
中国水稻科学 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 303-312.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8091
刘少文, 殷敏, 褚光, 徐春梅, 王丹英, 章秀福, 陈松*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-08-15
修回日期:2019-02-15
出版日期:2019-07-10
发布日期:2019-07-10
通讯作者:
陈松
基金资助:
Shaowen LIU, Min YIN, Guang CHU, Chunmei XU, Danying WANG, Xiufu ZHANG, Song CHEN*( )
)
Received:2018-08-15
Revised:2019-02-15
Online:2019-07-10
Published:2019-07-10
Contact:
Song CHEN
摘要:
土壤氮激发效应是土壤养分释放、植物养分吸收过程中的关键机制。对土壤氮素激发的深入了解,不仅有助于农业生产上更加合理制定氮肥运筹,从而提高氮肥的利用率,也有利于评估和控制环境污染并提供有效的治污方法。本文在介绍土壤氮素激发效应概念和机制的基础上,评估目前土壤氮素激发效应的主流测定方法及其在实际应用中的优劣,重点阐述了外源添加物(无机氮肥、有机物料和根系分泌物)对土壤氮素激发效应的作用效果及其微生物机理。土壤氮激发模式中,外源添加物对土壤C/N比的影响可能是土壤氮激发效应作用的关键。当系统中有效C冗余时,施用无机氮肥,促进土壤有机氮的分解,从而表现正的激发效应;反之,有效C不足但有效N富集时,则表现为固氮微生物活性相对增强,从而出现负的激发效应。微生物是激发效应的推动者。本文通过共代谢理论、微生物热区理论和微生物能量与物质转化理论三个理论假说解析了微生物在土壤氮激发过程中可能的作用机制,从而深化对激发效应的认识,为进一步明确土壤激发效应的微生物机制、因素之间的互作效应及通过激发效应为提高氮肥利用效率提供有效途径。
中图分类号:
