
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (5): 486-496.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.230203
黄奇娜1,#, 徐有祥2,#, 林光号3, 党洪阳3, 郑振权1, 张燕1, 王晗1, 邵国胜1,*( ), 尹献远4,*(
), 尹献远4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-14
修回日期:2023-03-22
出版日期:2023-09-10
发布日期:2023-09-13
通讯作者:
*email: 作者简介:第一联系人:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
HUANG Qina1,#, XU Youxiang2,#, LIN Guanghao3, DANG Hongyang3, ZHENG Zhenquan1, ZHANG Yan1, WANG Han1, SHAO Guosheng1,*( ), YIN Xianyuan4,*(
), YIN Xianyuan4,*( )
)
Received:2023-02-14
Revised:2023-03-22
Online:2023-09-10
Published:2023-09-13
Contact:
*email: About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】 探究在镉(Cadmium,Cd)胁迫下,外源硅(Silicon,Si)对水稻株高、干物质量、抗氧化酶系统及对Cd2+相关基因表达水平的影响,以期为阐明Si缓解Cd对水稻毒害作用机理提供理论依据。【方法】 以辐品36(FP36)和中嘉早17(ZJZ17)为研究对象,通过设置不同Cd胁迫浓度(0、5 µmol/L)和Si处理(0、10 µmol/L、1 mmol/L)进行水培实验,重点分析处理后水稻农艺性状和抗氧化酶活性,以及Cd2+吸收、转运相关基因表达水平的差异。【结果】 Cd胁迫可以显著抑制水稻株高、干物质量和抗氧化酶(SOD、POD、CAT和APX)活性;但Si能有效缓解Cd毒害,显著提高水稻生物量,增强抗氧化酶活性,其中1 mmol/L Si缓解效果更佳。此外,Si还能有效增加可溶性蛋白并降低MDA含量。Cd胁迫显著增加了FP36和ZJZ17不同组织的重金属含量,其中,根系中Cd积累量显著高于地上部。在添加较低浓度Si(10 µmol/L)后,水稻根系和地上部Cd含量无显著差异;但1 mmol/L Si能显著降低水稻根系和地上部Cd含量。OsNRAMP1、OsNRAMP5、OsIRT1、OsHMA2、OsHMA3等Cd2+吸收和转运相关基因的表达水平在镉胁迫和Si处理后呈不同的变化趋势。其中,OsNRAMP1、OsIRT1、OsHMA2的表达量受Cd胁迫影响有所上调,OsNRAMP5表达量呈下调趋势,而OsHMA3则无显著变化。而外源添加1 mmol/L Si可显著下调上述Cd2+吸收和转运相关基因的表达水平,重金属镉积累量下降。【结论】 Si通过改善水稻的农艺性状、激活抗氧化系统,以及调控重金属Cd2+吸收和转运相关基因的表达水平来缓解镉对水稻的毒害作用。
黄奇娜, 徐有祥, 林光号, 党洪阳, 郑振权, 张燕, 王晗, 邵国胜, 尹献远. 硅对镉胁迫下水稻苗期抗氧化酶系统及镉离子吸收和转运相关基因表达水平的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 486-496.
HUANG Qina, XU Youxiang, LIN Guanghao, DANG Hongyang, ZHENG Zhenquan, ZHANG Yan, WANG Han, SHAO Guosheng, YIN Xianyuan. Effects of Silicon on Antioxidant Enzyme System and Expression Levels of Genes Related to Cd2+ Uptake and Transportation in Rice Seedlings Under Cadmium Stress[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 486-496.
| 品种 Variety | Cd浓度 Cd concentration/(µmol·L−1) | Si浓度 Si concentration/(µmol·L−1) | 株高 Plant height/cm | 地上部干物质量 Shoot dry weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP36 | 0 | 0 | 66.7 ± 1.0 b | 5.32 ± 0.44 b |
| 10 | 67.2 ± 0.6 b | 5.46 ± 0.02 b | ||
| 1000 | 70.5 ± 1.0 a | 6.05 ± 0.05 a | ||
| 5.0 | 0 | 44.3 ± 0.4 e | 3.65 ± 0.19 cd | |
| 10 | 47.8 ± 1.7 d | 3.28 ± 0.36 d | ||
| 1000 | 50.4 ± 2.3 c | 3.73 ± 0.04 c | ||
| ZJZ17 | 0 | 0 | 64.6 ± 0.3 B | 6.52 ± 0.02 BC |
| 10 | 70.6 ± 2.0 A | 7.06 ± 0.49 AB | ||
| 1000 | 72.7 ± 2.4 A | 7.22 ± 0.52 A | ||
| 5.0 | 0 | 58.5 ± 1.4 D | 4.81 ± 0.16 D | |
| 10 | 57.7 ± 2.5 D | 5.08 ± 0.28 D | ||
| 1000 | 60.9 ± 1.4 C | 6.04 ± 0.53 C |
表1 不同Cd胁迫和Si处理下FP36和ZJZ17的株高和干物质量
Table 1. Agronomic traits of FP36 and ZJZ17 under different Cd stress and Si treatments.
