
中国水稻科学 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 467-478.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8098
• 研究报告 • 上一篇
何佳春1, 李波1,3, 谢茂成2, 赖凤香1, 胡国文1, 傅强1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-08-31
修回日期:2019-02-28
出版日期:2019-09-10
发布日期:2019-09-10
通讯作者:
傅强
基金资助:
Jiachun HE1, Bo LI1,3, Maocheng XIE2, Fengxiang LAI1, Guowen HU1, Qiang FU1,*( )
)
Received:2018-08-31
Revised:2019-02-28
Online:2019-09-10
Published:2019-09-10
Contact:
Qiang FU
摘要:
【目的】 系统评价市场上常用杀虫剂对褐飞虱不同虫态的作用特性,为选择对口药剂进行防治提供依据。【方法】 采用稻苗浸渍法,在室内条件下测定了9种新烟碱类药剂和10种其他类型杀虫剂对褐飞虱不同虫态的杀虫活性、速效性和持效性。【结果】 1)杀虫活性:不同杀虫剂活性存在显著差异。其中,烯啶虫胺、噻虫胺、毒死蜱、氟啶虫胺腈、呋虫胺和环氧虫啶活性最好,其次为哒嗪硫磷、乙基多杀菌素、吡蚜酮、异丙威,阿维菌素;其余药剂中噻虫嗪、甲维盐、氟啶虫酰胺对2~3龄若虫有一定活性而对4~5龄虫活性差,噻嗪酮、吡虫啉、噻虫啉、啶虫脒、氯噻啉对两种虫态的活性均较差。2)速效性:毒死蜱、哒嗪硫磷的速效性最好,异丙威、呋虫胺、烯啶虫胺、噻虫胺等次之,吡蚜酮最差。3)持效性:吡蚜酮、呋虫胺、烯啶虫胺、噻虫胺、环氧虫啶持效期>15 d,其中吡蚜酮最好,药后0、5和10 d连续3批接的试虫死亡率无显著差异。4)成虫:呋虫胺、烯啶虫胺、噻虫胺、环氧虫啶、毒死蜱、异丙威、吡蚜酮对雌雄成虫均有效,类似于若虫。5)卵:毒死蜱、烯啶虫胺、呋虫胺和噻虫胺对卵及孵化的若虫均有效;吡蚜酮、环氧虫啶、异丙威等无明显杀卵活性,但吡蚜酮对孵化若虫有较好的杀虫活性。【结论】 19种药剂中,适于褐飞虱防治的有吡蚜酮、烯啶虫胺、呋虫胺、噻虫胺、环氧虫啶、氟啶虫胺腈、毒死蜱、哒嗪硫磷、异丙威共9种。其中,吡蚜酮持效性最佳且对卵之外各虫态活性较好,但速效性最差。呋虫胺、烯啶虫胺、噻虫胺和环氧虫啶等的速效性、持效性均较突出,且前三者对各虫态均有效。氟啶虫胺腈杀虫活性和速效性均好,但持效性差于新烟碱类。毒死蜱和哒嗪硫磷可单独或在防治其他害虫时兼防治褐飞虱,其中毒死蜱速效性最好,适合于大虫量时快速压低虫量。异丙威杀虫活性弱于新烟碱类,但速效性强于新烟碱类药剂,适合与吡蚜酮等混用或复配。此外,用于鳞翅目害虫防治的乙基多杀菌素、阿维菌素、甲维盐对褐飞虱有一定活性,适合防治其他害虫时兼治褐飞虱。而其余药剂如吡虫啉、噻嗪酮、噻虫嗪等7种药剂不适用于褐飞虱的防治。
中图分类号:
何佳春, 李波, 谢茂成, 赖凤香, 胡国文, 傅强. 新烟碱类及其他稻田杀虫剂对褐飞虱的室内药效评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 467-478.
Jiachun HE, Bo LI, Maocheng XIE, Fengxiang LAI, Guowen HU, Qiang FU. Laboratory Bioactivity Study on Neonicotinoid and Other Rice Paddy Used Insecticides Against the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens(Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(5): 467-478.
