
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 12-22.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7055
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaoyun LIU, Xiao LI, Tengfei LI, Lufang SU
Received:2017-05-18
Revised:2017-09-15
Online:2018-01-10
Published:2018-01-10
刘小云, 李晓, 李腾飞, 苏鲁方
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xiaoyun LIU, Xiao LI, Tengfei LI, Lufang SU. Overexpression of OsENO2-2 Affects Heading Date in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(1): 12-22.
刘小云, 李晓, 李腾飞, 苏鲁方. 水稻OsENO2-2基因过表达对水稻抽穗期的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(1): 12-22.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7055
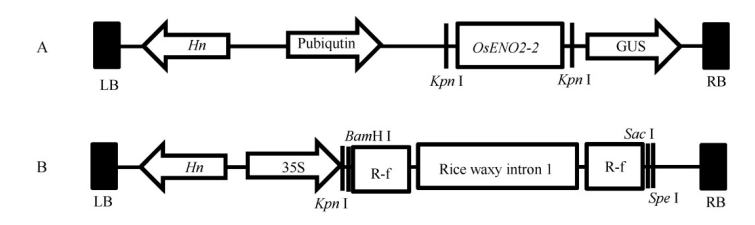
Fig. 1. Construction of overexpression vector and RNAi vector. A, Structure of overexpression vector; LB, Left border of T-DNA; Hn, Hygromycin; Pubiqutin, Promoter of ubiqutin; GUS, beta-glucuronidase; RB, Right border of T-DNA. B, Structure of RNAi vector. 35S, 35S promoter of CaMV; R-f, RNAi fragment of OsENO2-2.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| OsENO2-2-F | GGGGGTACCATGGTTCAACAGCTTGATGGAA |
| OsENO2-2-R | GGGGGTACCTTAGTACGGCTCCACAGGGG |
| R-OsENO2-2-F | AGAACTAGTGGTACCTGCTTCCACCGGAATATATGAG |
| R-OsENO2-2-R | AGAGAGCTCGGATCCCCCTCTTTGTTTTCCTGAATGTTA |
| Hn-F | TACACAGCCATCGGTCCAGA |
| Hn-R | TAGGAGGGCGTGGATATGTC |
| OsENO2-2-QF | GGCCAAGATGCCACAAATGT |
| OsENO2-2-QR | TTGCCTGTGTAGCCAGCCTTA |
| Actin-QF | TGTATGCCAGTGGTCGTACCA |
| Actin-QR | CCAGCAAGGTCGAGACGAA |
| RFT1-QF | TGGTGTTCGTGCTGTTCCA |
| RFT1-QR | TTGTAGAGCTCGGCGAAGTTC |
| RID1-QF | CGACGACAATAGCTCGATCGC |
| RID1-QR | GTGCATGGTCACGGAGCCTT |
| Hd3a-QF | GCTCACTATCATCATCCAGCATG |
| Hd3a-QR | CCTTGCTCAGCTATTTAATTGCATAA |
| Hd1-QF | TCAG CAACAGCATATCT TTCTCATCA |
| Hd1-QR | TCTGGAATTTGGCTATACTATCACC |
