
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 78-88.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0509
杨通, 吴俊男, 鲍婷, 李凤博, 冯金飞, 周锡跃, 方福平*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-05-12
修回日期:2020-06-08
出版日期:2021-01-10
发布日期:2021-01-10
通讯作者:
方福平
基金资助:
Tong YANG, Junnan WU, Ting BAO, Fengbo LI, Jinfei FENG, Xiyue ZHOU, Fuping FANG*( )
)
Received:2020-05-12
Revised:2020-06-08
Online:2021-01-10
Published:2021-01-10
Contact:
Fuping FANG
摘要: 目的 探明双季稻稻田土壤剖面CH4和N2O的时空分布特征,有利于揭示农艺措施对稻田土壤温室气体产生和排放过程的作用机制。方法通过小区试验,研究了旋耕(RT)和免耕(NT)在不同培肥措施[不施肥(CK)、仅施化肥(F)、化肥+秸秆还田(FS)]下对双季稻主要生育期田面水和土壤剖面CH4和N2O分布特征的影响。结果 早晚稻季田面水CH4浓度显著低于土壤剖面CH4浓度;而田面水N2O浓度高于土壤剖面N2O浓度。土壤剖面CH4浓度随深度增加而下降;而N2O浓度在土壤剖面中无显著变化。耕作方式对土壤剖面CH4和N2O浓度存在显著效应。与NT相比,RT显著增加了土壤剖面CH4浓度,尤其是0-5 cm和5-10 cm土层;而在部分生育期显著降低土壤剖面N2O浓度。早晚稻季CH4净排放通量与上层土壤CH4浓度相关性高于下层土壤和田面水。表层土壤是影响早稻季N2O排放的主要因素,而中下层土壤是影响晚稻季N2O排放的主要因素。结论 双季稻田土壤剖面CH4和N2O具有明显的时空变化特征,而耕作方式对其浓度具有显著影响。
杨通, 吴俊男, 鲍婷, 李凤博, 冯金飞, 周锡跃, 方福平. 耕作方式对双季稻田土壤剖面CH4和N2O分布特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 78-88.
Tong YANG, Junnan WU, Ting BAO, Fengbo LI, Jinfei FENG, Xiyue ZHOU, Fuping FANG. Effects of Tillage Methods on Distribution Characteristics of CH4 and N2O in Soil Profile ofDouble-cropping PaddyField[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(1): 78-88.
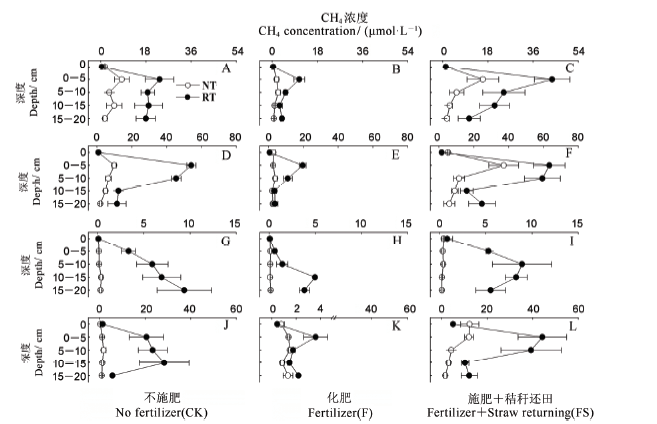
图1 早稻季各处理不同生育期土壤剖面CH4浓度. A、B和C一苗期; D、E和F一分蘖期: G、H和I-抽穗期: J、K和L-灌浆期。RT-旋耕: NT-免耕。纵坐标中0代表田面水层。
Fig.1. CH concentration in soil profile at different growth stages in the early rice growing season. A, B and C indicate seedling stage; D, E and F indicate fling stage; G, H and I indicate heading stage; J, K and L indicate flling stage. RT, Rotary tillage; NT, No tllge.0 represents surface water.
