
中国水稻科学 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 28-36.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.9082
陈涛1,2, 孙旭超1, 张善磊1, 梁文化1, 周丽慧1, 赵庆勇1, 姚姝1, 赵凌1, 赵春芳1, 朱镇1, 张亚东1, 王才林1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-07-12
修回日期:2019-11-20
出版日期:2020-01-10
发布日期:2020-01-10
通讯作者:
王才林
基金资助:
Tao CHEN1,2, Xuchao SUN1, Shanlei ZHANG1, Wenhua LIANG1, Lihui ZHOU1, Qingyong ZHAO1, Shu YAO1, Ling ZHAO1, Chunfang ZHAO1, Zhen ZHU1, Yadong ZHANG1, Cailin WANG1,*( )
)
Received:2019-07-12
Revised:2019-11-20
Online:2020-01-10
Published:2020-01-10
Contact:
Cailin WANG
摘要:
【目的】来自籼稻品种谷梅4号的Pigm是一个对稻瘟病菌具有广谱和持久抗性的重要基因。为有效提高Pigm基因的选择效率,有必要开发具有特异性的共显性分子标记进行辅助育种。【方法】本研究根据谷梅4号Pigm位点存在的特异性核苷酸变异,利用Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR和KASP两种不同的基因分型技术开发出分子标记T-Pigm和K-Pigm,对不同品种(品系)以及淮稻9号/谷梅4号的F2分离群体进行基因型检测,并结合穗颈瘟人工接种鉴定,对标记的准确性进行评价。【结果】序列比对分析表明,谷梅4号Pigm位点中Pigm-Nbs2基因起始密码子上游515 bp处存在一个特殊的单核苷酸变异。利用已开发的两种类型的分子标记能够有效区分3种不同的基因型,且基因型与穗颈瘟人工接种鉴定结果完全一致。【结论】利用分子标记T-Pigm和K-Pigm可以实现对Pigm基因型快速、准确的检测,加快抗稻瘟病水稻新品种的选育进程。
中图分类号:
陈涛, 孙旭超, 张善磊, 梁文化, 周丽慧, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 赵凌, 赵春芳, 朱镇, 张亚东, 王才林. 稻瘟病广谱抗性基因Pigm特异性分子标记的开发和应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 28-36.
Tao CHEN, Xuchao SUN, Shanlei ZHANG, Wenhua LIANG, Lihui ZHOU, Qingyong ZHAO, Shu YAO, Ling ZHAO, Chunfang ZHAO, Zhen ZHU, Yadong ZHANG, Cailin WANG. Development and Verification of Specific Molecular Markers for Pigm Gene Associated with Broad-spectrum Resistance to Rice Blast[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(1): 28-36.

图1 谷梅4号与测序品种及含Pi9、Pi2、Piz、Piz-t、Pi40、Pi50基因品种(系)部分序列的比对数字表示碱基在水稻基因组中的物理位置;斜体碱基表示有差异的核酸变异;灰色碱基表示起始密码子上游515 bp处存在的特异单核苷酸变异。
Fig. 1. Sequence alignment of Gumei 4, sequencing varieties and other varieties(lines) carrying Pi9, Pi2, Piz, Piz-t, Pi40, Pi50. The numbers indicate physical location in rice genomic sequence. The differential bases in sequences are in Italic and the specific single nucleotide variation in -515 bp of Pigm-Nbs2 gene initiation codon is in gray.
