
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 66-77.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220402
杨陶陶1, 邹积祥1, 伍龙梅1, 包晓哲1, 江瑜2, 张楠2, 张彬1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-06
修回日期:2022-06-17
出版日期:2023-01-10
发布日期:2023-01-10
通讯作者:
张彬
基金资助:
YANG Taotao1, ZOU Jixiang1, WU Longmei1, BAO Xiaozhe1, JIANG Yu2, ZHANG Nan2, ZHANG Bin1( )
)
Received:2022-04-06
Revised:2022-06-17
Online:2023-01-10
Published:2023-01-10
Contact:
ZHANG Bin
摘要: 目的 华南双季稻区是我国优质籼稻的主产区之一,研究气候变暖对华南双季稻稻米品质的影响具有重要意义。方法 采用稻田开放式主动增温系统对早稻(合丰丝苗,2020年;粤禾丝苗,2021年)和晚稻(粤禾丝苗,2020和2021年)进行全生育期昼夜不间断增温处理,分析增温对早、晚稻加工、外观、营养和食味品质的影响。结果 与不增温处理相比,增温(早稻,1.5~1.8 ℃;晚稻1.9~2.0 ℃)对早、晚稻糙米率均无显著影响。增温条件下,早稻精米率和整精米率均显著降低,而晚稻精米率和整精米率无显著变化。增温对垩白粒率和垩白度的影响在早、晚稻之间呈相反趋势;增温显著提高早稻垩白粒率和垩白度,而降低晚稻垩白粒率。增温条件下,早、晚稻直链淀粉含量均显著降低,而蛋白质含量呈升高趋势。此外,增温提高早、晚稻稻米峰值黏度和米饭黏性,降低其消减值及晚稻糊化温度和米饭硬度。相关分析表明,增温条件下,早、晚稻糊化特性和米饭质构的改变主要与直链淀粉含量的降低有关。结论 增温导致早稻加工和外观品质变差,而有利于改善其营养和食味品质。增温条件下,晚稻外观、营养和食味品质均有改善。
杨陶陶, 邹积祥, 伍龙梅, 包晓哲, 江瑜, 张楠, 张彬. 开放式增温对华南双季稻稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 66-77.
YANG Taotao, ZOU Jixiang, WU Longmei, BAO Xiaozhe, JIANG Yu, ZHANG Nan, ZHANG Bin. Effect of Free Air Temperature Increase on Grain Quality of Double-cropping Rice in South China[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 66-77.

图2 2020和2021年开放式增温条件下冠层日平均温度变化趋势 CK-不增温;W-全生育期增温。
Fig. 2. Trends of daily mean temperature in rice canopy under FATI conditions in 2020 and 2021. CK, Ambient temperature; W, Warming during the whole growth period.
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 移栽至成熟 Transplanting to maturity | 抽穗至成熟 Heading to maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗Hefengsimiao | 不增温CK | 29.3±0.1 | 31.1±0.2 |
| Early rice | 全生育期增温W | 30.8±0.1 | 32.4±0.3 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.7±0.1 | 28.8±0.2 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 29.5±0.4 | 31.0±0.3 | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.6±0.1 | 24.4±0.1 |
| Late rice | 全生育期增温W | 29.5±0.5 | 25.9±0.2 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.2±0.1 | 24.0±0.3 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 29.2±0.1 | 25.3±0.2 |
表1 开放式增温对早、晚稻冠层平均温度的影响
Table 1. Effect of FATI on average temperature of early and late rice canopy. ℃
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 移栽至成熟 Transplanting to maturity | 抽穗至成熟 Heading to maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗Hefengsimiao | 不增温CK | 29.3±0.1 | 31.1±0.2 |
| Early rice | 全生育期增温W | 30.8±0.1 | 32.4±0.3 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.7±0.1 | 28.8±0.2 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 29.5±0.4 | 31.0±0.3 | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.6±0.1 | 24.4±0.1 |
| Late rice | 全生育期增温W | 29.5±0.5 | 25.9±0.2 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.2±0.1 | 24.0±0.3 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 29.2±0.1 | 25.3±0.2 |
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 播种期 Sowing | 移栽期 Transplanting | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗Hefengsimiao | 不增温CK | 03-16 | 04-09 | 06-14 | 07-12 |
| Early rice | 全生育期增温W | 03-16 | 04-09 | 06-12 | 07-09 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 03-16 | 04-06 | 05-29 | 06-29 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 03-16 | 04-06 | 05-28 | 06-27 | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 07-21 | 08-05 | 10-03 | 11-10 |
| Late rice | 全生育期增温W | 07-21 | 08-05 | 10-06 | 11-12 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 07-19 | 08-05 | 09-29 | 11-07 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 07-19 | 08-05 | 10-01 | 11-09 |
表2 开放式增温对早、晚稻生育期的影响
Table 2. Effects of FATI on phenophase of early and late rice
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 播种期 Sowing | 移栽期 Transplanting | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗Hefengsimiao | 不增温CK | 03-16 | 04-09 | 06-14 | 07-12 |
