
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 78-88.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220307
张露1,#, 梁青铎1,#, 吴龙龙1, 黄晶1, 田仓1,2, 张均华1, 曹小闯1, 朱春权1, 孔亚丽1, 金千瑜1, 朱练峰1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-08
修回日期:2022-09-06
出版日期:2023-01-10
发布日期:2023-01-10
通讯作者:
朱练峰
作者简介:第一联系人:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
ZHANG Lu1,#, LIANG Qingduo1,#, WU Longlong1, HUANG Jing1, TIAN Cang1,2, ZHANG Junhua1, CAO Xiaochuang1, ZHU Chunquan1, KONG Yali1, JIN Qianyu1, ZHU Lianfeng1,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-08
Revised:2022-09-06
Online:2023-01-10
Published:2023-01-10
Contact:
ZHU Lianfeng
About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要: 目的 明确减氮和增氧灌溉对水稻生长、产量和氮肥利用的影响。 方法 以3个品种水稻中旱221(旱稻)、中浙优8号(水稻)和IR45765-3B(深水稻)为材料,并设常规施氮量(195.0 kg/hm2)、减施氮量(157.5 kg/hm2)2种氮水平和常规淹水灌溉(Conventional Flood Irrigation,WL)、微纳米气泡水增氧灌溉(Micro-nano Bubble Water Oxygenation Irrigation,MBWI)2个灌溉模式,对比分析了3个品种水稻的茎蘖动态、叶片叶绿素含量、叶面积、干物质量、产量和水稻的氮素吸收利用特征。 结果 研究结果表明,MBWI处理显著增加了水稻产量,中旱221、中浙优8号和IR45765-3B的2年平均产量MBWI处理分别比WL处理增加12.4%、7.5%和6.7%,这可能与水稻有效穗数、每穗粒数密切相关。微纳米气泡水增氧灌溉和增施氮肥用量显著增加水稻叶片叶绿素含量和叶面积,并增加水稻干物质积累量。氮肥和增氧灌溉均影响水稻各氮素利用率指标,与淹水灌溉相比,微纳米气泡水增氧灌溉均可以显著增加3个品种水稻的氮收获指数、氮肥偏生产力和氮素籽粒生产效率,降低了水稻了氮转运效率和氮转运贡献率。减氮处理可以显著增加氮转运效率、氮转运贡献率、氮素籽粒生产效率和氮肥偏生产力,降低了氮收获指数。 结论 增氧灌溉有助于提高水稻叶片叶绿素含量和叶面积,增加水稻分蘖数和干物质积累量,进而显著提高水稻产量,影响氮素利用特征,并且在稻田氮素减施的条件下采用增氧灌溉能有助于构建高产群体,维持较高的产量。
张露, 梁青铎, 吴龙龙, 黄晶, 田仓, 张均华, 曹小闯, 朱春权, 孔亚丽, 金千瑜, 朱练峰. 减氮和增氧灌溉对水稻产量和氮素利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 78-88.
ZHANG Lu, LIANG Qingduo, WU Longlong, HUANG Jing, TIAN Cang, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHU Chunquan, KONG Yali, JIN Qianyu, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Nitrogen-reducing and Oxygen-increasing Irrigation on Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 78-88.
| 年份 Year | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 单株有效穗 Effective panicles per plant | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Grain yield/(kg·hm−2) |
| 2020 | 中旱221 | MBWI-N13 | 10.91 a | 168.44 a | 88.09 b | 21.35 a | 7531.6 a |
| Zhonghan 221 | WL-N13 | 10.08 bc | 156.31 c | 84.01 c | 21.62 a | 6898.6 c | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 10.33 b | 160.57 b | 91.19 a | 21.75 a | 7138.0 b | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 9.83 c | 152.53 d | 89.15 b | 21.58 a | 6462.7 d | ||
| 中浙优8号 | MBWI-N13 | 10.41 a | 188.32 a | 87.30 b | 22.29 a | 9099.6 a | |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | WL-N13 | 9.79 b | 182.09 a | 83.73 c | 22.76 a | 8320.8 b | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 9.92 b | 183.50 a | 90.55 a | 22.72 a | 8147.8 bc | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 9.10 c | 178.73 b | 86.93 b | 22.23 a | 7683.6 c | ||
| IR45765-3B | MBWI-N13 | 12.25 a | 175.75 a | 83.13 ab | 25.90 a | 8724.2 a | |
| WL-N13 | 11.83 b | 174.28 a | 81.10 b | 25.31 a | 8420.3 ab | ||
| MBWI-N10.5 | 11.41 c | 169.40 b | 86.92 a | 25.71 a | 8175.6 bc | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 11.08 c | 169.93 b | 83.64 b | 25.75 a | 7079.4 c | ||
| 2021 | 中旱221 | MBWI-N13 | 10.83 a | 165.78 a | 88.85 ab | 22.68 a | 7754.2 a |