| 杀虫剂 Insecticide | 生产厂家 Manufacturer | 原药含量 Content/% | 有效成分推荐用药量 Dosage of active ingredient/(g∙667 m-2) | 供试浓度 Lab-trial concentration/(mg·L-1) | 登记对象 Object of registration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 环氧虫啶Cycloxaprid | 上海生农生化制品有限公司 | 96 | 4~6 | 111.11 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 噻虫胺Clothianidin | 江苏中旗作物保护股份有限公司 | 98 | 3~4 | 77.78 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 呋虫胺Dinotefuran | 日本三井化学AGRO株式会社 | 99 | 6~10 | 177.78 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 烯啶虫胺Nitenpyram | 连云港立本农药化工有限公司 | 97 | 4~6 | 111.11 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 噻虫嗪Thiamethoxam | 江苏绿叶农化有限公司 | 98 | 0.75~1.00 | 19.44 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 吡虫啉Imidacloprid | 苏州遍净植保科技有限公司 | 98 | 1~2 | 33.33 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 氯噻啉Imidaclothiz | 南通江山农药化工股份有限公司 | 95 | 1~2 | 33.33 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 噻虫啉Thiacloprid | 山东省联合农药工业有限公司 | 96 | 4.5~6.5 | 122.22 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 啶虫脒Acetamiprid | 宁波三江益农化学有限公司 | 99 | 1.5~2.4 | 43.33 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 吡蚜酮Pymetrozine | 江苏安邦电化有限公司 | 96 | 4~5 | 100.00 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 毒死蜱Chlorpyrifos | 浙江新农化工股份有限公司 | 97 | 43.2~48.0 | 1013.33 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 噻嗪酮Buprofezin | 江苏安邦电化有限公司 | 98 | 6.25~8.75 | 166.67 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 异丙威Isoprocarb | 湖南海利化工股份有限公司 | 98 | 30~40 | 777.78 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 阿维菌素Abamectin | 浙江升华拜克生物股份有限公司 | 85 | 0.6~0.9 | 16.67 | 二化螟Rice stem borer |
| 甲维盐Emamectin benzoate | 浙江升华拜克生物股份有限公司 | 92 | 0.15~0.25 | 4.44 | 小菜蛾Diamondback moth |
