
中国水稻科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 318-326.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022.210605
• 研究报告 • 上一篇
何佳春1,2, 何雨婷2, 万品俊2, 魏琪2, 赖凤香2, 陈祥盛1,*( ), 傅强2,*(
), 傅强2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-06-11
修回日期:2021-10-01
出版日期:2022-05-10
发布日期:2022-05-11
通讯作者:
陈祥盛,傅强
基金资助:
HE Jiachun1,2, HE Yuting2, WAN Pinjun2, WEI Qi2, LAI Fengxiang2, CHEN Xiangsheng1,*( ), FU Qiang2,*(
), FU Qiang2,*( )
)
Received:2021-06-11
Revised:2021-10-01
Online:2022-05-10
Published:2022-05-11
Contact:
CHEN Xiangsheng, FU Qiang
摘要:
【目的】黄腿双距螯蜂是我国南方稻区常见的褐飞虱天敌之一,本研究旨在明确不同温度对黄腿双距螯蜂生物学特性的影响。【方法】在室内条件下,系统测定了12℃、17℃、22℃、27℃、32℃、36℃和38℃恒温条件下该蜂成虫寿命、寄生率、取食率及子代结茧率、羽化率、发育历期、雌性占比等生物学特性,并计算了该蜂的种群生命表参数、世代发育起点温度及有效积温。【结果】1)温度对黄腿双距螯蜂雌、雄成虫的寿命、寄生率、取食率和子代生长发育均有显著影响。雌、雄成虫寿命均在17℃时最长,并随温度升高而缩短,温度高至38℃时存活不超过1 d。成虫寄生率和取食率均在32℃时最高,分别为52.3%和17.7%,这两个参数在27℃与32℃之间无显著差异,而在38℃时均为0。在17℃~36℃下子代均可化茧和羽化,其中在27℃时化茧率和羽化率均最高,子代雌虫比例在32℃时最高(28.6%),子代的雌虫数量在27℃最高(30.5头)。在17℃~36℃范围内,幼虫的发育历期均随着温度升高而缩短。2)综合估测的种群生命表参数结果中,27℃下种群的内禀增长率最高,为0.53,32℃和22℃次之,17℃时的内禀增长率最低。3)通过有效积温法则计算出的雌、雄虫发育起点温度分别为12.0℃和11.9℃,世代有效积温分别为343.8 d·℃和337.6 d·℃。【结论】黄腿双距螯蜂可在17℃~36℃范围生存,但生长发育和种群繁殖的适温范围为27℃~32℃,最适温度为27℃。本研究明确了温度对黄腿双距螯蜂生物学特征的影响,为进行该蜂的规模化饲养奠定了重要基础。
何佳春, 何雨婷, 万品俊, 魏琪, 赖凤香, 陈祥盛, 傅强. 温度对褐飞虱天敌黄腿双距螯蜂生物学特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 318-326.
HE Jiachun, HE Yuting, WAN Pinjun, WEI Qi, LAI Fengxiang, CHEN Xiangsheng, FU Qiang. Effects of Temperature on Biological Traits of the Pincer Wasp [Gonatopus flavifemur (Esaki & Hashimoto)], a Natural Enemy of the Brown Planthopper(Nilaparvata lugens)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 318-326.