| 标记名称 Marker name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence(5′-3′) | 物理位置 Physical location / bp |
|---|---|---|
| S-Primers | GGAATCGCTCCATTTTCGTA | 10 380 398-10 380 417 |
| GACGGTTTAGGTGCGCTTTA | 10 380 779-10 380 798 | |
| T-Pigm | T-Pigm-O-F: TAAGAATTGAGGTGGTTAGTTGAACGGAGA | 10 380 094-10 380 123 |
| T-Pigm-O-R: TTGCATGGCTCCACTACCCACTATAAG | 10 380 742-10 380 768 | |
| T-Pigm-I-F: TGAAAATAAAAATGGTATGATGGTTACG | 10 380 474-10 380 501 | |
| T-Pigm-I-R: TAGGGATGAAACGGCTCGAAAACGATCG | 10 380 501-10 380 528 | |
| K-Pigm | K-F(G): AAAAATGAAAATAAAAATGGTATGATGGTTTCG FAM-labelled | 10 380 469-10 380 501 |
| K-F(C): AAAAATGAAAATAAAAATGGTATGATGGTTTCC HEX-labelled | 10 380 469-10 380 501 | |
| K-R: AGGGATGAAACGGCTCGAAAACGAA | 10 380 503-10 380 527 |
表1 检测水稻Pigm基因特异SNP变异的测序引物和相关标记
Table 1 Sequencing primers and markers to detect the specific SNP variation for Pigm gene
| 标记名称 Marker name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence(5′-3′) | 物理位置 Physical location / bp |
|---|---|---|
| S-Primers | GGAATCGCTCCATTTTCGTA | 10 380 398-10 380 417 |
| GACGGTTTAGGTGCGCTTTA | 10 380 779-10 380 798 | |
| T-Pigm | T-Pigm-O-F: TAAGAATTGAGGTGGTTAGTTGAACGGAGA | 10 380 094-10 380 123 |
| T-Pigm-O-R: TTGCATGGCTCCACTACCCACTATAAG | 10 380 742-10 380 768 | |
| T-Pigm-I-F: TGAAAATAAAAATGGTATGATGGTTACG | 10 380 474-10 380 501 | |
| T-Pigm-I-R: TAGGGATGAAACGGCTCGAAAACGATCG | 10 380 501-10 380 528 | |
