
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 150-158.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210606
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
QIU Linlin1, LIU Qiao1, FU Yaping2, LIU Wenzhen2, HU Guocheng2, ZHAI Yufeng1, PANG Bo1, WANG Dekai1,*( )
)
Received:2021-06-17
Revised:2021-09-14
Online:2022-03-10
Published:2022-03-11
Contact:
WANG Dekai
裘霖琳1, 刘窍1, 付亚萍2, 刘文真2, 胡国成2, 翟玉凤1, 庞礴1, 汪得凯1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
汪得凯
基金资助:QIU Linlin, LIU Qiao, FU Yaping, LIU Wenzhen, HU Guocheng, ZHAI Yufeng, PANG Bo, WANG Dekai. Identification and Gene Cloning of DSP2 in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 150-158.
裘霖琳, 刘窍, 付亚萍, 刘文真, 胡国成, 翟玉凤, 庞礴, 汪得凯. 水稻矮化小穗基因DSP2的鉴定与克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 150-158.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210606
| 引物名称 | 正向引物序列 | 反向引物序列 | 实验目的 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primer name | Forward primer(5'-3') | Reverse primer(5'-3') | Purpose |
| ORF1-qPCR | AGATCAACCTCCAACTACTCTC | AAGCTCAGTAGTACACAGGC | RT-PCR |
| ORF2-qPCR | GTGGTTCCAGAAGATCGTGTC | TTGTCGATGGACAGGAGCTC | RT-PCR |
| ORF3-qPCR | CACGCCTACGACAACATGAAC | GTACTCGAACGCGTTGACATC | RT-PCR |
| ORF4-qPCR | CCGGTGATACAAAGAGGTGC | ATATGCTTCGGCCACCTTG | RT-PCR |
| ORF5-qPCR | AGCGGTTGTCTGGTGATATC | AGACAGAAAACCCCTTGACG | RT-PCR |
| ORF6-qPCR | CAGCTTCTGATCCTGCAGTAG | ATCTCCCTTACTGATGCTGAC | RT-PCR |
| UBQ5-qPCR | ACCACTTCGACCGCCACTACT | ACGCCTAAGCCTGCTGGTT | RT-PCR |
| HPTⅡ | CAGAAGAAGATGTTGGCGAC | ATGTCCTGCGGGTAAATAGC | 共分离分析 Co-segregation |
| DSP2-ORF | ATGTCGACATGGCTGGTGCTACGGCTGC | ATCTGCAGCTGAGAGTAGTTGGAGGTTGAT | 全长ORF Full length ORF |