| Early rice | 全生育期增温W | 03-16 | 04-09 | 06-12 | 07-09 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 03-16 | 04-06 | 05-29 | 06-29 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 03-16 | 04-06 | 05-28 | 06-27 | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 07-21 | 08-05 | 10-03 | 11-10 |
| Late rice | 全生育期增温W | 07-21 | 08-05 | 10-06 | 11-12 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 07-19 | 08-05 | 09-29 | 11-07 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 07-19 | 08-05 | 10-01 | 11-09 |
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 加工品质Milling quality/% | 外观品质Appearance quality/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糙米率 Brown rice rate | 精米率 Milled rice rate | 整精米率 Head rice rate | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate | 垩白度 Chalkiness | |||||
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗 | 不增温CK | 79.4 ab | 71.1 a | 50.4 c | 37.1 b | 14.1 b | |
| Early rice | Hefengsimiao | 全生育期增温W | 79.8 ab | 69.3 ab | 45.1 d | 50.5 a | 21.8 a | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 80.9 a | 69.0 b | 65.6 a | 6.7 d | 6.1 d | ||
| Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 78.8 b | 67.1 c | 61.4 b | 12.7 c | 11.6 c | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 81.3 b | 72.5 a | 66.7 a | 1.8 c | 0.5 b | |
| Late rice | Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 82.0 ab | 72.9 a | 67.3 a | 1.9 c | 0.4 b | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 81.9 ab | 72.8 a | 65.7 a | 7.0 a | 2.1 a | ||
| Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 82.2 a | 73.1 a | 66.0 a | 5.7 b | 1.9 a | |||
| 方差分析 | 早稻Early rice | 年份Year(Y) | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| ANOVA | 温度Temperature (T) | ns | * | ** | ** | ** | |||
| Y*T | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||
| 晚稻Late rice | 年份Year (Y) | ns | ns | ns | ** | * | |||
| 温度Temperature (T) | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||
| YsT | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||
表3 开放式增温对早、晚稻加工和外观品质的影响
Table 3. Effects of FATI on grain milling and appearance qualities of early and late rice.
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 加工品质Milling quality/% | 外观品质Appearance quality/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糙米率 Brown rice rate | 精米率 Milled rice rate | 整精米率 Head rice rate | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate | 垩白度 Chalkiness | |||||
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗 | 不增温CK | 79.4 ab | 71.1 a | 50.4 c | 37.1 b | 14.1 b | |
| Early rice | Hefengsimiao | 全生育期增温W | 79.8 ab | 69.3 ab | 45.1 d | 50.5 a | 21.8 a | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 80.9 a | 69.0 b | 65.6 a | 6.7 d | 6.1 d | ||
| Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 78.8 b | 67.1 c | 61.4 b | 12.7 c | 11.6 c | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 81.3 b | 72.5 a | 66.7 a | 1.8 c | 0.5 b | |
| Late rice | Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 82.0 ab | 72.9 a | 67.3 a | 1.9 c | 0.4 b | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 81.9 ab | 72.8 a | 65.7 a | 7.0 a | 2.1 a | ||
| Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 82.2 a | 73.1 a | 66.0 a | 5.7 b | 1.9 a | |||
| 方差分析 | 早稻Early rice | 年份Year(Y) | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| ANOVA | 温度Temperature (T) | ns | * | ** | ** | ** | |||
| Y*T | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||
| 晚稻Late rice | 年份Year (Y) | ns | ns | ns | ** | * | |||
| 温度Temperature (T) | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||
| YsT | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||

图3 精米率和整精米率与垩白粒率和垩白度之间的相关性 **表示P < 0.01显著水平 (n=24)。
Fig. 3. Correlations of milled rice rate and head rice rate with chalky grain rate and chalkiness. ** indicate significant correlation at P < 0.01 (n=24).
