
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (6): 561-573.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.0404
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Juan ZHOU1, Xiaowei SHU1, Shangkun LAI1,2, Gaoping XU1,3, Jianye HUANG1, Youli YAO1, Lianxin Yang1, Guichun DONG1, Yulong WANG1,*( )
)
Received:2020-04-23
Revised:2020-07-03
Online:2020-11-10
Published:2020-11-10
Contact:
Yulong WANG
周娟1, 舒小伟1, 赖上坤1,2, 许高平1,3, 黄建晔1, 姚友礼1, 杨连新1, 董桂春1, 王余龙1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
王余龙
基金资助:CLC Number:
Juan ZHOU, Xiaowei SHU, Shangkun LAI, Gaoping XU, Jianye HUANG, Youli YAO, Lianxin Yang, Guichun DONG, Yulong WANG. Differences in Response of Grain Yield, Nitrogen Absorption and Utilization to Elevated CO2Concentration in Different Rice Varieties[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(6): 561-573.
周娟, 舒小伟, 赖上坤, 许高平, 黄建晔, 姚友礼, 杨连新, 董桂春, 王余龙. 不同类型水稻品种产量和氮素吸收利用对大气CO2浓度升高响应的差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(6): 561-573.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.0404
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 产量 Grain yield /(g·m-2) | 单位面积穗数 Panicle number per 1 m2 | 每穗颖花数Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grainweight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 654.53 cB | 198.5 abABC | 143.6 bB | 77.7 aA | 29.87 bcBC |
| CJR | 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 659.15 cB | 221.0 aA | 139.8 bB | 74.3 abA | 28.70 cCD | |
| 杂交籼稻 | 汕优63SY63 | 870.33 abAB | 219.6 aA | 157.6 bB | 81.4 abA | 31.49 abAB | |
| HIR | 两优培九LYP9 | 929.96 aA | 209.7 aAB | 232.1 aA | 71.2 bA | 26.86 dD | |
| 常规籼稻 | 扬稻6号YD6 | 814.64 abAB | 174.6 cC | 167.2 bB | 87.0 aA | 32.36 aA | |
| CIR | 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 759.98 bcAB | 184.6 bcBC | 168.0 bB | 81.3 abA | 30.53 bABC | |
| 平均值 Average | 781.43 | 201.4 | 168.0 | 78.8 | 29.97 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 808.12 cBC | 255.8 abAB | 140.1 cCD | 76.0 bBC | 29.95 bAB |
| CJR | 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 760.12 cC | 279.1 aA | 128.2 cD | 73.7 bC | 29.47 bB | |
| 杂交籼稻 | 汕优63SY63 | 1093.28 abA | 244.5 abABC | 167.8 bBC | 84.6 aAB | 31.74 aA | |
| HIR | 两优培九LYP9 | 1139.50 aA | 225.4 bcBC | 224.9 aA | 83.2 aABC | 27.24 cC | |
| 常规籼稻 | 扬稻6号YD6 | 1061.24 abA | 199.5 cC | 188.6 bB | 88.6 aA | 32.11 aA | |
| CIR | 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 971.54 bAB | 201.5 cC | 182.7 bB | 86.4 aA | 30.70 abAB | |
| 平均值 Average | 972.30 | 234.3 | 172.1 | 82.1 | 30.20 | ||
| Ft | 40.428** | 29.900** | 0.336 | 1.875 | 0.260 | ||
| Fv | 31.329** | 22.983** | 24.066** | 6.355** | 8.612** | ||
| Ft×v | 1.137 | 4.213 | 1.174 | 1.126 | 0.095 | ||
| ry | 0.082 | 0.557** | 0.559** | 0.089 | |||
Table 1 Response of grain yield and yield components to the increase of atmospheric CO2 concentration in different rice varieties.
