
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 338-346.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8134
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Dongming WANG1,2, Ye TAO1,2, Jianguo ZHU1, Gang LIU1, Chunwu ZHU1,*( )
)
Received:2018-12-05
Revised:2019-04-02
Online:2019-07-10
Published:2019-07-10
Contact:
Chunwu ZHU
王东明1,2, 陶冶1,2, 朱建国1, 刘钢1, 朱春梧1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
朱春梧
基金资助:CLC Number:
Dongming WANG, Ye TAO, Jianguo ZHU, Gang LIU, Chunwu ZHU. Responses of Rice Appearance and Processing Quality to Elevated Atmospheric CO2 Concentration[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(4): 338-346.
王东明, 陶冶, 朱建国, 刘钢, 朱春梧. 稻米外观与加工品质对大气CO2浓度升高的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(4): 338-346.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8134
| 材料 Material | CO2处理 CO2 treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice percentage/% | 精米率 Milled rice percentage/% | 整精米率 Head rice percentage/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain percentage/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中花11 Zhonghua 11 | FACE | 82.9±0.7 | 72.3±1.2 | 68.0±1.2 | 13.2±0.9 | 5.8±0.7 |
| Ambient | 82.6±0.7 | 72.5±0.4 | 70.2±0.5 | 12.1±1.7 | 5.6±0.7 | |
| Change | 0.4 | -0.4 | -3.1 | 8.9 | 4.2 | |
| ZmK2.1-15 | FACE | 82.5±1.2 | 71.9±0.4 | 68.0±2.6 | 42.5±1.5 | 16.3±0.3 |
| Ambient | 81.8±0.2 | 71.4±0.8 | 66.6±3.4 | 43.7±4.3 | 17.8±2.1 | |
| Change | 0.8 | 0.8 | 2.1 | -2.7 | -8.7 | |
| ZmK2.1-20 | FACE | 83.0±0.2 | 72.7±0.2 | 68.5±0.8 | 39.0±0.6 | 15.7±0.6 |
| Ambient | 81.3±1.2 | 71.3±1.7 | 64.4±2.0 | 46.6±6.9 | 20.2±3.5 | |
| Change | 2.1 | 1.9 | 6.4 | -16.3 | -22.3 | |
| OsKAT3-26 | FACE | 82.5±0.5 | 72.3±0.2 | 70.9±0.1 | 24.0±3.7 | 9.9±1.2 |
| Ambient | 82.0±0.8 | 72.3±1.0 | 68.5±0.7 | 28.2±3.5 | 11.6±1.5 | |
| Change | 0.7 | 0.0 | 3.6 | -14.8 | -15.1 | |
| OsKAT3-30 | FACE | 80.1±1.5 | 68.3±4.5 | 62.1±3.2 | 33.9±5.5 | 13.7±1.2 |
| Ambient | 80.9±0.8 | 70.5±1.4 | 66.8±2.4 | 31.6±4.7 | 14.1±1.0 | |
| Change | -0.9 | -3.1 | -7.0 | 7.4 | -3.0 | |
| 方差分析Analysis of variance | ||||||
| 变异来源Source of variation | ||||||
| 材料Material(M) | * | 0.118 | *** | *** | *** | |
| CO2浓度([CO2]) | 0.383 | 0.805 | 0.746 | 0.167 | 0.127 | |
| M×[CO2] | 0.150 | 0.498 | 0.101 | 0.080 | 0.106 | |
Table 1 Brown rice percentage, milled rice percentage, head rice percentage, chalky grain percentage and chalkiness degree of Zhonghua 11 and its transpiration-promoting genetic materials (ZmK2.1-15, ZmK2.1-15, OsKAT3-26, OsKAT3-30) under elevated and ambient CO2 concentration in 2015.