| NPTⅡ | TATGTCCTGATAGCGGTCCG | GTGCCCTGAATGAACTCCAG | 转化植株检测 Detection of transgenic plants |
Table 1 Primers used for PCR identification and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis.
| 引物名称 | 正向引物序列 | 反向引物序列 | 实验目的 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primer name | Forward primer(5'-3') | Reverse primer(5'-3') | Purpose |
| ORF1-qPCR | AGATCAACCTCCAACTACTCTC | AAGCTCAGTAGTACACAGGC | RT-PCR |
| ORF2-qPCR | GTGGTTCCAGAAGATCGTGTC | TTGTCGATGGACAGGAGCTC | RT-PCR |
| ORF3-qPCR | CACGCCTACGACAACATGAAC | GTACTCGAACGCGTTGACATC | RT-PCR |
| ORF4-qPCR | CCGGTGATACAAAGAGGTGC | ATATGCTTCGGCCACCTTG | RT-PCR |
| ORF5-qPCR | AGCGGTTGTCTGGTGATATC | AGACAGAAAACCCCTTGACG | RT-PCR |
| ORF6-qPCR | CAGCTTCTGATCCTGCAGTAG | ATCTCCCTTACTGATGCTGAC | RT-PCR |
| UBQ5-qPCR | ACCACTTCGACCGCCACTACT | ACGCCTAAGCCTGCTGGTT | RT-PCR |
| HPTⅡ | CAGAAGAAGATGTTGGCGAC | ATGTCCTGCGGGTAAATAGC | 共分离分析 Co-segregation |
| DSP2-ORF | ATGTCGACATGGCTGGTGCTACGGCTGC | ATCTGCAGCTGAGAGTAGTTGGAGGTTGAT | 全长ORF Full length ORF |
| NPTⅡ | TATGTCCTGATAGCGGTCCG | GTGCCCTGAATGAACTCCAG | 转化植株检测 Detection of transgenic plants |
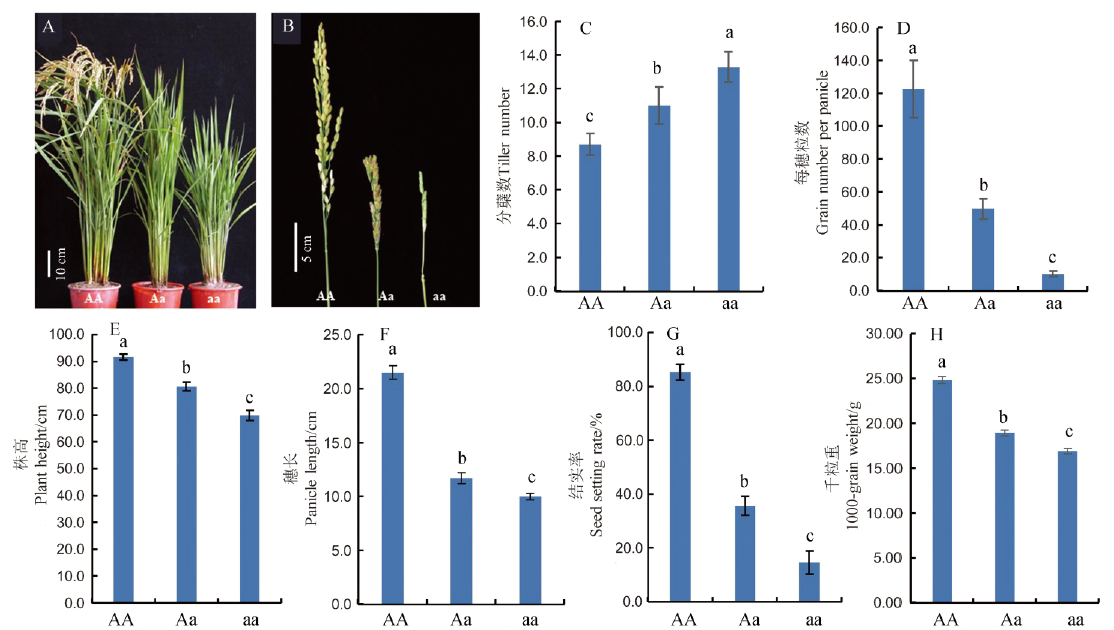
Fig. 1. Phenotypes of the dsp2-D mutant. AA, Wild-type ‘Nipponbare’ plants; Aa, dsp2-D heterozygous plants; aa, dsp2-D homozygous plants. Values are mean ± SD of ten biological replicates. Samples with different letters are significantly different (P < 0.01; Tukey’s test).
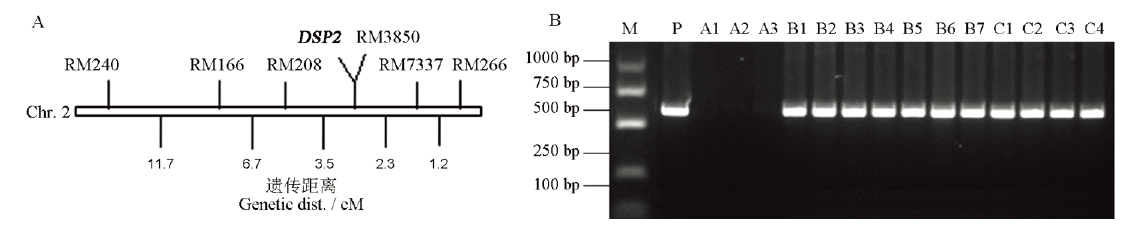
Fig. 2. Location of DSP2 on chromosome 2 and co-segregation analysis of T-DNA. A, Preliminary localization of DSP2 gene; B, Co-segregation analysis of T-DNA and dsp2-D phenotypes. M, 1 kb ladder, P, Plasmid positive control; A1-A3, Wild type; B1-B7, Heterozygote; C1-C4, Homozygous mutant.