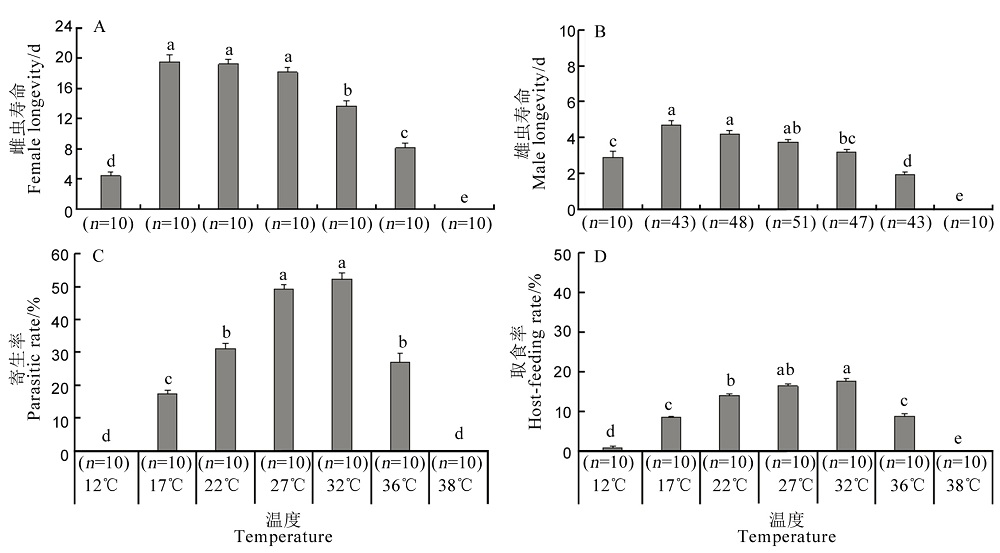
图1 不同温度下黄腿双距螯蜂雌、雄成寿命(A,B)、寄生率(C)和取食率(D) 图中数据为平均值±标准误,横坐标下方的数字表示样本数。柱上具相同英文字母者表示经Tukey检验无显著差异(P>0.05)。图2和3同。
Fig. 1. Longevity of female and male adults(A, B), parasitic rate(C) and host-feeding rate(D) of G. flavifemur at different temperatures. Data are mean±SE.The numbers below the abscissa are sample numbers of each treatment. Bars with common lowercase letters above show no significant difference (Tukey’s test,P>0.05). The same as in figure 2 and 3.
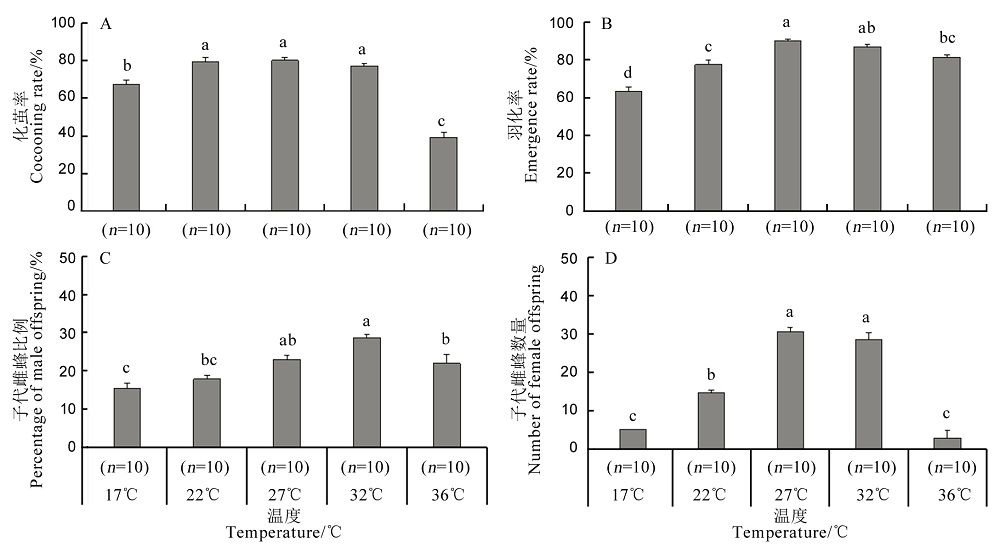
图2 不同温度下螯蜂子代的化茧率(A),羽化率(B),子代中雌虫数(C)和雌性占比(D)
Fig. 2. Cocooning rates (A), emergence rates (B), proportions of females (C) and numbers of females (D) of G. flavifemur offsprings at different temperatures.
