
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (4): 410-418.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.211107
张露1, 吴龙龙1, 黄晶1, 田仓1,2, 祈军3, 张均华1, 曹小闯1, 朱春权1, 孔亚丽1, 金千瑜1, 朱练峰1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-11
修回日期:2022-02-14
出版日期:2022-07-10
发布日期:2022-07-12
通讯作者:
朱练峰
基金资助:
ZHANG Lu1, WU Longlong1, HUANG Jing1, TIAN Cang1,2, QI Jun3, ZHANG Junhua1, CAO Xiaochuang1, ZHU Chunquan1, KONG Yali1, JIN Qianyu1, ZHU Lianfeng1,*( )
)
Received:2021-11-11
Revised:2022-02-14
Online:2022-07-10
Published:2022-07-12
Contact:
ZHU Lianfeng
摘要:
【目的】探讨增氧方式对稻田土壤微生物量碳、氮和土壤酶活性的影响。【方法】以中旱221(旱稻)、中浙优8号(水稻)和IR45765-3B(深水稻)为材料,研究微纳米气泡水增氧灌溉、干湿交替灌溉、淹水灌溉对稻田土壤微生物量碳、氮,土壤氮代谢作用强度和土壤氮素转化相关酶活性的影响。【结果】微纳米气泡水增氧灌溉和干湿交替灌溉可以显著提高稻田土壤微生物生物量碳、氮,中旱221、中浙优8号和IR45765-3B的增氧处理较淹水灌溉处理微生物生物量碳、氮分别增加了30.0%~46.1%和7.1%~92.1%,并且增氧处理降低了3个水稻品种的微生物量碳氮比;与淹水灌溉相比,微纳米气泡水增氧灌溉和干湿交替灌溉有助于提高稻田土壤脲酶、蔗糖酶、过氧化氢酶、蛋白酶、羟胺还原酶活性,降低硝酸还原酶活性和亚硝酸还原酶活性。【结论】微纳米气泡水增氧灌溉和干湿交替灌溉改善稻田土壤的氧化特性,提高土壤酶活性、微生物量碳、氮和硝化强度,有助于改善土壤环境和肥力状况,协调了C、N代谢的平衡。
张露, 吴龙龙, 黄晶, 田仓, 祈军, 张均华, 曹小闯, 朱春权, 孔亚丽, 金千瑜, 朱练峰. 增氧处理对稻田土壤微生物量碳、氮和酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 410-418.
ZHANG Lu, WU Longlong, HUANG Jing, TIAN Cang, QI Jun, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHU Chunquan, KONG Yali, JIN Qianyu, ZHU Lianfeng. Effect of Aeration Treatment on Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon, Nitrogen and Enzyme Activities in Paddy Field[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(4): 410-418.
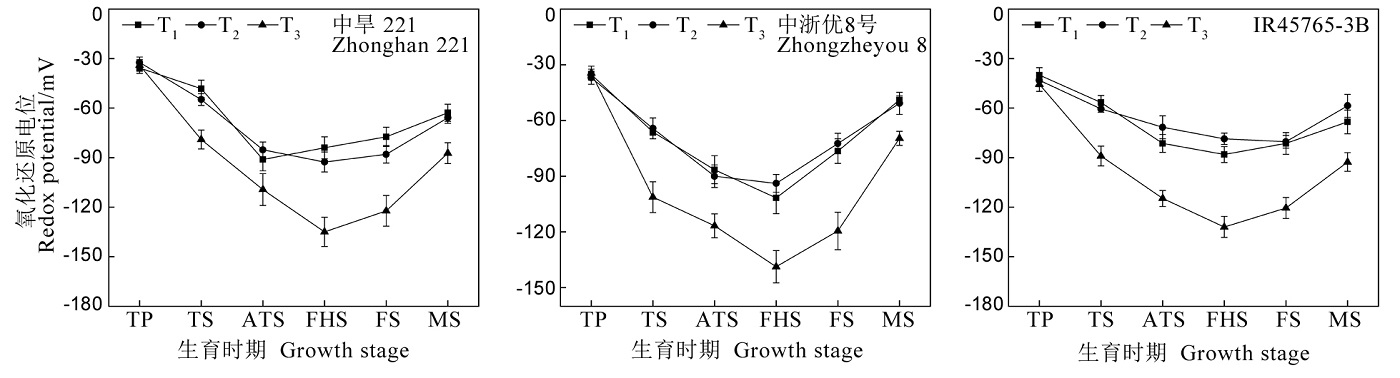
图1 不同增氧灌溉模式对稻田土壤氧化还原电位的影响 T1-微纳米气泡水增氧灌溉;T2-干湿交替灌溉;T3-淹水灌溉;TP-移栽期;TS-分蘖期;ATS-分蘖盛期;FHS-齐穗期;FS-灌浆期;MS-成熟期;图中数值为平均值±标准偏差(n=3)。
Fig. 1. Effects of different oxygenated irrigation patterns on paddy redox potential. T1, Micro-nano bubble water aerobic irrigation; T2, Alternate dry and wet irrigation; T3, Water-logging irrigation. TP, Transplanting stage; TS, Tillering stage; ATS, Active tillering stage; HS, Full heading stage; FHS, Filling stage; MS, Mature stage; t values are mean ± standard deviation(n=3).