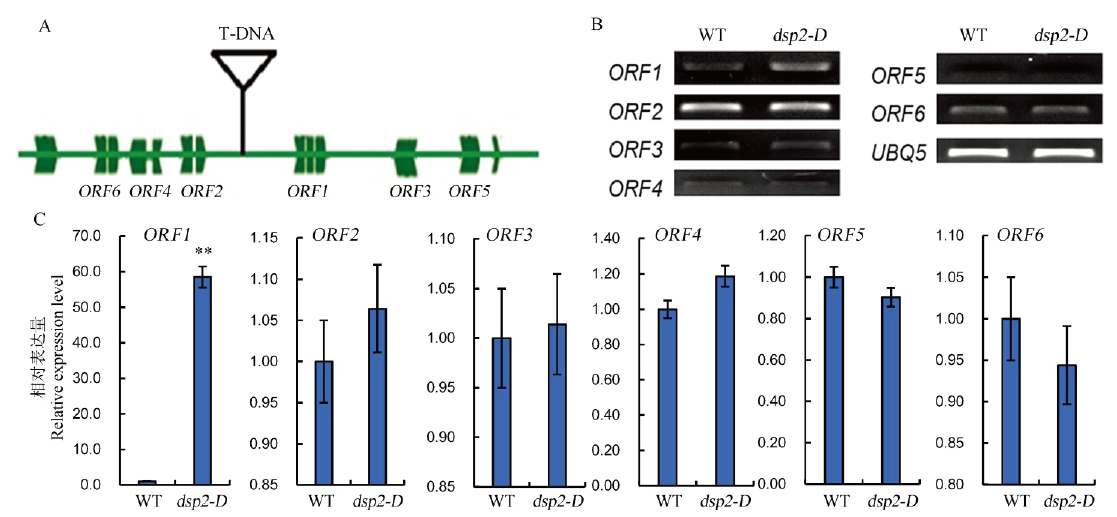
Fig. 3. Expression analysis of candidate gene DSP2. A, Schematic diagram of T-DNA insertion sites; B and C, Expression levels of six candidate genes in dsp2-D and wild type analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR and real time PCR; OsUBQ5 was amplified as a control. Bars represent standard deviation (n=3). ** indicates significant difference between Nipponbare and dsp2-D by t-test (P<0.01).
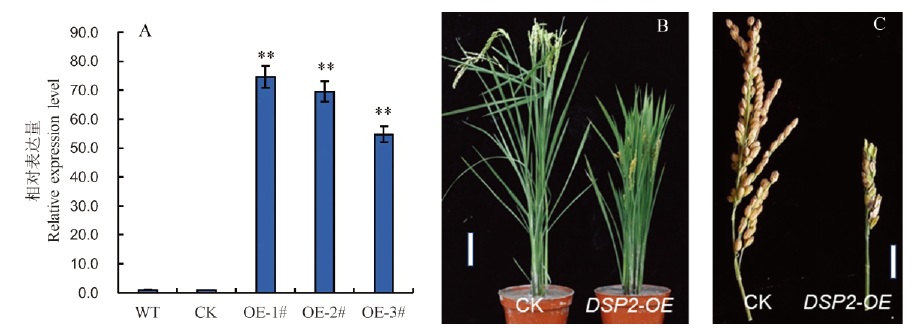
Fig. 4. Overexpression of DSP2 gene and functional identification. A, Expression levels of DSP2 gene in wild-type and transgenic plants. WT, Wild type Nipponbare; CK, Control plasmid transgenic plants; OE-1#-OE-3#, DSP2-OE transgenic plants; Bars represent standard deviation (n=3). **indicates significant difference between Nipponbare and dsp2-D by t-test (P<0.01). B and C, Phenotype of the dsp2-D mutant and transgenic plant. B, Bar=10 cm; C, Bar=5 cm.