| K-Pigm | K-F(G): AAAAATGAAAATAAAAATGGTATGATGGTTTCG FAM-labelled | 10 380 469-10 380 501 |
| K-F(C): AAAAATGAAAATAAAAATGGTATGATGGTTTCC HEX-labelled | 10 380 469-10 380 501 | |
| K-R: AGGGATGAAACGGCTCGAAAACGAA | 10 380 503-10 380 527 |
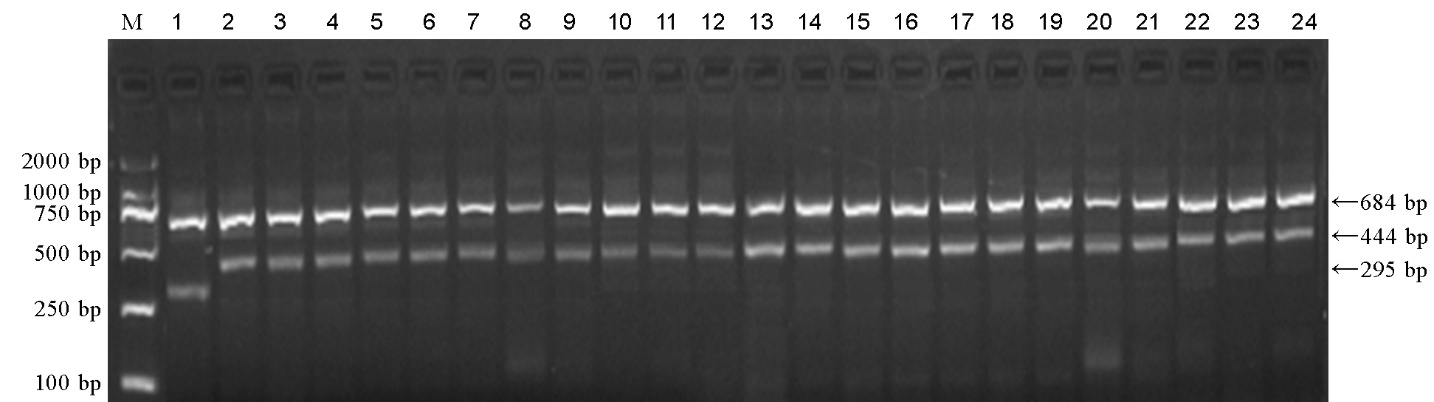
图2 T-Pigm标记对不同水稻品种(系)Pigm基因型的检测 M–DNA分子量标准(DL2000);1–谷梅4号;2–IRBL9-W(Pi9);3–IRBLz5-CA-1(Pi2);4–IRBLz-Fu(Piz);5–IRBLzt-T(Piz-t);6–IR65482-4-13(Pi40);7–二八占(Pi50);8–24–部分籼、粳稻品种(系)依次为93-11、中恢8006、成恢727、红恢589、先恢527、明恢63、广恢998、川香29B、珍汕97B、培矮64S、日本晴、嘉58、淮稻9号、南粳9108、盐丰47、吉粳88、龙粳29。
Fig. 2. Electrophoresis detection of Pigm genotypes by T-Pigm marker in different rice varieties or lines. M, DNA marker (DL2000); 1, Gumei 4; 2, IRBL9-W (Pi9); 3, IRBLz5-CA-1(Pi2); 4, IRBLz-Fu (Piz); 5, IRBLzt-T (Piz-t); 6, IR65482-4-13 (Pi40); 7, Erbazhan; 8-24, Parts of indica and japonica rice varieties or lines, including 93-11, Zhonghui 8006, Chenghui 727, Honghui 589, Xianhui 527, Minghui 63, Guanghui 998, Chuanxiang 29B, Zhenshan 97B, Peiai 64S, Nippobare, Jia 58, Huaidao 9, Nanjing 9108, Yanfeng 47, Jijing 88, Longjing 29.
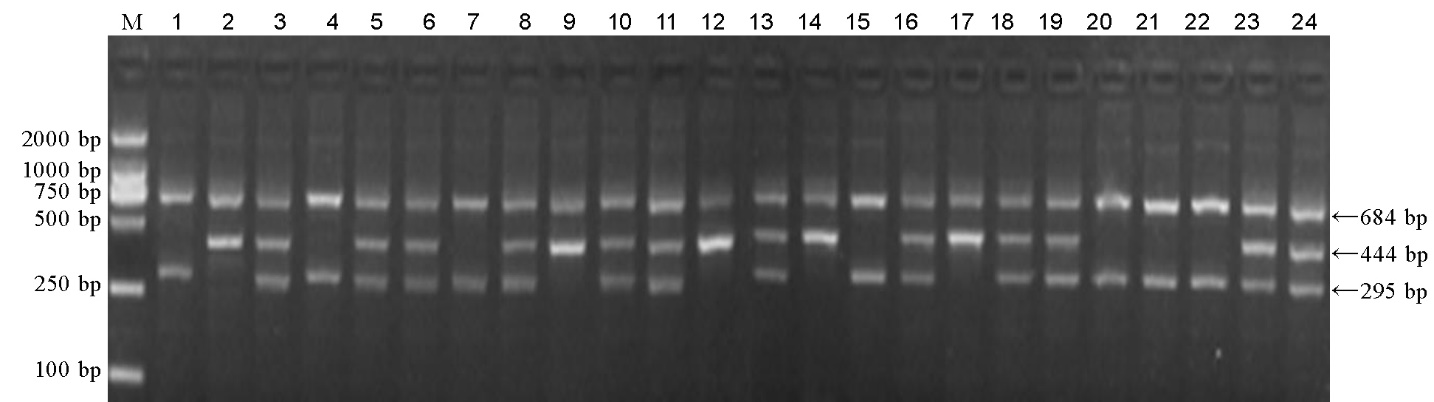
图3 T-Pigm标记对淮稻9号/谷梅4号F2群体Pigm基因型的检测 M–DNA分子量标准(DL2000);1–谷梅4号;2–淮稻9号;3–淮稻9号/谷梅4号 F1;4–24为部分F2分离单株。
Fig. 3. Electrophoresis detection of Pigm genotypes by T-Pigm marker in F2 population derived from Huaidao 9/Gumei 4. M, DNA marker (DL2000); 1, Gumei 4; 2, Huaidao 9; 3, F1 (Huaidao 9/Gumei 4); 4-24, Parts of plants from F2 population.