| 品种 Variety | 灌溉方式 Irrigation method | 微生物量碳 Soil microbial biomass carbon /(mg·g−1 h−1) | 微生物量氮 Soil microbial biomass nitrogen /(mg·g−1 h−1) | 微生物量碳氮比 SMBC/SMBN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中旱221 | T1 | 341.54±21.4 b | 43.79±0.46 b | 7.80±0.04 c |
| Zhonghan 221 | T2 | 431.37±13.6 a | 50.42±1.95 a | 8.55±0.45 b |
| T3 | 295.59±11.4 c | 30.73±1.25 c | 9.62±0.37 a | |
| 中浙优8号 | T1 | 368.93±10.7 a | 38.47±2.33 a | 9.60±0.48 a |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | T2 | 381.47±27.2 a | 39.44±1.13 a | 9.67±0.59 a |
| T3 | 294.28±11.4 b | 29.28±1.33 b | 10.05±0.46 a | |
| IR45765-3B | T1 | 329.15±13.5 a | 38.10±1.01 a | 8.60±0.18 b |
| T2 | 304.68±19.9 b | 35.81±1.99 ab | 8.51±0.53 b | |
| T3 | 307.07±19.1 b | 33.42±2.56 b | 9.20±0.49 a | |
| F值 | 品种Variety(V) | 82.59** | 9.79** | 0.27 |
| F value | 灌溉方式Irrigation(W) | 97.61** | 28.85** | 23.70** |
| V×W | 48.54** | 12.04** | 11.30** |
表1 不同增氧灌溉模式对稻田土壤微生物量碳、氮的影响
Table 1. Effects of different oxygenated irrigation patterns on soil microbial biomass carbon(SMBC) and soil microbial biomass nitrogen(SMBN) in paddy field.
