
中国水稻科学 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 37-45.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.9034
潘磊1,2, 王利华2, 朱凤3, 韩阳春2, 王培2, 方继朝1,2,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-03-27
修回日期:2019-06-14
出版日期:2020-01-10
发布日期:2020-01-10
通讯作者:
方继朝
作者简介:作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
Lei PAN1,2, Lihua WANG2, Feng ZHU3, Yangchun HAN2, Pei WANG2, Jichao FANG1,2,4,*( )
)
Received:2019-03-27
Revised:2019-06-14
Online:2020-01-10
Published:2020-01-10
Contact:
Jichao FANG
About author:About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】研究褐飞虱小分子量热激蛋白的表达特性和功能,明确其在褐飞虱温度胁迫适应中的作用。【方法】采用BLAST从转录组数据库中筛选褐飞虱小分子量热激蛋白基因序列;利用Bioedit、Mega等分子生物学软件进行序列分析;利用qPCR技术分析目的基因在不同处理下的表达特性;利用原核表达技术研究其功能。【结果】筛选到6个含有α-晶体结构的小分子量热激蛋白基因NlHsp20.9、NlHsp21.6、NlHsp21.9、NlHsp22.4、NlHsp23.1、NlHsp28.7,其ORF长度依次为561、531、570、570、588和735 bp,理论等电点为5.96、5.77、6.32、5.01、5.74和7.74。NlHsp28.7在3龄若虫中的表达量最高,而NlHsp21.9和NlHsp23.1在雌成虫中的表达量最高。雌虫在低温胁迫后所有小分量热激蛋白基因的表达量均下降,高温胁迫后除NlHsp22.4外的其他5个基因表达量不同程度上调;3龄若虫在低温胁迫后一半sHsps表达量下降,另一半上升,高温胁迫后全部上调。转化褐飞虱sHsps的重组大肠杆菌热激存活率显著上升。【结论】褐飞虱小分子量热激蛋白具有龄期和诱导表达特性及热胁迫保护功能,可能在其高温胁迫应激中具有重要作用,在低温胁迫应激中的作用与虫态有关。
中图分类号:
潘磊, 王利华, 朱凤, 韩阳春, 王培, 方继朝. 褐飞虱小分子量热激蛋白基因表达特性和功能[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 37-45.
Lei PAN, Lihua WANG, Feng ZHU, Yangchun HAN, Pei WANG, Jichao FANG. Expression Profiles and Functions of Small Heat Shock Proteins in Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(1): 37-45.
| 用途 Usage | 基因 Gene | 上游引物序列 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 下游引物序列 Reverse primer(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实时荧光定量PCR qPCR | NlHsp20.9 | AGCACGGCTTCATCTCTC | CCTCTCGCCTTTGGTTTC |
| NlHsp21.6 | GTCCTCCAGTATTCCGTTT | TTGTCCTGTTGTTCTTCGT | |
| NlHsp21.9 | TGTTAGCCGCTCCACTCCATT | CCGTGATTGTCCTTGCGTTCT | |
| NlHsp22.4 | TTTGGCGATTTCAGCGTTAT | CCACTGCCTCCTACATTCTT | |
| NlHsp23.1 | GTTTACTCGTCGCTACACC | CTCCATCTTCTCCTGCTT | |
| NlHsp28.7 | GAAATACAGATAAGCGGCACC | GAATACCGTCCTTGAAGTTGG | |
| Ref | TGTCTCTCACACAGTCCCCATCT | GTCAAGTCACGACCAGCCAAG | |
| 原核表达 Procaryotic expression | NlHsp20.9 | ATGTCGCTAGTTCCGCTGCTGT | TTACTGTCCTTCTTTTTCAGCTGGC |
| NlHsp21.6 | ATGTCGTTGTTTCCGTAC | TTAGGCCTTTATCTTCTCC | |
| NlHsp21.9 | ATGTCTCTGCTACCATATCTTTTTG | TCATGTTTCCATTTTATCCTGG | |
| NlHsp22.4 | ATGGCTGAGAGCGGCGTGAGAC | TTATGTGTGATTGGAATCAGTTTTT | |
| NlHsp23.1 | ATGTCTCTGCTACCGATTA | TTAGGTCTCCATCTTCTCC | |
| NlHsp28.7 | ATGAACTCTTGCCGAAAATTG | TCAATTGATAACAATGCGGC |
表1 qPCR和原核表达引物
Table 1 Primer sequences for quantitative real-time PCR and recombinant expression in E. coli.