| Zhonghan 221 | WL-N13 | 10.16 ab | 158.90 ab | 86.70 b | 22.31 ab | 6685.4 bc | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 10.16 ab | 155.22 bc | 90.08 a | 21.29 b | 7265.9 ab | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 9.50 c | 148.34 c | 88.45 ab | 21.23 b | 6366.1 c | ||
| 中浙优8号 | MBWI-N13 | 11.50 a | 177.44 a | 86.21 a | 24.40 a | 9299.5 a | |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | WL-N13 | 10.83 ab | 168.14 b | 83.41 c | 24.17 ab | 8582.4 b | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 11.00 ab | 171.04 b | 86.89 ab | 23.64 bc | 8593.9 b | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 10.16 c | 160.62 c | 84.61 bc | 23.40 c | 8096.1 c | ||
| IR45765-3B | MBWI-N13 | 11.50 a | 170.18 a | 83.43 ab | 25.76 a | 8398.1 a | |
| WL-N13 | 11.50 a | 169.95 ab | 81.74 b | 25.14 a | 8103.5 a | ||
| MBWI-N10.5 | 10.66 ab | 164.92 bc | 86.78 a | 25.42 a | 7749.8 ab | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 10.50 b | 161.91 c | 84.37 b | 25.13 a | 7449.7 b | ||
| F值 | Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| F value | V | 54.81** | 21.79** | 22.80** | 358.65** | 50.46** | |
| Y×N | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| Y×O | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| N×O | 29.31** | 9.50** | ns | 6.06* | 59.37** | ||
| Y×N×O | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
表1 不同处理水稻产量和产量构成因子
Table 1. Grain yield and its components of rice in different treatments.
| 年份 Year | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 单株有效穗 Effective panicles per plant | 每穗粒数 Grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 产量 Grain yield/(kg·hm−2) |
| 2020 | 中旱221 | MBWI-N13 | 10.91 a | 168.44 a | 88.09 b | 21.35 a | 7531.6 a |
| Zhonghan 221 | WL-N13 | 10.08 bc | 156.31 c | 84.01 c | 21.62 a | 6898.6 c | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 10.33 b | 160.57 b | 91.19 a | 21.75 a | 7138.0 b | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 9.83 c | 152.53 d | 89.15 b | 21.58 a | 6462.7 d | ||
| 中浙优8号 | MBWI-N13 | 10.41 a | 188.32 a | 87.30 b | 22.29 a | 9099.6 a | |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | WL-N13 | 9.79 b | 182.09 a | 83.73 c | 22.76 a | 8320.8 b | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 9.92 b | 183.50 a | 90.55 a | 22.72 a | 8147.8 bc | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 9.10 c | 178.73 b | 86.93 b | 22.23 a | 7683.6 c | ||
| IR45765-3B | MBWI-N13 | 12.25 a | 175.75 a | 83.13 ab | 25.90 a | 8724.2 a | |
| WL-N13 | 11.83 b | 174.28 a | 81.10 b | 25.31 a | 8420.3 ab | ||
| MBWI-N10.5 | 11.41 c | 169.40 b | 86.92 a | 25.71 a | 8175.6 bc | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 11.08 c | 169.93 b | 83.64 b | 25.75 a | 7079.4 c | ||
| 2021 | 中旱221 | MBWI-N13 | 10.83 a | 165.78 a | 88.85 ab | 22.68 a | 7754.2 a |
| Zhonghan 221 | WL-N13 | 10.16 ab | 158.90 ab | 86.70 b | 22.31 ab | 6685.4 bc | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 10.16 ab | 155.22 bc | 90.08 a | 21.29 b | 7265.9 ab | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 9.50 c | 148.34 c | 88.45 ab | 21.23 b | 6366.1 c | ||
