry matter translocation characteristics in stem and leaves and its contribution to grains in various water management modes.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 茎秆 Culm | 叶片 Leaf | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 转运量 Translocation amount/(kg·hm−2) | 转运率 Translocation rate/% | 转运贡献率 Contribution rate of translocation/% | 转运量 Translocation amount/(kg·hm−2) | 转运率 Translocation rate/% | 转运贡献率 Contribution rate of translocation/% | |||
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 419.1±30.2 b | 12.39±1.61 b | 17.57±2.97 b | 305.3±18.15 c | 22.13±1.18 b | 12.70±0.81 b | |
| D | 696.7±57.7 a | 20.55±1.63 a | 25.00±5.05 a | 496.7±29.05 a | 27.89±2.07 a | 17.76±2.84 a | ||
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 303.3±17.4 c | 9.02±0.19 c | 13.38±2.39 b | 250.6±7.25 d | 19.57±2.65 b | 10.98±1.13 b | |
| D | 791.8±77.3 a | 17.94±1.99 a | 27.39±5.45 a | 426.8±21.97 b | 25.83±2.49 a | 14.72±2.20 a | ||
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 源器官 Source organ/% | 籽粒 Grain/% | 源库比 Source/sink | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘 Culm | 叶 Leaf | 茎鞘+叶 Culm+sheath+leaf | ||||
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 44.64±1.64 a | 16.11±0.65 ab | 60.74±1.74 a | 39.25±1.74 b | 1.55±0.11 a |
| D | 37.46±1.78 b | 17.86±0.34 a | 55.32±1.45 b | 44.68±1.45 ab | 1.24±0.07 b | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 43.14±1.75 a | 14.69±1.80 b | 57.83±3.22 a | 42.17±3.22 b | 1.38±0.17 ab |
| D | 36.70±1.90 b | 14.49±1.08 b | 51.19±0.81 b | 48.81±0.81 a | 1.04±0.04 c | |
Table 2. Dry matter translocation characteristics in stem and leaves in various water management modes.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 源器官 Source organ/% | 籽粒 Grain/% | 源库比 Source/sink | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎鞘 Culm | 叶 Leaf | 茎鞘+叶 Culm+sheath+leaf | ||||
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 44.64±1.64 a | 16.11±0.65 ab | 60.74±1.74 a | 39.25±1.74 b | 1.55±0.11 a |