| 用途 Usage | 基因 Gene | 上游引物序列 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 下游引物序列 Reverse primer(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实时荧光定量PCR qPCR | NlHsp20.9 | AGCACGGCTTCATCTCTC | CCTCTCGCCTTTGGTTTC |
| NlHsp21.6 | GTCCTCCAGTATTCCGTTT | TTGTCCTGTTGTTCTTCGT | |
| NlHsp21.9 | TGTTAGCCGCTCCACTCCATT | CCGTGATTGTCCTTGCGTTCT | |
| NlHsp22.4 | TTTGGCGATTTCAGCGTTAT | CCACTGCCTCCTACATTCTT | |
| NlHsp23.1 | GTTTACTCGTCGCTACACC | CTCCATCTTCTCCTGCTT | |
| NlHsp28.7 | GAAATACAGATAAGCGGCACC | GAATACCGTCCTTGAAGTTGG | |
| Ref | TGTCTCTCACACAGTCCCCATCT | GTCAAGTCACGACCAGCCAAG | |
| 原核表达 Procaryotic expression | NlHsp20.9 | ATGTCGCTAGTTCCGCTGCTGT | TTACTGTCCTTCTTTTTCAGCTGGC |
| NlHsp21.6 | ATGTCGTTGTTTCCGTAC | TTAGGCCTTTATCTTCTCC | |
| NlHsp21.9 | ATGTCTCTGCTACCATATCTTTTTG | TCATGTTTCCATTTTATCCTGG | |
| NlHsp22.4 | ATGGCTGAGAGCGGCGTGAGAC | TTATGTGTGATTGGAATCAGTTTTT | |
| NlHsp23.1 | ATGTCTCTGCTACCGATTA | TTAGGTCTCCATCTTCTCC | |
| NlHsp28.7 | ATGAACTCTTGCCGAAAATTG | TCAATTGATAACAATGCGGC |
| 基因 Gene | 开放阅读框 长度 ORF length/bp | 预测蛋白质大小 Protein length/aa | 功能注释 Annotation | 理论等电点 Theoretical isoelectric point | 理论分子量 Theoretical molecular weight/kDa | Pfam编号 Pfam number | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NlHsp20.9 | 561 | 186 | 致死蛋白Protein lethal(2) essential for life | 5.96 | 20.9 | PF00011 | |||
| NlHsp21.6 | 531 | 176 | α-晶体蛋白α-crystallin A chain-like | 5.77 | 21.6 | PF00011 | |||
| NlHsp21.9 | 570 | 189 | α-晶体蛋白α-crystallin A chain-like | 6.32 | 21.9 | PF00011 | |||
| NlHsp22.4 | 570 | 189 | α-晶体蛋白α-crystallin A chain-like | 5.01 | 22.4 | PF00011 | |||
| NlHsp23.1 | 588 | 195 | 小分子热激蛋白22.0 Small heat shock protein 22.0 | 5.74 | 23.1 | PF00011 | |||
| NlHsp28.7 | 735 | 244 | 30 kDa小分子热激蛋白30 kDa small heat shock protein | 7.74 | 28.7 | PF00011 | |||
表2 褐飞虱小分子量热激蛋白序列特征
Table 2 Deduced protein sequences characteristics of NlHsps from N. lugens.