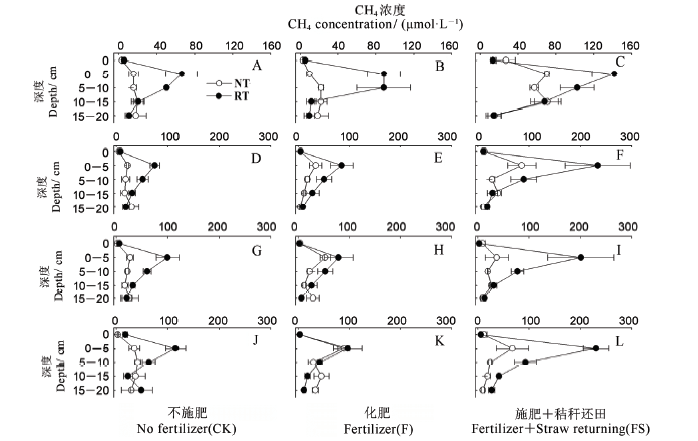
图2 晚稻季各处理不同生育期土壤剖面CH4含量 A、B和C—苗期;D、E和F—分蘖期;G、H和I—抽穗期;J、K和L—灌浆期。RT—旋耕;NT—免耕。纵坐标中0代表田面水层。
Fig. 2. CH4concentration in soil profile at different growth stages in the late rice growing season. A, B and C indicate seedling stage; D, E and F indicate filling stage; G, H and I indicate heading stage; J, K and L indicate filling stage. RT, Rotary tillage; NT, No tillage.0 represents surface water.
| 生长季Season | 影响因子Factor | 自由度df | 田面水 Surface water | 0-5cm土层 0-5 cm soil layer | 5-10cm土层 5-10 cm soil layer | 10-15cm土层10-15 cm soil layer | 15-20cm土层15-20 cm soil layer | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |||
| 早稻Early rice | T | 1 | 4 | >0.05 | 17.2 | <0.001 | 29.7 | <0.001 | 27.8 | <0.001 | 37.2 | <0.001 |
| F | 2 | 9 | <0.001 | 9.9 | <0.001 | 8.8 | <0.001 | 9.3 | <0.001 | 6.7 | <0.01 | |
| S | 3 | 16 | <0.001 | 36.7 | <0.001 | 20.1 | <0.001 | 2.3 | >0.05 | 4.9 | >0.05 | |
| T×F | 2 | 1.6 | >0.05 | 1.9 | >0.05 | 5.5 | <0.01 | 4.8 | <0.05 | 4.7 | <0.05 | |
| T×S | 3 | 2.9 | <0.05 | 7.7 | <0.001 | 9.4 | <0.001 | 1 | >0.05 | 1.2 | >0.05 | |
| F×S | 6 | 10.2 | <0.001 | 5.4 | <0.001 | 3 | <0.05 | 2 | >0.05 | 3 | >0.05 | |
| T×F×S | 6 | 3.2 | <0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | 1.8 | >0.05 | 1.6 | >0.05 | 1.5 | >0.05 | |
| 晚稻Late rice | T | 1 | 0.1 | >0.05 | 58.8 | <0.001 | 69.1 | <0.001 | 0.2 | >0.05 | 0.3 | >0.05 |
| F | 2 | 10.1 | <0.001 | 20.9 | <0.001 | 7.5 | <0.01 | 6.8 | <0.01 | 3.2 | <0.05 | |
| S | 3 | 3.4 | <0.05 | 2.5 | >0.05 | 1.7 | >0.05 | 2 | >0.05 | 2.1 | >0.05 | |
| T×F | 2 | 6.9 | <0.01 | 7.6 | <0.01 | 2.7 | >0.05 | 0.2 | >0.05 | 2.1 | >0.05 | |
| T×S | 3 | 0.9 | >0.05 | 0.2 | >0.05 | 0.4 | >0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | 0.6 | >0.05 | |
| F×S | 6 | 3.5 | <0.01 | 0.6 | >0.05 | 1.5 | >0.05 | 4.5 | <0.01 | 0.7 | >0.05 | |
| T×F×S | 6 | 1.1 | >0.05 | 1.1 | >0.05 | 0.9 | >0.05 | 1.9 | >0.05 | 0.9 | >0.05 | |
表1 早晚稻季田面水和土壤剖面CH4浓度的耕作方式(T)、培肥措施(F)和生育期(S)多因素方差分析
Table 1 Multivariate analysis of variance for tillage (T), fertilization (F) and growth stage (S) on CH4 concentration in the surface water and soil profile in the early and late rice growing seasons.