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 产量 Grain yield /(g·m-2) | 单位面积穗数 Panicle number per 1 m2 | 每穗颖花数Spikelet number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grainweight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 654.53 cB | 198.5 abABC | 143.6 bB | 77.7 aA | 29.87 bcBC |
| CJR | 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 659.15 cB | 221.0 aA | 139.8 bB | 74.3 abA | 28.70 cCD | |
| 杂交籼稻 | 汕优63SY63 | 870.33 abAB | 219.6 aA | 157.6 bB | 81.4 abA | 31.49 abAB | |
| HIR | 两优培九LYP9 | 929.96 aA | 209.7 aAB | 232.1 aA | 71.2 bA | 26.86 dD | |
| 常规籼稻 | 扬稻6号YD6 | 814.64 abAB | 174.6 cC | 167.2 bB | 87.0 aA | 32.36 aA | |
| CIR | 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 759.98 bcAB | 184.6 bcBC | 168.0 bB | 81.3 abA | 30.53 bABC | |
| 平均值 Average | 781.43 | 201.4 | 168.0 | 78.8 | 29.97 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 808.12 cBC | 255.8 abAB | 140.1 cCD | 76.0 bBC | 29.95 bAB |
| CJR | 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 760.12 cC | 279.1 aA | 128.2 cD | 73.7 bC | 29.47 bB | |
| 杂交籼稻 | 汕优63SY63 | 1093.28 abA | 244.5 abABC | 167.8 bBC | 84.6 aAB | 31.74 aA | |
| HIR | 两优培九LYP9 | 1139.50 aA | 225.4 bcBC | 224.9 aA | 83.2 aABC | 27.24 cC | |
| 常规籼稻 | 扬稻6号YD6 | 1061.24 abA | 199.5 cC | 188.6 bB | 88.6 aA | 32.11 aA | |
| CIR | 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 971.54 bAB | 201.5 cC | 182.7 bB | 86.4 aA | 30.70 abAB | |
| 平均值 Average | 972.30 | 234.3 | 172.1 | 82.1 | 30.20 | ||
| Ft | 40.428** | 29.900** | 0.336 | 1.875 | 0.260 | ||
| Fv | 31.329** | 22.983** | 24.066** | 6.355** | 8.612** | ||
| Ft×v | 1.137 | 4.213 | 1.174 | 1.126 | 0.095 | ||
| ry | 0.082 | 0.557** | 0.559** | 0.089 | |||
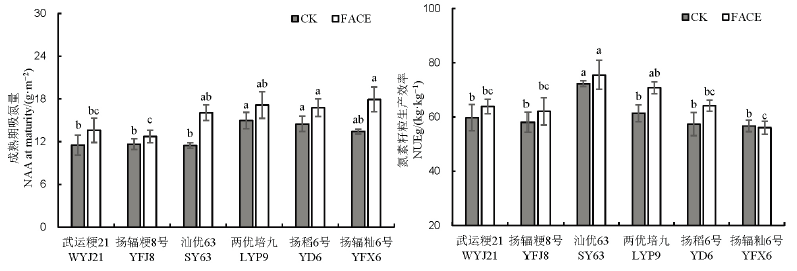
Fig. 1. Response of nitrogen absorption amount(NAA) at maturity and nitrogen use efficiency for grain yield(NUEg) to theincrease of atmospheric CO2 concentration in different rice varieties.
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 移栽期 Transplanting stage | 分蘖期 Tillering stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 成熟期 Maturity stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 2.34 aAB | 1.80 aA | 1.45 aA | 1.05 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 2.38 aAB | 1.75 aA | 1.20 bB | 0.92 abA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 2.22 bB | 1.99 aA | 1.16 bB | 0.85 bA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 2.24 aAB | 2.04 aA | 1.09 bB | 0.95 abA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.04 aA | 1.85 aA | 1.16 bB | 0.97 abA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 2.75 aAB | 1.86 aA | 1.18 bB | 0.98 abA | ||
| 平均值 Average | 2.50 | 1.89 | 1.21 | 0.95 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 2.34 aAB | 1.72 aA | 1.24 aA | 0.98 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 2.38 aAB | 1.71 aA | 1.12 aA | 0.87 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 2.22 bB | 1.98 aA | 1.03 aA | 0.86 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 2.24 aAB | 1.79 aA | 0.93 aA | 0.93 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.04 aA | 1.75 aA | 1.05 aA | 0.89 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 2.75 aAB | 1.78 aA | 1.12 aA | 0.98 aA | ||
| 平均值 Average | 2.50 | 1.79 | 1.08 | 0.92 | ||
| Ft | 1.530 | 8.459** | 0.714 | |||
| Fv | 10.014** | 1.986 | 7.979** | 0.849 | ||
| Ft×v | 0.032 | 0.222 | 0.127 | |||
| rNAA | -0.054 | -0.098 | -0.287* | 0.561** | ||
Table 2 Response of nitrogen content of oboveground parts to the increase of atmospheric CO2 concentration in different ricevarieties. %
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 移栽期 Transplanting stage | 分蘖期 Tillering stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 成熟期 Maturity stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 2.34 aAB | 1.80 aA | 1.45 aA | 1.05 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 2.38 aAB | 1.75 aA | 1.20 bB | 0.92 abA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 2.22 bB | 1.99 aA | 1.16 bB | 0.85 bA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 2.24 aAB | 2.04 aA | 1.09 bB | 0.95 abA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.04 aA | 1.85 aA | 1.16 bB | 0.97 abA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 2.75 aAB | 1.86 aA | 1.18 bB | 0.98 abA | ||
| 平均值 Average | 2.50 | 1.89 | 1.21 | 0.95 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 2.34 aAB | 1.72 aA | 1.24 aA | 0.98 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 2.38 aAB | 1.71 aA | 1.12 aA | 0.87 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 2.22 bB | 1.98 aA | 1.03 aA | 0.86 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 2.24 aAB | 1.79 aA | 0.93 aA | 0.93 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.04 aA | 1.75 aA | 1.05 aA | 0.89 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 2.75 aAB | 1.78 aA | 1.12 aA | 0.98 aA | ||
| 平均值 Average | 2.50 | 1.79 | 1.08 | 0.92 | ||
| Ft | 1.530 | 8.459** | 0.714 | |||
| Fv | 10.014** | 1.986 | 7.979** | 0.849 | ||
| Ft×v | 0.032 | 0.222 | 0.127 | |||