| 氟啶虫酰胺Flonicamid | 苏州奥特莱化有限公司 | 96 | 3~5 | 88.88 | 蚜虫Aphid |
| 氟啶虫胺腈Sulfoxaflor | 美国陶氏益农公司 | 95 | 3.3~4.4 | 85.55 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 乙基多杀菌素Spinetoram | 美国陶氏益农公司 | 81 | 1.2~1.8 | 33.33 | 稻纵卷叶螟Rice leaf roller |
| 哒嗪硫磷Pyridaphenthione | 安徽池州新赛特有限公司 | 95 | 13.3~16.7 | 333.33 | 叶蝉Leaf hopper |
表1 供试药剂信息与供试浓度
Table 1 Information and lab-trial concentration of the used insecticides.
| 杀虫剂 Insecticide | 生产厂家 Manufacturer | 原药含量 Content/% | 有效成分推荐用药量 Dosage of active ingredient/(g∙667 m-2) | 供试浓度 Lab-trial concentration/(mg·L-1) | 登记对象 Object of registration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 环氧虫啶Cycloxaprid | 上海生农生化制品有限公司 | 96 | 4~6 | 111.11 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 噻虫胺Clothianidin | 江苏中旗作物保护股份有限公司 | 98 | 3~4 | 77.78 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 呋虫胺Dinotefuran | 日本三井化学AGRO株式会社 | 99 | 6~10 | 177.78 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 烯啶虫胺Nitenpyram | 连云港立本农药化工有限公司 | 97 | 4~6 | 111.11 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 噻虫嗪Thiamethoxam | 江苏绿叶农化有限公司 | 98 | 0.75~1.00 | 19.44 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 吡虫啉Imidacloprid | 苏州遍净植保科技有限公司 | 98 | 1~2 | 33.33 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 氯噻啉Imidaclothiz | 南通江山农药化工股份有限公司 | 95 | 1~2 | 33.33 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 噻虫啉Thiacloprid | 山东省联合农药工业有限公司 | 96 | 4.5~6.5 | 122.22 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 啶虫脒Acetamiprid | 宁波三江益农化学有限公司 | 99 | 1.5~2.4 | 43.33 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 吡蚜酮Pymetrozine | 江苏安邦电化有限公司 | 96 | 4~5 | 100.00 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 毒死蜱Chlorpyrifos | 浙江新农化工股份有限公司 | 97 | 43.2~48.0 | 1013.33 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 噻嗪酮Buprofezin | 江苏安邦电化有限公司 | 98 | 6.25~8.75 | 166.67 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 异丙威Isoprocarb | 湖南海利化工股份有限公司 | 98 | 30~40 | 777.78 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 阿维菌素Abamectin | 浙江升华拜克生物股份有限公司 | 85 | 0.6~0.9 | 16.67 | 二化螟Rice stem borer |
| 甲维盐Emamectin benzoate | 浙江升华拜克生物股份有限公司 | 92 | 0.15~0.25 | 4.44 | 小菜蛾Diamondback moth |
| 氟啶虫酰胺Flonicamid | 苏州奥特莱化有限公司 | 96 | 3~5 | 88.88 | 蚜虫Aphid |
| 氟啶虫胺腈Sulfoxaflor | 美国陶氏益农公司 | 95 | 3.3~4.4 | 85.55 | 稻飞虱Rice planthoppers |
| 乙基多杀菌素Spinetoram | 美国陶氏益农公司 | 81 | 1.2~1.8 | 33.33 | 稻纵卷叶螟Rice leaf roller |
| 哒嗪硫磷Pyridaphenthione | 安徽池州新赛特有限公司 | 95 | 13.3~16.7 | 333.33 | 叶蝉Leaf hopper |
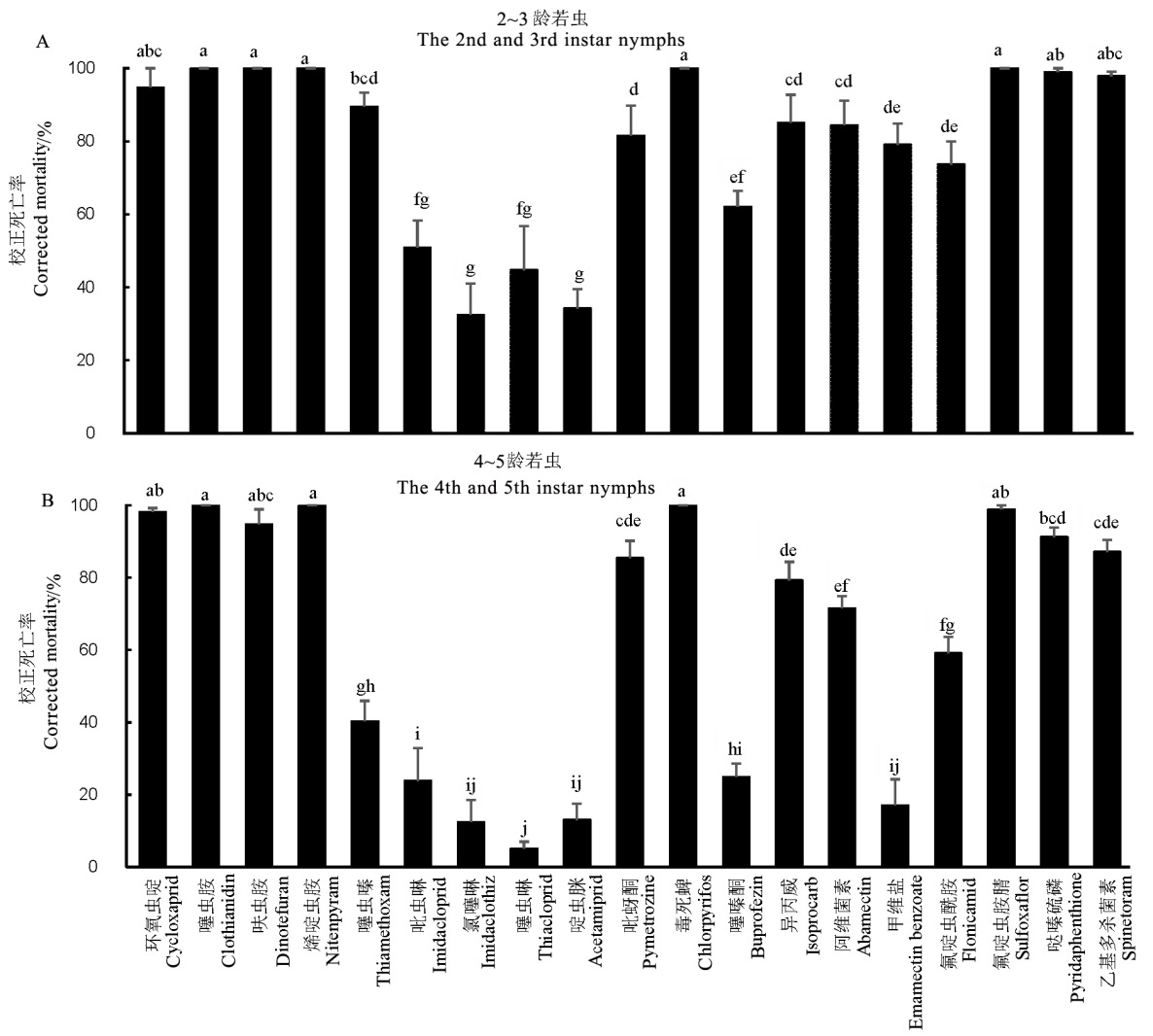
图1 药剂处理褐飞虱若虫4 d后的校正死亡率(平均值±标准误)柱上具相同英文字母者表示经邓肯新复极差比较无显著差异(P>0.05)。
Fig. 1. Corrected mortality of the nymphs of N. lugens 4 d after treatment by different insecticides (Mean ± SE). Bars with the same lowercase letter above show no significant difference by Duncan’s multiple range test(P>0.05).
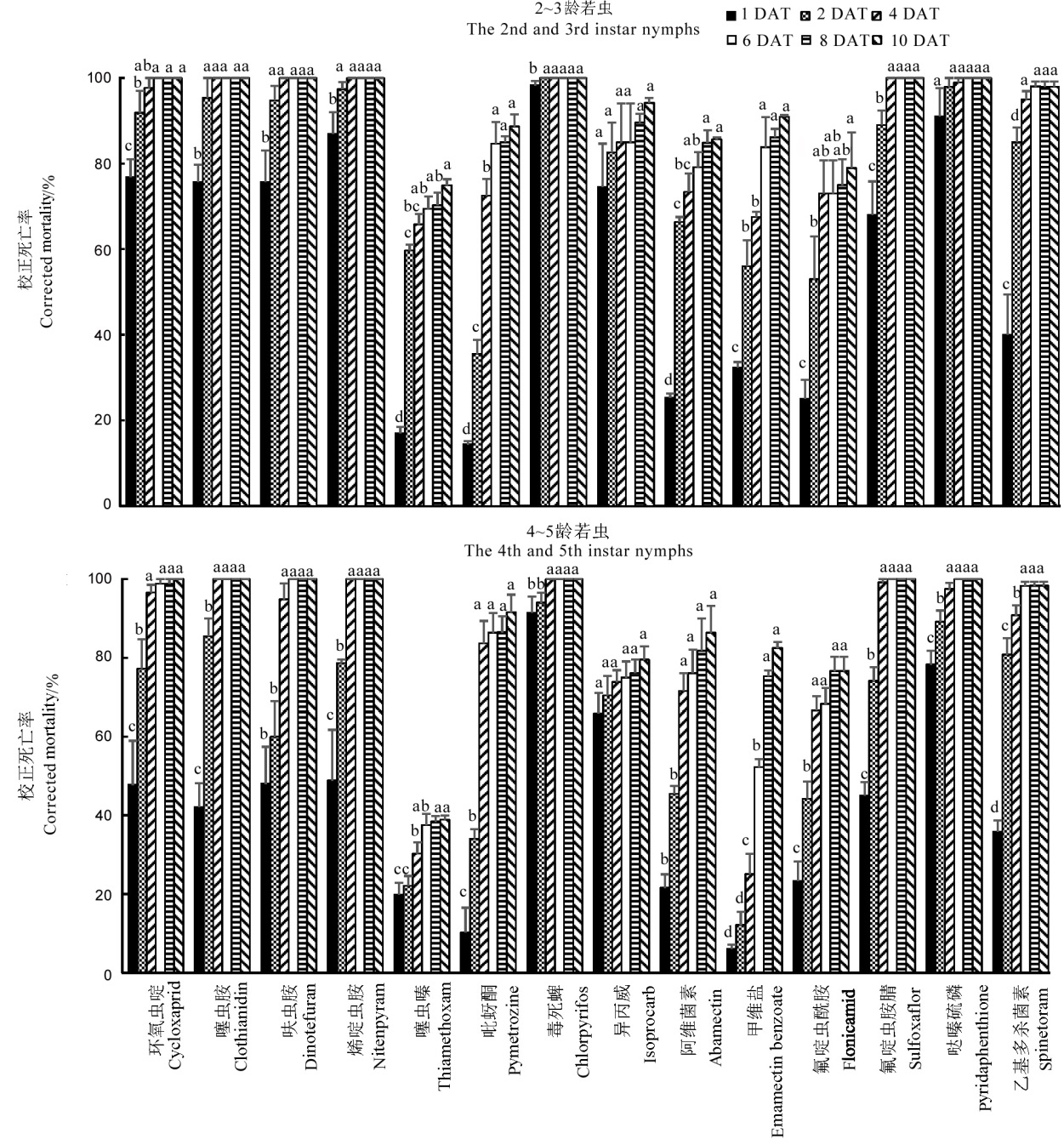
图2 药剂处理褐飞虱若虫1~10 d的校正死亡率(平均值±标准误) DAT, 用药后天数; 同一药剂在不同处理时间, 柱上具相同小写字母者示无显著差异(邓肯新复极差法,P>0.05)。下同。
Fig. 2. Corrected mortality of the nymphs of N. lugens treated by the insecticides for 1 to 10 days(Mean ± SE). DAT, Days after insecticide treatment. The bars with the same lowercase letters above show no significant difference (Duncan’s multiple range test, P>0.05). The same as in figures below.
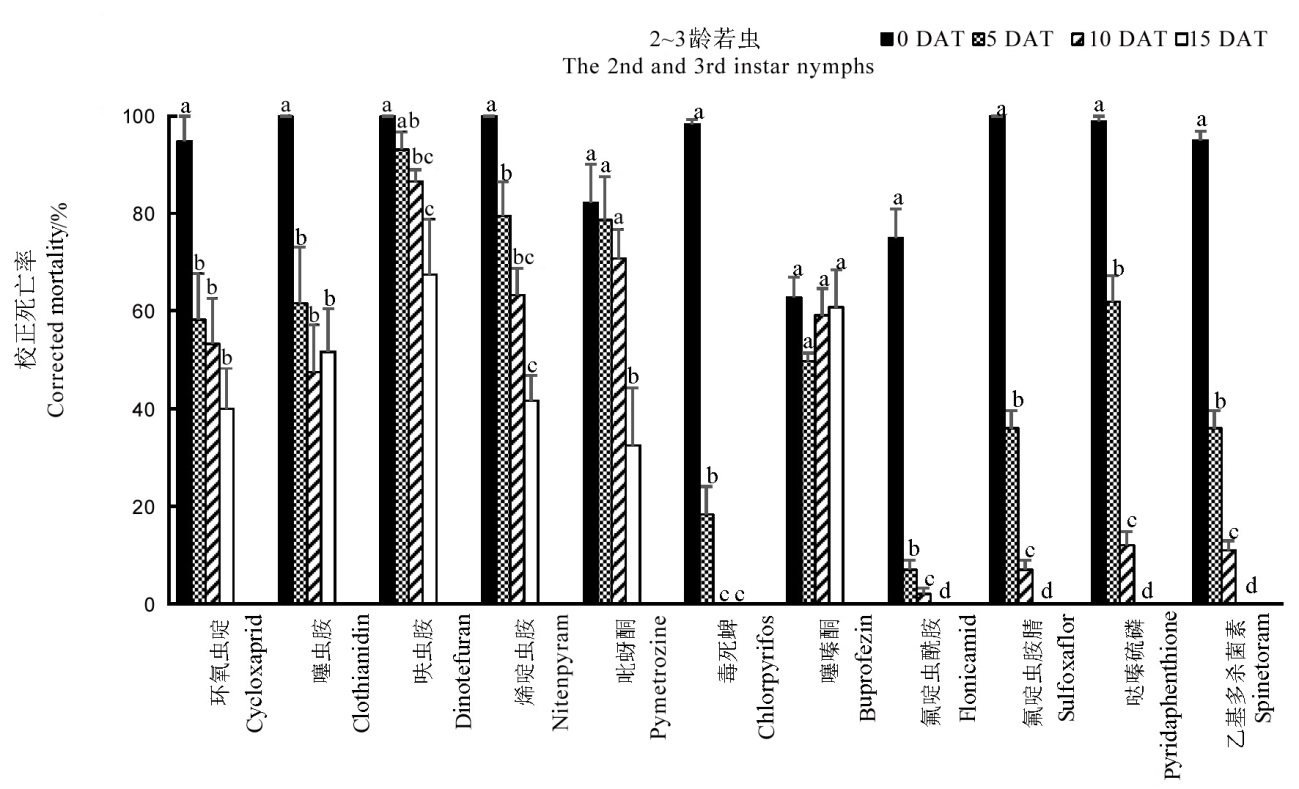
图3 药剂处理后不同时间接2~3龄褐飞虱若虫的校正死亡率(平均值±标准误)
Fig. 3. Mortality of the 2nd and 3rd instar nymphs of N. lugens treated by the insecticides for different days(Mean ± SE).