刘少文, 殷敏, 褚光, 徐春梅, 王丹英, 章秀福, 陈松. 土壤氮激发效应及其微生物机理研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(4): 303-312.
Shaowen LIU, Min YIN, Guang CHU, Chunmei XU, Danying WANG, Xiufu ZHANG, Song CHEN. Research Progress of Soil Nitrogen Priming Effect and Its Microbial Mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(4): 303-312.
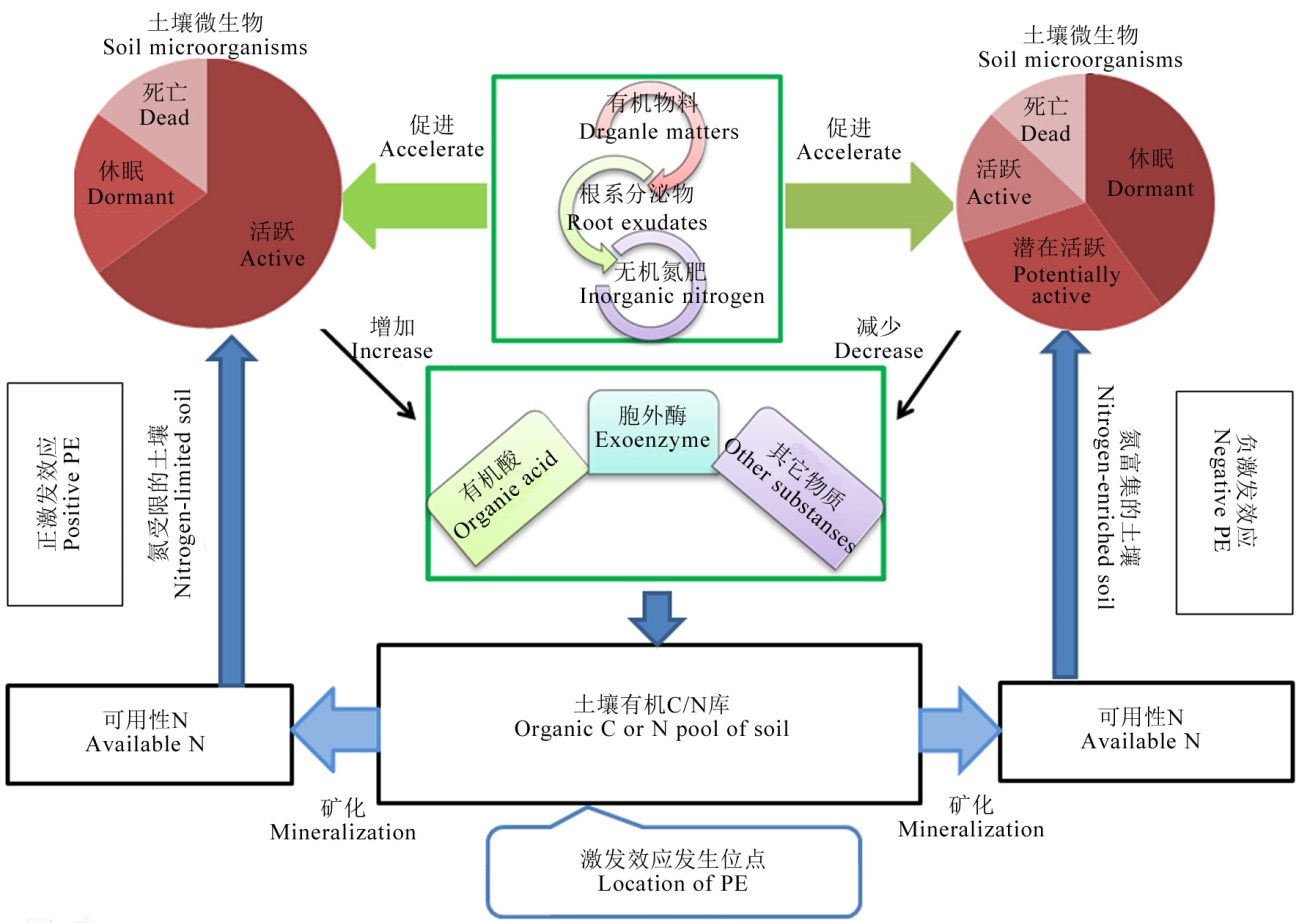
图1 土壤氮激发效应机制土壤中有效态氮含量受限会促进微生物分泌更多的胞外酶,从而加速土壤有机质的分解,产生正的激发效应;反之,在氮富集的土壤体系中,微生物活性降低、数量减少,同时产生胞外酶也减少,抑制有机氮的分解,产生负的激发效应。
Fig. 1. Mechanism of soil nitrogen priming effect. At low nitrogen levels, microbial biomass and activities increase and more extracellular enzymes are secreted to decompose soil organic matter. Therefore, a positive priming effect takes place. In contrast, at high nitrogen levels, the activity and quantity of microorganisms decrease, as does the production of extracellular enzymes. As a result, the decomposition of soil organic matter slows down and a negative priming effect occurs.