| Ehd1-QF | GGATGCAAGGAAATCATGGA |
| Ehd1-QR | AATCCCATCGGAAATCTTGG |
| OsGI-QF | TGGAGAAAGGTTGTGGATGC |
| OsGI-QR | GATAGACGGCACTTCAGCAGAT |
| Ghd7-QF | AAATCCGGTACGCGTCCAG |
| Ghd7-QR | GACATAGGTGGATGGCGGTG |
Table 1 Primers used in the study.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| OsENO2-2-F | GGGGGTACCATGGTTCAACAGCTTGATGGAA |
| OsENO2-2-R | GGGGGTACCTTAGTACGGCTCCACAGGGG |
| R-OsENO2-2-F | AGAACTAGTGGTACCTGCTTCCACCGGAATATATGAG |
| R-OsENO2-2-R | AGAGAGCTCGGATCCCCCTCTTTGTTTTCCTGAATGTTA |
| Hn-F | TACACAGCCATCGGTCCAGA |
| Hn-R | TAGGAGGGCGTGGATATGTC |
| OsENO2-2-QF | GGCCAAGATGCCACAAATGT |
| OsENO2-2-QR | TTGCCTGTGTAGCCAGCCTTA |
| Actin-QF | TGTATGCCAGTGGTCGTACCA |
| Actin-QR | CCAGCAAGGTCGAGACGAA |
| RFT1-QF | TGGTGTTCGTGCTGTTCCA |
| RFT1-QR | TTGTAGAGCTCGGCGAAGTTC |
| RID1-QF | CGACGACAATAGCTCGATCGC |
| RID1-QR | GTGCATGGTCACGGAGCCTT |
| Hd3a-QF | GCTCACTATCATCATCCAGCATG |
| Hd3a-QR | CCTTGCTCAGCTATTTAATTGCATAA |
| Hd1-QF | TCAG CAACAGCATATCT TTCTCATCA |
| Hd1-QR | TCTGGAATTTGGCTATACTATCACC |
| Ehd1-QF | GGATGCAAGGAAATCATGGA |
| Ehd1-QR | AATCCCATCGGAAATCTTGG |
| OsGI-QF | TGGAGAAAGGTTGTGGATGC |
| OsGI-QR | GATAGACGGCACTTCAGCAGAT |
| Ghd7-QF | AAATCCGGTACGCGTCCAG |
| Ghd7-QR | GACATAGGTGGATGGCGGTG |
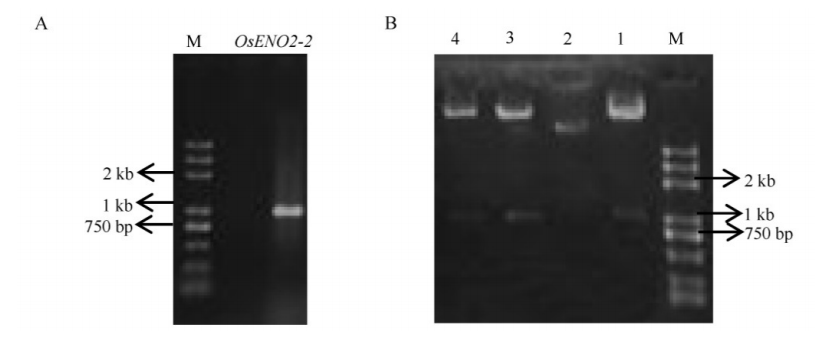
Fig. 2. PCR amplification of OsENO2-2 and identification of recombinant plasmid. A, PCR amplification of OsENO2-2 full open reading frame. B, Digesting identification of recombinant plasmid. Lanes 1-4, Four independent clones of recombinant plasmid. Lane 1, 3, 4, Positive clones; Lane 2, Negative control.
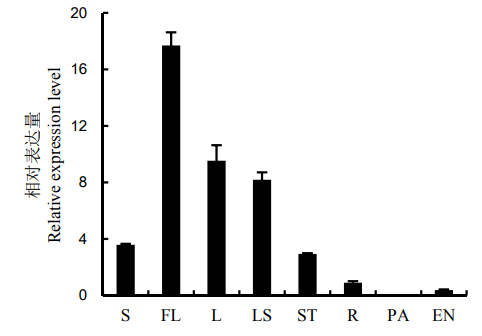
Fig. 3. Tissue-specific expression of OsENO2-2. S, Seedling; FL, Flag leaf; L, The second leaf from the top at the heading stage; LS, Leaf sheath; ST, Stem; R, Root; PA, Panicle; EN, Endosperm.