| 品种 Variety | 灌溉方式 Irrigation method | 微生物量碳 Soil microbial biomass carbon /(mg·g−1 h−1) | 微生物量氮 Soil microbial biomass nitrogen /(mg·g−1 h−1) | 微生物量碳氮比 SMBC/SMBN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中旱221 | T1 | 341.54±21.4 b | 43.79±0.46 b | 7.80±0.04 c |
| Zhonghan 221 | T2 | 431.37±13.6 a | 50.42±1.95 a | 8.55±0.45 b |
| T3 | 295.59±11.4 c | 30.73±1.25 c | 9.62±0.37 a | |
| 中浙优8号 | T1 | 368.93±10.7 a | 38.47±2.33 a | 9.60±0.48 a |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | T2 | 381.47±27.2 a | 39.44±1.13 a | 9.67±0.59 a |
| T3 | 294.28±11.4 b | 29.28±1.33 b | 10.05±0.46 a | |
| IR45765-3B | T1 | 329.15±13.5 a | 38.10±1.01 a | 8.60±0.18 b |
| T2 | 304.68±19.9 b | 35.81±1.99 ab | 8.51±0.53 b | |
| T3 | 307.07±19.1 b | 33.42±2.56 b | 9.20±0.49 a | |
| F值 | 品种Variety(V) | 82.59** | 9.79** | 0.27 |
| F value | 灌溉方式Irrigation(W) | 97.61** | 28.85** | 23.70** |
| V×W | 48.54** | 12.04** | 11.30** |
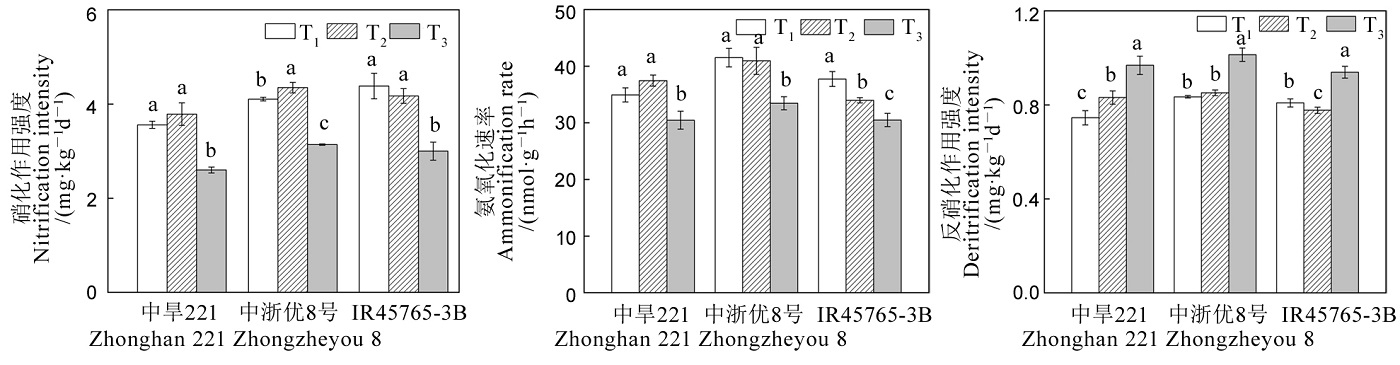
图2 不同增氧灌溉模式对稻田土壤硝化作用强度、氨氧化速率和反硝化作用强度的影响
Fig. 2. Effects of different oxygenation irrigation modes on soil nitrification intensity, ammonia oxidation rate and denitrification intensity in paddy field.
| 品种 Variety | 灌溉方式 Irrigation method | 脲酶 Urease /(µg·g−1d−1) | 蔗糖酶 Invertase /(mg·g−1h−1) | 过氧化氢酶 Hydrogen peroxidase /(mg·g−1min−1) | 蛋白酶 Protease /(µg·g−1d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中旱221 | T1 | 35.15±0.83 b | 1.50±0.02 b | 1.41±0.04 a | 32.27±0.17 a |
| Zhonghan 221 | T2 | 37.42±0.74 a | 1.57±0.04 a | 1.33±0.03 b | 33.03±0.78 a |
| T3 | 30.35±1.10 c | 1.16±0.02 c | 1.22±0.04 c | 31.27±2.09 a | |
| 中浙优8号 | T1 | 37.43±1.05 a | 1.67±0.04 a | 1.38±0.01 a | 38.15±0.98 a |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | T2 | 38.56±1.35 a | 1.71±0.03 a | 1.36±0.02 a | 37.73±1.00 a |
| T3 | 31.56±0.66 b | 1.27±0.02 b | 1.22±0.03 b | 36.42±1.23 a | |
| IR45765-3B | T1 | 38.15±0.74 a | 1.81±0.04 a | 1.45±0.04 a | 44.76±0.69 a |
| T2 | 36.62±1.17 a | 1.76±0.02 a | 1.47±0.04 a | 44.42±1.01 a | |
| T3 | 31.18±1.10 b | 1.29±0.04 b | 1.23±0.04 b | 35.86±0.96 b | |
| F值 | V | 0.16 | 4.70* | 6.49* | 47.15** |
| F value | W | 17.67** | 10.36** | 0.32 | 1.52 |
| V×W | 0.85 | 0.21 | 3.3 | 9.59** |
表2 不同增氧灌溉模式对稻田土壤有机氮转化相关酶活性的影响
Table 2. Effects of different oxygenated irrigation patterns on activities of enzymes associated with organic nitrogen transfor- mation in paddy soil.