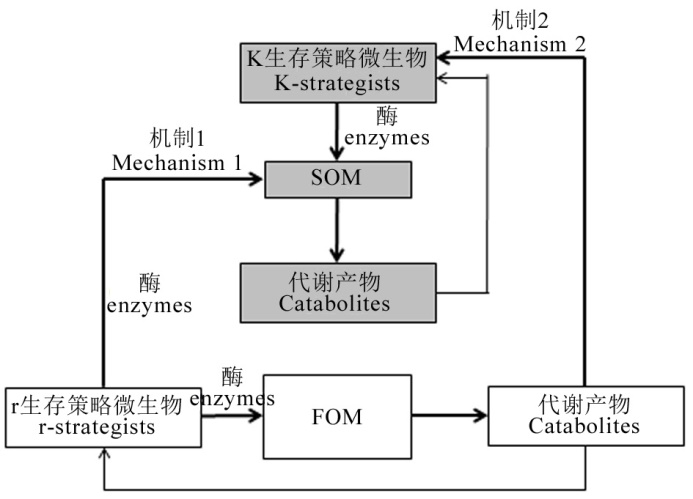
图2 激发效应的微生物机制假说[59] 机制1:r生存策略微生物为分解外源有机物料(FOM)而产生的胞外酶同时一定程度有效降解土壤固有有机质(SOM)。这种机制的强度取决于FOM和SOM之间的生化相似性。FOM的化学多样性越高,产生的酶的多样性和激发效应发生的概率就越高。机制2:SOM分解酶的产生触发了激发效应。这种机制的强度依赖于r和k生存策略微生物之间对FOM的竞争。
Fig. 2 Microbial mechanism hypothesis of PE[59]. Mechanisms 1: r-strategists produce extracellular enzymes for decomposition of fresh organic materials (FOM) while effectively degrading soil intrinsic organic matter (SOM) to a certain extent. The strength of this mechanism depends on the biochemical similarity between FOM and SOM. The higher the chemical diversity of FOM, the higher the diversity of enzymes produced and the probability of PE occurring. Mechanisms 2: The production of SOM catabolic enzymes triggers the PE. The strength of this mechanism depends on the competition between microorganisms with r- and k-strategists for FOM.
| [1] | 马雪峰, 高旻, 程治军. 植物氮素吸收与利用的分子机制研究进展. 作物杂志, 2013, 25(4): 32-38. |
| Ma X F, Gao F, Cheng Z J.Molecular regulation for uptake and utilization of nitrogen in plant.Crops, 2013, 25(4): 32-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Wang H Q, Chen J J.An united model and simulation of nitrogen transport, uptake and transformation in soil-crop system.J Environ Sci, 1998, 8(1): 2037-2046. |
| [3] | 张超兰, 徐建民. 外源营养物质对表征土壤质量的生物学指标的影响. 广西农业生物科学, 2004, 23(1): 81-85. |
| Zhang C L, Xu J M.Effect of organic and inorganic fertilizer application on the bioindicators of soil quality.J Guangxi Agric Biol Sci, 2004, 23(1): 81-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Lohnis F.Nitrogen availability of green manures.Soil Sci, 1926, 22(4): 253-290. |
| [5] | Broadbent, Francis E.Some factors affecting nitrogen transformations and organic matter decomposition in soils.Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc, 1948, 12(3): 246-249. |
| [6] | Bingeman C W, Varner J E, Martin W P.The effect of the addition of organic materials on the decomposition of an organic soil.Soil Sci Soc Amer J, 1953, 17(1): 34-38. |
| [7] | Kuzyakov Y, Friedel J K.Review of mechanisms and quantification of priming effects.Soil Biol Biochem, 2000, 32(1): 1485-1498. |
| [8] | 李世清, 李生秀. 淹水培养条件下铵态氮肥对土壤氮素的激发效应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2001, 7(4): 361-367. |
| Li S Q, Li S X.Priming effect of ammonium nitrogen fertilizer on soil nitrogen under waterlogged condition.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2001, 7(4): 361-367. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 黄文昭, 赵秀兰, 朱建国, 谢祖彬, 朱春梧. 土壤碳库激发效应研究. 土壤通报, 2007, 38(1): 149-154. |
| Huang W Z, Zhao X L, Zhu J G, Xie C W.Priming effect of soil carbon pools.Chin J Soil Sci, 2007, 38(1): 149-154. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 朱丽霞, 章家恩, 刘文高. 根系分泌物与根际微生物相互作用研究综述. 生态环境, 2003, 12(1): 102-105. |
| Zhu L X, Zhang J E, Liu W G.Review of studies on interactions between root exudates and rhizopheric microorganisms.Ecol Environ, 2003, 12(1): 102-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 吕殿青, 张树兰, 杨学云. 外加碳、氮对土壤氮矿化、固定与激发效应的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007, 13(2): 223-229. |