| rNAA | -0.054 | -0.098 | -0.287* | 0.561** | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 移栽期 Transplanting stage | 分蘖期 Tillering stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 成熟期 Maturity stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 5.21 bcBC | 90.67 dD | 686.34 dC | 1112.77 dD |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 5.35 bB | 113.01 cCD | 825.33 cBC | 1286.28 cBC | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 4.08 cdCD | 133.79 bBC | 1005.46 bA | 1358.31 bcAB | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 3.60 dD | 135.22 bBC | 1141.62 aA | 1576.69 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 9.07 aA | 186.86 aA | 1056.76 abA | 1495.99 abAB | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 8.17 aA | 153.67 bB | 972.17 bAB | 1369.15 bcAB | ||
| 平均值 Average | 5.91 | 135.54 | 947.95 | 1366.53 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 5.21 bcBC | 108.14 cD | 742.78 dC | 1382.25 bB |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 5.35 bB | 127.76 cCD | 1030.98 cB | 1473.58 bB | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 4.08 cdCD | 169.94 abAB | 1424.38 aA | 1863.12 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 3.60 dD | 156.70 bBC | 1253.98 bA | 1846.88 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 9.07 aA | 194.26 aA | 1256.34 bA | 1868.38 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 8.17 aA | 194.60 aA | 1212.74 bAB | 1826.99 aA | ||
| 平均值 Average | 5.91 | 158.57 | 1153.53 | 1710.20 | ||
| Ft | 10.513** | 28.006** | 60.370** | |||
| Fv | 62.539** | 35.617** | 36.345** | 25.871** | ||
| Ft×v | 0.280 | 0.361 | 0.185 | |||
| rNAA | 0.239* | 0.526** | 0.516** | 0.691** | ||
Table 3 Response of dry matter weight of aboveground parts to the increase of atmospheric CO2 concentration in different rice varieties.g/m2
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 移栽期 Transplanting stage | 分蘖期 Tillering stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 成熟期 Maturity stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 5.21 bcBC | 90.67 dD | 686.34 dC | 1112.77 dD |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 5.35 bB | 113.01 cCD | 825.33 cBC | 1286.28 cBC | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 4.08 cdCD | 133.79 bBC | 1005.46 bA | 1358.31 bcAB | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 3.60 dD | 135.22 bBC | 1141.62 aA | 1576.69 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 9.07 aA | 186.86 aA | 1056.76 abA | 1495.99 abAB | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 8.17 aA | 153.67 bB | 972.17 bAB | 1369.15 bcAB | ||
| 平均值 Average | 5.91 | 135.54 | 947.95 | 1366.53 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 5.21 bcBC | 108.14 cD | 742.78 dC | 1382.25 bB |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 5.35 bB | 127.76 cCD | 1030.98 cB | 1473.58 bB | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 4.08 cdCD | 169.94 abAB | 1424.38 aA | 1863.12 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 3.60 dD | 156.70 bBC | 1253.98 bA | 1846.88 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 9.07 aA | 194.26 aA | 1256.34 bA | 1868.38 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 8.17 aA | 194.60 aA | 1212.74 bAB | 1826.99 aA | ||
| 平均值 Average | 5.91 | 158.57 | 1153.53 | 1710.20 | ||
| Ft | 10.513** | 28.006** | 60.370** | |||
| Fv | 62.539** | 35.617** | 36.345** | 25.871** | ||
| Ft×v | 0.280 | 0.361 | 0.185 | |||
| rNAA | 0.239* | 0.526** | 0.516** | 0.691** | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 移栽-分蘖 Transplanting-tillering | 分蘖-抽穗 Tillering-heading | 抽穗-成熟 Heading-maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 1.50 cC | 8.25 aA | 1.64 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 1.82 cC | 7.95 aA | 1.74 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 2.56 bAB | 8.98 bA | -0.16 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 2.51 bB | 9.73 aA | 2.67 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.16 aA | 8.80 aA | 2.27 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 2.66 bAB | 8.62 aA | 1.92 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 2.37 | 8.72 | 1.68 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 1.68 cB | 7.32 bA | 4.47 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 2.03 bcB | 9.39 abA | 1.18 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 3.22 aA | 11.39 aA | 1.37 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 2.68 abAB | 9.01 abA | 5.39 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.14 aA | 9.93 abA | 3.44 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 3.29 aA | 9.89 abA | 4.53 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 2.67 | 9.49 | 3.40 | ||
| Ft | 5.278* | 2.119 | 4.467* | ||
| Fv | 34.713** | 3.022 | 0.379 | ||
| Ft×v | 0.221 | 0.299 | 0.134 | ||
| rNAA | 0.451** | 0.294* | 0.721** | ||
Table 4 Response of nitrogen absorption amount at different growth stages to the increase of atmospheric CO2 concentration in different rice varieties. g/m2