| 中浙优8号 | MBWI-N13 | 11.50 a | 177.44 a | 86.21 a | 24.40 a | 9299.5 a | |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | WL-N13 | 10.83 ab | 168.14 b | 83.41 c | 24.17 ab | 8582.4 b | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 11.00 ab | 171.04 b | 86.89 ab | 23.64 bc | 8593.9 b | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 10.16 c | 160.62 c | 84.61 bc | 23.40 c | 8096.1 c | ||
| IR45765-3B | MBWI-N13 | 11.50 a | 170.18 a | 83.43 ab | 25.76 a | 8398.1 a | |
| WL-N13 | 11.50 a | 169.95 ab | 81.74 b | 25.14 a | 8103.5 a | ||
| MBWI-N10.5 | 10.66 ab | 164.92 bc | 86.78 a | 25.42 a | 7749.8 ab | ||
| WL-N10.5 | 10.50 b | 161.91 c | 84.37 b | 25.13 a | 7449.7 b | ||
| F值 | Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| F value | V | 54.81** | 21.79** | 22.80** | 358.65** | 50.46** | |
| Y×N | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| Y×O | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| N×O | 29.31** | 9.50** | ns | 6.06* | 59.37** | ||
| Y×N×O | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
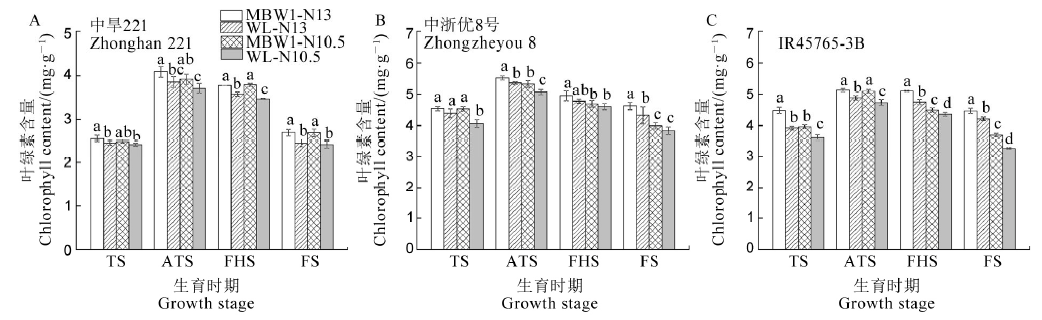
图2 不同氮肥和灌溉处理下不同水稻品种生育期叶绿素含量TS-分蘖期;ATS-分蘖盛期;FHS-齐穗期;FS-灌浆期;MS-成熟期;同一品种同一生育时期柱上不同字母表示在 0.05 水平上差异显著;下同。
Fig. 2. Chlorophyll contents of different rice varieties during different growth stages under different nitrogen fertilizer and irrigation treatments. TS, Tillering stage; ATS, Active tillering stage; HS, Full heading stage; FS, Filling stage; MS, Mature stage; Values in the same stage for a rice cultivar above the bars followed by different letter indicate significant difference at 0.05 level. The same below.
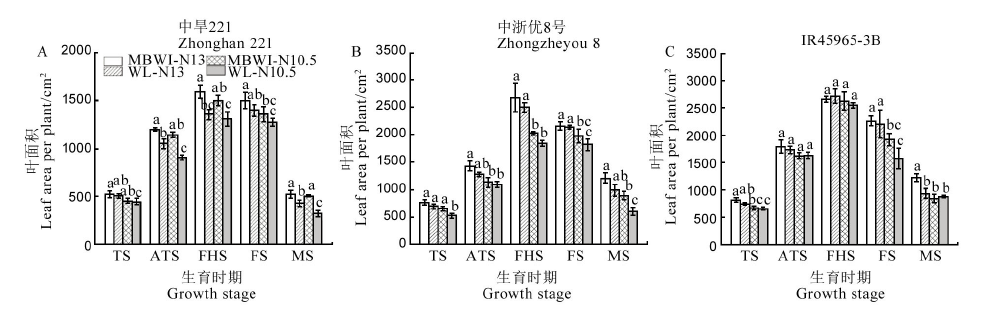
图3 不同氮肥和灌溉处理下不同水稻品种各生育时期叶面积
Fig. 3. Leaf area of different rice varieties during different growth stages under different nitrogen fertilizer and irrigation treatments.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 地上部干物质积累量 Dry matter accumulation of aboveground part/(t·hm-2) | 收获指数 Harvest index/% | ||||
| TS | ATS | FS | FHS | MS | |||
| 中旱221 | MBWI-N13 | 1.19 a | 3.94 a | 7.69 a | 10.20 a | 12.70 a | 45.63 a |
| Zhonghan 221 | WL-N13 | 1.10 ab | 3.77 a | 6.91 b | 9.08 b | 11.30 b | 43.34 bc |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 1.10 ab | 3.72 a | 6.72 b | 8.94 b | 12.60 a | 44.86 ab | |
| WL-N10.5 | 0.99 c | 3.63 a | 6.83 b | 8.52 c | 10.50 c | 41.94 c | |
| 中浙优8号 | MBWI-N13 | 1.20 a | 4.97 a | 13.38 a | 15.81 a | 18.68 a | 44.41 a |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | WL-N13 | 1.15 a | 4.78 a | 12.75 ab | 14.79 ab | 17.05 b | 42.96 b |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 1.07 a | 4.50 b | 13.08 a | 15.48 a | 17.75 b | 42.30 b | |
| WL-N10.5 | 1.16 a | 4.11 c | 12.10 b | 14.18 b | 16.14 c | 40.53 c | |
| IR45765-3B | MBWI-N13 | 1.40 a | 5.16 ab | 12.34 ab | 15.17 a | 16.80 a | 47.01 a |
| WL-N13 | 1.35 a | 5.44 a | 13.01 a | 14.26 b | 15.96 b | 45.70 ab | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 1.19 b | 4.83 bc | 11.71 b | 14.44 b | 14.70 c | 45.02 b | |
| WL-N10.5 | 1.28 b | 4.77 bc | 12.24 ab | 13.79 c | 14.62 c | 42.38 c | |
表2 不同氮肥和灌溉处理下水稻的地上部干物质积累量
Table 2. Aboveground dry matter accumulation of rice under different nitrogen fertilizer and irrigation treatments.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 地上部干物质积累量 Dry matter accumulation of aboveground part/(t·hm-2) | 收获指数 Harvest index/% | ||||