| Lv D Q, Zhang S L, Yang X Y.Effect of supplying C and N on the mineralization, immobilization and priming effect of soil nitrogen.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2007, 13(2): 223-229. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 娄燕宏, 诸葛玉平, 魏猛, 晁赢, 刘安辉. 外源有机物料对土壤氮矿化的影响. 土壤通报, 2009, 40(2): 315-320. |
| Lou Y H, Zhuge Y P, Wei M, Chao Y, Liu A H.Effect of extraneous organic materials on the mineralization of nitrogen in soil.Chin J Soil Sci, 2009, 40(2): 315-320. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 李紫燕. 黄土高原典型土壤有机氮矿化及铵态氮对土壤氮素激发效应的研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2006. |
| Li Z Y.Study on the priming effect caused by ammonium and mineralization of organic nitrogen in the typical soils on loess plateau. Yangling: Northwest Agricultural and Forest University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 沈善敏. 无机氮对土壤氮矿化与固定的影响-兼论土壤氮的“激发效应”. 土壤学报, 1986, 23(1): 10-16. |
| Shen S M.The effect of mineral nitrogen on the minieralization and immobilization of soil nitrogen.Acta Pedol Sin, 1986, 23(1): 10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 徐兴良, Kuzyakov Y, 孙悦. 根际激发效应的发生机制及其生态重要性. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(1): 62-75. |
| Xu X L, Kuzyakov Y, Sun Y.Mechanisms of rhizosphere priming effects and their ecological significance.Chin J Ecol, 2014, 38(1): 62-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Talbot J M, Allison S D, Treseder K K.Decomposers in disguise: mycorrhizal fungi as regulators of soil C dynamics in ecosystems under global change.Fun Ecol, 2008, 22(6): 955-963. |
| [17] | Fontaine S, Bardoux G, Abbadie L, Mariotti A.Carbon input to soil may decrease soil carbon content.Ecol Lett, 2010, 7(4): 314-320. |
| [18] | Blagodatskaya E, Kuzyakov Y.Mechanisms of real and apparent priming effects and their dependence on soil microbial biomass and community structure: critical review. Biol Fer Soils, 2008, 45(2): 115-131. |
| [19] | Drake J E, Darby B A, Giasson M A, Kramer M A.Stoichiometry constrains microbial response to root exudation-insights from a model and a field experiment in a temperate forest.Biogeosciences, 2013, 10(2): 821-838. |
| [20] | Fu S, Cheng W.Rhizosphere priming effects on the decomposition of soil organic matter in C4 and C3 grassland soils.Plant & Soil, 2002, 238(2): 289-294. |
| [21] | Hamer U, Marschner B.Priming effects in different soil types induced by fructose, alanine, oxalic acid and catechol additions.Soil Biol & Biochem, 2005, 37(3): 445-454. |
| [22] | Stanford G, Smith S J.Nitrogen mineralization potentials of soils.Soil Sci Soc Amer J, 1972, 36(3): 465-472. |
| [23] | 刘小兰, 李世清. 土壤中的氮素与环境. 干旱地区农业研究, 1998, 29(4): 36-43. |
| Liu X L, Li S Q.Nitrogen and environment in soil.Agric Res Arid Areas, 1998, 29(4): 36-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 赵琳, 李世清, 李生秀, 张兴昌, 吕丽红, 邵明安. 半干旱区生态过程变化中土壤硝态氮累积及其在植物氮素营养中的作用. 干旱地区农业研究, 2004, 22(4): 14-20. |