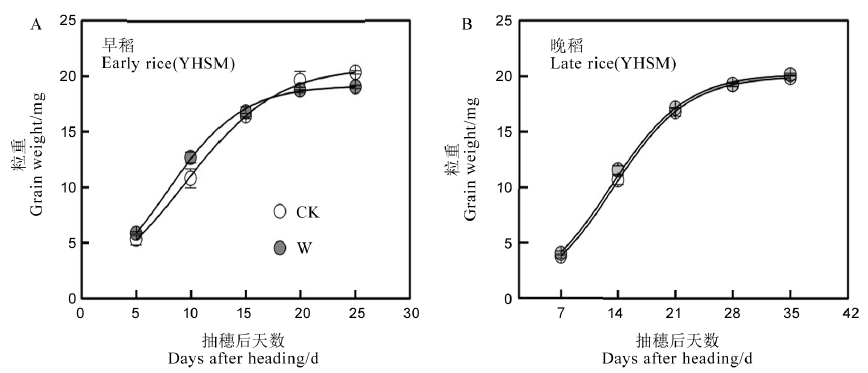
图4 开放式增温对早、晚稻籽粒灌浆过程的影响(2021年) CK-不增温;W-全生育期增温。YHSM-粤禾丝苗。
Fig. 4. Effects of FATI on grain-filling patterns of early and late rice in 2021. CK, Ambient temperature; W, Whole growth period warming. YHSM, Yuehesimiao.
| 季别 (品种) Season (Cultivar) | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | R2 | GR0 /(mg·grain−1d−1) | GRmax /(mg·grain−1d−1) | GRmean /(mg·grain−1d−1) | Tmax/d | D/d | K/mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 0.996 | 0.42 b | 1.26 b | 0.73 b | 9.7 a | 22.1 a | 21.12 a |
| Early rice (YHSM) | W | 0.999 | 0.48 a | 1.39 a | 0.81 a | 7.8 b | 18.0 b | 19.23 b |
| 晚稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 0.999 | 0.20 a | 1.11 a | 0.59 a | 13.5 a | 26.7 a | 19.99 a |
| Late rice (YHSM) | W | 0.998 | 0.22 a | 1.11 a | 0.59 a | 13.2 a | 26.6 a | 20.21 a |
表4 开放式增温对早、晚稻籽粒灌浆参数的影响(2021年)
Table 5. Effects of FATI on grain-filling parameters of early and late rice in 2021.