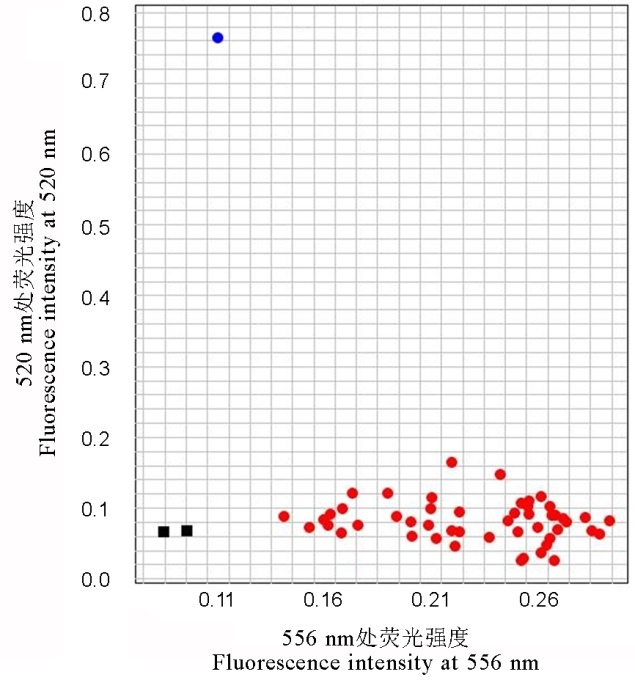
图4 K-Pigm标记对不同水稻品种(系)Pigm基因型的检测黑色方框代表无DNA模板的空白对照;蓝色和红色圆点分别代表PigmPigm纯合基因型(碱基G的等位变异)和pigmpigm纯合基因型(碱基C的等位变异)。供试品种(系)分别为谷梅4号、IRBL9-W(Pi9)、IRBLz5-CA-1 (Pi2)、IRBLz-Fu(Piz)、IRBLzt-T(Piz-t)、IR65482-4-13(Pi40)、二八占(Pi50)、镇恢084、93-11、中恢8006、成恢727、宜恢1577、红恢589、先恢527、明恢63、航1号、金恢2号、广恢998、宁香1B、川香29B、荃93-11B、珍汕97B、03S、Bph68S、P88S、培矮64S、日本晴、越光、一品、珍富10号、楚粳39、毕粳44、宝农34、浙粳97、嘉58、南粳505、南粳9108、淮稻9号、豫粳8号、临稻17、圣稻20、宁粳40号、伊粳12号、新稻32号、津粳263、沈农265、辽粳10号、盐丰47、吉粳88和龙粳29。
Fig. 4. Detection of Pigm genotypes by K-Pigm marker in different rice varieties or lines. Black boxes indicate the negative controls with no DNA template; Blue and red dots showed PigmPigm homozygous genotype (allelic variation G) and pigmpigm homozygous genotype (allelic variation C), respectively.The DNA of the tested varieties (lines) are Gumei 4, IRBL9-W(Pi9), IRBLz5-CA-1, IRBLz-Fu (Piz), IRBLzt-T (Piz-t), IR65482-4-13(Pi40), Erbazhan(Pi50), Zhenhui 084, 93-11, Zhonghui 8006, Chenghui 727, Yihui 1577, Honghui 589, Xianhui 527, Minghui 63, Hang 1, Jinghui 2, Guanghui 998, Ningxiang 1B, Chuanxiang 29B, Quan 93-11B, Zhenshan 97B, 03S, Bph68S, P88S, Peiai 64S, Nippobare, Koshihikari, Yipin, Zhenfu 10, Chujing 39, Bijing 44, Baonong 34, Zhejing 97, Jia 58, Nanjing 505, Nanjing 9108, Huaidao 9, Yujing 8, Lindao 17, Shengdao 20, Ningjing 40, Yijing 12, Xindao 32, Jinjing 263, Shennong 265, Liaojing10, Yanfeng 47, Jijing 88 and Longjing 29, respectively.