| [1] | 刘坚, 陶红剑, 施思, 叶卫军, 钱前, 郭龙彪. 水稻穗型的遗传和育种改良[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012,26(2):227-234. |
| Liu J, Tao H J, Shi S, Ye W J, Qian Q, Guo L B. Genetics and breeding improvement for panicle type in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012,26(2):227-234. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 冷语佳, 钱前, 曾大力. 水稻理想株型的遗传基础研究[J]. 中国稻米, 2014,20(2):1-6. |
| Leng Y J, Qian Q, Zeng D L. Progress on genetic basis of rice ideal plant type[J]. China Rice, 2014,20(2):1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 淳雁, 李学勇. 水稻穗型的遗传调控研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2017,52(1):19-29. |
| Chun Y, Li X Y. Research progress in genetic regulation of rice panicle architecture[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017,52(1):19-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush G S, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. A mutant gibberellin-synjournal gene in rice[J]. Nature, 2002,416(6882):701-702. |
| [5] | Peng J, Richards D E, Hartley N M, Murphy G P, Devos K M, Flintham J E, Beales J, Fish L J, Worland A J, Pelica F, Sudhakar D, Christou P, Snape J W, Gale M D, Harberd N P. “Green revolution” genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators[J]. Nature, 1999,400(6741):256-261. |
| [6] | Ogawa S, Toyomasu T, Yamane H, Murofushi N, Ikeda R, Morimoto Y, Nishimura Y, Omori T. A step in the biosynjournal of gibberellins that is controlled by the mutation in the semi-dwarf rice cultivar Tan-Ginbozu[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1996,37(3):363-368. |
| [7] | Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ishiyama K, Kobayashi M, Itoh H, Kayano T, Iwahori S, Matsuoka M, Tanaka H. Genetic manipulation of gibberellin metabolism in transgenic rice[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003,21(8):909-913. |
| [8] | Zhu Y, Nomura T, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Peng Y, Mao B, Hanada A, Zhou H, Wang R, Li P, Zhu X, Mander L N, Kamiya Y, Yamaguchi S, He Z. ELONGATED UPPERMOST INTERNODE encodes a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase that epoxidizes gibberellins in a novel deactivation reaction in rice[J]. Plant Cell, 2006,18(2):442-456. |
| [9] | Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Ashikari M, Nakajima M, Itoh H, Katoh E, Kobayashi M, Chow T, Hsing Y, Kitano H, Yamaguchi I, Matsuoka M. GIBBERELLIN INSENSITIVE DWARF1 encodes a soluble receptor for gibberellin[J]. Nature, 2005,437(7059):693-698. |
| [10] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Umemura K, Uozu S, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450[J]. Plant Cell, 2003,15(12):2900-2910. |
| [11] | Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ohnishi T, Sunohara H, Fujioka S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Mizutani M, Sakata K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Tanaka H, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency increase biomass production and grain yield in rice[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2006,24(1):105-109. |
| [12] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Hasegawa Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. The rice brassinosteroid-deficient dwarf2 mutant, defective in the rice homolog of Arabidopsis DIMINUTO/DWARF1, is rescued by the endogenously accumulated alternative bioactive brassinosteroid, dolichosterone[J]. Plant Cell, 2005,17(8):2243-2254. |
| [13] | Yamamuro C, Ihara Y, Wu X, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint[J]. Plant Cell, 2000,12(9):1591-1605. |
| [14] | Tong H, Jin Y, Liu W, Li F, Fang J, Yin Y, Qian Q, Zhu L, Chu C. DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING, a new member of the GRAS family, plays positive roles in brassinosteroid signaling in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2009,58(5):803-816. |
| [15] | Lin H, Wang R, Qian Q, Yan M, Meng X, Fu Z, Yan C, Jiang B, Su Z, Li J, Wang Y. DWARF27, an iron-containing protein required for the biosynjournal of strigolactones, regulates rice tiller bud outgrowth[J]. Plant Cell, 2009,21(5):1512-1525. |