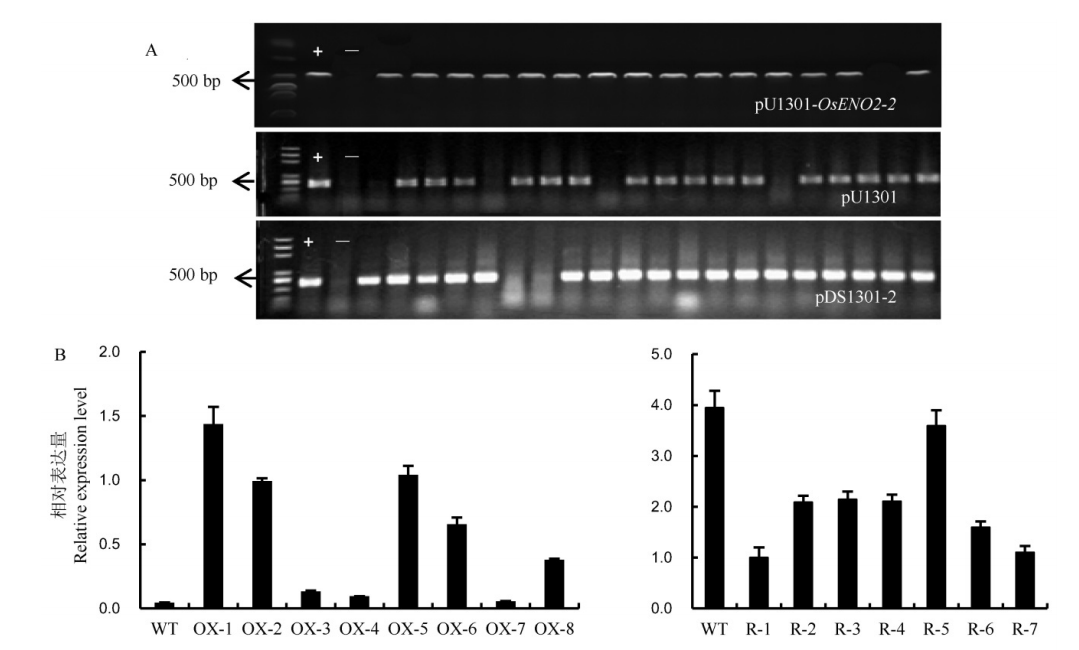
Fig. 4. PCR analysis of Hn gene in T0 transgenic positive plants and expression analysis of OsENO2-2 in transgenic lines. A, PCR identification of Hn gene of the transgenic plants. The transgenic plants of the overexpressed lines, the transgenic plants of the control group lines, the transgenic plants of the RNAi lines, from up to down, respectively. B, The relative expression level of OsENO2-2 in transgenic plants(Mean±SD). WT, Wild type; OX-1 to OX-8, Eight independent overexpression transgenic plants. R-1 to R-7, Seven independent RNAi transgenic plants.
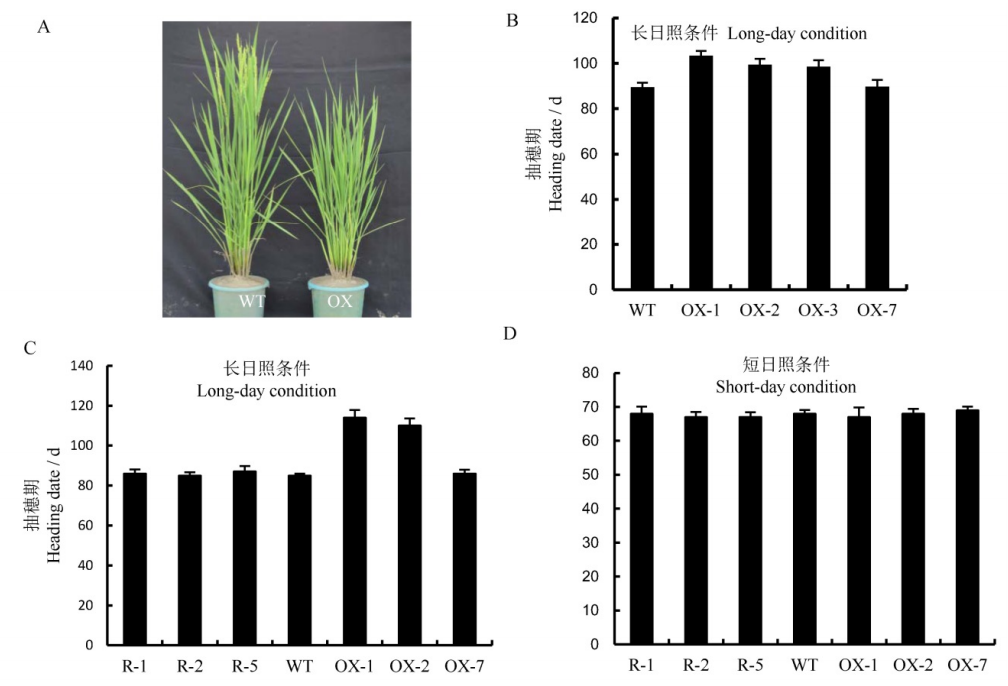
Fig. 5. Heading date of the transgenic plants(Mean±SD). A, Heading phenotypes of wild-type and overexpression plants. WT, Wild type; OX, Overexpression lines. B, Heading date of wild-type and overexpressing plants(n=30). WT, Wild type; OX-1, OX-2, OX-3, Overexpressed transgenetic positive plants; OX-7, The transgenic plants of the control group. C, Statistical analysis of heading date of wild-type, overexpressed plants and RNAi plants under long-day condition(14h light/10 h dark) (n=10). D, Statistical analysis of heading date of wild-type, overexpressed plants and RNAi plants under short-day condition(10h light/14h dark) (n=10). **The differences between wild type and transgenic plants are significant at 0.01 level(Student's t-test).