| 生长季Season | 影响因子Factor | 自由度df | 田面水 Surface water | 0-5cm土层 0-5 cm soil layer | 5-10cm土层 5-10 cm soil layer | 10-15cm土层10-15 cm soil layer | 15-20cm土层15-20 cm soil layer | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |||
| 早稻Early rice | T | 1 | 4 | >0.05 | 17.2 | <0.001 | 29.7 | <0.001 | 27.8 | <0.001 | 37.2 | <0.001 |
| F | 2 | 9 | <0.001 | 9.9 | <0.001 | 8.8 | <0.001 | 9.3 | <0.001 | 6.7 | <0.01 | |
| S | 3 | 16 | <0.001 | 36.7 | <0.001 | 20.1 | <0.001 | 2.3 | >0.05 | 4.9 | >0.05 | |
| T×F | 2 | 1.6 | >0.05 | 1.9 | >0.05 | 5.5 | <0.01 | 4.8 | <0.05 | 4.7 | <0.05 | |
| T×S | 3 | 2.9 | <0.05 | 7.7 | <0.001 | 9.4 | <0.001 | 1 | >0.05 | 1.2 | >0.05 | |
| F×S | 6 | 10.2 | <0.001 | 5.4 | <0.001 | 3 | <0.05 | 2 | >0.05 | 3 | >0.05 | |
| T×F×S | 6 | 3.2 | <0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | 1.8 | >0.05 | 1.6 | >0.05 | 1.5 | >0.05 | |
| 晚稻Late rice | T | 1 | 0.1 | >0.05 | 58.8 | <0.001 | 69.1 | <0.001 | 0.2 | >0.05 | 0.3 | >0.05 |
| F | 2 | 10.1 | <0.001 | 20.9 | <0.001 | 7.5 | <0.01 | 6.8 | <0.01 | 3.2 | <0.05 | |
| S | 3 | 3.4 | <0.05 | 2.5 | >0.05 | 1.7 | >0.05 | 2 | >0.05 | 2.1 | >0.05 | |
| T×F | 2 | 6.9 | <0.01 | 7.6 | <0.01 | 2.7 | >0.05 | 0.2 | >0.05 | 2.1 | >0.05 | |
| T×S | 3 | 0.9 | >0.05 | 0.2 | >0.05 | 0.4 | >0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | 0.6 | >0.05 | |
| F×S | 6 | 3.5 | <0.01 | 0.6 | >0.05 | 1.5 | >0.05 | 4.5 | <0.01 | 0.7 | >0.05 | |
| T×F×S | 6 | 1.1 | >0.05 | 1.1 | >0.05 | 0.9 | >0.05 | 1.9 | >0.05 | 0.9 | >0.05 | |
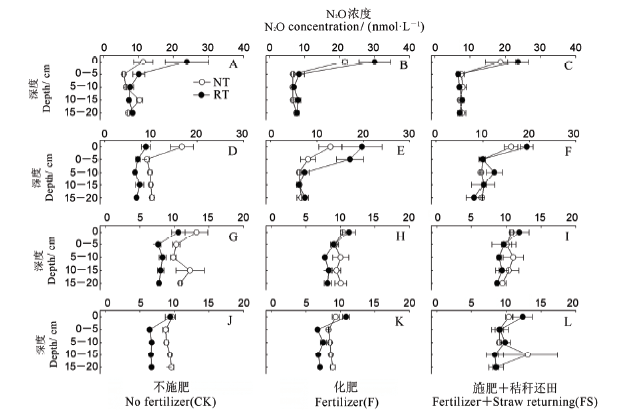
图3 早稻季各处理不同生育期土壤剖面N2O含量 A、B和C—苗期;D、E和F—分蘖期;G、H和I—抽穗期;J、K和L—灌浆期。RT—旋耕;NT—免耕。纵坐标中0代表田面水层。
Fig. 3. N2O concentration in soil profile at different growth stages in the early rice growing season. A, B and C indicate seedling stage; D, E and F indicate filling stage; G, H and I indicate heading stage; J, K and L indicate filling stage. RT, Rotary tillage; NT, No tillage.0 represents surface water.