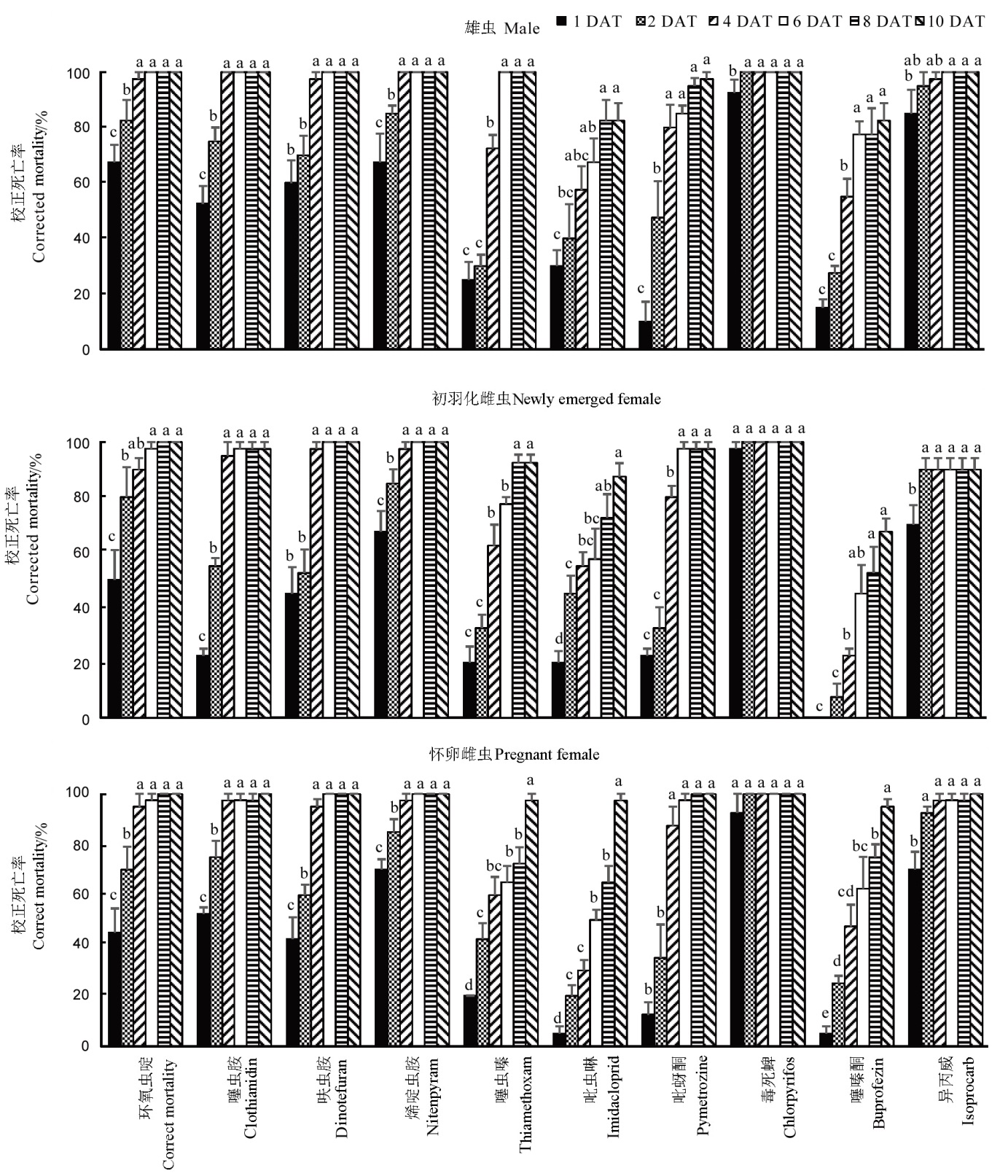
图4 药剂处理褐飞虱雄、雌成虫1~10 d后的校正死亡率(平均值±标准误)
Fig. 4. Corrected mortality of the male and female adults of N. lugens treated by insecticides for 1 to 10 days(Mean ± SE).