| D | 37.46±1.78 b | 17.86±0.34 a | 55.32±1.45 b | 44.68±1.45 ab | 1.24±0.07 b | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 43.14±1.75 a | 14.69±1.80 b | 57.83±3.22 a | 42.17±3.22 b | 1.38±0.17 ab |
| D | 36.70±1.90 b | 14.49±1.08 b | 51.19±0.81 b | 48.81±0.81 a | 1.04±0.04 c | |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 每平方米有效穗数 Panicle number per m2 | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Grain yield/(t·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 302.7±12.9 b | 152.8±8.2 c | 92.1±2.4 a | 21.7±0.0 d | 6.80±0.20 c |
| D | 410.7±15.0 a | 123.0±0.7 d | 85.8±1.3 b | 22.6±0.1 c | 7.76±0.22 b | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 257.3±12.9 c | 189.6±4.3 a | 92.1±0.3 a | 28.8±0.1 b | 7.50±0.16 b |
| D | 296.0±8.89 b | 172.7±2.7 b | 86.8±1.6 b | 30.3±0.0 a | 8.39±0.12 a |
Table 3. Effects of different water management methods on yield and its components of rice.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 每平方米有效穗数 Panicle number per m2 | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Grain yield/(t·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 302.7±12.9 b | 152.8±8.2 c | 92.1±2.4 a | 21.7±0.0 d | 6.80±0.20 c |
| D | 410.7±15.0 a | 123.0±0.7 d | 85.8±1.3 b | 22.6±0.1 c | 7.76±0.22 b | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 257.3±12.9 c | 189.6±4.3 a | 92.1±0.3 a | 28.8±0.1 b | 7.50±0.16 b |
| D | 296.0±8.89 b | 172.7±2.7 b | 86.8±1.6 b | 30.3±0.0 a | 8.39±0.12 a |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice rate/% | 精米率 Milled rice rate/% | 整精米率 Head rice rate/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness/% | 粒长 Grain length/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 78.9±0.7 a | 68.0±0.3 a | 65.1±0.1 a | 7.3±0.2 b | 1.2±0.2 b | 6.1±0.01 c |
| D | 76.9±0.4 a | 65.1±1.0 a | 62.3±1.0 a | 7.9±0.2 b | 1.6±0.7 b | 6.0±0.02 c | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 79.4±0.7 a | 66.1±1.0 a | 55.8±1.5 b | 6.4±0.3 b | 1.2±0.3 b | 6.5±0.03 a |
| D | 74.6±2.1 a | 64.5±1.5 a | 51.5±3.2 b | 12.4±1.9 a | 4.6±0.7 a | 6.3±0.08 b |