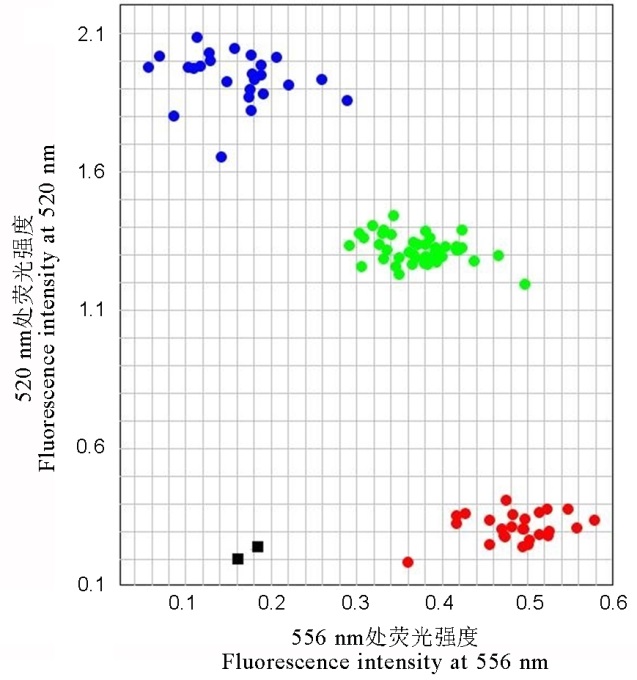
图5 K-Pigm标记对淮稻9号/谷梅4号F2群体Pigm基因型的检测黑色方框代表无DNA模板的空白对照;蓝色、绿色和红色圆点分别代表PigmPigm纯合基因型(碱基G的等位变异), Pigmpigm杂合基因型(同时具有碱基G/C的等位变异)和pigm pigm纯合基因型(碱基C的等位变异)。
Fig. 5. Detection of Pigm genotypes by K-Pigm marker in F2 population derived from Huaidao 9 and Gumei 4. Black boxes indicate the negative controls with no DNA template; Blue, green and red dots showed PigmPigm homozygous genotype (allelic variation G), Pigmpigm heterozygous (allelic variations G/C) and pigmpigm homozygous genotype (allelic variation C), respectively.
| 基因型 Genotype | 等位变异 Allelic variation | 不同基因型单株数 No. of individual plants | 不同病情等级的单株数 No. of individual plants with different disease grades | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高抗HR | 抗R | 中抗MR | 中感MS | 感S | 高感HS | |||
| PigmPigm | GG | 62 | 3 | 35 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pigmpigm | GC | 166 | 4 | 74 | 88 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| pigmpigm | CC | 72 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 31 | 28 | 8 |
表2 淮稻9号/谷梅4号F2群体中三种Pigm基因型单株对穗颈瘟的抗性表现
Table 2 Resistance to neck blast disease for individual plants of the three different genotypes derived from Huaidao 9 and Gumei 4.
| 基因型 Genotype | 等位变异 Allelic variation | 不同基因型单株数 No. of individual plants | 不同病情等级的单株数 No. of individual plants with different disease grades | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高抗HR | 抗R | 中抗MR | 中感MS | 感S | 高感HS | |||
| PigmPigm | GG | 62 | 3 | 35 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pigmpigm | GC | 166 | 4 | 74 | 88 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| pigmpigm | CC | 72 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 31 | 28 | 8 |
| [1] | 孙国昌. 关于水稻稻瘟病病原菌学名的正确使用[J]. 菌物学报, 1994, 13(2): 158-159. |
| Sun G C.Notes of the correct name of pathogen of rice blast fungus[J]. Acta Mycologica Sinica, 1994, 13(2): 158-159. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | Wilson R A, Talbot N J.Under pressure: Investigating the biology of plant infection by Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2009, 7(3): 185-195. |
| [3] | 陆明红, 刘万才, 朱凤, 张求东, 夏风. 2014年稻瘟病重发原因分析与治理对策探讨[J]. 中国植保导刊, 2015, 35(6): 35-39. |
| Lu M H, Liu W C, Zhu F, Zhang Q D, Xia F.Discussion and analysis of the solution and cause for rice blast outbroke in 2014[J]. China Plant Protection, 2015, 35(6): 35-39. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | Sharma T R, Rai A K, Gupta S K, Vijayan J, Devanna B N, Ray S.Rice blast management through host-plant resistance: Retrospect and prospects[J]. Agricultural Research, 2012, 1(1): 37-52. |
| [5] | 袁熹, 李大勇, 宋凤鸣. 水稻对稻瘟病的广谱抗性: 分子机制及其育种应用[J]. 植物生理学报, 2017, 53(8): 1348-1358. |
| Yuan X, Li D Y, Song F M.Rice broad-spectrum resistance against blast disease: Molecular mechanism and applications[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2017, 53(8): 1348-1358. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Deng Y W, Zhu X D, Shen Y, He Z H.Genetic characterization and fine mapping of the blast resistance locus Pigm(t) tightly linked to Pi2 and Pi9 in a broad-spectrum resistant Chinese variety[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 113(4): 705-713. |