| [16] | Zou J, Chen Z, Zhang S, Zhang W, Jiang G, Zhao X, Zhai W, Pan X, Zhu L. Characterizations and fine mapping of a mutant gene for high tillering and dwarf in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Planta, 2005,222(4):604-612. |
| [17] | Arite T, Iwata H, Ohshima K, Maekawa M, Nakajima M, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Kyozuka J. DWARF10, an RMS1/MAX4/DAD1 ortholog, controls lateral bud outgrowth in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2007,51(6):1019-1029. |
| [18] | Wang Y, Shang L, Yu H, Zeng L, Hu J, Ni S, Rao Y, Li S, Chu J, Meng X, Wang L, Hu P, Yan J, Kang S, Qu M, Lin H, Wang T, Wang Q, Hu X, Chen H, Wang B, Gao Z, Guo L, Zeng D, Zhu X, Xiong G, Li J, Qian Q. A strigolactone biosynjournal gene contributed to the green revolution in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020,13(6):923-932. |
| [19] | Jiang L, Liu X, Xiong G, Liu H, Chen F, Wang L, Meng X, Liu G, Yu H, Yuan Y, Yi W, Zhao L, Ma H, He Y, Wu Z, Melcher K, Qian Q, Xu H E, Wang Y, Li J. DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signaling in rice[J]. Nature, 2013,504(7480):401-405. |
| [20] | Zhou F, Lin Q, Zhu L, Ren Y, Zhou K, Shabek N, Wu F, Mao H, Dong W, Gan L, Ma W, Gao H, Chen J, Yang C, Wang D, Tan J, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang J, Jiang L, Liu X, Chen W, Chu J, Yan C, Ueno K, Ito S, Asami T, Cheng Z, Wang J, Lei C, Zhai H, Wu C, Wang H, Zheng N, Wan J. D14-SCF(D3)-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling[J]. Nature, 2013,504(7480):406-410. |
| [21] | Yao R, Ming Z, Yan L, Li S, Wang F, Ma S, Yu C, Yang M, Chen L, Li Y, Yan C, Miao D, Sun Z, Yan J, Sun Y, Wang L, Chu J, Fan S, He W, Deng H, Nan F, Li J, Rao Z, Lou Z, Xie D. DWARF14 is a non-canonical hormone receptor for strigolactone[J]. Nature, 2016,536(7617):469-473. |
| [22] | Wang L, Wang B, Yu H, Guo H, Lin T, Kou L, Wang A, Shao N, Ma H, Xiong G, Li X, Yang J, Chu J, Li J. Transcriptional regulation of strigolactone signalling in Arabidopsis[J]. Nature, 2020,583(7815):277-281. |
| [23] | Sazuka T, Kamiya N, Nishimura T, Ohmae K, Sato Y, Imamura K, Nagato Y, Koshiba T, Nagamura Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. A rice tryptophan deficient dwarf mutant, tdd1, contains a reduced level of indole acetic acid and develops abnormal flowers and organless embryos[J]. Plant Journal, 2009,60(2):227-241. |
| [24] | Song Y, You J, Xiong L. Characterization of OsIAA1 gene, a member of rice Aux/IAA family involved in auxin and brassinosteroid hormone responses and plant morphogenesis[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2009,70(3):297-309. |
| [25] | Qi W, Sun F, Wang Q, Chen M, Huang Y, Feng Y Q, Luo X, Yang J. Rice ethylene-response AP2/ERF factor OsEATB restricts internode elongation by down-regulating a gibberellin biosynthetic gene[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011,157(1):216-228. |
| [26] | Luan W, Liu Y, Zhang F, Song Y, Wang Z, Peng Y, Sun Z. OsCD1 encodes a putative member of the cellulose synthase-like D sub-family and is essential for rice plant architecture and growth[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2011,9(4):513-524. |
| [27] | Tabuchi M, Sugiyama K, Ishiyama K, Inoue E, Sato T, Takahashi H, Yamaya T. Severe reduction in growth rate and grain filling of rice mutants lacking OsGS1;1, a cytosolic glutamine synthetase1;1[J]. Plant Journal, 2005,42(5):641-651. |
| [28] | Sato Y, Sentoku N, Miura Y, Hirochika H, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Loss-of-function mutations in the rice homeobox gene OSH15 affect the architecture of internodes resulting in dwarf plants[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1999,18(4):992-1002. |
| [29] | Zhu Z Z, Fu Y P, Xiao H, Hu G C, Si H M, Yu Y H, Sun Z X. Ac/Ds Transposition activity in transgenic rice population and DNA flanking sequence of Ds insertion sites[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 2003(1):102-107. |
| [30] | Rogers S O, Bendich A J. Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 1985,5(2):69-76. |
| [31] | Michelmore R W, Kesseli I. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: A rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1991,88(21):9828-9832. |