| 品种 Variety | Cd浓度 Cd concentration/(µmol·L−1) | Si浓度 Si concentration/(µmol·L−1) | 株高 Plant height/cm | 地上部干物质量 Shoot dry weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP36 | 0 | 0 | 66.7 ± 1.0 b | 5.32 ± 0.44 b |
| 10 | 67.2 ± 0.6 b | 5.46 ± 0.02 b | ||
| 1000 | 70.5 ± 1.0 a | 6.05 ± 0.05 a | ||
| 5.0 | 0 | 44.3 ± 0.4 e | 3.65 ± 0.19 cd | |
| 10 | 47.8 ± 1.7 d | 3.28 ± 0.36 d | ||
| 1000 | 50.4 ± 2.3 c | 3.73 ± 0.04 c | ||
| ZJZ17 | 0 | 0 | 64.6 ± 0.3 B | 6.52 ± 0.02 BC |
| 10 | 70.6 ± 2.0 A | 7.06 ± 0.49 AB | ||
| 1000 | 72.7 ± 2.4 A | 7.22 ± 0.52 A | ||
| 5.0 | 0 | 58.5 ± 1.4 D | 4.81 ± 0.16 D | |
| 10 | 57.7 ± 2.5 D | 5.08 ± 0.28 D | ||
| 1000 | 60.9 ± 1.4 C | 6.04 ± 0.53 C |
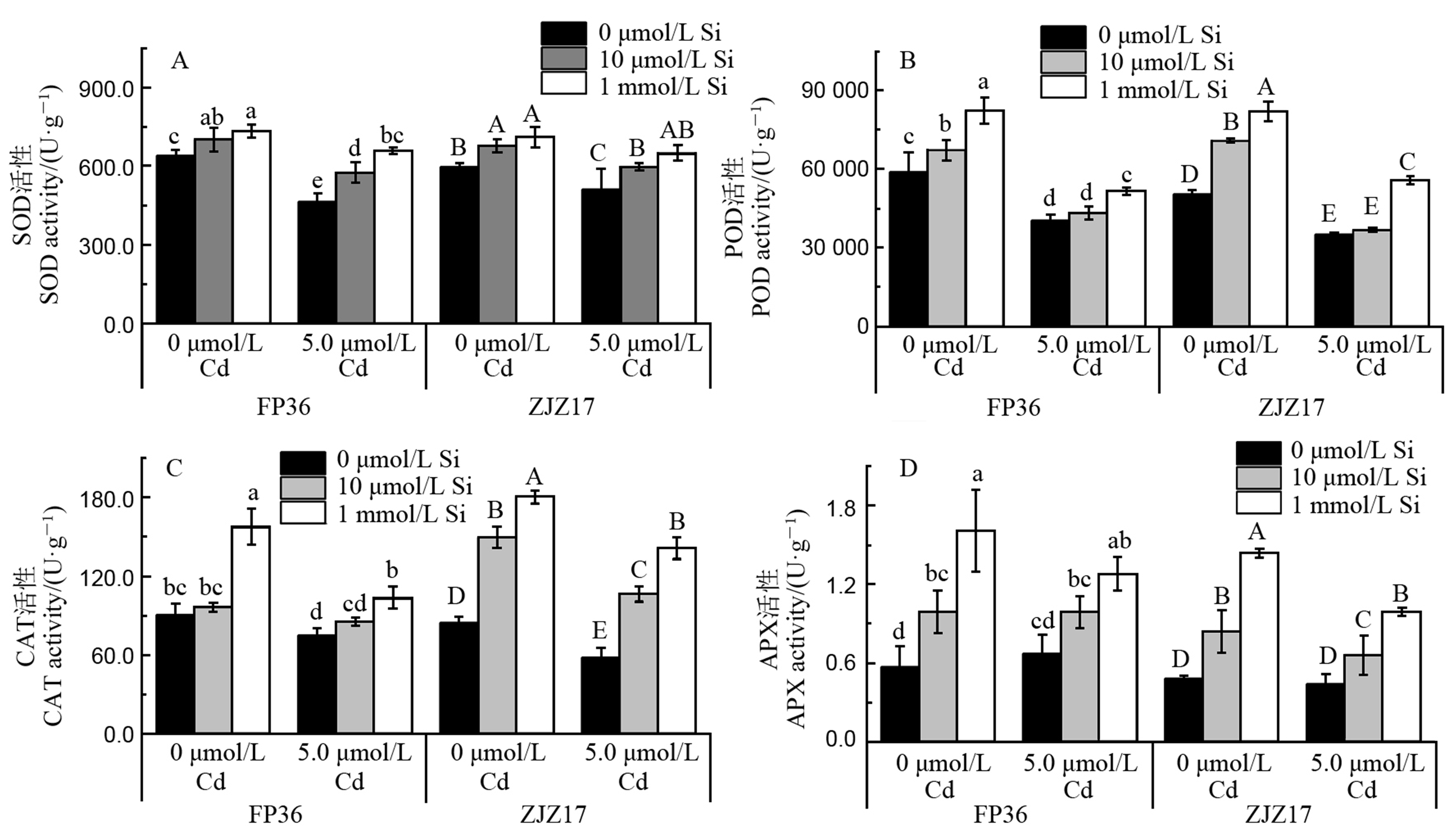
图1 不同Cd和Si处理下水稻FP36和ZJZ17根系中的抗氧化酶活性 A-超氧化物歧化酶(SOD);B-过氧化物酶(POD);C-过氧化氢酶(CAT);D-抗坏血酸氧化酶(APX)。平均数±标准差(n=3)。不同大小写字母分别表示不同Cd和Si处理下ZJZ17和FP36在P < 0.05水平上差异显著。
Fig. 1. Antioxidant enzyme activities in roots of FP36 and ZJZ17 under different Cd and Si treatments. A, Superoxide dismutase (SOD); B, Peroxidase (POD); C, Catalase (CAT); D, Ascorbic acid oxidase (APX). Data are means ± standard deviation (SD) from three replicated experiments (n = 3). Different uppercase and lowercase letters above the error bars represent significant differences of ZJZ17 and FP36, respectively under different Cd and Si treatments (P < 0.05).