| TS | ATS | FS | FHS | MS | |||
| 中旱221 | MBWI-N13 | 1.19 a | 3.94 a | 7.69 a | 10.20 a | 12.70 a | 45.63 a |
| Zhonghan 221 | WL-N13 | 1.10 ab | 3.77 a | 6.91 b | 9.08 b | 11.30 b | 43.34 bc |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 1.10 ab | 3.72 a | 6.72 b | 8.94 b | 12.60 a | 44.86 ab | |
| WL-N10.5 | 0.99 c | 3.63 a | 6.83 b | 8.52 c | 10.50 c | 41.94 c | |
| 中浙优8号 | MBWI-N13 | 1.20 a | 4.97 a | 13.38 a | 15.81 a | 18.68 a | 44.41 a |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | WL-N13 | 1.15 a | 4.78 a | 12.75 ab | 14.79 ab | 17.05 b | 42.96 b |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 1.07 a | 4.50 b | 13.08 a | 15.48 a | 17.75 b | 42.30 b | |
| WL-N10.5 | 1.16 a | 4.11 c | 12.10 b | 14.18 b | 16.14 c | 40.53 c | |
| IR45765-3B | MBWI-N13 | 1.40 a | 5.16 ab | 12.34 ab | 15.17 a | 16.80 a | 47.01 a |
| WL-N13 | 1.35 a | 5.44 a | 13.01 a | 14.26 b | 15.96 b | 45.70 ab | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 1.19 b | 4.83 bc | 11.71 b | 14.44 b | 14.70 c | 45.02 b | |
| WL-N10.5 | 1.28 b | 4.77 bc | 12.24 ab | 13.79 c | 14.62 c | 42.38 c | |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 氮收获指数 NHI/% | 氮转运效率 NTE/% | 氮转运贡献率 NTCR/% | 氮素籽粒生产效率 NGPE/(g·g−1) | 氮肥偏生产力 NPFP/(g·g−1) |
| 中旱221 | MBWI-N13 | 66.71 a | 50.40 c | 70.11 c | 45.04 c | 38.38 c |
| Zhonghan 221 | WL-N13 | 63.90 b | 52.88 ab | 72.89 b | 44.32 d | 35.85 d |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 62.56 c | 51.88 bc | 71.47 b | 49.28 a | 45.32 a | |
| WL-N10.5 | 59.88 d | 55.06 a | 73.66 a | 47.92 b | 41.03 b | |
| 中浙优8号 | MBWI-N13 | 61.82 a | 65.67 bc | 68.73 d | 39.06 b | 46.66 c |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | WL-N13 | 60.23 b | 66.23 b | 73.25 c | 38.46 b | 42.20 d |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 60.18 b | 67.75 b | 74.54 b | 42.56 a | 51.73 a | |
| WL-N10.5 | 56.32 c | 69.67 a | 77.30 a | 39.52 b | 48.78 b | |
| IR45765-3B | MBWI-N13 | 66.17 a | 63.67 c | 68.46 c | 36.66 b | 44.73 b |
| WL-N13 | 63.40 b | 65.99 b | 69.16 bc | 34.09 c | 41.76 c | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 63.67 b | 64.98 b | 71.73 b | 37.44 a | 50.00 a | |
| WL-N10.5 | 60.85 c | 70.18 a | 75.18 a | 36.16 b | 44.94 b |
表3 不同氮肥和灌溉处理下水稻的氮素利用特征
Table 3. Nitrogen utilization characteristics of rice under different nitrogen fertilizer and irrigation treatments.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 氮收获指数 NHI/% | 氮转运效率 NTE/% | 氮转运贡献率 NTCR/% | 氮素籽粒生产效率 NGPE/(g·g−1) | 氮肥偏生产力 NPFP/(g·g−1) |
| 中旱221 | MBWI-N13 | 66.71 a | 50.40 c | 70.11 c | 45.04 c | 38.38 c |
| Zhonghan 221 | WL-N13 | 63.90 b | 52.88 ab | 72.89 b | 44.32 d | 35.85 d |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 62.56 c | 51.88 bc | 71.47 b | 49.28 a | 45.32 a | |
| WL-N10.5 | 59.88 d | 55.06 a | 73.66 a | 47.92 b | 41.03 b | |
| 中浙优8号 | MBWI-N13 | 61.82 a | 65.67 bc | 68.73 d | 39.06 b | 46.66 c |
| Zhongzheyou 8 | WL-N13 | 60.23 b | 66.23 b | 73.25 c | 38.46 b | 42.20 d |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 60.18 b | 67.75 b | 74.54 b | 42.56 a | 51.73 a | |
| WL-N10.5 | 56.32 c | 69.67 a | 77.30 a | 39.52 b | 48.78 b | |