| [7] | Zhao H J, Wang X Y, Jia Y L, Minkenberg B, Wheatley M, Fan J B, Jia M H, Famoso A, Edwards J D, Wamishe Y S, Valent B, Wang G L, Yang Y N.The rice blast resistance gene Ptr encodes an atypical protein required for broad-spectrum disease resistance[J]. Nature Communication, 2018, 9(1): 2039. |
| [8] | Li W T, Zhu Z W, Chern M S, Yin J J, Yang C, Ran L, Cheng M P, He M, Wang K, Zhao W, Ma B T, Qin P, Chen W L, Wang Y P, Liu J L, Wang W M, Wu J J, Li P, Wang J R, Zhu L H, Li S G, Chen X W.A natural allele of a transcription factor in rice confers broad-spectrum blast resistance[J]. Cell, 2017, 170(1): 114-126. |
| [9] | Fukuoka S, Saka N, Koga H, Ono K, Shimizu T, Ebana K, Hayashi N, Takahashi A, Hirochika H, Okuno K, Yano M.Loss of function of a proline-containing protein confers durable disease resistance in rice[J]. Science, 2009, 325(5943): 998-1001. |
| [10] | Wu Y Y, Chen Y, Pan C H, Xiao N, Yu N, Li Y H, Zhang X X, Pan X B, Chen X J, Liang C Z, Dai Z Y, Li A H.Development and evaluation of near-isogenic lines with different blast resistance alleles at the Piz locus in japonica rice from the lower region of the Yangtze River, China[J]. Plant Disease, 2017, 101(7): 1283-1291. |
| [11] | Deng Y W, Zhai K R, Xie Z, Yang D Y, Zhu X D, Liu J Z, Wang X, Qin P, Yang Y Z, Zhang G M, Li Q, Zhang J F, Wu S Q, Milazzo J, Mao B Z, Wang E T, Xie H A, Tharreau D, He Z H.Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328): 962-965. |
| [12] | 张礼霞, 王林友, 范宏环, 王建军. 利用Pigm基因改良粳稻保持系的稻瘟病抗性研究[J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(3): 424-431 |
| Zhang L X, Wang L Y, Fan H H, Wang J J.Study on improving rice blast resistance of japonica maintainer line by introducing Pigm gene[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(3): 424-431. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 曾生元, 李闯, 杜灿灿, 孙立亭, 景德道, 林添资, 余波, 钱华飞, 姚维成, 周义文, 龚红兵. Pigm特异性选择标记的开发及其在粳稻穗颈瘟抗性育种中的利用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 453-461. |
| Zeng S Y, Li C, Du C C, Sun L T, Jing D D, Lin T Z, Yu B, Qian H F, Yao W C, Zhou Y W, Gong H B.Development of specific markers for Pigm in marker-assisted breeding of panicle blast resistant japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(5): 453-461. (In Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Ye S, Dhillon S, Ke X Y, Collins A R, Day I N M. An efficient procedure for genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2001, 29(17): E88. |
| [15] | He C L, Holme J, Anthony J.SNP genotyping: the KASP assay[J]. Crop Breeding, 2014, 1145: 75-86. |
| [16] | Chen X, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho Y G, McCouch S R. Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1997, 95(4): 553-567. |
| [17] | 中华人民共和国农业部. 水稻品种试验稻瘟病抗性鉴定与评价技术规程: NY/T 2646-2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. |
| Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Technical specification for identification and evaluation of blast resistance in rice variety region test: NY/T 2646-2014[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2014. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 刘辉, 孟德龙, 查日扬, 徐大勇. 江苏水稻品种主效抗性基因鉴定及应用评价[J]. 福建农业学报, 2015, 30(5): 452-458. |
| Liu H, Meng D L, Zha R Y, Xu D Y.Identification and evaluation on blast resistance of rice varieties in Jiangsu[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 30(5): 452-458. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 王军, 宫丹妮, 杨杰, 朱金燕, 范方军, 李文奇, 王芳权, 仲维功. 江苏省粳稻品种抗稻瘟病基因型与穗颈瘟抗性分析[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2016, 32(2): 250-256. |
| Wang J, Gong D N, Yang J, Zhu J Y, Fan F J, Li W Q, Wang F Q, Zhong W G.Relationship between rice blast resistance genotypes and neck blast resistance of japonica rice in Jiangsu Province[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 32(2): 250-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 宋兆强, 刘艳, 王宝祥, 王芳权, 迟铭, 刘金波, 陈庭木, 方兆伟, 邢运高, 徐波, 杨波, 杨杰, 徐大勇. 稻瘟病抗性基因Pi-ta、Pi-b、Pi-54、Pi-km的育种应用价值评价[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2017, 33(5): 968-974. |
| Song Z Q, Liu Y, Wang B X, Wang F Q, Chi M, Liu J B, Chen T M, Fang Z W, Xing Y G, Xu B, Yang B, Yang J, Xu D Y.Application value of blast resistant genes Pi-ta, Pi-b, Pi-54 and Pi-km in rice breeding[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 33(5): 968-974. (In Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Zhou B, Qu S H, Liu G F, Dolan M, Sakai H, Lu G D, Bellizzi M, Wang G L.The eight amino-acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2006, 19(11): 1216-1228. |
| [22] | Qu S H, Liu G F, Zhou B, Bellizzi M, Zeng L R, Dai L Y, Han B, Wang G L.The broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of multigene family in rice[J]. Genetics, 2006, 172(3): 1901-1904. |
| [23] | Su J, Wang W J, Han J L, Chen S, Wang C Y, Zeng L X, Feng A Q, Yang J Y, Zhou B, Zhu X Y.Functional divergence of duplicated genes results in a novel blast resistance gene Pi50 at the Pi2/9 locus[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2015, 128(11): 2213-2225. |
| [24] | 郭长江. 抗稻瘟病基因快速演化位点的遗传分析和人工进化研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2017. |
| Guo C J.Genetic analysis and artificial evolution of rapidly evolving rice blast resistance genes[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 田红刚, 陈红旗, 胡江, 雷财林, 朱旭东, 钱前. 抗稻瘟病基因Pigm导入对寒地粳稻抗病性和产量性状的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2016, 47(5): 520-526. |
| Tian H G, Chen H Q, Hu J, Lei C L, Zhu X D, Qian Q.Effect of introgressed Pigm gene on rice blast and yield traits of japonica rice in cold area[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2016, 47(5): 520-526. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 王飞, 王立广, 潘梅瑶, 钮中一, 周勇, 梁国华. 水稻抗稻瘟病Pigm(t)基因的分子标记辅助选择和利用[J]. 华北农学报, 2016, 31(1): 51-56. |
| Wang F, Wang L G, Pan M Y, Niu Z Y, Zhou Y, Liang G H.Marker-assisted selection and application of blast resistant gene Pigm(t) in rice[J]. Acta Agricultural Boreali-Sinica, 2016, 31(1): 51-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 吕学莲, 白海波, 惠建, 蔡正云, 张龙飞, 李树华. 利用广谱抗病基因Pigm改良水稻稻瘟病抗性[J]. 分子植物育种, 2017, 15(11): 4336-4342. |