| 材料 Material | CO2处理 CO2 treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice percentage/% | 精米率 Milled rice percentage/% | 整精米率 Head rice percentage/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain percentage/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中花11 Zhonghua 11 | FACE | 82.9±0.7 | 72.3±1.2 | 68.0±1.2 | 13.2±0.9 | 5.8±0.7 |
| Ambient | 82.6±0.7 | 72.5±0.4 | 70.2±0.5 | 12.1±1.7 | 5.6±0.7 | |
| Change | 0.4 | -0.4 | -3.1 | 8.9 | 4.2 | |
| ZmK2.1-15 | FACE | 82.5±1.2 | 71.9±0.4 | 68.0±2.6 | 42.5±1.5 | 16.3±0.3 |
| Ambient | 81.8±0.2 | 71.4±0.8 | 66.6±3.4 | 43.7±4.3 | 17.8±2.1 | |
| Change | 0.8 | 0.8 | 2.1 | -2.7 | -8.7 | |
| ZmK2.1-20 | FACE | 83.0±0.2 | 72.7±0.2 | 68.5±0.8 | 39.0±0.6 | 15.7±0.6 |
| Ambient | 81.3±1.2 | 71.3±1.7 | 64.4±2.0 | 46.6±6.9 | 20.2±3.5 | |
| Change | 2.1 | 1.9 | 6.4 | -16.3 | -22.3 | |
| OsKAT3-26 | FACE | 82.5±0.5 | 72.3±0.2 | 70.9±0.1 | 24.0±3.7 | 9.9±1.2 |
| Ambient | 82.0±0.8 | 72.3±1.0 | 68.5±0.7 | 28.2±3.5 | 11.6±1.5 | |
| Change | 0.7 | 0.0 | 3.6 | -14.8 | -15.1 | |
| OsKAT3-30 | FACE | 80.1±1.5 | 68.3±4.5 | 62.1±3.2 | 33.9±5.5 | 13.7±1.2 |
| Ambient | 80.9±0.8 | 70.5±1.4 | 66.8±2.4 | 31.6±4.7 | 14.1±1.0 | |
| Change | -0.9 | -3.1 | -7.0 | 7.4 | -3.0 | |
| 方差分析Analysis of variance | ||||||
| 变异来源Source of variation | ||||||
| 材料Material(M) | * | 0.118 | *** | *** | *** | |
| CO2浓度([CO2]) | 0.383 | 0.805 | 0.746 | 0.167 | 0.127 | |
| M×[CO2] | 0.150 | 0.498 | 0.101 | 0.080 | 0.106 | |
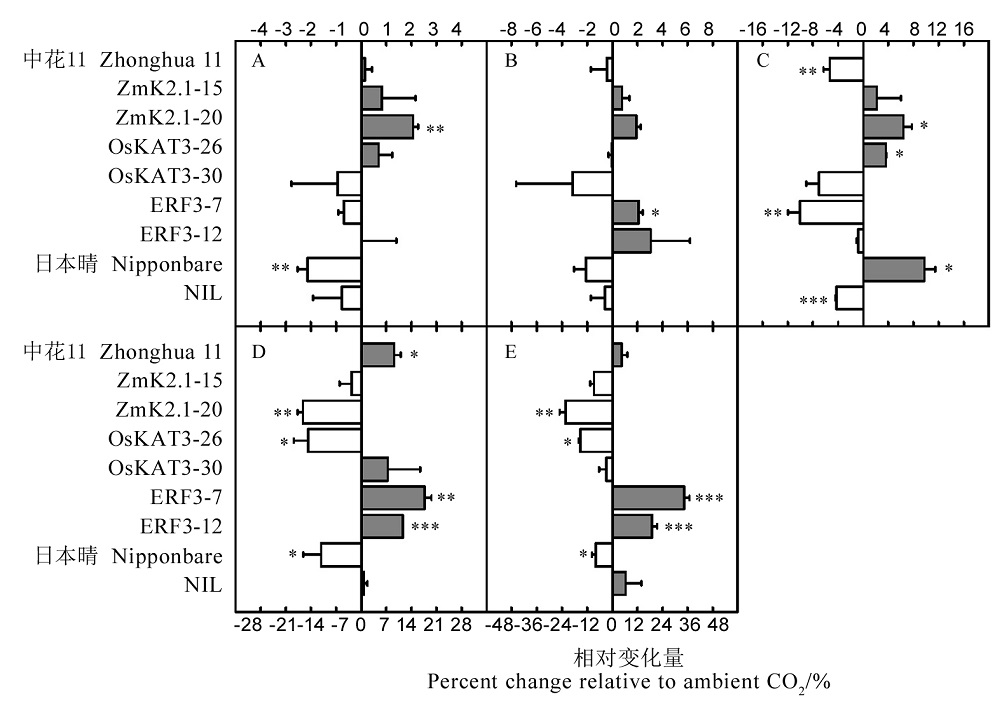
Fig. 1. Average change in milling quality and appearance quality at elevated CO2 concentration for Zhonghua 11 (wild type) and its transpiration-promoting overexpression genetic materials (ZmK2.1-15, ZmK2.1-15, OsKAT3-26, OsKAT3-30) and crown root-promoting overexpression genetic materials (ERF3-7 and ERF3-12), Nipponbare (wild type) and its nitrate-absorption promoting overexpression genetic material(NIL). A, Brown rice percentage; B, Milled rice percentage; C, Head rice percentage D, Chalky grain percentage; E, Chalkiness degree. Bars represent standard deviation, and statistically significant effects by independent sample t-test are indicated: *** P<0.001; ** P<0.01; * P<0.05.