| IR45765-3B | MBWI-N13 | 66.17 a | 63.67 c | 68.46 c | 36.66 b | 44.73 b |
| WL-N13 | 63.40 b | 65.99 b | 69.16 bc | 34.09 c | 41.76 c | |
| MBWI-N10.5 | 63.67 b | 64.98 b | 71.73 b | 37.44 a | 50.00 a | |
| WL-N10.5 | 60.85 c | 70.18 a | 75.18 a | 36.16 b | 44.94 b |
| [1] | 白志刚. 氮肥运筹对水稻氮代谢及稻田氮肥利用率的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2019. |
| Bai Z G. Effects of N management strategy on N metabolism in rice plant and N use efficiency in paddy soil[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 孙波, 陆雅海, 张旭东, 卢升高, 韦革宏, 杨劲松, 朱安宁, 刘满强, 段英华. 耕地地力对化肥养分利用的影响机制及其调控研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2017, 49(2): 209-216. |
| Sun B, Lu Y H, Zhang X D, Lu S G, Wei G H, Yang J S, Zhu A N, Liu M Q, Duan Y H. Research progress on impact mechanisms of cultivated land fertility on nutrient use of chemical fertilizers and their regulation[J]. Soils, 2017, 49(2): 209-216. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 于飞, 施卫明. 近10年中国大陆主要粮食作物氮肥利用率分析[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(6): 1311-1324. |
| Yu F, Shi W M. Analysis of nitrogen fertilizer utilization efficiency of major food crops in mainland China in the past 10 years[J]. Journal of Soil Sciences, 2015, 52(6): 1311-1324.. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Sutton M A, Bleeker A. The shape of nitrogen to come[J]. Nature (London), 2013, 494(7438): 435-437. |
| [5] | 肖娟, 严欢欢, 杨永清, 梁永书, 南文斌, 张汉马, 秦小健. 不同品种水稻苗期硝态氮吸收与利用效率差异的筛选及研究[J]. 植物生理学报, 2016, 52(12): 1941-1949. |
| Xiao J, Yan H H, Yang Y Q, Liang Y S, Nan W B, Zhang H M, Qin X J. Screening and research of different rice (Oryza sativa) varieties based on nitrate absorption and utilization in seedlings[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2016, 52(12): 1941-1949. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 刘红江, 郭智, 郑建初, 陈留根, 张岳芳, 童红玉. 太湖地区氮肥减量对水稻产量和氮素流失的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(3): 713-718. |
| Liu H J, Guo Z, Zheng J C, Chen L G, Zhang Y F, Tong H Y. Effects of nitrogen reduction on rice yield and nitrogen loss in Taihu Lake[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(3): 713-718. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 汪峰, 谌江华, 陈若霞, 史骏, 任少鹏, 金树权, 姚红燕, 朱德峰, 戴瑶璐. 减氮对甬优籼粳杂交稻产量和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(6): 984-992. |
| Wang F, Chen J H, Chen R X, Shi J, Ren S P, Jin S Q, Yao H Y, Zhu D F, Dai Y L. Effects of reduced nitrogen application on yield and nitrogen agronomic efficiency of Yongyou indica-japonica hybrid rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(6): 984-992. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 王伟妮, 鲁剑巍, 鲁明星, 李小坤, 李云春, 李慧. 湖北省早、中、晚稻施氮增产效应及氮肥利用率研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(3):545-553. |
| Wang W N, Lu J W, Lu M X, Li X K, Li Y C, Li H. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer application and nitrogen use efficiency of early, middle and late rice in Hubei Province[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(3): 545-553. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] |
Limami A M, Diab H, Lothier J. Nitrogen metabolism in plants under low oxygen stress[J]. Planta, 2014, 239(3): 531-541.