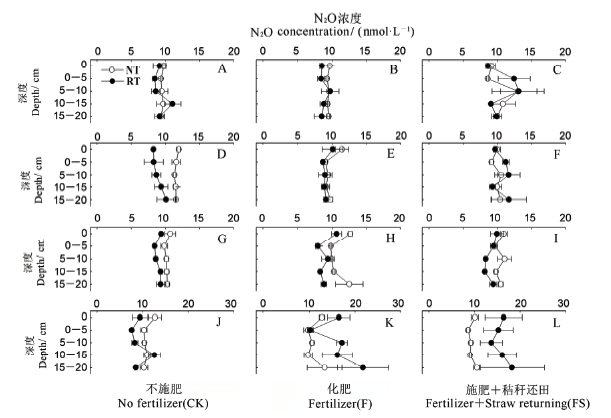
图4 晚稻季各处理不同生育期土壤剖面N2O含量 A、B和C—苗期;D、E和F—分蘖期;G、H和I—抽穗期;J、K和L—灌浆期。RT—旋耕;NT—免耕。纵坐标中0代表田面水层。
Fig. 4. N2O concentration in soil profile at different growth stages in the late rice growing season. A, B and C indicate seedling stage; D, E and F indicate filling stage; G, H and I indicate heading stage; J, K and L indicate filling stage. RT, Rotary tillage; NT, No tillage.0 represents surface water.
| 生长季Season | 影响因子Factor | 自由度df | 田面水 Surface water | 0-5cm土层 0-5cm soil layer | 5-10cm土层 5-10cm soil layer | 10-15cm土层10-15cm soil layer | 15-20cm土层15-20cm soil layer | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |||
| 早稻Early rice | T | 1 | 2.8 | >0.05 | 0.5 | >0.05 | 1.9 | >0.05 | 9.1 | <0.01 | 12.6 | <0.001 |
| F | 2 | 1.2 | >0.05 | 1 | >0.05 | 8 | <0.001 | 5.1 | <0.01 | 1.2 | >0.05 | |
| S | 3 | 26.5 | <0.001 | 8.5 | <0.001 | 10 | <0.001 | 2 | >0.05 | 5.6 | <0.05 | |
| T×F | 2 | 0.6 | >0.05 | 2.2 | >0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | 2.3 | >0.05 | 1.8 | >0.05 | |
| T×S | 3 | 4.3 | <0.01 | 4.9 | <0.01 | 3.2 | <0.05 | 1.6 | >0.05 | 3.4 | <0.05 | |
| F×S | 6 | 1.8 | >0.05 | 3.1 | <0.05 | 2.9 | <0.05 | 1.6 | >0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | |
| T×F×S | 6 | 1.8 | >0.05 | 5.4 | <0.001 | 3.6 | <0.01 | 0.6 | >0.05 | 2.6 | <0.05 | |
| 晚稻 Late rice | T | 1 | 0.5 | >0.05 | 0.3 | >0.05 | 0 | >0.05 | 0.7 | >0.05 | 0.3 | >0.05 |
| F | 2 | 1.5 | >0.05 | 4.7 | <0.05 | 3.1 | <0.05 | 0.3 | >0.05 | 1.2 | >0.05 | |
| S | 3 | 10.2 | <0.001 | 1.5 | >0.05 | 2.5 | >0.05 | 8.9 | <0.001 | 4.7 | <0.01 | |
| T×F | 2 | 2.4 | >0.05 | 12.7 | <0.001 | 2.5 | >0.05 | 0.2 | >0.05 | 0.7 | >0.05 | |
| T×S | 3 | 3.3 | <0.05 | 2.2 | >0.05 | 3.6 | <0.05 | 10 | <0.001 | 2.7 | >0.05 | |
| F×S | 6 | 1 | >0.05 | 1.3 | >0.05 | 2.9 | <0.05 | 0.6 | >0.05 | 2 | >0.05 | |
| T×F×S | 6 | 1.8 | >0.05 | 1.7 | >0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | 1 | >0.05 | |
表2 早晚稻季田面水和土壤剖面N2O浓度的耕作方式(T)、培肥措施(F)和生育期(S)多因素方差分析
Table 2 Multivariate analysis for tillage practice (T), fertilization method (F) and growth stage (S) on N2O concentration in the surface water and soil profile in the early and late rice growing seasons.