| 基因 Gene | 开放阅读框 长度 ORF length/bp | 预测蛋白质大小 Protein length/aa | 功能注释 Annotation | 理论等电点 Theoretical isoelectric point | 理论分子量 Theoretical molecular weight/kDa | Pfam编号 Pfam number | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NlHsp20.9 | 561 | 186 | 致死蛋白Protein lethal(2) essential for life | 5.96 | 20.9 | PF00011 | |||
| NlHsp21.6 | 531 | 176 | α-晶体蛋白α-crystallin A chain-like | 5.77 | 21.6 | PF00011 | |||
| NlHsp21.9 | 570 | 189 | α-晶体蛋白α-crystallin A chain-like | 6.32 | 21.9 | PF00011 | |||
| NlHsp22.4 | 570 | 189 | α-晶体蛋白α-crystallin A chain-like | 5.01 | 22.4 | PF00011 | |||
| NlHsp23.1 | 588 | 195 | 小分子热激蛋白22.0 Small heat shock protein 22.0 | 5.74 | 23.1 | PF00011 | |||
| NlHsp28.7 | 735 | 244 | 30 kDa小分子热激蛋白30 kDa small heat shock protein | 7.74 | 28.7 | PF00011 | |||
| 蛋白质 Protein | NlHSP20.9 | NlHSP21.6 | NlHSP21.9 | NlHSP22.4 | NlHSP23.1 | NlHSP28.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NlHSP20.9 | 100.0 | |||||
| NlHSP21.6 | 33.5 | 100.0 | ||||
| NlHSP21.9 | 42.4 | 49.4 | 100.0 | |||
| NlHSP22.4 | 24.1 | 17.2 | 19.3 | 100.0 | ||
| NlHSP23.1 | 39.1 | 50.0 | 68.2 | 20.5 | 100.0 | |
| NlHSP28.7 | 6.9 | 9.8 | 9.8 | 8.2 | 10.6 | 100.0 |
表3 褐飞虱小分子量热激蛋白氨基酸序列间的一致性
Table 3 Identities of six NlHSPs from N. lugens.
| 蛋白质 Protein | NlHSP20.9 | NlHSP21.6 | NlHSP21.9 | NlHSP22.4 | NlHSP23.1 | NlHSP28.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NlHSP20.9 | 100.0 | |||||
| NlHSP21.6 | 33.5 | 100.0 | ||||
| NlHSP21.9 | 42.4 | 49.4 | 100.0 | |||
| NlHSP22.4 | 24.1 | 17.2 | 19.3 | 100.0 | ||
| NlHSP23.1 | 39.1 | 50.0 | 68.2 | 20.5 | 100.0 | |
| NlHSP28.7 | 6.9 | 9.8 | 9.8 | 8.2 | 10.6 | 100.0 |
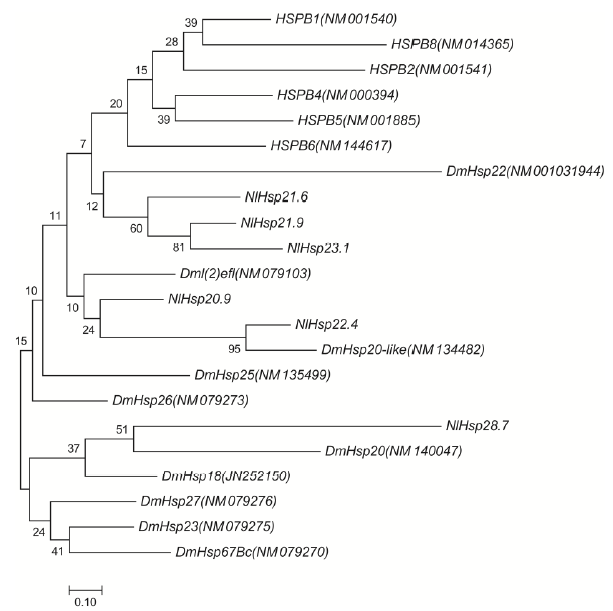
图1 邻接法构建褐飞虱、黑腹果蝇和人类小分子量热激蛋白开放阅读框DNA序列进化树 HSPB开头的基因来自人类,Dm前缀的基因来自于黑腹果蝇,Nl前缀的基因来自褐飞虱。
Fig. 1. Molecular Phylogenetic tree of ORF DNA sequences of sHsps from Nilaparvata lugens, Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens by Neighbor-Joining method. The genes with HSPB starts from Homo sapiens, the genes prefixed with Dm from Drosophila melanogaster, and prefixed with Nl from N. lugens.