PMID |
| [10] | 郑小兰, 王瑞娇, 赵群法, 刘勇鹏, 王媛媛, 孙治强. 根际氧含量影响植物生长的生理生态机制研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(7): 805-814. |
| Zheng X L, Wang R J, Zhao Q F, Liu Y P, Wang Y Y, Sun Z Q. Ecophysiological mechanisms of plant growth under the influence of rhizosphere oxygen con-centration: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2017, 41(7): 805-814. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 周晚来, 易永健, 屠乃美, 谭志坚, 汪洪鹰, 杨媛茹, 王朝云, 易镇邪. 根际增氧对水稻根系形态和生理影响的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(3): 367-376. |
| Zhou W L, Yi Y J, Tu N M, Tan Z J, Wang H Y, Yang Y R, Wang C Y, Yi Z X. Research progress in the effects of rhizosphere oxygen-increasing on rice root morphology and physiology[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(3): 367-376. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 徐国伟, 王贺正, 翟志华, 孙梦, 李友军. 不同水氮耦合对水稻根系形态生理、产量与氮素利用的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(10): 132-141. |
| Xu G W, Wang H Z, Zhai Z H, Sun M, Li Y J. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling on root morphology and physiology, yield and nutrition utilization for rice[J]. Transactions of Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(10): 132-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Cao X C, Zhong C, Zhu C Q, Zhang J H, Zhu L F, Wu L H, Jin Q Y. Variability of leaf photosynthetic characteristics in rice and its relationship with resistance to water stress under different nitrogen nutrition regimes[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2019, 167(4): 613-627. |
| [14] | Zhong C, Bai Z G, Zhu L F, Zhang J H, Zhu C Q, Huang Jian-Liang,Jin Qian-Yu,Cao Xiao-Chuang. Nitrogen-mediated alleviation of photosynthetic inhibition under moderate water deficit stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2019, 157: 269-282. |
| [15] | 徐云姬, 许阳东, 李银银, 钱希旸, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 干湿交替灌溉对水稻花后同化物转运和籽粒灌浆的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(4): 554-568. |
| Xu Y J, Xu Y D, Li Y Y, Qian X Y, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Effects of alternating wetting and drying irrigation on post-anthesis remobilization of assimilates and grain filling of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(4): 554-568. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Liu L J, Chen T T, Wang Z Q, Zhang H, Yang J C, Zhang J H. Combination of site-specific nitrogen management and alternate wetting and drying irrigation increases grain yield and nitrogen and water use efficiency in super rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 154: 226-235. |
| [17] | 才硕. 微纳米气泡增氧灌溉技术在水稻灌区节水减排中的应用研究[J]. 节水灌溉, 2016(9): 117-120, 128. |
| Cai S. Application research of micro-nano bubble aerated irrigation technique in water conservation and wastewater discharge from rice irrigation area[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2016(9): 117-120, 128. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Sang H H, Jiao X Y, Wang S F, Guo W H, Mohamed Khaled Salahou, Kaihua Liu. Effects of micro-nano bubble aerated irrigation and nitrogen fertilizer level on tillering, nitrogen uptake and utilization of early rice[J]. Plant, Soil and Environment, 2018, 64(7): 297-302. |
| [19] | 胡继杰, 朱练峰, 胡志华, 钟楚, 林育炯, 张均华, 曹小闯, James A B, 禹盛苗, 金千瑜. 土壤增氧方式对其氮素转化和水稻氮素利用及产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(1): 167-174. |
| Hu J J, Zhu L F, Hu Z H, Zhong C, Lin Y J, Zhang J H, Cao X C, James A B, Yu S M, Jin Q Y. Effects of soil aeration methods on soil nitrogen transformation, rice nitrogen utilization and yield[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(1): 167-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 胡志华, 朱练峰, 林育炯, 张均华, 胡继杰, 禹盛苗, 曹小闯, 金千瑜. 根部增氧模式对水稻产量与氮素利用的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(6): 1503-1512. |
| Hu Z H, Zhu L F, Lin Y J, Zhang J H, Hu J J, Yu S M, Cao X C, Jin Q Y. Effect of root aeration methods on rice yield and nitrogen utilization[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2016, 22(6): 1503-1512. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 朱练峰, 刘学, 禹盛苗, 欧阳由男, 金千瑜. 增氧灌溉对水稻生理特性和后期衰老的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(3): 257-263. |