| 生长季Season | 影响因子Factor | 自由度df | 田面水 Surface water | 0-5cm土层 0-5cm soil layer | 5-10cm土层 5-10cm soil layer | 10-15cm土层10-15cm soil layer | 15-20cm土层15-20cm soil layer | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |||
| 早稻Early rice | T | 1 | 2.8 | >0.05 | 0.5 | >0.05 | 1.9 | >0.05 | 9.1 | <0.01 | 12.6 | <0.001 |
| F | 2 | 1.2 | >0.05 | 1 | >0.05 | 8 | <0.001 | 5.1 | <0.01 | 1.2 | >0.05 | |
| S | 3 | 26.5 | <0.001 | 8.5 | <0.001 | 10 | <0.001 | 2 | >0.05 | 5.6 | <0.05 | |
| T×F | 2 | 0.6 | >0.05 | 2.2 | >0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | 2.3 | >0.05 | 1.8 | >0.05 | |
| T×S | 3 | 4.3 | <0.01 | 4.9 | <0.01 | 3.2 | <0.05 | 1.6 | >0.05 | 3.4 | <0.05 | |
| F×S | 6 | 1.8 | >0.05 | 3.1 | <0.05 | 2.9 | <0.05 | 1.6 | >0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | |
| T×F×S | 6 | 1.8 | >0.05 | 5.4 | <0.001 | 3.6 | <0.01 | 0.6 | >0.05 | 2.6 | <0.05 | |
| 晚稻 Late rice | T | 1 | 0.5 | >0.05 | 0.3 | >0.05 | 0 | >0.05 | 0.7 | >0.05 | 0.3 | >0.05 |
| F | 2 | 1.5 | >0.05 | 4.7 | <0.05 | 3.1 | <0.05 | 0.3 | >0.05 | 1.2 | >0.05 | |
| S | 3 | 10.2 | <0.001 | 1.5 | >0.05 | 2.5 | >0.05 | 8.9 | <0.001 | 4.7 | <0.01 | |
| T×F | 2 | 2.4 | >0.05 | 12.7 | <0.001 | 2.5 | >0.05 | 0.2 | >0.05 | 0.7 | >0.05 | |
| T×S | 3 | 3.3 | <0.05 | 2.2 | >0.05 | 3.6 | <0.05 | 10 | <0.001 | 2.7 | >0.05 | |
| F×S | 6 | 1 | >0.05 | 1.3 | >0.05 | 2.9 | <0.05 | 0.6 | >0.05 | 2 | >0.05 | |
| T×F×S | 6 | 1.8 | >0.05 | 1.7 | >0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | 1.4 | >0.05 | 1 | >0.05 | |
| 土壤层次 Soil profile | 早稻Early rice season | 晚稻Late rice season | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | N2O | CH4 | N2O | ||
| 田面水 Surface water | 0.281* | -0.024 | 0.277* | 0.413** | |
| 0-5cm | 0.647** | 0.329** | 0.357** | 0.201 | |
| 5-10cm | 0.698** | 0.202 | 0.436** | 0.255* | |
| 10-15cm | 0.424** | 0.176 | 0.479** | 0.324** | |
| 15-20cm | 0.443** | 0.017 | -0.089 | 0.460** | |
表3 双季稻CH4和N2O净排放通量与田面水和土壤剖面浓度的相关性
Table 3 Correlation between the net flux rates of CH4 and N2O and the concentrations of CH4 and N2O in the surface water and soil profile of early and late rice.
| 土壤层次 Soil profile | 早稻Early rice season | 晚稻Late rice season | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | N2O | CH4 | N2O | ||
| 田面水 Surface water | 0.281* | -0.024 | 0.277* | 0.413** | |
| 0-5cm | 0.647** | 0.329** | 0.357** | 0.201 | |
| 5-10cm | 0.698** | 0.202 | 0.436** | 0.255* | |
| 10-15cm | 0.424** | 0.176 | 0.479** | 0.324** | |
| 15-20cm | 0.443** | 0.017 | -0.089 | 0.460** | |
| [1] | 李祎君, 王春乙, 赵蓓, 刘文军. 气候变化对中国农业气象灾害与病虫害的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2010, 26(S1): 263-271. |
| Li Y J, Wang C Y, Zhao B, Liu W J.Effects of climate change on agricultural meteorological disaster and crop insects diseases[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2010, 26(S1): 263-271. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 秦大河, 罗勇, 陈振林, 任贾文, 沈永平. 气候变化科学的最新进展:IPCC第四次评估综合报告解析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2007, 6: 311-314. |
| Qin D H, Luo Y, Chen Z L, Ren J W, Shen Y P.Latest advances in climate change sciences: Interpretation of the synthesis report of the IPCC fourth assessment report[J]. Climate Change Research, 2007, 6: 311-314.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 中华人民共和国国家统计局.主要农作物产品产量[DB].. National Bureau of Statistics. Main agricultural product output[DB]. . |
| [4] | FAO. Food and agriculture data[DB/OL]. . |
| [5] | 刘巧辉. 基于IPCC排放因子方法学的中国稻田和菜地氧化亚氮直接排放量估算[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2017. |
| Liu Q H.Statistic estimation of direct N2O emissions from paddy rice and vegetable fields in mainland China based on IPCC methodology[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Conrad R.Contribution of hydrogen to methane production and control of hydrogen concentrations in methanogenic soils and sediments[J]. FEMS (Federation of European Microbiological Societies) Microbiology-Ecology, 1999, 28(3): 193-202. |