| 品种 Variety | 灌溉方式 Irrigation method | 脲酶 Urease /(µg·g−1d−1) | 蔗糖酶 Invertase /(mg·g−1h−1) | 过氧化氢酶 Hydrogen peroxidase /(mg·g−1min−1) | 蛋白酶 Protease /(µg·g−1d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中旱221 | T1 | 35.15±0.83 b | 1.50±0.02 b | 1.41±0.04 a | 32.27±0.17 a |
| Zhonghan 221 | T2 | 37.42±0.74 a | 1.57±0.04 a | 1.33±0.03 b | 33.03±0.78 a |
| T3 | 30.35±1.10 c | 1.16±0.02 c | 1.22±0.04 c | 31.27±2.09 a | |
| 中浙优8号 | T1 | 37.43±1.05 a | 1.67±0.04 a | 1.38±0.01 a | 38.15±0.98 a |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | T2 | 38.56±1.35 a | 1.71±0.03 a | 1.36±0.02 a | 37.73±1.00 a |
| T3 | 31.56±0.66 b | 1.27±0.02 b | 1.22±0.03 b | 36.42±1.23 a | |
| IR45765-3B | T1 | 38.15±0.74 a | 1.81±0.04 a | 1.45±0.04 a | 44.76±0.69 a |
| T2 | 36.62±1.17 a | 1.76±0.02 a | 1.47±0.04 a | 44.42±1.01 a | |
| T3 | 31.18±1.10 b | 1.29±0.04 b | 1.23±0.04 b | 35.86±0.96 b | |
| F值 | V | 0.16 | 4.70* | 6.49* | 47.15** |
| F value | W | 17.67** | 10.36** | 0.32 | 1.52 |
| V×W | 0.85 | 0.21 | 3.3 | 9.59** |
| 品种 Variety | 灌溉方式 Irrigation method | 羟胺还原酶 Hydroxylamine reductase /(µg·g−1d−1) | 硝酸还原酶 Nitrate reductase /(µmol·g−1d−1) | 亚硝酸还原酶 Nitrite reductase /(µmol·g−1d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中旱221 | T1 | 672.96±16.5 b | 2.51±0.09 c | 2.54±0.05 c |
| Zhonghan 221 | T2 | 706.58±14.3 a | 2.80±0.10 b | 2.95±0.05 b |
| T3 | 637.54±19.0 c | 4.92±0.21 a | 3.65±0.12 a | |
| 中浙优8号 | T1 | 682.96±40.2 a | 4.07±0.08 c | 3.38±0.19 b |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | T2 | 703.47±23.0 a | 4.62±0.06 b | 2.94±0.16 c |
| T3 | 633.00±26.6 b | 5.69±0.07 a | 4.35±0.28 a | |
| IR45765-3B | T1 | 714.22±20.6 a | 2.66±0.09 c | 3.87±0.12 b |
| T2 | 704.05±4.45 a | 3.38±0.05 b | 3.54±0.07 c | |
| T3 | 729.64±11.2 a | 3.82±0.12 a | 4.54±0.07 a |
表3 不同增氧模式对稻田土壤硝化-反硝化关键酶活性的影响
Table 3. Effects of different aeration modes on the activities of key nitrification-denitrification enzymes in paddy soil.