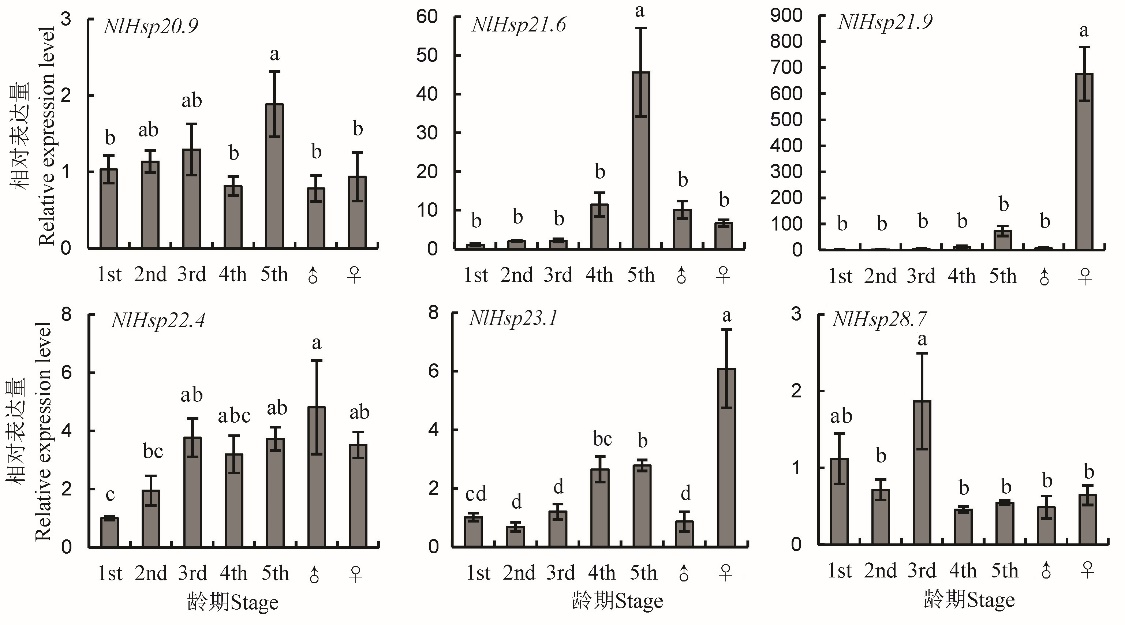
图2 褐飞虱小分子量热激蛋白基因在不同龄期间的相对表达量 柱上标相同小写字母者表示材料间差异未达0.05显著水平。
Fig. 2. Relative expression level of NlHsps in different stage of N. lugens. The same lowercase letters above the bars indicate no significant difference among the materials at the 0.05 level.
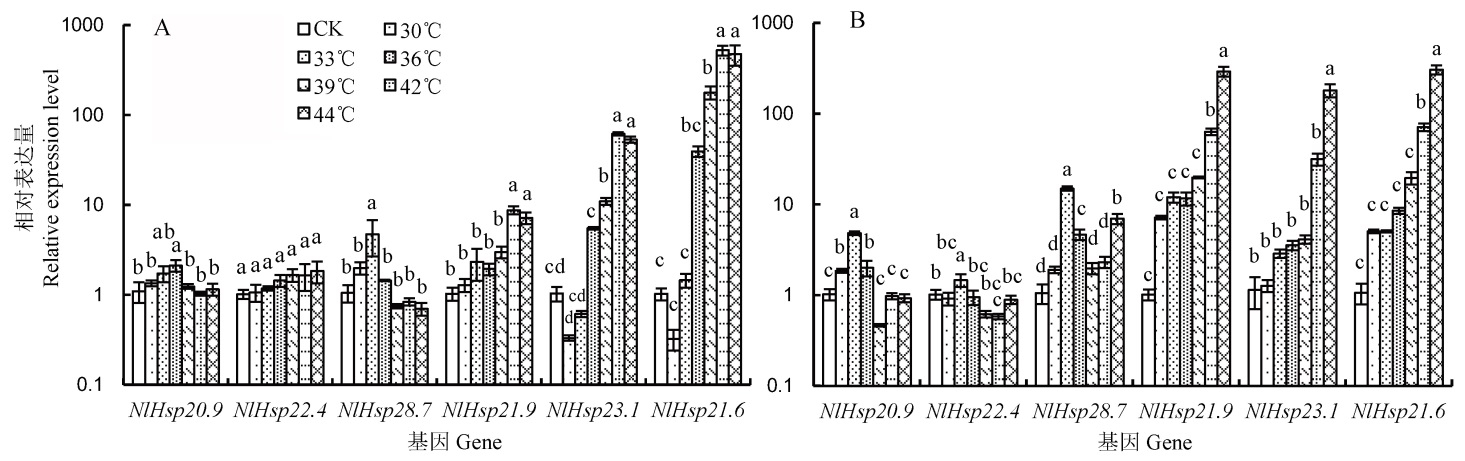
图3 高温热激后褐飞虱雌成虫和3龄若虫小分子量热激蛋白基因的相对表达量 A-雌成虫中的相对表达量; B-3龄若虫中的相对表达量。柱上标相同小写字母者表示处理间差异未达0.05显著水平。
Fig. 3. The diagram showed the relative expression level of sHsps of N. lugens after heat treatment. A, Relative expression level of sHsps of female; B, Relative expression level of