| Zhao L, Li S Q, Li S X, Zhang X C, Lv L H, Shao M A.Accumulation of soil nitrate nitrogen in the process of ecological and its effcts in plant nitrogen nutrition in semiarid areas.Agric Res Arid Areas, 2004, 22(4): 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Waring S A, Bremner J M.Ammonium Production in soil under waterlogged conditions as an index of nitrogen availability.Nature, 1964, 201: 951-952. |
| [26] | Bodelier P L E, Wijlhuizen A G, Blom C W P M, Laanbroek H J. Effects of photoperiod on growth of and denitrification by Pseudomonas chlororaphis in the root zone of Glyceria maxima, studied in a gnotobiotic microcosm. Plant & Soil, 1997, 190(1): 91-103. |
| [27] | Jenkinson D S, Fox R H, Rayner J H.Interactions between fertilizer nitrogen and soil nitrogen-the so-called priming effect.J Soil Sci, 1985, 36(3): 425-444. |
| [28] | Jansson S L.Use of 15N in studies of soil nitrogen.Soil Biochem, 1971, 2(10): 129-166. |
| [29] | Jansson S L, Persson J.Mineralization and immobilization of soil nitrogen// Stevenson F J. Nitrogen in Agricultural Soils. Madison, USA: ASA, 1982: 229-252. |
| [30] | Hauck R D, Bremner J M.Use of tracers for soil and fertilizer nitrogen research.Adv Agron, 1976, 28(23): 219-266. |
| [31] | Singh J S, Raghubanshi A S, Singh R S, Srivastava S C.Microbial biomass acts as a source of plant nutrients in dry tropical forest and savanna.Nature, 1989, 338(6215): 499-500. |
| [32] | 陈曦. 秸秆还田对土壤有机质元素组成及化学结构的影响. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2016. |
| Chen X.Effects of straw returning on the composition and chemical structure of soil organic matter. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | Dalenberg J W, Jager G.Priming effect of some organic additions to 14C-labelled soil.Soil Biol & Biochem, 1989, 21(3): 443-448. |
| [34] | 严德翼, 周建斌, 邱桃玉, 杨绒, 马勤安. 黄土区不同土壤类型及土地利用方式对土壤氮素矿化作用的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 35(10): 103-109. |
| Yan D Y, Zhou J B, Qiu T Y, Yang R, Ma Q A.Effects of the different soil types and land use on nitrogen mineralization on the Loess Plateau.Journal of Northwest A&F University: Nat Sci Edn, 2007, 35(10): 103-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | Bird J A, Herman D J, Firestone M K.Rhizosphere priming of soil organic matter by bacterial groups in a grassland soil.Soil Biol Biochem, 2011, 43(4): 718-725. |
| [36] | Nottingham A T, Griffiths H, Chamberlain P M, Stott A W, Tanner E V J. Soil priming by sugar and leaf-litter substrates: A link to microbial groups.Appl Soil Ecol, 2009, 42(3): 183-190. |
| [37] | Falchini L, Naumova N, Kuikman P J, Bloem J, Nannipieri P.CO2 evolution and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles of bacterial communities in soil following addition of low molecular weight substrates to simulate root exudation.Soil Biol Biochem, 2003, 35(6): 775-782. |
| [38] | Martin T, Anderson L, Goates R.Influence of the chemical composition of organic matter on the development of mold flora in soil.Soil Sci, 1942, 54(4): 297. |
| [39] | Langer U, Rinklebe J.Priming effect after glucose amendment in two different soils evaluated by SIR- and PLFA-technique.Ecol Engineer, 2011, 37(3): 465-473. |
| [40] | 廖中建, 黎理. 土壤氮素矿化研究进展. 湖南农业科学, 2007, 4(1): 56-59. |