| 季别 (品种) Season (Cultivar) | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | R2 | GR0 /(mg·grain−1d−1) | GRmax /(mg·grain−1d−1) | GRmean /(mg·grain−1d−1) | Tmax/d | D/d | K/mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 0.996 | 0.42 b | 1.26 b | 0.73 b | 9.7 a | 22.1 a | 21.12 a |
| Early rice (YHSM) | W | 0.999 | 0.48 a | 1.39 a | 0.81 a | 7.8 b | 18.0 b | 19.23 b |
| 晚稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 0.999 | 0.20 a | 1.11 a | 0.59 a | 13.5 a | 26.7 a | 19.99 a |
| Late rice (YHSM) | W | 0.998 | 0.22 a | 1.11 a | 0.59 a | 13.2 a | 26.6 a | 20.21 a |
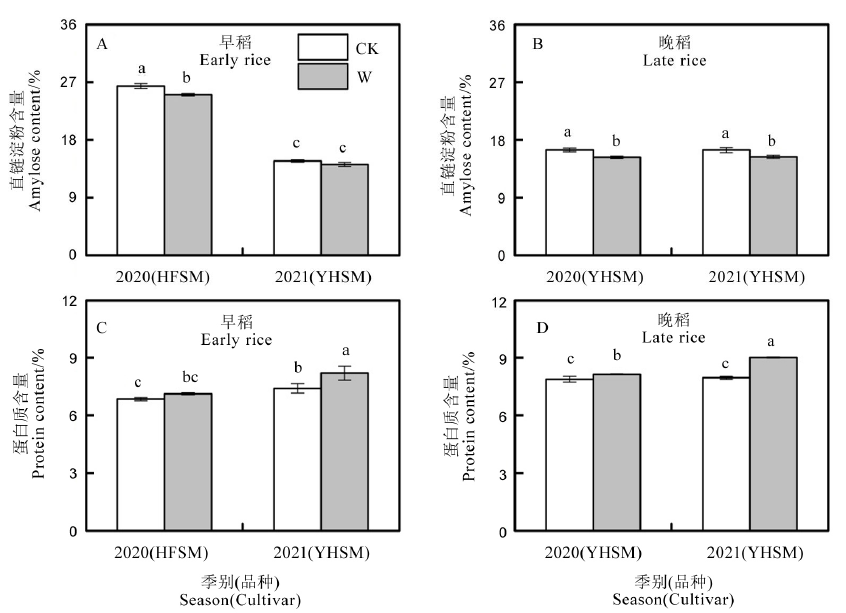
图5 开放式增温对早、晚稻直链淀粉和蛋白质含量的影响 CK-不增温;W-全生育期增温。HFSM-合丰丝苗;YHSM-粤禾丝苗。不同小写字母表示同一季节内差异显著(P < 0.05,LSD检验,n=3)。
Fig. 5. Effects of FATI on amylose and protein contents of early and late rice. CK, Ambient temperature; W, Whole growth period warming. HFSM, Hefengsimiao; YHSM, Yuehesimiao. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference in the same season (P < 0.05, LSD test, n=3).
| 季别 (品种) Season (Cultivar) | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 糊化特性Pasting property | 米饭质构Cooked rice texture | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity /cP | 崩解值 Breakdown /cP | 消减值 Setback /cP | 糊化温度 Pasting temperature/℃ | 硬度 Hardness /g | 黏度 Stickiness /(g·s) | |||
| 早稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 3405.0 b | 1240.3 a | −225.7 a | 78.0 a | 1403.4 a | 288.8 b | |
| Early rice (YHSM) | W | 3573.7 a | 1268.3 a | −368.3 b | 77.9 a | 1359.3 a | 329.1 a | |
| 晚稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 3032.0 b | 1008.7 a | 85.7 a | 88.5 a | 2364.9 a | 267.7 b | |
| Late rice (YHSM) | W | 3117.0 a | 979.7 a | 22.7 b | 87.5 b | 2155.4 b | 319.7 a | |
表5 开放式增温对早、晚稻糊化特性和米饭质构的影响(2021 年)
Table 5. Effects of FATI on rice pasting property and cooked rice texture of early and late rice in 2021.