sHsps of the 3rd larvae. The same lowercase letters above the bars indicate no significant difference among the treatments at the 0.05 level.
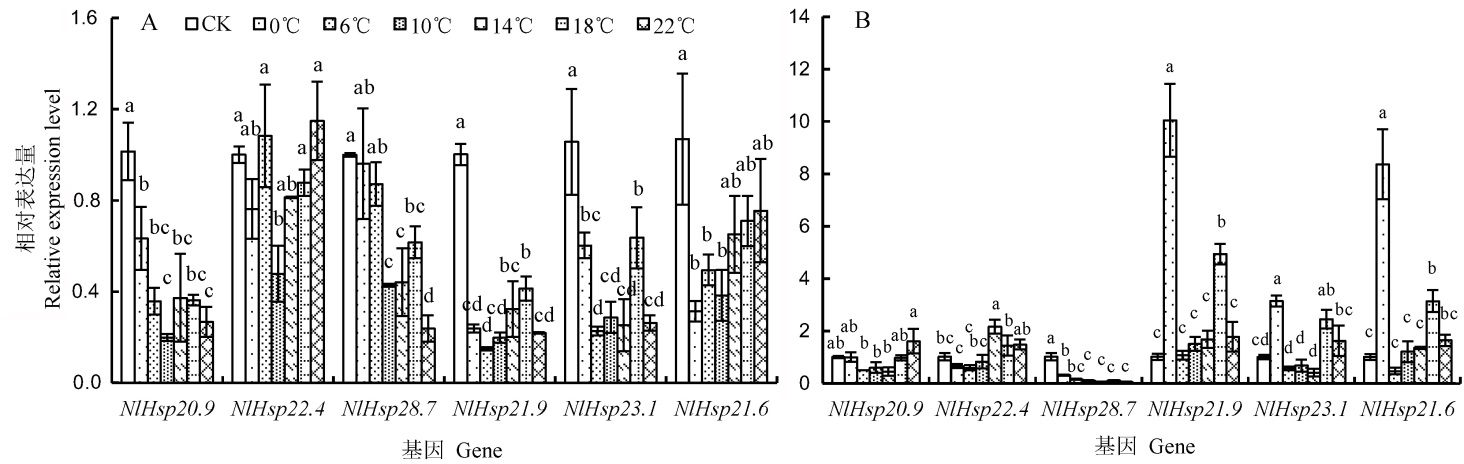
图4 低温处理后褐飞虱雌成虫和3龄若虫小分子量热激蛋白基因的相对表达量 A-雌成虫中的相对表达量; B-3龄若虫中的相对表达量。柱上标相同小写字母者表示处理间差异未达0.05显著水平。
Fig. 4. Relative expression levels of sHsps of N. lugens after cold treatment. A, Relative expression level of sHsps of female after cold shock; B, Relative expression level of sHsps of the 3rd larvae after cold shock. The same lowercase letters above the bars indicate no significant difference among the treatments at the 0.05 level.