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 移栽-分蘖 Transplanting-tillering | 分蘖-抽穗 Tillering-heading | 抽穗-成熟 Heading-maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 1.50 cC | 8.25 aA | 1.64 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 1.82 cC | 7.95 aA | 1.74 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 2.56 bAB | 8.98 bA | -0.16 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 2.51 bB | 9.73 aA | 2.67 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.16 aA | 8.80 aA | 2.27 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 2.66 bAB | 8.62 aA | 1.92 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 2.37 | 8.72 | 1.68 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 1.68 cB | 7.32 bA | 4.47 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 2.03 bcB | 9.39 abA | 1.18 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 3.22 aA | 11.39 aA | 1.37 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 2.68 abAB | 9.01 abA | 5.39 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.14 aA | 9.93 abA | 3.44 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 3.29 aA | 9.89 abA | 4.53 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 2.67 | 9.49 | 3.40 | ||
| Ft | 5.278* | 2.119 | 4.467* | ||
| Fv | 34.713** | 3.022 | 0.379 | ||
| Ft×v | 0.221 | 0.299 | 0.134 | ||
| rNAA | 0.451** | 0.294* | 0.721** | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 成熟期 Maturity | 抽穗后 After heading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 58.32 bcB | 49.18 bcAB | 8.54 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 52.64 cB | 44.15 cB | 7.92 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 52.90 cB | 53.60 bcAB | -1.06 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 71.82 abAB | 59.05 abcAB | 12.41 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 83.46 aA | 68.84 aA | 13.07 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 72.74 abAB | 61.09 abAB | 10.47 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 65.31 | 55.99 | 8.56 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 54.04 cdC | 35.94 bC | 17.63 bB |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 46.27 dC | 41.75 bBC | 4.06 cC | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 65.68 bcBC | 59.97 aAB | 5.39 cC | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 76.41 abAB | 51.41 abABC | 24.66 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 83.84 aAB | 65.13 aA | 17.37 bAB | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 89.22 aA | 65.99 aA | 22.15 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 69.24 | 53.37 | 15.21 | ||
| Ft | 0.954 | 1.256 | 3.009 | ||
| Fv | 23.652** | 23.625** | 1.039 | ||
| Ft×v | 0.954 | 1.744 | 0.288 | ||
| rNAA | 0.317** | 0.848** | 0.708** | ||
Table 5 Response of nitrogen absorption amount per panicle to the increase of atmospheric CO2 concentration in different rice varieties.mg
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 成熟期 Maturity | 抽穗后 After heading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 58.32 bcB | 49.18 bcAB | 8.54 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 52.64 cB | 44.15 cB | 7.92 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 52.90 cB | 53.60 bcAB | -1.06 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 71.82 abAB | 59.05 abcAB | 12.41 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 83.46 aA | 68.84 aA | 13.07 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 72.74 abAB | 61.09 abAB | 10.47 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 65.31 | 55.99 | 8.56 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 54.04 cdC | 35.94 bC | 17.63 bB |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 46.27 dC | 41.75 bBC | 4.06 cC | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 65.68 bcBC | 59.97 aAB | 5.39 cC | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 76.41 abAB | 51.41 abABC | 24.66 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 83.84 aAB | 65.13 aA | 17.37 bAB | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 89.22 aA | 65.99 aA | 22.15 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 69.24 | 53.37 | 15.21 | ||
| Ft | 0.954 | 1.256 | 3.009 | ||
| Fv | 23.652** | 23.625** | 1.039 | ||
| Ft×v | 0.954 | 1.744 | 0.288 | ||
| rNAA | 0.317** | 0.848** | 0.708** | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 播种-抽穗 Sowing-heading | 全生育期 Whole growth duration | 抽穗-成熟 Heading-maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 84.8 dC | 132.5 cCD | 47.7 bcB |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 92.2 bB | 146.5 aA | 54.3 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 87.8 cC | 131.5 cD | 43.7 cB | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 98.0 aA | 144.2 aA | 46.2 bcB | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 94.2 bAB | 137.8 bB | 43.7 cB | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 91.8 bB | 136.3 bBC | 44.5 bcB | ||