| [7] | Anderson I C, Poth M A.Controls on fluxes of trace gases from Brazilian cerrado soils[J].Journal of Environmental Quality, 1998, 27(5): 1117-1124. |
| [8] | 薛建福, 濮超, 张冉, 赵鑫, 刘胜利, 陈阜, 张海林. 农作措施对中国稻田氧化亚氮排放影响的研究进展[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(11): 1-9. |
| Xue J F, Pu C, Zhang R, Zhao X, Liu S L, Chen F, Zhang H L.Review on management-induced nitrous oxide emissions from paddy ecosystems[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(11):1-9.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 江长胜, 王跃思, 郑循华, 王明星. 稻田甲烷排放影响因素及其研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 2004, 5: 663-669. |
| Jiang C S, Wang Y S, Zheng X H, Wang M X.Advances in the research on methane emission from paddy fields and its affecting factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2004, 5:663-669.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Yoh M, Toda H, Kanda K, Tsuruta H.Diffusion analysis of N2O cycling in a fertilized soil[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 1997, 49(1): 29-33. |
| [11] | Xu X, Wu Z, Dong Y B, Zhou Z Q, Xiong Z Q.Effects of nitrogen and biochar amendment on soil methane concentration profiles and diffusion in a rice-wheat annual rotation system[J/OL].Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 38688. |
| [12] | Yang B, Chen Z Z, Zhang M, Zhang H, Zhang X H, Pan G X, Zou J W, Xiong Z Q.Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration and temperature on the soil profile methane distribution and diffusion in rice-wheat rotation system[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 2015, 32(6): 62-71. |
| [13] | Zhou Z Q, Xu X, Bi Z C, Li L, Xiong Z Q.Soil concentration profiles and diffusion and emission of nitrous oxide influenced by the application of biochar in a rice-wheat annual rotation system[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(8): 7949-7961. |
| [14] | 刘平丽. 稻田土壤剖面CH4、N2O、CO2分布特征及周转规律研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011. |
| Liu P L.Distribution characteristics and turnover of soil profile methane, nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide in paddy fields[D].Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Li D M, Liu M Q, Cheng Y H, Wang D, Qin J T, Jiao J G, Li H J, Hu F.Methane emissions from double-rice cropping system under conventional and no tillage in southeast china[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 2011, 113(2): 77-81. |
| [16] | Zhang H L, Bai X L, Xue J F, Chen Z D, Tang H M, Chen F.Emissions of CH4 and N2O under different tillage systems from double-cropped paddy fields in southern China[J/OL].PloS ONE, 2013, 8(6):e65277. |
| [17] | 白小琳, 张海林, 陈阜, 孙国峰, 胡清, 李永. 耕作措施对双季稻田CH4与N2O排放的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2010, 26(1): 282-289. |
| Bai X L, Zhang H L, Chen F, Sun G P, Hu Q, Li Y.Tillage effects on CH4 and N2O emission from double cropping paddy field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2010, 26(1): 282-289.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 秦晓波, 李玉娥, 万运帆, 廖育林, 范美蓉, 高清竹, 刘硕, 马欣. 耕作方式和稻草还田对双季稻田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(11): 216-224. |
| Qin X B, Li Y E, Wan Y F, Liao Y L, Fan M R, Gao Q Z, Liu S, Ma X.Effect of tillage and rice residue return on CH4 and N2O emission from double rice field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(11): 216-224.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 伍芬琳, 张海林, 李琳, 陈阜, 黄凤球, 肖小平. 保护性耕作下双季稻农田甲烷排放特征及温室效应[J]. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(9): 2703-2709. |