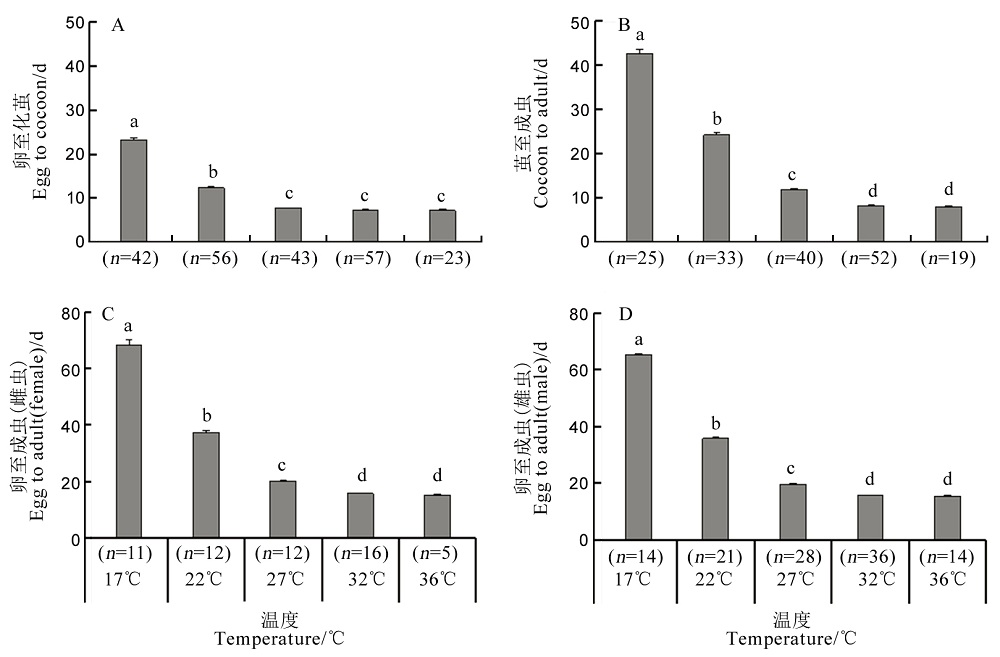
图3 不同温度下螯蜂子代卵至化茧(A),茧至成虫(B),雌虫、雄虫卵至成虫(C,D)的发育历期
Fig. 3. Developmental duration of egg to cocoon(A), cocoon to adult(B), female egg to adult(C) and male egg to adult(D) of G. flavifemur at different temperatures.
| 温度 Temperature/℃ | 世代周期(T) Generation time/d | 净增长率(R0) Net reproductive rate | 内禀增长率(r) Intrinsic rate of increase | 周限增长率(λ) Finite rate of increase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 10.20 | 5.10 | 0.16 | 1.17 |
| 22 | 9.22 | 15.60 | 0.30 | 1.35 |
| 27 | 6.47 | 30.50 | 0.53 | 1.70 |
| 32 | 6.91 | 28.50 | 0.49 | 1.62 |
| 36 | 6.17 | 2.90 | 0.17 | 1.19 |
表1 不同温度下黄腿双距螯蜂种群生命表参数
Table 1. Population life table parameters of G. flavifemur at different temperatures.
| 温度 Temperature/℃ | 世代周期(T) Generation time/d | 净增长率(R0) Net reproductive rate | 内禀增长率(r) Intrinsic rate of increase | 周限增长率(λ) Finite rate of increase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 10.20 | 5.10 | 0.16 | 1.17 |
| 22 | 9.22 | 15.60 | 0.30 | 1.35 |
| 27 | 6.47 | 30.50 | 0.53 | 1.70 |
| 32 | 6.91 | 28.50 | 0.49 | 1.62 |
| 36 | 6.17 | 2.90 | 0.17 | 1.19 |
| 发育阶段 Stage of development | 发育起点温度 Developmental threshold temperature/℃ | 有效积温 Effective accumulated temperature/(d·℃) | 回归方程 Regression equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卵-茧Egg to cocoon | 10.8±0.9 | 144.1±17.1 | Y=144.06/(X–10.77) | 0.979 |
| 茧-成虫Cocoon to adult | 12.3±0.8 | 202.6±29.4 | Y=202.64/(X–12.30) | 0.979 |
| 雌虫卵-成虫Female egg to adult | 12.0±0.6 | 343.8±32.3 | Y=343.82/(X–11.99) | 0.990 |
| 雄虫卵-成虫Male egg to adult | 11.9±0.5 | 337.6±29.4 | Y=337.62/(X–11.85) | 0.991 |
表2 黄腿双距螯蜂各阶段发育起点温度及有效积温
Table 2. Developmental threshold temperature and effective accumulated temperature of G. flavifemur in different development stages.