| 平均值Average | 91.5 | 138.1 | 46.7 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 82.8 dD | 130.0 cC | 47.2 bcB |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 90.3 cBC | 144.5 aA | 54.2 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 89.2 cC | 132.5 cC | 43.3 cB | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 95.5 aA | 143.5 aA | 48.0 bB | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 93.7 abAB | 137.7 bB | 44.0 bcB | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 91.5 bcABC | 136.2 bB | 44.7 bcB | ||
| 平均值Average | 90.5 | 137.4 | 46.9 | ||
| Ft | 0.963 | 0.268 | 0.056 | ||
| Fv | 12.093** | 0.311 | 19.128** | ||
| Ft×v | 0.229 | 0.272 | 0.111 | ||
| rNAA | 0.325** | 0.043 | -0.268* | ||
Table 6 Response of the growth duration to the increase of atmospheric CO2 concentration in different rice varieties.d
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 播种-抽穗 Sowing-heading | 全生育期 Whole growth duration | 抽穗-成熟 Heading-maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 84.8 dC | 132.5 cCD | 47.7 bcB |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 92.2 bB | 146.5 aA | 54.3 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 87.8 cC | 131.5 cD | 43.7 cB | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 98.0 aA | 144.2 aA | 46.2 bcB | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 94.2 bAB | 137.8 bB | 43.7 cB | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 91.8 bB | 136.3 bBC | 44.5 bcB | ||
| 平均值Average | 91.5 | 138.1 | 46.7 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 82.8 dD | 130.0 cC | 47.2 bcB |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 90.3 cBC | 144.5 aA | 54.2 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 89.2 cC | 132.5 cC | 43.3 cB | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 95.5 aA | 143.5 aA | 48.0 bB | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 93.7 abAB | 137.7 bB | 44.0 bcB | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 91.5 bcABC | 136.2 bB | 44.7 bcB | ||
| 平均值Average | 90.5 | 137.4 | 46.9 | ||
| Ft | 0.963 | 0.268 | 0.056 | ||
| Fv | 12.093** | 0.311 | 19.128** | ||
| Ft×v | 0.229 | 0.272 | 0.111 | ||
| rNAA | 0.325** | 0.043 | -0.268* | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | 抽穗后 After heading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 116.21 aA | 86.80abA | 32.04 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 107.32 aA | 79.57 bA | 32.09 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 132.14 aA | 87.08 abA | -4.01 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 125.60 aA | 103.52 aA | 55.69 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 129.62 aA | 105.30 aA | 51.22 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 124.27 aA | 98.41 abA | 40.49 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 122.53 | 93.45 | 34.59 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 109.84 bB | 104.54 bcAB | 90.89 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 127.76 bAB | 88.25 cB | 23.76 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 164.67 aA | 121.31 abAB | 30.23 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 123.13 bAB | 120.21 abAB | 121.82 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 142.03 abAB | 121.83 abAB | 78.80 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 146.01 abAB | 131.34 aA | 104.21 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 135.57 | 114.58 | 74.95 | ||
| Ft | 5.189* | 16.917** | 5.109* | ||
| Fv | 5.787** | 8.143** | 0.647 | ||
| Ft×v | 0.286 | 0.595 | 0.184 | ||
| rNAA | 0.344** | 0.987** | 0.735** | ||
Table 7 Response of nitrogen absorption intensity to the increase of atmospheric CO2 concentration in different rice varieties.mg/(m2·d)
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | 抽穗后 After heading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 116.21 aA | 86.80abA | 32.04 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 107.32 aA | 79.57 bA | 32.09 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 132.14 aA | 87.08 abA | -4.01 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 125.60 aA | 103.52 aA | 55.69 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 129.62 aA | 105.30 aA | 51.22 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 124.27 aA | 98.41 abA | 40.49 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 122.53 | 93.45 | 34.59 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 109.84 bB | 104.54 bcAB | 90.89 aA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 127.76 bAB | 88.25 cB | 23.76 aA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 164.67 aA | 121.31 abAB | 30.23 aA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 123.13 bAB | 120.21 abAB | 121.82 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 142.03 abAB | 121.83 abAB | 78.80 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 146.01 abAB | 131.34 aA | 104.21 aA | ||
| 平均值Average | 135.57 | 114.58 | 74.95 | ||
| Ft | 5.189* | 16.917** | 5.109* | ||
| Fv | 5.787** | 8.143** | 0.647 | ||
| Ft×v | 0.286 | 0.595 | 0.184 | ||