| 季别 (品种) Season (Cultivar) | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 糊化特性Pasting property | 米饭质构Cooked rice texture | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity /cP | 崩解值 Breakdown /cP | 消减值 Setback /cP | 糊化温度 Pasting temperature/℃ | 硬度 Hardness /g | 黏度 Stickiness /(g·s) | |||
| 早稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 3405.0 b | 1240.3 a | −225.7 a | 78.0 a | 1403.4 a | 288.8 b | |
| Early rice (YHSM) | W | 3573.7 a | 1268.3 a | −368.3 b | 77.9 a | 1359.3 a | 329.1 a | |
| 晚稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 3032.0 b | 1008.7 a | 85.7 a | 88.5 a | 2364.9 a | 267.7 b | |
| Late rice (YHSM) | W | 3117.0 a | 979.7 a | 22.7 b | 87.5 b | 2155.4 b | 319.7 a | |
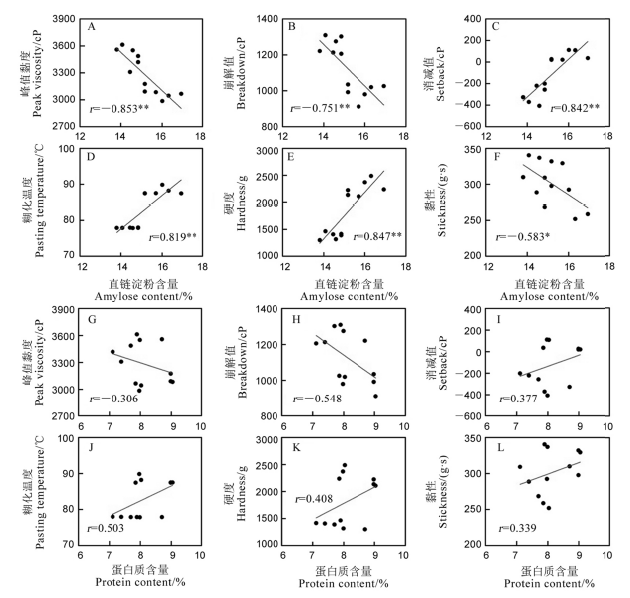
图6 稻米糊化特性和米饭质构与直链淀粉和蛋白质含量之间的相关性(2021年) *和**分别表示P < 0.05和P < 0.01显著水平 (n=12)。
Fig. 6. Correlations of rice pasting property and cooked rice texture with amylose and protein content(2021). * and ** indicate significant correlation at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively (n=12).
| [1] | IPCC. Summary for policymakers. In: Climate Change 2021:The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021: 14. |
| [2] | 秦大河. 气候变化与干旱[J]. 科技导报, 2009, 27(11): 3-9. |
| Qin D H.Climate change and drought[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2009, 27(11): 3-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 国家统计局农村社会经济调查司. 中国农村统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020: 113-139. |
| Department of Rural Socio-Economic Survey, National Bureau of Statistics. China rural statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2020: 113-139. | |
| [4] | Liu Y J, Tang L, Qiu X L, Liu B, Chang X N, Liu L L, Zhang X H, Cao W X, Zhu Y. Impacts of 1.5 and 2.0 °C global warming on rice production across China[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2020, 284: 107900. |
| [5] | Zhou Y J, Xu L, Xu Y Z, Xi M, Tu D B, Chen J H, Wu W G. A meta‐analysis of the effects of global warming on rice and wheat yields in a rice-wheat rotation system[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2021, 10(4): e316. |
| [6] | Chen C Q, van Groenigen K J, Yang H Y, Hungate B A, Yang B, Tian Y L, Chen J, Dong W J, Huang S, Deng A X, Jiang Y, Zhang W J. Global warming and shifts in cropping systems together reduce China's rice production[J]. Global Food Security, 2020, 24: 100359. |
| [7] | 凌霄霞, 张作林, 翟景秋, 叶树春, 黄见良. 气候变化对中国水稻生产的影响研究进展[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(3): 323-334. |
| Ling X X, Zhang Z L, Zhai J Q, Ye S C, Huang J L. A review for impacts of climate change on rice production in China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(3): 323-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Chen Y, Wang M, Ouwerkerk P B F. Molecular and environmental factors determining grain quality in rice[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2012, 1(2): 111-132. |
| [9] |
Chun A, Lee H J, Hamaker B R, Janaswamy S. Effects of ripening temperature on starch structure and gelatinization, pasting, and cooking properties in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2015, 63(12): 3085-3093.
PMID |
| [10] | Tsukaguchi T, Iida Y. Effects of assimilate supply and high temperature during grain-filling period on the occurrence of various types of chalky kernels in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Production Science, 2008, 11(2): 203-210. |
| [11] |
Ahmed N, Tetlow I J, Nawaz S, Iqbal A, Mubin M, Rehman M S N, Butt A, Lightfoot D A, Maekawa M. Effect of high temperature on grain filling period, yield, amylose content and activity of starch biosynthesis enzymes in endosperm of basmati rice[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2015, 95(11): 2237-2243.