Table 4. Effects of different water management methods on rice milling and appearance quality.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice rate/% | 精米率 Milled rice rate/% | 整精米率 Head rice rate/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness/% | 粒长 Grain length/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 78.9±0.7 a | 68.0±0.3 a | 65.1±0.1 a | 7.3±0.2 b | 1.2±0.2 b | 6.1±0.01 c |
| D | 76.9±0.4 a | 65.1±1.0 a | 62.3±1.0 a | 7.9±0.2 b | 1.6±0.7 b | 6.0±0.02 c | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 79.4±0.7 a | 66.1±1.0 a | 55.8±1.5 b | 6.4±0.3 b | 1.2±0.3 b | 6.5±0.03 a |
| D | 74.6±2.1 a | 64.5±1.5 a | 51.5±3.2 b | 12.4±1.9 a | 4.6±0.7 a | 6.3±0.08 b |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/% | 砷含量 As content/(mg·kg−1) | 镉含量 Cd content/(mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 15.13±0.26 a | 8.41±0.11 c | 0.18±0.01 a | 0.0412±0.00 b |
| D | 14.51±0.21 b | 9.14±0.08 ab | 0.14±0.00 b | 0.0726±0.00 a | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 13.85±0.21 c | 8.33±0.63 c | 0.15±0.00 b | 0.0424±0.00 b |
| D | 12.80±0.18 d | 9.61±0.42 a | 0.12±0.00 c | 0.0653±0.00 a |
Table 5. Effects of different water management methods on nutritional quality and As/Cd concentrations in milled rice.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 蛋白质含量 Protein content/% | 砷含量 As content/(mg·kg−1) | 镉含量 Cd content/(mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄华占 Huanghuazhan | W | 15.13±0.26 a | 8.41±0.11 c | 0.18±0.01 a | 0.0412±0.00 b |
| D | 14.51±0.21 b | 9.14±0.08 ab | 0.14±0.00 b | 0.0726±0.00 a | |
| 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | W | 13.85±0.21 c | 8.33±0.63 c | 0.15±0.00 b | 0.0424±0.00 b |
| D | 12.80±0.18 d | 9.61±0.42 a | 0.12±0.00 c | 0.0653±0.00 a |
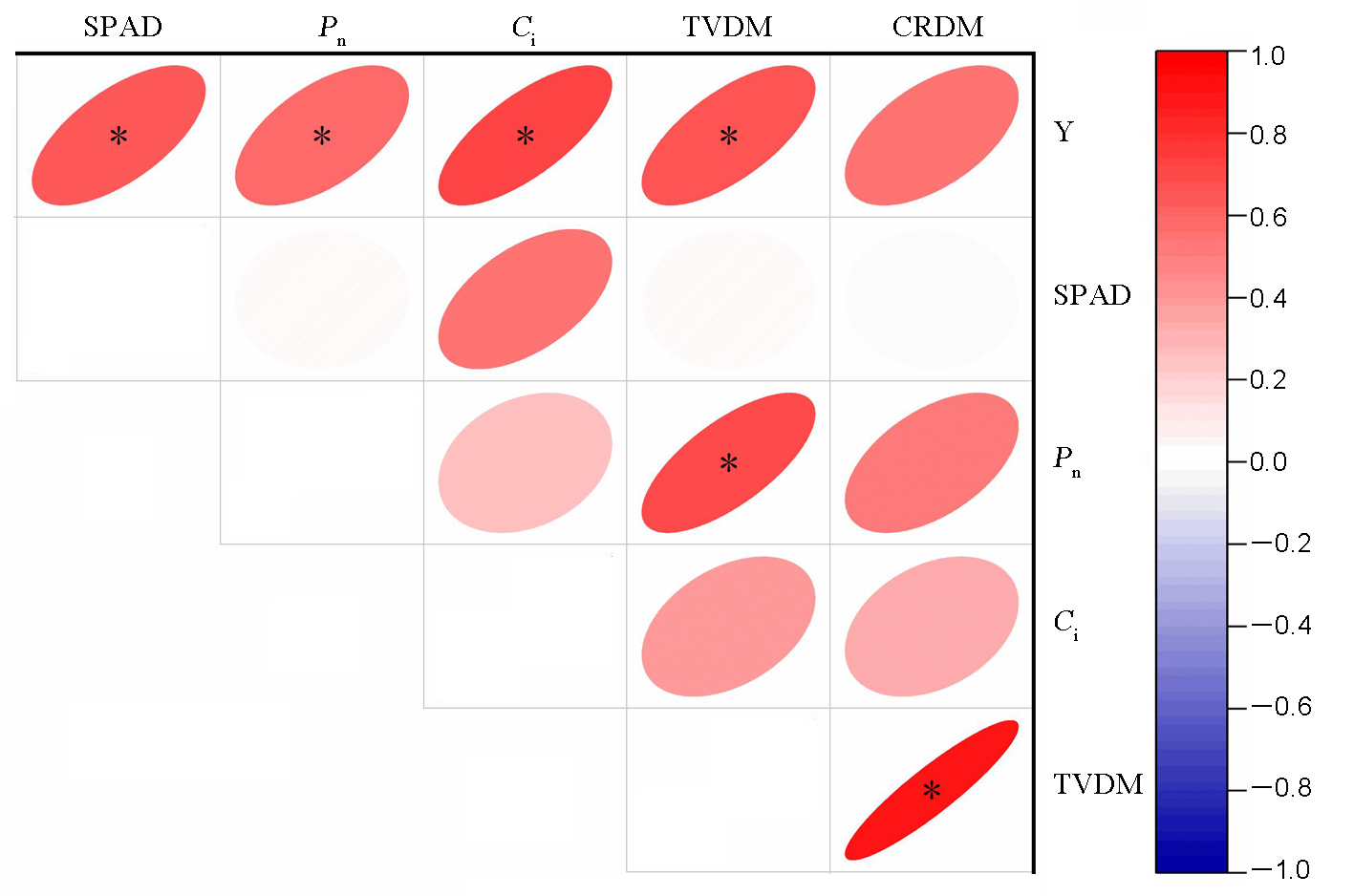
Fig. 4. Correlation analysis between yield, dry matter transport and physiological indicators. Y, Yield; Pn, Net photosynthetic rate; Ci, Intercellular CO2 concentration; TVDM, Transport volume of dry matter; CRDM, Contribution rate of dry matter transport to panicle. *Significantly correlated at the 0.05 probability level.