| 发育阶段 Stage of development | 发育起点温度 Developmental threshold temperature/℃ | 有效积温 Effective accumulated temperature/(d·℃) | 回归方程 Regression equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卵-茧Egg to cocoon | 10.8±0.9 | 144.1±17.1 | Y=144.06/(X–10.77) | 0.979 |
| 茧-成虫Cocoon to adult | 12.3±0.8 | 202.6±29.4 | Y=202.64/(X–12.30) | 0.979 |
| 雌虫卵-成虫Female egg to adult | 12.0±0.6 | 343.8±32.3 | Y=343.82/(X–11.99) | 0.990 |
| 雄虫卵-成虫Male egg to adult | 11.9±0.5 | 337.6±29.4 | Y=337.62/(X–11.85) | 0.991 |
| [1] | 程遐年, 吴进才, 马飞. 褐飞虱研究与防治[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2003: 1-37. |
| Chen X N, Wu J C, Ma F. Brown Planthopper: Occurrence and Control[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2003: 1-37. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 王鹏, 甯佐苹, 张帅, 蒋田田, 谭利蓉, 董嵩, 高聪芬. 我国主要稻区褐飞虱对常用杀虫剂的抗性监测[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(2): 191-197. |
| Wang P, Ning Z P, Zhang S, Jiang T T, Tan L R, Dong S, Gao C F. Resistance monitoring to conventional insecticides in brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in main rice growing regions in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(2): 191-197. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Wu S F, Zeng B, Zheng C, Mu X C, Zhang Y, Hu J, Zhang S, Gao C F, Shen J L. The evolution of insecticide resistance in the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) of China in the period 2012-2016[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 4586. |
| [4] | Wu J, Ge L, Liu F, Song Q, Stanley D. Pesticide-induced planthopper population resurgence in rice cropping systems[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 2020, 65: 409-429. |
| [5] | 何俊华, 马云, 王洪全, 史永善, 丘念曾, 任树芝, 杨集昆, 陈学新, 陈樟福, 郑乐怡, 蒲天胜, 虞佩玉. 中国水稻害虫天敌名录[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1991: 18-62. |
| He J H, Ma Y, Wang H Q, Shi Y S, Qiu N Z, Ren S Z, Chen X X, Chen Z F, Zhen L Y, Pu T S, Yu P Y. Directory of Natural Enemies of Rice Insect Pests in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1991: 18-62. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 张晓燕, 翟一凡, 林清彩, 孙玉霞, 李强, 陶玫, 周仙红, 李丽莉, 于毅. 寄生蜂对稻飞虱控害作用研究进展[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2014, 36(6): 1025-1032. |
| Zhang X Y, Zhai Y F, Lin Q C, Sun Y X, Li Q, Tao M, Zhou H X, Li L L, Yu Y. Research progress of controlling action of parasitoids on rice planthoppers[J]. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 2014, 36(6): 1025-1032. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Li Y, Zhang Q, Liu Q, Meissle M, Yang Y, Wang Y, Hua H, Chen X, Peng Y, Romeis J. Bt rice in China-Focusing the nontarget risk assessment[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(10): 1340-1345. |
| [8] | 何佳春. 浙江、湖南稻飞虱天敌调查及原色特征图片采集[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2014. |
| He J C. Investigation for rice planthoppers related natural enemies and their characteristic photoesin Zhejiang and Hunan provinces[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | He J, He Y, Lai F, Chen X, Fu Q. Biological traits of the pincer wasp Gonatopus flavifemur (Esaki & Hashimoto) associated with different stages of its host, the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)[J]. Insects, 2020, 11(5): 279. |