| Liao Z J, Li L.Progress on mineralization of soil nitrogen.Hunan Agric Sci, 2007, 4(1): 56-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | Jones D L, Hodge A, Kuzyakov Y.Plant and mycorrhizal regulation of rhizodeposition.New Phytol, 2004, 163(3): 459-480. |
| [42] | Kuzyakov Y, Xu X.Competition between roots and microorganisms for nitrogen: mechanisms and ecological relevance.New Phytol, 2013, 198(3): 656-669. |
| [43] | Bodelier P L E, Wijlhuizen A G, Blom C W P M, Haanbroek H J. Effects of photoperiod on growth of and denitrification by Pseudomonas chlororaphis in the root zone of Glyceria maxima, studied in a gnotobiotic microcosm.Plant & Soil, 1997, 190(1): 91-103. |
| [44] | Kuzyakov Y.Review: Factors affecting rhizosphere priming effects.J Plant Nut Soil Sci, 2002, 165(4): 66-70. |
| [45] | Kuzyakov Y, Cheng W.Photosynthesis controls of rhizosphere respiration and organic matter decomposition.Soil Biol Biochem, 2001, 33(14): 1915-1925. |
| [46] | Warembourg F R, Estelrich H D.Plant phenology and soil fertility effects on below-ground c arbon allocation for an annual (Bromus madritensis) and a perennial (Bromus erectus) grass species.Soil Biol Biochem, 2001, 33(10):1291-1303. |
| [47] | Cheng W, Johnson D W.Rhizosphere effects on decomposition: Controls of plant species, phenology, and fertilization.Soil Sci Soc Amer J, 2003, 67(20): 1418-1427. |
| [48] | Kuzyakov Y, Bol R.Sources and mechanisms of priming effect induced in two grassland soils amended with slurry and sugar.Soil Biol Biochem, 2006, 38(4): 747-758. |
| [49] | Asmar F, Eiland F, Nielsen N E.Effect of extracellular-enzyme activities on solubilization rate of soil organic nitrogen.Biol Fert Soils, 1994, 17(1): 32-38. |
| [50] | Schmitt L, Mueller K, Ahrens E.Chemical and microbiological changes in a Rigosole after mineral fertilization in long-term field experiments and short-term aerobic incubation trials.Class Rev, 1991, 41(84): 191-225. |
| [51] | Kuzyakov Y.Priming effects: Interactions between living and dead organic matter.Soil Biol Biochem, 2010, 42(9): 1363-1371. |
| [52] | Nannipieri P, Ascher J, Ceccherini M T, Landi L, Pietramellara G, Renella G.Microbial diversity and soil functions.Eur J Soil Sci, 2010, 54(4): 655-670. |
| [53] | Kuzyakov Y, Blagodatskaya E .Microbial hotspots and hot moments in soil: Concept & review.Soil Biol Biochem, 2015, 83(20): 184-199. |
| [54] | Schimel J P, Weintraub M N.The implications of exoenzyme activity on microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation in soil: A theoretical model.Soil Biol Biochem, 2003, 35(4): 549-563. |
| [55] | Talbot, Nicholas J.Fungal biology: Coming up for air and sporulation.Nature, 1999, 398(6725): 295-296. |
| [56] | Theuerl S, Buscot F.Laccases: toward disentangling their diversity and functions in relation to soil organic matter cycling.Biol Fer Soils, 2010, 46(3): 215-225. |
| [57] | Feng X, Simpson M J.Temperature and substrate controls on microbial phospholipid fatty acid composition during incubation of grassland soils contrasting in organic matter quality.Soil Biol Biochem, 2009, 41(4): 804-812. |