| [1] | Li Y Y, Shao X H, Sheng Z P, Guan W L, Xiao M H. Water conservation and nitrogen loading reduction effects with controlled and mid-gathering irrigation in a paddy field[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2016, 25(3): 1085-1091. |
| [2] | Peng S B, Tang Q Y, Zou Y B. Current status and challenges of rice production in China[J]. Plant Production Science, 2009, 12(1): 3-8. |
| [3] | 马世浩, 杨丞, 王贵兵, 张赓, 李小坤. 水稻节水灌溉技术模式研究进展[J]. 节水灌溉, 2021, 8: 19-24. |
| Ma S H, Yang C, Wang G B, Zhang G, Li X K. Research progress of rice water-saving irrigation technology mode[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2021, 8: 19-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Bouman B A M, Peng S B, Castaneda A R, Visperas A R. Yield and water use of irrigated tropical aerobic rice systems[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2005, 74: 87-105. |
| [5] | Singh S, Ladha J K, Gupta R K, Bhushan L, Rao A N, Sivaprasad B, Singh P P. Evaluation of mulching, intercropping with Sesbania and herbicide use for weed management in dry-seeded rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Crop Protection, 2007, 26(4): 518-524. |
| [6] | 杜云峰, 江颂颂, 陈宗奎, 毛紫琳, 张志娟, 曹凑贵, 李萍. 播期与补灌对节水抗旱稻旱优73产量、品质与资源利用效率的影响[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2022, 41(1): 123-132. |
| Du Y F, Jiang S S, Chen Z K, Mao Z L, Zhang Z J, Cao C G, Li P. Effects of sowing dates and periods of supplementary irrigation on yield, quality and resource utilization efficiency of water-saving and drought-resistant rice[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022, 41(1): 123-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Fqrooq M, Siddique K H M, Rehman H, Aziz T, Lee D J, Wahid A. Rice direct seeding: experiences, challenges and opportunities[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2011, 111(2): 87-98. |
| [8] | 余灿, 王直华, 张家亮, 曹金华, 刘东华, 黄峰, 靳德明. 水稻半期旱作的节水效果及其对产量和品质的影响[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2009, 28(2): 136-140. |
| Yu C, Wang Z H, Zhang J L, Cao J H, Liu D H, Huang F, Jin D M. The water saving effect of half period dry management of paddy field and its impacts on the yield and grain quality of rice[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2009, 28(2): 136-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Liu H Y, Hussain S, Zheng M M, Peng S B, Huang J L, Cui K H, Nie L X. Dry direct-seeded rice as an alternative to transplanted-flooded rice in Central China[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2015, 15:285-294. |
| [10] | 刘宏岩. 旱直播水稻在不同水分管理下高产高效的生理基础研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017. |
| Liu H Y. Physiological mechanism of high yield and high resources use efficiency of dry seeded rice under different water managements[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 魏永霞, 季俊超, 刘慧, 郭彦君, 郑衍波, 石蕴. 水分管理对旱直播稻温室气体排放与土壤无机氮的影响[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(11): 305-314. |
| Wei Y X, Ji J C, Liu H, Guo Y J, Zheng Y B, Shi Y. Effects of water management on greenhouse gas emission and soil inorganic nitrogen of dry direct seeding rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52(11): 305-314. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Nagarjun P, Nanjappa D G, Sanjay M T, Boregowda Y S, Ramaiah M. Reduction of soil weedseedbank with increased yield in dry direct-seeded rice through weed management[J]. Indian Journal of Weed Science, 2021, 53(4): 363-366. |
| [13] | Joshi E, Kumar D, Lal B, Nepalia V, Gautam P, Vyas A K. Management of direct seeded rice for enhanced resource - use efficiency[J]. Plant Knowledge Journal, 2013, 2(3): 119-134. |
| [14] | Wang W Q, Peng S B, Liu H Y, Tao Y, Huang J L, Cui K H, Nie L X. The possibility of replacing puddled transplanted flooded rice with dry seeded rice in central China: A review[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 214: 310-320. |
| [15] | Zahra N, Hafeez M B, Nawaz A, Farooq M. Rice production systems and grain quality[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2022, 105: 103463. |
| [16] | Rizwan M, Ali S, Abbas T, Adrees M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Qayyum M F, Nawaz R. Residual effects of biochar on growth, photosynthesis and cadmium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Cd stress with different water conditions[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 206: 676-683. |