| [10] | 何俊华, 许再福. 中国动物志, 昆虫纲第二十九卷, 膜翅目, 螯蜂科[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 360-364. |
| He J H, Xu Z F. Fauna Sinica, Insecta Vol. 29, Hymenoptera, Dyrinidae[M]. Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002: 360-364. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | Gurr G M, Liu J, Read D M Y, Catindig J L A, Cheng J A, Lan L P, Heong K L. Parasitoids of Asian rice planthopper (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) pests and prospects for enhancing biological control by ecological engineering[J]. Annals of Applied Biology, 2011, 158(2): 149-176. |
| [12] | Olmi M, Xu Z. Dryinidae of the eastern palaearctic region (Hymenoptera: Chrysidoidea)[J]. Zootaxa, 2015, 3996: 1-253. |
| [13] | 杨绍龙, 黄建新, 金孟肖. 稻飞虱、稻叶蝉天敌-螯蜂的研究[J]. 昆虫天敌, 1982, 4(2): 1-12. |
| Yang S L, Huang J X, Jin M X. Studies on dryinid wasp (Hymenoptera: Dryinidae), the natural enemy of rice planthopper and rice leafhopper[J]. Natural Enemies of Insects, 1982, 4(2): 1-12. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | Guglielmino A. Dryinidae Hymenoptera Chrysidoidea: An interesting group among the natural enemies of the Auchenorrhyncha Hemiptera[J]. Denisia, 2002, 176(4): 549-556. |
| [15] | 黄信飞. 褐稻虱的天敌-黄腿螯蜂的初步观察[J]. 昆虫知识, 1982(5): 12-15. |
| Huang X F. Preliminary observations on Pseudogonatopus flavifemur (Hymenoptera: Dryinidae), the natural enemy of Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Entomological Knowledge, 1982(5): 12-15. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 何雨婷, 何佳春, 魏琪, 赖凤香, 杨中侠, 傅强. 三种稻田常见螯蜂对半翅目害虫的寄主偏好性及控害作用[J]. 昆虫学报, 2020, 63(8): 999-1009. |
| He Y T, He J C, Wei Q, Lai F X, Yang Z X, Fu Q. Host preferences and control effects of three common rice field dryinids on hemipteran pests[J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2020, 63(8): 999-1009. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Hayakawa D L, Grafius E, Stehr F W. Effects of temperature on longevity, reproduction and development of the Asparagus aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) and the parasitoid, Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae)[J]. Environmental Entomology, 1990, 19(4): 890-897. |
| [18] | 阮长春, 郭若天, 胡晓暄, 杜文梅, 臧连生, 张俊杰. 温度对稻螟赤眼蜂在米蛾卵上的生长发育和寄生潜能的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 398-404. |
| Ruan C C, Guo R T, Hu X X, Du W M, Zang L S, Zhang J L. Effect of temperature on development and parasitizing capacity of Trichogramma japonicum reared on the eggs of rice moth (Corcyra cephalonica)[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(4): 398-404. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 潘飞, 陈绵才, 肖彤斌, 吉训聪, 谢圣华. 变温对昆虫生长发育和繁殖影响的研究进展[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2014, 36(2): 240-246. |
| Pan F, Chen M C, Xiao T B, Ji X C, Xie S H. Research advances on effect of variable temperature on growth, development and reproduction of insect[J]. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 2014, 36(2): 240-246. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Hagstrum D W, Milliken G A. Quantitative analysis of temperature, moisture, and diet factors affecting insect development[J]. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 1988, 81(4): 539-546. |