| 品种 Variety | Cd浓度 Cd concentration/(µmol·L−1) | Si浓度 Si concentration/(µmol·L−1) | 可溶性蛋白含量 Soluble protein contents/(mg·g−1) | MDA含量 Malondialdehyde content/(µmol·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP36 | 0 | 0 | 30.89 ± 0.46 c | 29.68 ± 0.81 b |
| 10 | 34.62 ± 0.25 a | 25.27 ± 0.84 cd | ||
| 1000 | 33.60 ± 0.62 b | 19.68 ± 1.49 e | ||
| 5.0 | 0 | 18.69 ± 0.20 f | 37.10 ± 4.24 a | |
| 10 | 23.72 ± 0.06 e | 28.50 ± 3.00 bc | ||
| 1000 | 28.16 ± 0.81 d | 22.91 ± 2.18 de | ||
| ZJZ17 | 0 | 0 | 32.89 ± 4.01 AB | 22.15 ± 2.02 B |
| 10 | 36.79 ± 3.84 A | 22.26 ± 1.59 B | ||
| 1000 | 36.46 ± 4.76 A | 15.70 ± 1.33 D | ||
| 5.0 | 0 | 19.62 ± 0.60 C | 25.81 ± 1.70 A | |
| 10 | 23.32 ± 0.50 C | 24.30 ± 1.58 AB | ||
| 1000 | 30.36 ± 1.79 B | 19.25 ± 0.44 C |
表2 在不同Cd和Si处理下水稻FP36和ZJZ17根系中可溶性蛋白和MDA含量
Table 2. Soluble protein and MDA contents in roots of FP36 and ZJZ17 under different Cd and Si treatments.
| 品种 Variety | Cd浓度 Cd concentration/(µmol·L−1) | Si浓度 Si concentration/(µmol·L−1) | 可溶性蛋白含量 Soluble protein contents/(mg·g−1) | MDA含量 Malondialdehyde content/(µmol·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP36 | 0 | 0 | 30.89 ± 0.46 c | 29.68 ± 0.81 b |
| 10 | 34.62 ± 0.25 a | 25.27 ± 0.84 cd | ||
| 1000 | 33.60 ± 0.62 b | 19.68 ± 1.49 e | ||
| 5.0 | 0 | 18.69 ± 0.20 f | 37.10 ± 4.24 a | |
| 10 | 23.72 ± 0.06 e | 28.50 ± 3.00 bc | ||
| 1000 | 28.16 ± 0.81 d | 22.91 ± 2.18 de | ||
| ZJZ17 | 0 | 0 | 32.89 ± 4.01 AB | 22.15 ± 2.02 B |
| 10 | 36.79 ± 3.84 A | 22.26 ± 1.59 B | ||
| 1000 | 36.46 ± 4.76 A | 15.70 ± 1.33 D | ||
| 5.0 | 0 | 19.62 ± 0.60 C | 25.81 ± 1.70 A | |
| 10 | 23.32 ± 0.50 C | 24.30 ± 1.58 AB | ||
| 1000 | 30.36 ± 1.79 B | 19.25 ± 0.44 C |
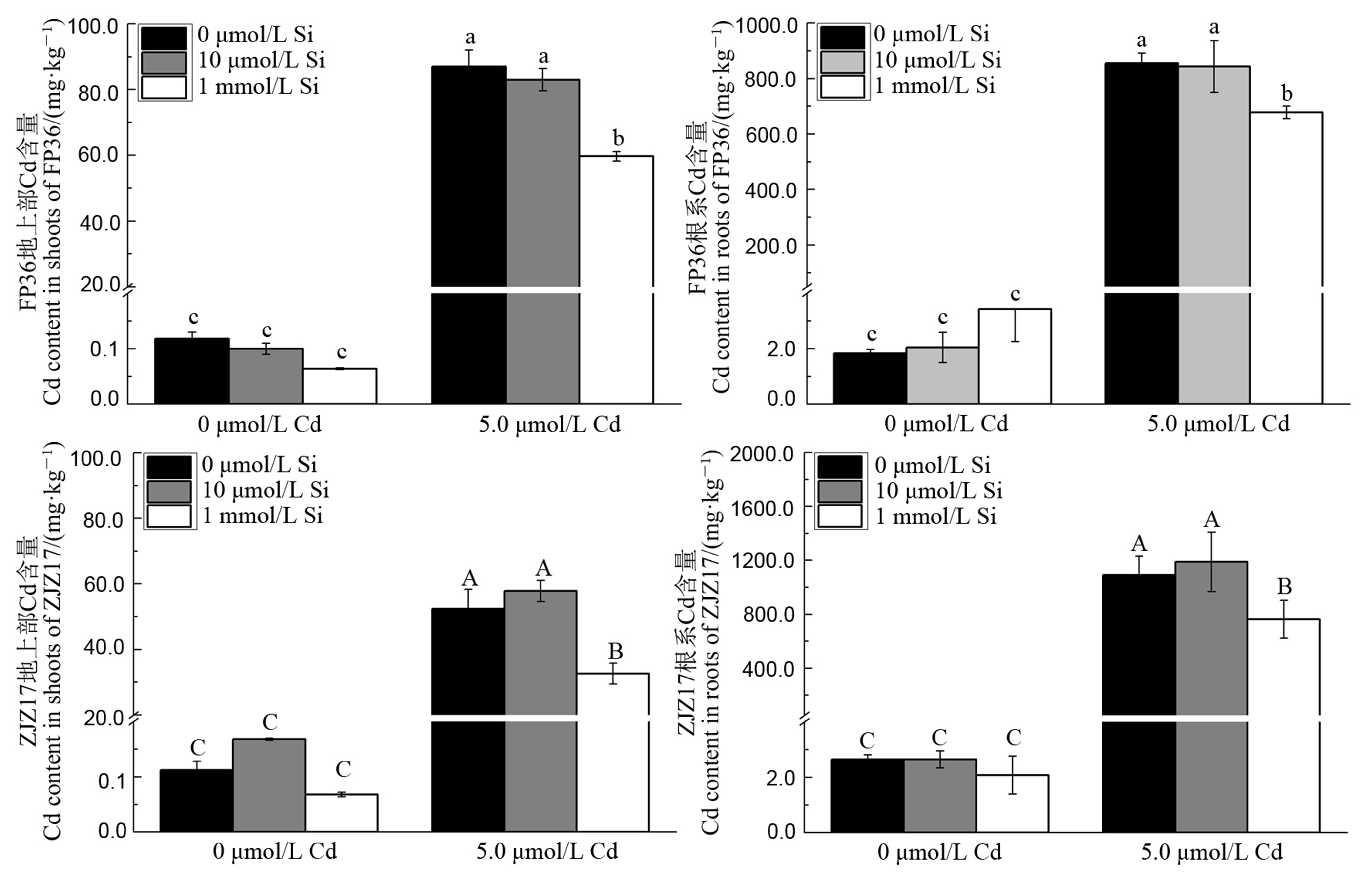
图2 不同Cd胁迫和Si处理下水稻FP36和ZJZ17地上部(A,C)和根系(B,D)中Cd含量
Fig. 2. Cd content in shoots (A, C) and roots (B, D) of FP36 and ZJZ17 under different Cd stress and Si treatments.
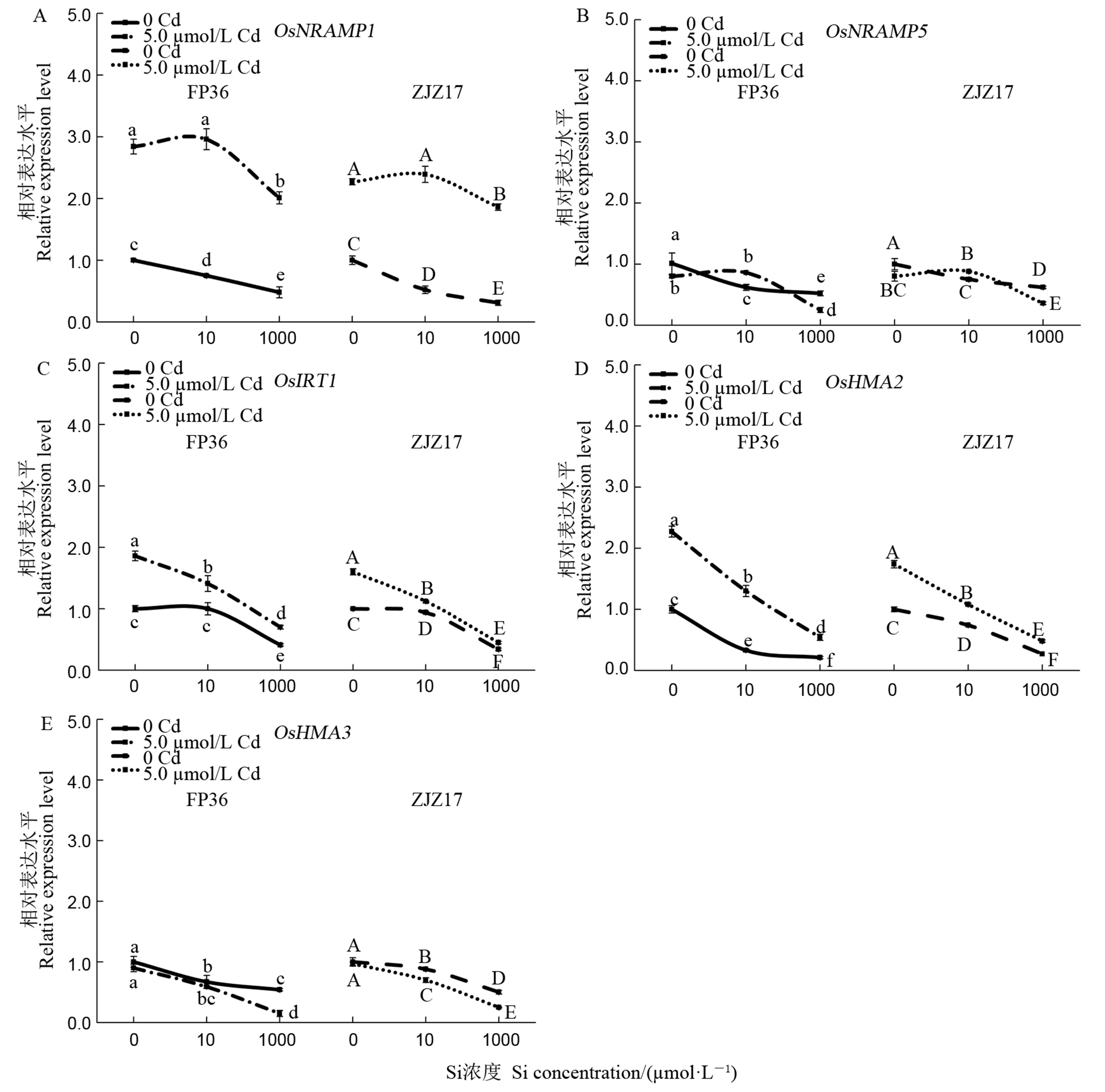
图3 不同Cd和Si处理下水稻 FP36和ZJZ17 根系中Cd2+吸收和转运相关基因的表达水平 数值表示平均数±SD(n=3)。A~E分别表示OsNRAMP1、OsNRAMP5、OsIRT1、OsHMA2、OsHMA3基因的表达水平。
Fig. 3. Relative expression of Cd2+ uptake/transport-related genes in roots of FP36 and ZJZ17 under different Cd and Si treatments. Data are means ± standard deviation (SD) from three replicated experiments (n = 3). A-E mean the relative expression of OsNRAMP1, OsNRAMP5, OsIRT1, OsHMA2, OsHMA3.
| [1] | Chang C, Yin R, Zhang H, Yao L. Bioaccumulation and health risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil-rice system in a typical seleniferous area in Central China[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2019, 38(7): 1577-1584. |
| [2] | Mclaughlin M J, Whatmuff M, Warne M, Heemsbergen D, Barry G, Bell M, Nash D, Pritchard D. A field investigation of solubility and food chain accumulation of biosolid-cadmium across diverse soil types[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2006, 3: 428-432. |
| [3] | Ismael M A, Elyamine A M, Moussa M G, Cai M, Zhao X, Hu C. Cadmium in plants: Uptake, toxicity, and its interactions with selenium fertilizers[J]. Metallomics, 2019, 11(2): 255-277. |
| [4] | Uraguchi S, Kiyono M, Sakamoto T, Watanabe I, Kuno K. Contributions of apoplasmic cadmium accumulation, antioxidative enzymes and induction of phytochelatins in cadmium tolerance of the cadmium-accumulating cultivar of black oat (Avena strigosa Schreb.)[J]. Planta, 2009, 230(2): 267-276. |