PMID |
| [12] |
Shi W J, Muthurajan R, Rahman H, Selvam J, Peng S B, Zou Y B, Jagadish K S V. Source-sink dynamics and proteomic reprogramming under elevated night temperature and their impact on rice yield and grain quality[J]. New Phytologist, 2013, 197(3): 825-837.
PMID |
| [13] |
Rehmani M I A, Zhang J Q, Li G H, Ata-Ul-Karim S T, Wang S H, Kimball B A, Yan C, Liu Z H, Ding Y F. Simulation of future global warming scenarios in rice paddies with an open-field warming facility[J]. Plant Methods, 2011, 7: 41.
PMID |
| [14] | 阮俊梅, 张俊, 刘猷红, 董文军, 孟英, 邓艾兴, 杨万深, 宋振伟, 张卫建. 田间开放式增温对东北水稻氮素利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(1): 193-202. |
| Ruan J M, Zhang J, Liu Y H, Dong W J, Meng Y, Deng A X, Yang W S, Song Z W, Zhang W J. Effects of free air temperature increase on nitrogen utilization of rice in northeastern China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinia, 2022, 48(1): 193-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Tang S, Chen W Z, Liu W Z, Zhou Q Y, Zhang H X, Wang S H, Ding Y F. Open-field warming regulates the morphological structure, protein synthesis of grain and affects the appearance quality of rice[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2018, 84: 20-29. |
| [16] | Yang T T, Yang H F, Zhang B, Wu L M, Huang Q, Zou J X, Jiang Y, Zhang N. Effects of warming on starch structure, rice flour pasting property, and cooked rice texture in a double rice cropping system[J]. Cereal Chemistry, 2022, 99(3): 680-691. |
| [17] | 邓艾兴, 刘猷红, 孟英, 陈长青, 董文军, 李歌星, 张俊, 张卫建. 田间增温 1.5 °C对高纬度粳稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(1): 51-60. |
| Deng A X, Liu Y H, Meng Y, Chen C Q, Dong W J, Li G X, Zhang J, Zhang W J. Effects of 1.5 °C field warming on rice yield and quality in high latitude planting area[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(1): 51-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Rehmani M I A, Wei G B, Hussain N, Ding C Q, Li G H, Liu Z H, Wang S H, Ding Y F. Yield and quality responses of two indica rice hybrids to post-anthesis asymmetric day and night open-field warming in lower reaches of Yangtze River delta[J]. Field Crops Research, 2014, 156: 231-241. |
| [19] | Dou Z, Tang S, Li G H, Liu Z H, Ding C Q, Chen L, Wang S H, Ding Y F. Application of nitrogen fertilizer at heading stage improves rice quality under elevated temperature during grain-filling stage[J]. Crop Science, 2017, 57(4): 2183-2192. |
| [20] | Dou Z, Tang S, Chen W Z, Zhang H X, Li G H, Liu Z H, Ding C Q, Chen L, Wang S H, Zhang H C, Ding Y F. Effects of open-field warming during grain-filling stage on grain quality of two japonica rice cultivars in lower reaches of Yangtze River delta[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2018, 81: 118-126. |
| [21] |
Tang S, Zhang H X, Liu W Z, Dou Z, Zhou Q Y, Chen W Z, Wang S H, Ding Y F. Nitrogen fertilizer at heading stage effectively compensates for the deterioration of rice quality by affecting the starch-related properties under elevated temperatures[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 277: 455-462.