| 年份 Year | 材料 Material | CO2处理 CO2 treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice percentage/% | 精米率 Milled rice percentage/% | 整精米率 Head rice percentage/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain percentage/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 中花11 | FACE | 80.8±0.6 | 69.2±0.4 | 59.5±3.4 | 32.6±0.8 | 11.7±0.9 |
| Zhonghua 11 | Ambient | 80.5±0.1 | 68.2±0.2 | 65.5±0.3 | 29.4±0.1 | 9.7±0.1 | |
| Change | 0.4 | 1.5 | -9.1 | 11.1 | 21.5 | ||
| ERF3-7 | FACE | 78.2±1.1 | 66.4±1.0 | 54.9±1.9 | 78.2±0.9 | 40.2±0.6 | |
| Ambient | 78.2±0.4 | 63.0±0.7 | 60.3±0.3 | 65.3±1.4 | 29.2±0.7 | ||
| Change | -0.1 | 5.3 | -9.0 | 19.8 | 37.7 | ||
| ERF3-12 | FACE | 80.6±1.8 | 67.3±2.6 | 59.1±1.5 | 83.2±0.5 | 46.3±2.0 | |
| Ambient | 79.9±1.7 | 64.9±5.4 | 57.6±0.4 | 77.0±1.1 | 38.9±1.2 | ||
| Change | 0.9 | 3.7 | 2.7 | 8.1 | 19.1 | ||
| 2017 | 中花11 | FACE | 80.9±0.3 | 69.4±2.0 | 60.1±0.7 | 10.3±0.6 | 2.9±0.5 |
| Zhonghua 11 | Ambient | 81.2±0.6 | 71.0±1.2 | 62.4±1.4 | 9.9±0.8 | 4.3±0.8 | |
| Change | -0.3 | -2.3 | -3.7 | 4.0 | -33.2 | ||
| ERF3-7 | FACE | 77.1±0.3 | 63.8±1.0 | 51.3±1.2 | 30.3±2.6 | 11.1±1.3 | |
| Ambient | 78.1±1.0 | 64.5±1.1 | 57.8±1.8 | 26.9±1.0 | 9.0±0.2 | ||
| Change | -1.2 | -1.1 | -11.2 | 12.4 | 23.6 | ||
| ERF3-12 | FACE | 78.2±0.6 | 65.4±1.7 | 53.5±2.2 | 60.2±1.8 | 24.9±0.9 | |
| Ambient | 78.9±2.7 | 63.8±3.3 | 56.0±1.6 | 51.6±1.8 | 20.9±1.3 | ||
| Change | -0.9 | 2.4 | -4.4 | 16.7 | 19.1 | ||
| 方差分析Analysis of variance | |||||||
| 变异来源Source of variation | |||||||
| 年际Year(Y) | * | 0.780 | * | *** | *** | ||
| 材料Material(M) | * | 0.062 | *** | *** | *** | ||
| CO2浓度([CO2]) | 0.505 | 0.353 | * | * | ** | ||
| Y×M | * | 0.056 | 0.451 | *** | *** | ||
| Y×[CO2] | 0.204 | 0.101 | 0.641 | 0.128 | * | ||
| M×[CO2] | 0.688 | 0.078 | ** | ** | ** | ||
| Y×M×[CO2] | 0.845 | 0.306 | 0.110 | ** | * | ||
Table 2 Brown rice percentage, milled rice percentage, head rice percentage, chalky grain percentage and chalkiness degree of Zhonghua 11 and its crown root-promoting genetic materials (ERF3-7 and ERF3-12) under elevated and ambient CO2 concentration in 2016-2017.