| [5] | Wu Z, Yin X, Bañuelos G S, Lin Z Q, Liu Y, Li M, Yuan L. Indications of selenium protection against cadmium and lead toxicity in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1875. |
| [6] | 戴青云, 刘代欢, 王德新, 李鹏祥, 朱维, 桂娟. 硅对水稻生长的影响及其缓解镉毒害机理研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(5): 86-92. |
| Dai Q Y, Liu D H, Wang D X, Li P X, Zhu W, Gui J. A review on silicon: Effect on rice growth and its mechanism of relieving cadmium toxicity[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(5): 86-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Khan I, Awan S A, Rizwan M, Ali S, Hassan M J, Brestic M, Zhang X, Huang L. Effects of silicon on heavy metal uptake at the soil-plant interphase: A review[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 222: 112510. |
| [8] | 高子翔, 周航, 杨文弢, 辜娇峰, 陈立伟, 杜文琪, 徐珺, 廖柏寒. 基施硅肥对土壤镉生物有效性及水稻镉累积效应的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2017(12): 5299-5307. |
| Gao Z X, Zhou H, Yang W T, Gu J F, Chen L W, Du W Q, Xu J, Liao B H. Impacts of silicon fertilizer as base manure on cadmium bioavailability in soil and on cadmium accumulation in rice plants[J]. Environmental Science, 2017(12): 5299-5307. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 魏晓, 张鹏博, 赵丹丹, Bocharnikova E, Matichenkov V, Dmitry D. 水稻土施硅对土壤-水稻系统中镉的降低效果[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(5): 1600-1606. |
| Wei X, Zhang P B, Zhao D D, Elena B, Vladimir M, Demin D. Cadmium status in paddy soil in a rice system under silicon fertilization[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(5): 1600-1606. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 秦淑琴, 黄庆辉. 硅对水稻吸收镉的影响[J]. 新疆环境保护, 1997, 19(3): 51-53. |
| Qin S Q, Huang Q H. Effect of silicon on cadmium uptake by rice[J]. Environmental Protection of Xingjiang, 1997, 19(3): 51-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 郑文杰, 卢剑, 刘模发. 施用液体硅肥降低稻米中镉含量效果研究[J]. 现代化农业, 2016(7): 30-31. |
| Zheng W J, Lu J, Liu M F. Effect of liquid silicon fertilizer on reducing cadmium content in rice[J]. Modernization Agriculture, 2016(7): 30-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Wang H Y, Wen S L, Chen P, Zhang L, Cen K, Sun G X. Mitigation of cadmium and arsenic in rice grain by applying different silicon fertilizers in contaminated fields[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2016, 23(4): 3781-3788. |
| [13] | 赵明柳, 唐守寅, 董海霞, 李荭荭, 吴竹麟, 黄俊星, 王果. 硅酸钠对重金属污染土壤性质和水稻吸收Cd Pb Zn的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(9): 1653-1659. |
| Zhao M L, Tang S Y, Dong H X, Li H H, Wu Z L, Huang J X, Wang G. Effects of sodium silicate on soil properties and Cd, Pb and Zn absorption by rice plant[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(9): 1653-1659. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Nwugo C C, Huerta A J. Silicon-induced cadmium resistance in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2008, 171(6):841-848. |
| [15] | 龚金龙, 张洪程, 龙厚元, 胡雅杰, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 高辉. 水稻中硅的营养功能及生理机制的研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2012, 48(1): 1-10. |