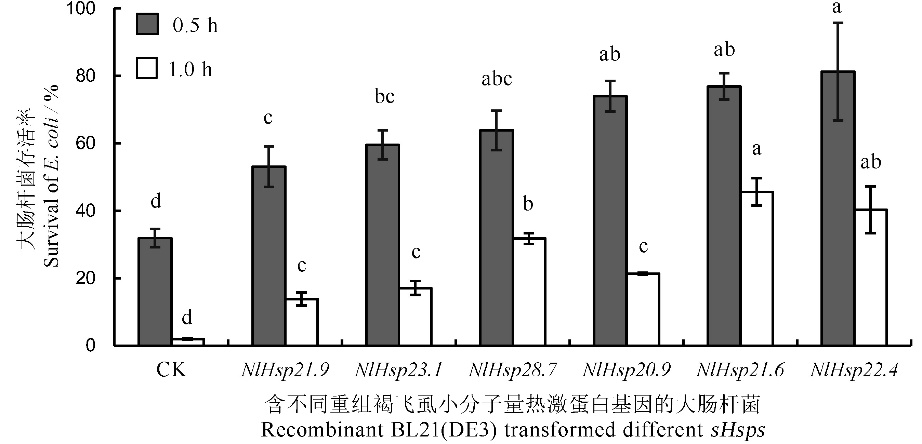
图5 重组大肠杆菌高温热激存活率 柱上标相同小写字母者表示材料间差异未达0.05显著水平。
Fig. 5. Survival of recombinant BL21(DE3) transformed sHsps after heat treatment. The same lowercase letters above the bars indicate no significant difference among the materials at the 0.05 level.
| [1] | Kong L H, Cheng J, Escalada M M.Rice Planthoppers[M]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press, 2015: 1-34. |
| [2] | 石保坤, 胡朝兴, 黄建利, 候茂林. 温度对褐飞虱发育、存活和产卵影响的关系模型[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(20): 5868-5874. |
| Shi B K, Hu C X, Huang J L, Hou M L.The relationship model of temperature on the development, survival and spawning of brown planthopper[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(20): 5868-5874. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Jiranan P, Jeremy P, Jeff B.Heat stress impedes development and lowers fecundity of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)[J]. PLoS ONE, 2012, 7(10): e47413. |
| [4] | 李干金, 徐显浩, 张海亮, 朱敏, 崔旭红. 短时高温暴露对褐飞虱存活和生殖特性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(9): 1747-1755. |
| Li G J, Xu X H, Zhang H L, Zhu M, Cui X H.Effects of short-term high temperature exposure on the survival and reproductive characteristics of brown planthopper[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(9): 1747-1755. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 张焓娇, 杨煌朕, 李保玲. 低温胁迫对褐飞虱种群发生的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2018, 46(31): 146-148, 153. |
| Zhang X J, Yang H B, Li B L.Effects of low temperature stress on the population of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(31): 146-148, 153. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Long Y, Hu C, Shi B, Yang X, Hou M.Effects of temperature on mate location in the planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Environmental Entomology, 2012, 41(5): 1231-1238. |
| [7] | 夏佳音, 张耀洲. 小热休克蛋白的结构和功能[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2013, 23(11): 911-915. |
| Xia J Y, Zhang Y Z.Structure and function of small heat shock proteins[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2013, 23(11): 911-915. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Haslbeck M, Braun N, Stromer T, Richter B, Model N, Weinkauf S, Buchner J.Hsp42 is the general small heat shock protein in the cytosol of Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. EMBO Journal, 2004, 23(3): 638-649. |
| [9] | Friedrich K L, Giese K C, Buan N R, Vierling E.Interactions between small heat shock protein subunits and substrate in small heat shock protein substrate complexes[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2004, 279(2): 1080-1089. |
| [10] | Basha E, Lee G J, Breci L A, Hausrath A C, Buan N, Giese K C, Vierling E.The identity of proteins associated with a small heat shock protein during heat stress in vivo indicates that these chaperones protect a wide range of cellular functions[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2004, 279(9): 7566-7575. |
| [11] | Narberhaus F.Alpha-crystalin-type heat shock proteins: socializing minichaperones in the context of a multichaperone network[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2002, 66(1): 64-93. |
| [12] | Vgh L, Török Z, Balogh G, Glatz A, Piotto S, Horváth I.Membrane regulated stress response: A theoretical and practical approach[J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 2007, 594: 114-131. |