| 年份 Year | 材料 Material | CO2处理 CO2 treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice percentage/% | 精米率 Milled rice percentage/% | 整精米率 Head rice percentage/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain percentage/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 中花11 | FACE | 80.8±0.6 | 69.2±0.4 | 59.5±3.4 | 32.6±0.8 | 11.7±0.9 |
| Zhonghua 11 | Ambient | 80.5±0.1 | 68.2±0.2 | 65.5±0.3 | 29.4±0.1 | 9.7±0.1 | |
| Change | 0.4 | 1.5 | -9.1 | 11.1 | 21.5 | ||
| ERF3-7 | FACE | 78.2±1.1 | 66.4±1.0 | 54.9±1.9 | 78.2±0.9 | 40.2±0.6 | |
| Ambient | 78.2±0.4 | 63.0±0.7 | 60.3±0.3 | 65.3±1.4 | 29.2±0.7 | ||
| Change | -0.1 | 5.3 | -9.0 | 19.8 | 37.7 | ||
| ERF3-12 | FACE | 80.6±1.8 | 67.3±2.6 | 59.1±1.5 | 83.2±0.5 | 46.3±2.0 | |
| Ambient | 79.9±1.7 | 64.9±5.4 | 57.6±0.4 | 77.0±1.1 | 38.9±1.2 | ||
| Change | 0.9 | 3.7 | 2.7 | 8.1 | 19.1 | ||
| 2017 | 中花11 | FACE | 80.9±0.3 | 69.4±2.0 | 60.1±0.7 | 10.3±0.6 | 2.9±0.5 |
| Zhonghua 11 | Ambient | 81.2±0.6 | 71.0±1.2 | 62.4±1.4 | 9.9±0.8 | 4.3±0.8 | |
| Change | -0.3 | -2.3 | -3.7 | 4.0 | -33.2 | ||
| ERF3-7 | FACE | 77.1±0.3 | 63.8±1.0 | 51.3±1.2 | 30.3±2.6 | 11.1±1.3 | |
| Ambient | 78.1±1.0 | 64.5±1.1 | 57.8±1.8 | 26.9±1.0 | 9.0±0.2 | ||
| Change | -1.2 | -1.1 | -11.2 | 12.4 | 23.6 | ||
| ERF3-12 | FACE | 78.2±0.6 | 65.4±1.7 | 53.5±2.2 | 60.2±1.8 | 24.9±0.9 | |
| Ambient | 78.9±2.7 | 63.8±3.3 | 56.0±1.6 | 51.6±1.8 | 20.9±1.3 | ||
| Change | -0.9 | 2.4 | -4.4 | 16.7 | 19.1 | ||
| 方差分析Analysis of variance | |||||||
| 变异来源Source of variation | |||||||
| 年际Year(Y) | * | 0.780 | * | *** | *** | ||
| 材料Material(M) | * | 0.062 | *** | *** | *** | ||
| CO2浓度([CO2]) | 0.505 | 0.353 | * | * | ** | ||
| Y×M | * | 0.056 | 0.451 | *** | *** | ||
| Y×[CO2] | 0.204 | 0.101 | 0.641 | 0.128 | * | ||
| M×[CO2] | 0.688 | 0.078 | ** | ** | ** | ||