| Gong J L, Zhang H C, Long H Y, Hu Y J, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, Gao H. Progress in research of nutrition functions and physiological mechanisms of silicon in rice[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2012, 48 (1): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 胡瑞芝, 方水娇, 陈桂秋. 硅对杂交水稻生理指标及产量的影响[J]. 湖南农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2001, 27(5): 335-338. |
| Hu R Z, Fang S J, Chen G Q. Effects of silicon on the physiological targets and yield of hybrid rice[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University: Natural Sciences, 2001, 27(5): 335-338. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | Enstone D E, Peterson C A, Ma F. Root endodermis and exodermis: Structure, function, and responses to the environment[J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2002, 21: 335-351. |
| [18] | Sasaki A, Yamaji N, Yokosho K, Ma J F. Nramp5 is a major transporter responsible for manganese and cadmium uptake in rice[J]. Plant Cell, 2012, 24(5): 2155-2167. |
| [19] | Takahashi R, Ishimaru Y, Senoura T, Shimo H, Ishikawa S, Arao T, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa N K. The OsNRAMP1 iron transporter is involved in Cd accumulation in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(14): 4843-4850. |
| [20] | Nakanishi H, Ogawa I, Ishimaru Y, Mori S, Nishizawa N K. Iron deficiency enhances cadmium uptake and translocation mediated by the Fe2+ transporters OsIRT1 and OsIRT2 in rice[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2006, 52(4): 464-469. |
| [21] | Ishimaru Y, Takahashi R, Bashir K, Shimo H, Senoura T, Sugimoto K, Ono K, Yano M, Ishikawa S, Arao T, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa N K. Characterizing the role of rice NRAMP5 in manganese, iron and cadmium transport[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2: 286. |
| [22] | Takahashi R, Ishimaru Y, Shimo H, Ogo Y, Senoura T, Nishizawa N K, Nakanishi H. The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice[J]. Plant Cell Environment, 2012, 35(11): 1948-1957. |
| [23] | Sasaki A, Yamaji N, Ma J F. Overexpression of OsHMA3 enhances Cd tolerance and expression of Zn transporter genes in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(20): 6013-6021. |
| [24] | Kim Y H, Khan A L, Kim D H, Lee S Y, Kim K M, Waqas M, Jung H Y, Shin J H, Kim J G, Lee I J. Silicon mitigates heavy metal stress by regulating P-type heavy metal ATPases, Oryza sativa low silicon genes, and endogenous phytohormones[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2014, 14: 13. |
| [25] | Ma J, Cai H, He C, Zhang W, Wang L. A hemicellulose-bound form of silicon inhibits cadmium ion uptake in rice (Oryza sativa) cells[J]. New Phytologist, 2015, 206(3): 1063-1074. |
| [26] | Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Zia-Ur-Rehman M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum M F, Irshad M K. Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: A review[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015, 119: 186-197. |
| [27] | Chen D, Chen D, Xue R, Long J, Lin X, Lin Y, Jia L, Zeng R, Song Y. Effects of boron, silicon and their interactions on cadmium accumulation and toxicity in rice plants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 367: 447-455. |