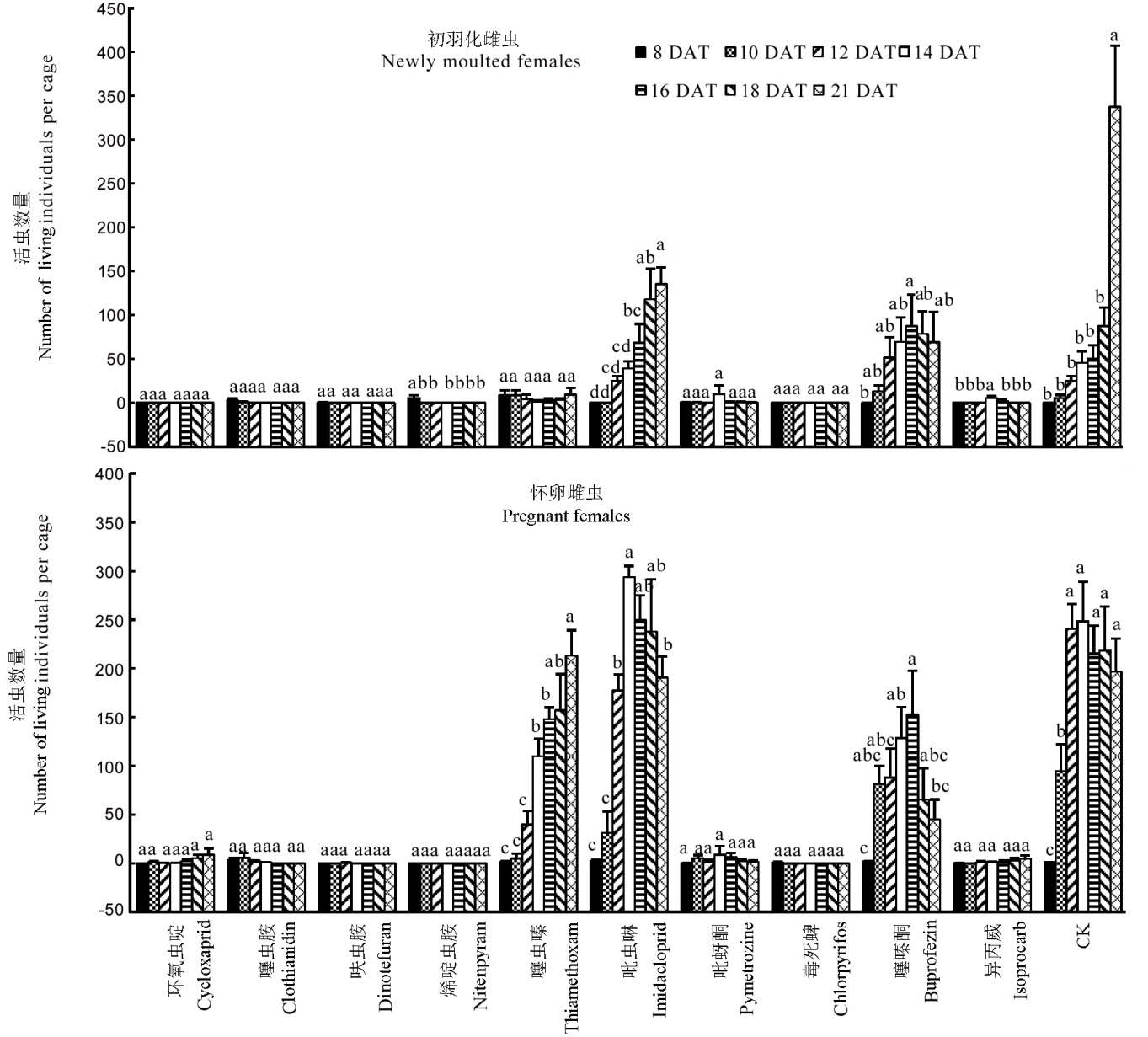
图5 药剂处理褐飞虱初羽化、怀卵雌虫后8~21 d的平均子代数(平均值±标准误)
Fig. 5. Average offspring number of N. lugens on rice seedlings with newly moulted and pregnant females treated by the insecticides for 8 to 21 days(Mean ± SE).
| [1] | 程遐年, 吴进才, 马飞. 褐飞虱研究与防治. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2003: 1-37. |
| Chen X N, Wu J C, Ma F.Brown planthopper:occurrence and control. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2003: 1-37. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | Gurr G M, Liu J, Read D M Y, Catindig J L A, Cheng J A, Lan L P, Heong L K. Parasitoids of Asian rice planthopper (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) pests and prospects for enhancing biological control by ecological engineering.Ann Appl Biol, 2011, 158(2): 149-76. |
| [3] | 李汝铎, 丁锦华,胡国文, 苏德明. 褐飞虱及其种群管理. 上海:复旦大学出版社, 1996: 239-255. |
| Li R D, Ding J H, Hu G W, Su D M.The Brown Planthopper and Its Population Management.Shanghai:Fudan University Press, 1996: 239-255. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | Zhang X, Liu X, Zhu F, Li J, You H, Lu P.Field evolution of insecticide resistance in the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) in China. Crop Prot, 2014, 58: 61-6. |
| [5] | 廖世纯, 韦桥现, 黄所生, 黄立飞, 黎柳锋. 16种杀虫剂对稻飞虱的田间防治效果. 中国农学通报, 2008(9): 345-347. |
| Liao S C, Wei Q X, Huang S S, Huang L F, Li L F.The control effect of 16 insecticides againstNilaparvata lugens. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2008(9): 345-347. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 刘叙杆, 赵兴华, 王彦华, 韦锦捷, 沈晋良, 孔健, 曹明章, 周威君, 罗才宏. 褐飞虱对氟虫腈和新烟碱类药剂的抗性动态变化. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(1): 73-80. |
| Liu X G, Zhao X H, Wang Y H, Wei J J, Shen J L, Kong J, Cao M Z, Zhou W J, Luo C H.Dynamic changes of resistance to fipronil and neonicotinoid insecticides in brown planthopper,Nilaparvata lugens(Homoptera: Delphacidae). Chin J Rice Sci, 2010, 24(1): 73-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 于福强, 黄耀师, 苏州, 武恩明, 王徵, 于春睿. 新颖杀虫剂氟啶虫胺腈. 农药, 2013, 10: 753-755. |
| Yu F Q, Huang Y S, Su Z, Wu E M, Wang H, Yu C R. A novel insecticides sulfoxaflor. Agrochemicals, 2013, 10: 753-755. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 刘康成, 刘文彬, 徐嫣, 梁正坤. 20%呋虫胺SG防治稻褐飞虱田间药效研究. 农业灾害研究, 2013(9): 18-20. |
| Liu K C, Liu W B, Xu Y, Liang Z S. Research on field efficacy of 20% dinotefuran SG for contrilling brown planthopper. J Agric Catastrophol, 2013(9): 18-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 张小磊, 李建洪, 朱福兴, 周锋. 烯啶虫胺和阿维菌素及其复配药剂对褐飞虱的田间防效. 湖北农业科学, 2013, 17: 4110-4112. |
| Zhang X L, Li J B, Zhu F X, Zhou F.Control effect of nitenpyram,avermectin and their mixture to brown planthopper,Nilaparvata lugens. Hubei Agric Sci, 2013, 17: 4110-4112. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 仇是胜, 柏亚罗, 顾林玲. 氟啶虫酰胺的研究开发及市场前景. 现代农药, 2014(5): 6-11. |
| Qiu S S, Bai Y L, Gu L L.Researche development and market prospece of flonicamid.Mod Agochem, 2014(5): 6-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 刘其全,邱良妙, 林仁魁, 占志雄. 10种杀虫剂对水稻稻飞虱的田间药效与评价. 现代农药, 2016(2): 50-53. |
| Liu Q Q, Qiu L M, Lin R K, Zhan Z X.Field efficacy and appraisal of various insecticides on rice planthopper.Mod Agochem, 2016(2): 50-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 肖汉祥, 李燕芳, 张扬, 廖永林, 张振飞. 烯啶虫胺对稻飞虱室内毒力测定及田间药效评价试验. 现代农药, 2013(4): 45-48. |