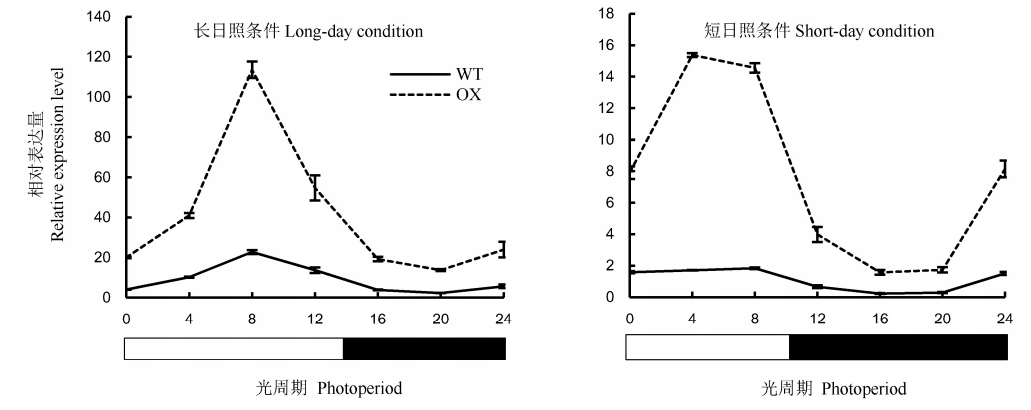
Fig. 6. Circadian rhythm expression of OsENO2-2 under different photoperiods(Mean±SD). LD, Long-day condition(light 14 h/dark 10 h); SD, Short-day condition(light 10 h/dark 14 h); WT, Wild type; OX, OsENO2-2 overexpressed plants.
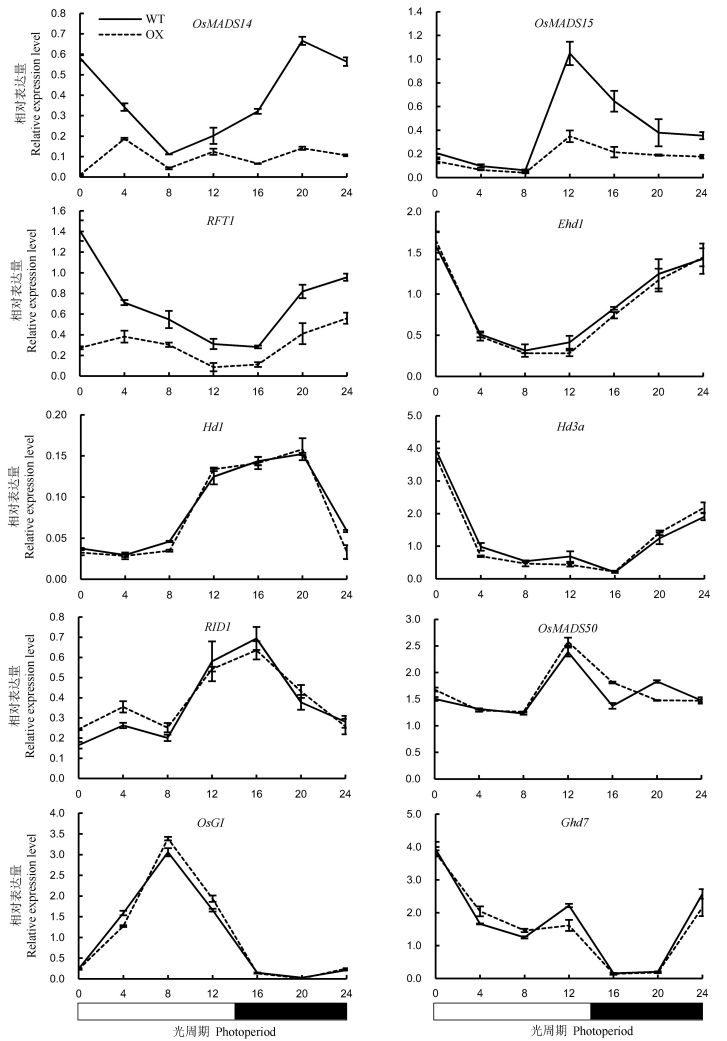
Fig. 7. Expression levels of key heading regulatory genes in leaves of OsENO2-2 overexpression plants(OX) compared to wild type(WT) under long-day condition(Mean±SD).