| [32] | Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch S R. Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular & General Genetics, 1996,259(5):597-607. |
| [33] | Lander E S, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly M J, Lincoln S E, Newburg L. Mapmaker: An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations[J]. Genomics, 1987,1(2):174-181. |
| [34] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 -ΔΔCT method [J]. Methods, 2001,25(4):402-408. |
| [35] | Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T. Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA[J]. Plant Journal, 1994,6(2):271-282. |
| [36] | 郭龙彪, 程式华, 钱前. 水稻基因设计育种的研究进展与展望[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2008,22(6):650-657. |
| Guo L B, Chen S H, Qian Q. Progress and prospects of breeding by gene design in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2008,22(6):650-657. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Wang Y H, Li J Y. Molecular basis of plant architecture[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2008,59(1):253-279. |
| [38] | Gurdv K. Productivity improvements in rice[J]. Nutrition Reviews, 2010,61(6):S114-116. |
| [39] | Majer C, Hochholdinger F. Defining the boundaries: structure and function of LOB domain proteins[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2011,16(1):47-52. |
| [40] | Zhang Y, Li Z, Ma B, Hou Q, Wan X. Phylogeny and functions of LOB domain proteins in plants[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020,21(7):2278. |
| [41] | Yang Y, Yu X, Wu P. Comparison and evolution analysis of two rice subspecies LATERAL ORGAN BOUNDARIES domain gene family and their evolutionary characterization from Arabidopsis[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2006,39(1):248-262. |
| [42] | Liu H, Wang S, Yu X, Yu J, He X, Zhang S, Shou H, Wu P. ARL1, a LOB-domain protein required for adventitious root formation in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2005,43(1):47-56. |
| [43] | Inukai Y, Sakamoto T, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Shibata Y, Gomi K, Umemura I, Hasegawa Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Crown rootless1, which is essential for crown root formation in rice, is a target of an Auxin Response Factor in auxin signaling[J]. Plant Cell, 2005,17(5):1387-1396. |
| [44] | Li A, Zhang Y, Wu X, Tang W, Wu R, Dai Z, Liu G, Zhang H, Chen G, Pan X. DH1, a LOB domain-like protein required for glume formation in rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2008,66(5):491-502. |
| [45] | Zhang J, Tang W, Huang Y, Niu X, Zhao Y, Han Y, Liu Y. Down-regulation of a LBD-like gene, OsIG1, leads to occurrence of unusual double ovules and developmental abnormalities of various floral organs and megagametophyte in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015,66(1):99-112. |
| [46] | Lu H, Dai Z, Li L, Wang J, Miao X, Shi Z. OsRAMOSA2 shapes panicle architecture through regulating pedicel length[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017,8(12):1538. |
| [47] | Li C, Zhu S, Zhang H, Chen L, Cai M, Wang J, Chai J, Wu F, Cheng Z, Guo X, Zhang X, Wan J. OsLBD37 and OsLBD38, two class II type LBD proteins, are involved in the regulation of heading date by controlling the expression of Ehd1 in rice[J]. Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications, 2017,486(3):720-725. |
| [48] | Huang X Z, Qian Q, Liu Z, Sun H, He S, Luo D, Xia G, Chu C, Li J, Fu X. Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2009,41(4):494-497. |
| [49] | Zhou Y, Zhu J, Li Z, Yi C, Liu J, Zhang H, Tang S, Gu M, Liang G. Deletion in a quantitative trait gene qPE9-1 associated with panicle erectness improves plant architecture during rice domestication[J]. Genetics, 2009,183(1):315-324. |
| [50] | Miura K, Ikeda M, Matsubara A, Song X J, Ito M, Asano K J, Matsuoka M, Kitano H, Ashikari M. OsSPL14 promotes panicle branching and higher grain productivity in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2010,42(6):545-549. |
| [51] | Jiao Y, Wang Y, Xue D, Wang J, Yan M, Liu G, Dong G, Zeng D, Lu Z, Zhu X, Qian Q, Li J. Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2010,42(6):541-544. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||