| Xiao H X, Li Y F, Zhang Y, Liao Y L, Zhang Z F. Toxicity tests and field effect trials of nitenpyram against rice planthopper. Mod Agochem, 2013(4): 45-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 汪爱娟, 李阿根, 张舟娜.呋虫胺等几种新药剂防治水稻稻飞虱与黑尾叶蝉药效试验. 江西农业学报, 2015(3): 53-55. |
| Wang A J, Li A G, Zhang Z N.Control effects of dinotefuran and several new chemicals against rice planthopper andNephotettix bipunctatus in paddy field. Acta Agric Jiangxi, 2015(3): 53-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 朱昌稳. 不同剂量20%呋虫胺SG对水稻褐飞虱的防效. 安徽农业科学, 2014, 16: 5012-5013, 5141. |
| Zhu Z W.Control effect of different doses of 20%cefuroxime insect amine SG on rice BPH (brown palnthopper).J Anhui Agric Sci, 2014, 16: 5012-5013, 5141.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 张洪玉, 吴清阳, 张芝平, 毕强, 董建生, 施顺发, 叶振君. 环氧虫啶的合成新工艺. 世界农药, 2014(6): 21-24. |
| Zhang H Y, Wu Q Y, Zhang Z P, Bi Q, Dong J S, Shi S F, Ye Z J.New technology of cycloxaprid synthesis.World Pestic, 2014(6): 21-24. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 刘萍, 徐海燕, 张芝平, 施顺发, 袁静, 陈杰. 环氧虫啶对褐飞虱毒力的温度效应. 现代农药, 2014(2): 13-14. |
| Liu P, Xu H Y, Zhang Z P, Shi S F, Yuan J, Chen J.Temperature effect on virulence of cycloxaprid aganist Nilaparvata lugens. Mod Agochem, 2000(3): 114-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 农业部农药检定所. 2016农药登记产品信息汇编. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2016: 25-1124. |
| Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals. 2016 Information Compilation of Pesticide Registration Products. Beijing:China Agricultural Press, 2016: 25-1124. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 中华人民共和国农业部. 农药室内生物测定试验准则:杀虫剂第11部分. 稻茎浸渍法. NY/T 1154.11-2008. |
| Ministry of Agriculture, the People’s Republic of China. The People’s Republic of China Agriculture Industry Standard. Guideline for Laboratory Bioassay of Pesticides part 11: Rice Stem-dipping Method. NY/T 1154.11-2008. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | Tang Q Y, Zhang C X.Data processing system(DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research.Insect Sci, 2013, 20(2): 254-260. |
| [20] | 王鹏, 甯佐苹, 张帅, 蒋田田, 谭利蓉, 董嵩, 高聪芬. 我国主要稻区褐飞虱对常用杀虫剂的抗性监测. 中国水稻科学, 2013(2): 191-197. |
| Wang p,Ning Z P,Zhang S, Jiang T T, Tan L R,Dong S,Gao C F. Resistance monitoring to conventional insecticides in brown planthopper,Nilaparvata lugens(Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in main rice growing regions in China. Chin J Rice Sci, 2013(2): 191-197. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 张帅, 邵振润, 李永平. 2013年全国农业有害生物抗药性监测结果及科学用药建议. 中国植保导刊, 2014, 34(3): 55-58. |
| Zhang S, Shao Z Y, Li Y P.Monitoring results of insecticide resistance of agricultural pests in China(2013)and suggestions for scientific use of insecticide.Chin Plant Prot, 2014, 34(3): 55-58. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 张帅. 2017年全国农业有害生物抗药性监测结果及科学用药建议. 中国植保导刊, 2018, 38(4): 52-56. |
| Zhang S.Monitoring results of insecticide resistance of agricultural pests in China 2017 and suggestions for scientific use of insecticide.Chin Plant Prot, 2018, 38(4): 52-56. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 王彦华, 陈进, 沈晋良, 高聪芬, 黄悦, 张久双, 李文红, 周威君.防治褐飞虱的高毒农药替代药剂的室内筛选及交互抗性研究. 中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(5): 519-526. |
| Wang Y H, Chen J, Shen J L, Gao C F, Huang Y, Zhang J S, Li W H, Zhou W J.Laboratory screening and cross-resistance analysis of alternative insecticides for highly-toxic pesticides for controlling brown planthop pers,Nilaparvata lugens. Chin J Rice Sci, 2008, 22(5): 519-526. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 林仁魁, 邹华娇, 吴德飞. 氟啶虫胺腈对褐飞虱的田间防治效果. 农药, 2012(8): 619-620. |