| Y×M×[CO2] | 0.845 | 0.306 | 0.110 | ** | * | ||
| 年份 Year | 材料 Material | CO2处理 CO2 treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice percentage/% | 精米率 Milled rice percentage/% | 整精米率 Head rice percentage/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain percentage/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 日本晴 | FACE | 71.4±0.3 | 57.9±1.0 | 53.8±1.8 | 12.5±0.9 | 3.8±0.2 | |
| Nipponbare | Ambient | 75.0±4.7 | 60.9±3.6 | 48.8±4.9 | 13.4±1.0 | 4.1±0.1 | ||
| Change | -4.9 | -4.8 | 10.3 | -6.9 | -6.6 | |||
| NIL | FACE | 78.0±1.4 | 63.8±0.8 | 56.8±2.0 | 8.6±0.2 | 2.7±0.2 | ||
| Ambient | 79.5±0.4 | 64.7±0.3 | 62.1±0.6 | 8.1±0.3 | 2.2±0.2 | |||
| Change | -1.8 | -1.3 | -8.6 | 6.8 | 21.8 | |||
| 2017 | 日本晴 | FACE | 81.8±0.4 | 68.7±0.2 | 67.3±0.6 | 24.3±1.6 | 8.2±0.7 | |
| Nipponbare | Ambient | 81.5±0.3 | 68.5±0.3 | 61.6±1.0 | 28.0±0.3 | 8.9±0.2 | ||
| Change | 0.4 | 0.3 | 9.3 | -13.1 | -8.5 | |||
| NIL | FACE | 81.5±0.4 | 68.0±0.9 | 64.7±1.7 | 22.1±5.3 | 7.1±2.0 | ||
| Ambient | 81.3±0.1 | 67.9±0.4 | 64.8±1.0 | 22.4±2.5 | 7.0±0.7 | |||
| Change | 0.3 | 0.2 | -0.1 | -1.5 | 1.5 | |||
| 方差分析Analysis of variance | ||||||||
| 变异来源Source of variation | ||||||||
| 年际Year(Y) | ** | ** | * | ** | * | |||
| 材料Material(M) | 0.100 | 0.088 | ** | ** | * | |||
| CO2浓度([CO2]) | 0.393 | 0.430 | 0.318 | 0.535 | 0.711 | |||
| Y×M | 0.053 | * | *** | 0.549 | 0.988 | |||
| Y×[CO2] | 0.250 | 0.253 | 0.089 | 0.499 | 0.582 | |||
| M×[CO2] | 0.392 | 0.460 | * | 0.164 | 0.063 | |||
| Y×M×[CO2] | 0.340 | 0.324 | 0.533 | 0.705 | 0.894 | |||
Table 3 Brown rice percentage, milled rice percentage, head rice percentage, chalky grain percentage and chalkiness degree of Nipponbare and its nitrate-absorption promoting genetic material(NIL)under elevated and ambient CO2 concentration in 2016-2017.