| [21] | 徐汝梅. 昆虫种群生态学[M]. 北京: 北京师范大学出版社, 1987: 61-82. |
| Xu R M. Insect population ecology[M]. Beijing: Beijing Normal University Press, 1987: 61-82. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 张孝羲. 昆虫生态及预测预报[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2004: 218-219. |
| Zhang X X. Insect ecology and prediction[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2004: 218-219. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | Tang Q Y, Zhang C X. Data processing system (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research[J]. Insect Science, 2013, 20(2): 254-260. |
| [24] | Nouhuys S V, Lei N G. Parasitoid-host metapopulation dynamics: the causes and consequences of phenological asynchrony[J]. Journal of Animal Ecology, 2004, 73(3): 526-535. |
| [25] | 李倩, 程云霞, 罗礼智, 雷朝亮, 江幸福, 张蕾. 温度对绿眼赛茧蜂寄生率及生长发育的影响[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2017, 33(5): 575-583. |
| Li Q, Cheng Y X, Luo L Z, Lei C L, Jiang X F, Zhang L. Effect of temperature on parasitism rate and life history parameters of a solitary endoparasitoid, Zele chlorophthalmus (Hymenoptera: Brachonidae)[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2017, 33(5): 575-583. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Qiu B, Zhou Z S, Luo S P, Xu Z F. Effect of temperature on development, survival, and fecundity of Microplitis manilae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae)[J]. Environmental Entomology, 2012, 41(3): 657-664. |
| [27] | Spanoudis C G, Andreadis S S. Temperature-dependent survival, development, and adult longevity of the koinobiont endoparasitoid Venturia canescens (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) parasitizing Plodia interpunctella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae)[J]. Journal of Pest Science, 2012, 85(1): 75-80. |
| [28] | Kitamura K. Comparative studies on the biology of dryinid wasps in Japan (9). Development of Haplogonatopus apicalis (Hymenoptera, Dryinidae)[J]. Bulletin of the Faculty of Agriculture, Shimane University, 1989, 23: 55-59. (in Japanese with English abstract). |
| [29] | Kitamura K. Comparative studies on the biology of dryinid wasps in Japan (10). Development of Pseudogonatopus fulgori (Hymenoptera, Dryinidae)[J]. Bulletin of the Faculty of Agriculture, Shimane University, 1989, 23: 60-63. (in Japanese with English abstract) |
| [30] | 郭明昉. 赤眼蜂寄生行为研究: Ⅱ. 雌蜂交配行为与子代性比[J]. 昆虫天敌, 1992, 14(2): 51-53. |
| Guo M F. Study of parasitic behavior of Trichogramma:Ⅱ. Affect of mating behavior on sex ratio of progeny[J]. Natural Enemies of Insects, 1992, 14(2): 51-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Godfray H C J. Parasitoids behavioral and evolutionary ecology[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1994: 307-360. |
| [32] | 陈若篪, 綦立正, 程遐年. 褐飞虱种群动态的研究: Ⅰ. 温度、食料条件对种群增长的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 1986, 9(3): 23-33. |
| Chen R C, Qi L Z, Cheng X N. Studies on the population dynamics of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål):Ⅰ. effects of temperature and diet conditions on the growth of experimental population[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 1986, 9(3): 23-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | Vinson S B, Barras D J. Effects of the parasitoid, Cardiochiles nigriceps, on the growth, development, and tissues of Heliothis virescens[J]. Journal of Insect Physiology, 1970, 16(9): 1329-1338. |