| [58] | Pietri J C A, Brookes P C. Substrate inputs and pH as factors controlling microbial biomass, activity and community structure in an arable soil.Soil Biol Biochem, 2009, 41(7): 1396-1405. |
| [59] | Fontaine S, Mariotti A, Abbadie L.The priming effect of organic matter: a question of microbial competition?Soil Biol Biochem, 2003, 35(6): 837-843. |
| [60] | Sørensen L H.Rate of decomposition of organic matter in soil as influenced by repeated air drying-rewetting and repeated additions of organic material.Soil Biol Biochem, 1974, 6(5): 287-292. |
| [61] | 刘德燕, 宋长春. 外源氮输入对土壤有机碳矿化和凋落物分解的影响. 土壤通报, 2008, 39(3): 675-680. |
| Liu D Y, Song C C.Effects of elevated nitrogen supply on soil organic carbon mineralization and litter decomposition.Chin J Soil Sci, 2008, 39(3): 675-680. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [62] | 葛晓改, 周本智, 肖文发, 王小明, 曹永慧. 生物质炭输入对土壤碳排放的激发效应研究进展. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(2): 339-345. |
| Ge X G, Zhou B Z, Xiao W F, Wang X M, Cao Y H.Priming effect of biochar addition on soil carbon emission: A review.Ecol Environ Sci, 2016, 25(2): 339-345. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [63] | De Nobili M, Contin M, Mondini A C, Brookes P C.Soil microbial biomass is triggered into activity by trace amounts of substrate.Soil Biol Biochem, 2001, 33(9): 1163-1170. |
| [64] | Moore-Kucera J, Dick R P.Application of 13C-labeled litter and root materials for in situ decomposition studies using phospholipid fatty acids.Soil Biol Biochem, 2008, 40(10): 2485-2493. |
| [65] | Fontaine S, Henault C, Aamor A.Fungi mediate long term sequestration of carbon and nitrogen in soil through their priming effect.Soil Biol Biochem, 2011, 43(1): 86-96. |
| [66] | Otten W, Hall D, Harris K, Pitz K, Young I M, Gilligam C A. Soil Physics, Fungal Epidemiology and the Spread of Rhizoctonia solani.New Phytol, 2001, 151(2): 459-468. |
| [67] | Blagodatskaya E V, Blagodatsky S A, Anderson T H, Yuzyakov Y.Priming effects in Chernozem induced by glucose and N in relation to microbial growth strategies.Appl Soil Ecol, 2007, 37(1): 95-105. |
| [68] | Blagodatsky S A, Richter O.Microbial growth in soil and nitrogen turnover: A theoretical model considering the activity state of microorganisms. Soil Biol Biochem, 1998, 30(13): 1743-1755. |
| [69] | Sinsabaugh R L, Carreiro M M, Repert D A.Allocation of extracellular enzymatic activity in relation to litter composition, N deposition, and mass loss.Biogeochem (Dordrecht), 2002, 60(1): 1-24. |
| [70] | Cusack D F, Torn M S, Mcdowell W H, Silver W L.The response of heterotrophic activity and carbon cycling to nitrogen additions and warming in two tropical soils.Global Chang Biol, 2010, 16(9): 2555-2572. |
| [71] | Khan S A, Mulvaney R L, Ellsworth T R, Boast C W.The myth of nitrogen fertilization for soil carbon sequestration.J Environ Qual, 2007, 36(6): 1821. |
| [72] | Grandy A S, Salam D S, Wickings K, McDaniel M D, Culman S W, Snapp S S. Soil respiration and litter decomposition responses to nitrogen fertilization rate in no-till corn systems.Agric, Ecosys Environ, 2013, 179(20): 35-40. |