| 年份 Year | 材料 Material | CO2处理 CO2 treatment | 糙米率 Brown rice percentage/% | 精米率 Milled rice percentage/% | 整精米率 Head rice percentage/% | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain percentage/% | 垩白度 Chalkiness degree/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 日本晴 | FACE | 71.4±0.3 | 57.9±1.0 | 53.8±1.8 | 12.5±0.9 | 3.8±0.2 | |
| Nipponbare | Ambient | 75.0±4.7 | 60.9±3.6 | 48.8±4.9 | 13.4±1.0 | 4.1±0.1 | ||
| Change | -4.9 | -4.8 | 10.3 | -6.9 | -6.6 | |||
| NIL | FACE | 78.0±1.4 | 63.8±0.8 | 56.8±2.0 | 8.6±0.2 | 2.7±0.2 | ||
| Ambient | 79.5±0.4 | 64.7±0.3 | 62.1±0.6 | 8.1±0.3 | 2.2±0.2 | |||
| Change | -1.8 | -1.3 | -8.6 | 6.8 | 21.8 | |||
| 2017 | 日本晴 | FACE | 81.8±0.4 | 68.7±0.2 | 67.3±0.6 | 24.3±1.6 | 8.2±0.7 | |
| Nipponbare | Ambient | 81.5±0.3 | 68.5±0.3 | 61.6±1.0 | 28.0±0.3 | 8.9±0.2 | ||
| Change | 0.4 | 0.3 | 9.3 | -13.1 | -8.5 | |||
| NIL | FACE | 81.5±0.4 | 68.0±0.9 | 64.7±1.7 | 22.1±5.3 | 7.1±2.0 | ||
| Ambient | 81.3±0.1 | 67.9±0.4 | 64.8±1.0 | 22.4±2.5 | 7.0±0.7 | |||
| Change | 0.3 | 0.2 | -0.1 | -1.5 | 1.5 | |||
| 方差分析Analysis of variance | ||||||||
| 变异来源Source of variation | ||||||||
| 年际Year(Y) | ** | ** | * | ** | * | |||
| 材料Material(M) | 0.100 | 0.088 | ** | ** | * | |||
| CO2浓度([CO2]) | 0.393 | 0.430 | 0.318 | 0.535 | 0.711 | |||
| Y×M | 0.053 | * | *** | 0.549 | 0.988 | |||
| Y×[CO2] | 0.250 | 0.253 | 0.089 | 0.499 | 0.582 | |||
| M×[CO2] | 0.392 | 0.460 | * | 0.164 | 0.063 | |||
| Y×M×[CO2] | 0.340 | 0.324 | 0.533 | 0.705 | 0.894 | |||
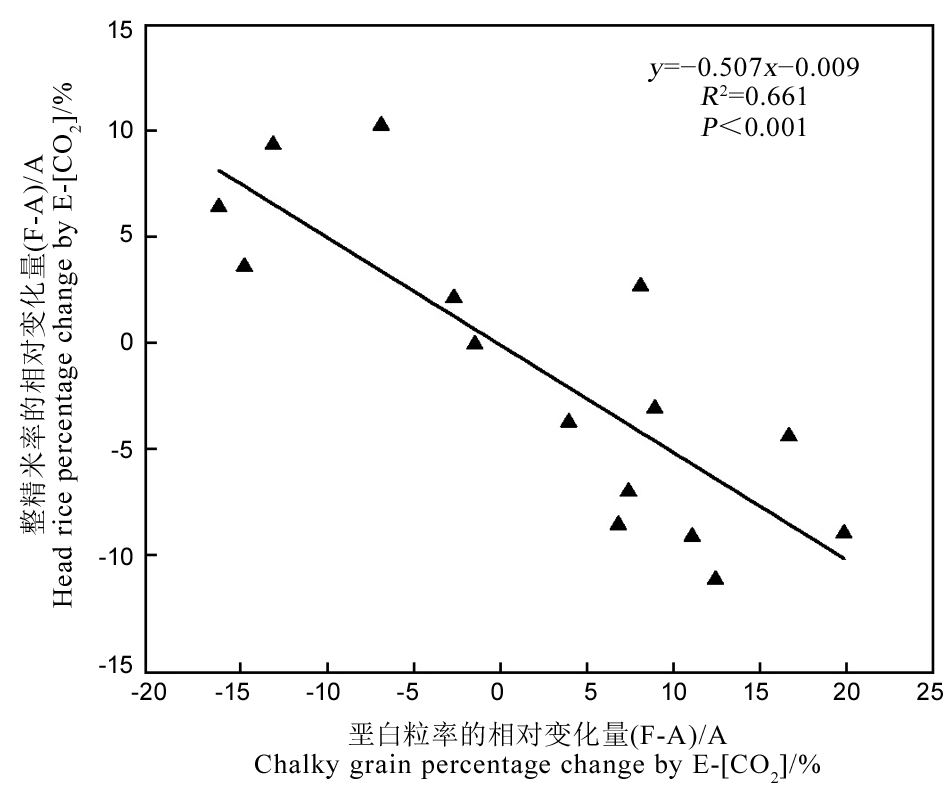
Fig. 2. A linear regression relationship between the change of head rice percentage and chalky grain percentage at elevated [CO2] to ambient [CO2] for all rice varieties of contrasting genetic backgrounds (Zhonghua 11, ZmK2.1-15, ZmK2.1-15, OsKAT3-26, OsKAT3-30, ERF3-7, ERF3-12, Nipponbare, NIL).