| [34] | 祝树德, 陆自强, 杭杉保, 徐海. 温度对褐飞虱种群调控作用研究[J]. 华东昆虫学报, 1994, 3(1): 53-59. |
| Zhu S D, Lu Z Q, Hang S B, Xu H. Study of the temperature regulation on brown planthopper population[J]. Entomological Journal of East China, 1994, 3(1): 53-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 张世泽, 郭建英, 万方浩, 张帆. 温度对不同品系丽蚜小蜂发育、存活和寿命的影响[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2004, 20(3): 174-177. |
| Zhang S Z, Guo J Y, Wan F H, Zhang F. Effect of temperature on the development survival and longevity of Encarsia formosa[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2004, 20(3): 174-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 马梦然, 曹鹤, 申家轩, 暴可心, 刘程, 崔建州. 云南派姬小蜂的发育起点温度和有效积温[J]. 植物保护, 2020, 46(3): 194-197. |
| Ma M R, Cao H, Shen J X, Bao K X, Liu C, Cui J Z. Threshold temperature and effective accumulated temperature of Pediobius yunnanensis Liao[J]. Plant Protection, 2020, 46(3): 194-197. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 杨奇欣, 赖凤香, 何佳春, 魏琪, 王渭霞, 万品俊, 傅强. 不同抗感水稻品种对褐飞虱胁迫的高光谱响应特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 81-90. |
| [2] | 王军, 周晶, 陶亚军, 李文奇, 朱建平, 范方军, 王芳权, 许扬, 陈智慧, 蒋彦婕, 李霞, 杨杰. 基于HRM技术开发水稻糊化温度基因ALK功能标记[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 106-110. |
| [3] | 段敏, 谢留杰, 高秀莹, 唐海娟, 黄善军, 潘晓飚. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制广亲和水稻温敏雄性不育系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 233-243. |
| [4] | 程玲, 黄福钢, 邱一埔, 王心怡, 舒宛, 邱永福, 李发活. 籼稻材料570011抗褐飞虱基因的遗传分析及鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 244-252. |
| [5] | 罗举, 杨素文, 贝文勇, 余军伟, 唐健, 刘淑华. 直接多重TaqMan qPCR方法快速鉴定褐飞虱属3种飞虱[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 329-336. |
| [6] | 曹跃炫, 严绘景, 王克剑, 刘朝雷. 苗期快速分选水稻人工无融合生殖克隆种子[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 656-662. |
| [7] | 罗举, 唐健, 王爱英, 杨保军, 刘淑华. 基于重组酶介导扩增-侧流层析试纸条的褐飞虱快速鉴定方法[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 96-104. |
| [8] | 马银花, 李萍芳, 董文静, 易松望, 杨芳, 杜波, 金晨钟. 水稻抗性蛋白OsRRK1抗褐飞虱机理分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 512-519. |
| [9] | 陈专专, 杨勇, 冯琳皓, 孙晔, 张昌泉, 范晓磊, 李钱峰, 刘巧泉. Wx与ALK主要等位基因不同组合对稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 228-236. |
| [10] | 潘磊, 王利华, 朱凤, 韩阳春, 王培, 方继朝. 褐飞虱小分子量热激蛋白基因表达特性和功能[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 37-45. |
| [11] | 陈专专, 李先锋, 仲敏, 葛家奇, 范晓磊, 张昌泉, 刘巧泉. 籼稻背景下抑制不同ALK等位基因表达对稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 513-522. |
| [12] | 朱永生, 白建林, 谢鸿光, 吴方喜, 罗曦, 姜身飞, 何炜, 陈丽萍, 蔡秋华, 谢华安, 张建福. 聚合白背飞虱和褐飞虱抗性基因创制杂交水稻恢复系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 421-428. |
| [13] | 何佳春, 李波, 谢茂成, 赖凤香, 胡国文, 傅强. 新烟碱类及其他稻田杀虫剂对褐飞虱的室内药效评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 467-478. |
| [14] | 降好宇, 曾盖, 郝明, 黄湘桂, 肖应辉. 广谱抗稻瘟病种质75-1-127的褐飞虱抗性基因鉴定及分子标记辅助选择育种[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 227-234. |
| [15] | 张珏锋, 李芳, 钟海英, 陈建明. 制霉菌素对褐飞虱若虫解毒酶、尿酸酶含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 186-190. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||