PMID |
| [22] | 杨陶陶, 胡启星, 黄山, 曾研华, 谭雪明, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 张俊. 双季优质稻产量和品质形成对开放式主动增温的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 572-580. |
| Yang T T, Hu Q X, Huang S, Zeng Y H, Tan X M, Zeng Y J, Pan X H, Shi Q H, Zhang J. Response of yield and quality of double-cropping high quality rice cultivars under free-air temperature increasing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(6): 572-580. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 杨陶陶, 孙艳妮, 曾研华, 黄山, 张俊, 谭雪明, 曾勇军, 潘晓华. 花后增温对双季优质稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2019, 33(3): 583-591. |
| Yang T T, Sun Y N, Zeng Y H, Huang S, Zhang J, Tan X M, Zeng Y J, Pan X H. Effect of post-anthesis warming on the grain yield and quality of double-cropped high-quality rice cultivars[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 33(3): 583-591. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Chen H, Chen D, He L H, Wang T, Lu H, Yang F, Deng F, Chen Y, Tao Y F, Li M, Li G Y, Ren W J. Correlation of taste values with chemical compositions and Rapid Visco Analyser profiles of 36 indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties[J]. Food Chemistry, 2021, 349: 129176. |
| [25] |
Li H Y, Gilbert R G. Starch molecular structure: The basis for an improved understanding of cooked rice texture[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 195: 9-17.
PMID |
| [26] | Jing L Q, Wang J, Shen S B, Wang Y X, Zhu J G, Wang Y L, Yang L X. The impact of elevated CO2 and temperature on grain quality of rice grown under open-air field conditions[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2016, 96(11): 3658-3667. |
| [27] | Xiong D L, Ling X X, Huang J L, Peng S B. Meta-analysis and dose-response analysis of high temperature effects on rice yield and quality[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2017, 141: 1-9. |
| [28] | Lyman N B, Jagadish K S V, Nalley L L, Dixon B L, Siebenmorgen T. Neglecting rice milling yield and quality underestimates economic losses from high-temperature stress[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(8): e72157. |
| [29] | Wang X Q, Wang K L, Yin T Y, Zhao Y F, Liu W Z, Shen Y Y, Ding Y F, Tang S. Nitrogen fertilizer regulated grain storage protein synthesis and reduced chalkiness of rice under actual field warming[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 715436. |
| [30] |
Sanchez B, Rasmussen A, Porter J R. Temperatures and the growth and development of maize and rice: a review[J]. Global Change Biology, 2014, 20: 408-417.
PMID |
| [31] | Chen C, Huang J L, Zhu L Y, Shah F, Nie L X, Cui K H, Peng S B. Varietal difference in the response of rice chalkiness to temperature during ripening phase across different sowing dates[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 151: 85-91. |
| [32] | Dong W J, Chen J, Wang L L, Tian Y L, Zhang B, Lai Y C, Meng Y, Qian C R, Guo J. Impacts of nighttime post-anthesis warming on rice productivity and grain quality in East China[J]. The Crop Journal, 2014, 2(1): 63-69. |
| [33] |
Yamakawa H, Hakata M. Atlas of rice grain filling-related metabolism under high temperature: Joint analysis of metabolome and transcriptome demonstrated inhibition of starch accumulation and induction of amino acid accumulation[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2010, 51(5): 795-809.
PMID |
| [34] | Jing L Q, Chen C, Hu S W, Dong S P, Pan Y, Wang Y X, Lai S K, Wang Y L, Yang L X. Effects of elevated atmosphere CO2 and temperature on the morphology, structure and thermal properties of starch granules and their relationship to cooked rice quality[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2021, 112: 106360. |
| [35] | Huang L C, Tan H Y, Zhang C Q, Li Q F, Liu Q Q. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperms: An updated review over the last decade[J]. Plant Communications, 2021, 2(5): 100237. |
| [36] | Cao Z Z, Pan G, Wang F B, Wei K S, Li Z W, Shi C H, Geng W, Cheng F M. Effect of high temperature on the expressions of genes encoding starch synthesis enzymes in developing rice endosperms[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2015, 14(4): 642-659. |
| [37] | Zhong Y Y, Qu J G, Li Z H, Tian Y, Zhu F, Blennow A, Liu X X. Rice starch multi-level structure and functional relationships[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2022, 275: 118777. |
| [38] | Chung H J, Liu Q, Lee L, Wei D Z. Relationship between the structure, physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of rice starches with different amylose contents[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2011, 25(5): 968-975. |
| [39] | Li C, Luo J X, Zhang C Q, Yu W W. Causal relations among starch chain-length distributions, short-term retrogradation and cooked rice texture[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2020, 108: 106064. |
| [40] | Zhang C Q, Zhou L H, Zhu Z B, Lu H W, Zhou X H, Qian Y T, Li Q F, Lu Y, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Characterization of grain quality and starch fine structure of two japonica rice (Oryza Sativa) cultivars with good sensory properties at different temperatures during the filling stage[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2016, 64(20): 4048-4057. |
| [41] |
Li H Y, Prakash S, Nicholson T M, Fitzgerald M A, Gilbert R G. The importance of amylose and amylopectin fine structure for textural properties of cooked rice grains[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 196: 702-711.