| [1] | Dlugokencky D, Tans P.Globally Averaged Marine Surface Annual Mean Data.NOAA/ESRL, 2017. |
| [2] | International Energy Agency.Global Energy and CO2 Status Report 2017. GECO, 2018. |
| [3] | The Core Writing Team, Pachauri R K, Meyer L. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC, 2014. |
| [4] | Lobell D B, Schlenker W, Costaroberts J.Climate trends and global crop production Since 1980.Science, 2011, 333(6042): 616-620. |
| [5] | Zhu C W, Zhu J G, Cao J, Jiang Q, Liu G, Ziska L H.Biochemical and molecular characteristics of leaf photosynthesis and relative seed yield of two contrasting rice cultivars in response to elevated [CO2].J Exp Bot, 2014, 65(20): 6049-6056. |
| [6] | Yang L X, Wang Y L, Dong G C, Gu H, Huang J Y, Zhu J G, Yang H J, Liu G, Han Y.The impact of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) and nitrogen supply on grain quality of rice.Field Crops Res, 2007, 102(2): 128-140. |
| [7] | Myers S S, Zanobetti A, Kloog I, Huybers P J, Leakey A D B, Bloom A J, Carlisle E, Dietterich L H, Fitzgerald G J, Hasegawa T, Holbrook M, Nelson R L, Ottman M J, Raboy V, Sakai H, Sartor K, Schwartz J, Seneweera S, Tausz M, Usui Y. Rising CO2 threatens human nutrition.Nature, 2014, 510(7503): 139-142. |
| [8] | Zhu C W, Kobayashi K, Loladze I, Zhu J G, Jiang Q, Xu X, Liu G, Seneweera S, Ebi K L, Drewnowski A, Fukagawa N K, Ziska L H. Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels this century will alter the protein, micronutrients, and vitamin content of rice grains with potential health consequences for the poorest rice-dependent countries. Sci Adv, 2018, 4(5): eaaq1012. |
| [9] | Smith M R, Myers S S.Impact of anthropogenic CO2 emissions on global human nutrition.Nat Clim Chan, 2018, 8(9): 834-839. |
| [10] | Usui Y, Sakai H, Tokida T, Nakamura H, Nakagawa H, Hasegawa T.Rice grain yield and quality responses to free-air CO2 enrichment combined with soil and water warming.Glob Chan Biol, 2016, 22(3): 1256-1270. |
| [11] | 董桂春, 王余龙, 黄建晔, 杨洪建, 顾晖, 彭斌, 居静, 杨连新, 朱建国, 单玉华. 稻米品质性状对开放式空气二氧化碳浓度增高的响应. 应用生态学报, 2004, 15(7): 1217-1222. |
| Dong G C, Wang Y L, Huang J Y, Yang H J, Gu H, Peng B, Ju J, Yang L X, Zhu J G, Shan Y H.Response of rice grain quality traits to free-air CO2 enrichment.Chin J Appl Ecol, 2004, 15(7): 1217-1222. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 常二华, 张耗, 张慎凤, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 结实期氮磷营养水平对水稻根系分泌物的影响及其与稻米品质的关系. 作物学报, 2007, 33(12): 1949-1959. |
| Chang E H, Zhang H, Zhang S F, Wang Z Q, Yang J C.Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on the root exudates during grain filling and their relations with grain quality of rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2007, 33(12): 1949-1959. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 全国明, 章家恩, 许荣宝, 谢利, 刘金苓. 环境生态因子对稻米品质的影响研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(4): 158-162. |
| Quan G M, Zhang J E, Xu R B, Xie L, Liu J L.Review on the effect of environmental factors on rice quality.Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2006, 22(4): 158-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Taub D R, Miller B, Allen H.Effects of elevated CO2 on the protein concentration of food crops: A meta-analysis.Glob Chan Biol, 2008, 14(3): 565-575. |
| [15] | Mcgrath J M, Lobell D B.Reduction of transpiration and altered nutrient allocation contribute to nutrient decline of crops grown in elevated CO2 concentrations.Plant Cell & Environ, 2013, 36(3): 697-705. |
| [16] | Yoshimoto M, Oue H, Takahashi N, Kobayashi K.The effects of FACE (free-air CO2 enrichment) on temperatures and transpiration of rice panicles at flowering stage.J Agric Meteorol, 2005, 60(5): 597-600. |
| [17] | 杨洪建, 杨连新, 刘红江, 黄建晔, 董桂春, 朱建国, 王余龙. FACE对水稻根系及产量的影响. 作物学报, 2005, 31(9): 1221-1226. |
| Yang H J, Yang L X, Liu H J, Huang J Y, Dong G C, Zhu J G, Wang Y L.Effects of free-air CO2 enrichment on root system and yield in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Acta Agron Sin, 2005, 31(9): 1221-1226. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 林赵淼, 郑德益, 张新城, 刘正辉, 王绍华, 丁艳锋. 稻米垩白形成的生理与分子机制研究进展. 中国稻米, 2015, 21(4): 14-19. |