| [28] | Liu J, Ma J, He C, Li X, Zhang W, Xu F, Lin Y, Wang L. Inhibition of cadmium ion uptake in rice (Oryza sativa) cells by a wall-bound form of silicon[J]. New Phytologist, 2013, 200(3): 691-699. |
| [29] | 李江遐, 张军, 马友华, 蔡慢弟, 高飞. 硅对镉胁迫条件下两个水稻品种镉亚细胞分布、非蛋白巯基物质含量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 36(6): 1066-1071. |
| Li J, Zhang J, Ma Y, Cai M D, Gao F. Effects of silicon on cadmium accumulation and non-protein thiol content in the seedlings of two rice varieties under cadmium stress[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(6): 1066-1071. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | Riaz M, Kamran M, Rizwan M, Ali S, Parveen A, Malik Z, Wang X. Cadmium uptake and translocation: Selenium and silicon roles in Cd detoxification for the production of low Cd crops: A critical review[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 273: 129690. |
| [31] | Zhou Q, Shao G S, Zhang Y X, Dong Q, Wang H, Chen S H, Cao L Y, Shen X H. The difference of cadmium accumulation between the indica and japonica subspecies and the mechanism of it[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2017, 81: 523-532. |
| [32] | Huang Q N, An H, Yang Y J, Liang Y, Shao G S. Effects of Mn-Cd antagonistic interaction on Cd accumulation and major agronomic traits in rice genotypes by different Mn form[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2017, 82: 317-331. |
| [33] | 赵世杰, 苍晶. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2015: 143-145, 225-236. |
| Zhao S J, Cang J. Laboratory Guides for Plant Physiology[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2015: 143-145, 225-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | Huang Q N, Wu Y L, Shao G S. Root aeration promotes the cadmium accumulation in rice by regulating the iron uptake system[J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28(5): 511-520. |
| [35] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔct method[J]. Methods, 2001, 25: 402-408. |
| [36] | 陈喆, 张淼, 叶长城, 毛懿德, 周细红, 雷鸣, 魏祥东, 铁柏清. 富硅肥料和水分管理对稻米镉污染阻控效果研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(12): 4003-4011. |
| Chen Z, Zhang M, Ye C C, Mao Y D, Zhou X H, Lei M, Wei X D, Tie B Q. Mitigation of Cd accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) with Si fertilizers and irrigation managements[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(12): 4003-4011. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 李园星露, 叶长城, 刘玉玲, 李丹阳, 刘寿涛, 罗海艳, 刘孝利, 铁柏清, 孙健. 硅肥耦合水分管理对复合污染稻田土壤As-Cd生物有效性及稻米累积阻控[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(2): 944-952. |
| LI-Yuan X L, Ye C C, Liu Y L, Li D Y, Liu S T, Luo H Y, Liu X L, Tie B Q, Sun J. Bioavailability of silicon fertilizer coupled water management on soil bioavailability and cumulative control of rice in compound contaminated paddy soils[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(2): 944-952. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | Vaculík M, Lux A, Luxová M, Tanimoto E, Lichtscheidl I. Silicon mitigates cadmium inhibitory effects in young maize plants[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2009, 67(1): 52-58. |
| [39] | Vatehová Z, Kollárová K, Zelko I, Richterová-Kučerová D, Bujdoš M, Lišková D. Interaction of silicon and cadmium in Brassica juncea and Brassica napus[J]. Biologia, 2012, 67(3): 498-504. |