| Lin R K, Zhou H J, Wu D F.Field efficacy of sulfoxafl or 240 g/L SC againstNilaparvata lugens(Stål). Agrochemicals, 2012(8): 619-620. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 夏华兴, 陈明亮, 刘维新, 王健生. 氟啶虫胺腈与乙基多杀菌素混用防治水稻迁飞性害虫田间药效试验. 现代农药, 2013(3): 52-53, 56. |
| Xia H X, Chen M L, Liu W X, Wang J S.Field effect trials on the mixture of sulfoxaflor and spinetoram against rice migratory pests.Mod Agochem, 2013(3): 52-53, 56. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Wu S F, Zeng B, Zheng C, Mu X C, Zhang Y, Hu J, Zhang S, Gao C F, Shen, J L.The evolution of insecticide resistance in the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) of China in the period 2012-2016. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 4586. |
| [27] | 吴春梅, 何木兰, 石丙楼, 余兵, 周爱萍. 50%氟啶虫酰胺水分散粒剂防治水稻稻飞虱田间药效试验. 安徽农学通报, 2016(6): 92, 131. |
| Wu C M, He M L, Shi B L,Yu B, Zhou A P. Field efficacy of 50% sulfoxafl SC against Nilaparvata lugens. Anhui Agric Sci Bull, 2016(6): 92, 131. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | Zhang X, Liao X, Mao K, Zhang K X, Hu W, Li J H. Insecticide resistance monitoring and correlation analysis of insecticides in field populations of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) in China 2012-2014. Pestic Biochem Physiol, 2016, 132: 13-20. |
| [1] | 杨奇欣, 赖凤香, 何佳春, 魏琪, 王渭霞, 万品俊, 傅强. 不同抗感水稻品种对褐飞虱胁迫的高光谱响应特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 81-90. |
| [2] | 程玲, 黄福钢, 邱一埔, 王心怡, 舒宛, 邱永福, 李发活. 籼稻材料570011抗褐飞虱基因的遗传分析及鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 244-252. |
| [3] | 罗举, 杨素文, 贝文勇, 余军伟, 唐健, 刘淑华. 直接多重TaqMan qPCR方法快速鉴定褐飞虱属3种飞虱[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 329-336. |
| [4] | 何佳春, 何雨婷, 万品俊, 魏琪, 赖凤香, 陈祥盛, 傅强. 温度对褐飞虱天敌黄腿双距螯蜂生物学特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 318-326. |
| [5] | 罗举, 唐健, 王爱英, 杨保军, 刘淑华. 基于重组酶介导扩增-侧流层析试纸条的褐飞虱快速鉴定方法[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 96-104. |
| [6] | 马银花, 李萍芳, 董文静, 易松望, 杨芳, 杜波, 金晨钟. 水稻抗性蛋白OsRRK1抗褐飞虱机理分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 512-519. |
| [7] | 潘磊, 王利华, 朱凤, 韩阳春, 王培, 方继朝. 褐飞虱小分子量热激蛋白基因表达特性和功能[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 37-45. |
| [8] | 朱永生, 白建林, 谢鸿光, 吴方喜, 罗曦, 姜身飞, 何炜, 陈丽萍, 蔡秋华, 谢华安, 张建福. 聚合白背飞虱和褐飞虱抗性基因创制杂交水稻恢复系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 421-428. |
| [9] | 降好宇, 曾盖, 郝明, 黄湘桂, 肖应辉. 广谱抗稻瘟病种质75-1-127的褐飞虱抗性基因鉴定及分子标记辅助选择育种[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 227-234. |
| [10] | 张珏锋, 李芳, 钟海英, 陈建明. 制霉菌素对褐飞虱若虫解毒酶、尿酸酶含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 186-190. |
| [11] | 朱欢欢, 陈洋, 万品俊, 王渭霞, 赖凤香, 傅强. 共生菌Arsenophonus、水稻品种和温度对褐飞虱黄绿绿僵菌发病率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 643-651. |
| [12] | 单丹, 王利华, 张月亮, 韩阳春, 牛洪涛, 潘磊, 方继朝. 褐飞虱热激蛋白70在不同温度胁迫下的差异表达特性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(5): 533-541. |
| [13] | 赵晨星, 俞叶微, 许益鹏, 俞晓平. 褐飞虱两个dynamin-1-like基因的克隆、多克隆抗体制备及 表达定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(4): 345-354. |
| [14] | 陈龙飞, 万品俊, 王渭霞, 傅强, 朱廷恒. 褐飞虱NlTgo基因的克隆及功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(6): 653-660. |
| [15] | 郑瑜, 何佳春, 万品俊, 赖凤香, 孙燕群, 林晶晶, 傅强. 褐飞虱IR56种群的致害特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(5): 552-558. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||