| Lv X L, Bai H B, Hui J, Cai Z Y, Zhang L F, Li S H.The improvement of rice blast resistance by broad-spectrum gene Pigm[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2017, 15(11): 4336-4342. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 于苗苗, 戴正元, 潘存红, 陈夕军, 余玲, 张晓祥, 李育红, 肖宁, 龚红兵, 盛生兰, 潘学彪, 张洪熙, 李爱宏. 广谱稻瘟病抗性基因Pigm和Pi2的抗谱差异及与Pi1的互作效应[J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(11): 1927-1934. |
| Yu M M, Dai Z Y, Pan C H, Chen X J, Yu L, Zhang X X, Li Y H, Xiao N, Gong H B, Sheng S L, Pan X B, Zhang H X, Li A H.Resistance spectrum difference between two broad-spectrum blast resistance genes, Pigm and Pi2, and their interaction effect on Pi1[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(11): 1927-1934. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Wu Y Y, Xiao N, Yu L, Pan C H, Li Y H, Zhang X X, Liu G Q, Dai Z Y, Pan X B, Li A H.Combination patterns of major R genes determine the level of resistance to the M. oryzae in rice[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6): e0126130. |
| [1] | 杨好, 黄衍焱, 王剑, 易春霖, 石军, 谭楮湉, 任文芮, 王文明. 水稻中八个稻瘟病抗性基因特异分子标记的开发及应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 525-534. |
| [2] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [3] | 童琪, 王春燕, 阙亚伟, 肖宇, 王政逸. 稻瘟病菌热激蛋白(HSP)40编码基因MoMHF6的鉴定及功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 563-576. |
| [4] | 陈明亮, 熊文涛, 沈雨民, 熊焕金, 罗世友, 吴小燕, 胡兰香, 肖叶青. 广谱抗稻瘟病水稻保持系赣香B的抗性遗传解析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 470-477. |
| [5] | 李刚, 高清松, 李伟, 张雯霞, 王健, 程保山, 王迪, 高浩, 徐卫军, 陈红旗, 纪剑辉. 定向敲除SD1基因提高水稻的抗倒性和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 359-367. |
| [6] | 王雨, 孙全翌, 杜海波, 许志文, 吴科霆, 尹力, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 左示敏. 利用抗稻瘟病基因Pigm和抗纹枯病数量性状基因qSB-9TQ、qSB-11HJX改良南粳9108的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 125-132. |
| [7] | 周永林, 申小磊, 周立帅, 林巧霞, 王朝露, 陈静, 冯慧捷, 张振文, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsLOX10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(4): 348-356. |
| [8] | 曹煜东, 肖湘谊, 叶乃忠, 丁晓雯, 易晓璇, 刘金灵, 肖应辉. 生长素调控因子OsGRF4协同调控水稻粒形和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(6): 629-638. |
| [9] | 刘树芳, 董丽英, 李迅东, 周伍民, 杨勤忠. 持有Pi9基因的水稻单基因系IRBL9-W对稻瘟病菌苗期和成株期抗性差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(3): 303-310. |
| [10] | 朱华珺, 周瑚, 任佐华, 刘二明. 枯草芽孢杆菌JN005胞外抗菌物质及对水稻叶瘟防治效果[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 470-478. |
| [11] | 许赵蒙, 李利华, 高晓庆, 袁正杰, 李莘, 田旭丹, 王岚岚, 瞿绍洪. 转Pi9抗稻瘟病基因水稻株系的比较转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 245-255. |
| [12] | 孟峰, 张亚玲, 靳学慧. 黑龙江省稻瘟病菌无毒基因AVR-Pita及其同源基因的检测与分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 143-149. |
| [13] | 李金璐, 张慧, 焦泽宇, 刘剑宇, 韩光煜, 卓晓轩, 罗琼. 水稻子预44和江南香糯基因组比较鉴定稻瘟病抗性相关基因[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(1): 8-16. |
| [14] | 曹妮, 陈渊, 季芝娟, 曾宇翔, 杨长登, 梁燕. 水稻抗稻瘟病分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 489-498. |
| [15] | 徐鹏, 王宏, 涂燃冉, 刘群恩, 吴玮勋, 傅秀民, 曹立勇, 沈希宏. 利用CRISPR/Cas9系统定向改良水稻稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(4): 313-322. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||