| 品种 Variety | 灌溉方式 Irrigation method | 羟胺还原酶 Hydroxylamine reductase /(µg·g−1d−1) | 硝酸还原酶 Nitrate reductase /(µmol·g−1d−1) | 亚硝酸还原酶 Nitrite reductase /(µmol·g−1d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中旱221 | T1 | 672.96±16.5 b | 2.51±0.09 c | 2.54±0.05 c |
| Zhonghan 221 | T2 | 706.58±14.3 a | 2.80±0.10 b | 2.95±0.05 b |
| T3 | 637.54±19.0 c | 4.92±0.21 a | 3.65±0.12 a | |
| 中浙优8号 | T1 | 682.96±40.2 a | 4.07±0.08 c | 3.38±0.19 b |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | T2 | 703.47±23.0 a | 4.62±0.06 b | 2.94±0.16 c |
| T3 | 633.00±26.6 b | 5.69±0.07 a | 4.35±0.28 a | |
| IR45765-3B | T1 | 714.22±20.6 a | 2.66±0.09 c | 3.87±0.12 b |
| T2 | 704.05±4.45 a | 3.38±0.05 b | 3.54±0.07 c | |
| T3 | 729.64±11.2 a | 3.82±0.12 a | 4.54±0.07 a |
| [1] | 姚槐应, 黄昌勇. 土壤微生物生态学及其实验技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007. |
| Yao H Y, Huang C Y. Soil Microbial Ecology and Its Experimental Technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 赵锋, 徐春梅, 张卫建, 章秀福, 程建平, 王丹英. 根际溶氧量与氮素形态对水稻根系特征及氮素积累的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(2): 195-200. |
| Zhao F, Xu C M, Zhang W J, Zhang X F, Wang D Y. Effects of rhizosphere dissolved oxygen and nitrogen form on root characteristics and nitrogen accumulation of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(2): 195-200. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 胡志华, 朱练峰, 林育炯, 张均华, 胡继杰, 禹盛苗, 曹小闯, 金千瑜. 根部增氧模式对水稻产量与氮素利用的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(6): 1503-1512. |
| Hu Z H, Zhu L F, Lin Y J, Zhang J H, Hu J J, Yu S M, Cao X C, Jin Q Y. Effect of root aeration methods on rice yield and nitrogen utilization[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2016, 22(6): 1503-1512. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 侯俊, 徐洲, 张丁月, 朱建强. 增氧型复混肥提高土壤氧化还原电位促进水稻养分吸收[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(8): 1546-1555. |
| Hou J, Xu Z, Zhang D Y, Zhu J Q. Oxygenated compound fertilizer could effectively increase redox potential of paddy soil and nutrient uptake of rice[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(8): 1546-1555. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 杜君, 孙克刚, 张运红, 和爱玲, 孙克振. 控释尿素对水稻生理特性、氮肥利用率及土壤硝态氮含量的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2016, 33(2): 134-141. |
| Du J, Sun K G, Zhang Y H, He A L, Sun K Z. Effects of controlled release urea on physiological characteristics and nitrogen use efficiency of rice and NO3−-N contents in soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2016, 33(2): 134-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 肖新, 朱伟, 肖靓, 邓艳萍, 赵言文, 汪建飞. 适宜的水氮处理提高稻基农田土壤酶活性和土壤微生物量碳氮[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(21): 91-98. |
| Xiao X, Zhu W, Xiao J, Deng Y P, Zhao Y W, Wang J F. Suitable water and nitrogen treatment improves soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and enzyme activities of paddy field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2013, 29(21): 91-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 黄炳林, 王孟雪, 金喜军, 胡国华, 张玉先. 不同耕作处理对土壤微生物、酶活性及养分的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2019(6): 104-113. |
| Huang B L, Wang M X, Jin X J, Hu G H, Zhang Y X. Effects of different tillage treatments on soil microorganisms, enzyme activities and nutrients[J]. Crops, 2019(6): 104-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Vale M, Nguyena C, Dambrineb E, Dupoueyc J L. Microbial activity in the rhizosphere soil of six herbaceous species cultivated in a greenhouse is correlated with shoot biomass and root C concentrations[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2005, 37(12): 2329-2333. |
| [9] | 胡继杰, 朱练峰, 胡志华, 钟楚, 林育炯, 张均华, 曹小闯, James A B, 禹盛苗, 金千瑜. 土壤增氧方式对其氮素转化和水稻氮素利用及产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(1): 167-174. |