| [13] | Kedersha N L, Gupta M, Li W, Miller I, Anderson P.RNA binding proteins TIA-1 and TIAR link the phophorylation of eIF-2 alpha to the assembly of mammalian stress granules[J]. Journal of Cell Biology, 1999, 147(7): 1431-1442. |
| [14] | Duverger O, Paslaru L, Morange M.HSP25 is involved in two steps of the differentiation of PAM212 keratinocytes[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2004, 279(11): 10252-10260. |
| [15] | Lu K, Chen X, Liu W, Zhou Q.Characterization of heat shock cognate protein 70 gene and its differential expression in response to thermal stress between two wing morphs of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology: Part A, 2016, 199: 47-53. |
| [16] | Lu K, Chen X, Liu W, Zhou Q.Identification of a heat shock protein 90 gene involved in resistance to temperature stress in two wing-morphs of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology: Part A, 2016, 197: 1-8. |
| [17] | Huang H J, Xue J, Zhuo J C, Cheng R L, Xu H J, Zhang C X.Comparative analysis of the transcriptional responses to low and high temperatures in three rice planthopper species[J]. Molecular Ecology, 2017, 26(10): 2726-2737. |
| [18] | Chen X E, Zhang Y L.Identification of multiple small heat-shock protein genes in Plutella xylostella (L.) and their expression profiles in response to abiotic stresses[J]. Cell Stress&Chaperones, 2015, 20(1): 23-35. |
| [19] | Zhang Y Y, Liu Y L, Guo X L, Li Y L, Gao H R, Guo X Q, Xu B H. sHsp22.6, an intronless small heat shock protein gene, is involved in stress defense and development in Apis cerana[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2014, 53: 1-12. |
| [20] | Wang L H, Zhang Y L, Pan L, Hang Y C, Niu H T, Shan D, Fang J C.Induced expression of small heat shock proteins is associated with thermotolerance in female Laodelphax striatellus planthoppers[J]. Cell Stress& Chaperones, 2019, 24(1): 115-123. |
| [21] | 单丹, 王利华, 张月亮, 韩阳春, 牛洪涛, 潘磊, 方继朝. 褐飞虱热激蛋白70在不同温度胁迫下的差异表达特性研究. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(5): 533-541. |
| Shan D, Wang L H, Zhang Y L, Hang Y C, Niu H T, Pan L, Fang J C.Differential expression characteristics of heat shock protein 70 from brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens under different temperature stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Sciences, 2017, 31(5): 533-541. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Jiang J J, Huang L F, Chen H S, Yang L.Identification of reference genes and expression analysis of heat shock protein genes in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae), after exposure to heat stress[J]. Acta Entomology Sinica, 2015, 58(5): 479-486. |
| [23] | Crack J A, Mansour M, Sun Y, MacRae T H. Functional analysis of a small heat shock/α-crystallin protein from Artemia franciscana[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 2002, 269(3): 933-942. |
| [24] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D.Analysis of relative geneexpression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2[-Delta Delta C (T)] method[J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [25] | Kriehuber T, Rattei T, Weinmaier T, Bepperling A, Haslbeck M, Buchner J.Independent evolution of the core domain and its flanking sequences in small heat shock proteins[J]. Faseb Journal, 2010, 24(10): 3633-3642. |