| Zhu L F, Liu X, Yu S M, Ouyang Y N, Jin Q Y. Effects of aerated irrigation on physiological characteristics and senescence at late growth stage of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2010, 24(3): 257-263. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. |
| Li H S. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological and Biochemical Experiments[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. |
| Lu R K. Methods for Soil Agrochemical Analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 徐国伟, 陆大克, 王贺正, 陈明灿, 李友军. 干湿交替灌溉与施氮量对水稻叶片光合性状的耦合效应[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(5): 1225-1237. |
| Xu G W, Lu D K, Wang H Z, Chen M C, Li Y J. Coupling effect of wetting and drying alternative irrigation and nitrogen application rate on photosynthetic characteristics of rice leaves[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(5): 1225-1237. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 胡继杰, 朱练峰, 钟楚, 林育炯, 张均华, 曹小闯, 禹盛苗, Allen Bohr JAMES, 金千瑜. 增氧模式对水稻光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(03):278-287. |
| Hu J J, Zhu L F, Zhong C, Zhang J H, Cao X C, Yu S M, James Allen Bohr, Jin Q Y. Effects of dissolved oxygen on nitrogen transformation in paddy soil and nitrogen metabolism of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 36(7): 2019-2028. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 从夕汉, 施伏芝, 阮新民, 罗玉祥, 马廷臣, 罗志祥. 氮肥水平对不同基因型水稻氮素利用率、产量和品质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(4): 1219-1226. |
| Cong X H, Shi F Z, Ruan X M, Luo Y X, Ma T C, Luo Z X. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application rate on nitrogen use efficiency and grain yield and quality of different rice varieties[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(4): 1219-1226. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 李思平, 曾路生, 吴立鹏, 张玉晓, 解军蕊, 丁效东. 氮肥水平与栽植密度对植稻土壤养分含量变化与氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 69-79. |
| Li S P, Zeng L S, Wu L P, Zhang Y X, Xie J R, Ding X D. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer level and planting density on changes in soil nutrient contents and nitrogen use efficiency in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(1): 69 -79. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 赵锋, 张卫建, 章秀福, 王丹英, 徐春梅. 稻田增氧模式对水稻籽粒灌浆的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(6): 605-612. |
| Zhao F, Zhang W J, Zhang X F, Wang D Y, Xu C M. Effects of oxygen-increasing patterns in paddy fields on rice rice grain-filling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(6): 605-612. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 曹小闯, 吴龙龙, 朱春权, 朱练峰, 孔亚丽, 陆若辉, 孔海民, 胡兆平, 戴锋, 张均华, 金千瑜. 不同灌溉和施肥模式对水稻产量、氮利用和稻田氮转化特征的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(7): 1482-1498. |
| Cao X C, Wu L L, Zhu C Q, Zhu L F, Kong Y L, Lu R H, Kong H M, Hu Z P, Dai F, Zhang J H, Jin Q Y. Effects of different irrigation and nitrogen application regimes on the yield, nitrogen utilization of rice and nitrogen transformation in paddy Soil[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(7): 1482-1498. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 段里成, 吕伟生, 方加海, 曾勇军, 石庆华, 潘晓华, 蔡海生, 吴自明. 施氮量和每穴苗数对双季杂交早稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(10): 2959-2967. |
| Duan L C, Lv W S, Fang J H, Zeng Y J, Shi Q H, Pan X H, Cai H S, Wu Z M. Effects of nitrogen application rate and seedlings per hole on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of double-season early hybrid rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(10): 2959-2967. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 杨丞, 汪洋, 张万洋, 叶廷红, 鲁剑巍, 张赓, 李小坤. 灌溉模式与施氮量互作对水稻茎蘖产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 155-165. |
| Yang C, Wang Y, Zhang W Y, Ye T H, Lu J W, Zhang G, Li X K. Effects of interaction between irrigation mode and nitrogen application rate on the yield formation of main stem and tillers of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(2): 155-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 江孟孟, 赵喜辉, 谢小文, 陆大克, 徐国伟. 氮肥形态与干湿交替灌溉下水稻土壤酶及养分差异[J]. 植物生理学报, 2021, 57(5): 1123-1134. |
| Jiang M M, Zhao X H, Xie X W, Lu D K, Xu G W. Difference of soil enzyme activity and soil nutrient content of rice under alternative wetting and drying irrigation and nitrogen form interaction[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2021, 57(5): 1123-1134. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 张自常, 李鸿伟, 曹转勤, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 施氮量和灌溉方式的交互作用对水稻产量和品质影响[J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(1): 84-92. |