| Hu J J, Zhu L F, Hu Z H, Zhong C, Lin Y J, Zhang J H, Cao X C, James A B, Yu S M, Jin Q Y. Effects of soil aeration methods on soil nitrogen transformation, rice nitrogen utilization and yield[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(1): 167-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 徐春梅, 王丹英, 陈松, 陈丽萍, 章秀福. 增氧对水稻根系生长与氮代谢的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(3): 320-324. |
| Xu C M, Wang D Y, Chen S, Chen L P, Zhang X F. Effect of aeron root growth and nitrogen metabolismin rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(3): 320-324. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 才硕. 微纳米气泡增氧灌溉技术在水稻灌区节水减排中的应用研究[J]. 节水灌溉, 2016(9): 117-120, 128. |
| Cai S. Application research of micro-nano bubble aerated irrigation technique in water conservation and wastewater discharge from rice irrigation area[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2016(9): 117-120, 128. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 庄林杰. 干湿交替条件对土壤中厌氧氨氧化细菌和氨氧化古菌丰度的影响[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2017. |
| Zhuang L J. Effects of wetting and drying conditions on the abundance of anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria and ammonia oxidizing archaea in soil[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2017.. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 曹小闯, 吴龙龙, 朱春权, 朱练峰, 孔亚丽, 陆若辉, 孔海民, 胡兆平, 戴锋, 张均华, 金千瑜. 不同灌溉和施肥模式对水稻产量、氮利用和稻田氮转化特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(7): 1482-1498. |
| Cao X C, Wu L L, Zhu C Q, Zhu L F, Kong Y L, Lu R H, Kong H M, Hu Z P, Dai F, Zhang J H, Jin Q Y. Effects of different irrigation and nitrogen application regimes on the yield, nitrogen utilization of rice and nitrogen transformation in paddy soil[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(7): 1482-1498. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 徐国伟, 陆大克, 孙会忠, 王贺正, 李友军. 干湿交替灌溉与施氮耦合对水稻根际环境的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(4): 186-194. |
| Xu G W, Lu D K, Sun H Z, Wang H Z, Li Y J. Effect of alternative wetting and drying irrigation and nitrogen coupling on rhizosphere environment of rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(4): 186-194.. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Sang H H, Jiao X Y, Wang S F, Guo W H, Salahou M K, Liu K H. Effects of micro-nano bubble aerated irrigation and nitrogen fertilizer level on tillering, nitrogen uptake and utilization of early rice[J]. Plant Soil Environment, 2018, 64(7): 297-302. |
| [16] | 彭卫福. 土壤肥力对水稻氮素利用效率和氮循环相关微生物的影响[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2017. |
| Pang W F. Effects of soil fertility on nitrogen use efficiency and nitrogen cycle-related microorganisms in rice[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 农业出版社, 1986. |
| Guan S Y. Soil Enzyme and its research method[M]. Agricultural Press, 1986. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Ajwa H A, Dell C J, Rice C W. Changes in enzyme activities and microbial biomass of tallgrass prairie soil as related to burning and nitrogen fertilization[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 1999, 31(5): 769-777. |
| [19] | 谢志煌, 高志颖, 郭丽丽, 张锦源, 于镇华. 土壤微生物活性和生物量对干湿交替的响应[J]. 土壤与作物, 2020, 9(4): 348-354. |
| Xie Z H, Gao Z Y, Guo L L, Zhang J Y, Yu Z H. Responses of soil microbial activities and biomass to drying and wetting: A review[J]. Soils and Crops, 2020, 9(4): 348-354. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 贺纪正, 张丽梅. 土壤氮素转化的关键微生物过程及机制[J]. 微生物学通报, 2013, 40(1): 98-108. |