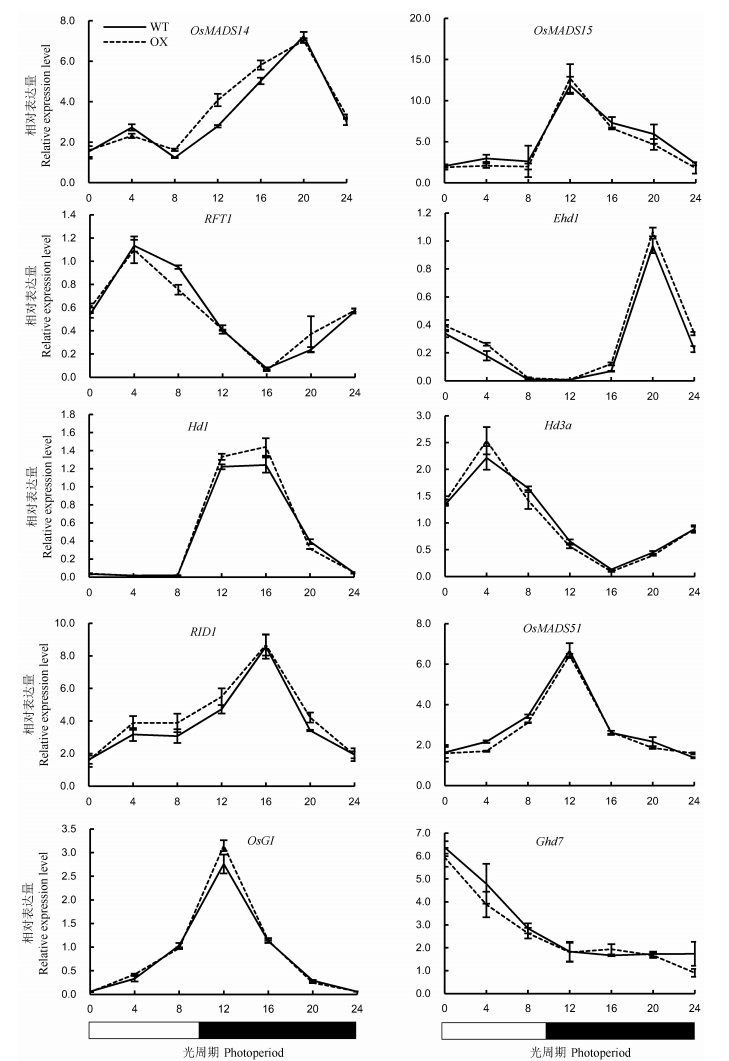
Fig. 8. Expression levels of key heading regulatory genes in leaves of OsENO2-2 overexpression plants(OX) compared to wild type(WT) under short-day condition(Mean±SD).