PMID |
| [42] | Yang T T, Xiong R Y, Tan X M, Huang S, Pan X H, Guo L, Zeng Y J, Zhang J, Zeng Y H. The impacts of post-anthesis warming on grain yield and quality of double-cropping high-quality indica rice in Jiangxi Province, China[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2022, 139: 126551. |
| [1] | 唐志伟, 朱相成, 张俊, 邓艾兴, 张卫建. 水分调控下绿肥种植和石灰施用对双季稻稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 211-222. |
| [2] | 易晓璇, 刘玮琦, 曾盖, 罗丽华, 肖应辉. 灌浆期高温胁迫对早籼稻品质性状的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 72-80. |
| [3] | 吴玉红, 李艳华, 王吕, 秦宇航, 李杉杉, 郝兴顺, 张庆路, 崔月贞, 肖飞. 陕南稻区紫云英稻草联合还田配施减量氮肥协同提升水稻产量与稻米品质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 628-641. |
| [4] | 杨晓龙, 王彪, 汪本福, 张枝盛, 张作林, 杨蓝天, 程建平, 李阳. 不同水分管理方式对旱直播水稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 285-294. |
| [5] | 陈丽明, 杨陶陶, 熊若愚, 谭雪明, 黄山, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 张俊, 曾研华. 开放式主动增温对双季优质籼稻籽粒淀粉积累及其关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 166-177. |
| [6] | 景文疆, 顾汉柱, 张小祥, 吴昊, 张伟杨, 顾骏飞, 刘立军, 王志琴, 杨建昌, 张耗. 中籼水稻品种改良过程中米质和根系特征对灌溉方式的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 505-519. |
| [7] | 杨晨, 郑常, 袁珅, 徐乐, 彭少兵. 再生稻肥料管理对不同品种产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 65-76. |
| [8] | 闫浩亮, 王松, 王雪艳, 党程成, 周梦, 郝蓉蓉, 田小海. 不同水稻品种在高温逼熟下的表现及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 617-628. |
| [9] | 唐先干, 谢金水, 徐昌旭, 刘佳, 袁福生, 刘光荣, 李祖章. 红壤性稻田紫云英与化肥减施对早稻品质与养分吸收的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 466-474. |
| [10] | 王丰, 廖亦龙, 柳武革, 刘迪林, 曾学勤, 傅友强, 朱满山, 李金华, 付崇允, 马晓智, 霍兴. 籼型杂交稻恢复系动态株型与光能利用率评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 141-154. |
| [11] | 杨通, 吴俊男, 鲍婷, 李凤博, 冯金飞, 周锡跃, 方福平. 耕作方式对双季稻田土壤剖面CH4和N2O分布特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 78-88. |
| [12] | 王志东, 陈宜波, 龚蓉, 周少川, 王重荣, 李宏, 黄道强, 周德贵, 赵雷, 潘阳阳, 杨义强, 李晓芳. 优质籼稻剑叶SPAD值与稻米品质相关性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 89-97. |
| [13] | 文春燕, 熊运华, 姚晓云, 陈春莲, 胡标林, 黄永萍, 吴延寿. 氮肥施用对米粉专用稻产量、米质及加工特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 574-585. |
| [14] | 汪浩, 刘祥臣, 张强, 余贵龙, 张文地, 黄健, 朱安, 刘立军. 豫南地区头季和再生季水稻产量与品质差异分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 425-434. |
| [15] | 叶春, 李艳大, 曹中盛, 黄俊宝, 孙滨峰, 舒时富, 吴罗发. 不同育秧盘对机插双季稻株型与产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 435-442. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||