| He J Z, Zhang L M. Key processes and microbial mechanisms of soil nitrogen transformation[J]. Microbiology China, 2013, 40(1): 98-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 郭天财, 宋晓, 马冬云, 王永华, 谢迎新, 岳艳军, 查菲娜. 施氮量对冬小麦根际土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(1): 110-114. |
| Guo T C, Song X, Ma D Y, Wang Y H, Xie Y X, Yue Y J, Cha F N. Effects of nitrogen application rate on soil enzyme activities in wheat rhizosphere[J]. China Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(1): 110-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 梁燕菲, 张潇潇, 李伏生. “薄浅湿晒”灌溉稻田土壤微生物量碳、氮和酶活性研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(6): 1403-1410. |
| Liang Y F, Zhang X X, Li F S. Soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and enzyme activities in paddy soil under “thin-shallow-wet-dry” irrigation method[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2013, 19(6): 1403-1410. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 贺纪正, 张丽梅. 土壤氮素转化的关键微生物过程及机制[J]. 微生物学通报, 2013, 40(1): 98-108. |
| He J Z, Zhang L M. Key processes and microbial mechanisms of soil nitrogen transformation[J]. Microbiology China, 2013, 40(1): 98-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Liang B, Yang X Y, He X H. Effects of 17-year fertilization on soil microbial biomass C and N and soluble organic C and N in loessial soil during maize growth[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2011, 47(2): 121-128. |
| [25] | Liang B, Zhao W, Yang X Y. Fate of nitrogen-15 as influenced by soil and nutrient management history in a 19-year wheat-maize experiment[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 144: 126-134. |
| [26] | 谢秋发, 刘经荣, 石庆华, 李木英. 不同施肥方式对水稻产量、吸氮特性和土壤氮转化的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2004(5): 462-467. |
| Xie Q F, Liu J R, Shi Q H, Lin M Y. Effect of different fertilization Patterns on rice yield and nitrogen uptake and transformation in soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2004(5): 462-467. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Hai M T, Xiao P, Wen G T, Chao L, Ke W, Kai K C, GEN S. Dynamic change of soil enzyme activities and soil microbe during rice main growth stages in different long-term fertilizer regimes[J]. Journal of Pure & Applied Microbiology, 2017, 11(2): 649-660. |
| [28] | 曹小闯, 李晓艳, 朱练峰, 张均华, 禹盛苗, 吴良欢, 金千瑜. 水分管理调控水稻氮素利用研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(13): 3882-3890. |
| Cao X C, Li X Y, Zhu L F, Zhang J H, Yu S M, Wu L H, Jin Q Y. Effects of water management on rice nitrogen utilization[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(13): 3882-3890. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 白志刚, 张均华, 黄洁, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 朱春权, 钟楚, 金千瑜. 氮肥运筹对水稻氮代谢及稻田土壤氮素迁移转化的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(11): 3440-3448. |
| Bai Z G, Zhang J H, Huang J, Zhu L F, Cao X C, Zhu C Q, Zhong C, Jin Q Y. Effects of nitrogen regime on nitrogen metabolism of rice and nitrogen transformation and translocation in paddy soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(11): 3440-3448. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 胡华英, 殷丹阳, 曹升, 张虹, 周垂帆, 何宗明. 生物炭对杉木人工林土壤养分、酶活性及细菌性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(11): 4138-4148. |
| Hu H Y, Yin D Y, Cao S, Zhang H, Zhou C F, He Z M. Effects of biochar on soil nutrient, enzyme activity, and bacterial properties of Chinese fir plantation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(11): 4138-4148. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 孙瑞莲, 赵秉强, 朱鲁生, 徐晶, 张夫道. 长期定位施肥对土壤酶活性的影响及其调控土壤肥力的作用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2003(4): 406-410. |