| Wu F L, Zhang H L, Li L, Chen F, Huang F Q, Xiao X P.Characteristics of CH4 emission and greenhouse effects in double paddy soil with conservation tillage[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(9):2703-2709.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Bayer C, Costa F D S,Pedroso G M,Zschornack T,Camargo E S,Lima M A,Frigheto R T S,Gomes J,Marcolin E,Mussoi M V R. Yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions from flood irrigated rice under long-term conventional tillage and no-till systems in a humid subtropical climate[J]. Field Crop Research, 2014, 162: 60-69. |
| [21] | Krμger M, Frenzel P, Conrad R.Microbial processes influencing methane emission from rice fields[J]. Global Change Biology, 2001, 7(1): 49-63. |
| [22] | 周自强, 李露, 张恒, 熊正琴. 氮肥配施小麦秸秆生物炭对稻麦轮作土壤剖面CH4和N2O浓度的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2015, 38(3): 431-438. |
| Zhou Z Q, Li L, Zhang H, Xiong Z Q.Effects of wheat straw biochar and nitrogen amendment on methane and nitrous oxide distribution characteristics within soil profile in rice-wheat annual rotations[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015, 38(3): 431-438.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Schutz H, Seiler W, Conrad R, 杜道灯. 土壤温度对水稻田甲烷排放的影响[J]. 农业环境与发展, 1992(4): 19-22. |
| Schutz H, Seiler W, Conrad R, Du D D.Effects of soil temperature on methane emissions from rice paddies[J].Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 1992(4):19-22.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 丁维新, 蔡祖聪. 植物在CH4产生、氧化和排放中的作用[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 8: 1379-1384. |
| Ding W X, Cai Z C.Effect of plants on methane production, oxidation and emission[J]. ActaEcologicaSinica, 2003, 8:1379-1384.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Elberling B, Askaer L, Jørgensen C J, Joensen H P, Kühl M, Glud R N, Lauritsen F R.Linking soil O2, CO2, and CH4 concentrations in a wetland soil: Implications for CO2 and CH4 fluxes[J]. Environmental Science& Technology, 2011, 45(8): 3393-3399. |
| [26] | Holzapfel A, Conrad R, Seiler W.Effects of vegetation on the emission of methane from submerged paddy soil[J]. Plant Soil, 1986, 92(2):223-233. |
| [27] | Schutz H, Seiler W, Conrad R.Influence of soil temperature on methane emission from rice paddy fields[J]. Biogeochemistry, 1990, 11(2): 77-95. |
| [28] | Inubushi K, Umebayashi M, Wada H. Methane emission from paddy fields//Transaction of 14th International Congress of Soil Science[C]. Kyoto, Japan, 1990: 249-254. |
| [29] | Zhou M H, Wang X G, Wang Y Q, Zhu B.A three-year experiment of annual methane and nitrous oxide emissions from the subtropical permanently flooded rice paddy fields of China: Emission factor, temperature sensitivity and fertilizer nitrogen effect[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2018, 250: 299-307. |
| [30] | Yagi K, Minami K.Effect of organic matter application on methane emission from some Japanese paddy fields[J].Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 1990, 36(4): 599-610. |
| [31] | Watanabe A, Yoshida M, Kimura M.Contribution of rice straw carbon to CH4 emission from rice paddies using 13C-enriched rice straw[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1998, 103: 8237-8242. |
| [32] | Zhang L, Zheng J, Chen L, Shen M, Zhang X, Zhang M, Bian X, Zhang J, Zhang W.Integrative effects of soil tillage and straw management on crop yields and greenhouse gas emissions in a rice-wheat cropping system[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2015, 63: 47-54. |
| [33] | Li C, Zhang Z, Guo L, Cai M, Cao C.Emissions of CH4 and CO2 from double rice cropping systems under varying tillage and seeding methods[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 80: 438-444. |
| [34] | 刘平丽, 张啸林, 熊正琴, 黄太庆, 丁敏, 王金阳. 不同水旱轮作体系稻田土壤剖面N2O的分布特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(9): 2363-2369. |