| [40] | Guo B, Liu C, Ding N F, Fu Q L, Li N Y. Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in two cypress varieties by strengthening the exodermis tissues and stimulating phenolic exudation of roots[J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2016, 35(2): 420-429. |
| [41] | Wu J, Guo J, Hu Y, Gong H. Distinct physiological responses of tomato and cucumber plants in silicon-mediated alleviation of cadmium stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 453. |
| [42] | Shi G R, Zhang Z, Liu C F. Silicon influences cadmium translocation by altering subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in peanut roots[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2017, 63(1) : 117-123. |
| [43] | Wang H Y, Wen S L, Chen P, Zhang L, Cen K, Sun G X. Mitigation of cadmium and arsenic in rice grain by applying different silicon fertilizers in contaminated fields[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2016, 23(4): 3781-3788. |
| [44] | Wang Y C, Hu Y H, Duan Y K, Feng R, Gong H. Silicon reduces long-term cadmium toxicities in potted garlic plants[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2016, 38: 211. |
| [45] | Cui J, Liu T, Li F, Yi J, Liu C, Yu H. Silica nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice cells: Mechanisms and size effects[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 228: 363-369. |
| [46] | Bhat J A, Shivaraj S M, Singh P, Navadagi D B, Tripathi D K, Dash P K, Solanke A U, Sonah H, Deshmukh R. Role of silicon in mitigation of heavy metal stresses in crop plants[J]. Plants (Basel), 2019, 8(3): 71. |
| [47] | Cui J, Li Y, Jin Q, Li F. Silica nanoparticles inhibit arsenic uptake into rice suspension cells via improving pectin synthesis and the mechanical force of the cell wall[J]. Environmental Science: Nano, 2020, 7: 162-171. |
| [48] | 赵颖, 李军. 硅对水稻吸收镉的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2010, 41(3): 59-64. |
| Zhao Y, Li J. Effect of silicon on cadmium uptake by rice[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2010, 41(3): 59-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [49] | Shi X H, Zhang C C, Wang H, Zhang F S. Effect of Si on the distribution of Cd in rice seedlings[J]. Plant and Soil, 2005, 272: 53-60. |
| [50] | Guo L, Chen A, He N, Yang D, Liu M D. Exogenous silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in rice seedlings in relation to Cd distribution and ultrastructure changes[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2018, 18: 1691-1700. |
| [51] | 黄秋蝉, 黎晓峰, 沈方科, 阳继辉, 李耀燕, 张维珺. 硅对水稻幼苗镉的解毒作用及其机制研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2007, 26(4): 1307-1311. |
| Huang Q C, Li X F, Shen F K, Yang J H, Li Y Y, Zhang W J. Cadmium resistance improved by silicon and corresponding mechanisms in Oryza sativa L. seedlings[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2007, 26(4): 1307-1311. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [52] | 孙梦梦, 徐劼, 张玲玲, 施德剑, 赵玺童. 硅对镉胁迫下植物生长影响的研究进展[J]. 广州化工, 2019, 47(13): 41-43. |