| Sun R L, Zhao B Q, Zhu L S, Xu J, Zhang F D. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil enzyme activities and its role in adjusting-controlling soil fertility[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2003(4): 406-410. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 吴晓丽, 李朝苏, 汤永禄, 刘于斌, 李伯群, 樊高琼, 熊涛. 氮肥运筹对小麦产量、氮素利用效率和光能利用率的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(6): 1889-1898. |
| Wu X L, Li C S, Tang Y L, Liu Y B, Li B Q, Fan G Q, Xiong T. Effect of nitrogen management modes on grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency and light use efficiency of wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(6): 1889-1898. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 江孟孟, 赵喜辉, 谢小文, 陆大克, 徐国伟. 氮肥形态与干湿交替灌溉下水稻土壤酶及养分差异[J]. 植物生理学报, 2021, 57(5): 1123-1134. |
| Jiang M M, Zhao X H, Xie X W, Lu D G, Xu G W. Differences of nitrogen fertilizer forms and soil enzymes and nutrients in rice under alternating dry and wet irrigation[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Physiology, 2021, 57(5): 1123-1134. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 李丽, 韩周, 张昀, 燕香梅, 张广才, 高晓丹, 张雅楠, 叶超, 李少博. 减氮配施微生物菌剂对水稻根系发育及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2019, 50(4): 932-939. |
| Li L, Han Z, Zhang Y, Yan X M, Zhang G C, Gao X D, Zhang Y N, Ye C, Li S B. Effects of reducing nitrogen fertilizer combined with microbial agents on rice root growth and soil enzyme activities[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2019, 50(4): 932-939. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | Ma G H, Yu L P. Hybrid rice achievements, development and prospect in China[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2015, 14(2): 197-205. |
| [36] | Liu E K, Zhao B Q, Mei X R, Li J, Li X Y. Effects of no-tillage management on soil biochemical characteristics in northern China[J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 2010, 148(2): 217-223. |
| [1] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [2] | 黄锦文, 李日坤, 陈志诚, 张汴泓, 雷涵, 潘睿欣, 杨铭榆, 潘美清, 唐莉娜. 不同稻草还田技术对烟-稻轮作系统土壤养分、有机碳及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 415-426. |
| [3] | 张露, 梁青铎, 吴龙龙, 黄晶, 田仓, 张均华, 曹小闯, 朱春权, 孔亚丽, 金千瑜, 朱练峰. 减氮和增氧灌溉对水稻产量和氮素利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 78-88. |
| [4] | 陈云, 刘昆, 李婷婷, 李思宇, 李国明, 张伟杨, 张耗, 顾骏飞, 刘立军, 杨建昌. 结实期干湿交替灌溉对水稻根系、产量和土壤的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 269-277. |
| [5] | 唐先干, 谢金水, 徐昌旭, 刘佳, 袁福生, 刘光荣, 李祖章. 红壤性稻田紫云英与化肥减施对早稻品质与养分吸收的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 466-474. |
| [6] | 黄锦文, 吴珈谊, 陈鸿飞, 张志兴, 方长旬, 邵彩虹, 林伟伟, 翁佩莹, 林文雄. 头季稻氮肥运筹对再生稻根际机能及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 383-395. |
| [7] | 柳开楼, 韩天富, 李文军, 余喜初, 胡志华, 叶会财, 胡丹丹, 宋惠洁, 李大明, 黄庆海. 紫云英不同翻压年限下驱动水稻产量变化的土壤理化因子 分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(3): 291-302. |
| [8] | 杨通, 吴俊男, 鲍婷, 李凤博, 冯金飞, 周锡跃, 方福平. 耕作方式对双季稻田土壤剖面CH4和N2O分布特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 78-88. |
| [9] | 李思平, 曾路生, 吴立鹏, 张玉晓, 解军蕊, 丁效东. 氮肥水平与栽植密度对植稻土壤养分含量变化与氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 69-79. |
| [10] | 刘少文, 殷敏, 褚光, 徐春梅, 王丹英, 章秀福, 陈松. 土壤氮激发效应及其微生物机理研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(4): 303-312. |
| [11] | 徐强, 马晓鹏, 吕廷波, 王东旺, 白蒙, 王泽林, 牛靖冉. 滴灌条件下不同土壤质地对水稻苗期根系生长和分布的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 249-256. |
| [12] | 张浪, 周玲红, 魏甲彬, 成小琳, 徐华勤, 肖志祥, 唐启源, 唐剑武. 冬季种养结合对双季稻生长与土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(3): 226-236. |
| [13] | 傅强, 李保平, 孟玲. 土壤施用生物质炭对取食水稻的灰飞虱生活史特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 1(1): 200-206. |
| [14] | 高继平, 隋阳辉, 张文忠, 姚晨, 高明超. 水稻灌浆期冠层温度对植株生理性状及稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(5): 501-510. |
| [15] | 张书捷, 张新疆, 王娟, 黄倩楠, 白如霄, 危常州. 施用土壤酸化剂和调整播期防治膜下滴灌水稻苗期缺铁黄化的效果研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(5): 519-527. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||