| rNAA | 0.344** | 0.987** | 0.735** | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶 Leaf | 穗 Panicle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 2.14 cB | 1.23 bA | 8.14 abA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 3.15 abAB | 1.63 abA | 6.87 bA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 2.72 bcAB | 1.36 bA | 7.37 abA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 3.72 aA | 1.57 abA | 9.68 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.29 abA | 2.30 aA | 8.92 abA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 3.49 abA | 1.95 abA | 7.98 abA | ||
| 平均值Average | 3.09 | 1.67 | 8.16 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 2.59 bB | 1.31 cB | 9.69 abA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 3.46 aA | 1.37 cB | 7.89 bA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 4.05 aAB | 1.81 cAB | 10.21 abA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 3.22 abAB | 4.05 abAB | 9.88 abA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.75 aAB | 2.26 bcAB | 10.77 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 3.56 aAB | 4.62 aA | 9.76 abA | ||
| 平均值Average | 3.44 | 2.57 | 9.70 | ||
| Ft | 2.508 | 4.784* | 10.081** | ||
| Fv | 3.751* | 3.911* | 2.586 | ||
| Ft×v | 0.040 | 1.447 | 0.099 | ||
| rNAA | 0.641** | 0.682** | 0.748** | ||
Table 8 Response of nitrogen absorption amount in plant organs at maturity to the increase of atmospheric CO2 concentration in different rice varieties.g/m2
| 处理 Treatment | 类型 Type | 品种 Variety | 茎鞘 Stem and sheath | 叶 Leaf | 穗 Panicle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 2.14 cB | 1.23 bA | 8.14 abA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 3.15 abAB | 1.63 abA | 6.87 bA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 2.72 bcAB | 1.36 bA | 7.37 abA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 3.72 aA | 1.57 abA | 9.68 aA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.29 abA | 2.30 aA | 8.92 abA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 3.49 abA | 1.95 abA | 7.98 abA | ||
| 平均值Average | 3.09 | 1.67 | 8.16 | ||
| FACE | 常规粳稻 CJR | 武运粳21 WYJ21 | 2.59 bB | 1.31 cB | 9.69 abA |
| 扬辐粳8号YFJ8 | 3.46 aA | 1.37 cB | 7.89 bA | ||
| 杂交籼稻HIR | 汕优63SY63 | 4.05 aAB | 1.81 cAB | 10.21 abA | |
| 两优培九LYP9 | 3.22 abAB | 4.05 abAB | 9.88 abA | ||
| 常规籼稻CIR | 扬稻6号YD6 | 3.75 aAB | 2.26 bcAB | 10.77 aA | |
| 扬辐籼6号YFX6 | 3.56 aAB | 4.62 aA | 9.76 abA | ||
| 平均值Average | 3.44 | 2.57 | 9.70 | ||
| Ft | 2.508 | 4.784* | 10.081** | ||
| Fv | 3.751* | 3.911* | 2.586 | ||
| Ft×v | 0.040 | 1.447 | 0.099 | ||
| rNAA | 0.641** | 0.682** | 0.748** | ||
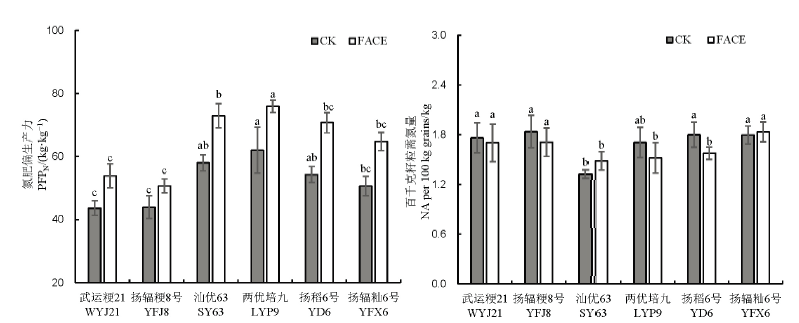
Fig. 2. Response of partial productivity of nitrogen fertilizer(PFPN) and nitrogen absorption amount(NAA) per 100kg grains to the increase of atmospheric CO2 concentration in different rice varieties.
| [1] | Stocker T F, Qin D, Plattner G K.IPCC:Climate change: The physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change[M].Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013:1-1535. |
| [2] | Cracknell A P, Varotsos C A.The IPCC fourth assessment report and the fiftieth anniversary of Sputnik[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2007, 14(6): 384-387. |
| [3] | Ainsworth E A, Long S P.What have we learned from 15 years of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) A meta-analytic review of the responses of photosynthesis, canopy[J]. New Phytologist, 2005, 165(2): 351-371. |
| [4] | Wei D, Cui K, Pan J, Ye G, Xiang J, Nie L, Huang J.Genetic dissection of grain nitrogen use efficiency and grain yield and their relationship in rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2011, 124(3):340-346. |
| [5] | Roberts TL, Ross WJ, Norman RJ, Slaton NA, Jr. Wilson CE.Predicting nitrogen fertilizer needs for rice in arkansas using alkaline hydrolyzable-nitrogen[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2011, 75(3):1161-1171. |
| [6] | Liang XQ, Li H, Wang SX, Ye YS, Ji YJ, Tian GM, van Kessel C, Linquist BA. Nitrogen management to reduce yield-scaled global warming potential in rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 146:66-74. |
| [7] | Wang B, Guo C, Wan Y, Li J, Ju X, Cai W, You S, Qin X, Wilkes A, Li Y.Air warming and CO2 enrichment increase N use efficiency and decrease N surplus in a Chinese double rice cropping system[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 706(136063). |
| [8] | 杨连新,王余龙,黄建晔,杨洪建,刘红江. 开放式空气CO2浓度增高对水稻生长发育影响的研究进展[J].应用生态学报,2006(7):1331-1337. |
| Yang L X, Wang Y L, Huang J Y, YangH J, Liu H J. Responses of rice growth and development to free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE): A research review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2006(7):1331-1337. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 杨连新, 王云霞, 朱建国. 十年水稻FACE的产量响应[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(3): 1486-1497. |
| Yang L X, Wang Y X,Zhu J G.What have we learned from 10 years of free air CO2 enrichment (FACE) experiments on riceCO2 and grain yield[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(3): 1486-1497. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 杨连新,王云霞,朱建国,Toshihiro H,王余龙.开放式空气中CO2浓度增高(FACE)对水稻生长和发育的影响[J].生态学报,2010,30(6):1573-1585. |