| Sun M M, Xu J, Zhang L L, Shi D J, Zhao X T. Research progress on effects of silicon on plant growth under cadmium stress[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2019, 47(13): 41-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [53] | Farooq M A, Ali S, Hameed A, Ishaque W, Mahmood K, Iqbal Z. Alleviation of cadmium toxicity by silicon is related to elevated photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes; suppressed cadmium uptake and oxidative stress in cotton[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2013, 96: 242-249. |
| [54] | Feng J, Shi Q, Wang X, Wei M, Yang F, Xu H. Silicon supplementation ameliorated the inhibition of photosynthesis and nitrate metabolism by cadmium (Cd) toxicity in Cucumis sativus L[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2010, 123(4): 521-530. |
| [55] | Keller C, Rizwan M, Davidian J C, Pokrovsky O S, Bovet N, Chaurand P, Meunier J D. Effect of silicon on wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L.) grown in hydroponics and exposed to 0 to 30 μM Cu[J]. Planta, 2015, 241(4): 847-860. |
| [56] | 贾茜茹, 刘奋武, 樊文华. 硅对Cd胁迫下黄瓜苗期光合及抗氧化酶系统的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(4): 321-326. |
| Jia Q R, Liu F E, Fan W H. Effects of silicon on photosynthesis and antioxidant enzymes of cucumber seedling under cadmium stress[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(4): 321-326. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [57] | 孟红梅, 汤燕. 硅对镉胁迫下板蓝根种子萌发及生理特性的影响[J]. 种子, 2011, 30(11): 37-40. |
| Meng H M, Tang Y. Effect of silicon on radix isatidis seed germination and seedings growth phyiological characteristics under cadmium stress[J]. Seed, 2011, 30(11): 37-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [58] | Wang S H, Wang F Y, Gao S C. Foliar application with nano-silicon alleviates Cd toxicity in rice seedlings[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2015, 22(4): 2837-2845. |
| [59] | Srivastava R K, Pandey P, Rajpoot R, Rani A, Gautam A, Dubey R S. Exogenous application of calcium and silica alleviates cadmium toxicity by suppressing oxidative damage in rice seedlings[J]. Protoplasma, 2015, 252(4): 959-975. |
| [60] | Wu Z, Wang F, Liu S, Du Y, Li F, Du R, Wen D, Zhao J. Comparative responses to silicon and selenium in relation to cadmium uptake, compartmentation in roots, and xylem transport in flowering Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis var. utilis) under cadmium stress[J]. Environment and Experimental Botany, 2016, 131: 173-180. |
| [61] | Miyadate H, Adachi S, Hiraizumi A, Tezuka K, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Katou K, Kodama I, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Satoh-Nagasawa N, Watanabe A, Fujimura T, Akagi H. OsHMA3, a P1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles[J]. New Phytologist, 2011, 189(1): 190-199. |
| [62] | Zhang X F, Hu Z H, Yan T X, Lu R R, Peng C L, Li S S, Jing Y X. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate Cd phytotoxicity by altering Cd subcellular distribution and chemical forms in Zea mays[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 171: 352-360. |
| [63] | Huang H, Li M, Rizwan M, Dai Z, Yuan Y, Hossain M M, Cao M, Xiong S, Tu S. Synergistic effect of silicon and selenium on the alleviation of cadmium toxicity in rice plants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 401: 123393. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||