| [1] | 徐铨,奥本裕,王晓雪.水稻开花期调控分子机理研究进展.植物遗传资源学报,2014,15(1):129-136. |
| Xu Q,Okumoto Y,Wang X E.Research progress on regulatory molecular mechanisms of flowering time in riceJ Plant Genet Resour,2014,15(1):129-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Imaizumi T,Kay S.Photoperiodic control of flowering: not only by coincidence.Trends Plant Sci,2006,11(11):550-558. |
| [3] | Itoh H,Nonoue Y,Yano M,Izawa T.A pair of floral regulators sets critical day length forHd3a florigen expression in rice. Nat Genet,2010,42(7):635-638. |
| [4] | Tsuji H,Taoka K I,Shimamoto K.Regulation of flowering in rice: Two florigen genes, a complex gene network, and natural variation.Curr Opin Plant Biol,2011,14(1):45-52. |
| [5] | Yano M,Katayose Y,Ashikari M,Yamanouchi U,Monna L,Fuse T,Baba T,Yamamoto K,Umehara Y,Nagamura Y,Sasaki T. Hd1, a major photoperiod sensitivity quantitative trait locus in rice, is closely related to the Arabidopsis flowering time gene CONSTANS. Plant Cell,2000,12(12):2473-2484. |
| [6] | Tamaki S,Matsuo S,Wong H L,Yokoi S,Shimamoto K.Hd3a protein is a mobile flowering signal in rice.Science,2007,316(5827):1033-1036. |
| [7] | Hayama R,Coupland G.The molecular basis of diversity in the photoperiodic flowering responses ofArabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol,2004,135(2):677-684. |
| [8] | Komiya R,Yokoi S,Shimamoto K.A gene network for long-day flowering activates RFT1 encoding a mobile flowering signal in rice.Development,2009,136(20):3443-3450. |
| [9] | Hayama R,Yokoi S,Tamaki S,Yano M,Shimamoto K.Adaptation of photoperiodic control pathways produces short-day flowering in rice.Nature,2003,422: 719-722. |
| [10] | Kim S L,Lee S,Kim H J,Nam H G,An G.OsMADS51 is a short-day flowering promoter that functions upstream ofEhd1, OsMADS14, and Hd3a. Plant Physiol,2007,145(4):1484-1494. |
| [11] | Xue W,Xing Y,Weng X,Zhao Y,Tang W,Wang L,Zhou H,Yu S,Xu C,Li X,Zhang Q.Natural variation inGhd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice. Nat Genet,2008,40(6):761-767. |
| [12] | Wu C,You C,Li C,Long T,Chen G,Byrne M E,Zhang Q.RID1, encoding a Cys2/His2-type zinc finger transcription factor, acts as a master switch from vegetative to floral development in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2008,105(35):12915-12920. |
| [13] | Matsubara K,Yamanouchi U,Wang Z X,Minobe Y,Izawa T,Yano M.Ehd2, a rice ortholog of the maize INDETERMINATE1 gene, promotes flowering by up-regulating Ehd1. Plant Physiol,2008,148(3):1425-1435. |
| [14] | Park S J,Kim S L,Lee S,Je B I,Piao H L,Park S H,Kim C M,Ryu C H,Xuan Y H,Colasanti J,An G,Han C D.RiceIndeterminate 1 (OsId1) is necessary for the expression of Ehd1 (Early heading date 1) regardless of photoperiod. Plant J,2008,56(6):1018-1029. |
| [15] | Lu S J,Wei H,Wang Y,Wang H M,Yang R F,Zhang X B,Tu J M.Overexpression of a transcription factorOsMADS15 modifies plant architecture and flowering time in rice(Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol Rep,2012,30(6):1461-1469. |
| [16] | Arora R,Agarwal P,Ray S,Singh A,Singh V,Tyagi A K,Kapoor S.MADS-box gene family in rice: Genome-wide identification, organization and expression profiling during reproductive development and stress.BMC Genom,2007,8(1):242. |
| [17] | Pancholi V.Multifunctional α-enolase: Its role in diseases.Cell Mol Life Sci,2001,58: 902-920. |
| [18] | Àngels D R,Anna R B,Ana G M,Roser L A.α-enolase, a multifunctional protein: Its role on pathophysiological situations. J Biomed Biotechnol, 2012(7):1-12. |
| [19] | Kang M,Abdelmageed H,Lee S,Reichert A,Mysore K S,Allen R D.AtMBP-1, an alternative translation product of LOS2, affects abscisic acid responses and is modulated by the E3 ubiquitin ligase AtSAP5.Plant J,2013,76(3):481-493. |
| [20] | Eremina M,Rozhon W,Yang S,Poppenberger B.ENO2 activity is required for the development and reproductive success of plants, and is feedback-repressed by AtMBP-1.Plant J,2015,81(6):895-906. |
| [21] | Sun X,Cao Y,Yang Z,Xu C,Li X,Wang S.Xa26, a gene conferring resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein. Plant J,2004,37: 517-527. |
| [22] | 卢扬江,郑康乐.提取水稻DNA 的一种简易方法.中国水稻科学,1992,6(1):47-48. |
| Lu Y J,Zheng K L.A simple method for isolation of rice DNA.Chin J Rice Sci,1992,6(1):47-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Livak K J,Schmittgen T D.Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2[-Delta Delta C(T)] method.Methods,2001,25(4):402-408. |
| [24] | Hiei Y,Ohta S,Komari T,Kumashiro T.Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA.Plant J,1994,6(2):271-282. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||