| Lin Z M, Zheng D Y, Zhang X C, Liu Z H, Wang S H, Ding Y F.Research advances in the physiological and molecular mechanisms of chalkiness formation in rice.China Rice, 2015, 21(4): 14-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Su Y H, North H, Grignon C, Thibaud J B, Sentenac H, Very A A.Regulation by external K+ in a maize inward shaker channel targets transport activity in the high concentration range.Plant Cell, 2005, 17(5): 1532-1548. |
| [20] | Wang L, Yang S Y, Guo M Y, Huang Y N, Sentenac H, Very A A, Su Y H.The S1-S2 linker determines the distinct pH sensitivity between ZmK2.1 and KAT1.Plant J, 2016, 85(5): 675-685. |
| [21] | Zhao Y, Cheng S F, Song Y L, Huang Y L, Zhou S L, Liu X Y, Zhou D X.The Interaction between rice ERF3 and WOX11 promotes crown root development by regulating gene expression involved in cytokinin signaling.Plant Cell, 2015, 27(9): 2469-2483. |
| [22] | Hu B, Wang W, Ou S J, Tang J Y, Li H, Che R H, Zhang Z H, Chai X Y, Wang H R, Wang Y Q, Liang C Z, Liu L C, Piao Z Z, Deng Q Y, Deng K, Xu C, Liang Y, Zhang L H, Li L G, Chu C C.Variation in NRT1.1B contributes to nitrate-use divergence between rice subspecies.Nat Genet, 2015, 47(7): 834-840. |
| [23] | Wei W, Hu B, Yuan D, Liu Y Q, Che R H, Hu Y C, Ou S J, Liu Y X, Zhang Z H, Wang H R, Li H, Jiang Z M, Zhang Z L, Gao X K, Qiu Y H, Meng X B, Bai Y, Liang Y, Wang Y Q, Zhang L H, Li L G, Sodmergen, Jing H C, Li J Y, Chu C C. Expression of the nitrate transporter gene OsNRT1.1A/OsNPF6.3 confers high yield and early maturation in rice.Plant Cell, 2018, 30(3): 638-651. |
| [24] | Yang L X, Huang J Y, Yang H J, Dong G C, Liu H J, Liu G, Zhu J G, Wang Y L.Seasonal changes in the effects of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) on nitrogen (N) uptake and utilization of rice at three levels of N fertilization.Field Crops Res, 2007, 100(2): 189-199. |
| [25] | 黄建晔, 杨连新, 杨洪建, 刘红江, 董桂春, 朱建国, 王余龙.开放式空气CO2浓度增加对水稻生育期的影响及其原因分析. 作物学报, 2005, 31(7): 882-887. |
| Huang J Y, Yang L X, Yang H J, Liu H J, Dong G C, Zhu J G, Wang Y L.Effects of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) on growth duration of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and its cause.Acta Agron Sin, 2005, 31(7): 882-887. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Siebert S, Ewert F, Rezaei E E, Kage H, Gras R.Impact of heat stress on crop yield: On the importance of considering canopy temperature.Environm Res Lett, 2014, 9(4): 044012. |
| [27] | 罗卫红, Yoshimoto M, 戴剑峰, 朱建国, 韩勇, 刘钢. 开放式空气CO2浓度增高对水稻冠层微气候的影响. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(10): 1235-1239. |
| Luo W, Yoshimoto M, Dai J, Zhu J G, Han Y, Liu G.Effects of free-air CO2 enrichment on rice canopy microclimate.Chin J Appl Ecol, 2002, 13(10): 1235-1239. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Kobayashi A, Bao G L, Ye S H, Tomita K.Detection of quantitative trait loci for white-back and basal-white kernels under high temperature stress in japonica rice varieties.Breeding Sci, 2007, 57: 107-116. |
| [29] | 庞静, 朱建国, 谢祖彬, 刘钢, 陈改萍. CO2浓度升高条件下水稻蒸腾与N吸收的关系. 中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(2): 205-209. |
| Pang J, Zhu J G, Xie Z B, Liu G, Chen G P.Relations between transpiration and N uptake of rice grown in elevated air carbon dioxide concentration.Chin J Rice Sci, 2006, 20(2): 205-209. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 徐习. 高浓度CO2条件下提升水稻增产效应的初步研究.南京: 中国科学院南京土壤研究, 2017. |
| Xu X.Preliminary study on raising rice yield response to elevated carbon dioxide. Nanjing: Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Lawlor D W.Carbon and nitrogen assimilation in relation to yield: Mechanisms are the key to understanding production systems.J Exper Bot, 2002, 53(370): 773-787. |
| [32] | Ambardekar A A, Siebenmorgen T J, Counce P A, Lanning S B, Mauromoustakos A.Impact of field-scale nighttime air temperatures during kernel development on rice milling quality.Field Crops Res, 2011, 122(3): 179-185. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||