| [73] | Hartmann M, Frey B, Mayer J, Mader P, Widmer F.Distinct soil microbial diversity under long-term organic and conventional farming. ISME J, 2015, 9(5): 1177-1194. |
| [74] | Jimenez-Bueno N G, Valenzuela-Encinas C, Marsch R, Ortiz-Gutierrez D, Verhulst N. Bacterial indicator taxa in soils under different long-term agricultural management.J Appl Microbiol, 2016, 120(4): 921-933. |
| [75] | Fierer N, Ladau J, Clemente J C, Leff J W, Owens S M, Pollard K S, Knight R.Reconstructing the Microbial Diversity and Function of Pre-Agricultural Tallgrass Prairie Soils in the United States.Science, 2013, 342(6158): 621-624. |
| [76] | Fierer N, Lauber C L, Ramirez K S, Zaneveld J, Bradford M A, Knight R.Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients.Isme J, 2012, 6(5): 1007-1017. |
| [77] | Finn D, Page K, Catton K, Strounina E, Kienzle M, Robertson F, Dalal R.Effect of added nitrogen on plant litter decomposition depends on initial soil carbon and nitrogen stoichiometry. Soil Biol Biochem, 2015, 91(3): 160-168. |
| [1] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [2] | 吴玉红, 李艳华, 王吕, 秦宇航, 李杉杉, 郝兴顺, 张庆路, 崔月贞, 肖飞. 陕南稻区紫云英稻草联合还田配施减量氮肥协同提升水稻产量与稻米品质[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 628-641. |
| [3] | 肖大康, 胡仁, 韩天富, 张卫峰, 侯俊, 任科宇. 氮肥用量和运筹对我国水稻产量及其构成因子影响的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [4] | 黄锦文, 李日坤, 陈志诚, 张汴泓, 雷涵, 潘睿欣, 杨铭榆, 潘美清, 唐莉娜. 不同稻草还田技术对烟-稻轮作系统土壤养分、有机碳及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 415-426. |
| [5] | 张露, 梁青铎, 吴龙龙, 黄晶, 田仓, 张均华, 曹小闯, 朱春权, 孔亚丽, 金千瑜, 朱练峰. 减氮和增氧灌溉对水稻产量和氮素利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 78-88. |
| [6] | 任维晨, 常庆霞, 张亚军, 朱宽宇, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 不同氮利用率粳稻品种的碳氮积累与转运特征及其生理机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 586-600. |
| [7] | 张宇杰, 王志强, 马鹏, 杨志远, 孙永健, 马均. 麦秆还田下水氮耦合对水稻氮素吸收利用及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 388-398. |
| [8] | 张露, 吴龙龙, 黄晶, 田仓, 祈军, 张均华, 曹小闯, 朱春权, 孔亚丽, 金千瑜, 朱练峰. 增氧处理对稻田土壤微生物量碳、氮和酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 410-418. |
| [9] | 陈云, 刘昆, 李婷婷, 李思宇, 李国明, 张伟杨, 张耗, 顾骏飞, 刘立军, 杨建昌. 结实期干湿交替灌溉对水稻根系、产量和土壤的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 269-277. |
| [10] | 张小祥, 邵士梅, 赵步洪, 张耗, 季红娟, 肖宁, 潘存红, 李育红, 吴云雨, 蔡跃, 刘建菊, 吉春明, 张秀琴, 刘广青, 周长海, 黄年生, 李爱宏. 氮肥减施模式对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 278-294. |
| [11] | 余锋, 李思宇, 邱园园, 卓鑫鑫, 黄健, 汪浩, 朱安, 刘昆, 刘立军. 稻田甲烷排放的微生物学机理及节水栽培对甲烷排放的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 1-12. |
| [12] | 张庆, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 张洪程, 徐玉峰, 徐晓杰, 朱邦辉, 徐洁芬, 钮中一, 凃荣文. 不同氮肥水平下优质高产软米粳稻的产量与品质差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 606-616. |
| [13] | 唐先干, 谢金水, 徐昌旭, 刘佳, 袁福生, 刘光荣, 李祖章. 红壤性稻田紫云英与化肥减施对早稻品质与养分吸收的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 466-474. |
| [14] | 王亚梁, 朱德峰, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 向镜, 王志刚, 张义凯. 籼粳杂交稻精准条播育秧机插减氮增产的效应研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 495-502. |
| [15] | 黄锦文, 吴珈谊, 陈鸿飞, 张志兴, 方长旬, 邵彩虹, 林伟伟, 翁佩莹, 林文雄. 头季稻氮肥运筹对再生稻根际机能及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 383-395. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||