| YangL X, Wang Y X, Zhu J G,Toshihiro H, Wang Y L. What have we learned from 10 years of free-air CO2enrichment(FACE)experiments on rice growth and development[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(6): 1573-1585. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Noguchi K, Tsunoda T, Miyagi A, Kawai-Yamada M, Sugiura D, Miyazawa S, Tokida T, Usui Y, Nakamura H, Sakai H.Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on respiratory rates in mature leaves of two rice cultivars grown at a free-air CO2enrichment site and analyses of the underlying mechanisms[J]. Plant and Cell Physlology, 2018, 59(3): 637-649. |
| [12] | Cai C, Yin X, He S, Jiang W, Si C, Struik PC, Luo W, Li G, Xie Y, Xiong Y.Responses of wheat and rice to factorial combinations of ambient and elevated CO2 and temperature in FACE experiments[J]. Global Change Biology, 2016, 22(2): 856-874. |
| [13] | Cai C, Li G, Yang H, Yang J, Liu H, Struik PC, Luo W, Yin X, Di L, Guo X.Do all leaf photosynthesis parameters of rice acclimate to elevated CO2, elevated temperature, and their combination, in FACE environments[J]? Global Change Biology, 2018, 24(4):1685-1707. |
| [14] | Wang W, Cai C, He J, Gu J, Zhu G, Zhang W, Zhu J, Liu G.Yield, dry matter distribution and photosynthetic characteristics of rice under elevated CO2 and increased temperature conditions[J]. Field Crops Research, 2020, 248:107605. |
| [15] | Kim HY, Lieffering M, Miura S, Kobayashi K, Okada M.Growth and nitrogen uptake of CO2-enriched rice under field conditions[J]. New Phytologist, 2001, 150(2): 223-229. |
| [16] | 谢祖彬, 朱建国, 张雅丽, 马红亮, 刘钢, 韩勇, 曾青, 蔡祖聪. 水稻生长及其体内C、N、P 组成对开放式空气 CO2浓度增高和N、P施肥的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(10): 1223-1230. |
| Xie Z B, Zhu J G, Zhang Y L, Liu G, Han Y, Zeng Q, Cai Z C.Responses of rice (Oryza sativa) growth and its C,N and P composition to FACE (Free-air Carbon Dioxide Enrichment) and N,P fertilization[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(10): 1223-1230.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 董桂春, 王余龙, 杨洪建,黄建晔, 朱建国, 杨连新, 单玉华. 开放式空气 CO2浓度增高对水稻N素吸收利用的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(10): 1219-1222. |
| Dong G C, Wang Y L, Yang H J, Huang J Y, Yang L X, Shan Y H.Effect of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) on nitrogen accumulation and utilization efficiency in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002,13(10): 1219-1222.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 黄建晔, 杨洪建, 杨连新,王余龙, 朱建国, 刘红江, 董桂春, 单玉华. 水稻不同生育时期N素营养对FACE响应的研究[J]. 作物学报, 2004, 30(12): 1237-1243. |
| Huang J Y, Yang H J, Yang L X, Wang Y L, Zhu J G, Liu H J,Dong G C, Shan Y H.Effects of free-air CO2enrichment(FACE) on nitrogen nutrition at different growth stages in rice(Oryza sativa L.) cultivar Wuxiangjing 14[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2004,30(12): 1237-1243.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 庞静, 朱建国, 谢祖彬,刘刚, 陈改苹.CO2浓度升高条件下水稻蒸腾与N吸收的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(2):205-209. |
| Pang J, Zhu J G, Xie Z B, Liu G, Chen G P.Relations between transpiration and N uptake of rice grown in elevated air carbon dioxide concentration[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2006, 20(2):205-209.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 刘红江, 杨连新, 黄建晔, 董桂春, 朱建国, 刘钢, 王余龙. FACE对三系杂交籼稻汕优63氮素吸收利用的影响[J].农业环境科学学报, 2008, 27(3): 1015-1021. |
| Liu H J, Yang L X, Huang J Y, Dong G C, Zhu J G, Liu G, Wang Y L.Effect of free-air CO2 enrichment(FACE)on phosphorus uptake and utilization of three-line indica hybrid rice cultivar Shanyou 63[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2008, 27(3): 1015-1021.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Cotrufo MF, Ineson P, Scott AY.Elevated CO2 reduces thenitrogen concentration of plant tissues[J]. Global Change Biology, 1998, 4: 43-54. |
| [22] | Lin H W, Bai K Z, Kuang T Y.Effects of elevated CO2 and hightemperature on single leaf and canopy photosynthesis of rice.Acta Botanica Sinica, 1999, 41(6): 624-628. |
| [23] | 黄建晔, 杨洪建, 董桂春. 开放式空气CO2对水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(10): 1210-1214. |
| Huang J Y, Yang H J, Dong G C.Effects of free-air CO2enrichment(FACE) on yield formation in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(10): 1210-1214.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 张立极, 潘根兴, 张旭辉,李恋卿, 郑经伟, 郑聚峰, 俞欣妍, 王家芳. 大气CO2浓度和温度升高对水稻植株碳氮吸收及分配的影响[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47(1):26-32. |
| Zhang L J, Pan G X, Zhang X H, Li L Q, Zheng J W, Zheng J F, Yu X Y, Wang J F.Effect of experimental CO2 enrichment and warming on uptake and distribution of C and N in rice plant[J]. Soils, 2015, 47(1): 26-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 刘红江, 杨连新, 黄建晔,董桂春, 杨欢, 朱建国, 刘钢, 王余龙.FACE对三系杂交籼稻汕优63产量形成的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2008,27(6):2285-2290. |