| [17] | 郭咏梅, 穆平, 刘家富, 卢义宣, 李自超. 水、旱栽培条件下稻米品质主要品质性状的比较研究[J]. 作物学报, 2005, 31(11): 59-64. |
| Guo Y M, Mu P, Liu J F, Lu Y X, Li Z C. Comparative studies on quality characters of rice under water-and-dry cultivation conditions[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2005, 31(11): 59-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Wang G J, Zeng F L, Song P, Sun B, Wang Q, Wang J Y. Effects of reduced chlorophyII content on photosystem functions and photosynthetic electron transport rate in rice leaves[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2022, 272: 153669. |
| [19] | Nan S, Xi L, Zhang Q, Li N F, Xu D L, Cao B S. Better revisiting chlorophyll content retrieval with varying senescent material and solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence simulation on paddy rice during the entire growth stages[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 130: 108057. |
| [20] | Song Q F, Chu C C, Parry M A J, Zhu X G. Genetics-based dynamic systems model of canopy photosynthesis: The key to improve light and resource use efficiencies for crops[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2016, 5(1): 18-25. |
| [21] | 刘宇峰, 李伏生. 灌溉方式与施肥水平对超级稻光合生理的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 21(4): 416-425. |
| Liu Y F, Li F S. Effect of irrigation method and fertilization dose on photosynthetic physiology of super rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2012, 21(4): 416-425. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 蔡昆争, 吴学祝, 骆世明. 不同生育时期土壤干旱后复水对水稻生长发育的补偿效应[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2008, 27(5): 34-36. |
| Cai K Z, Wu X Z, Luo S M. Compensatory effects of re-watering after soil drying on rice growth and development[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2008, 27(5): 34-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 易子豪, 朱德峰, 王亚梁, 胡国辉, 张玉屏, 向镜, 张义凯, 陈惠哲. 水稻生长对干旱的响应及其补偿效应研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2020, 26(4): 1-6. |
| Yi Z H, Zhu D F, Wang Y L, Hu G H, Zhang Y P, Xiang J, Zhang Y K, Chen H Z. Advances of rice growth response to drought and its compensatory effects[J]. China Rice, 2020, 26(4): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 朱海平, 李贵勇, 夏琼梅, 龙瑞平, 邓安凤, 黄军, 相罕章, 杨从党. 不同时期干旱胁迫对水稻产量和生长特性的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2017, 23(4): 135-138. |
| Zhu H P, Li G Y, Xia Q M, Long R P, Deng A F, Huang J, Xiang H Z, Yang C D. Effects of drought stress on yield and growth characteristics of rice in different periods[J]. China Rice, 2017, 23(4): 135-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 杨晓龙, 程建平, 汪本福, 李阳, 张枝盛, 李进兰, 李萍. 灌浆期干旱胁迫对水稻生理性状和产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 38-46. |
| Yang X L, Cheng J P, Wang B F, Li Y, Zhang Z S, Li J L, Li P. Effects of drought stress at grain filling stage on rice physiological characteristics and yield[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(1): 38-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Yang X L, Wang B F, Chen L, Li P, Cao C G. The different influences of drought stress at the flowering stage on rice physiological traits, grain yield, and quality[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 3742. |
| [27] | 何海兵, 武立权, 杨茹, 马富裕, 黄义德. 干旱区控制灌溉下水稻光合特性与蒸腾效率研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(9):186-193. |
| He H B, Wu L Q, Yang R, Ma F Y, Huang Y D. Photosynthesis characteristics and transpiration efficiency of rice plants under controlled irrigation technology in arid region[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(9): 186-193. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 王熹, 陶龙兴, 黄效林, 闵绍楷, 程式华. 滴灌稻田水稻旱作法研究-水稻的生育与生理特性[J]. 中国农业科学, 2004, 37(9): 1274-1281. |
| Wang X, Tao L X, Huang X L, Min S K, Cheng S H. Study on no-flooding farming technique in irrigated paddy field-physiological and developmental characteristics of rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2004, 37(9): 1274-1281. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 王志军, 叶春秀, 董永梅, 李有忠, 田又升, 陈林, 孙国清, 谢宗铭. 滴灌和淹灌栽培模式下水稻光合生理、荧光参数及产量构成因素分析[J]. 植物生理学报, 2016, 52(5): 723-735. |