| [26] | Dou W, Tian Y, Liu H, Shi Y, Smagghe G, Wang J J.Characteristics of six small heat shock protein genes from Bactrocera dorsalis: Diverse expression under conditions of thermal stress and normal growth[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology: Part B, 2017, 11: 8-16. |
| [27] | Quan G X, Duan J, Fick W, Kyei-Poku G, Candau J N.Expression profiles of 14 small heat shock protein (sHSP) transcripts during larval diapause and under thermal stress in the spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana (L.)[J]. Cell Stress&Chaper, 2018, 23(6): 1247-1256. |
| [28] | Lu M X, Hua J, Cui Y D, Du Y Z.Five small heat shock protein genes from Chilo suppressalis: Characteristics of gene, genomic organization, structural analysis, and transcription profiles[J]. Cell Stress&Chaper, 2014, 19: 91-104. |
| [29] | Daugaard M, Rohde M, Jäättelä M.The heat shock protein 70 family: Highly homologous proteins with overlapping and distinct functions[J]. FEBS Letters, 2007, 581: 3702-3710. |
| [30] | Jagla T, Dubińska-Magiera M, Poovathumkadavil P, Daczewska M, Jagla K.Developmental expression and functions of the small heat shock proteins in Drosophila[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19: 3441. |
| [1] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [2] | 伏荣桃, 陈诚, 王剑, 赵黎宇, 陈雪娟, 卢代华. 转录组和代谢组联合分析揭示稻曲病菌的致病因子[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 375-385. |
| [3] | 胡丽, 杨范敏, 陈薇兰, 袁华. 水稻SPL家族转录因子的生物学功能研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 223-232. |
| [4] | 杨奇欣, 赖凤香, 何佳春, 魏琪, 王渭霞, 万品俊, 傅强. 不同抗感水稻品种对褐飞虱胁迫的高光谱响应特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 81-90. |
| [5] | 王军, 周晶, 陶亚军, 李文奇, 朱建平, 范方军, 王芳权, 许扬, 陈智慧, 蒋彦婕, 李霞, 杨杰. 基于HRM技术开发水稻糊化温度基因ALK功能标记[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 106-110. |
| [6] | 齐盼盼, 郭留明, 李静, 吕明芳, 袁正杰, 张恒木. 水稻TAF12b基因cDNA克隆及其分子特性鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 577-586. |
| [7] | 黄奇娜, 徐有祥, 林光号, 党洪阳, 郑振权, 张燕, 王晗, 邵国胜, 尹献远. 硅对镉胁迫下水稻苗期抗氧化酶系统及镉离子吸收和转运相关基因表达水平的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 486-496. |
| [8] | 段敏, 谢留杰, 高秀莹, 唐海娟, 黄善军, 潘晓飚. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制广亲和水稻温敏雄性不育系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 233-243. |
| [9] | 程玲, 黄福钢, 邱一埔, 王心怡, 舒宛, 邱永福, 李发活. 籼稻材料570011抗褐飞虱基因的遗传分析及鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 244-252. |
| [10] | 罗举, 杨素文, 贝文勇, 余军伟, 唐健, 刘淑华. 直接多重TaqMan qPCR方法快速鉴定褐飞虱属3种飞虱[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 329-336. |
| [11] | 曹跃炫, 严绘景, 王克剑, 刘朝雷. 苗期快速分选水稻人工无融合生殖克隆种子[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 656-662. |
| [12] | 黄奇娜, 江苏, 汪利民, 张燕, 俞林飞, 李春福, 丁利群, 邵国胜. 低温胁迫后水分对水稻幼苗根系活力和水孔蛋白相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 367-376. |
| [13] | 何佳春, 何雨婷, 万品俊, 魏琪, 赖凤香, 陈祥盛, 傅强. 温度对褐飞虱天敌黄腿双距螯蜂生物学特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 318-326. |
| [14] | 张涛荟, 王海宇, 万华, 张莉萍, 谢振威, 陈可毅, 何晓栋, 赵志刚, 万建民. 水稻雌雄不育突变体Osfma2的细胞学观察及基因图位克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 13-26. |
| [15] | 罗举, 唐健, 王爱英, 杨保军, 刘淑华. 基于重组酶介导扩增-侧流层析试纸条的褐飞虱快速鉴定方法[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 96-104. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||