| Liu H J,Yang L X, Huang J Y, Dong G C, Yang H, Zhu J G, Liu G, Wang Y L.Effect of free-air CO2enrichment(FACE)on phosphorus uptake and utilization of three-line indica hybrid rice cultivar shanyou 63[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2008, 27(6): 2285-2290. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Kim H Y, Lieffering M, Kobayashi K, Okada M, Miura S.Seasonal changes in the effects of elevated CO2 on rice at three levels of nitrogen supply: A free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) experiment[J]. Global Change Biology, 2003, 9(6): 826-837. |
| [27] | 刘红江, 杨连新, 黄建晔,董桂春, 朱建国, 刘钢, 王余龙. FACE对常规籼稻扬稻6号产量形成的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(2): 299-304. |
| Liu H J,Yang L X, Huang J Y, Dong G C, Zhu J G, Liu G, Wang Y L.Effect of free air CO2 enrichment(FACE)on yield formation of indica rice cultivar Yangdao 6[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2009, 28(2): 299-304.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 黄建晔, 董桂春, 杨洪建,王余龙, 朱建国, 杨连新, 单玉华. 开放式空气CO2增高对水稻物质生产与分配的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(2): 253-257. |
| Huang J Y, Dong G C,Yang H J, Wang Y L, Zhu J G, Yang L X, Shan Y H.Effect of free-air CO2 enrichment on biomass accumulation and distribution in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(2): 253-257. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 黄建晔, 杨洪建, 杨连新, 刘红江, 董桂春, 朱建国, 王余龙. 开放式空气CO2浓度增加(FACE)对水稻产量形成的影响及其与氮的互作效应[J]. 中国农业科学, 2004, 37(12): 1824-1830. |
| Huang J Y, Yang H J, Yang L X, Liu H J, Dong G C, Zhu J G, Wang Y L.Effects of free-air CO2enrichment (FACE) on yield formation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and its interaction with nitrogen[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica , 2004, 37(12): 1824-1830. | |
| [30] | 蔡威威, 艾天成, 万运帆, 李健陵, 郭晨. 环境温度和CO2浓度升高对湖北早稻氮素含量及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2016, 37(2): 231-237. |
| CaiW W, Ai T C, Wan Y F, Li J L, Guo C. Influence of elevated atmospheric temperature and CO2 concentration on plant and soil N concentration and yield of early rice in Hubei[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2016, 37(2): 231-237. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 龚金龙, 邢志鹏, 胡雅杰, 张洪程, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕, 高辉. 籼、粳超级稻氮素吸收利用与转运差异研究[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(4):796-810. |
| Gong J L, Xing Z P, Hu Y J, Zhang H C, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y, GaoH. Differences of nitrogen uptake utilization and translocation between indica and japonica super rice[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2014, 20(4): 796-810. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 李超, 韦还和, 许俊伟,王子杰, 许轲, 张洪程, 戴其根, 霍中洋, 魏海燕, 郭保卫. 甬优系列籼粳杂交稻氮素积累与转运特征[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(5):1177-1186. |
| Li C, Wei H H, Xu J W, Wang Z J, Xu K, Zhang H C, Dai Q G, Huo Z Y, Wei H Y,Guo B W.Characteristics of nitrogen uptake, utilization and translocation in the indica-japonica hybrid rice of Yongyou series[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2016, 22(5): 1177-1186. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 陈贵, 陈梅, 张红梅, 王士磊, 施卫明, 程旺大. 籼粳杂交稻与常规粳稻产量、干物质氮素累积转运及氮素利用差异研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(12): 1992-2000. |
| Chen G, Chen M, Zhang H M, Wang S L, Shi W M, Cheng W D.Differences of yield, accumulation and translocation properties of dry matter and N, and N use efficiency between indica-japonica hybrid rice and japonica rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2018, 30(12): 1992-2000. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 董桂春,于小凤,赵江宁,居静, 田昊, 李进前, 张燕, 王余龙.不同穗型常规籼稻品种氦素吸收利用的基本特点[J].作物学报,2009,35(11):2091-2100. |
| Dong G C, Yu X F, Zhao J L,Ju J, Tian H, Li Q J, Zhang Y, Wang Y L.General characteristics of nitrogen uptake and utilization in conven-tional indica rice cultivars with different panicle weight types[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2009, 35(11): 2091-2100.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 陈琛, 王熠, 羊彬,朱正康, 曹文雅, 罗刚, 周娟, 王祥菊, 于小凤, 袁秋梅. 株高对遗传群体水稻株系氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(22): 4450-4459. |
| Chen C, Wang Y, Yang B, Cao W Y, Luo G, Zhou J, Wang X J, Yu X F, Yuan Q M.Plant height affects nitrogen absorption and utilization in rice with similar genetic background[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(22): 4450-4459. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 马红亮, 朱建国, 谢祖彬,曾青, 刘钢. CO2浓度升高对水稻生物量及 C、N吸收分配的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2005, 13(3): 38-41. |
| Ma H L, Zhu J G, Xie Z B, Zeng Q, Liu G.Effect of CO2 enrichment on the allocation of biomass and C, N uptake in rice organs[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2005, 13(3): 38-41.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | ZHAO Yiting, XIE Keran, GAO Ti, CUI Kehui. Effects of Drought Priming During Tillering Stage on Panicle Development and Yield Formation Under High Temperature During Panicle Initiation Stage in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||