| Zhang Z C, Li H W, Cao Z Q, Wang Z Q, Yang J C. Effect of interaction between nitrogen rate and irrigation regime on grain yield and quality of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(1): 84-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 张鸿, 朱从桦, 李其勇, 李星月, 郭展, 郑家国, 李旭毅. 灌溉方式和施氮量对直播稻氮素和水分利用的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(12): 1802-1814. |
| Zhang H, Zhu C H, Li Q Y, Li X Y, Guo Z, Zheng J G, Li X Y,. Effect of irrigation management and nitrogen rate on nitrogen and water utilization of direct-seeded rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(12): 1802-1814. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 张露, 陈书融, 吴龙龙, 等. 减施氮肥和增氧灌溉对水稻氮代谢关键酶活性及氮素利用的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(9): 81-90. |
| Zhang L, Chen S R, Wu L L, Huang J, Tian C, Zhang J H, Cao X C, Zhu C Q, Kong Y L, Jin Q Y, Zhu L F. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer reduction and oxygen-enhancing irrigation on the key enzyme activities of nitrogen metabolism and nitrogen utilization in rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(9): 81-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 张绍文, 何巧林, 王海月, 蒋明金, 李应洪, 严奉君, 杨志远, 孙永健, 郭翔, 马均. 控制灌溉条件下施氮量对杂交籼稻F优498氮素利用效率及产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(1): 82-94. |
| Zhang S W, He Q L, Wang H Y, Jiang M J, Li Y H, Yan F J, Yang Z Y, Sun Y J, Guo X, Ma J. Effects of nitrogen application rates on nitrogen use efficiency and grain yield of indica hybrid rice F You 498 under controlled intermittent irrigation[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2018, 24(1): 82-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 王肖娟, 陈林, 王永强, 李丽, 朱江艳, 赵双玲, 刘小武, 李高华. 不同灌溉方式及施氮量对水稻生长和氮素利用效率的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2017, 23(3): 88-91. |
| Wang X J, Chen L, Wang Y Q, Li L, Zhu J Y, Zhao S L, Liu X W, Li G H. Effects of irrigation methods and different N application rate on rice growth and nitrogen use efficiency of rice[J]. China Rice, 2017, 23(3): 88-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 马军, 徐田, 叶迎, 赵考诚, 林奕呈, 沙琳贤, 朱涛, 庄恒扬. 土壤类型与施氮水平耦合对水稻产量及氮素利用率的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(6): 1677-1686. |
| Ma J, Xu T, Ye Y, Zhao K C, Lin Y C, Sha L X, Zhu T. Effects of coupling of soil type and nitrogen application level on rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(6): 1677-1686. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 汪邑晨, 朱本顺, 周磊, 朱骏, 杨仲南. 光/温敏核不育系的不育机理及两系杂交稻的发展与展望 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 463-474. |
| [2] | 许用强, 徐军, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 王丹英, 曾宇翔, 符冠富. 水稻花粉管生长及其对非生物逆境胁迫的响应机理研究进展 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 495-506. |
| [3] | 何勇, 刘耀威, 熊翔, 祝丹晨, 王爱群, 马拉娜, 王廷宝, 张健, 李建雄, 田志宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑OsOFP30基因创制水稻粒型突变体 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [4] | 吕阳, 刘聪聪, 杨龙波, 曹兴岚, 王月影, 童毅, Mohamed Hazman, 钱前, 商连光, 郭龙彪. 全基因组关联分析(GWAS)鉴定水稻氮素利用效率候选基因 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 516-524. |
| [5] | 杨好, 黄衍焱, 王剑, 易春霖, 石军, 谭楮湉, 任文芮, 王文明. 水稻中八个稻瘟病抗性基因特异分子标记的开发及应用 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 525-534. |
| [6] | 蒋鹏, 张林, 周兴兵, 郭晓艺, 朱永川, 刘茂, 郭长春, 熊洪, 徐富贤. 冬水田轻简化栽培杂交稻蓄留再生稻产量形成特点 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| [7] | 杨铭榆, 陈志诚, 潘美清, 张汴泓, 潘睿欣, 尤林东, 陈晓艳, 唐莉娜, 黄锦文. 烟-稻轮作下减氮配施生物炭对水稻茎鞘同化物转运和产量 形成的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 555-566. |
| [8] | 熊家欢, 张义凯, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 王亚梁, 王志刚, 姚坚, 张玉屏. 覆膜稻田施用炭基肥对水稻产量及氮素利用的影响 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 567-576. |
| [9] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [10] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [11] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [12] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [13] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [14] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [15] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||