| Liu P L, Zhang X L, Xiong Z Q, Huang T Q, Ding M, Wang J Y.Distribution characteristics of soil profile nitrous oxide concentration in paddy fields with different rice-upland crop rotation systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(9):2363-2369.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 姜珊珊, 庞炳坤, 张敬沙, 蒋静艳. 减氮及不同肥料配施对稻田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(5): 1741-1750. |
| Jiang S S, Pang B K, Zhang J S, Jiang J J.Effects of reduced nitrogen and combined application of different fertilizers on CH4 and N2O emissions in paddy fields[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(5):1741-1750.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Wu D M, Dong W X, Oenema O, Wang Y Y, Trebs I, Hu C S.N2O consumption by low-nitrogen soil and its regulation by water and oxygen[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2013, 60(1): 165-172. |
| [37] | Schlesinger W H.An estimate of the global sink for nitrous oxide in soils[J]. Global Change Biology, 2013, 19(10): 2929-2931. |
| [38] | 王玲, 李昆, 宋雅琦, 公勤, 李兆华. 浅表层水稻土N2O消耗能力及其与N2O还原微生物的耦合关系研究[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 20: 1-9. |
| Wang L, Li K, Song Y Q, Gong Q, Li Z H.The N2O consumption ability in the surface paddy soil layer and its coupling relationship to N2O reducing microorganisms[J]. ActaEcologicaSinica, 2019, 20:1-9.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | Six J, Feller C, Denef K, Ogle S M, Sa J, Albrecht A.Soil organic matter, biota and aggregation in temperate and tropical soils-effects of no-tillage[J]. Agronomie, 2002, 22: 755-775. |
| [40] | Liu X, Mosier A R, Halvorson A D, Zhang F S.The impact of nitrogen placement and tillage on NO, N2O, CH4 and CO2 fluxes from a clay loam soil[J]. Plant Soil, 2006, 280(1): 177-188. |
| [41] | Rochette P.No-till only increases N2O emissions in poorly-aerated soils[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 2008, 101(1): 97-100. |
| [1] | 唐志伟, 朱相成, 张俊, 邓艾兴, 张卫建. 水分调控下绿肥种植和石灰施用对双季稻稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 211-222. |
| [2] | 袁沛, 周旋, 杨威, 尹凌洁, 靳拓, 彭建伟, 荣湘民, 田昌. 化肥减氮配施对洞庭湖区双季稻产量和田面水氮磷流失风险的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 518-528. |
| [3] | 杨陶陶, 邹积祥, 伍龙梅, 包晓哲, 江瑜, 张楠, 张彬. 开放式增温对华南双季稻稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 66-77. |
| [4] | 曾文静, 邱岚英, 陈俊杰, 钱浩宇, 张楠, 丁艳锋, 江瑜. 秸秆还田下大气CO2浓度升高对水稻生长和CH4排放的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 543-550. |
| [5] | 王丰, 廖亦龙, 柳武革, 刘迪林, 曾学勤, 傅友强, 朱满山, 李金华, 付崇允, 马晓智, 霍兴. 籼型杂交稻恢复系动态株型与光能利用率评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 141-154. |
| [6] | 叶春, 李艳大, 曹中盛, 黄俊宝, 孙滨峰, 舒时富, 吴罗发. 不同育秧盘对机插双季稻株型与产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 435-442. |
| [7] | 钟雪梅, 黄铁平, 彭建伟, 卢文璐, 康兴蓉, 孙梦飞, 宋思明, 唐启源, 陈裕新, 湛冬至, 周旋. 机插同步一次性精量施肥对双季稻养分累积及利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 436-446. |
| [8] | 陈中督, 徐春春, 纪龙, 方福平. 基于农户调查的长江中游地区双季稻生产碳足迹及其构成[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 601-609. |
| [9] | 陈中督 徐春春 纪龙 方福平*. 基于农户调查的长江中游地区双季稻生产碳足迹及其构成[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 601-609. |
| [10] | 杨陶陶, 胡启星, 黄山, 曾研华, 谭雪明, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 张俊. 双季优质稻产量和品质形成对开放式主动增温的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 572-580. |
| [11] | 田昌, 周旋, 谢桂先, 刘强, 荣湘民, 张玉平, 谭力彰, 彭建伟. 控释尿素减施对双季稻田氨挥发损失和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 387-397. |
| [12] | 张浪, 周玲红, 魏甲彬, 成小琳, 徐华勤, 肖志祥, 唐启源, 唐剑武. 冬季种养结合对双季稻生长与土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(3): 226-236. |
| [13] | 吕伟生, 曾勇军, 石庆华, 潘晓华, 黄山, 商庆银, 谭雪明, 李木英, 胡水秀, 曾研华. 近30年江西双季稻安全生产期及温光资源变化[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(3): 323-334. |
| [14] | 陈佳娜, 谢小兵, 伍丹丹, 曹放波, 单双吕, 高伟, 李志斌, 邹应斌. 机插密度与氮肥运筹对中嘉早17产量形成及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(6): 628-636. |
| [15] | 马义虎,顾道健,刘立军,王志琴,张耗,杨建昌*. 玉米秸秆源有机肥对水稻产量与温室气体排放的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(5): 520-528. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||