| Wang Z J, Ye C X, Dong Y M, Li Y Z, Tian Y S, Chen L, Sun G Q, Xie Z M. Photosynthetic physiology, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and yield components of rice under drip irrigation with plastic film mulching and continuous flooding[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2016, 52(5): 723-735. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Chen Z K, Yang X L, Song W Z, Khan A, Najeeb U, Li P, Cao C G. Water-saving cultivation plus super rice hybrid genotype improves water productivity and yield[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2020, 112(3): 1764-1777. |
| [31] | 殷春渊, 王书玉, 刘贺梅, 孙建权, 胡秀明, 王和乐, 田芳慧, 马朝阳, 张栩, 张瑞平, 马晓红. 节水灌溉与常规灌溉对旱直播水稻叶片生理特性、产量及品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(18): 1-9. |
| Yin C Y, Wang S Y, Liu H M, Sun J Q, Hu X M, Wang H L, Tian F H, Ma C Y, Zhang X, Zhang R P, Ma X H. Effects on leaf physiological characteristics, yield and quality of dry seeding rice: water-saving irrigation and conventional irrigation[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(18): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Mahajan G, Chauhan B S, Timsina J, Singh P P, Singh K. Crop performance and water- and nitrogen-use efficiencies in dry-seeded rice in response to irrigation and fertilizer amounts in northwest India[J]. Field Crops Research, 2012, 134: 59-70. |
| [33] | Pan S G, Wen X C, Wang Z M, Ashraf U, Tian H, Duan M Y, Mo Z W, Fan P S, Tang X R. Benefits of mechanized deep placement of nitrogen fertilizer in direct-seeded rice in South China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 203:139-149. |
| [34] | 夏朵, 周浩, 何予卿. 稻米品质的遗传研究及分子育种进展[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2022, 41(1): 48-61. |
| Xia D, Zhou H, He Y Q. Progress on genetic study and molecular breeding of rice quality[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022, 41(1): 48-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | Li X K, Wu L, Geng X, Xia X H, Wang X H, Xu Z J, Xu Q. Deciphering the environmental impacts on rice quality for different rice cultivated areas[J]. Rice, 2018, 11(1): 1-10 |
| [36] | 杨丞, 汪洋, 张万洋, 叶廷红, 鲁剑巍, 张赓, 李小坤. 灌溉模式与施氮量互作对水稻茎蘖产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 155-165. |
| Yang C, Wang Y, Zhang W Y, Ye T H, Lu J W, Zhang G, Li X K. Effects of interaction between irrigation mode and nitrogen application rate on the yield formation of main stem and tillers of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(2): 155-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Li Y B, Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Yun P, Luo L J, Yan B, Peng B, Xie W B, Wang G W, Li X H, Xiao J H, Xu C G, He Y Q. Chalk5 encodes a vacuolar H +-translocating pyrophosphatase influencing grain chalkiness in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2014, 46(4): 398-404. |
| [38] | 刘东华. 干旱胁迫对稻谷品质性状及WX基因表达的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2014. |
| Liu H D. The impacts of drought stress on grain quality and Wx gene expression in rice[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 金正勋, 杨静, 钱春荣, 刘海英, 金学泳, 秋太权. 灌浆成熟期温度对水稻籽粒淀粉合成关键酶活性及品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(4): 377-380. |
| Jin Z X, Yang J, Qian C R, Liu H Y, Jin X Y, Qiu T Q. Effects of temperature during grain filling period on activities of key enzymes for starch synthesis and rice grain quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2005, 19(4): 377-380. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 陈璐, 杨斗龙, 米艳华, 李倩, 王丹, 王文治, 杜丽娟, 尹本林. 水分管理对复合污染稻田Pb、Cd和As迁移特性及稻米质量安全的影响[J]. 土壤与作物, 2022, 11(1): 96-103. |
| Chen L, Yang D L, Mi Y H, Li Q, Wang D, Wang W Z, Du L J, Yin B L. Effects of water management on soil heavy metal transport and rice quality safety[J]. Soils and Crops, 11(1): 96-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | Zhang Q, Chen H F, Huang D Y, Xu C, Zhu H H, Zhu Q H. Water managements limit heavy metal accumulation in rice: Dual effects of iron-plaque formation and microbial communities[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 618: 790-799. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | ZHAO Yiting, XIE Keran, GAO Ti, CUI Kehui. Effects of Drought Priming During Tillering Stage on Panicle Development and Yield Formation Under High Temperature During Panicle Initiation Stage in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||